Abstract
This study aims to explore the role of customer knowledge management (CKM) and satisfaction as antecedents of customer trust, and the mediating function of customer trust in the knowledge–loyalty and satisfaction–loyalty in the Saudi banking sector. This study intends to provide light on the significance of CKM and the ways in which it can support consumer trust, loyalty, and satisfaction. Data came from 600 consumers who responded to an online survey. By using regression analysis and descriptive statistics, seven hypotheses were created and tested. The findings exhibited that customer trust has a major impact on loyalty and that customer trust is positively impacted by CKM and satisfaction. Additionally, trust partially mediates the relationship between knowledge, loyalty, and satisfaction. The study contributes to the literature by examining the factors that influence customer loyalty, CKM engagement, satisfaction, and trust in the context of the Saudi banking industry. These research findings are helpful for managers and strategists in figuring out how to create customer loyalty programs that are a fit for their target market. The study is limited to the Saudi banking sector and may not be generalizable to other industries. Additionally, the study is based on self-reported data from customers, which may not accurately reflect their true opinions and behaviors.
1. Introduction
The banking sector plays an essential role in the economy of Saudi Arabia. As the country aims to diversify its economy and reduce its dependence on oil, the banking sector has become increasingly important. In this context, it is crucial for banks to understand the aspects that influence customer loyalty, customer satisfaction, and customer trust (Zafar et al. 2012). Customer Knowledge Management (CKM) is an emerging concept in the banking industry and is seen as a critical tool for building and maintaining customer relationships.
CKM refers to the systematic collection, analysis, and dissemination of customer information to create value for both the organization and the customer. This process helps the organization to obtain a deeper understanding of its customers, their needs, and preferences (Al Ali 2021). By using CKM, banks can tailor their services and products to meet the specific needs of their customers, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The extent at which a customer is pleased with services or products offered by a business or organisation is known as “Customer satisfaction.” It is a crucial factor in developing and sustaining strong customer relationships, as it directly affects customer loyalty (Pasaribu et al. 2022). If the customers are satisfied with a bank’s products or services, there is a greater possibility that the customers will continue to engage in business with the bank and will also recommend it to others.
Customer loyalty refers to the extent to which a customer remains committed to an organization over time. Customer loyalty is closely related to customer satisfaction, as customers that are satisfied with a bank’s services or products are more likely to remain loyal to the bank (Ebrahim 2020).
It is essential for a business to successfully manage customer relationships and deliver happiness to its clients in the cutthroat business world of today (Albarq 2021). A company must draw in fresh clients while retaining its current clientele. Customer switching behavior is common in the banking industry as a result of increased competition, as well as the uniformity of the goods and services provided by all retail banks. In order to eliminate such client behavior, banks must concentrate on fostering and preserving customer loyalty (Hride et al. 2022).
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Building
2.1. Customer Knowledge Management (CKM)
CKM is a management approach that seeks to build, maintain, and apply a comprehensive knowledge base about customers (Hride et al. 2022). The goal of CKM is to enhance the ability of organizations to understand, predict, and satisfy customer needs and preferences (Yim et al. 2004). CKM is a customer-centric approach that places the needs of customers at the center of organizational decision-making and seeks to align all aspects of the organization around a shared understanding of customers and their needs.
According to Majid et al. (2023), there are a number of benefits associated with the effective implementation of CKM in organizations such as:
- Improved customer satisfaction: By having a deep and accurate understanding of customer needs and preferences, organizations are better equipped to meet customer needs and deliver high-quality products and services that meet customer expectations.
- Increased customer loyalty: Customers are more likely to stay loyal to the bank/organisation when they feel that their needs are being met (Bhat et al. 2018). This can lead to increased customer retention, repeat business, and word-of-mouth referrals.
- Enhanced customer insight: By having access to detailed customer data and insights, organizations are better able to identify opportunities for growth and innovation, and to respond quickly to changes in customer preferences and needs.
- Improved decision-making: CKM provides organizations with a wealth of information about customers, which can be used to inform decision-making at all levels of the organization (Ebrahim 2020). By having access to this information, organizations are better equipped to make informed decisions about product development, marketing, and customer service.
Despite the many benefits of CKM, there are also a number of challenges that organizations face in implementing this approach effectively. These challenges include: (1) Data quality and accuracy: In order to be effective, CKM requires the collection and analysis of large amounts of customer data. Ensuring the quality and accuracy of these data can be a significant challenge for organizations. (2) Data integration and management: CKM requires the integration of customer data from customer relationship management (CRM) systems, customer feedback and surveys, and sales data. Ensuring the effective integration and management of these data can be a complex and time-consuming process. (3) Data privacy and security: In order to collect and use customer data, organizations must be able to ensure that customer data are secure and that customer privacy is protected. This can be a challenge, particularly in light of increasing concerns about data privacy and security. (4) Organizational culture: CKM requires a customer-centric culture in which all employees understand the importance of customer knowledge and are committed to putting customer needs at the center of organizational decision-making. This can be difficult to achieve in organizations with a more traditional, product-focused culture (Bhat et al. 2018).
Despite these challenges, the literature suggests that the benefits of CKM far outweigh the challenges, and that organizations that are able to effectively implement this approach are likely to see significant benefits in terms of customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and business performance (Pasaribu et al. 2022).
2.2. Customer Satisfaction
The level of a client’s happiness with the goods and services they receive from a certain business is referred to as customer satisfaction. Zia (2020) asserts that a variety of variables affect customer satisfaction: (1) Product quality: One of the key factors influencing how satisfied customers are with a company’s goods or services is their quality. Customers anticipate that goods and services will fulfil their needs and fulfil their expectations and operate as promised. (2) Service quality: The quality of customer service can also have a significant impact on customer satisfaction. This includes factors such as the responsiveness of customer service representatives, the availability of support resources, and the level of empathy and understanding displayed by customer service staff. (3) Price: The price of products and services is another important driver of customer satisfaction. Customers expect to receive good value for their money, and may be dissatisfied if they feel that the price of products or services is unreasonable. (4) Convenience: The ease and convenience of doing business with an organization can also have a significant impact on customer satisfaction. This includes factors such as the availability of products and services, the ease of ordering and payment, and the speed and reliability of delivery (Zia 2020).
There are a number of methods for measuring customer satisfaction, including:
- Surveys: Surveys are one of the most common methods for measuring customer satisfaction. Open-ended and closed-ended questions can both be used in surveys, which can be carried out in person, over the phone, or online.
- Customer feedback: Customer feedback can be collected through a variety of channels, including customer service interactions, online reviews, and social media. This feedback can provide valuable insights into customer satisfaction levels and the areas where organizations can improve (Siagian et al. 2022).
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): The NPS is a metric for measuring customer loyalty that gauges both customer happiness and the likelihood that customers will refer a business to others. The NPS is determined by deducting the proportion of detractors (clients who are not inclined to refer the business) from the proportion of promoters (customers who are highly likely to recommend the organization) (Zia 2020).
- Customer complaints: Customer complaints can provide valuable insights into areas where customers are dissatisfied with an organization’s products and services. Tracking and responding to customer complaints can help organizations to identify and address areas for improvement (Al-Ghamdi and Badawi 2019).
2.3. Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty refers to the degree to which customers are committed to a particular brand or organization. There are several different types of customer loyalty, including: (1) Behavioral loyalty: Behavioral loyalty refers to the frequency with which customers purchase products or services from a particular organization. Customers who exhibit high levels of behavioral loyalty are more likely to make repeat purchases from the same organization over time (Zafar et al. 2012). (2) Attitudinal loyalty: Attitudinal loyalty refers to the positive attitudes and beliefs that customers have towards a particular brand or organization. Customers who exhibit high levels of attitudinal loyalty are more likely to recommend the organization to others and to have positive perceptions of the organization’s products and services. (3) Affective loyalty: Affective loyalty refers to the emotional attachment that customers have to a particular brand or organization. Customers who exhibit high levels of affective loyalty are more likely to be passionate about the organization and to have a strong sense of identity with the brand (Akhtar et al. 2020).
There are several methods for measuring customer loyalty, including:
- Repeat purchase rate: It measures the proportion of customers who make repeat purchases from a particular organization. This metric can provide valuable insights into the level of customer loyalty and the likelihood of customers to remain loyal over time.
- Loyalty program participation: Participation in a loyalty program can be used as a proxy for customer loyalty, as customers who participate in loyalty programs are more likely to be engaged with the organization and to have a higher level of commitment (Akhtar et al. 2020).
- Customer feedback: Customer feedback can also provide valuable insights into customer loyalty. For example, customers who provide positive feedback and are highly likely to recommend the organization to others are more likely to exhibit high levels of customer loyalty.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): CLV is a metric that measures the total value of a customer to an organization over the course of their lifetime. CLV can be used to identify customers who are highly valuable to the organization and to prioritize resources and efforts to retain these customers (Almohaimmeed 2019).
2.4. Customer Trust
Customer trust refers to the level of confidence that customers have in an organization and its ability to meet their needs and expectations. There are several factors that can impact customer trust, including:
- Brand reputation: The reputation of a brand is an important factor that can impact customer trust. Customers are more likely to trust brands that have a strong reputation for quality, reliability, and customer service (Siagian et al. 2022).
- Transparency: Transparency is another important factor that can impact customer trust. Customers are more likely to trust organizations that are open and transparent about their business practices, policies, and procedures.
- Personalization: Personalization is the process of tailoring the customer experience to meet the individual needs and preferences of customers. Personalization can help to build customer trust by demonstrating the organization’s commitment to understanding and meeting the needs of its customers (Mian 2014).
There are several methods for measuring customer trust, including:
- Surveys: Surveys can be used to gather customer feedback on their level of trust in an organization. For example, customers can be asked to rate their level of trust in the organization on a scale, or to provide written feedback on specific aspects of the organization that they feel impact their trust (Al-Ghamdi and Badawi 2019).
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): The possibility that customers will suggest a business to others is gauged by the customer satisfaction indicator known as NPS. It can be used as a proxy for customer trust, as customers who are highly likely to recommend the organization to others are more likely to have a high level of trust in the organization.
- Customer complaints: The number of customer complaints can also provide insights into the level of customer trust. Organizations that receive a high volume of customer complaints are more likely to have lower levels of customer trust, as customers are more likely to be dissatisfied with the organization and its products and services (Akhtar et al. 2020).
2.5. The Impact of CKM on Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty
A number of empirical studies have been directed to investigate the impact of CKM on customer loyalty and customer satisfaction. These studies have demonstrated that CKM can play a substantial role in improving both customer loyalty and customer satisfaction. One study conducted by Albarq (2021) found that CKM can positively impact customer satisfaction by providing customers with access to more relevant and personalized information and services. The authors discovered that companies who use CKM are better able to comprehend the wants and needs of their clients, allowing them to offer more pertinent and specially designed goods and services that satisfy those needs. This can enhance client happiness and foster more client loyalty as a result.
Another study conducted by Al Ali (2021) found that CKM can also positively impact customer loyalty. The authors discovered that companies who use CKM are better able to comprehend the wants and needs of their clients, allowing them to offer more customized and pertinent goods and services that satisfy their clients’ expectations. Additionally, the authors found that CKM can improve customer engagement and increase customer retention, which can lead to higher levels of customer loyalty.
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
A positive relationship exists between customer trust and customer loyalty.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
A positive relationship exists between CKM and customer trust.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
A positive relationship exists between CKM and customer satisfaction.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
A positive relationship exists between customer satisfaction and customer trust.
2.6. The Mediating Role of Customer
The relationship between customer knowledge management (CKM), customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty is an important one for businesses to understand (Cho et al. 2019). It is essential for businesses to recognize the mediating role of customer trust in this relationship in order to maximize customer loyalty. However, customer trust is the key mediator in this relationship. Customers must trust that their data are being used responsibly and that their needs and preferences are being taken into account. If customers do not trust a business, they will not be satisfied and, consequently, will not be loyal (Ahmed et al. 2020; Doghan and Albarq 2022). Therefore, businesses must prioritize building customer trust in order to maximize customer loyalty (Ranaweera and Prabhu 2003).
One study conducted by Al-Ghamdi and Badawi (2019) found that customer trust can play a substantial role in mediating the relationship between CKM and customer satisfaction. The authors found that organizations that implement CKM are able to understand the preferences and needs and preferences of their customers in a better way, which can improve customer trust and lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction. Additionally, the authors found that customer trust can play a significant role in mediating the relationship between CKM and customer loyalty, as customers who trust the organization are more likely to remain loyal over time.
Another study conducted by Albarq (2021) found similar results, with the authors finding that customer trust can play a significant role in mediating the relationship between CKM and customer loyalty. The authors discovered that firms that use CKM are better able to comprehend the wants and preferences of their clients, which can increase client trust and loyalty. The authors also discovered that the relationship between CKM, customer loyalty, and customer satisfaction might be significantly mediated by consumer trust, as customers who trust the organization are more likely to be satisfied with the products and services they receive, which can lead to higher levels of customer loyalty over time, as shown in Figure 1.
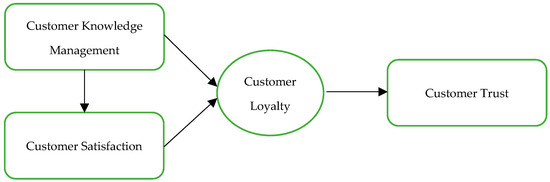
Figure 1.
Research structural model.
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
Customer trust mediates the effect of CKM on loyalty.
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Customer trust mediates the effect of customer satisfaction on loyalty.
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
Customer satisfaction mediates the effect of CKM on trust.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection and Sampling Method
Two sampling methods used in this research: convenient sampling and random sampling. Convenient sampling used to select a sample of participants from the population of customers of the selected banks in the Saudi banking sector. Random sampling can then be used to select the participants from the identified banks (Sharma 2017). An online survey was applied in 1–30 December 2022 to gather data for this investigation. The surveys were used to gather information from many participants, which included both closed- and open-ended inquiries about the impact of CKM, as well as inquiries about customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and customer trust. The online questionnaire used filter questions asking whether the respondents have an account with one of Saudi banks for more than one year to ensure that they experienced the services offered by the banks during that period. Only those who answered “yes” could participate in this survey. The authors set a minimum target of 500 respondents as the sample size because the research model incorporates many constructs (Hair et al. 2010, p. 574).
3.2. Survey Instruments
The questionnaire was divided in two parts. First, different personal and demographic variables: this section obtained the respondent’s information about gender, age, income, education, and status. A second part measured includes the latent variables that are important in the current study. These variables include CKM, customer satisfaction, customer trust, and customer loyalty. This section of the study is developed based on the past literature and already-used questionnaires.
This study comprises 19 measurement items as indicators to examine 9 constructs with 5 items per construct. The items were borrowed and/or adapted from several previous studies, as shown in Table 1. Some words in the original sources were refined to the context of this study. The research instrument was piloted through personal interviews with a few customers to check the content validity of items and to test its appropriateness. Pre-testing was insightful for examining and evaluating the research instrument which led to some minor alterations in the items developed. Table 1 shows the number of items used to calculate each variable and their sources, along with the modern studies that tested these parameters. However, certain modifications were done to suit the banking sector. A five-point Likert scale was used in all the items with ranks 5 (strongly agree) to 1 (strongly disagree). A 19-item questionnaire has been used to calculate the 4 construct values. To ensure the reliability and validity of the results, the measurement instruments used in the study will be assessed for their reliability and validity. This will ensure that the results obtained from the study are accurate and credible (Taherdoost 2016).

Table 1.
Variables, number of items, and recent validation sources.
The questionnaire was translated from English to Arabic by Arabian teachers. Two bilingual Arabic/English lecturers at the King Faisal University Language Center translated the questionnaire into Arabic. We used the double-translation method to avoid confusion or misinterpretation and to ensure that the Arabic version accurately represented the English version.
3.3. Analysis
The structural equation modeling (SEM) technique, using AMOS 20.0 software, was deployed for analysis, along with a two-step approach. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was also performed on the basis of goodness and badness indices, and the model fit summary was followed. The various fit indices used for the assessment of the measurement model include—χ2/df (<2 is good and 2–5 acceptable); goodness-of-fit index (GFI > 0.90 is good and > 0.80 acceptable); normed fit index (NFI > 0.90); comparative fit index (CFI > 0.90); root mean residual (RMR < 0.10); and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA < 0.10). Factor loadings are standardized regression weights of variables with its items. While loadings above 0.70 are considered good, those above 0.60 are also acceptable (Hair et al. 2010).
4. Results
The demographics achieved by analyzing the data of the respondents are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Demographic profile of respondents.
Four constructs were made which illustrated the relationship between observed and unobserved variables, which were tested for validity and authenticity using CFA. The results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Measurement model (CFA).
The model was assessed by various indices, mainly the ratio of the chi-square minimum to the degree of freedom (CMIN/df) which, if below the cut-off criterion of 3.00 (Hair et al. 2010), was considered a good fit. Hair et al. (2010) also suggests that the goodness-of-fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness-of-fit index (AGFI), Bentler’s comparative fit index (CFI), the Bentler–Bonett normed fit index (NFI), and the Tucker–Lewis index (TLI) should all be greater than 0.9, along with the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) value, which should be less than 0.1.
The statistical significance of the variables was determined by the critical ratio. Factor loadings of all items from all four constructs were found to be greater than 0.60 which suggested a notably higher convergent validity, as shown in Table 4. The average variance extracted (AVE), which reflects “the variation between the constructed structures as compared to the error which occurs due to wrong measurements”, should be 0.50 to have reliability. The discriminant validity Hair et al. (2010) was calculated by the square root average variance and was compared with the factors’ correlation coefficients of other factors. Table 5 presents the results of the discriminant validity test.

Table 4.
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) of all measurement models.

Table 5.
Test of discriminant validity.
The SEM method and the maximum likelihood estimation method were used to analyze the research model. The strength of the model was based on the intrinsic and extrinsic variables. The results shown in Table 6 illustrate a good fit of the hypothesized model; thus, it is authentic for evaluation.

Table 6.
Goodness of fit of the hypothesized model.
A parameter’s standardization is judged on the basis of regression weights (SE) and (CR) Hair et al. (2010), and then the critical ratio (CR) is divided by SE. It is clear from the results shown in Table 7 that the structural model supports the study’s hypotheses.

Table 7.
Structural model results.
Mediating Effect of the Hypothesized Model
The bias-corrected percentile with a 95 per cent confidence interval was analyzed to get standardized effects for testing the H5, H6, and H7 mediation. However, it should be noted that H5 uses the CKM method of loyalty, and the results are shown in Table 8. The results for H6 and H7 are shown in Table 8. The results show that trust of a customer partially affects its loyalty to the brand which, in turn, is related to customer satisfaction.

Table 8.
Mediating results for the hypothesized model.
5. Discussion
The survey was administered to 600 consumers, and each item was scored on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being the best. “The bank provides channels to enable ongoing two-way communication between customers and employees”. The mean score for this statement is 4.235, which is near to the midpoint of the scale (4.0), and the standard deviation is 0.4244, indicating that the responses to this statement are generally close to the mean. This shows that clients have a favorable opinion of the bank’s communication channels in general. “The customers are kept informed about the latest benefits and offers regarding various products and services.” In terms of mean and standard deviation, this statement has a mean score of 4.257 and a standard deviation of 0.4372, which is comparable to the first statement. Customers appear to be generally happy with the bank’s attempts to keep them informed. “The bank fully understands the needs of customers”. This statement has a mean score of 4.195 and a standard deviation of 0.4872, which is lower than the previous two statements and implies that answers are more spread. This shows that some consumers believe the bank understands their demands completely, while others do not. The “Bank always provides statements with accurate data.” In terms of mean and standard deviation, this statement has a mean score of 4.268 and a standard deviation of 0.4435, which is identical to the second statement. This indicates that clients trust the bank offers accurate data in their statements. “The bank provides services to customers according to their business policy but not according to customer expectations.” This statement has a mean score of 4.382 and a standard deviation of 0.4862, which is greater than the preceding statements and suggests that the responses are pretty close to the mean. This implies that consumers usually feel the bank offers services in accordance with their business policies but not necessarily with customer expectations. “I feel secure while authorizing transactions with the bank.” This statement has a mean score of 4.562 and a standard deviation of 0.4966, making it one of the statements with the highest scores.
This implies that clients are at ease while approving transactions with the bank. “I prefer this bank each time I make any financial transaction.” This statement has a mean score of 4.462 and a standard deviation of 0.4989, which is identical to the preceding statement. This shows that clients favor this bank for its financial transactions in general. “The bank maintains the RBI norms fully.” This statement has a mean score of 4.462 and a standard deviation of 0.4989, which is identical to the preceding statement. This shows that clients favor this bank for its financial transactions in general. “I consider this bank as my preferred one.” This statement has a mean score of 4.463 and a standard deviation of 0.4991, which is identical to the mean and standard deviation of the preceding two statements. This indicates that customers regard this bank to be their favored one. “I trust the know-how of this bank.” This statement has a mean score of 4.300 and a standard deviation of 0.4586, which is lower than the previous three but still near to the mean. This indicates that clients typically trust this bank’s expertise. “When the bank suggests that I buy a new product it is because it is best for my situation.” This statement has a 4.320 average rating and a standard deviation of 0.4669. This indicates that the majority of consumers feel the bank recommends new products that are best suited to their needs. “The bank treats me in an honest way in every transaction.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.523 and a standard deviation of 0.4999. This suggests that a substantial proportion of consumers believe the bank is honest in all transactions. “I have intention to recommend the bank to others.” This statement’s average rating is 4.153, with a standard deviation of 0.4621. This shows that while some consumers are inclined to promote the bank to others, there may be a subset of customers who are not. “I have no intention to switch over to other bank.” This statement has a 4.120 average rating and a standard deviation of 0.5060. This shows that some customers are considering moving to another bank, but a sizable minority of consumers have no plans to do so. “I like to use the services provided by the bank.” This statement has an average rating of 4.328 and a standard deviation of 0.5517. This shows that a modest number of clients are satisfied with the bank’s services. “I will prefer new services if offered by the bank.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.343 and a standard deviation of 0.5562.
Customers are more willing to consider new services offered by the bank as a result of this. “I prefer this bank over other banks.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.355 and a standard deviation of 0.5593. This implies that a sizable proportion of clients prefer this bank above others. “I will do more business with my bank in the next few years.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.277 and a standard deviation of 0.6640. This shows that while some customers are likely to do more business with the bank in the subsequent years, there may be a part of customers who are not. “Complaints are welcomed and individual attention is given to every customer complaint.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.297 and a standard deviation of 0.7277. This indicates that clients have a favorable impression of the bank’s handling of customer complaints. “The bank maintains personal relationship with the customer.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.377 and a standard deviation of 0.7455. This suggests that a sizable proportion of clients feel the bank has a personal relationship with them. “Periodic feedback review is sought after raising complaint.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.337 and a standard deviation of 0.5482. This shows that clients feel the bank solicits input after receiving complaints. “I am satisfied with the overall interaction with the staff.” This statement has a mean rating of 4.338 and a standard deviation of 0.5487. This shows that a reasonable number of consumers are pleased with their entire engagement with bank personnel.
The structural model demonstrates CKM and customer satisfaction as chief determinants of customer trust. Trust is a prerequisite for generational customer loyalty and CKM positively impacts customer satisfaction. The study revealed that CKM and customer satisfaction better explicate variance in customer trust (R2 = 0.30) than customer loyalty (R2 = 0.18), where CKM attributes to only 19 per cent of variance in the customer satisfaction (R2 = 0.21). Customer knowledge and customer information can be used by banks as tools for developing a foundation by enhancing satisfaction, cultivating trust, building loyalty, and maintaining cordial relationships with customers (Patwa and Patwa 2014). On the other hand, the findings prove that companies which fail to incorporate the concept of CKM towards development of their products and services lose their customers to the competition. Findings depict CKM and customer trust as the major components for customer satisfaction and customer loyalty, respectively. The results are justified by the fact that a mediating variable may exist between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty which holds satisfaction and loyalty together (Sirdeshmukh et al. 2002; Ahmed et al. 2020; Mansouri et al. 2022).
Furthermore, the research concludes that there is a strong link between customer trust and customer loyalty and is further reinforced by the earlier findings of Lin et al. (2023). However, some business professionals and academicians. Halim et al. (2023) argue that customers who display satisfaction can cease to be loyal, hence suggesting that all loyal customers may not be satisfied whereas all satisfied customers do tend to be loyal.
This study infers that the impact of CKM is more on customer trust than on customer satisfaction. Furthermore, mediation analysis highlighted customer trust as the precursor to customer loyalty (Utz et al. 2023). Thus, a bank can enhance customer loyalty by understanding the dynamic behavior of the customers and maintaining their up-to-date information. Building a knowledge base of customers and developing customer trust leads to a positive impact on customer loyalty management initiatives. Managerial competence, knowledge management, and technological innovations contribute to developing customer trust and ensure cultural integrity in customer loyalty management. Moreover, trust plays an intermediary role between the satisfaction and the loyalty of a customer. Nonetheless, a few studies claim that satisfied customers are not always loyal customers. Therefore, this study recommends the need for developing strategic interventions of trust between customer satisfaction and loyalty by highlighting the role of trust in building satisfaction, which results in loyalty. For banks to improve their customer relationships, constant monitoring of customer behavior and internal processes is necessary, without which the relationship can be strained by making customers re-consider their loyalties and form a negative opinion of the bank. This results in the loss of a bank’s reputation and long-term competitiveness.
5.1. Managerial Implications
For managers in the Saudi banking industry, the study’s conclusions will have significant ramifications. Managers will be better prepared to plan and implement customer-centric strategies that increase customer satisfaction and loyalty by comprehending the influence of CKM on these two metrics, as well as the mediating function of customer trust.
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
The study is limited to the Saudi banking sector and may not be generalizable to other industries. Additionally, the study is based on self-reported data from customers, which may not accurately reflect their true opinions and behaviors. Further research is needed to validate the findings of this study and explore the impact of CKM on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in other industries and regions.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [Grant No. 3074].
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study received full ethical approval from King Faisal University.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data associated with this study are not publicly available, as per the agreement with research participants when they gave informed consent.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmed, Rizwan Raheem, Jolita Vveinhardt, Usman Warraich, Syed Hasan, and Akhter Baloch. 2020. Customer satisfaction & loyalty and organizational complaint handling: Economic aspects of business operation of airline industry. Engineering Economics 31: 114–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Nadeem, Syed Azeem, Abdullah Basiouni, Kok Ban Teoh, and Abdul Khaliq Alvi. 2020. Service quality and customer satisfaction: An investigation from Saudi Arabian banking sector. PalArch’s Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology 17: 13764–77. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ali, Abdulsattar. 2021. The Impact of Information Sharing and Quality Assurance on Customer Service at UAE Banking Sector. International Journal of Technology, Innovation and Management (IJTIM) 1: 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarq, Abbas. 2021. The effect of brand perceptions on repurchases when using the e-commerce website for shopping. Jindal Journal of Business Research 10: 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, Shumookh Abdul Aziz, and Nada Saleh Badawi. 2019. Do corporate social responsibility activities enhance customer satisfaction and customer loyalty? Evidence from the Saudi banking sector. Cogent Business & Management 6: 1662932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohaimmeed, Bader. 2019. Pillars of customer retention: An empirical study on the influence of customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, customer profitability on customer retention. Serbian Journal of Management 14: 421–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Suhail, Mushtaq Darzi, and Shakir Parrey. 2018. Antecedents of customer loyalty in banking sector: A mediational study. Vikalpa 43: 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Hichang, Sungjong Roh, and Byung Ho Park. 2019. Of promoting networking and protecting privacy: Effects of defaults and regulatory focus on social media users’ preference settings. Computers in Human Behavior 101: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, Jyh-Shen, and Cornelia Droge. 2006. Service quality, trust, specific asset investment, and expertise: Direct and indirect effects in a satisfaction-loyalty framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 34: 613–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghan, Mohammed Al, and Abbas Albarq. 2022. The effects of hedonic and utilitarian values on e-loyalty: Understanding the mediating role of e-satisfaction. International Journal of Data and Network Science 6: 325–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, Martina. 2009. Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience-Based Approach in a Tourism Context. Master’s thesis, Waterford Institute of Technology, Waterford, Ireland. Available online: http://repository-testing.wit.ie/id/eprint/1396 (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Ebrahim, Reham. 2020. The role of trust in understanding the impact of social media marketing on brand equity and brand loyalty. Journal of Relationship Marketing 19: 287–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, Joseph, William Black, and Rolph Anderson. 2010. Multivariate Data Analysis. London: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, Hasnita, Suria Abu Basar, Hanissah Hamzah, Nik Nor Amalina Nik Mohd Sukrri, and Abul Bashar Bhuiyan. 2023. Customer satisfaction on e-banking services among university students in Malaysia. Asian Finance & Banking Review 7: 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hride, Fabliha, Farhana Ferdousi, and Sajjad Jasimuddin. 2022. Linking perceived price fairness, customer satisfaction, trust, and loyalty: A structural equation modeling of Facebook-based e-commerce in Bangladesh. Global Business and Organizational Excellence 41: 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Xiang-Qian, You-Cheng Chen, Chih-Hsing Liu, and Yong-Quan Li. 2023. Measuring creativity: Role of service quality management, knowledge sharing and social interaction. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 34: 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, Muhammad, Mohamad Faizal Ramli, Basri Badyalina, Azreen Roslan, Azreen Hashim, and Wan Nadiah Mohd Nadzri. 2023. Consumer purchase decision in the malaysian retail market: A study of RM2 stores. International Journal of Management Studies 30: 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, Hossein, Saeed Sadeghi Boroujerdi, and Maizaitulaidawati Md Husin. 2022. The influence of sellers’ ethical behavior on customer’s loyalty, satisfaction and trust. Spanish Journal of Marketing-ESIC 26: 267–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, Tariq Saeed. 2014. The role of service quality in developing customer loyalty in the banking sector: A case study of the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting 4: 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaribu, Fajar, Warsani Purnama Sari, Tapi Rondang Ni Bulan, and Widia Astuty. 2022. The effect of e-commerce service quality on customer satisfaction, trust and loyalty. International Journal of Data and Network Science 6: 1077–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwa, Love Kumar, and Kush Patwa. 2014. An analytical study of CRM practices in public and private sector banks in the state of Uttar Pradesh. Pacific Business Review International 6: 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ranaweera, Chatura, and Jaideep Prabhu. 2003. The influence of satisfaction, trust and switching barriers on customer retention in a continuous purchasing setting. International Journal of Service Industry Management 14: 374–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Gaganpreet. 2017. Pros and cons of different sampling techniques. International Journal of Applied Research 3: 749–52. [Google Scholar]
- Siagian, Hotlan, Zeplin Jiwa Husada Tarigan, and Sahnaz Ubud. 2022. The effect of electronic word of mouth on online customer loyalty through perceived ease of use and information sharing. International Journal of Data and Network Science 6: 1155–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirdeshmukh, Deepak, Jagdip Singh, and Barry Sabol. 2002. Consumer trust, value and loyalty in relational exchanges. Journal of Marketing 66: 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, Hamed. 2016. Validity and Reliability of the Research Instrument; How to Test the Validation of a Questionnaire/Survey in a Research. International Journal of Academic Research in Management 5: 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utz, Manuel, Simon Johanning, Tamara Roth, Thomas Bruckner, and Jens Strüker. 2023. From ambivalence to trust: Using blockchain in customer loyalty programs. International Journal of Information Management 68: 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, Frederick, Rolph E. Anderson, and Srinivasan Swaminathan. 2004. Customer relationship management: Its dimensions and effect on customer outcomes. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management 24: 263–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Mohsin, Sana Zafar, Aasia Asif, Ahmed Imran Hunjra, and Mushtaq Ahmad. 2012. Service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty: An empirical analysis of banking sector in Pakistan. Information Management and Business Review 4: 159–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, Adil. 2020. Discovering the linear relationship of service quality, satisfaction, attitude and loyalty for banks in Albaha, Saudi Arabia. PSU Research Review 6: 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).