Modeling the Connection between Bank Systemic Risk and Balance-Sheet Liquidity Proxies through Random Forest Regressions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Marginal Expected Shortfall
3.2. Random Forest Regression
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
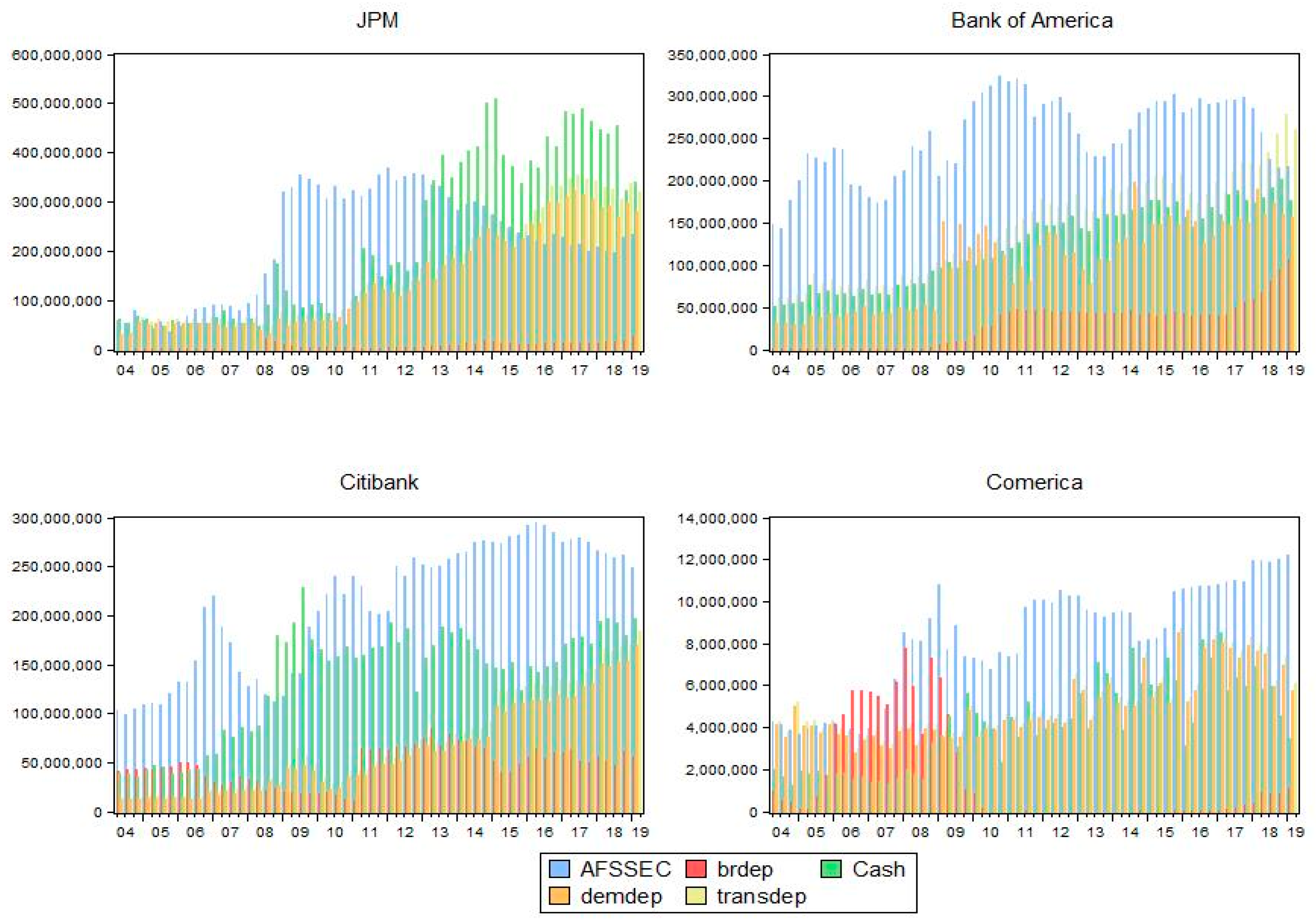
Appendix A

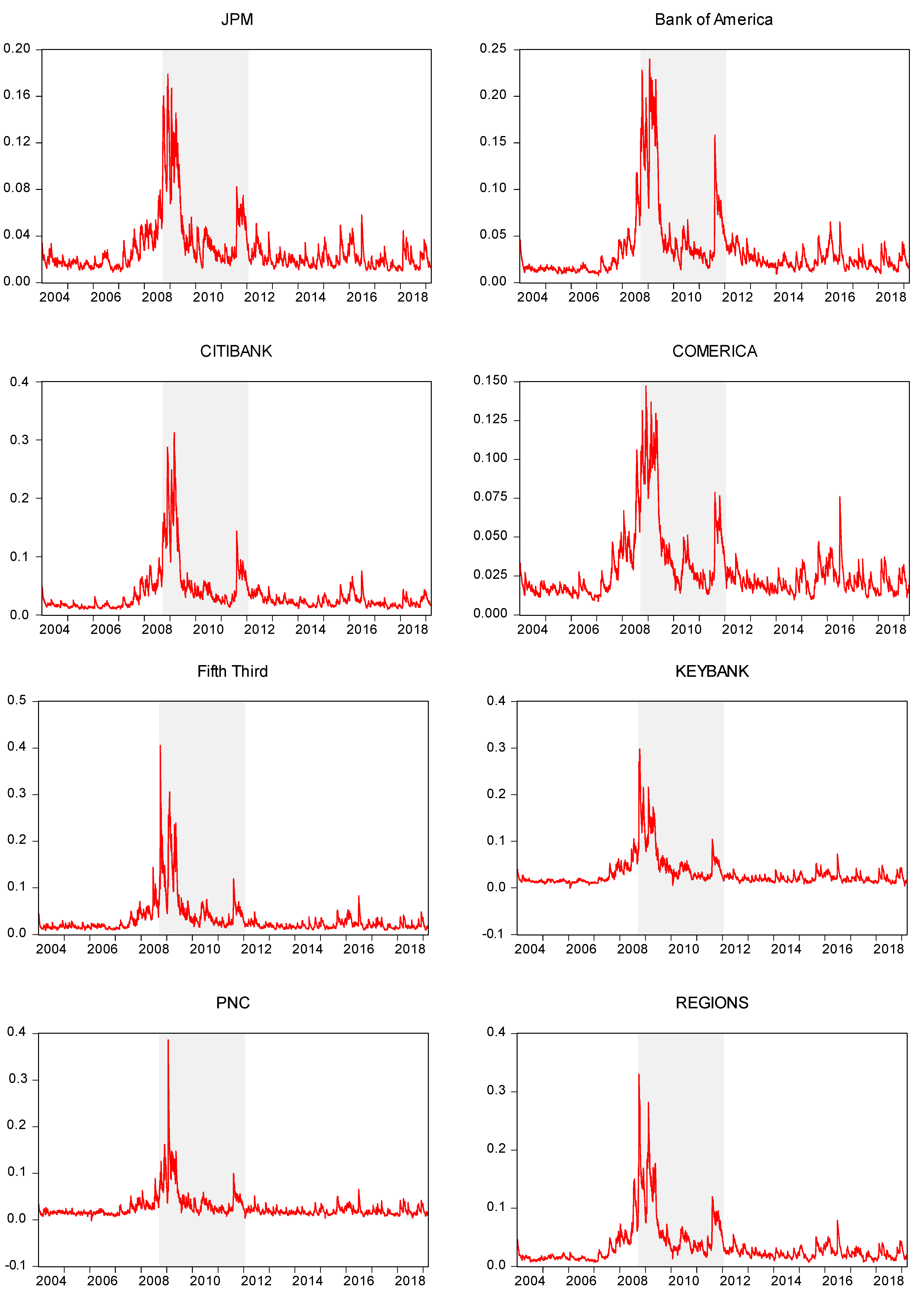
Appendix B
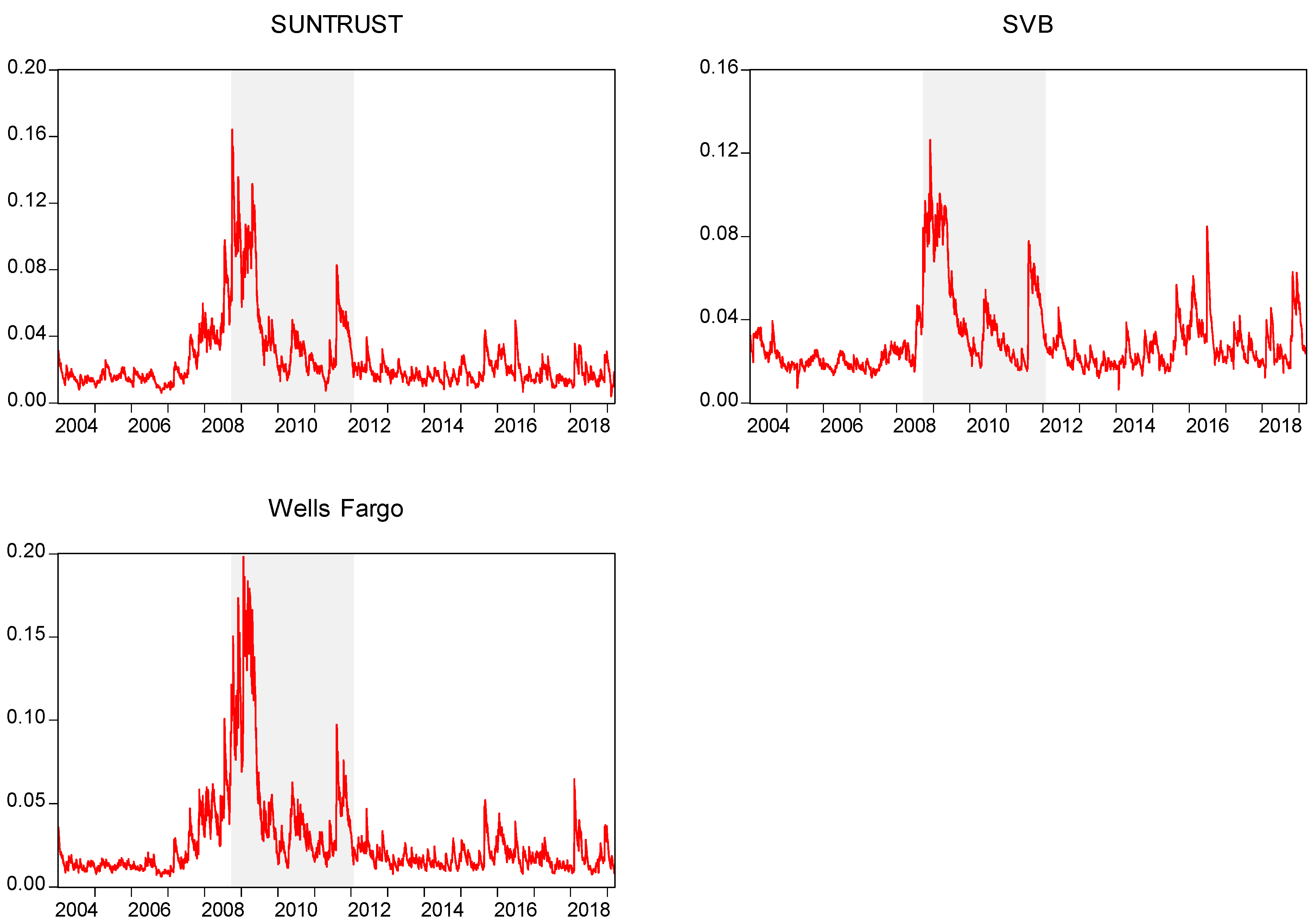
References
- Acharya, Viral V., Lasse H. Pedersen, Thomas Philippon, and Matthew Richardson. 2010. Measuring Systemic Risk. Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland Working Paper 2010. Available online: https://www.clevelandfed.org/en/newsroom-and-events/publications/working-papers/working-papers-archives/2010-working-papers/wp-1002-measuring-systemic-risk.aspx (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Adrian, Tobias, and Nina Boyarchenko. 2018. Liquidity policies and systemic risk. Journal of Financial Intermediation 35: 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, T., and M. K. Brunnermeier. 2016. CoVaR. American Economic Review 106: 1705–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrend, Rudiger, and Antoine Goujard. 2015. Global banking, global crises? The role of the bank balance-sheet channel for the transmission of financial crises. European Economic Review 80: 253–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldasoro, Iñaki, and Ester Faia. 2016. Systemic loops and liquidity regulation. Journal of Financial Stability 27: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, Lucia, and Carsten Detken. 2018. Identifying excessive credit growth and leverage. Journal of Financial Stability 35: 215–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Linda, Turan G. Bali, and Yi Tang. 2012. Does systemic risk in the financial sector predict future economic downturns? The Review of Financial Studies 25: 3000–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakoush, Mohamed, Enrico H. Gerding, and Simon Wolfe. 2019. Margin requirements and systemic liquidity risk. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 58: 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballings, Michel, Dirk Van den Poel, Nathalie Hespeels, and Ruben Gryp. 2015. Evaluating multiple classifiers for stock price direction prediction. Expert Systems with Applications 42: 7046–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănulescu, Georgiana-Denisa, and Elena-Ivona Dumitrescu. 2015. Which are the SIFIs? A Component Expected Shortfall approach to systemic risk. Journal of Banking & Finance 50: 575–88. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, Francesca, and Angela Gallo. 2013. Securitization and systemic risk: An empirical investigation on Italian banks over the financial crisis. International Review of Financial Analysis 30: 274–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, Stephen, and Andrew Hindmoor. 2018. Are the major global banks now safer? Structural continuities and change in banking and finance since the 2008 crisis. Review of International Political Economy 25: 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ameur, Hachmi, Fredj Jawadi, Wael Louhichi, and Abdoulkarim Idi Cheffou. 2017. Modeling International Stock Price Comovements with High-Frequency Data. Macroeconomic Dynamics, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billio, Monica, Roberto Casarin, Michele Costola, and Andrea Pasqualini. 2016. An entropy-based early warning indicator for systemic risk. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 45: 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, Benjamin M., Tyler J. Brough, and Todd G. Griffith. 2017. Bank opacity and the efficiency of stock prices. Journal of Banking & Finance 76: 32–47. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, Leo. 1996. Bagging predictors. Machine learning 24: 123–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, Leo, Joseph Friedman, Charles Stone, and Richared Olshen. 1984. Classification and Regression Trees. Boca Raton: CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlees, Christian, and Robert F. Engle. 2016. SRISK: A conditional capital shortfall measure of systemic risk. The Review of Financial Studies 30: 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, Claudia M., Thomas Krause, and Lena Tonzer. 2019. Drivers of systemic risk: Do national and European perspectives differ? Journal of International Money and Finance 91: 160–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Juan-Juan, John H. J. Einmahl, Laurens de Haan, and Chen Zhou. 2015. Estimation of the marginal expected shortfall: The mean when a related variable is extreme. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B: Statistical Methodology 77: 417–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporin, Massimiliano, and Paolo Santucci de Magistris. 2012. On the evaluation of marginal expected shortfall. Applied Economics Letters 19: 175–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Carolyn W., Xiaodan Li, Edward M. H. Lin, and Min-The Yu. 2018. Systemic risk, interconnectedness, and non-core activities in Taiwan insurance industry. International Review of Economics & Finance 55: 273–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cipra, Tomáš, and Radek Heyndrich. 2017. Systemic Risk in Financial Risk Regulation. Czech Journal of Economics and Finance 67: 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, Thomas F., Alex LaPlante, and Alexey Rubtsov. 2018. Analysis of the SRISK measure and its appli-cation to the Canadian banking and insurance industries. Annals of Finance 14: 547–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cont, Rama, Artur Kotlicki, and Laura Valderrama. 2020. Liquidity at risk: Joint stress testing of solvency and liquidity. Journal of Banking & Finance 118: 105871. [Google Scholar]
- Couronné, Raphael, Philipp Probst, and Anne-Laure Boulesteix. 2018. Random forest versus logistic regression: A large-scale benchmark experiment. BMC Bioinformatics 19: 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, Douglas W., and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2005. Liquidity shortages and banking crises. Journal of Finance 60: 615–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den End, Jan Willem, and Mostafa Tabbae. 2012. When liquidity risk becomes a systemic issue: Empirical evidence of bank behaviour. Journal of Financial Stability 8: 107–20. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, Robert. 2009. Anticipating Correlations: A New Paradigm for Risk Management. Princeton: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, Robert, Eric Jondeau, and Michael Rockinger. 2014. Systemic Risk in Europe. Review of Finance 19: 145–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, Robin, Augustin Landier, and David Thesmar. 2015. Vulnerable banks. Journal of Financial Economics 115: 471–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke, Peter, and Michael Tuchscherer. 2018. Global systemic risk measures and their forecasting power for systemic events. The European Journal of Finance 25: 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautsch, Nikolaus, Julia Schaumburg, and Melanie Schienle. 2015. Financial network systemic risk contributions. Review of Finance 19: 685–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idier, Julien, Gildas Lamé, and Jean-Stéphane Mésonnier. 2014. How useful is the Marginal Expected Shortfall for the measurement of systemic exposure? A practical assessment. Journal of Banking & Finance 47: 134–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jabeur, Sami Ben, and Youssef Fahmi. 2018. Forecasting financial distress for French firms: A comparative study. Empirical Economics 54: 1173–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Loup, Soula. 2017. Measuring heterogeneity in bank liquidity risk: Who are the winners and losers? The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance 66: 302–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kleinow, Jacob, Fernando Moreira, Sascha Strobl, and Sami Vähämaa. 2017. Measuring systemic risk: A comparison of alternative market-based approaches. Finance Research Letters 21: 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Yi, Changfu Zou, Maitane Berecibar, Elise Nanini-Maury, Jonathan C. W. Chan, Peter van den Bossche, Joeri Van Mierlo, and Noshin Omar. 2018. Random forest regression for online capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries. Applied Energy 232: 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Edward MH, Edward W. Sun, and Min-Teh Yu. 2018. Systemic risk, financial markets, and performance of financial institutions. Annals of Operations Research 262: 579–603. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, Gunter, and Peter Raupach. 2013. Robustness and Informativeness of Systemic Risk Measures. Deutsche Bundesbank Research Centre, Discussion Papers 04/2013. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/70922/1/739429647.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Morris, Stephen, and Hyun Song Shin. 2008. Financial regulation in a system context. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 2008: 229–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Thach Vu Hong, Shamim Ahmed, Thanaset Chevapatrakul, and Enrico Onali. 2020. Do stress tests affect bank liquidity creation? Journal of Corporate Finance 64: 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederzoli, Chiara, and Costanza Torricelli. 2017. Systemic risk measures and macroprudential stress tests: An assessment over the 2014 EBA exercise. Annals of Finance 13: 237–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, Diane. 2015. Systemic Risk and the Solvency-Liquidity Nexus of Banks. International Journal of Central Banking 11: 193–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qi, Yanjun. 2012. Random forest for bioinformatics. In Ensemble Machine Learning. Boston: Springer, pp. 307–23. [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann, Til. 2014. Stress testing banks. International Journal of Forecasting 30: 717–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikhina, Torgyn, Dave Lowe, Sunil Daga, David Briggs, Robert Higgins, and Natasha Khovanova. 2019. Decision tree and random forest models for outcome prediction in antibody incompatible kidney transplantation. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 52: 456–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, Katarzyna. 2015. Basic indicators of systemic risk in the EU banking sector. Implications for banking regulation. International Journal of Management and Economics 47: 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Katsuyuki, Takuji Kinkyo, and Shigeyuki Hamori. 2016. Random forests-based early warning system for bank failures. Economics Letters 148: 118–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirole, Jean. 2011. Illiquidity and all its friends. Journal of Economic Literature 49: 287–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, Danilo Lopomo Beteto. 2020. Liquidity policies and financial fragility. International Review of Economics & Finance. In press, Journal Pre-Proof. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, Citibank, Comerica, Wells Fargo, SunTrust, Fifth Third, SVB, Regions, and PNC. |
| Bank | Feature Importance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPM | AFSSEC | Brdep | Demdep | Cash | Transdep |
| 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.14 | |
| Bank of America | Cash | Brdep | AFSSEC | Transdep | Demdep |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.13 | |
| Citibank | Cash | AFSSEC | Brdep | Demdep | Transdep |
| 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.1 | |
| Comerica | Cash | AFSSEC | Brdep | Demdep | Transdep |
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.13 | |
| Wells Fargo | Brdep | Cash | Transdep | AFSSEC | Demdep |
| 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |
| SunTrust | AFSSEC | Cash | Brdep | Transdep | Demdep |
| 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.11 | |
| Fifth Third | Brdep | AFSSEC | Cash | Transdep | Demdep |
| 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.11 | |
| KeyBank | Cash | Brdep | AFSSEC | Transdep | Demdep |
| 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.1 | |
| SVB | Cash | AFSSEC | Demdep | Transdep | - |
| 0.3 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.2 | ||
| Regions | Cash | Brdep | AFSSEC | Demdep | Transdep |
| 0.29 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.12 | |
| PNC | Cash | AFSSEC | Brdep | Demdep | Transdep |
| 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.13 | |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeldea, C. Modeling the Connection between Bank Systemic Risk and Balance-Sheet Liquidity Proxies through Random Forest Regressions. Adm. Sci. 2020, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci10030052
Zeldea C. Modeling the Connection between Bank Systemic Risk and Balance-Sheet Liquidity Proxies through Random Forest Regressions. Administrative Sciences. 2020; 10(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci10030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeldea, Cristina. 2020. "Modeling the Connection between Bank Systemic Risk and Balance-Sheet Liquidity Proxies through Random Forest Regressions" Administrative Sciences 10, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci10030052
APA StyleZeldea, C. (2020). Modeling the Connection between Bank Systemic Risk and Balance-Sheet Liquidity Proxies through Random Forest Regressions. Administrative Sciences, 10(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci10030052





