Assessment of the Levels of Pollution and of Their Risks by Radioactivity and Trace Metals on Marine Edible Fish and Crustaceans at the Bay of Bengal (Chattogram, Bangladesh)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Methods for Determining Radioactivity and Trace Metals
2.2.1. Gamma Spectrometry Analysis
2.2.2. Determination of Trace Metals
2.3. Radiation Dose and Risk Assessment
2.3.1. Radiation Dose Assessment
Activity Concentration
Total Effective Dose
2.3.2. Radiation Risk Assessment
Internal Hazard Index (Hin)
Excess Lifetime Cancer Risk (ELCR)
2.4. Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals
2.4.1. Estimated Daily Intake (EDI)
2.4.2. Target Hazard Quotient (THQ)
2.4.3. Hazard Index (HI)
2.4.4. Target Cancer Risk
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Radiation Dose and Risk Assessment by Radioactivity Analysis
3.2. Pollution Level and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Analysis
3.2.1. Trace Metal Concentration
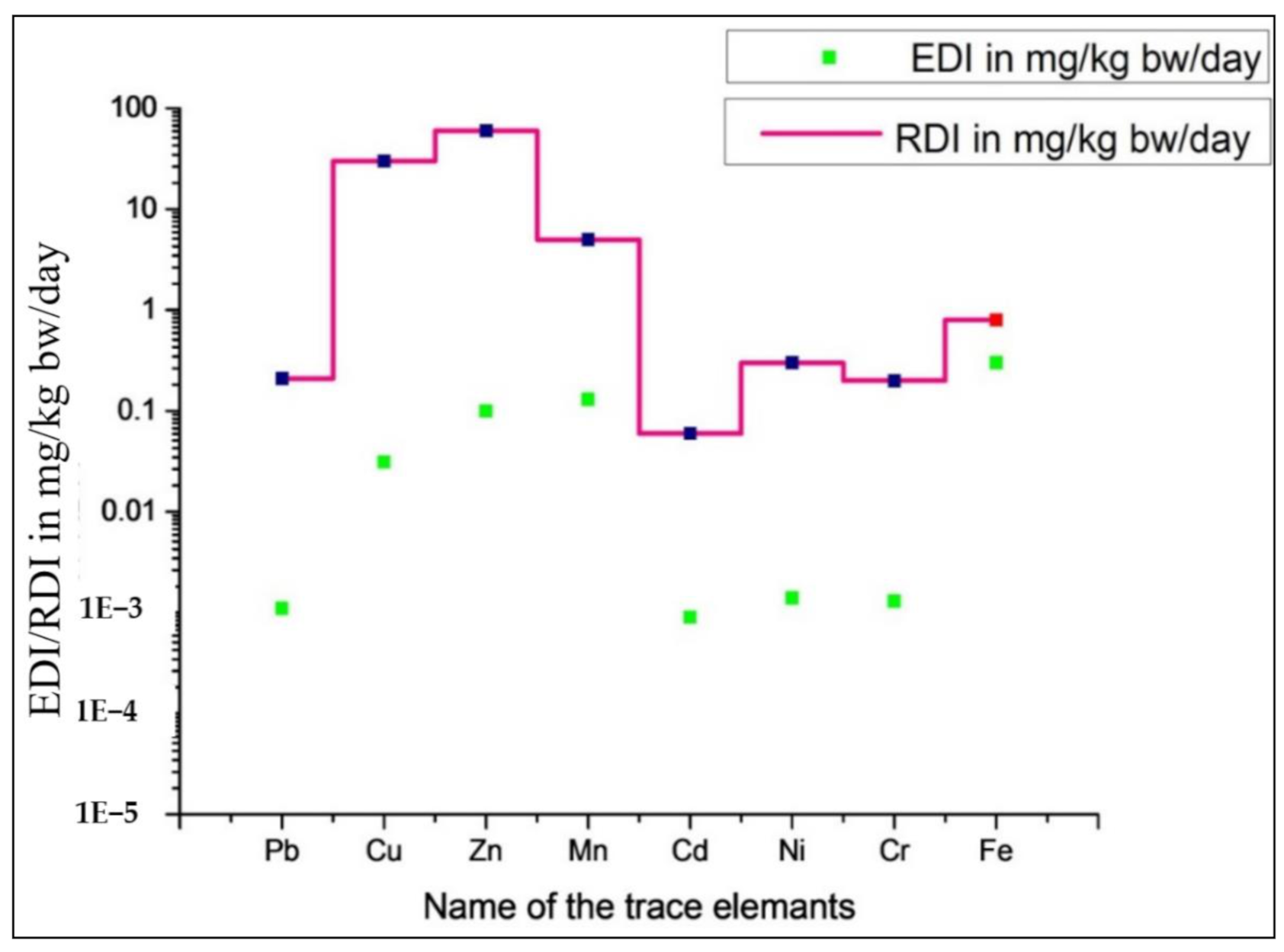
3.2.2. Estimated Daily Intake (EDI)
3.2.3. Target Hazard Quotients (THQ)
3.2.4. Hazard Index (HI)
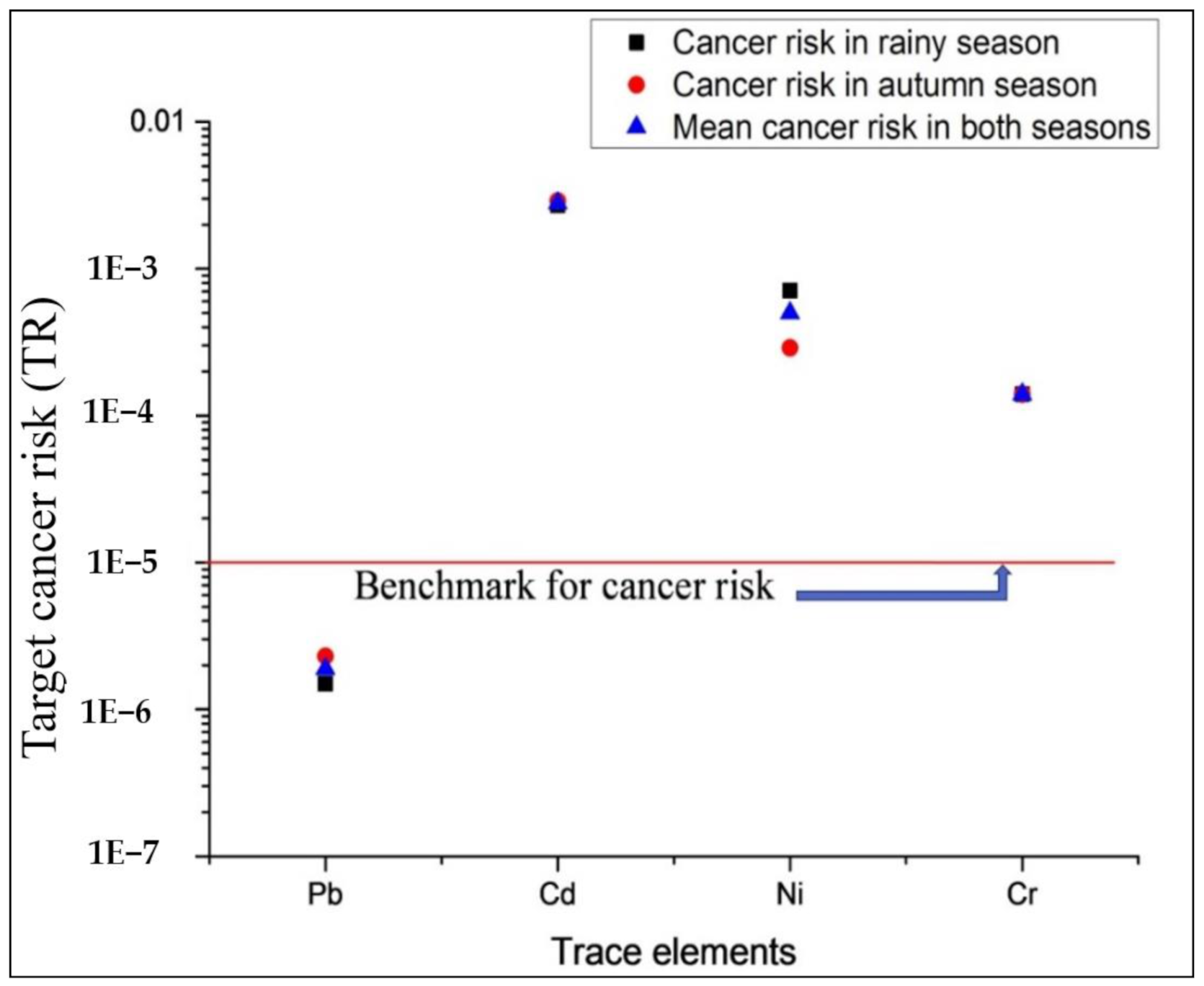
3.2.5. Target Cancer Risk (TR)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghorab, M.A. Environmental pollution by heavy metals in the aquatic ecosystems of Egypt. Open Access J. Toxicol. 2018, 3, 555603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.; Ali, M.; Rahman, M. Marine boundary confirmation of Bangladesh: Potentials of sea resources and challenges ahead. Cost Manag. 2015, 43, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.K.; Chakraborty, S.R.; Rahman, A.R.; Deb, A.K.; Kamal, M.; Bhuian, A.S.I. Measurement of radioactivity and hence define the radiological risk associated with the Chittagong city site coastal sediment containing all types of wastes (mills, factories, industries, and municipalities) in Bangladesh. Radiat. Prot. Environ. 2011, 34, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, T.; Hoque, S.; Akter, S. Pollution in the bay of Bengal: Impact on marine ecosystem. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K. Sources of radioactivity in the ocean environment: From low level waste to nuclear powered submarines. J. Hazard. Mater. 1988, 18, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Saoca, C.; Ferrantelli, V.; Cammilleri, G.; Capillo, G.; Piccione, G. Relationship between arsenic accumulation in tissues and hematological parameters in mullet caught in Faro Lake: A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8821–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mille, T.; Cresson, P.; Chouvelon, T.; Bustamante, P.; Brach-Papa, C.; Bruzac, S.; Rozuel, E.; Bouchoucha, M.; Tiphaine, M.; Pierre, C.; et al. Trace metal concentrations in the muscle of seven marine species: Comparison between the Gulf of Lions (North-West Mediterranean Sea) and the Bay of Biscay (North-East Atlantic Ocean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Piccione, G.; Tribulato, K.; Ferrantelli, V.; Giangrosso, G.; Arfuso, F.; Faggio, C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two italian lakes. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammilleri, G.; Vazzana, M.; Arizza, V.; Giunta, F.; Vella, A.; Dico, G.L.; Giaccone, V.; Giofrè, S.V.; Giangrosso, G.; Cicero, N.; et al. Mercury in fish products: What’s the best for consumers between bluefin tuna and yellowfin tuna? Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammilleri, G.; Galluzzo, F.G.; Fazio, F.; Pulvirenti, A.; Vella, A.; Dico, G.M.L.; Macaluso, A.; Ciaccio, G.; Ferrantelli, V. Mercury detection in benthic and pelagic fish collected from Western Sicily (Southern Italy). Animals 2019, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandkumar, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Prabakaran, K.; Bing, C.H.; Rajaram, R.; Li, J.; Du, D. Bioaccumulation of trace metals in the coastal Borneo (Malaysia) and health risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, M.U.; Asaduzzaman, K.; Nawi, S.M.; Usman, A.R.; Amin, Y.M.; Daar, E.; Bradley, D.A.; Ahmed, H.; Okhunov, A.A. assessment of radiation and heavy metals risk due to the dietary intake of marine fishes (Rastrelliger kanagurta) from the straits of Malacca. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalay, M.; Canli, M. Elimination of essential (Cu, Zn) and non-essential (Cd, Pb) metals from tissues of a freshwater fish Tilapia zilli. Turk. J. Zool. 2000, 24, 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Gorur, F.K.; Keser, R.; Akçay, N.; Dizman, S. Radioactivity and heavy metal concentrations of some commercial fish species consumed in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalewska, T.; Suplińska, M. Fish pollution with anthropogenic 137Cs in the southern Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantillo, A. Comparison of results of Mussel Watch Programs of the United States and France with Worldwide Mussel Watch Studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- i Batlle, J.V. Radioactivity in the Marine Environment. In Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 8387–8425. [Google Scholar]
- Elnabris, K.J.; Muzyed, S.K.; El-Ashgar, N.M. Heavy metal concentrations in some commercially important fishes and their contribution to heavy metals exposure in Palestinian people of Gaza Strip (Palestine). J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 13, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, M.U.; Heffny, N.; Adillah, B.; Amin, Y.M.; Bradley, D. Elevated concentration of radioactive potassium in edible algae cultivated in Malaysian seas and estimation of ingestion dose to humans. Algal Res. 2019, 38, 101386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, M.U.; Uwatse, O.B.; Khairi, K.A.B.S.; Faruque, M.R.I.; Bradley, D.A. Terrestrial radionuclides in surface (DAM) water and concomitant dose in metropolitan Kuala Lumpur. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2019, 185, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulah, N.-U.; Karim, M.R.; Hossain, S.; Deb, N.; Barua, B.S. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in surface and sub surface sediments of the coastal area of Kutubdia Island, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Barua, B.S.; Karim, R.; Kamal, M. Investigation of heavy metals and radionuclide’s impact on environment due to the waste products of different iron processing industries in Chittagong, Bangladesh. J. Environ. Prot. 2017, 8, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L.A. Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1699–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, R.M.; Ahmed, F. Estimation of annual effective dose to the adult Egyptian population due to natural radioactive elements in ingestion of spices. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP. Dose Coefficents for Intakes of Radionuclides by Workers; Publication 68; ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pulhani, V.; Dafauti, S.; Hegde, A.; Sharma, R.; Mishra, U. Uptake and distribution of natural radioactivity in wheat plants from soil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2005, 79, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DoF. Yearbook of Fisheries Statistics of Bangladesh 2017–18; Fisheries Resources Survey System (FRSS), Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries: Dhaka, Bangladesh , December 2018; Volume 35, p. 86.
- Aliyu, A.O.; Yakubu, A.; Ajagbe, O.O. Determination of radionuclide concentrations, hazard indices and physiochemical parameters of water, fishes and sediments in River Kaduna, Nigeria. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2018, 11, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, H.M.; Nouh, S.A.; Hamdy, A.; EL-Fiki, S.A. Evaluation of natural radioactivity in a cultivated area around a fertilizer factory. J. Nucl. Radiat. Phys. 2008, 3, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pawel, D.; Leggett, R.W.; Eckerman, K.F.; Nelson, C.B. Uncertainties in Cancer Risk Coefficients for Environmental Exposure to Radionuclides. An Uncertainty Analysis for Risk Coefficients Reported in Federal Guidance Report No. 13; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Asaduzzaman, K.; Khandaker, M.; Amin, Y.; Mahat, R. Uptake and distribution of natural radioactivity in rice from soil in north and west part of peninsular Malaysia for the estimation of ingestion dose to man. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 76, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBS. Statistical Year Book Bangladesh 2018; BBS: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2019.
- Patra, A.C.; Mohapatra, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Lenka, P.; Dubey, J.S.; Tripathi, R.M.; Puranik, V.D. Age-dependent dose and health risk due to intake of uranium in drinking water from Jaduguda, India. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2013, 155, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Mollah, M.; Alam, M.; Rahman, M.S. Seasonal investigation of heavy metals in marine fishes captured from the Bay of Bengal and the implications for human health risk assessment. Food Control 2016, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Bismark Eshun, F.; Darko, G.; Adei, E. Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in fish from the Fosu Lagoon. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shaheen, N.; Islam, S.; Mamun, H.; Mohiduzzaman, A.; Bhattacharjee, L. Dietary intake of trace elements from highly consumed cultured fish (Labeo rohita, Pangasius pangasius and Oreochromis mossambicus) and human health risk implications in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. In Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund—Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; 1, pp. 1–288.
- Wang, X.; Sato, T.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. Accumulation of heavy metals and human health risk assessment via the consumption of freshwater fish Mastacembelus armatus inhabiting, thermal power plant effluent loaded canal. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Wei, W.; Li, M.; Huang, R.; Yang, F.; Duan, Y. Heavy metal contamination in rice-producing soils of Hunan Province, China and potential health risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15584–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollution of Karnafully River Water—Causes, Effects and Recommendations. 2003. Available online: https://gspmarinebd.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/River.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Yasmin, S.; Barua, B.S.; Khandaker, M.U.; Kamal, M.; Rashid, A.; Sani, S.A.; Ahmed, H.; Nikouravan, B.; Bradley, D. The presence of radioactive materials in soil, sand and sediment samples of Potenga sea beach area, Chittagong, Bangladesh: Geological characteristics and environmental implication. Results Phys. 2018, 8, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Sediment Distribution Coefficients and Concentration Factors for Biota in the Marine Environment; Technical Report No. 422; IAEA: Wien, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.F.; Wesley, S.G. Radionuclides in resident and migratory fishes of a wedge bank region: Estimation of dose to human beings, South India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowol, O.; Giwa, K.W. Estimation of annual dose rate of natural radionuclides in man from crabs in River Odeomi Ijebu waterside Ogun State Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 438–441. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Kamal, M.; Ghose, S. Radioactivity in marine fish of the Bay of Bengal. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1995, 46, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, S.; Alam, M.; Islam, M. Radiation dose estimation from the analysis of radionuclides in marine fish of the Bay of Bengal. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2000, 87, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.H.; Miah, M.M.H.; Rahman, M.H.; Kamal, M.; Chowdhury, M.T. Study of the naturally occurring radionuclide concentrations and the estimation of dose rates for the samples collected from the St. Martin’s Island, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Materials A 2017, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Busaidi, M.; Yesudhason, P.; Almughairi, S.; Alrahbi, W.A.K.; Al-Harthy, K.; Al-Mazrooei, N.; Al-Habsi, S. Toxic metals in commercial marine fish in Oman with reference to national and international standards. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Maksud, M.; Khan, S.; Lutfa, L.; Quraishi, S.B. Dietary intake of heavy metals from eight highly consumed species of cultured fish and possible human health risk implications in Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, F.H.; Othman, M.S.; Mazlan, A.G.; Rahim, S.M.; Simon, K.D. Heavy metal concentration in fishes from the coastal waters of Kapar and Mersing, Malaysia. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, M.; Samat, S.; Yasir, M.; Yusof, M. Analysis of heavy metal accumulation in fish at terengganu coastal area, Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bahr, S.M.; Abdelghany, A. Heavy metal and trace element contents in edible muscle of three commercial fish species, and assessment of possible risks associated with their human consumption in Saudi Arabia. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2015, 2, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.J.; Dos Santos, L.M.G.; Freire, A.S.; Santelli, R.E.; Braga, A.M.C.; Krauss, T.M.; Jacob, S.D.C. Determination of inorganic trace elements in edible marine fish from Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Food Control 2012, 23, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, P.; Lavanya, R.; Veerappan, N.; Balasubramanian, T. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Three Commercial Fish Species in Cuddalore Coast, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Exp. Sci. 2011, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- De, T.K.; De, M.; Das, S.; Ray, R.; Ghosh, P.B. Level of heavy metals in some edible marine fishes of mangrove dominated tropical estuarine areas of Hooghly river, North East Coast of Bay of Bengal, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Sajwan, K.S.; Mukherjee, D.P. Distribution of heavy metals in valuable coastal fishes from North East Coast of India. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 12, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Mustafa, A.; Mirza, A.; Safiullah, S. Trace metals in tropical marine fish from the Bay of Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 1991, 107, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Mustafa, A.; Amin, M.; Safiullah, S. Trace element concentrations in tropical marine fish from the Bay of Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 1993, 138, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Biaswas, S.; Hadi, D. Trace elements in marine fish from the Bay of Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
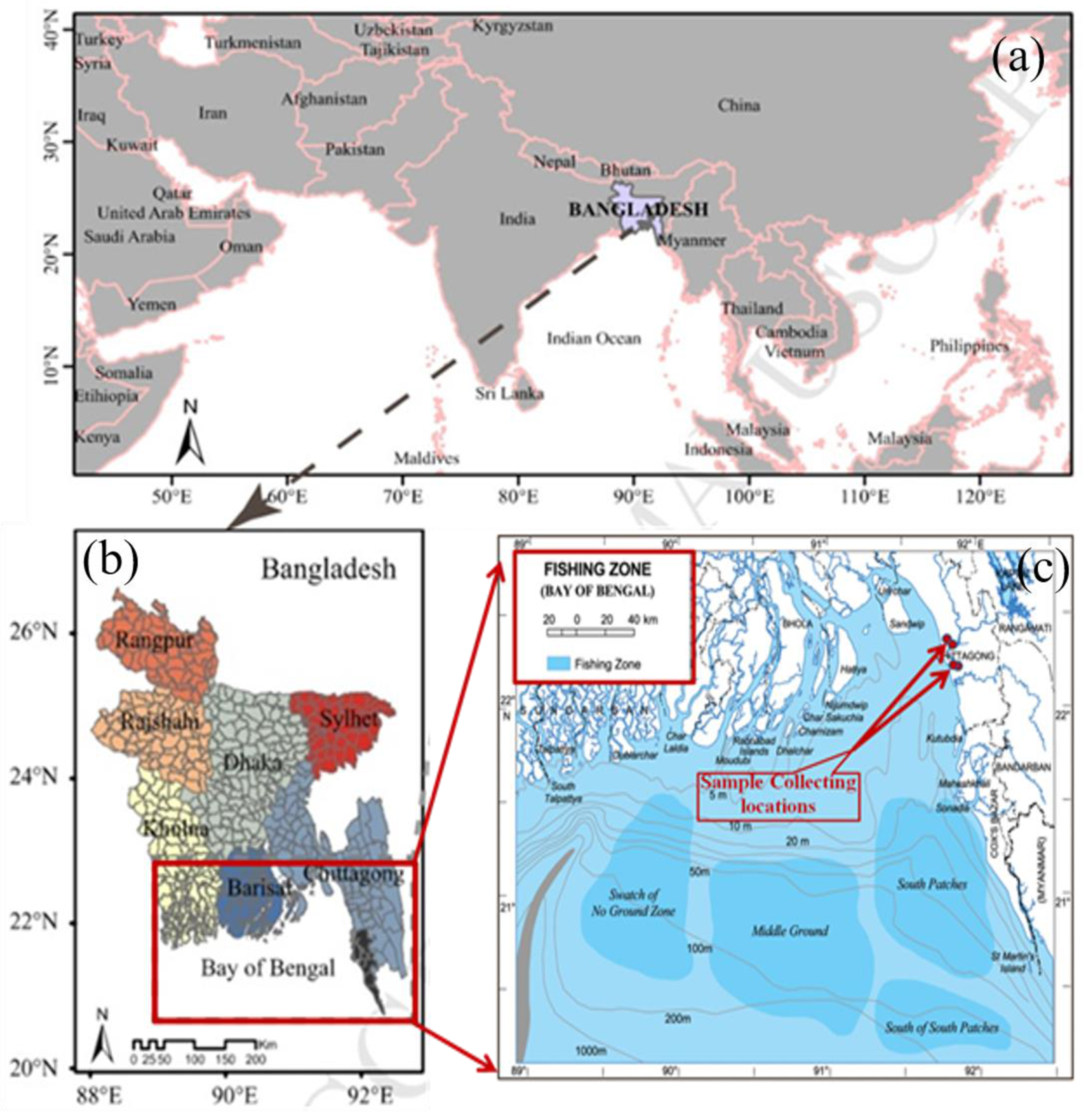

| Sample Type | Name of the Organism/Local Name | Scientific Name | Range of the Weight in gm | Range of the Length in cm | Average Moisture | Total Sample Weight in Kg | Sampling Location and Season |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 Fish samples | Hilsa fish/ Ilish fish | Tenualosa ilisha | 588–626 | 38.0–38.5 | 86.01% | 1.214 | (L-1) and R |
| 274–306 | 29.0–30.0 | 1.204 | (L-2) and A | ||||
| Bombay duck/ Lotia fish | Harpodon neherues | 62–102 | 22.0–25.5 | 90.22% | 0.844 | (L-1) and R | |
| 22–88 | 18.0–27.0 | 0.890 | (L-2) and A | ||||
| Flathead sillago/ Sundara Baila | Sillaginopsis panijus | 82–150 | 25.0–29.0 | 83.01% | 0.960 | (L-1) and R | |
| 168–320 | 30.0–38.0 | 1.152 | (L-1) and A | ||||
| Indian oil sardine/ Colombo fish | Sardinella longiceps | 50–68 | 18.5–19.5 | 77.85% | 1.014 | (L-1) and R | |
| 42–62 | 18.5–20.5 | 1.176 | (L-1) and A | ||||
| Belt fish/ Churi Fish | Trichiurus lepturus | 84–106 | 44.0–51.0 | 80.88% | 0.964 | (L-1) and R | |
| 240–322 | 62.0–73.0 | 1.116 | (L-1) and A | ||||
| Dotted gizzard shad/ Shard fish | Konosirus punctatus | 270–292 | 22.0–25.0 | 73.41% | 0.850 | (L-1) and R | |
| 255–285 | 21.0–23.0 | 0.820 | (L-1) and A | ||||
| 4 Crustacean samples | Three-spot swimming crab | Portunus sanguinolentus | 90–140 | - | 76.44% | 1.452 | (L-3) and R |
| 93–145 | - | 1.485 | (L-3) and A | ||||
| Mud crab | Scylla serrata | 60–120 | - | 82.82% | 1.441 | (L-4) and R | |
| 55–120 | - | 1.411 | (L-4) and A | ||||
| Asian Shore crab/ Chati Kakra | Hemigrapsus takanoi | 8–18 | - | 78.00% | 1.438 | (L-3) and R | |
| 8–20 | - | 1.410 | (L-3) and A | ||||
| Cat tiger shrimp/ Harina Chingri | Penaeus semisulcatus | 12–24 | 12.0–14.5 | 76.51% | 0.880 | (L-1) and R | |
| 10–26 | 12.0–16.0 | 0.850 | (L-1) and A |
| Trace Elements | RfD(Mg/Kg/Day) | CSFo(Mg/Kg bw/Day)−1 | Reference of CSFo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 4 × 10−3 | 8.5 × 10−3 | [37] |
| Cu | 4 × 10−2 | - | [37] |
| Zn | 3 × 10−1 | - | [40] |
| Mn | 1.4 × 10−1 | - | [40] |
| Cd | 1 × 10−3 | 1.5 × 101 | [41] |
| Ni | 2 × 10−2 | 1.7 × 100 | [40] |
| Cr | 3 × 10−3 | 5 × 10−1 | [41] |
| Fe | 7 × 10−1 | - | [40] |
| Sl. No. | Types of Samples | Name of Organism/Local Name | Scientific Name | No. of Samples | Mean Activity for 226Ra (Bqkg−1) | Mean Activity for 232Th (Bqkg−1) | Mean Activity for 40K (Bqkg−1) | ELCR for 226Ra | ELCR for 232Th | ELCR for 40K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fish | Hilsa fish/ Ilish fish | Tenualosa ilisha | 2 | BDL | 7 ± 1 | 310 ± 30 | BDL | 2.60 × 10−5 | 2.96× 10−4 |
| 2 | Bombay duck/ Lotia fish | Harpodon neherues | 2 | 5 ± 2 | 170 ± 30 | 270 ± 60 | 7.07 × 10−5 | 6.87 × 10−4 | 2.62× 10−4 | |
| 3 | Flathead sillago/ Sundara Baila | Sillaginopsis panijus | 2 | BDL | 190 ± 10 | 300 ± 60 | BDL | 7.60 × 10−4 | 2.86 × 10−4 | |
| 4 | Indian oil sardine/ Colombo fish | Sardinella longiceps | 2 | BDL | BDL | 210 ± 50 | BDL | BDL | 2.03 × 10−4 | |
| 5 | Belt fish/ Churi fish | Trichiurus lepturus | 2 | BDL | 11 ± 2 | 360 ± 40 | BDL | 4.23 × 10−5 | 3.44 × 10−4 | |
| 6 | Dotted gizzard shad/ Shard fish | Konosirus punctatus | 2 | BDL | BDL | 250 ± 70 | BDL | BDL | 2.37 × 10−4 | |
| 7 | Crustacean | Three-spot swimming crab | Portunus sanguinolentus | 2 | BDL | BDL | 190 ± 30 | BDL | BDL | 1.79 × 10−6 |
| 8 | Mud crab | Scylla serrata | 2 | BDL | 53 ± 10 | 240 ± 70 | BDL | 2.12 × 10−4 | 2.32 × 10−4 | |
| 9 | Asian shore crab/ Chati Kakra | Hemigrapsus takanoi | 2 | BDL | 37 ± 6 | 220 ± 50 | BDL | 1.47 × 10−4 | 2.08 × 10−4 | |
| 10 | Cat tiger shrimp/ Harina Chingri | Penaeus semisulcatus | 2 | BDL | 5 ± 2 | 130 ± 40 | BDL | 2.01 × 10−5 | 1.30 × 10−4 |
| Sl. No. | Study Year | Number of Species | 226Ra | 232Th | 40K | 137Cs | 238U | 228Ra | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | |||||||||
| 1 | 1995 | 15 | - | 0.31 ± 0.05 to 1.67 ± 0.48 | 8.5 ± 1.2 to 57.1 ± 5.3 | BDL to 1.98 ± 0.33 | 0.31 ± 0.05 to 1.19 ± 0.17 | - | M. N. Alam [47] |
| 2 | 2000 | 15 | 0.10 ± 0.03 to 1.66 ± 0.24 | - | 18.1 ± 3.4 to 86.4 ± 6.7 | 0.19 ± 0.04 to 1.47 ± 0.28 | - | 0.39 ± 0.07 to 1.35 ± 0.19 | S. Ghose [48] |
| 3 | 2017 | 2 | - | 8.5 ± 9.6 to 13 ± 17 | 265 ± 417 to 460 ± 310 | - | 9 ± 19 to 13 ± 14 | - | M. H. Kabir [49] |
| 4 | 2020 | 6 | BDL to 5 ± 2 | BDL to 190 ± 10 | 210 ± 50 to 360 ± 40 | BDL | - | - | Present Study |
| Crustacean | |||||||||
| 1 | 1995 | 5 | - | 0.36 ± 0.10 to 0.78 ± 0.23 | 7.32 ± 0.88 to 16.7 ± 1.8 | BDL to 0.47 ± 0.07 | 0.11 ± 0.01 to 0.49 ± 0.18 | - | M. N. Alam [47] |
| 2 | 2020 | 4 | BDL | BDL to 53 ± 10 | 130 ± 40 to 240 ± 70 | BDL | BDL | - | Present Study |
| Sl. No. | Types of Samples | Name of the Organism/Local Name | Scientific Name | No. of Samples | Annual Effective Dose for 226Ra (Svy−1) | Annual Effective Dose for 232Th (Svy−1) | Annual Effective Dose for 40K (Svy−1) | Total Annual Effective Dose (Svy−1) | Total Internal Hazard Index (Hin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fish | Hilsa fish/ Ilish fish | Tenualosa ilisha | 2 | BDL | 3.39 × 10−5 | 4.33 × 10−5 | 7.72 × 10−5 | 0.09 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | Bombay duck/ Lotia fish | Harpodon neherues | 2 | 2.88 × 10−5 | 8.96 × 10−4 | 3.82 × 10−5 | 9.63 × 10−4 | 0.74 ± 0.13 | |
| 3 | Flathead sillago/ Sundara Baila | Sillaginopsis panijus | 2 | BDL | 9.90 × 10−4 | 4.18 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−3 | 0.79 ± 0.06 | |
| 4 | Indian oil sardine/ Colombo fish | Sardinella longiceps | 2 | BDL | BDL | 2.97 × 10−5 | 2.97 × 10−5 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | |
| 5 | Belt fish/ Churi Fish | Trichiurus lepturus | 2 | BDL | 5.52 × 10−5 | 5.03 × 10−5 | 1.05 × 10−4 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | |
| 6 | Dotted gizzard shad/ Shard fish | Konosirus punctatus | 2 | BDL | BDL | 3.47 × 10−5 | 3.47 × 10−5 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | |
| 7 | Crustacean | Three-spot swimming crab | Portunus sanguinolentus | 2 | BDL | BDL | 2.62 × 10−5 | 2.62 × 10−5 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | Mud crab | Scylla serrata | 2 | BDL | 2.76 × 10−4 | 3.40 × 10−5 | 3.10 × 10−4 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | |
| 9 | Asian shore crab/ Chati Kakra | Hemigrapsus takanoi | 2 | BDL | 1.92 × 10−4 | 3.04 × 10−5 | 2.22 × 10−4 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | |
| 10 | Cat tiger shrimp/ Harina Chingri | Penaeus semisulcatus | 2 | BDL | 2.63 × 10−5 | 1.90 × 10−5 | 4.52 × 10−5 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| Name of the Organism/Local Name | Hilsa Fish/ Ilish Fish | Bombay Duck/ Lotia Fish | Flathead Sillago/ Sundara Baila | Indian Oil Sardine/ Colombo Fish | Belt Fish/ Churi Fish | Dotted Gizzard Shad/ Shard Fish | Three-Spot Swimming Crab | Mud Crab | Asian Shore Crab/ Chati Kakra | Cat Tiger Shrimp/ Harina Chingri |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Tenualosa ilisha | Harpodon neherues | Sillaginopsis panijus | Sardinella longiceps | Trichiurus lepturus | Konosirus punctatus | Portunus sanguinolentus | Scylla serrata | Hemigrapsus takanoi | Penaeus semisulcatus |
| Sample Type | Fish | Crustacean | ||||||||
| No. of samples from two seasons | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Mean Pb conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 0.37 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| Mean Cu conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 4.1 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 62 ± 20 | 100 ± 0 | 75 ± 6 | 44 ± 0 |
| Mean Zn conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 73 ± 0 | 58 ± 0 | 61 ± 0 | 170 ± 0 | 63 ± 0 | 74 ± 0 | 130 ± 1 | 140 ± 1 | 120 ± 1 | 83 ± 1 |
| Mean Mn conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 16 ± 0 | 5.8 ± 0.0 | 18 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 | 11 ± 0 | 10 ± 0 | 89 ± 1 | 610 ± 1 | 450 ± 3 | 17 ± 0 |
| Mean Cd conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 0.14 ± 0.00 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.39 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 3.3 ± 0.0 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 1.8 ± 0.0 |
| Mean Ni conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 6.9 ± 0.1 | BDL | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | BDL | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| Mean Cr conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 0.45 ± 0.00 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 0.58 ± 0.00 | 0.79 ± 0.00 | 0.79 ± 0.00 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 0.70 ± 0.00 |
| Mean Fe conc. in mgkg−1 DW | 790 ± 10 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 140 ± 1 | 370 ± 2 | 120 ± 1 | 130 ± 1 | 330 ± 1 | 400 ± 2 | 560 ± 3 | 55 ± 0 |
| Sl. No. | Area | Species | Pb | Cd | Ni | Cr | Cu | Zn | Mn | Fe | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | Five species: P. carcinus, W. attu, S. sinensis, R. rita, S. sihama, and B. strogylurus | - | - | 2.70–15.20 | - | 0.65–66.00 | 26.00–78.80 | 1.89–7.11 | 37.90–182.00 | [61] |
| 2 | Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | Six species: C. neglecta, C. reba, J. argentus, H. nehereus, S. fhasa, and L. savala | 1.67–2.58 | 0.009–0.17 | 6.44–7.58 | - | 3.33–4.69 | 18.86–33.89 | 5.01–11.14 | 60.55–451.10 | [59] |
| 3 | Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | Nine species: L. calcarifer, P. pangasius, P. indicus, I. megaloptera, R. russelliana, L. stylifetus, R. kanagurta, S. guttatum, P. paradiseus, and O. militaris | 0.58–4.03 | 0.04–0.13 | 0.73–6.11 | - | 0.46–7.74 | 25.67–119.36 | 1.46–9.02 | 37.70–118.91 | [60] |
| 4 | Northeast Coast of the Bay of Bengal, India | Five species: S. phasa, P. argentus, G. sparsipapillus, L. parsia, and C. sp. | 12.40–19.96 | 0.62–1.20 | 2.20–3.69 | ND–3.89 | 16.22–47.97 | 12.13–44.74 | - | - | [57] |
| 5 | Cuddalore Coast, Tamil Nadu, India | Three species: R. kanagurta, K. axillaris, and S. longiceps | - | 0.35–0.43 | 0.62–0.79 | 0.66–0.86 | 0.42–0.61 | 20.10–26.20 | - | - | [56] |
| 6 | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | Eleven species: S. salar, S. brasiliensis, P. saltatrix, M. furnieri, C. leiarchus, C. crysos, P. arenatus, M. cephalus, G. brasiliensis, L. villarii, and P. numida | 0.04–0.30 | 0.001–0.09 | - | - | 1.20–2.90 | 2.70–9.30 | 0.30–1.70 | 1.60–7.50 | [55] |
| 7 | Northeast Coast of India | Nine species: H. nehereus, T. trichiurus, S. laticaudus, D. albida, P. argentius, A. sp., F. niger, H. ilisha, and R. kanagurta | - | 0.01–1.10 | - | - | 0.50–28.20 | 3.00–99.10 | 0.50–12.00 | 10.40–249.70 | [58] |
| 8 | Mersing, Malaysia | Two species: A. thalassinus, and J. belangeri | - | 2.20–2.34 | - | - | 8.80–12.91 | 120.91–217.37 | 4.34–9.67 | - | [52] |
| 9 | Saudi Arabia | Three species: L. nebulosus, P. major, and S. cantharu | 0.002–0.003 | 0.001–0.001 | - | - | 0.026–0.093 | 0.037–0.376 | 0.008–0.036 | 0.222–1.016 | [54] |
| 10 | Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | Ten species: L. calcarifer, P. pangasius, P. indicus, I. megaloptera, A. cruciger, P. chinensis, S. phasa, S. guttatum, C. reba, and A. arius | 0.80–6.26 | 0.02–0.47 | 1.88–7.56 | 1.27–4.66 | ≤ 8.54 | 13.22–74.36 | 3.63–17.80 | - | [35] |
| 11 | Terengganu Coastal Area, Malaysia | Ten species: S. leptolepis, D. maraudsi, E. lanceolatus, P. tayenus, Rastrelliger, M. cordyla, N. soldado, P. filamentosus, Bramidae, and S. canaliculatus | 0.0002–0.007 | 0.0008–0.015 | - | - | 0.0021–0.012 | 0.0488–0.151 | 0.0068–0.041 | 0.3995–0.667 | [53] |
| 12 | Northwest Mediterranean Sea | Six species: G. melastomus, S. canicula, H. dactylopterus, L. boscii, M. poutassou, and P. blennoides | 0.00–0.90 | 0.00–0.03 | 0.02–7.00 | - | 0.10–10.60 | 12.10–60.30 | - | - | [7] |
| 13 | Northeast Atlantic Ocean | Six species: G. melastomus, S. canicula, H. dactylopterus, L. boscii, M. poutassou, and P. blennoides | 0.01–0.26 | 0.00–0.04 | 0.00–0.53 | - | 0.40–5.80 | 9.90–40.00 | - | - | [7] |
| 14 | Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | Six species: T. ilisha, H. neherues, S. panijus, S. longiceps, T. lepturus, and K. punctatus | 0.12–4.6 | 0.11–2 | BDL–6.9 | 0.45–1.8 | 1.6–4.1 | 58–170 | 5.8–20 | 5.5–790 | PS |
| Sampling Time | Rainy Season | Autumn Season | Mean EDI (mgkg−1 Body Weight per Day) | Mean THQ | HI | ||||
| Trace Metals | Average Concentration (mgkg−1) DW | EDI (mgkg−1 Body Weight per Day) | THQ | Average Concentration (mgkg−1) DW | EDI (mgkg−1 Body Weight per Day) | THQ | |||
| Pb | 0.79 | 8.29 × 10−4 | 4.31 × 10−5 | 1.26 | 1.31 × 10−3 | 8.54 × 10−5 | 1.07 × 10−3 | 6.43 × 10−5 | 8.82 × 10−4 |
| Cu | 27.20 | 2.84 × 10−2 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 33.10 | 3.45 × 10−2 | 1.80 × 10−4 | 3.15 × 10−2 | 1.64 × 10−4 | |
| Zn | 93.92 | 9.80 × 10−2 | 6.79 × 10−5 | 98.69 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 7.14 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−1 | 6.96 × 10−5 | |
| Mn | 122.51 | 1.28 × 10−1 | 1.90 × 10−4 | 128.20 | 1.34 × 10−1 | 1.99 × 10−4 | 1.31 × 10−1 | 1.94 × 10−4 | |
| Cd | 0.84 | 8.80 × 10−4 | 1.83 × 10−4 | 0.88 | 9.18 × 10−4 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 8.99 × 10−4 | 1.87 × 10−4 | |
| Ni | 1.93 | 2.01 × 10−3 | 2.09 × 10−5 | 0.78 | 8.09 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−5 | 1.41 × 10−3 | 1.65 × 10−5 | |
| Cr | 1.29 | 1.35 × 10−3 | 9.36 × 10−5 | 1.26 | 1.32 × 10−3 | 9.15 × 10−5 | 1.34 × 10−3 | 9.26 × 10−5 | |
| Fe | 308.62 | 3.22 × 10−1 | 9.56 × 10−5 | 272.24 | 2.84 × 10−1 | 9.37 × 10−5 | 3.03 × 10−1 | 9.47 × 10−5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, K.P.; Hossain, S.; Deb, N.; Bhuian, A.K.M.S.I.; Gonçalves, S.C.; Hossain, S.; Hossen, M.B. Assessment of the Levels of Pollution and of Their Risks by Radioactivity and Trace Metals on Marine Edible Fish and Crustaceans at the Bay of Bengal (Chattogram, Bangladesh). Environments 2021, 8, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8020013
Biswas KP, Hossain S, Deb N, Bhuian AKMSI, Gonçalves SC, Hossain S, Hossen MB. Assessment of the Levels of Pollution and of Their Risks by Radioactivity and Trace Metals on Marine Edible Fish and Crustaceans at the Bay of Bengal (Chattogram, Bangladesh). Environments. 2021; 8(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Krishna Prasad, Shahadat Hossain, Nipa Deb, A.K.M. Saiful Islam Bhuian, Sílvia C. Gonçalves, Shahadat Hossain, and Mohammad Belal Hossen. 2021. "Assessment of the Levels of Pollution and of Their Risks by Radioactivity and Trace Metals on Marine Edible Fish and Crustaceans at the Bay of Bengal (Chattogram, Bangladesh)" Environments 8, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8020013
APA StyleBiswas, K. P., Hossain, S., Deb, N., Bhuian, A. K. M. S. I., Gonçalves, S. C., Hossain, S., & Hossen, M. B. (2021). Assessment of the Levels of Pollution and of Their Risks by Radioactivity and Trace Metals on Marine Edible Fish and Crustaceans at the Bay of Bengal (Chattogram, Bangladesh). Environments, 8(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8020013









