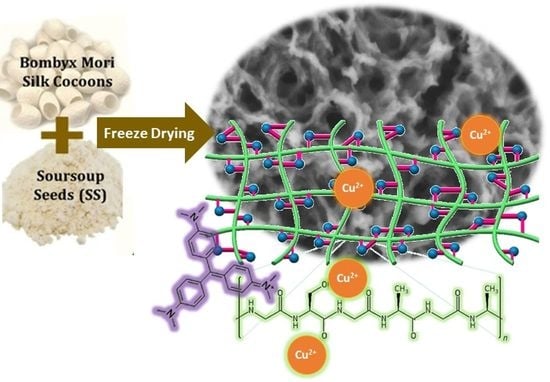
Hierarchically 3-D Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Regenerated Silk Fibroin Solution
2.3. Preparation of SF:SS Composite Adsorbent Using Freeze Drying
2.4. Organic Dye and Heavy Metal Adsorption Test
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussions
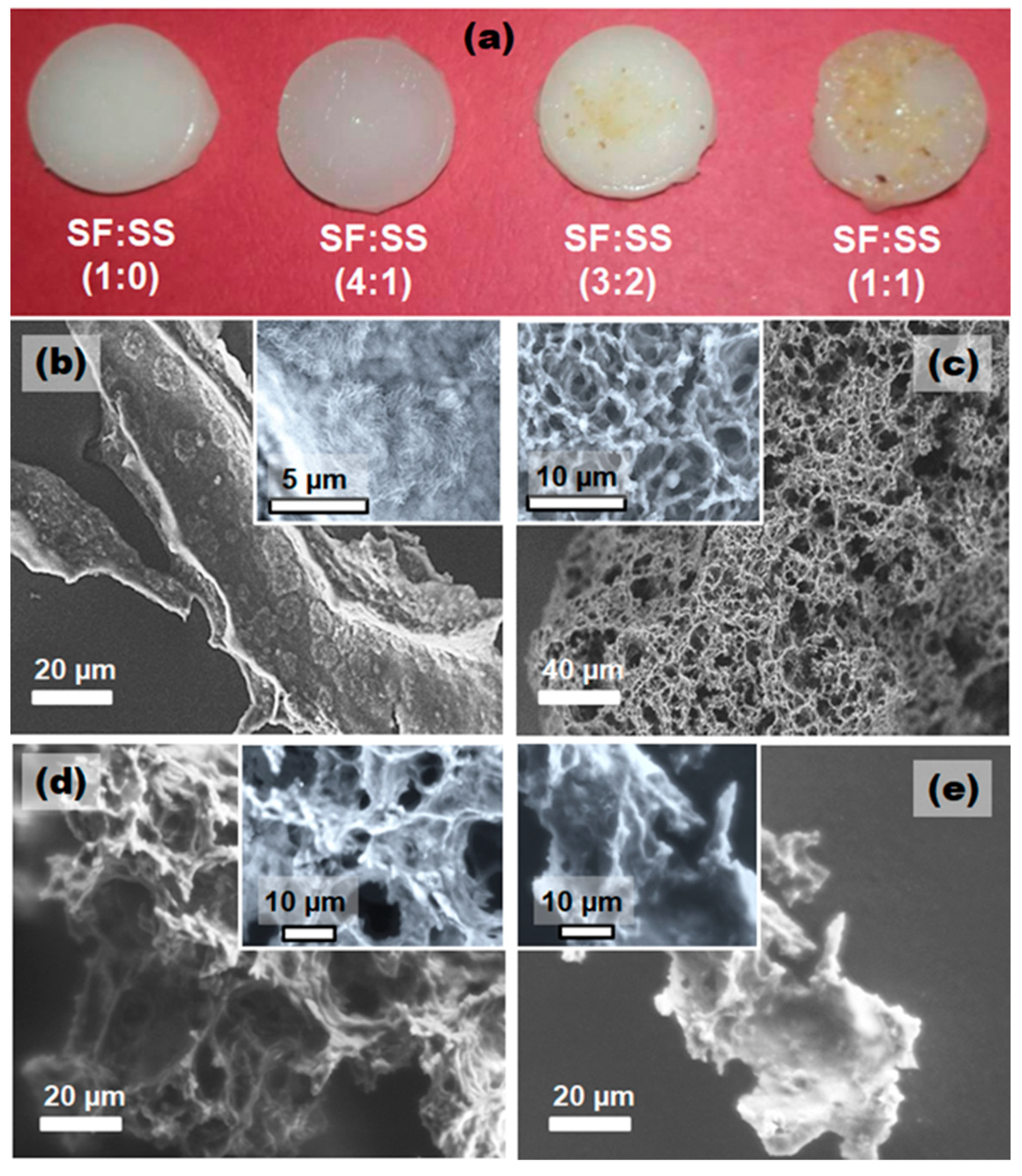
3.1. Micromorphology of SF:SS Composite Adsorbent
3.2. Physical Properties of SF:SS Composite Adsorbent
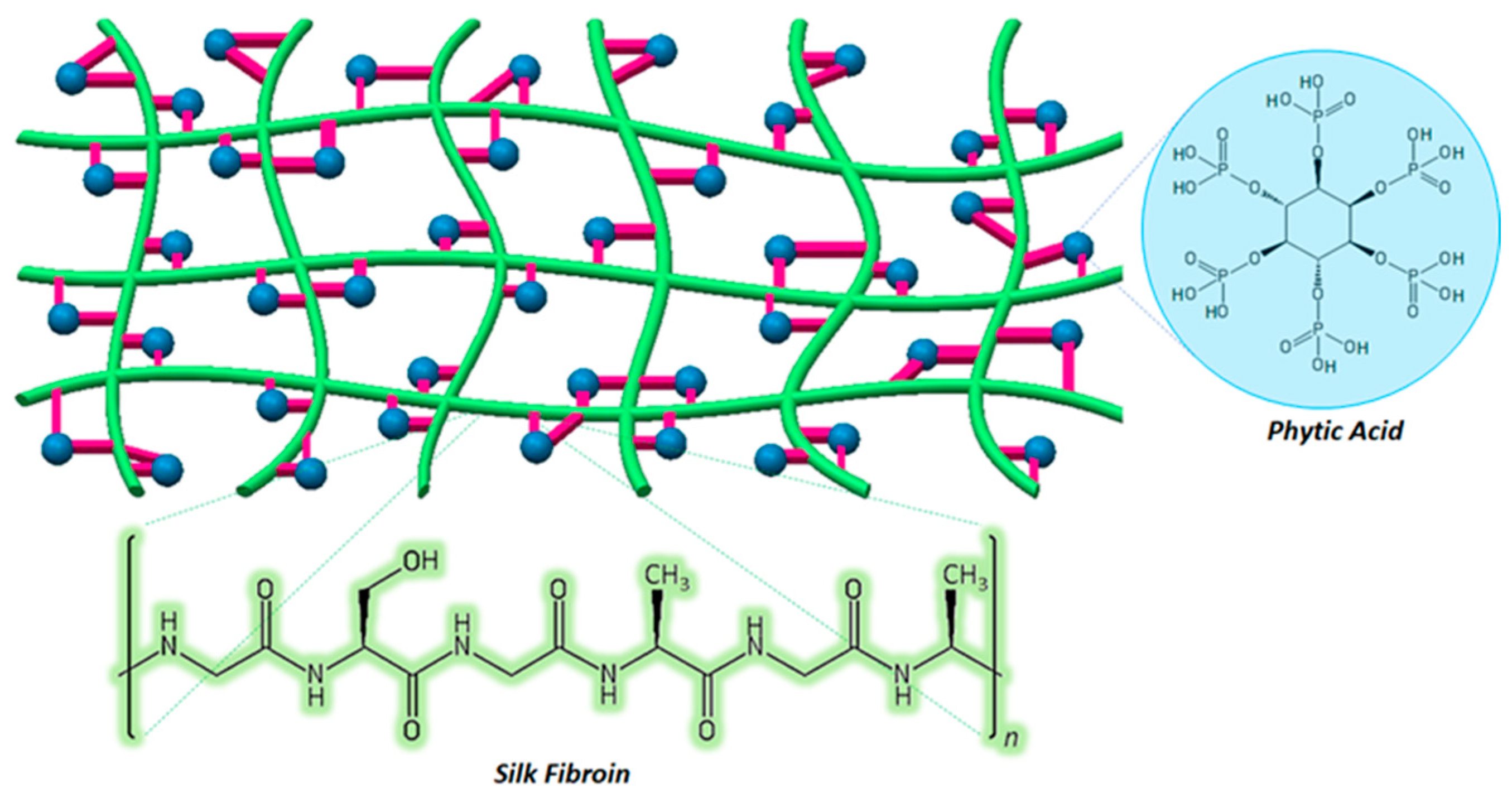
3.3. Proposed Pore Formation in SF:SS Composite Adsorbent
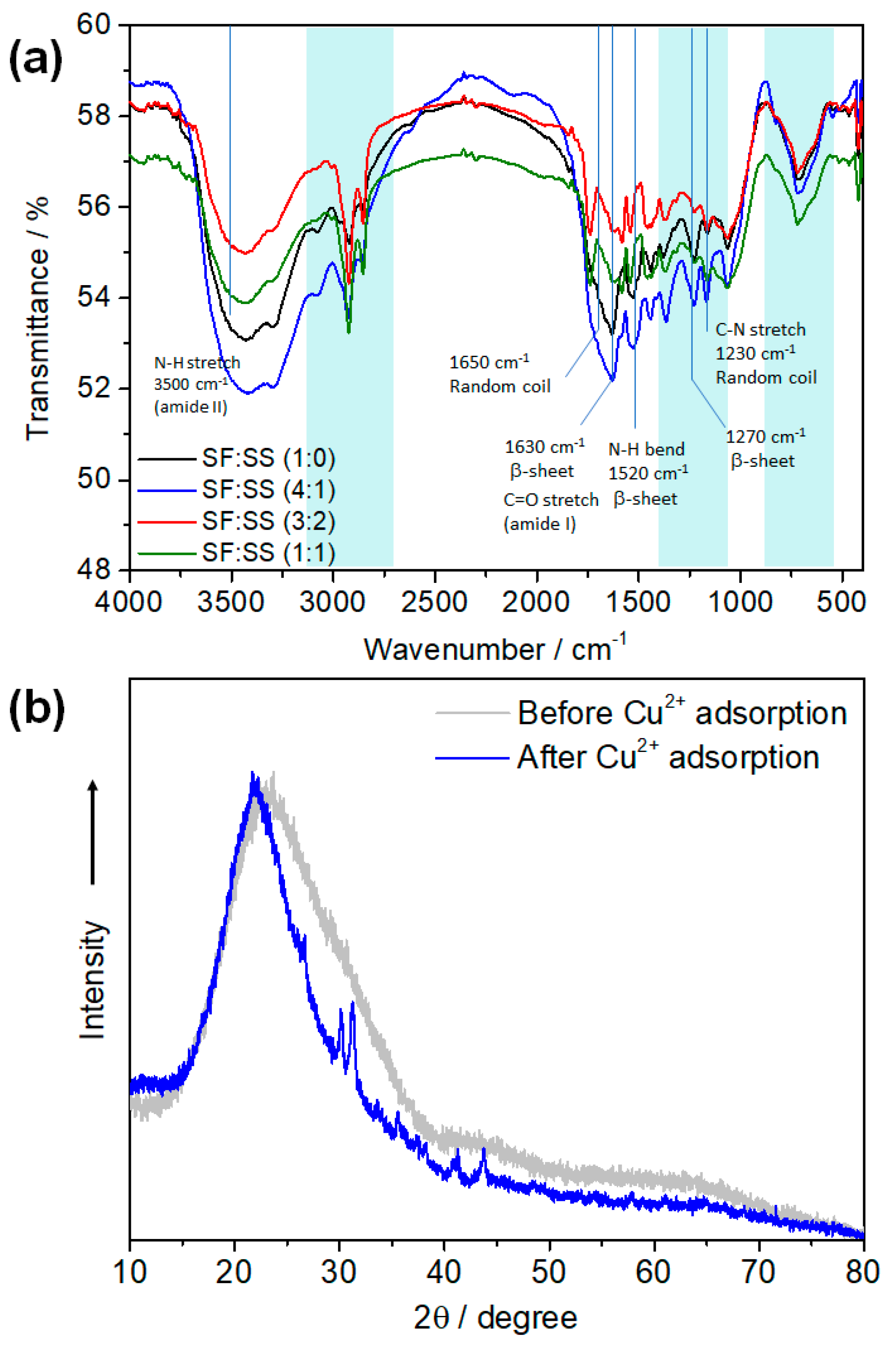
3.4. Thermal Properties of SF:SS Composite Adsorbent
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics of Crystal Violet and Cu2+ onto SF:SS Composite
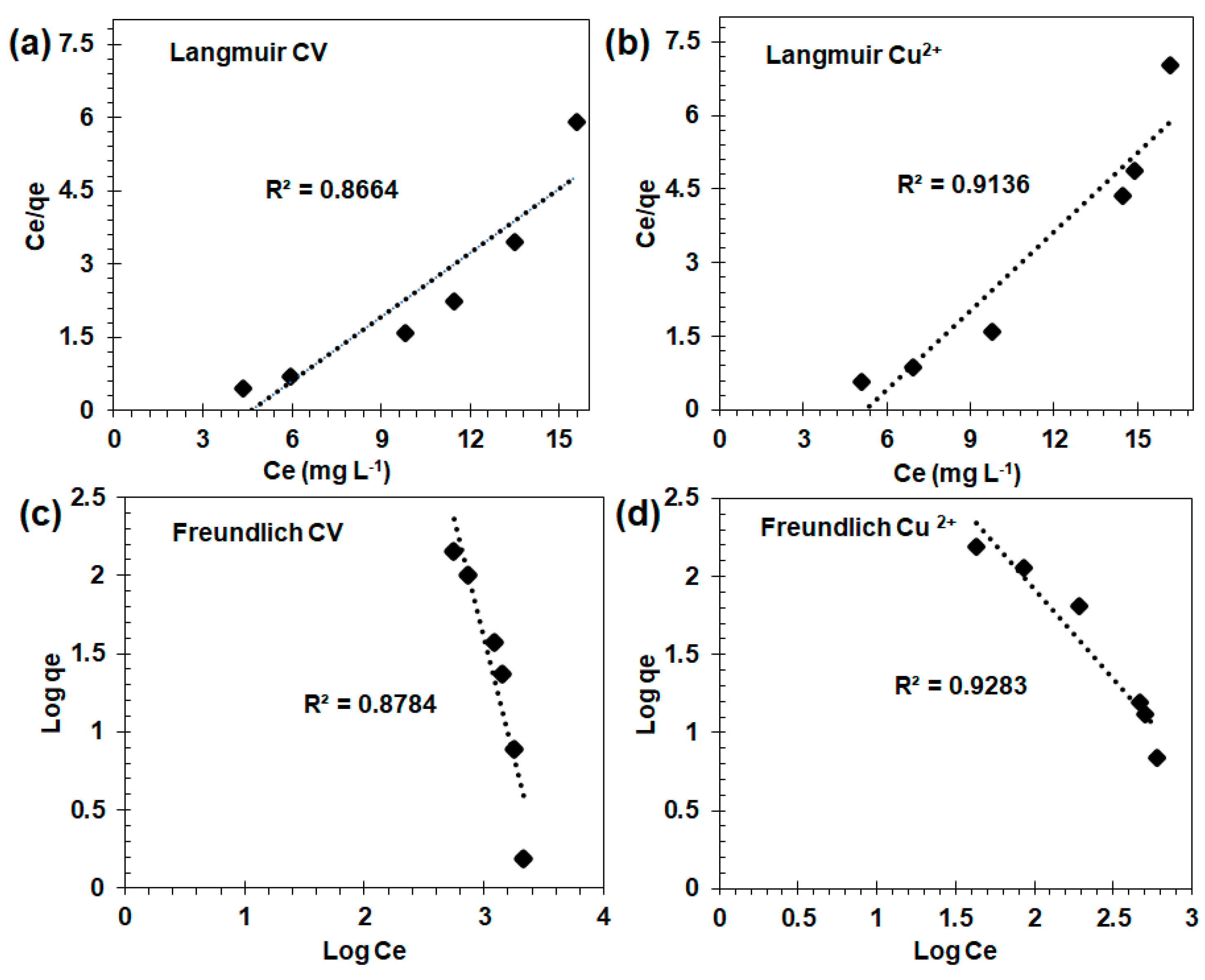
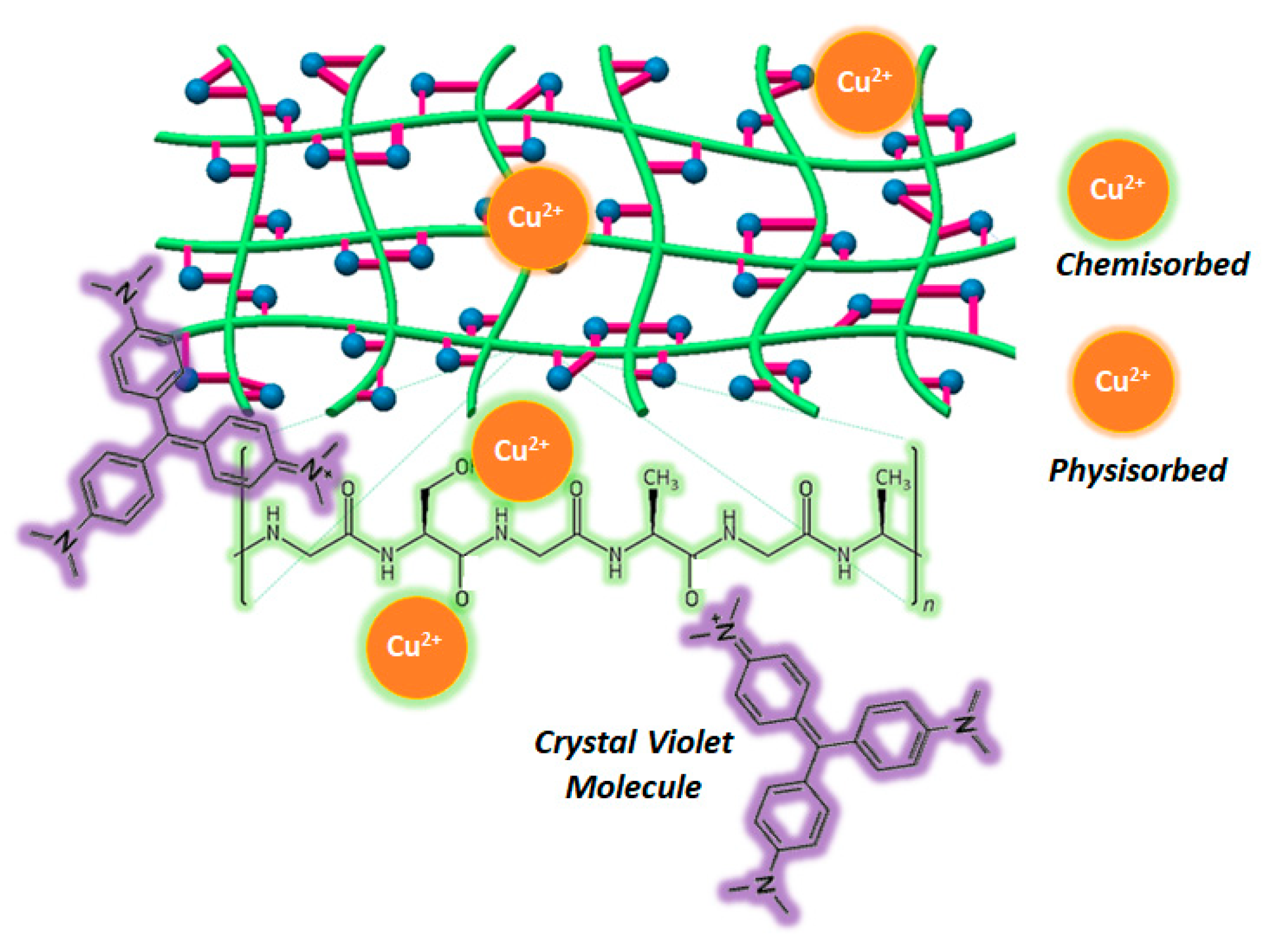
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm and Mechanism of CV and Cu2+ onto SF:SS Composite
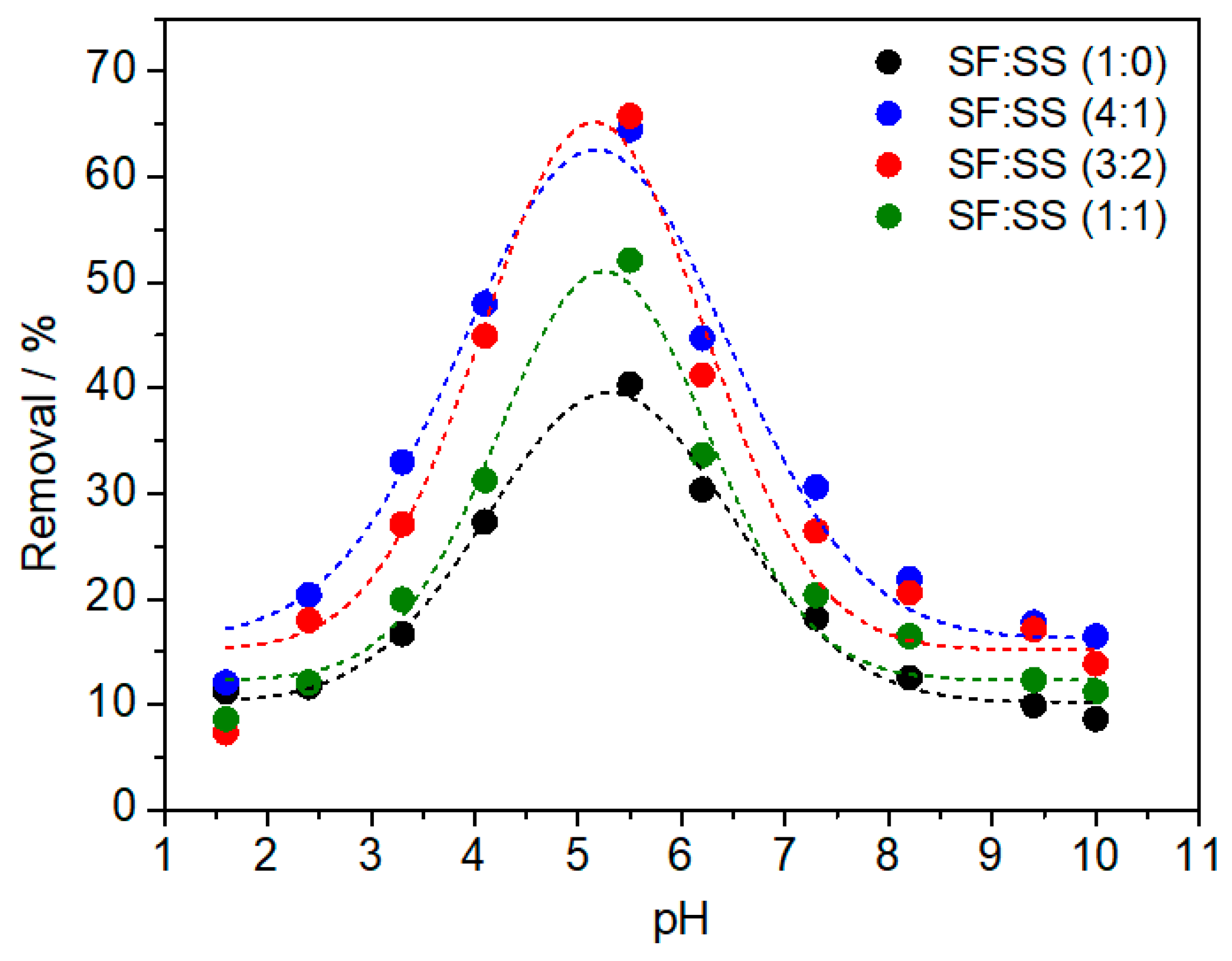
3.7. Effect of pH Solution on Cu2+ Removal Using SF:SS Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karbarz, M.; Khalil, A.M.; Wolowicz, K.; Kaniewska, K.; Romanski, J.; Stojek, Z. Enhancement of adsorption characteristics of Cr (III) and Ni (II) by surface modification of jackfruit peel biosorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3962–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; et al. Utilizations of agricultural waste as adsorbent for the removal of contaminants: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M. Green adsorbents for wastewaters: A critical review. Materials 2014, 7, 333–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meili, L.; Lins, P.V.S.; Costa, M.T.; Almeida, R.L.; Abud, A.K.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Dotto, G.L.; Tanabe, E.H.; Sellaoui, L.; Carvalho, S.H.V.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue on agroindustrial wastes: Experimental investigation and phenomenological modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 141, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Tiwari, D.P.; Pant, K.K. Model-fitting approach for methylene blue dye adsorption on Camelina and Sapindus seeds-derived adsorbents. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Dai, C.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Gao, S.; Wang, C. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using agricultural residue walnut shell: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 8404965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, Y.; Bhatti, H.N.; Sultan, M.; Sadaf, S. Synthesis, characterization and application of wheat bran/zinc aluminium and tea leaves waste/zinc aluminium biocomposites: Kinetics and thermodynamics modeling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5914–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chu, Y.; Fang, C.; Huang, F.; Song, Y.; Xue, X. Sorption of tetracycline on biochar derived from rice straw under different temperatures. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0182776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayomi, K.S.; Bello, J.O.; Nnoruka, J.S.; Adediran, A.A.; Olajide, P.O. Development of low-cost bio-adsorbent from agricultural waste composite for Pb (II) and As (III) sorption from aqueous solution. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1687274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Deng, G.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Silk fibroin/polyethylenimine functional hydrogel for metal ion adsorption and upcycling utilization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ning, H.; Hu, N.; Huang, K.; Weng, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Alamusi, A. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/silk fibroin hybrid aerogel for dye and heavy metal adsorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progressive trends in heavy metal ions and dyes adsorption using silk fibroin composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 210–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.H.; Wang, H.S.; Huang, C.; Su, Y.; Mo, X.M.; Ikada, Y. Fabrication of silk fibroin blended P (LLA-CL) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.H.; Gu, Y.; Yan, X.L.; Liu, J.; Ding, F.; Gu, X.S. Degradation behaviors of nerve guidance conduits made up of silk fibroin in vitro and in vivo. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Vepari, C.; Jin, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, R.; Gil, E.S.; Kluge, J.; Numata, K.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, X.D.; Kaplan, D.L. Reinforcing silk scaffolds with silk particles. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, E.; Meinel, A.J.; Wildy, S.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Microporous silk fibroin scaffolds embedding PLGA microparticles for controlled growth factor delivery in tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Non-bioengineered silk fibroin protein 3D scaffolds for potential biotechnological and tissue engineering applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, K.; Feng, Q.L.; Cui, F.Z. Growth of fibroblast and vascular smooth muscle cells in fibroin/collagen scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, R.; Jin, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Porous 3-D scaffolds from regenerated silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bella, E.; Lee, C.S.D.; Migliaresi, C.; Pelcastre, L.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D.; Motta, A. The synergistic effects of 3-D porous silk fibroin matrix scaffold properties and hydrodynamic environment in cartilage tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4672–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, S.; Wu, Z.; Yan, H. Study on porous silk fibroin materials: 3. Influence of repeated freeze–thawing on the structure and properties of porous silk fibroin materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2002, 13, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, S.; Wu, Z.; Tan, H.; Minoura, N.; Kuga, S. Structure and properties of silk fibroin–poly (vinyl alcohol) gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 30, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, C.; Cascardo, G.; Morra, M.; Draghi, L.; Motta, A.; Catapano, G. Physical-chemical and biological characterization of silk fibroin-coated porous membranes for medical applications. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2006, 29, 881–892. [Google Scholar]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Tomkins, M.; Fajardo, R.; Meinel, L.; Snyder, B.; Wade, K.; Chen, J.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Porous silk fibroin 3-D scaffolds for delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, Y. New process to form a silk fibroin porous 3-D structure. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3100–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, Z.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wang, X.; Wan, X. Flexible Water-Absorbing Silk-Fibroin Biomaterial Sponges with Unique Pore Structure for Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, A.; Ebrahimi, R.; Emadi, R.; Beni, B.H.; Chermahini, A.N. Nano-composite of silk fibroin–chitosan/Nano ZrO2 for tissue engineering applications: Fabrication and morphology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 76, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, H.; Du, S.; Huo, Y.; He, J.; Cui, S. Removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by adsorption onto novel polyelectrolyte film-coated nanofibrous silk fibroin non-wovens. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Xie, K.; Song, X.; Zhang, K.; Hou, A. Removal of the heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using modified natural biomaterial membrane based on silk fibroin. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Gang, E.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Nanofibrous membrane of wool keratose/silk fibroin blend for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 302, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, J.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. The removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by amine functionalized cellulose pretreated with microwave-H2O2. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34182–34191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, Q.; Ji, X.; Wang, F.; Gao, X.; Zhao, M. High and fast adsorption of Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by a waste biomass based hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallampati, R.; Xuanjun, L.; Adin, A.; Valiyaveettil, S. Fruit Peels as Efficient Renewable Adsorbents for Removal of Dissolved Heavy Metals and Dyes from Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Q.; Yue, X.; Zuo, B.; Qin, M.; Li, F.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zhang, X. Regeneration of high-quality silk fibroin fiber by wet spinning from CaCl2–formic acid solvent. Acta Biomater. 2015, 12, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, F.S.; Fiorica, C.; Pitarresi, G.; Agnello, S.; Giammona, G. Interpenetrated 3D porous scaffolds of silk fibroin with an amino and octadecyl functionalized hyaluronic acid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61440–61448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Yao, J.; Yamane, T.; Umemura, K.; Ulrich, A.S. Heterogeneous Structure of Silk Fibers from Bombyx mori Resolved by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8794–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Z.; King, W.J.; Murphy, W.L. Protein-Based Hydrogels with Tunable Dynamic Responses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coria-Téllez, A.V.; Montalvo-Gónzalez, E.; Yahia, E.M.; Obledo-Vázquez, E.N. Annona muricata: A comprehensive review on its traditional medicinal uses, phytochemicals, pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action and toxicity. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 662–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrie, N.; Schauss, A.G. Biactive Foods in Promoting Health; Oxford Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 621–643. [Google Scholar]
- Tashi, Z.; Zare, M.; Parvin, N. Application of phytic-acid as an in-situ crosslinking agent in electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Mater. Lett. 2020, 264, 127275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ayaz, P.; Jin, W.; Zhou, W. Improving the Color Stability of Naturally Colored Silk by Cross-Linking the Sericin with Phytic Acid. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 2019, 6936437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, B.D.; Wharram, S.; Kluge, J.A.; Leisk, G.G.; Omenetto, F.G.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of hydration on silk film material properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y. Fabrication of water-stable silk fibroin scaffolds through self-assembly of proteins. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61402–61409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, K.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, R.Y.; Kim, I.; Zhang, K.Q. A review of structure construction of silk fibroin biomaterials from single structures to multi-level structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.J.; Park, J.; Li, C.; Jin, H.J.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Structure and properties of silk hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Son, A.; Her, N.; Yu, M.; Snyder, S.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, Y. Aqueous removal of inorganic and organic contaminants by graphene-based nanoadsorbents: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1104–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Seki, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Ito, S. Adsorption of cesium ion on silk fibroin in aqueous solution. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 42, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Djordjevíc, C. Metal-oxygen vibration modes in the infra-red spectra of aluminium, gallium and indium tris-acetylacetonates. Spectrochim. Acta 1961, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derun, E.M.; Tugrul, N.; Senberber, F.T.; Kipcak, A.S.; Piskin, S. The Optimization of Copper Sulfate and Tincalconite Molar Ratios on the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Borates. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2014, 8, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschner, I.S.; Aubuchon, E.; Schrage, B.R.; Ziegler, C.J.; van der Est, A. Synthesis and structural studies of copper (II) complex with N2S2 based N-substituted pendant phosphonic acid arms. Dalton Trans. 2020, 11, 3545–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder, V.; Ludwig, T.; Opitz, S.; Christoffels, R.; Fischer, T.; Maleki, H. Hierarchical Assembly of Surface Modified Silk Fibroin Biomass into Micro-, and Milli-Metric Hybrid Aerogels with Core-Shell, Janus, and Composite Configurations for Rapid Removal of Water Pollutants. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2001892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyi, P.P.; Quansah, J.O.; Lee, C.G.; Moon, J.K.; Park, S.J. The Removal of Crystal Violet from Textile Wastewater Using Palm Kernel Shell-Derived Biochar. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.N.; Kang, J.K.; Lee, C.G.; Park, S.J. Removal of Heavy Metals (Cd2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+) from Aqueous Solution Using Hizikia fusiformis as an Algae-Based Bioadsorbent. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.T.; Hong, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.G. Removal of Cu (II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Amine-Doped Polyacrylonitrile Fibers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Perju, M.M.; Dinu, M.V. Preparation and characterization of IPN composite hydrogels based on polyacrylamide and chitosan and their interaction with ionic dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
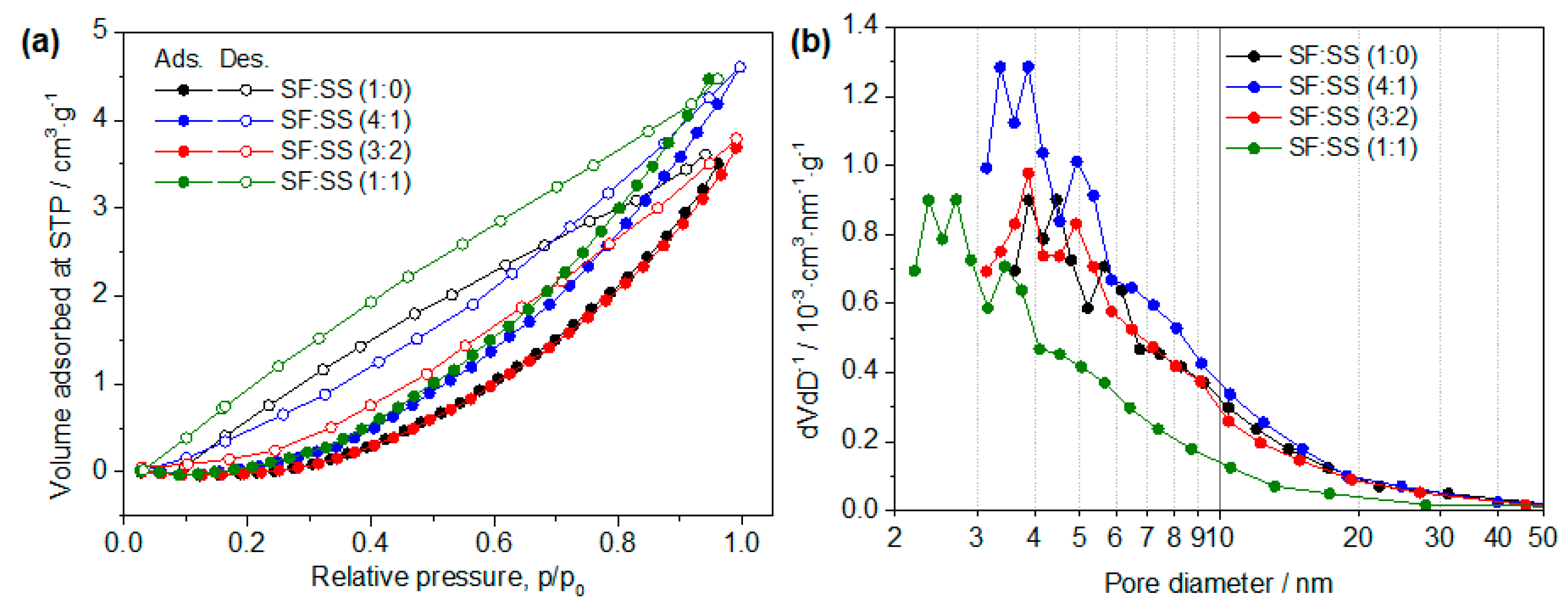



| SF:SS Compositions | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Specific Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cc·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF:SS (1:0) | 2.17 | 5.33 | 0.00227 |
| SF:SS (4:1) | 39.19 | 19.47 | 0.00811 |
| SF:SS (3:2) | 38.57 | 17.19 | 0.00562 |
| SF:SS (1:1) | 3.73 | 7.45 | 0.00528 |
| Pollutant | Bioadsorbent Composition | k1 × 10 (min−1) | R2 | k2 × 10 (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal Violet (20 mg·L−1) | SF:SS = (0:1) | 12.71 | 0.9645 | 4.19 | 0.9286 |
| SF:SS = (1:0) | 15.82 | 0.9605 | 5.87 | 0.9295 | |
| SF:SS = (4:1) | 21.85 | 0.9576 | 14.65 | 0.8275 | |
| SF:SS = (3:2) | 18.19 | 0.9404 | 9.37 | 0.9101 | |
| SF:SS = (1:1) | 16. 34 | 0.9656 | 6.59 | 0.9379 | |
| Cu2+ (20 mg·L−1) | SF:SS = (0:1) | 7.18 | 0.759 | 13.17 | 0.839 |
| SF:SS = (1:0) | 10.82 | 0.827 | 15.82 | 0.846 | |
| SF:SS = (4:1) | 17.23 | 0.957 | 20.77 | 0.917 | |
| SF:SS = (3:2) | 15.76 | 0.852 | 19.81 | 0.851 | |
| SF:SS = (1:1) | 11.61 | 0.838 | 17.55 | 0.823 |
| Isotherm | Parameter | CV | Cu2+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm (mg·g−1) | 83.31 | 73.22 |
| KL (mg·L−1) | 0.537 | 0.283 | |
| R2 | 0.866 | 0.913 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg·g−1) | 5.229 | 7.164 |
| 1/n | 0.711 | 0.673 | |
| R2 | 0.878 | 0. 928 |
| Silk Fibroin | Model Pollutants | Adsorption Characteristic | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF-PEI-2 | Cu2+ | Langmuir KL = 0.14 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 186.7 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 134.4 mg·g−1 (n = 19.2) | [54] |
| Methyl Orange | Langmuir KL = 0.0061 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 811.3 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 32.8 mg·g−1 (n = 2.09) | ||
| SF-PEI-2-GO | Cu2+ | Langmuir KL = 0.23 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 171.6 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 121.6 mg·g−1 (n = 17.3) | |
| Methyl Orange | Langmuir KL = 0.0046 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 791.9 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 20.8 mg·g−1 (n = 1.88) | ||
| SF:PEI (5:5) | Cu2+ | Langmuir qmax = 160 mg·g−1 | [11] |
| Methylene Blue | Langmuir qmax = 75 mg·g−1 | ||
| SF | Cu2+ | Langmuir qmax = 20 mg·g−1 | |
| SF0-GO | Methylene Blue | Langmuir KL = 2.155 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 1411.194 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 0.363 L·g−1 (n = 3.799) | [12] |
| SF20-GO | Methylene Blue | Langmuir KL = 4.779 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 1521.6 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 0.199 L·g−1 (n = 5.013) | |
| SF:SS | Cu2+ | Langmuir KL = 0.283 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 73.22 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 7.164 mg·g−1 (n = 6.49) | This Work |
| Crystal Violet | Langmuir KL = 0.537 (mg·L)−1 qmax = 83.31 mg·g−1 Freundlich KF = 5.229 mg·g−1 (n = 1.41) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ernawati, L.; Wahyuono, R.A.; Halim, A.; Noorain, R.; Widiyastuti, W.; Dewi, R.T.; Enomae, T. Hierarchically 3-D Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal. Environments 2021, 8, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110127
Ernawati L, Wahyuono RA, Halim A, Noorain R, Widiyastuti W, Dewi RT, Enomae T. Hierarchically 3-D Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal. Environments. 2021; 8(11):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110127
Chicago/Turabian StyleErnawati, Lusi, Ruri Agung Wahyuono, Abdul Halim, Roslan Noorain, Widiyastuti Widiyastuti, Rizna Triana Dewi, and Toshiharu Enomae. 2021. "Hierarchically 3-D Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal" Environments 8, no. 11: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110127
APA StyleErnawati, L., Wahyuono, R. A., Halim, A., Noorain, R., Widiyastuti, W., Dewi, R. T., & Enomae, T. (2021). Hierarchically 3-D Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal. Environments, 8(11), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110127