Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Digester Startup
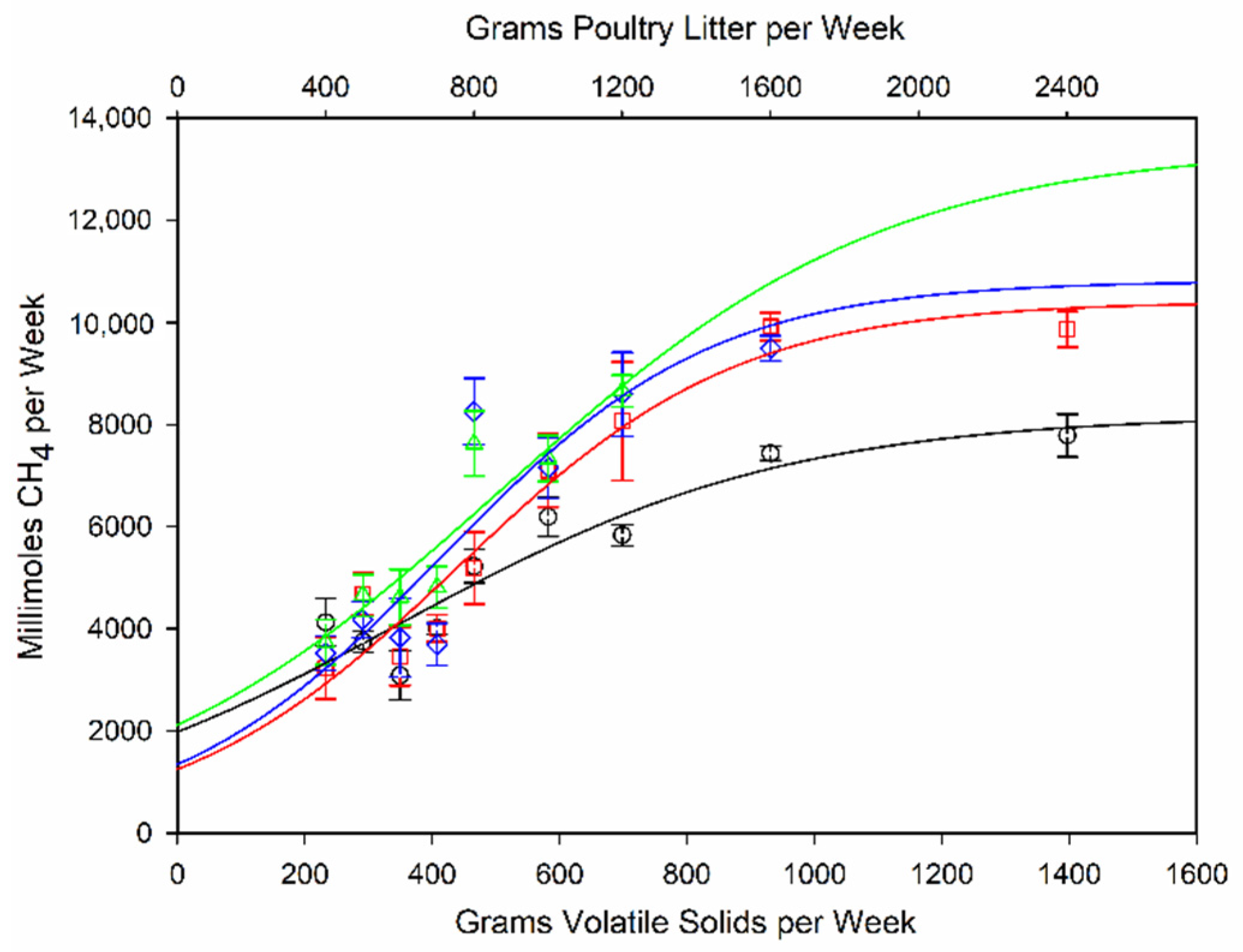
3.2. Biogas Production
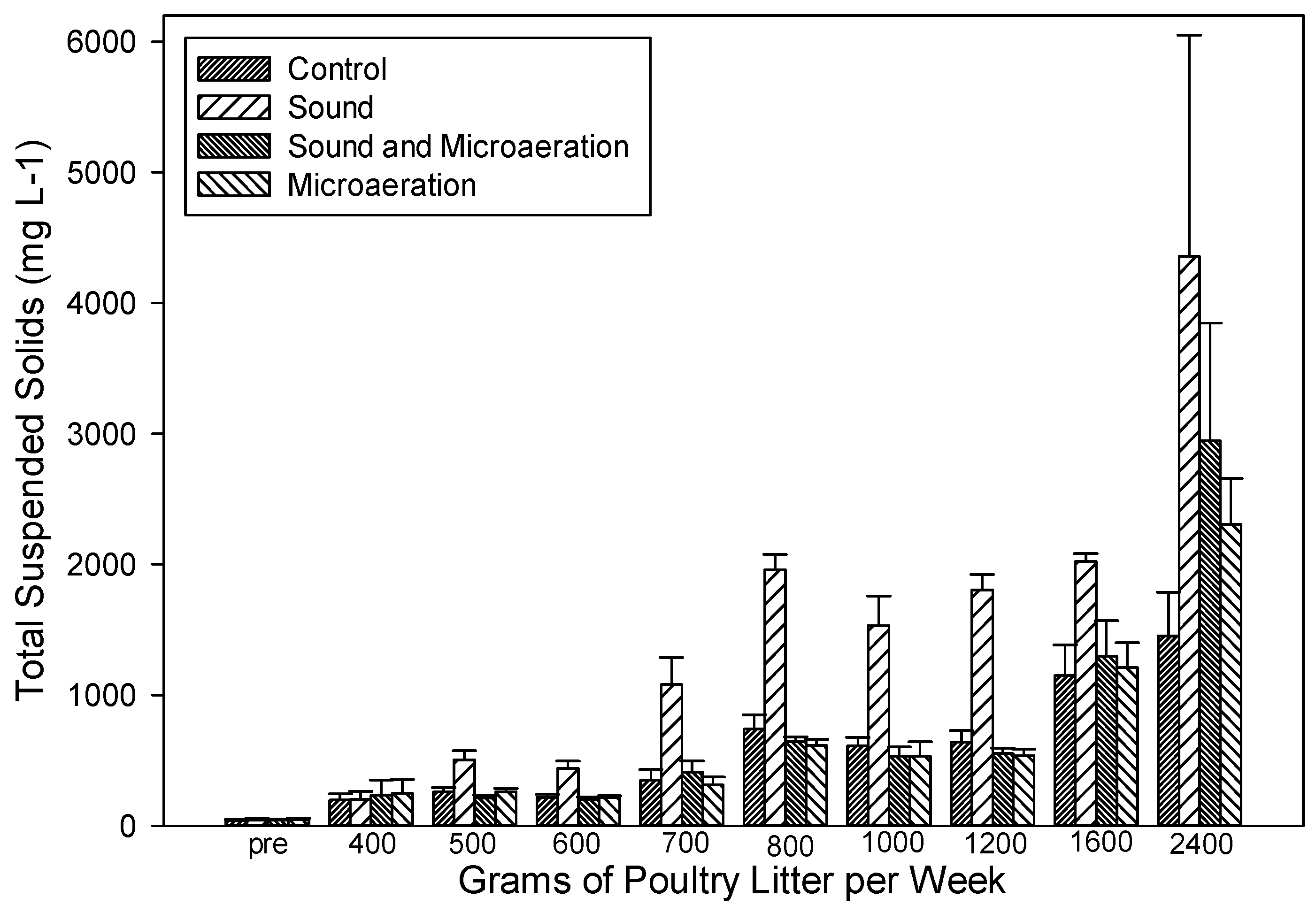
3.3. Wastewater Quality
3.4. Ion Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacDonald, J.M.; McBride, W.D. The Transformation of U.S. Livestock Agriculture: Scale, Efficiency, and Risks; United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. Available online: http://www.ers.usda.gov/Publications/EIB43/EIB43.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Szogi, A.A.; Vanotti, M.B.; Ro, K.S. Methods for treatment of animal manures to reduce nutrient pollution prior to soil application. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.; Bhogal, A.; Cardenas, L.; Chadwick, D.; Misselbrook, T.; Rollett, A.; Taylor, M.; Thorman, R.; Wi, J. Nitrogen losses to the environment following food-based digestate and compost applications to agricultural land. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghball, B.; Gilley, J.E. Phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff following beef cattle manure or compost application. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch, E.V.; Barr, K. Controlled struvite crystallisation for removing phosphorus from anaerobic digester sidestreams. Water Res. 2001, 25, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.N.; Kai, P.; Møller, H.B. Effects of anaerobic digestion and separation of pig slurry on odor emission. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroot, P.G.; McMahon, K.D.; Mackie, R.I.; Raskin, L. Anaerobic codigestion of municipal solid waste biosolids under various mixing conditions, I. Digester performance. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Integration of mixing, heat transfer, and biochemical reaction kinetics in anaerobic methane fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Wang, J.-Y. Enhanced hydrolysis and methane yield by applying microaeration pretreatment to the anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, W.; Qi, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Z. Review on microaeration-based anaerobic digestion: State of the art, challenges, and prospectives. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 710, 136388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, A.; Nickel, K.; Neis, U. The use of ultrasound to accelerate the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilli, S.; Bhunia, P.; Yan, S.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughrin, J.H.; Lovanh, N.; Antle, S.W.; Bryant, M.D.; Berry, Z.P. Sound enhances wastewater degradation and improves anaerobic digester performance. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.; Antle, S.; Sistani, K.; Lovanh, N. In situ acoustic treatment of anaerobic digesters to improve biogas yields. Environments 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.H.; Lovanh, N. Aeration to improve biogas production by recalcitrant feedstock. Environments 2019, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Clesceri, L.; Greenberg, A.; Franson, M. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Georgacakis, D.; Sievers, D.M.; Iannotti, E.L. Buffer stability in manure digesters. Agric. Wastes 1982, 4, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Assay Method for Anaerobic Digestion Research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Mannucchi, G.A.; Salvi, S.M.L.; Stuckey, D.C. Characterization of soluble residual chemical oxygen demand (COD) in anaerobic wastewater treatment effluents. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Inoue, Y.; Katayama, A. Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradation of phenol derivatives in various paddy soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2006, 31, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggio, R.B.M.; Obolonkin, V.; Vills-Bôas, S.G. Sonic vibration affects the metabolism of yeast cells growing in liquid culture: A metabolomic study. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.A.; Xu, Z.; Finch, J.A.; Masliyah, J.H.; Chow, R.S. On the role of cavitation in particle collection in flotation—A critical review. II. Min. Eng. 2009, 22, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu y Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Utsumi, Y.; Lee, D.-J. A novel anaerobic digestion system coupling biogas recirculation with MgCl2 addition for multipurpose sewage sludge treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Chiba, K.; Li, P. Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Different micro-aeration rates facilitate production of different end-products from source-diverted blackwater. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancharaiaha, Y.V.; Venkata Mohan, S.; Lens, P.N.L. Recent advances in nutrient removal and recovery in biological and bioelectrochemical systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Aeration | Sound | Aeration/Sound | |
| Biogas Characteristics | ||||
| Weekly Biogas (L) a | 172 ± 8.79 c | 238 ± 14.8 a | 202 ± 13.0 b | 228 ± 14.2 a |
| Carbon dioxide (µmole L−1) b | 14,200 ± 784 a | 13,700 ± 727 a,b | 13,700 ± 2000 b | 13,400 ± 713 b |
| Methane (µmole L−1) b | 25,400 ± 1930 a | 25,200 ± 1740 a,b | 24,400 ± 2040 b | 24,400 ± 1730 b |
| Digestate Characteristics b | ||||
| pH | 7.23 ± 0.08 a | 7.22 ± 0.05 b | 7.23 ± 0.06 a | 7.23 ± 0.05 a,b |
| Bicarbonate | 92.9 ± 5.42 a | 91.4 ± 5.41 b | 91.5 ± 5.97 a,b | 89.5 ± 5.31 a,b |
| Solvated carbon dioxide | 10.1 ± 0.39 b | 10.7 ± 0.44 a | 10.1 ± 0.44 b | 10.1 ± 0.41 b |
| Solvated methane | 24.0 ± 1.29 b | 27.7 ± 0.88 a | 24.9 ± 1.16 b | 25.5 ± 0.92 b |
| Chemical oxygen demand | 5070 ± 353 b | 4440 ± 289 d | 5390 ± 350 a | 4580 ± 319 c |
| Total suspended solids | 410 ± 63.0 b | 591 ± 80.4 b | 1360 ± 198 a | 650 ± 120 b |
| Dissolved carbon c | 5210 ± 157 a | 4130 ± 158 c | 5290 ± 161 a | 4460 ± 174 b |
| Dissolved nitrogen c | 1480 ± 62.6 a | 1050 ± 56.0 d | 1400 ± 56.3 b | 1180 ±58.6 c |
| Ion | Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Aeration | Sound | Aeration/Sound | |
| Concentration (mg L−1) a | ||||
| Phosphate | 13.9 ± 2.2 a | 13.6 ± 2.2 a | 13.7 ± 2.3 a | 14.2 ± 2.4 a |
| Ammonium | 89.0 ± 10.8 a | 90.3 ± 10.1 a | 91.3 ± 10.45 a | 89.1 ± 9.9 a |
| Nitrate | nd b | 0.7 ± 0.1 a | nd b | 0.9 ± 0.2 a |
| Sulfate | 4.3 ± 0.5 a | 4.2 ± 0.6 a | 4.3 ± 0.6 a | 4.2 ± 0.6 a |
| Magnesium | 18.1 ± 1.6 b | 16.7 ± 1.5 c | 19.5 ± 1.7 a | 17.9 ± 1.5 b |
| Calcium | 24.0 ± 3.3 a | 22.8 ± 2.8 a,b | 22.1 ± 3.0 b | 24.3 ± 2.9 a |
| Sodium | 299 ± 31.0 a | 264 ± 25.8 b | 289 ± 28.6 a | 266 ± 26.5 b |
| Potassium | 809 ± 95.9 a | 684 ± 79.2 c | 759 ± 87.0 b | 693 ± 79.4 b |
| Chloride | 667 ± 66.4 a | 580 ± 53.4 c | 630 ± 52.1 b | 577 ± 53.2 c |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loughrin, J.; Antle, S.; Bryant, M.; Berry, Z.; Lovanh, N. Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter. Environments 2020, 7, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080062
Loughrin J, Antle S, Bryant M, Berry Z, Lovanh N. Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter. Environments. 2020; 7(8):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080062
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoughrin, John, Stacy Antle, Michael Bryant, Zachary Berry, and Nanh Lovanh. 2020. "Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter" Environments 7, no. 8: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080062
APA StyleLoughrin, J., Antle, S., Bryant, M., Berry, Z., & Lovanh, N. (2020). Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter. Environments, 7(8), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080062






