Abstract
We conducted 3D ecosystem model simulations over a 10-year period, supplemented by socio-economic data, to evaluate the ecosystem services provided by the large, shallow Oder/Szczecin Lagoon. Our analysis focused on three scenarios reflecting the progressive deepening of the navigational waterway across the lagoon: from 6 m (1880) to 10.5 m (1984) and finally to 12.5 m (2023). For the 10.5 m scenario, the total value of all six ecosystem services was estimated at EUR 272 million/year, or approximately EUR 0.4 million/year/km2. The individual contributions of each ecosystem service were as follows: nitrogen retention, EUR 166 million/a; phosphorus retention, EUR 5 million/a; carbon storage, EUR 0.4 million/a; active recreation, EUR 61 million/a; landscape aesthetics, EUR 36 million/a; wild fish catches, EUR 3.2 million/a; and transportation, EUR 32 million/a. Among these, denitrification emerged as the most economically important process, valued at EUR 178 million/year, or EUR 0.26 million/year/km2. Regulating ecosystem services displayed substantial interannual variability and pronounced seasonality. Additionally, the two parts of the lagoon, Kleines Haff (Germany) and Wielki Zalew (Poland), exhibited distinct patterns. Our model indicates that channel deepening enhances sediment burial and significantly increases phosphorus and carbon retention. However, the associated increase in connectivity to the Baltic Sea appears to have a minor effect.
1. Introduction
The Baltic Sea region is home to several important lagoons, including the Curonian, Vistula, and Szczecin/Oder Lagoons, which are some of the largest in Europe. For centuries, these lagoons have been focal points of human activity, particularly fishing, which has played a crucial economic and social role for the local residents [1,2]. In recent decades, however, there have been substantial transformations. Recreational activities and tourism have become the primary sources of income [3]. Additionally, there is growing recognition that these lagoons are an important part of Europe’s natural heritage, providing essential ecological functions such as serving as resting places for migratory birds [4]. This awareness has led to extensive protection measures. Despite these efforts, the lagoons continue to suffer from poor ecological conditions, including inadequate water quality and low transparency, which hinder nature protection as well as tourism development [5,6].
Another significant factor impacting the Baltic lagoons is the ongoing expansion of maritime transport. Over the past centuries, navigational waterways have been established and progressively deepened to accommodate larger ships [7]. This has had significant economic implications, increasing ship traffic, trade, and harbor development. However, artificial waterways also affect ecological processes in the lagoons. These effects include changes in water flow patterns and velocities, the distribution of riverine nutrients, and the alteration of water and matter exchange between the lagoons and the Baltic Sea [8,9].
Ongoing anthropogenic interventions and infrastructural measures, such as the deepening of navigational waterways, interact with other ongoing changes, particularly climate change [10]. Climate change impacts the Baltic Sea and its lagoons in various ways [11], notably by increasing the intensity and frequency of extreme events. These events include extreme storms and sea levels, river floods, and droughts [12], as well as heat waves, which are potentially associated with oxygen depletion and algal blooms [11]. An important question is how these technical human interventions influence the socio-economic and natural conditions of the lagoons and their capacity to provide ecosystem services, especially in the context of these extreme events.
The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment [13] defines ecosystem services as benefits that humans derive from ecosystems. Today, ecosystem services play a significant role in European coastal and marine policies. The expectation is that ecosystem service assessments provide an understanding of the interdependencies between humans and the environment [14] beyond existing disciplinary assessments.
Since coastal lagoons are world-wide considered as highly important ecosystems, many publications on ecosystem services exist and address a wide spectrum of questions [15,16,17,18]. This is true for Baltic lagoons as well [19,20,21]. Existing assessments of ecosystem services face several significant challenges. For instance, data are often insufficient, heterogeneous, and difficult to compare. Variations in data across individual ecosystem services, combined with inadequate spatio-temporal resolution, further exacerbate the problem. As a result, complementary estimations, statistical analyses, and expert knowledge are frequently required to fill these gaps. Additionally, the methods used to calculate individual ecosystem services vary in robustness and reliability, making cross-comparisons problematic. These shortcomings have been widely documented [22,23] and substantially limit the acceptance and practical applicability of ecosystem service assessment outcomes.
In the Baltic Sea, several three-dimensional ecosystem models exist. One example is the 3D biogeochemical model ERGOM (Ecological ReGional Ocean Model) [24], which was recently evaluated by the European Commission [25] and rated as one of the best marine biogeochemical and lower trophic level models in Europe. In general, the utilization of ecologic models is assumed to overcome many existing weaknesses of ecosystem service assessments [26]. A recent approach to assess ecosystem services based on the ERGOM model results covering the entire Baltic Sea over 150 years underlined the potential but also indicated limitations [27]. Among the challenges are an improved spatial model resolution, a better integration between socio-economic and model data, a higher ecosystem service assessment accuracy to enable shorter assessment time periods, and an increase in the number of addressed ecosystem services. To overcome the present limitations, smaller spatial units need to be addressed along with coastal lagoons. Oder Lagoon is not only one of the largest Baltic lagoons, but it is also of outstanding socio-economic importance and a prime example for the changes and transformations that have taken place and are taking place during the last centuries. Therefore, it can be considered as ideal test case.
Our objectives are to (a) provide a consistent database for the calculation of ecosystem services in Oder Lagoon by applying a new 3D ecosystem model in combination with socio-economic data; (b) analyze how ongoing human technical interventions during the last centuries, namely, the stepwise deepening of the navigational waterway in the lagoon, have affected different provisioning, regulating, and cultural ecosystem services; (c) assess the relevance of and reasons for interannual variabilities in ecosystem service values; (d) calculate the monetary values of the ecosystem services to enable direct comparisons; and (e) discuss the practical relevance of the results for managing the lagoon.
2. Study Site and Methods
2.1. Oder/Szczecin Lagoon
Oder/Szczecin Lagoon (53°48′ N, 14°08′ E) covers a surface area of 687 km2. Approximately 40% (277 km2) of the lagoon, referred as the “Kleines Haff” or “small bay”, lies within Germany, while 60% (410 km2), called the “Wielki Zalew” or “large bay”, is situated in Poland. This shallow lagoon has an average depth of 3.8 m and reaches a natural maximum depth of 8.5 m [28]. Its total coastline measures 209 km, with 89 km in the Kleines Haff and 120 km in the Wielki Zalew (extending to Trzebież and excluding the riverine bay Roztoka Odrzańska) (Figure 1).
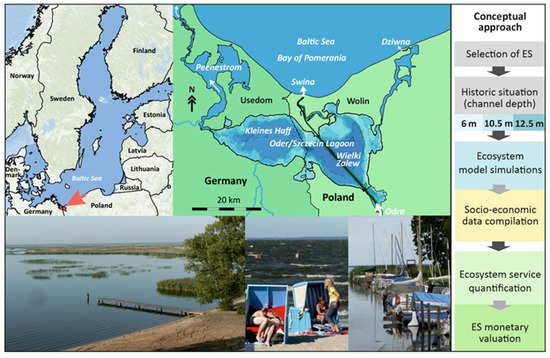
Figure 1.
Oder/Szczecin Lagoon in the Baltic Sea region, map of the lagoon and impressions of the nature and human uses as well as the stepwise conceptual ecosystem service (ES) assessment approach of this study.
According to the OECD, the lagoon is classified as hypertrophic due to high nutrient inflows from rivers, primarily from the Oder (Polish: Odra). The Oder, with a catchment area of 120,000 km2, accounts for approximately 98% of the water discharge as well as nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) inputs to the lagoon. In contrast, the Zarow and Uecker Rivers have only minor impacts. Around 1880, riverine nutrient loads were estimated at 14,000 t N/a and 1000 t P/a. These loads increased, peaking in the 1980s at 115,000 t N/a and 10,500 t P/a [29]. Between 1995 and 2019, the average water discharge into the lagoon was 518 m3/s, with mean nutrient loads of 46,266 t N/a and 1635 t P/a [30].
The recent official HELCOM assessment rated both the integrated contamination status as well as the eutrophication status of Oder Lagoon as “bad” [31]. Similarly, under the European Water Framework Directive (WFD, which additionally considers benthic flora and fauna, the lagoon’s ecological quality is classified as “insufficient” [32].
Despite these environmental challenges, the lagoon forms part of the Natura 2000 network, established to protect rare and threatened species. Large areas of the lagoon are designated as landscape protection zones, and the surrounding coastal zone features two national parks and several nature reserves. While fishing has historically been the primary economic activity, tourism is of increasing importance [33].
2.2. Human Interventions—The Navigation Waterway Across the Lagoon
Oder/Szczecin Lagoon connects to the Baltic Sea through three outlets: the Swina, Peenestrom, and Dziwna channels. The lagoon’s theoretical average annual water residence time is 60 days but varies between 37 and 99 days, depending on river discharge quantities. Approximately 70% of the lagoon’s water exits via the Swina channel, the major navigation waterway [34]. Periodic inflow of Baltic Sea water maintains the lagoon’s oligohaline state, with salinity concentrations between 1 and 3 PSU.
The Swina channel represents the most significant technical human intervention in the lagoon. Spanning 67 km, it connects the Baltic Sea to the city of Szczecin through Oder Lagoon. Historically, the Swina River crossed the about 6 km wide Wolin/Usedom spit separating the lagoon from the Baltic Sea. Modifications to the Swina River date back to 1721, when the maximum depths ranged between 2 and 2.5 m [35]. In 1880, a shortened and deepened artificial channel was completed, featuring a fairway depth of 6 m and a river cross-section of approximately 1400 m2 [36,37]. Subsequent deepening projects included an increase to 9.6 m in 1939 and to 10.5 m in 1984 across the entire lagoon. By 1984, the total cross-section of the Świna River/channel system (Piastowski Canal/Kaiserfahrt) had expanded to about 2500 m2.
Between 2018 and 2023, the entire waterway across Oder Lagoon was further deepened to 12.5 m, increasing the total cross-section to about 2700 m2. This deepening was part of the EU Strategy for the Baltic Sea Region, adopted by the European Council in 2009, aimed at enhancing the Baltic Sea region’s potential, including improved internal and external transport [35]. The demand for enhanced shipping infrastructure reflects the ongoing growth in shipping activities. For example, cargo transshipments in the ports of Szczecin and Świnoujście increased sharply, from 20.8 million tons in 2010 to 36.8 million tons in 2022. Additionally, the number of Ro-Ro ship units (including vehicles, passengers, and cargo) and container reloading activities grew significantly, with container handling rising from 21,860 TEU in 2000 to 67,952 TEU by 2023 [38].
The channel’s deepening to a fairway depth of 10.5 m initially enabled vessels with a maximum draft of 9.15 m and lengths of up to 215 m to access Szczecin. Following the deepening to 12.5 m, the channel can now accommodate container and bulk carrier ships up to 240 m in length, 32.4 m in width, with drafts of 11 m, as well as cruise ships up to 260 m long [35]. This upgrade supports larger ships, facilitates efficient two-way vessel traffic, improves navigation safety, and reduces transit times [39].
The increased cross-section of the channel enhances the interface between the mesohaline Baltic Sea and the oligohaline lagoon, enabling faster water exchange and further altering the lagoon’s hydrodynamics.
2.3. The 3D Ecosystem Model
We utilized a modified version of the coupled circulation and biogeochemical model documented by Neumann et al. [24]. The circulation component is based on the Modular Ocean Model (MOM5.1), while the biogeochemical component employs ERGOM version 1.2 (Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research, 2015). For this study, the model was specifically adapted for Oder Lagoon, featuring a high horizontal grid resolution of 150 m. The vertical structure consists of 28 layers, with thicknesses ranging from 25 cm at the surface to 50 cm near the bottom. Open boundary conditions from a 2 km resolution Baltic Sea model were applied at the lagoon’s three outlets connecting to the Baltic Sea.
ERGOM simulates the biogeochemical cycles of nitrogen, phosphorus, carbon, oxygen, and partially sulfur. Primary production is driven by photosynthetically active radiation and is facilitated by four functional phytoplankton groups: large cells, small cells, limnic phytoplankton, and cyanobacteria. An optical sub-model calculates the underwater light climate based on chlorophyll and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) concentrations. Dead organic material accumulates as detritus, while zooplankton grazing on phytoplankton represents the highest trophic level in the model. Particulate organic carbon (POC) from sources such as phytoplankton and detritus can sink through the water column, accumulating in a sediment layer.
The model incorporates temperature- and oxygen-dependent mineralization processes, releasing dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus from organic matter in both the water column and sediment. In oxygen-rich conditions, phosphate binds with iron oxides to form particles that settle in sediments. These particles can be resuspended by erosion and redistributed by currents to deposition zones. Under anoxic conditions, iron oxides are reduced, releasing dissolved phosphate back into the water. Oxygen is produced through primary production and consumed during metabolism and mineralization. Additionally, extracellular excretion by phytoplankton leads to non-Redfield carbon uptake.
In contrast to Neumann et al. [24], we introduced a fourth phytoplankton group, limnic phytoplankton, designed for low-salinity, turbid coastal environments where growth is constrained by salinity and increased light sensitivity. All organic particles (e.g., phytoplankton and detritus) are modeled in nitrogen units. To compare modeled phytoplankton outputs with observed chlorophyll levels, we sum all phytoplankton groups and apply a constant chlorophyll-to-carbon ratio. The lagoon model validation and application are presented in [30].
Meteorological data were sourced from the coastDat-3 dataset [40] and the Norwegian Meteorological Institute. Data on discharge and riverine nutrient loads from the Oder, Uecker, and Zarow Rivers were supplied by the Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej and Friedland et al. [29].
2.4. Model Simulations and Scenarios
We analyzed three scenarios: (1) the situation after the deepening in 1880, with a channel water depth of 6 m; (2) the situation between 1984 and 2022, with a channel depth of 10.5 m; and (3) the state after the recent deepening that was finished in 2023, representing a channel water depth of 12.5 m. It is called a future scenario. Historic changes in the waterways connecting the lagoon with the Baltic Sea were derived from historic maps. The cross-section and profile of the waterway newly deepened to 12.5 m were taken from Environmental Impact Assessment planning documents [41]. These morphometric changes were implemented in three distinct model bathymetries.
The ERGOM model simulations covered the years 2010–2019, representing a shipping depth/draft of 10.5 m in the Świna channel. Simulations for the same 10-year period were repeated under the assumed conditions of the future 12.5 m depth and the historic post-1880 depth of 6 m. While the historic and future scenarios employed different bathymetries, all simulations were based on the same input data (e.g., weather, river discharge) from the years 2010–2019. This approach overcomes the problem of the lack of reliable historical weather and discharge data and enables a direct analysis of the mere consequences of the channel deepening. From these simulations, we extracted two-day averages of relevant state variables, processes, and transports, which served as the basis for our assessments.
2.5. Socio-Economic Data Collection
The socio-economic data were gathered from various German and Polish sources. The population data were compiled for areas within two kilometers and 2–20 km of the lagoon coastline [42,43,44]. Existing data on tourism overnight stays were incorporated [45], with any gaps estimated using per capita metrics. The number of sport-boat berths was determined by analyzing the websites of individual sport-boat harbors around the lagoon, supplemented by Google Earth for missing information. Similarly, data on beach sizes were compiled, with details that were lacking being estimated through satellite imagery. Official statistics were utilized for passenger transport and commercial shipping volumes [46,47]. The numbers of fishing boats and fishermen were sourced from [48,49], while information on angling tourism was drawn from [50,51].
2.6. Ecosystem Service and Assessment Approach
Our assessments were based on the Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES), a comprehensive framework for ecosystem mapping, assessment, and natural capital accounting [52]. CICES is widely adopted internationally and aligns closely with European environmental policies. The system is hierarchical, with the top level distinguished by three sections: provisioning services, regulating and maintenance services, and cultural services. For this study, we focused on the most detailed classification level (classes), adapting definitions from CICES V5.1 [53].
Selected ecosystem services were quantified directly or indirectly using outputs from our 3D ecosystem model, supplemented with socio-economic data. To ensure granularity and country-specific accuracy, Oder Lagoon was subdivided into two basins: Kleines Haff (Germany) and Wielki Zalew (Poland). This subdivision also aligns with the water body delineations under the European Water Framework Directive (WFD).
2.7. Provisioning Ecosystem Services
Wild animal food and products: This service encompasses edible fish, seafood, fish meal, and fish oil. In Oder/Szczecin Lagoon, only edible wild fish is relevant. The data on fish catches were obtained from official statistics in Germany [54] and in Poland [55]. The average country-specific fish market prices were extracted from different official sources [56,57]. Aquaculture and benthic animal extraction are not significant in the lagoon. We assumed that the potential total commercially viable fish biomass depends on the lagoon’s productivity, which is represented by phytoplankton concentrations.
Based on Scheffold and Hense [58], we used a phytoplankton-to-commercial wild fish biomass ratio of 2.2 (gC/m2). The carbon-to-dry weight ratio (0.43) and fish dry weight-to-wet weight ratio (0.2) were applied to calculate fish wet weight [59,60]. Data from Thurow [61] validated the relationship between fish catches and wild fish biomass.
The ecosystems services “wild plants and products” were estimated using literature-based calculations. The detailed literature data are indicated in Section 3.3.
The ecosystem service “transportation” accounts for the lagoon’s role in providing space and enabling shipping activities. The calculations are explained in Section 3.4 and were based on existing literature data and statistics [47,62].
2.8. Cultural Ecosystem Services
Active recreation: This service includes outdoor activities and tourism related to the local environment, such as sports, leisure, and outdoor pursuits. Coastal tourism and water-related activities at Oder Lagoon are concentrated during summer and are heavily influenced by water temperature and quality. We assumed that tourists perceive water quality as favorable when water transparency is high, bathing water meets official standards, and there are no visual pollutants or nuisances (e.g., toxic algae blooms, algae accumulations) [63,64,65]. Indices (I), with a minimum of 0 and a maximum of 100, were calculated for the modeled average summer water surface temperature (I = 77.7 ln (temperature) − 164.74), cyanobacteria concentrations in summer (I = 36.1 (ln (cyanobacteria) + 125), water transparency (Secchi-depth in summer) (I = 22.76 ln (Secchi-depth) + 52.4), and riverine phosphorus emissions (proxy for sewage) (I = −15.53 ln (P-emissions) + 110.77). These indices, equally weighted, were averaged into a total recreation index. All regression formulas scale the relevant upper and lower levels of the data to an index between 0 and 100. It is assumed that the benefit (increase in index value) is decreasing with higher values. For example, an increase in water transparency of 0.5 m has a higher index increase at low water transparencies than if the transparency is already high.
Monetarization exclusively considered annual guest overnight stays within 2 km of the lagoon coast in Germany [66] and Poland [67] multiplied by country-specific added value per overnight stay. Specifically, EUR 216 and EUR 148 per night were assumed for Germany and for Poland, respectively [68,69,70].
Landscape aesthetics (observational recreation): This service relates to the visual quality of landscapes and ecosystems, which enhance human well-being. The landscape aesthetics index included water transparency (Secchi-depth in summer) (I = 22.76 ln (Secchi-depth) + 52.4) and the eutrophication level (summer chl.a concentrations) (I = −36.07 ln (chl.a) + 183.05). Additionally, the coastal population density within 2 km from the coastline (habitants per km of coastline) (I = −13.96 ln (habitants) + 183.05) and tourism density, namely, overnight stay less than 2 km from the lagoon coastline (no. of tourists staying per km of coastline) (I = −9.241 ln (tourists) + 120.93), were included. Higher population and tourism densities were assumed to reduce landscape aesthetics. The indices, equally weighted, were averaged into a landscape aesthetics quality index.
For monetization, local studies and suitable transferable literature were unavailable. Thus, we based calculations on local inhabitants, assuming a per capita benefit equivalent to two times the country-specific added value per tourist overnight stay of EUR 432 per year in Germany and EUR 296 per year in Poland for residents living within 2 km of the coastline. For residents living 2–20 km away, we assumed 10% of these values.
2.9. Regulating Ecosystem Services
Water quality regulation and purification (nitrogen and phosphorus): For nitrogen, we considered processes in the water column and sediments, including nitrogen fixation, denitrification, and nitrogen burial. For phosphorus, we included only phosphorus burial in sediments. These data were directly extracted from model simulations for both basins. The costs of reducing nitrogen were based on average sewage treatment costs: EUR 15.8/kg N in Germany and EUR 12.7/kg N in Poland. For phosphorus, we used EUR 64.3/kg P in Germany and EUR 43.2/kg P in Poland. These figures, from Gren et al. [71], were adjusted to 2015 prices using an annual inflation rate of 1.5%.
Carbon sequestration/burial (climate regulation): Carbon burial data in sediments were also directly extracted from model simulations. Monetization was based on CO2 emission prices in the European Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS). For 2019, a certificate cost of EUR 25 per ton of CO2 (EUR 92/t C) was applied [72].
3. Results
3.1. Model Simulation Data—20-Year Averages
Table 1 provides a summary of the model simulation results that serve as the basis for the calculation of ecosystem services. The model data on nutrient and carbon burial in sediments are presented later. The channel deepening from 6 m to 12.5 m has no effect on water temperatures and causes only a minor increase in dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) concentrations, remaining below 1 µmol/L, with negligible changes in dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) concentrations. However, major nitrogen processes, such as denitrification and nitrogen fixation, are significantly impacted.

Table 1.
Over 20-year averaged 3D ecosystem model (ERGOM) simulation results for the three waterway deepening scenarios (6 m before 1880, 10.5 m representing 1984–2023 and 12.5 after 2024). The relative changes indicate the difference between the 6 m and the 12.5 m scenarios. The data are aggregated over the surface area of each part of Oder/Szczecin Lagoon, the German Kleines Haff and the Polish Wielki Zalew.
The model indicates that channel deepening increases nitrogen fixation by an average of 57 t/a (8%) in the Kleines Haff and 229 t/a (46%) in the Wielki Zalew, leading to a total increase of 286 t N/a (24%) across the entire lagoon. Nitrogen fixation also exhibits strong interannual variability. During hot summers, such as in 2015 and 2018, the model predicts high nitrogen fixation of 2849 t N/a and 2507 t N/a, respectively, under the 10.5 m scenario. Conversely, during the cooler year of 2010, nitrogen fixation is calculated at only 364 t N/a.
Denitrification, a key process for nitrogen removal from the lagoon, decreases in both basins due to channel deepening. The model estimates an average total decline of 12%, equivalent to 1595 t N/a. Unlike nitrogen fixation, the interannual variability in denitrification is relatively low, ranging from 9510 t N/a in 2015 to 15,573 t N/a in 2010.
The model also predicts reductions in summer chlorophyll-a concentrations and annual average phytoplankton concentrations by approximately 20% across all lagoon sections due to channel deepening. However, summer cyanobacteria concentrations increase by an average of 16%. This rise in cyanobacteria drives the observed increase in nitrogen fixation, as the model assumes that cyanobacteria are responsible for atmospheric nitrogen fixation.
The changes in phytoplankton and nutrient processes are strongly influenced by altered carbon and nutrient burial dynamics in the sediments of the deepened channel. The increased water depth and cross-section of the Świna channel potentially enhance water exchange between the lagoon and the Baltic Sea. This results in a relative salinity increase of 135% in the Wielki Zalew and 89% across the entire lagoon. Despite these percentages, the absolute salinity changes are minor—less than 1 PSU or 1 g/kg—and are ecologically negligible. In the Wielki Zalew, salinity ranges between 0.3 g/kg (2010) and 1.6 g/kg (2015), controlled primarily by Oder River discharge and sporadic saltwater intrusions from the Baltic Sea.
The Baltic Sea, being a micro-tidal sea with a tidal range below 0.2 m and salinity of approximately 8 g/kg in the Pomeranian Bay, does not contribute substantial saltwater quantities or significant salinity increases to the lagoon. The areas affected by Baltic water intrusions remain confined to the vicinity of the Świna channel, with no notable expansion resulting from the channel deepening.
3.2. Socio-Economic Data
The total number of inhabitants living within 2 km of the lagoon coastline is 76,244 (Table 2). With an average population density of approximately 70 inhabitants per km2, the area surrounding the lagoon is relatively sparsely populated. Within a 2–20 km area of the lagoon coast, the population increases to about 273,000. This includes the seaside resorts along the Baltic Sea and approximately 72,000 residents in the northern outskirts of Szczecin. The city of Szczecin itself, with a population of 391,000, is not included in these figures.

Table 2.
Socio-economic data of Oder/Szczecin Lagoon differentiated between the Kleines Haff (Germany) and the Wielki Zalew (Poland). The population number is compiled for a zone closer than 2 km and a zone closer than 20 km from the lagoon coastline.
Tourism is a growing economic sector in the region, with approximately 300,000 overnight stays annually around the lagoon. This growth has been supported by regional infrastructure developments, including the creation and expansion of beaches, sport boat harbors, and cycling trails. The number of ship passengers primarily consists of tourists on boat trips, while most cargo ships transit through the lagoon on their route between the Baltic Sea and the Port of Szczecin.
In 2013, 80 fishing boats were registered in the Kleines Haff, supporting 34 full-time fishermen, 9 non-commercial fishermen, and 27 hobby fishermen. Data from 2007–2016 suggest that 126 fishing boats operate in the Wielki Zalew, providing livelihoods for 360 fishermen. Additionally, 110 individuals hold fishing permits. These relatively low numbers highlight the declining economic significance of fisheries in the region.
The calculated ecosystem services, based on the model simulation results and the complementing socio-economic data, are fully documented in Appendix A. The subsequent monetary ecosystem services are presented in Appendix B. Because of the methodological and conceptual heterogeneities, the following chapters address comparable groups of ecosystem services.
3.3. Provisioning Ecosystem Services—Wild Fish and Plants
Wild fish: Between 2010 and 2019, an average of approximately 2271 tons of wild fish was caught annually in the lagoon [54,55]. Of this, 79% was harvested from the Wielki Zalew in Poland, and 21% from the Kleines Haff in Germany (Table 3). The weighted average market price of fish differed between the two countries: EUR 1.90/kg in Germany and EUR 1.26/kg in Poland. Consequently, Germany accounted for 29% of the total annual economic value, while Poland contributed 71%. The overall economic value of the fish catch was approximately EUR 3.17 million, or EUR 4618 per square kilometer of lagoon surface area.

Table 3.
Wild fish catches, market prices (in Euro) and economic value of fisheries in Oder/Szczecin Lagoon differentiated between the Kleines Haff (Germany) and the Wielki Zalew (Poland).
Among the various species, eel, salmon (both Salmo salar and Salmo trutta trutta), and pike perch commanded the highest market prices. These species constituted only 9% of the total catch but generated nearly 50% of the economic value. In contrast, the more abundant bony white fish species, such as roach (Rutilus rutilus), bream (Abramis brama), whitefish (Coregonus oxyrinchus), silver bream (Blicca bjoerkna), and asp (Aspius aspius), are mainly used for soup or feed and have a lower market value [73].
Based on phytoplankton model simulations, the total commercially usable fish biomass in the lagoon during the same period was estimated at 13,497 tons of wet weight. Of this, 66% was located in the Wielki Zalew and 32% in the Kleines Haff. The larger share in the Wielki Zalew can be attributed to higher phytoplankton concentrations (Figure 2). The reported annual catch of 2271 tons indicates that approximately 16% of the total fish biomass is harvested each year. Fishing pressure is higher in the Wielki Zalew, where 20% of the fish stock is caught annually, compared to only 10% in the Kleines Haff.
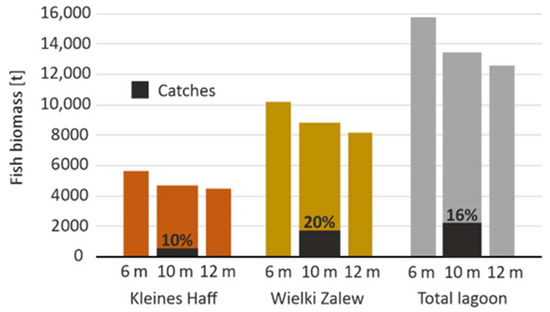
Figure 2.
Calculated commercially usable fish biomass in different parts of Oder/Szczecin Lagoon and for the three channel deepening scenarios (6 m, 10.5 m, and 12.5 m). Additionally, the reported catches (t/a) during the period 2010–2019 are indicated in comparison.
Model simulations suggest that channel deepening from 6 m to 12.5 m would reduce phytoplankton biomass, leading to an approximate 20% decline in commercially usable fish stocks across the lagoon. Given the already high fishing pressure on valuable species, most of the remaining catchable biomass would, very likely, consist of white fish, with market values of EUR 0.43/kg in Poland and EUR 0.70/kg in Germany. Under these conditions, the total potential market value of the entire fish stock in the lagoon is estimated at EUR 15 million, equivalent to EUR 22,000 per square kilometer of lagoon surface area.
Wild plants and products: The only commercially utilized plant in Oder Lagoon is common reed (Phragmites australis), primarily used as a material for roof thatching [74]. Along the coastline of the lagoon, reed beds cover an area of approximately 6.0 km2 in the Kleines Haff and 8.3 km2 in the Wielki Zalew [1,75]. The average width of the reed belt across the lagoon is around 69 m, potentially yielding a total dry weight of 14,320 tons: 5980 tons in the Kleines Haff and 8340 tons in the Wielki Zalew.
Market prices for reed are typically EUR 3.4 per 5 kg bundle or EUR 640/ton, giving the total reed stock an estimated value of EUR 9.2 million. However, local reed is no longer harvested or utilized around Oder Lagoon due to a lack of market demand. Reed harvesting typically occurs on land, involves smaller areas, and is not directly influenced by the lagoon itself. As a result, despite its potential economic value, reed provision was not further assessed. Other wild plants have no significant economic or ecological role in Oder Lagoon.
3.4. Provisioning Ecosystem Services—Transportation
The deepened waterway across the lagoon acts as trap [21] for approximately 425.000 t/a suspended particular material entering the lagoon via the Oder River as well as for resuspended and translocated lagoon sediments. Between 1949 and 2000, maintaining the shipping channel’s depth required the annual dredging of an average of 1.5 million tons of sediment (wet weight) [76]. The recent channel deepening to a fairway depth of 12.5 m necessitated the removal of approximately 24 million cubic meters of sediment [77].
The dredging costs for the channel deepening were estimated at approximately EUR 335 million, with an additional EUR 470 million invested in complementary infrastructure [78]. This translates to a dredging cost of EUR 14 per cubic meter of wet sediment. It is assumed that the combined costs of channel deepening, amortized over 30 years, along with the annual maintenance dredging expenses, represent the monetary value of the ecosystem service “transportation.”
Based on this assumption, the total annual monetary value of the waterway is estimated at EUR 32, comprising EUR 11 million per year for the deepening costs (spread over 30 years) and EUR 21 million per year for maintenance dredging. Based on ship arrival data and ship passenger numbers, about 95% of the value can be attributed to the Wielki Zalew.
3.5. Cultural Ecosystem Services—Tourism, Recreation, and Aesthetics
Cultural ecosystem services are grouped into two categories: those derived from tourism (recreational ecosystem services) and those benefiting the local population (observational ecosystem services).
For the recreation index, significant differences between the two parts of the lagoon are evident, driven by sub-indices such as algae blooms, water transparency, water temperature, and emissions. The low sub-index value for algae blooms is primarily due to frequent summer blooms of potentially toxic cyanobacteria, particularly in the Kleines Haff. Additionally, summer water transparency, typically below 1 m (Secchi depth), negatively impacts bathing tourism, leading to sub-index values below 50. Conversely, the shallow lagoon’s summer water temperatures are higher than those of the neighboring Baltic Sea, averaging 20.6 °C between June and August from 2010 to 2019, which makes it favorable for swimming. However, the inflow of the Oder/Odra River into the Wielki Zalew negatively impacts microbial bathing water quality, as reflected in the very low emission sub-index values.
The overall recreation index, which averages the four sub-indices, shows no significant differences across the three channel deepening scenarios. The recreation index is slightly higher in the Kleines Haff compared to the Wielki Zalew (Figure 3a). Nonetheless, the eutrophic nature of the lagoon significantly limits its value for recreation, particularly for summer bathing tourism. The full data are shown in Appendix A.
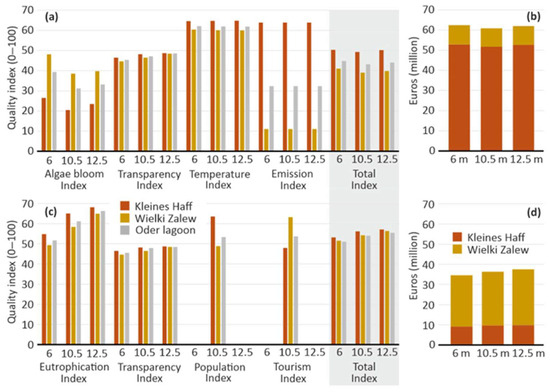
Figure 3.
(a) Recreational ecosystem services: The values of the four sub-indices algae blooms, water transparency, water temperature, and emissions are averaged into the total recreation index for the three channel deepening scenarios and (b) the monetary recreation values. (c) Aesthetics ecosystem services: The values of the four sub-indices eutrophication, water transparency, population, and tourism density are averaged into the total aesthetics index for the three channel deepening scenarios and (d) the monetary aesthetics values. Table 1 and Table 2 and Appendix A show the underlying data.
The monetary value of recreational ecosystem services is estimated at approximately EUR 60 million per year (Figure 3b). Tourism is more concentrated in the Kleines Haff, where overnight stays are four times higher than in the Wielki Zalew (Table 2). Furthermore, overnight stays in the Kleines Haff generate higher gross value added (EUR 216 per overnight stay compared to EUR 148 in the Wielki Zalew). Consequently, the monetary value of recreation in the Kleines Haff is about five times greater than in the Wielki Zalew.
The total aesthetics ecosystem index comprises sub-indices for eutrophication (summer chlorophyll-a concentration), water transparency, population, and tourism density. Population and tourism density reflect the real current state with a channel depth of 10.5 m and are assumed to be similar for the other two deepening scenarios. The differences in the sub-indices between the Wielki Zalew and Kleines Haff are minor. However, the eutrophication sub-index significantly increases with greater channel depth. As a result, the overall aesthetics ecosystem index also shows a slight increase with deeper channel scenarios due to the higher eutrophication sub-index, mainly resulting from lower annual average chlorophyll-a concentrations with increasing channel depth (Figure 3c).
3.6. Regulating Ecosystem Services—Nutrient and Carbon Retention
Nitrogen retention: On average over the lagoon, the model suggests a nitrogen retention of 17,862 kg N a−1 km2 (100%) that results from 18,757 kg a−1 km2 denitrification (105%) plus 1098 kg N a−1 km2 burial in sediments (6%) minus 1993 kg N a−1 km2 nitrogen fixation (−11%) (Figure 4a). Therefore, denitrification is the dominating process. The model suggests that presently, about 12,156 t N/a are kept back in the entire lagoon, with a monetary value of EUR 166 million/a (EUR 241,882 a−1 km2). For the period 2010–2019, this means that on average, 39% of the annual total nitrogen loads to the lagoon were kept back.
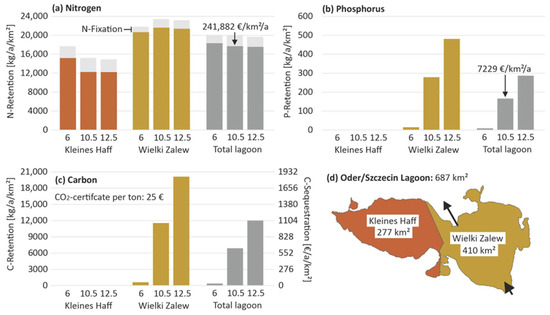
Figure 4.
Model calculated annual nutrient and carbon retention in the two bays of Oder/Szczecin Lagoon. (a) Quantity and exemplary monetary value (Euro) of nitrogen retention, covering denitrification, burial in sediments, and N-fixation. The latter adds nitrogen to the lagoon. Quantity and exemplary monetary value of (b) phosphorus retention and (c) carbon retention or sequestration (burial in sediments). (d) Area of the lagoon and its basins.
According to the model, in the Kleines Haff, the channel deepening caused a decrease in N-retention of 20%, while in the Wielki Zalew, it suggests an increase of 3%. In total over the lagoon, this results in a decrease of more than 4%. The deepened channel serves as sediment trap and increases the nutrient burial, but, because of its location, this is only in the Wielki Zalew. The different behavior of both bays results from a complex interplay between water exchange, denitrification, and N-fixation.
Phosphorus retention: On average over the lagoon, the model suggests a minor P-retention of 9 kg P a−1 km2 for the situation with a 6 m channel depth that increases with increasing channel depth to 287 kg P a−1 km2 (Figure 4b). In the present situation (10.5 m channel depth), altogether 114 t P/a are kept back, and in the future (12.5 m channel depth), it is 197 t P/a. Retention exclusively takes place in the Wielki Zalew. The model suggests no permanent sediment burial in the Kleines Haff. The reason for the increase in the Wielki Zalew is the increasing sediment trap function of the deepened channel. The monetary value of the P-retention is EUR 5 million/a (10.5 m) resp. EUR 8.6 million/a (12.5 m). For the period 2010–2019, this means that on average, 12% of the annual total phosphorus loads to the lagoon were kept back in the lagoon.
Carbon retention/sequestration: Carbon retention shows a similar behavior compared to phosphorus since burial in sediments is the only sink-function (Figure 4c). On average over the lagoon, the model suggests a minor C-retention of 0.4 t C a−1 km2 for the situation with 6 m channel depth that increases with increasing channel depth to 12 t C a−1 km2. In the present situation (10.5 m channel depth), altogether 4740 t C/a are kept back, and in the future (12.5 m channel depth), the value is 8254 t P/a. The monetary value of the C-retention is about EUR 435,000/a (10.5 m) resp. EUR 757,000 million/a (12.5 m).
3.7. Regulating Ecosystem Services—Inter-Annual Variability
An advantage of a model-based ecosystem service assessment approach is flexibility with respect to the spatial and temporal resolution of the assessment. This enables addressing questions such as how strong is the spatio-temporal variability and what are reasonable spatial and temporal aggregation levels of assessments? Specifically, the regulating services nitrogen and phosphorus retention as well as carbon sequestration are suitable for this analysis. Concrete questions are as follows: Do these ecosystem services show an interannual variability, how strong is it, has it changed with changing channel depths, which parameters control the value of ecosystem services, and what are the consequences for temporally aggregated ecosystem service assessments?
The retention of nitrogen in the lagoon does not differ much between the scenarios over the period 2010 to 2019. This is very different for the nitrogen retention in the entire lagoon between single years. It ranges between 10,500 (2015) and 23,600 kg N a−1 km2 (2010) for a channel depth of 10.5 m (Figure 5c). The year 2010 was a wet year, while 2015 was one of the years with the lowest ever reported water discharge (Figure 5b).
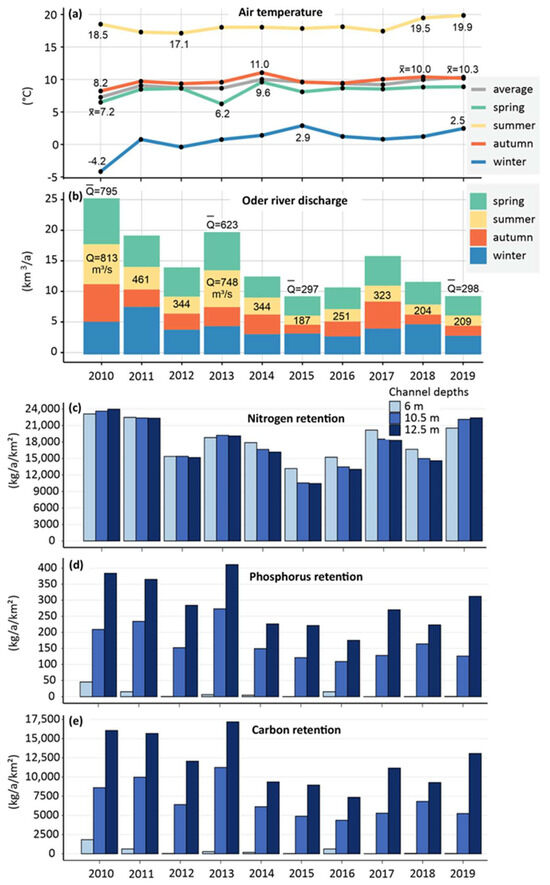
Figure 5.
(a) Average annual air temperature above Oder Lagoon for different seasons (summer includes the months JJA) (data: Norwegian Meteorological Institute). (b) Annual Oder River water discharge (data: Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej) separated into seasons. The Q-values indicate the average discharge for selected summer seasons (JJA) and years. Annual model-based nitrogen retention (including N-burial, N-fixation, and denitrification) (c), phosphorus retention (d), and carbon retention/sequestration (e) in the entire Oder Lagoon for the three channel deepening scenarios.
The relationship between annual water discharge and the annual nitrogen retention in the lagoon is close (R2 = 0.46). This is not surprising since the annual riverine nitrogen load and the annual water discharge show a close positive relationship as well. This means the higher the riverine N-load is, the higher the retention in the lagoon. A clear dependency between average annual temperature and N-retention does not exist (Figure 5a,c).
For phosphorus and carbon, the difference between the three channel deepening scenarios is strong. The model generally suggests no burial in the sediment of the Kleines Haff. Storage only takes place in the Wielki Zalew, namely, in the shipping channel. The deeper the channel is, the higher the buried carbon and phosphorus (Figure 5d,e). The annual water discharge and the retention of phosphorus and carbon show a close positive correlation (R2 = 0.6) as well. These elements also show a certain negative relationship (R2 = 0.27) to temperature. This means that higher water discharge increases the quantitative retention, and higher temperature shows a tendency to reduce the quantitative retention.
The high interannual variabilities of these regulating ecosystem services indicate that assessment based on merely one year may be misleading and that an assessment over a decade is required to obtain reliable results that can be quantitatively compared to other ecosystem services.
3.8. Regulating Ecosystem Services—Seasonality and the Role of Extreme Events
Annual average temperatures or discharge cannot explain the strong differences in N-retention between the two dry years 2015 and 2019. An analysis of the annual course of the retention processes is required. It raises general questions about the seasonality of ecosystem services and how this impacts interannual variability.
Figure 6 shows the annual course of nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon retention for several channel deepening scenarios for the entire lagoon. In general, the channel deepening does not affect the annual course of nutrient retention, but the patterns between the elements differ. While nitrogen retention is very low in winter, showing a maximum in May and June and later in the year a decline, the maximum burial of phosphorus and carbon takes place in spring, between March and May, and already by mid-summer, no burial in sediments takes place any more. In general, one can say that the retention that happens during three months of a year, between May and July with respect to nitrogen and between March and May with respect to carbon and phosphorus, largely determines the annual retention.
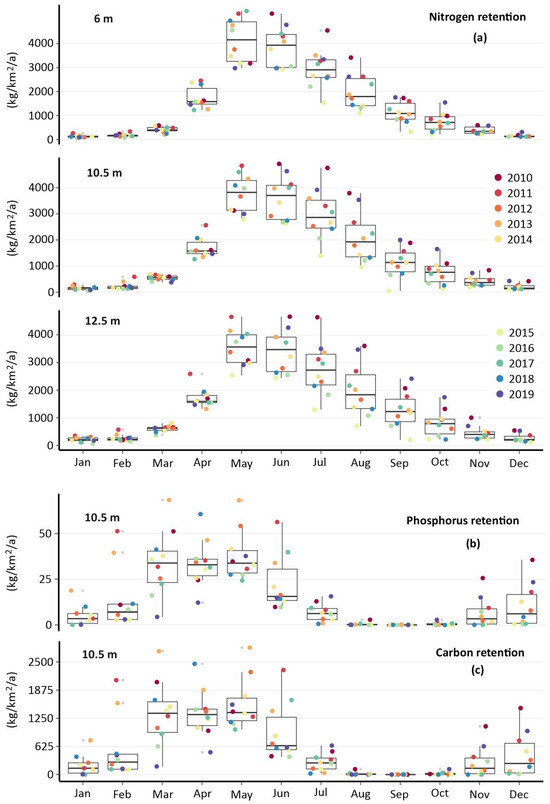
Figure 6.
(a) Monthly model-based nitrogen retention (including N-burial, N-fixation, and denitrification) in the entire Oder Lagoon for the three channel deepening scenarios, as well as phosphorus retention (b) and carbon retention/sequestration (c) for a channel depth of 10.5 m.
The nutrient retention values for spring and summer do not show a strong relationship to the water discharge during this season. Assuming a delay in processes and analyzing the role of discharges in spring on the retention in summer gives a very good correlation (R = 0.91) for nitrogen retention, but only if the year 2019 is neglected.
Figure 6 clearly indicates a strong variability between the months of a year. This is especially true for carbon and phosphorus retention. For example, the carbon retention in March is only 177 kg C km−2 a−1 in 2019 and 2681 kg C km−2 a−1 in 2013 for a channel depth of 10.5 m, and this variability significantly affects annual values. For example, in the years 2018 and 2013, the retention during March accounts for 24% of the total annual retention, while in 2019, it is merely 3%. The retention in March 2013 alone is above 50% of the entire annual retention of the year 2019 (5245 kg C km−2 a−1). This underlines the importance of seasonal and short-term events.
3.9. Synthesis
The monetary values of the assessed ecosystem services vary in a wide range. While the historically important provisioning ecosystem service “wild fish catches” generates a total annual value of EUR 3.2 million (10.5 m scenario), “transport” generates an annual value of EUR 32.1 million (Figure 7). In comparison, the cultural services “recreation” (EUR 60.8 million per year) and “landscape aesthetics/observation” (EUR 36.4 million per year) generate a high annual monetary benefit. However, the most important ecosystem service monetarily is nitrogen retention (EUR 166.2 million per year). The most important process for cleaning the lagoon from nitrogen is denitrification. “Phosphorus retention” (EUR 5.0 million per year) and “carbon storage” (EUR 0.4 million per year) are much less important. Both services merely depend on burial in sediments and on the assumed compensation costs per removed ton. Especially with respect to carbon, the CO2-certificates are still comparatively cheap causing a low monetary carbon storge value. All monetary values are related to the 10.5 m scenario.
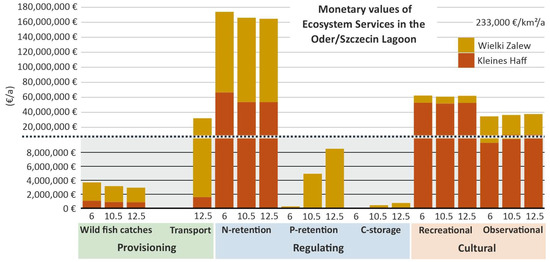
Figure 7.
Monetary values (Euro) of ecosystem services in Oder/Szczecin Lagoon for three different Swina channel deepening scenarios: 6 m (historic situation after 1880), 10.5 m (after 1984), and 12.5 m (after 2024). The dashed line indicates a break in y-axis scale.
For most ecosystem services, the differences between the scenarios are minor. Strong differences only exist for phosphorus retention (EUR 0.3–EUR 8.6 million per year) and carbon storage (EUR 0.02–EUR 0.8 million per year). Some background for the differences is that the model calculates strongly increasing sediment burial in the channel with increasing channel depth. The full data are shown in Appendix B.
4. Discussion
4.1. Critical Evaluation of Approach and Quantifications
The reliability of our results largely depends on the quality and the predictive capacity of the 3D ecosystem model. This model has been applied to various scenarios in the Baltic Sea and undergone calibration, validation, and continuous development [24,30]. According to an evaluation by the European Commission [25], ERGOM is ranked among the top two European models in the category of “biogeochemical and lower trophic level models”. For its application to Oder Lagoon, ERGOM has been specifically modified and applied in a very high spatial resolution. A recent study confirms the model’s suitability, reliability, and long-term stability for Oder Lagoon [30]. One key lesson learned from Neumann et al. [30] is that the quality and temporal resolution of the input parameters—such as riverine discharge, nutrient loads, and wind conditions—are critical to model performance in lagoon environments. To address this, we utilized the most accurate and up-to-date official input data available.
The regulating services, nitrogen and phosphorus retention and carbon storage, were directly derived from model output. Their reliability is therefore closely tied to the model’s robustness.
Our approach also integrates socio-economic and statistical data from a variety of sources, which collectively provide a strong foundation. However, challenges arose with certain ecosystem service calculation methods, which were diverse and partly subjective [27]. For instance, recalculating fish stock into biomass relied on literature data from the Baltic Sea [58,61]. The applicability and reliability of these data for the lagoon remain uncertain. Similarly, the development of the “recreation quality index” and “aesthetics quality index” involved subjective decisions in selecting, combining, and scaling parameters. These indices provide only a general indication of the lagoon’s potential for recreation and tourism. Furthermore, some overlap exists between the two indices. However, the distinction was maintained to differentiate between benefits accruing to tourists and those relevant to the local population.
4.2. Monetarization of Ecosystem Services
Monetizing ecosystem services offers the advantage of making them directly comparable and easily understandable for a wide audience, including policymakers. However, this highly aggregated level of information has limitations and involves risks, as it relies on assumptions, simplifications, and various calculation methods [79,80,81]. The monetary values calculated are highly dependent on human demand for ecosystem services, existing policy frameworks, and cultural conditions, and they can change significantly over time.
Compared to broader studies encompassing large regions with multiple countries [27], our localized study benefits from a more consistent and comparable dataset. This allows us to account for country-specific market conditions and prices, reflecting the economic gradients between Germany and Poland.
The data on fish catches and their monetary value are considered reliable. Nonetheless, fisheries play a relatively minor role in the lagoon’s economy today, in stark contrast to medieval times when they were a primary source of local income [33]. Even when secondary economic effects, such as fish processing, are included, this conclusion remains unchanged. Artisanal fishing in the lagoon has gained importance as a cultural heritage asset, attracting tourists. Recreational angling has also grown in significance and appears to generate economic values comparable to those of commercial fishing. However, due to insufficient spatially resolved statistics, these activities could not be assessed separately. The declining role of fishing is a trend observed across much of the Baltic Sea [82]. Despite growing protein demand, changing consumer preferences have led to only a few fish species being marketable, leaving the many bony whitefish species with little to no economic value [73].
Transportation, or the provision of space for commercial shipping, is assessed based on dredging and maintenance costs within the lagoon. It represents a major ecosystem service, particularly in the Polish part of the lagoon. However, this assessment does not account for significant secondary effects generated by nearby ports, such as Szczecin, since most economic activity occurs on land. Our analysis focuses on the current scenario and does not attempt to estimate historical transportation scenarios with shallower channel depths, as such estimates would be too speculative.
Cultural ecosystem services were separated into two categories: “recreation” and “observation/landscape aesthetics”. Recreation was calculated based on the number and value of tourist overnight stays and is considered reliable. In contrast, the “observational” service, reflecting the lagoon’s value to the local population, relies on simplified assumptions and provides little more than an approximate monetary value. No local surveys using common economic valuation methods, such as willingness-to-pay, travel cost, or hedonic pricing methods, were conducted. Additionally, transferring values from other case studies was not feasible due to various constraints [83], despite existing compilations by de Groot et al. [84]. However, cultural services at the lagoon generate comparatively high values, and their importance is increasing over time, consistent with trends across the Baltic Sea region [27].
Regulating services, including carbon storage/sequestration, nitrogen retention, and phosphorus retention, were also assessed. The monetary value of carbon storage in the lagoon is comparatively low (EUR 0.4 million per year for the 10.5 m scenario) and depends on the price of CO2 emission certificates in the European Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS). We used the average value for 2019 of EUR 92/t CO2 [73]. A rise to EUR 140/t [85] in the future would increase the value of this ecosystem service by approximately 50%. This illuminates the dependency of monetary ecosystem services on policy frameworks.
Phosphorus retention is a quantitatively important service in the lagoon (EUR 5 million per year for the 10.5 m scenario). It results from assuming avoidance costs of EUR 43/kg P for Poland and EUR 64/kg P for Germany [71]. Baltic Sea wide calculations used a lower averaged value of EUR 30/kg P, which met the order of magnitude of other studies by HELCOM [86].
Our model suggests that most organic material is trapped in the channel, leading to increased burial of phosphorus and carbon with greater channel depth. This finding aligns with field studies by Leipe et al. [87], who concluded that net sedimentation is negligible in other parts of Oder Lagoon due to frequent resuspension and transport processes. This view is further supported by the quantities of sediment removed from the channel during maintenance dredging in recent decades [76].
Nitrogen retention, valued at EUR 166 million per year for the 10.5 m scenario, is the lagoon’s most economically significant ecosystem service. The lagoon acts as an effective sink for the large nutrient loads discharged by the Oder River [30]. This ecosystem service involves three mechanisms: sediment burial (EUR 10.5 million per year), denitrification (EUR 178 million per year), and nitrogen fixation, which adds nitrogen to the water body (−EUR 22 million per year). Denitrification is the most critical of these processes. These values are derived from assumed avoidance costs of EUR 12.7/kg N for Poland and EUR 15.8/kg N for Germany [71]. The quantity of these processes is realistic [30].
4.3. Consequences of Temporal Variabilities
The provisioning and cultural ecosystem services exhibit strong interannual variability, primarily due to inconsistencies in the data. Consequently, ecosystem service assessments require temporal integration of data to ensure reliable results. We consider our integration period of 10 years highly appropriate, as it provides stable results while also enabling the detection of long-term changes in ecosystem values over extended periods, such as several decades.
The quantification of regulating ecosystem services is entirely derived from model simulation outputs. These data feature high spatial and temporal consistency, allowing for the assessment of shorter periods, such as individual years, seasonal patterns, or specific extreme events (e.g., heatwaves, storms, droughts, or floods).
Interannual variability is particularly pronounced for all regulating services. For nitrogen retention, the variability ranges from 60% to 134%, while for phosphorus retention and carbon storage, it spans 63% to 163%, compared to the 10-year average. These variations highlight that assessments based on single years may lead to misleading conclusions. Therefore, assessments over a 10-year period are essential for generating reliable results that are meaningful compared to other monetary ecosystem services.
The model indicates that all regulating ecosystem services exhibit strong, albeit distinct, seasonality. In some years, over 50% of the total annual retention may occur within a single month. However, these seasonal patterns vary substantially between years, underscoring the influence of seasonal and short-term events. Extreme events lasting days to weeks can significantly impact annual ecosystem service values. Nonetheless, the role of such events is better understood when analyzed at the process level rather than the ecosystem service level.
Ecosystem service analyses on timescales shorter than a year are generally less meaningful, as human responses to changes in ecosystem services tend to occur over longer periods and through accumulated experience. However, recurring short-term phenomena, such as summer algal blooms, can have long-term implications for ecosystem service provision, particularly for services such as recreation.
4.4. Relevance, Transferability, and Research Needs
Ecosystem service assessments, particularly those involving comparable monetary evaluations, are increasingly required by numerous European policies [88]. The strengths and weaknesses of such assessments have been widely discussed [89]. For Oder Lagoon, several key policies are relevant and must be implemented, including the Water Framework Directive (WFD, 2000/60/EC), the Bathing Water Directive (2006/7/EC), and the Habitats Directive (FFH, 92/43/EEC). A management plan under the Habitats Directive exists for large parts of the lagoon [90]. The lagoon’s currently insufficient environmental state, coupled with the requirements of these policies, underscores the need for implementing effective environmental management measures. However, the implementation of such measures is often hindered more by low public acceptance than by financial constraints. Our monetary ecosystem service evaluations quantify the benefits humans derive from the lagoon and help raise awareness of its significant economic value. de Groot et al. [85] provide summarized monetary estimates for ecosystem services in coastal systems (USD 28,917/ha/year) and rivers and lakes (USD 4267/ha/year) at 2007 price levels. Our calculated total value for all ecosystem services, approximately USD 4000/ha/year, falls within this range.
The full application of our approach requires a suitable and validated ecosystem model. However, some of our calculation methods can be adapted and transferred to other lagoon systems. For similar large lagoons in the Baltic region, monetary values for selected ecosystem services can be directly estimated using comparable methodologies.
The availability of suitable ecosystem models and their application provide a strongly improved and consistent database for the calculation of several provision and especially regulating services. Despite that, there is still space for further developments, since these models are usually restricted to lower trophic levels and focus on the water body and do not include benthic organisms and nearshore habitats. However, a major scientific challenge remains the inclusion of cultural ecosystem services. A recent review by Smardon [91] underscores their benefits and importance, with a focus on landscape aesthetics, but addresses shortcomings as well. One deficit exists with respect to quantifying, visualizing, and valuing cultural ecosystem services [92]. For coastal and marine cultural ecosystem services, a review by Garcia Rodrigues et al. [93] names several other deficits, such as a lack of integrated valuation assessments or insufficient links to benefits on human well-being. As a consequence, a generally applicable methodology for estimating different cultural ecosystem services does not exist. The few examples that address comparable lagoons address only some aspects and/or remain too conceptual [94] and suffer from the problem of a limited transferability [83].
5. Conclusions
Our model simulations suggest that channel deepening leads to a 20% decrease in annual average phytoplankton concentrations while simultaneously causing a 16% increase in summer cyanobacteria concentrations. This rise in cyanobacteria contributes to a 24% increase in nitrogen fixation within the lagoon. Additionally, a notable rise in nitrogen burial in sediments take place. These processes are compensated for by a 12% reduction in denitrification, which slightly reduces the lagoon’s overall nitrogen retention. In the 10.5 m channel depth scenario, an average of 17,862 kg N a−1 km2, equivalent to 39% of the annual total nitrogen load, is retained in the lagoon. This nitrogen retention is valued at EUR 166.2 million per year and is the lagoon’s most important ecosystem service.
The interannual variability in nitrogen retention is substantial, ranging from 10,500 kg N a−1 km2 (2015) to 23,600 kg N a−1 km2 (2010) in the 10.5 m scenario. This highlights the importance of assessing ecosystem services over extended periods (e.g., a decade) rather than relying on single-year evaluations, as short-term assessments may provide misleading results.
The deepened channel also acts as a sediment trap, significantly increasing carbon and phosphorus burial rates. On average, 12% of the annual total phosphorus loads are retained in the lagoon. These regulatory ecosystem services exhibit pronounced seasonality and variability; for instance, carbon storage in March 2013 alone exceeded 50% of the total annual retention in 2019, emphasizing the critical role of seasonal and short-term events in ecosystem dynamics.
Phytoplankton-based simulations estimate the total commercially usable fish biomass in the lagoon at 13,497 tons of wet weight, with the reported annual catch of 2271 tons representing approximately 16% of this stock. However, channel deepening is projected to cause a 20% decline in commercially usable fish stocks. The total market value of the fish stock is estimated at EUR 15 million, while the annual monetary value of transportation associated with the deepened channel amounts to EUR 32 million. These findings highlight the diminishing economic significance of commercial fisheries, which once constituted the primary income source in the region.
The overall recreation index shows no significant differences across the three channel deepening scenarios. The lagoon’s eutrophic condition limits its suitability for recreational activities such as summer bathing tourism. Despite these limitations, the monetary value of recreational ecosystem services is estimated at approximately EUR 60 million per year, underscoring their considerable and increasing importance.
For most ecosystem services, differences between the assessed channel deepening scenarios are minor, and the impact of ongoing human interventions appears limited. Changes in salinity remain below 1 PSU (1 g/kg) and are considered ecologically negligible. The model suggests that alterations in the lagoon–Baltic Sea connectivity resulting from channel deepening are of limited importance.
The high quantitative and monetary importance of regulating services, namely, nutrient retention, suggests that these ecosystem services and potential changes, resulting from the implementation of human interventions, need to be taken into account in the planning process of measures. They should be considered in Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S.; methodology, G.S. and T.N.; software, T.N. and S.P.; validation, G.S., T.N. and S.P.; formal analysis, G.S., T.N., S.P. and N.M.S.; investigation, G.S., T.N. and N.M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S.; writing—review and editing, T.N., S.P. and N.M.S.; visualization, G.S., T.N., S.P. and N.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, projects “Coastal Futures II” (grant number 03F0980B) and “Prime Prevention” (grant number 03F0911B).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the following institutions for providing data: the Norwegian Meteorological Institute, the Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej and the Landesamt für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Geologie—LUNG.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Quantitative Ecosystem Services in Oder/Szczecin Lagoon.
| Provisioning services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Wild fish catches | Wild fish biomass | Transportation | ||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (kg wet weight/km2) | (kg wet weight/km2) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | |||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 2071 | 1726 | 1647 | 20,358 | 16,965 | 16,186 | |||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 5037 | 4373 | 4031 | 24,910 | 21,624 | 19,933 | |||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 3861 | 3305 | 3086 | 22,952 | 19,647 | 18,343 | |||
| Regulating services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Water quality regulation-nitrogen | Water quality regulation-phosphorus | Climate regulation-carbon sequestation | ||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (kg/a/km2) | (kg/a/km2) | (kg/a/km2) | |||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | |||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 15,199 | 12,249 | 12,229 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 0 |
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 20,653 | 21,608 | 21,371 | 15 | 279 | 481 | 616 | 11,561 | 20,132 |
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 18,341 | 17,695 | 17,551 | 9 | 166 | 287 | 371 | 6900 | 12,015 |
| Cultural services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Active recreation-quality index | Landscape aesthetics-quality index | |||||||
| (km2) | (km) | Index (0–100) | Index (0–100) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | ||||||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 50.3 | 49.3 | 50.2 | 53.2 | 56.2 | 57.1 | |||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 41.0 | 39.0 | 39.8 | 51.5 | 54.2 | 56.4 | |||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 44.8 | 43.2 | 44.0 | 51.1 | 54.0 | 55.5 | |||
Appendix B
Monetary (Euro) Ecosystem Services in Oder/Szczecin Lagoon.
| Provisioning services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Wild fish catches | Transportation | |||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/a) | (EUR/a) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | ||||||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 1,088,718 | 907,286 | 865,627 | 1,605,208 | |||||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 2,609,629 | 2,265,407 | 2,088,212 | 30,498,958 | |||||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 3,698,347 | 3,172,693 | 2,953,839 | 32,104,167 | |||||
| Provisioning services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Wild fish catches | Transportation | |||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/km2/a) | (EUR/a/km2) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | ||||||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 3930 | 3275 | 3125 | 5795 | |||||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 6365 | 5525 | 5093 | 74,388 | |||||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 5383 | 4618 | 4300 | 46,731 | |||||
| Regulating services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Water quality regulation–nitrogen | Water quality regulation–phosphorus | Carbon sequestration | ||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/a) | (EUR/a) | (EUR/a) | |||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | |||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 66,601,728 | 53,676,079 | 53,587,648 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 229 | 17 | 10 |
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 107,352,392 | 112,320,539 | 111,088,233 | 266,946 | 4,939,794 | 8,521,102 | 23,164 | 434,500 | 756,641 |
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 174,001,191 | 166,173,006 | 164,846,359 | 268,378 | 4,966,300 | 8,566,825 | 23,342 | 434,517 | 756,651 |
| Regulating services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Water quality regulation–nitrogen | Water quality regulation–phosphorus | Carbon sequestration | ||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/a/km2) | (EUR/a/km2) | (EUR/a/km2) | |||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | |||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 240,439 | 193,776 | 193,457 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 261,835 | 273,953 | 270,947 | 651 | 12,048 | 20,783 | 56 | 1060 | 1845 |
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 253,277 | 241,882 | 239,951 | 391 | 7229 | 12,470 | 34 | 632 | 1101 |
| Cultural services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Active recreation-quality index | Landscape aesthetics-quality index | |||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/a) | (EUR/a) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | ||||||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 52,825,238 | 51,724,004 | 52,678,264 | 9,386,207 | 9,915,370 | 10,075,479 | |||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 9,576,697 | 9,105,768 | 9,290,863 | 25,211,951 | 26,531,460 | 27,581,335 | |||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 62,401,934 | 60,829,772 | 61,969,126 | 34,598,159 | 36,446,830 | 37,656,814 | |||
| Cultural services | |||||||||||
| Oder Lagoon | Surface area | Coast-line | Active recreation-quality index | Landscape aesthetics-quality index | |||||||
| (km2) | (km) | (EUR/a/km2) | (EUR/a/km2) | ||||||||
| 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | 6 m | 10.5 m | 12.5 m | ||||||
| Kleines Haff | 277 | 89 | 190,705 | 186,729 | 190,174 | 33,885 | 35,796 | 36,374 | |||
| Wielki Zalew | 410 | 120 | 23,358 | 22,209 | 22,661 | 61,493 | 64,711 | 67,272 | |||
| Total lagoon | 687 | 209 | 90,833 | 88,544 | 90,203 | 50,361 | 53,052 | 54,813 | |||
References
- Wolnomiejski, N.; Witek, Z. The Szczecin Lagoon Ecosystem; De Gruyter Open Poland: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, M.; Różyński, G. Management conflicts in the Vistula Lagoon area. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 101, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Baltranaitė, E.; Kataržytė, M.; Balčiūnas, A.; Čerkasova, N.; Mėžinė, J. Establishing new bathing sites at the Curonian Lagoon coast: An ecological-social-economic assessment. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkevičiūtė, L.; Pranskūnienė, R.; Makutėnienė, D. Opportunities for Ecosystem Services in the Protected Areas in the Coastal–Rural Area of the Nemunas Delta and the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania). Sustainability 2022, 14, 9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Friedland, R.; Buer, A.-L.; Dahlke, S.; Drews, B.; Höft, S.; Klumpe, T.; Schadach, M.; Schumacher, J.; Zaiko, A. Ecological-social-economic assessment of zebra-mussel cultivation scenarios for the Oder (Szczecin) Lagoon. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyński, G.; Bielecka, M.; Schönhofer, J. Application of Systems Approach Framework (SAF) to the Vistula Lagoon case in Poland. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 168, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśliński, R.; Chlost, I.; Szydłowski, M. Impact of new, navigable canal through the Vistula spit on the hydrologic balance of the Vistula lagoon (Baltic Sea). J. Mar. Syst. 2024, 241, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakėnienė, R.; Jokšas, K.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Jakimavičius, D.; Raudonytė-Svirbutavičienė, E. Nutrient Loadings and Exchange between the Curonian Lagoon and the Baltic Sea: Changes over the Past Two Decades (2001–2020). Water 2023, 15, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, B.V.; Zakirov, R.B. Water Exchange of Nontidal Estuarine Coastal Vistula Lagoon with the Baltic Sea. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2021, 147, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckermann, M.; Omstedt, A.; Soomere, T.; Aigars, J.; Akhtar, N.; Bełdowska, M.; Bełdowski, J.; Cronin, T.; Czub, M.; Eero, M.; et al. Human impacts and their interactions in the Baltic Sea region. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.E.M.; Kniebusch, M.; Dieterich, C.; Gröger, M.; Zorita, E.; Elmgren, R.; Myrberg, K.; Ahola, M.P.; Bartosova, A.; Bonsdorff, E.; et al. Climate change in the Baltic Sea region: A summary. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 457–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgersson, A.; Kjellström, E.; Haapala, J.; Stendel, M.; Danilovich, I.; Drews, M.; Jylhä, K.; Kujala, P.; Larsén, X.G.; Halsnæs, K.; et al. Natural hazards and extreme events in the Baltic Sea region. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 251–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/documents/document.356.aspx.pdf (accessed on 18. November 2024).
- European Commission. Commission Staff Working Document. EU Guidance on Integrating Ecosystems and Their Services into Decision-Making. SWD (2019) 305 Final. Part 2/3. Available online: https://data.consilium.europa.eu/doc/document/ST-11395-2019-ADD-1/en/pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inácio, M.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki Sy, M.; Rey-Valette, H.; Simier, M.; Pasqualini, V.; Figuières, C.; De Wit, R. Identifying Consensus on Coastal Lagoons Ecosystem Services and Conservation Priorities for an Effective Decision Making: A Q Approach. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Newton, A.; Marcos, C. Coastal Lagoons: Environmental Variability, Ecosystem Complexity, and Goods and Services Uniformity. Coasts Estuaries 2019, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, R.; Leruste, A.; Le Fur, I.; Sy, M.M.; Bec, B.; Ouisse, V.; Derolez, V.; Rey-Valette, H. A Multidisciplinary Approach for Restoration Ecology of Shallow Coastal Lagoons, a Case Study in South France. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 108. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/ecology-and-evolution/articles/10.3389/fevo.2020.00108 (accessed on 9 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Inácio, M.; Schernewski, G.; Nazemtseva, Y.; Baltranaitė, E.; Friedland, R.; Benz, J. Ecosystem services provision today and in the past: A comparative study in two Baltic lagoons. Ecol. Res. 2018, 33, 1255–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Inacio, M.; Nazemtseva, Y. Expert Based Ecosystem Service Assessment in Coastal and Marine Planning and Management: A Baltic Lagoon Case Study. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 19. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/environmental-science/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00019 (accessed on 9 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Jekat, M.; Kösters, F.; Neumann, T.; Steffen, S.; von Thenen, M. Ecosystem Services Supporting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Assessments of Navigation Waterways Deepening Based on Data, Experts, and a 3D Ecosystem Model. Land. 2024, 13, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppelt, R.; Fath, B.; Burkhard, B.; Fisher, J.L.; Grêt-Regamey, A.; Lautenbach, S.; Pert, P.; Hotes, S.; Spangenberg, J.; Verburg, P.H.; et al. Form follows function? Proposing a blueprint for ecosystem service assessments based on reviews and case studies. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouri, P.; Alamanos, A.; Dellis, K.; Stratopoulou, A. Ecosystem Services into Water Resource Planning and Management 2022. Available online: https://EconPapers.repec.org/RePEc:aue:wpaper:2230 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Neumann, T.; Radtke, H.; Cahill, B.; Schmidt, M.; Rehder, G. Non-Redfieldian carbon model for the Baltic Sea (ERGOM version 1.2)—Implementation and budget estimates. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 8473–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Marine Biodiversity Modelling Study. In Publications Office of the European Union; European Comission: Brusells, Belgium, 2022; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/213731 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Inacio, M.; Karnauskaitė, D.; Baltranaitė, E.; Kalinauskas, M.; Bogdzevič, K.; Gomes, E.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem services of the Baltic Sea: An assessment and mapping perspective. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Neumann, T.; Bučas, M.; von Thenen, M. Ecosystem Services of the Baltic Sea—State and Changes during the Last 150 Years. Environments 2024, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziejewska, T.; Schernewski, G. The Szczecin (Oder-) Lagoon. In Ecology of Baltic Coastal Waters; Schiewer, U., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, R.; Schernewski, G.; Gräwe, U.; Greipsland, I.; Palazzo, D.; Pastuszak, M. Managing Eutrophication in the Szczecin (Oder) Lagoon-Development, Present State and Future Perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.; Schernewski, G.; Friedland, R. Transformation Processes in the Oder Lagoon as seen from a Model Perspective. EGUsphere preprint. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. State of the Baltic Sea. Third HELCOM Holistic Assessment 2016–2021. Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings 194. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/State-of-the-Baltic-Sea-2023.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- IKSO. Zweite Aktualisierung des Bewirtschaftungsplans für die Internationale Flussgebietseinheit. Int. Komm. Zum Schutz. Der Oder Gegen Verunreinig. Oder. 2022. Available online: http://www.mkoo.pl/download.php?fid=6996&lang=DE (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Schernewski, G.; Friedland, R.; Paysen, S.; Bucas, M.; Dahlke, S.; von Weber, M. Macrophytes and water quality in a large Baltic lagoon: Relevance, development and restoration perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1049181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrholz, V.; Lass, H.U. Transports between Oderhaff and Pomeranian Bight—A simple barotropic box model. Ger. J. Hydrogr. 1998, 50, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GDA SK S—SZCZECIN. Modernization Swinoujscie—Szczecin to a Depth of 12.5 m. Volume II 2015. Available online: https://atradiusdutchstatebusiness.nl/nl/documenten/poland_report_tom_ii.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Siedlik, K. Changes in the Szczecin Lagoon Shoreline as Determined from Selected Seventeenth and Nineteenth Century Maps. In Coastline Changes of the Baltic Sea from South to East; Harff, J., Furmańczyk, K., von Storch, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, K. Ueber das Stettiner Haff. Kommission zur wissenschaftlichen Untersuchung der Deutschen Meere in Kiel und der Biologischen Anstalt auf Helgoland, Kiel und Leipzig. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1896, 2, 105–144. Available online: https://www.zobodat.at/pdf/MON-ALLGEMEIN_0294_0001-0640.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Port Szczecin. Summary Statistics. Available online: https://port.szczecin.pl/en/ports/szczecin/summary-statistics/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Filina-Dawidowicz, L.; Durczak, W. Organization of Vessel Traffic on Dredged Świnoujście Szczecin Fairway: VTS Operators’ Viewpoint on the Use of Infrastructure for Ships Passing. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2023, XXVI, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, B.; Rockel, B. coastDat-2 COSMOCLM Atmospheric Reconstruction, 2013. Available online: https://www.wdc-climate.de/ui/entry?acronym=coastDat-2_COSMO-CLM (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- MV. UVP-Dokumentation Für den Geplanten Bau Eines Containerterminals im Außenhafen in Swinemünde. Available online: https://www.regierung-mv.de/Landesregierung/wm (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Laender-Regionen/Regionales/Gemeindeverzeichnis/Administrativ/Archiv/GVAuszugQ/AuszugGV1QAktuell.html (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Landesamt für innere Verwaltung. Available online: https://www.laiv-mv.de/Statistik/Zahlen-und-Fakten/Gesellschaft-&-Staat/Bevoelkerung/Statistische-Berichte (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Główny Urząd Statystyczny. Available online: https://bdl.stat.gov.pl/bdl/dane/podgrup/tablica (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Landesamt für innere Verwaltung. Available online: https://www.laiv-mv.de/Statistik/Ver%C3%B6ffentlichungen/Statistische-Berichte/G/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Statistical Yearbook of Maritime Economy 2023. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/statistical-yearbooks/statistical-yearbooks/statistical-yearbook-of-maritime-economy-2023,8,16.html (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Landesamt für innere Verwaltung. Available online: https://www.laiv-mv.de/Statistik/Zahlen-und-Fakten/Wirtschaftsbereiche/Verkehr/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Stybel, N.; Kleißler, K.; Schulz, N.; Gruzka, P. Fisheries Management in the Szczecin Lagoon. Coastline Rep. 2014, 22, 1–22. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316991505_Fisheries_management_in_the_Szczecin_Lagoon (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- GIOS. Update of the Initial Assessment of The Environmental Status of Marine Waters. Available online: https://rdsm.gios.gov.pl/images/Pliki/Update-of-initial-assessment-of-the-environmental-status-of-marine-waters.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Lewin, W.-C.; Weltersbach, M.S.; Haase, K.; Strehlow, H.V. Who travels how far: German Baltic sea anglers’ travel distances as precondition for fisheries management and coastal spatial planning. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesamt für Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelsicherheit und Fischerei Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Available online: https://www.lallf.de/fischerei/statistik/fischereidokumente/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin-Young, M. Revision of the Common International Classification for Ecosystem Services (CICES V5.1): A Policy Brief. One Ecosyst. 2018, 3, e27108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin, M. Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES) V5.1 and Guidance on the Application of the Revised Structure. 2018. Available online: www.cices.eu (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Landesamt für Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelsicherheit und Fischerei Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Available online: https://www.lallf.de/fischerei/statistik/fangstatistik-kuestengewaesser/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- GIOS. Available online: https://rdsm.gios.gov.pl/en/6-year-assessments/second-update-of-the-initial-assessment-2016-2021 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Landesamt für Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelsicherheit und Fischerei Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Available online: https://www.laiv-mv.de/Statistik/Ver%C3%B6ffentlichungen/Jahrbuecher/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- European Commission. Economic and Social Analyses. Available online: https://stecf.ec.europa.eu/reports/economic-and-social-analyses_en (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Scheffold, M.; Hense, I. Quantifying Contemporary Organic Carbon Stocks of the Baltic Sea Ecosystem. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 571956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRESP. Wet to Dry Weight Conversations for Biota from Amchitka to Kiska. 2006. Available online: https://www.cresp.org/Amchitka/Final_WW_DW_3_13_06.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Czamanski, M.; Nugraha, A.; Pondaven, P.; Lasbleiz, M.; Masson, A.; Caroff, N.; Bellail, R.; Treguer, P. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elemental stoichiometry in aquacultured and wild-caught fish and consequences for pelagic nutrient dynamics. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 2847–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurow, F. Estimation of the total fish biomass in the Baltic Sea during the 20th century. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 54, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff und Hafen. Available online: https://www.schiffundhafen.de/nachrichten/schifffahrt/detail/industriehafen-bei-ueckermuende-wird-ausgebaut.html (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Dolch, T.; Schernewski, G. Hat Wasserqualität eine Bedeutung für Touristen? Eine Studie am Beispiel des Oderästuars. In Aktuelle Ergebnisse der Küstenforschung. Berichte aus dem Forschung; Daschkeit, A., Sterr, H., Eds.; Und Technologiezentrum Westküste der: Büsum, Germany, 2003; Volume 28, pp. 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Preißler, S. Wasserqualität an Europäischen Küsten und ihre Bewertung durch TOURISTEN—Eine Wahrnehmungsgeographische Untersuchung in Hamburg und auf Sylt. In IKZM-Oder Berichte; Universität Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2008; Volume 54, p. 134; ISSN 1614-5968; Available online: https://databases.eucc-d.de/files/documents/00000738_IKZM-Oder_Berichte54.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2024)ISSN 1614-5968.
- Bertram, C.; Ahtiainen, H.; Meyerhoff, J.; Pakalniete, K.; Pouta, E.; Rehdanz, K. Contingent Behavior and Asymmetric Pref-erences for Baltic Sea Coastal Recreation. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, 75, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourismus in Deutschland im Jahr 2023. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2024/02/PD24_053_45.html#:~:text=Die%20Zahl%20der%20%C3%9Cbernachtungen%20von,%2C9%20%25%20h%C3%B6her%20als%202022 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Statistische Ämter. Available online: https://www.statistikportal.de/de/ugrdl/ergebnisse/wirtschaft-und-bevoelkerung/bipbws (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi). Wirtschaftsfaktor Tourismus in Deutschland. Available online: https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/DE/Publikationen/Tourismus/wirtschaftsfaktor-tourismus-in-deutschland-lang.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=1 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Europäische Union. Available online: https://european-union.europa.eu/principles-countries-history/eu-countries/germany_de (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Europäische Union. Available online: https://european-union.europa.eu/principles-countries-history/eu-countries/poland_de (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Gren, I.-M.; Jonzon, Y.; Lindqvist, M. Costs of Nutrient Reductions to the Baltic Sea: Technical Report; Department of Economics, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2008; Working Paper. [Google Scholar]
- Umweltbundesamt. Preisentwicklung für Emissionsberechtigungen (EUA) seit 2008. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/daten/klima/der-europaeische-emissionshandel#teilnehmer-prinzip-und-umsetzung-des-europaischen-emissionshandels (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Institut für Binnenfischerei, e.V. Recherche und Analyse der Möglichkeiten der Weißfischverwertung in Nordbrandenburg und Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Projektabschlussbericht, FFUS-004-2019. Available online: https://chara-seen.de/ (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Köbbing, J.F.; Thevs, N.; Zerbe, S. The utilisation of reed (Phragmites australis): A review. Mires Peat 2013, 13, 1–14. Available online: http://mires-and-peat.net/media/map13/map_13_01.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Copernicus. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/coastal-zones/coastal-zones-2012#download (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Minning, M. Der Schifffahrtskanal im Oderhaff—Eine Sediment-, Nähr- und Schadstofffalle? Diplomarbeit zur Diplomprüfung im Fach Geographie an der Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel. 2003. Available online: https://eucc-d-inline.databases.eucc-d.de/files/documents/00000695_Diplomarbeit_Minning2.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- IADC. Modernisation of the Swinouscie—Szczecin Fairway. Available online: https://www.iadc-dredging.com/article/modernisation-of-the-swinoujscie-szczecin-fairway/#:~:text=With%20more%20approximately%2024%20million,the%20next%20generation%20of%20vessels (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Interreg Central Europe. The Action Plan for the Implementation of Environmentally Friendly Solutions in Freight Transport of Szczecin and Świnoujście Multimodal Node and Transport Connections. Available online: https://programme2014-20.interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/D.T-2.5.9-Action-Plan-Port-of-Szczecin----winouj-cie---ENERG.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Mehvar, S.; Filatova, T.; Dastgheib, A.; De Ruyter van Steveninck, E.; Ranasinghe, R. Quantifying Economic Value of Coastal Ecosystem Services: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagebiel, J.; Schwartz, C.; Rhozyel, M.; Rajmis, S.; Hirschfeld, J. Economic valuation of Baltic marine ecosystem services: Blind spots and limited consistency. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, M.; Budziński, W.; Zandersen, M.; Zawadzki, W.; Aslam, U.; Angelidis, I.; Zagórska, K. The Recreational Value of the Baltic Sea Coast: A Spatially Explicit Site Choice Model Accounting for Environmental Conditions. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2024, 87, 135–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, S.; Haapasaari, P.; Karjalainen, T.P.; Kuikka, S.; Pakarinen, T.; Parkkila, K.; Romakkaniemi, A.; Vuorinen, P. Ecosystem services provided by Baltic salmon: A regional perspective to the socio-economic benefits associated with a keystone species. Econ. Ecosyst. Biodiveristy Nord. Synth. 2013, 266–276. Available online: https://www.teebweb.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/TEEB-case_TEEBNordic_Ecosystem-services-provided-by-Baltic-salmon.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Liu, S.; Costanza, R.; Farber, S.; Troy, A. Valuing ecosystem services: Theory, practice, and the need for a transdisciplinary synthesis. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2010, 1185, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaio. 2030 EUA Price Predictions: Expert Analysis of 3 Scenarios. Available online: https://www.homaio.com/post/2030-eua-price-predictions-expert-analysis-of-3-scenarios (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- HELCOM. Thematic Assessment of Economic and Social Analyses 2016–2021. Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings 188. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/HELCOM-Thematic-assessment-of-economic-and-social-analyses-2016-2021.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Leipe, T.; Eidam, J.; Lampe, R. Das Oderhaff—Beiträge zur Rekonstuktion der holozänen geologischen Entwicklung und anthropogenen Beeinflussung des Oder-Ästuars. Meereswissenschaftliche Berichte 1998, 28, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwma, I.; Schleyer, C.; Primmer, E.; Winkler, K.J.; Berry, P.; Young, J.; Preda, E. Adoption of the ecosystem services concept in EU policies. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.W.; Jobstvogt, N.; Böhnke-Henrichs, A.; Mascarenhas, A.; Sitas, N.; Baulcomb, C.; Lambini, C.; Rawlins, M.; Baral, H.; Zähringer, J.; et al. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats: A SWOT analysis of the ecosystem services framework. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staatliches Amt für Landwirtschaft und Umwelt Vorpommern. Managementplan. Available online: https://www.stalu-mv.de/ms/Themen/Naturschutz-und-Landschaftspflege/NATURA-2000/Managementplanung/?racr=a (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Smardon, R.C. Ecosystem Services for Scenic Quality Landscape Management: A Review. Land 2021, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.; Schleifer, S.; Wrbka, T. The concept of ecosystem services regarding landscape research; A review. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2011, 5, 1–37. Available online: http://www.livingreviews.org/lrlr-2011-1 (accessed on 9 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Garcia Rodrigues, J.; Conides, A.; Rivero Rodriguez, S.; Raicevich, S.; Pita, P.; Kleisner, K.; Pita, C.; Lopes, P.; Roldán, V.A.; Ramos, S.; et al. Marine and Coastal Cultural Ecosystem Services: Knowledge gaps and research priorities. One Ecosyst. 2017, 2, e12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkeviciute, L.; Pranskuniene, R. Cultural Ecosystem “employing” available natural resources, i.e., the ecosystems. Services: The Case of Coastal-Rural Area (Nemunas Delta and Curonian Lagoon, Lithuania). Sustainability 2021, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).