Legacy of Chemical Pollution from an Underwater Tire Dump in Alver Municipality, Norway: Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Site Mapping
2.2. Site Sampling
2.3. Trace Metal Analysis
2.4. Phthalate Analysis
2.5. Non-Target Analysis
2.6. Quality Control
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence of Trace Metals
3.2. Occurrence of Phthalates
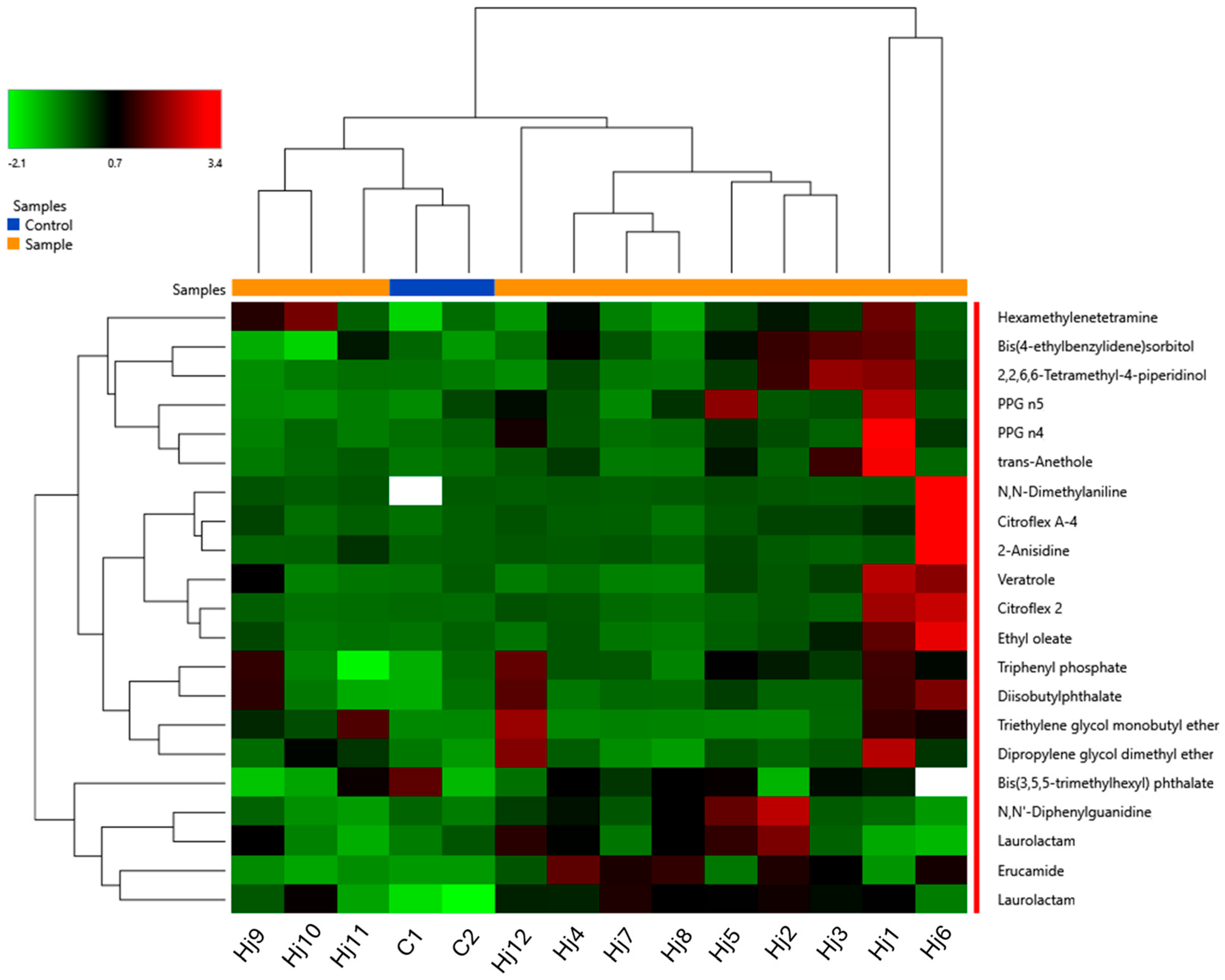
3.3. Non-Target Analysis
3.4. Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, F.R.; Rødland, E.S.; Kole, P.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Jaén-Gil, A.; Hansen, S.F.; Gomiero, A. An Overview of the Key Topics Related to the Study of Tire Particles and Their Chemical Leachates: From Problems to Solutions. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 172, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obanya, H.E.; Khan, F.R.; Carrasco-Navarro, V.; Rødland, E.S.; Walker-Franklin, I.; Thomas, J.; Cooper, A.; Molden, N.; Amaeze, N.H.; Patil, R.S.; et al. Priorities to Inform Research on Tire Particles and Their Chemical Leachates: A Collective Perspective. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, P.M.; Moran, K.D.; Miller, E.L.; Brander, S.M.; Harper, S.; Garcia-Jaramillo, M.; Carrasco-Navarro, V.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M.; Thornton Hampton, L.M.; et al. Where the Rubber Meets the Road: Emerging Environmental Impacts of Tire Wear Particles and Their Chemical Cocktails. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.; Hübner, D.; Huppertsberg, S.; Knepper, T.P.; Zahn, D. Probing the Chemical Complexity of Tires: Identification of Potential Tire-Borne Water Contaminants with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Unice, K.; Panko, J.; Ferrari, B.J.D.; Breider, F.; Wagner, S. Risk Assessment of Tire Wear in the Environment—A Literature Review. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2025, 27, 2212–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanadi, M.; Caubrière, L.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. Tire-Wear Particles and Tire-Related Emerging Contaminants: Characteristics, Occurrence, and Toxicity in the Environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2025, 48, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Huffer, T.; Klockner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire Wear Particles in the Aquatic Environment—A Review on Generation, Analysis, Occurrence, Fate and Effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A. Acute and Long-Term Toxicity of Micronized Car Tire Wear Particles to Hyalella Azteca. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarulli, S.; Sørensen, L.; Amat, L.M.; Farkas, J.; Khan, E.A.; Arukwe, A.; Gomiero, A.; Booth, A.M.; Gomes, T.; Hansen, B.H. Particles, Chemicals or Both? Assessing the Drivers of the Multidimensional Toxicity of Car Tire Rubber Microplastic on Early Life Stages of Atlantic Cod. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwood, C.; McAtee, B.; Kreider, M.; Ogle, R.S.; Finley, B.; Sweet, L.; Panko, J. Acute Aquatic Toxicity of Tire and Road Wear Particles to Alga, Daphnid, and Fish. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical Composition and Ecotoxicity of Plastic and Car Tire Rubber Leachates to Aquatic Organisms. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsband, C.; Sørensen, L.; Booth, A.M.; Herzke, D. Car Tire Crumb Rubber: Does Leaching Produce a Toxic Chemical Cocktail in Coastal Marine Systems? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Jensen, A.; Hansen, T.; Khan, F.R. Tire Wear Particle and Leachate Exposures from a Pristine and Road-Worn Tire to Hyalella Azteca: Comparison of Chemical Content and Biological Effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 232, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibwe, L.; Parrott, J.L.; Shires, K.; Khan, H.; Clarence, S.; Lavalle, C.; Sullivan, C.; O’Brien, A.M.; De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.G.; et al. A Deep Dive into the Complex Chemical Mixture and Toxicity of Tire Wear Particle Leachate in Fathead Minnow. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, K.E.; Holtze, K.E.; Metcalfe-Smith, J.L.; Bishop, C.T.; Dutka, B.J. Toxicity of Leachate from Automobile Tires to Aquatic Biota. Chemosphere 1993, 27, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Nilsson, E.; Källqvist, T.; Tobiesen, A.; Dave, G. Toxicity Assessment of Sequential Leachates of Tire Powder Using a Battery of Toxicity Tests and Toxicity Identification Evaluations. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of Micronized Tire Rubber: Past, Present and Future Considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R. A Ubiquitous Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical Induces Acute Mortality in Coho Salmon. Science (1979) 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, M.; Montgomery, D.; Selinger, S.; Miller, J.G.P.; Stock, E.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Challis, J.K.; Weber, L.; Janz, D.; Hecker, M. Acute Toxicity of the Tire Rubber-Derived Chemical 6PPD-Quinone to Four Fishes of Commercial, Cultural, and Ecological Importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauert, C.; Charlton, N.; Okoffo, E.D.; Stanton, R.S.; Agua, A.R.; Pirrung, M.C.; Thomas, K. V Concentrations of Tire Additive Chemicals and Tire Road Wear Particles in an Australian Urban Tributary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Lashuk, B.; Yargeau, V.; Metcalfe, C.D. The Tire Wear Compounds 6PPD-Quinone and 1,3-Diphenylguanidine in an Urban Watershed. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Metcalfe, C.D. Detection of Selected Tire Wear Compounds in Urban Receiving Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiwert, B.; Klöckner, P.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T. Source-Related Smart Suspect Screening in the Aqueous Environment: Search for Tire-Derived Persistent and Mobile Trace Organic Contaminants in Surface Waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4909–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challis, J.K.; Popick, H.; Prajapati, S.; Harder, P.; Giesy, J.P.; McPhedran, K.; Brinkmann, M. Occurrences of Tire Rubber-Derived Contaminants in Cold-Climate Urban Runoff. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meland, S.; Granheim, G.M.; Rundberget, J.T.; Rødland, E. Screening of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Tire Wear Particles in a Road Tunnel Wash Water Treatment Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 11, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.J. Environmental Impact of Tires Used in Marine Construction. In Tire Waste and Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 275–296. [Google Scholar]
- Lintner, M.; Henkel, C.; Peng, R.; Heinz, P.; Stockhausen, M.; Hofmann, T.; Hüffer, T.; Keul, N. Tire-Derived Compounds, Phthalates, and Trace Metals in the Kiel Fjord (Germany). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lei, M.; Hou, J. Phthalates Contamination in Sediments: A Review of Sources, Influencing Factors, Benthic Toxicity, and Removal Strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344, 123389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H.-S.; Ohandja, D.-G.; Voulvoulis, N. The Role of Sediments as a Source of Metals in River Catchments. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo Ardila, P.A.; Álvarez-Alonso, R.; Árcega-Cabrera, F.; Durán Valsero, J.J.; Morales García, R.; Lamas-Cosío, E.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; Del Valls, A. Assessment and Review of Heavy Metals Pollution in Sediments of the Mediterranean Sea. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siaka, M.; Owens, C.M.; Birch, G.F. Evaluation of Some Digestion Methods for the Determination of Heavy Metals in Sediment Samples by Flame-AAS. Anal. Lett. 1998, 31, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idera, F.; Omotola, O.; Paul, U.J.; Adedayo, A. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Different Acid Digestion on Sediments. Matrix 2014, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čelić, M.; Jaén-Gil, A.; Briceño-Guevara, S.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Gros, M.; Petrović, M. Extended Suspect Screening to Identify Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Riverine and Coastal Ecosystems and Assessment of Environmental Risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GraphPad Prism, version 8.0; Dotmatics: Boston, MA, USA, 2018.
- Rhodes, E.P.; Ren, Z.; Mays, D.C. Zinc Leaching from Tire Crumb Rubber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12856–12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Loughlin, D.P.; Haugen, M.J.; Day, J.; Brown, A.S.; Braysher, E.C.; Molden, N.; Willis, A.E.; MacFarlane, M.; Boies, A.M. Multi-Element Analysis of Tyre Rubber for Metal Tracers. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; Degryse, F. Fate and Effect of Zinc from Tire Debris in Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degaffe, F.S.; Turner, A. Leaching of Zinc from Tire Wear Particles under Simulated Estuarine Conditions. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauser, P.; Tjell, J.C.; Mosbaek, H.; Pilegaard, K. Quantification of Tire-Tread Particles Using Extractable Organic Zinc as Tracer. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, P.; Reemtsma, T.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Ruhl, A.S.; Wagner, S. Tire and Road Wear Particles in Road Environment—Quantification and Assessment of Particle Dynamics by Zn Determination after Density Separation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A. Metal Bioavailability and Toxicity in Sediments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 852–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of Sediment Geochemical Properties on Heavy Metal Bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Net, S.; Sempéré, R.; Delmont, A.; Paluselli, A.; Ouddane, B. Occurrence, Fate, Behavior and Ecotoxicological State of Phthalates in Different Environmental Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4019–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llompart, M.; Sanchez-Prado, L.; Pablo Lamas, J.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Roca, E.; Dagnac, T. Hazardous Organic Chemicals in Rubber Recycled Tire Playgrounds and Pavers. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goksøyr, A. Endocrine Disruptors in the Marine Environment: Mechanisms of Toxicity and Their Influence on Reproductive Processes in Fish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2006, 69, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, F.B. Organic Rubber Accelerators. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1926, 18, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Cai, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Leaching Hazards of Tire Wear Particles in Hydrothermal Treatment of Sludge: Exploring Molecular Composition, Transformation Mechanism, and Ecological Effects of Tire Wear Particle-Derived Compounds. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.; CDC/ATSDR. Synthetic Turf Field Recycled Tire Crumb Rubber Research Under the Federal Research Action Plan Final Report: Part 1—Tire Crumb Characterization; EPA/600/R-19/051.1; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 1 and 2.
- Peter, K.T.; Tian, Z.; Wu, C.; Lin, P.; White, S.; Du, B.; McIntyre, J.K.; Scholz, N.L.; Kolodziej, E.P. Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry to Identify Organic Contaminants Linked to Urban Stormwater Mortality Syndrome in Coho Salmon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10317–10327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USTMA, U.S.; Tire Manufacturers Association and U.S. Geological Survey Partner for Joint Research into 6PPD Alternatives. Available online: https://www.ustires.org/newsroom/us-tire-manufacturers-association-and-us-geological-survey-partner-joint-research-6ppd (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Trudsø, L.L.; Nielsen, M.B.; Hansen, S.F.; Syberg, K.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R.; Palmqvist, A. The Need for Environmental Regulation of Tires: Challenges and Recommendations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, K.J.; Backhaus, T.; Carney-Almroth, B.; Geueke, B.; Inostroza, P.A.; Lennquist, A.; Leslie, H.A.; Maffini, M.; Slunge, D.; Trasande, L.; et al. Overview of Known Plastic Packaging-Associated Chemicals and Their Hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
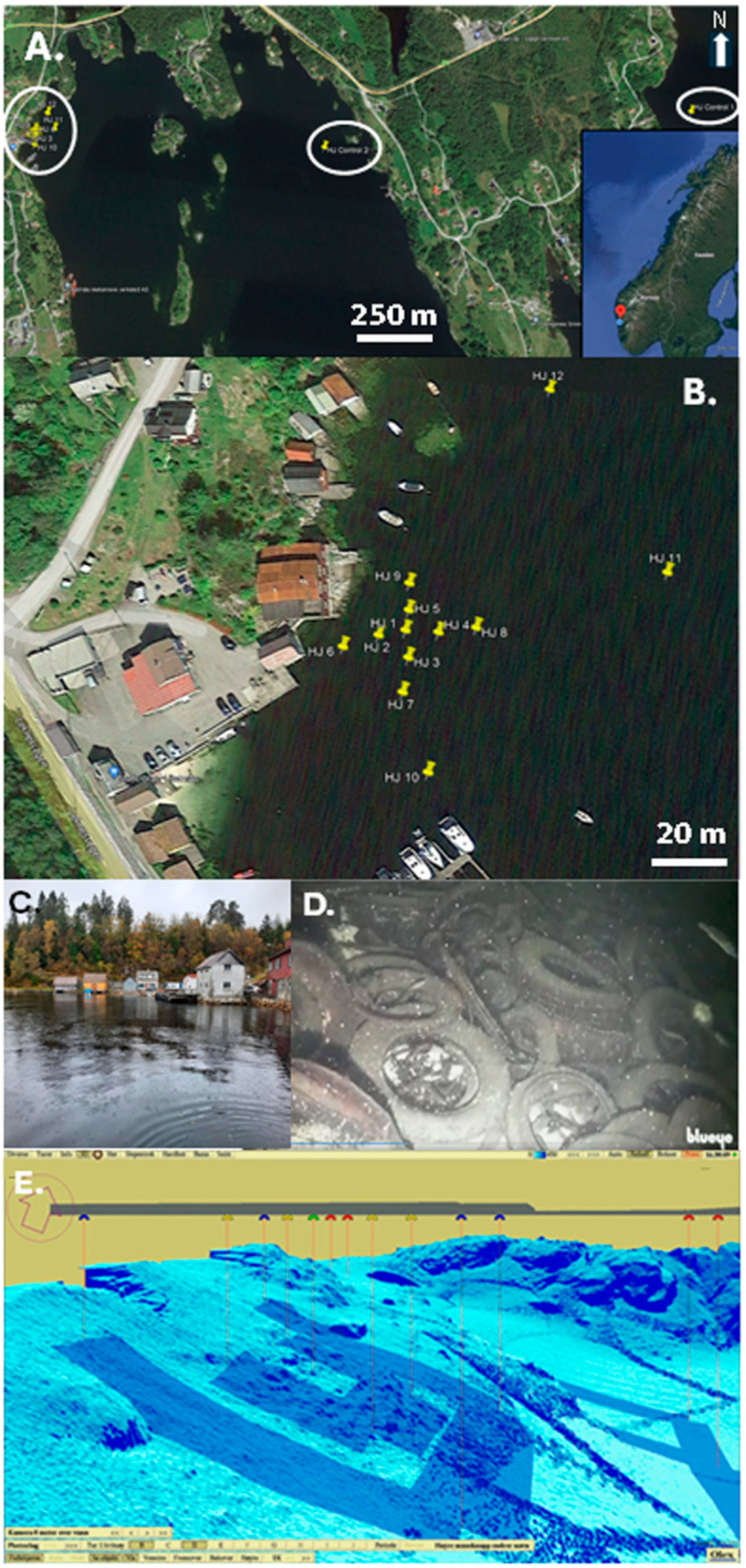
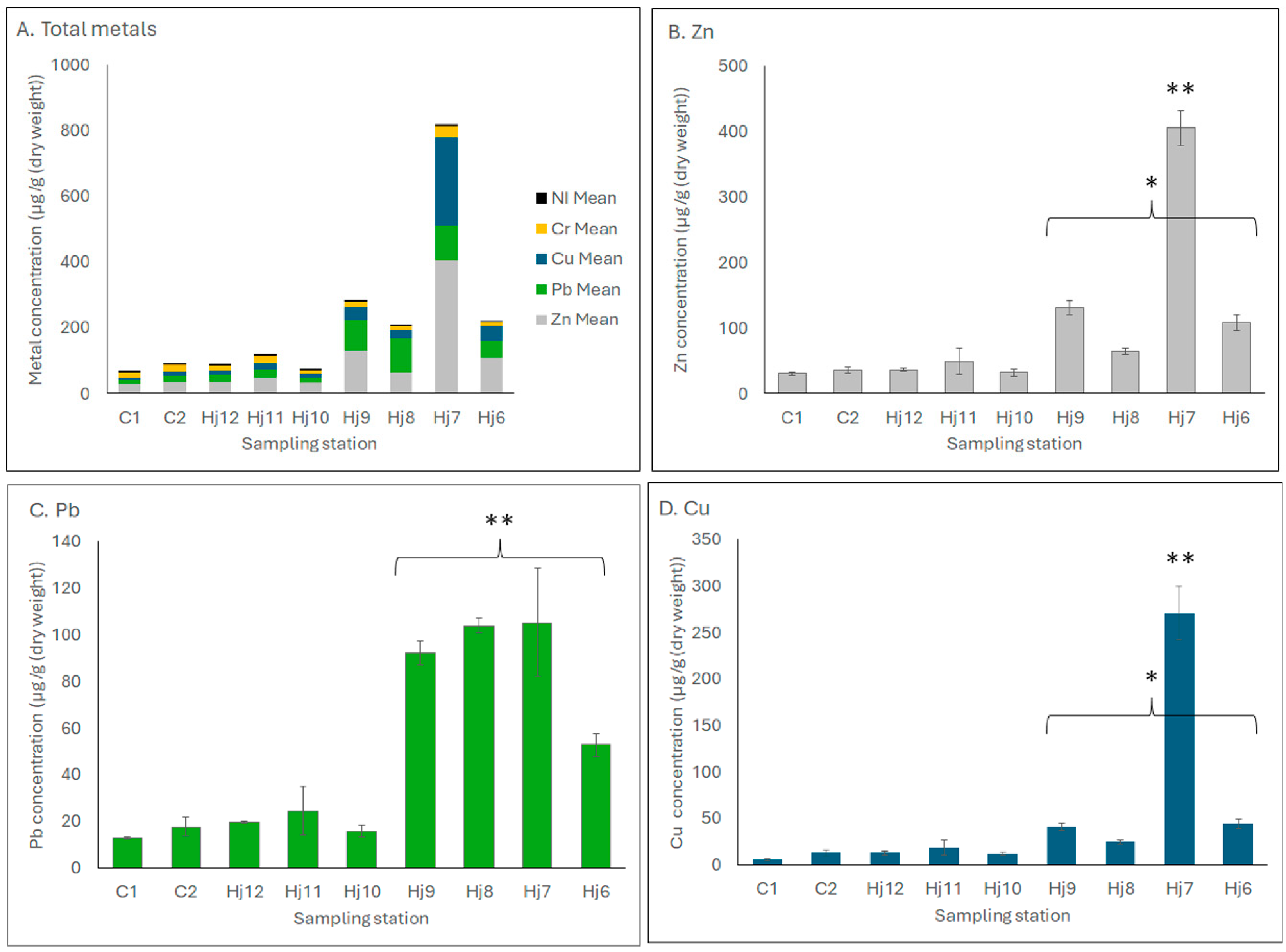
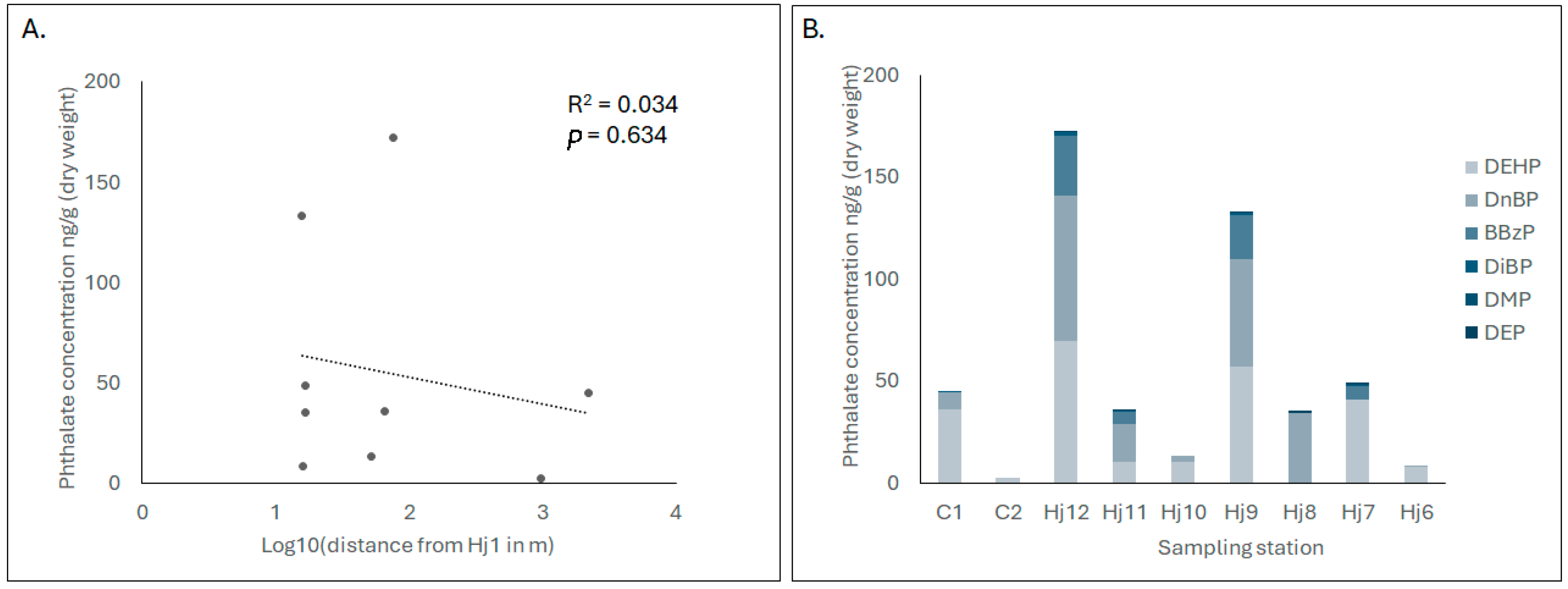
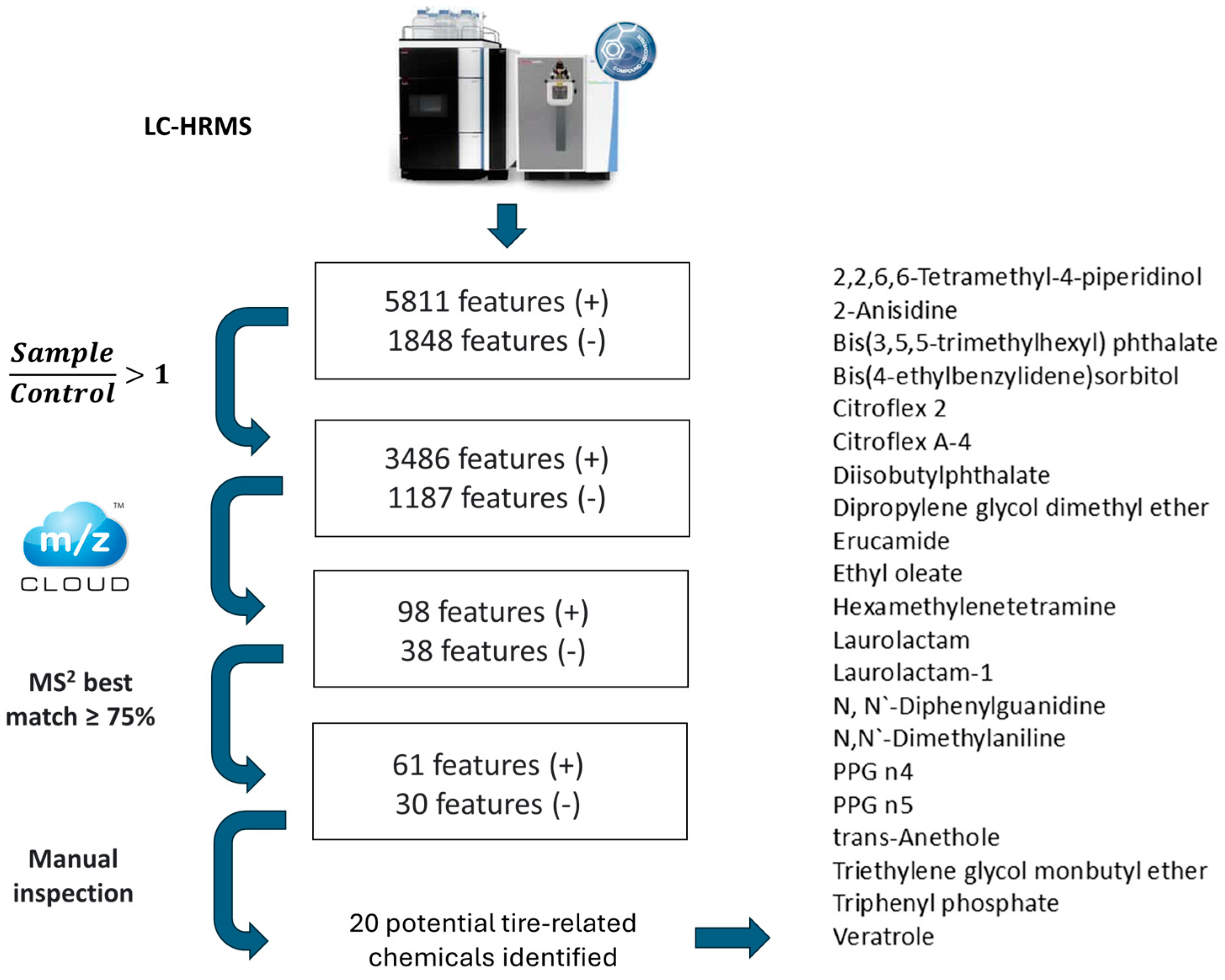
| Site Name | Latitude | Longitude | Depth (m) | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hj 1 | N60 35.549′ | E5 21.922′ | 7.8 | Tire dump center |
| Hj 2 | N60 35.548′ | E5 21.915′ | 8.6 | First ring—5 m West |
| Hj 3 | N60 35.545′ | E5 21.924′ | 9.6 | First ring—5 m South |
| Hj 4 | N60 35.549′ | E5 21.931′ | 10.2 | First ring—5 m East |
| Hj 5 | N60 35.552′ | E5 21.922′ | 8.0 | First ring—5 m North |
| Hj 6 | N60 35.546′ | E5 21.906′ | 4.4 | Second ring—15–20 m West |
| Hj 7 | N60 35.540′ | E5 21.924′ | 11.2 | Second ring—15–20 m South |
| Hj 8 | N60 35.550′ | E5 21.941′ | 16 | Second ring—15–20 m East |
| Hj 9 | N60 35.556′ | E5 21.921′ | 5.1 | Second ring—15–20 m North |
| Hj10 | N60 35.529′ | E5 21.934′ | 13.0 | Third ring—50–80 m South |
| Hj 11 | N60 35.560′ | E5 21.991′ | 15.0 | Third ring—50–80 m East |
| Hj 12 | N60 35.588′ | E5 21.952′ | 6.1 | Third ring—50–80 m North |
| Control 1 | N60 35.671′ | E5 24.318′ | 31.0 | Next bay at Eikangervågen (2.2 km from Hj1) |
| Control 2 | N60 35.560′ | E5 22.987′ | 36.0 | Hjelmåsvågen (1 km from Hj1) |
| Chemical | Use in Tires | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| N,N′-Diphenylguanidine (DPG) | A sulfur vulcanization accelerator used in tires to promote crosslinking; known to appear in tire leachate | Siewert et al., 2020 [23]; Johannessen et al., 2021 [22] |
| Hexamethylenetetramine | Organic compound used as a vulcanization accelerator | Leach et al., 1926 [47] |
| N,N-Dimethylaniline | Derivative of aniline, a degradation of amine-based tire additive | Sun et al., 2024 [48] |
| Diisobutyl phthalate | Phthalate commonly found in tire and rubber additive mixes | U.S. EPA & CDC/ATSDR. (2019) [49] |
| Bis(3,5,5-trimethylhexyl) phthalate | Phthalate commonly found in tire and rubber additive mixes | U.S. EPA & CDC/ATSDR. (2019) [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaén-Gil, A.; Tisserand, A.A.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Gomiero, A.; Langeland, E.; Khan, F.R. Legacy of Chemical Pollution from an Underwater Tire Dump in Alver Municipality, Norway: Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation. Environments 2025, 12, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100356
Jaén-Gil A, Tisserand AA, Santos LHMLM, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Gomiero A, Langeland E, Khan FR. Legacy of Chemical Pollution from an Underwater Tire Dump in Alver Municipality, Norway: Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation. Environments. 2025; 12(10):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100356
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaén-Gil, Adrián, Amandine A. Tisserand, Lúcia H. M. L. M. Santos, Sara Rodríguez-Mozaz, Alessio Gomiero, Eirik Langeland, and Farhan R. Khan. 2025. "Legacy of Chemical Pollution from an Underwater Tire Dump in Alver Municipality, Norway: Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation" Environments 12, no. 10: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100356
APA StyleJaén-Gil, A., Tisserand, A. A., Santos, L. H. M. L. M., Rodríguez-Mozaz, S., Gomiero, A., Langeland, E., & Khan, F. R. (2025). Legacy of Chemical Pollution from an Underwater Tire Dump in Alver Municipality, Norway: Implication for the Persistence of Tire-Derived Chemicals and Site Remediation. Environments, 12(10), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100356







