Evaluating Native Grassland Species for Application in Extensive Green Roofs in Japan †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Planting Selection and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Substrate Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Plant Performance
3.2.1. Performance of Imperata cylindrica
3.2.2. Performance of Patrinia scabiosifolia
3.2.3. Performance of Dianthus superbus var. longicalycinus
3.2.4. Performance of Sanguisorba officinalis
3.2.5. Performance of Prunella vulgaris subsp. asiatica
3.2.6. Performance of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica
3.3. Feasibility of Substrate Reuse and Nutrient Dynamics of EGRs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGRs | Extensive green roofs |
| RGR | Relative growth rate |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| WHC | Water-holding capacity |
Appendix A
References
- Leite, F.R.; Antunes, M.L.P. Green Roof Recent Designs to Runoff Control: A Review of Building Materials and Plant Species Used in Studies. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 189, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugita, J.; Tsuchiya, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Yamada, S.; Okuro, T. Effects of Biochar Usage and Plant Species Selections on the Storm Water Runoff Mitigations by Green Roofs. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveg. Technol. 2018, 44, 69–74. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIvor, J.S.; Margolis, L.; Perotto, M.; Drake, J.A.P. Air Temperature Cooling by Extensive Green Roofs in Toronto Canada. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Ishii, K. Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect by Light and Thin Rooftop Greening. J. Jpn. Inst. Landsc. Archit. 2005, 68, 509–512. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, Y.; El Zakhem, H.; Hamami, A.E.A.; El Bachawati, M.; Belarbi, R. Comprehensive Assessment of the Impact of Green Roofs and Walls on Building Energy Performance: A Scientific Review. Energies 2024, 17, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronuma, T.; Watanabe, H.; Ishihara, T.; Kou, D.; Toushima, K.; Ando, M.; Shindo, S. CO2 Payoff of Extensive Green Roofs with Different Vegetation Species. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Xue, X.; Luo, X. An Overview of Carbon Sequestration of Green Roofs in Urban Areas. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 47, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, E.; Terzano, K. Modelling the Optimal Green Roof Type for Carbon Capture in an Urbanised University Campus. Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 112, 128946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.L.; Payne, S.G.; Palmer, M.I.; Gillikin, C.M.; Keefe, D.; Kim, S.J.; Gedallovich, S.M.; Discenza, J.; Rangamannar, R.; Koshner, J.A.; et al. Digging the New York City Skyline: Soil Fungal Communities in Green Roofs and City Parks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, N.; Yanai, S. A Study on the Characteristics of Bird Distribution in Rooftop Vegetation in Tokyo Ward. J. Jpn. Inst. Landsc. Archit. 2005, 68, 597–600. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- MacIvor, J.S.; Lundholm, J. Performance Evaluation of Native Plants Suited to Extensive Green Roof Conditions in a Maritime Climate. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratet, A.; Barra, M.; Hardion, L.; Chiron, F. Origins and Drivers of Roof Plant Assemblages: Designing Green Roofs for Biodiversity Conservation. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 94, 128247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksiazek-Mikenas, K.; Chaudhary, V.B.; Skogen, K.A. Combinations of Plant Species with Complementary Traits Have the Potential to Maximize Ecosystem Services on Green Roofs. Urban Ecosyst. 2023, 26, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green Roofs Equivalent to Three Tokyo Domes Created In 2023: Results of the National Survey on Rooftop and Wall Greening Projects. (In Japanese). Available online: https://www.mlit.go.jp/report/press/toshi10_hh_000515.html (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Iwata, T.; Shimoda, R. Spontaneous Vegetation in Mandatory Green Roofs at Public Educational Facilities in Sumida-Ku, Tokyo. J. Jpn. Inst. Landsc. Archit. Online Collect. Pap. 2024, 17, 38–46. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Moriyama, M. Study of the Maintenance of Green Roof. AIJ J. Technol. Des. 2010, 16, 221–226. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, J.T. Green Roof Plant Species Diversity Improves Ecosystem Multifunctionality. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, T.F.; Furukawa, T. Nation-Wide Agrarian Depopulation Threatens Semi-Natural Grassland Species in Japan: Sub-National Application of the Red List Index. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 167, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.J.; Fa, J.E.; Oldfield, S.; Harrop, S.R. Bring the Captive Closer to the Wild: Redefining the Role of Ex Situ Conservation. Oryx 2012, 46, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, J.T. Green Roofs and Facades: A Habitat Template Approach. Urban Habitats 2006, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, A.; Bartoli, F.; Kumbaric, A.; Casalini, R.; Caneva, G. Evaluation of Mediterranean Perennials for Extensive Green Roofs in Water-Limited Regions: A Two-Year Experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 209, 107399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenta, M.; Quadri, A.; Sambuco, B.; Perez Garcia, C.A.; Barbaresi, A.; Tassinari, P.; Torreggiani, D. Green Roof Management in Mediterranean Climates: Evaluating the Performance of Native Herbaceous Plant Species and Green Manure to Increase Sustainability. Buildings 2025, 15, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shrestha, P.; Skabelund, L.R.; Todd, T.; Decker, A.; Kirkham, M.B. Growth of Prairie Plants and Sedums in Different Substrates on an Experimental Green Roof in Mid-Continental USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.K.; Harrington, J.A.; Skabelund, L.; MacDonagh, P.; Coffman, R.R.; Koch, G. PRAIRIE-BASED GREEN ROOFS: LITERATURE, TEMPLATES, AND ANALOGS. J. Green Build. 2012, 7, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, A.; Tashiro-Ishii, Y. Habitat Template Approach for Green Roofs Using a Native Rocky Sea Coast Plant Community in Japan. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 206, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, M.; Morimoto, J.; Katsuno, T. Planting Experiment Using the Coastal Plant Glehnia littoralis for Rooftop Greening. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveg. Technol. 2005, 31, 21–26. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y. Creation of Semi-Natural Grassland on Rooftop. J. Jpn. Inst. Landsc. Archit. 2023, 86, 326–329. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, J.-C.; Dusza, Y.; Abbadie, L.; Barot, S.; Carmignac, D.; Gendreau, E.; Kraepiel, Y.; Mériguet, J.; Motard, E.; Raynaud, X. Role of Substrate Properties in the Provision of Multifunctional Green Roof Ecosystem Services. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolaro, T.P.; Ghisi, E. Life Cycle Assessment of Green Roofs: A Literature Review of Layers Materials and Purposes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, A.J.; Sadler, J.P.; Greswell, R.B.; Mackay, R. Effects of Recycled Aggregate Growth Substrate on Green Roof Vegetation Development: A Six Year Experiment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 135, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molineux, C.J.; Gange, A.C.; Connop, S.P.; Newport, D.J. Using Recycled Aggregates in Green Roof Substrates for Plant Diversity. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksi, M.; Sevgi, O.; Akburak, S.; Yurtseven, H.; Esin, İ. Assessment of Recycled or Locally Available Materials as Green Roof Substrates. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, S.; Gratchev, I.; Michael, R.N. Recycled Waste Substrates: A Systematic Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Cook, L.M.; Huang, J.; Lensky, I.M.; Tan, T. Substrate Microorganisms Can Be an Ideal Tool for Improving Green Roof Sustainability. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 91, 128179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Weather, Climate and Earthquake Information. (In Japanese). Available online: https://www.jma.go.jp/jma/index.html (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Mitsui Kinzoku Perlite Co., Ltd. Available online: https://mitsui-perlite.co.jp/ (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Yamato, M.; Hattori, T.; Asami, K. Comparison of Floristic Composition of Imperata cylindrica var. koenigii Communities Growing on Consolidated and on Traditional Levee Slopes in Sanda, Hyogo Pref. Western Japan. J. Weed Sci. Technol. 1999, 44, 170–179. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Yamato, M.; Hattori, T. Characteristics of the Imperata cylindrica—Erigeron Annuus Community. Veg. Sci. 1998, 15, 33–45. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Hattori, T.; Akamatsu, H. A Study on Management by Cutting of the Embankment Vegetation. J. Jpn. Inst. Landsc. Archit. 1994, 58, 125–128. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, H.; Asami, K.; Tamura, K.; Hukui, S.; Hattori, T. Change after 16 years of artificial Imperata cylindrica var. koenigii grassland and possibility of creating the grassland. Hum. Nat. 2009, 20, 81–91. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokyo Red Data Book (Mainland) 2023. (In Japanese). Available online: https://www.kankyo.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/nature/animals_plants/red_data_book/400100a20230424184941875 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Kitamura, S.; Murata, G.; Koyama, T. Illustrated Flora of Japan, Herbaceous Plants; Revised, Ed.; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1964; Volume 3, ISBN 978-4-586-30017-4. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Flora of Japan Volume 3a; Iwatsuki, K., Yamazaki, T., Boufford, D.E., Ohba, H., Eds.; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; ISBN 978-4-06-153420-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, S.; Murata, G. Illustrated Flora of Japan, Herbaceous Plants; Revised, Ed.; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1961; Volume 2, ISBN 978-4-586-30016-7. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- FLL. (Forschungsgesellschaft Landschaftsentwicklung Landschaftsbau e.V). Green Roof Guidelines: Guidelines for the Planning, Construction and Maintenance of Green Roofs, 2018th ed.; FLL: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hiradate, S.; Kusumoto, Y.; Yoshitake, H.; Baba, Y. Biodiversity Supported by Soils. In Conservation Ecology of Familiar Nature: Understanding Biodiversity; Nemoto, M., Ed.; Baifukan: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 131–148. ISBN 978-4-563-07810-2. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, S. Chemical Properties of Forest Soil. Tree For. Health 2011, 15, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Unirrigated Extensive Green Roofs in Humid Subtropics—Plant Selection and Substrate Design for Low Maintenance and Climate Resilience. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 101, 128554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçük, N.; Ekşi, M. Evaluation of Native Herbaceous Plants for Green Roof Applications in Istanbul. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 196, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberse, W.T.; Berendse, F. A Comparative Study of the Growth and Morphology of Eight Grass Species from Habitats with Different Nutrient Availabilities. Funct. Ecol. 1993, 7, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenberg, H. Zeigerwerte Der Gefäßpflanzen Mitteleuropas; Goltze: Göttingen, Germany, 1974; Volume 9, pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tichý, L.; Axmanová, I.; Dengler, J.; Guarino, R.; Jansen, F.; Midolo, G.; Nobis, M.P.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Aćić, S.; Attorre, F.; et al. Ellenberg-Type Indicator Values for European Vascular Plant Species. J. Veg. Sci. 2023, 34, e13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.J.; Stevens, P.A.; Stevens, D.P.; Mountford, J.O.; Manchester, S.J.; Pywell, R.F. The Restoration and Re-Creation of Species-Rich Lowland Grassland on Land Formerly Managed for Intensive Agriculture in the UK. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 119, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, S.C. Trade-Offs in Life-History Evolution. Funct. Ecol. 1989, 3, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, F.A.; Ackerly, D.D.; Reekie, E.G. Reproductive Allocation in Plants. In Seeds: The Ecology of Regeneration in Plant Communities; CABI Books: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kuramoto, N. Gravel-Bar in the Tama River as Habitat of Endemic Plants. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveg. Technol. 2019, 44, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, S.; Hirose, F. Seed Density within the Topsoil and Seed Germination Ability of Dianthus Superbus Var. Longicalycinus on a Coastal Dune. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveg. Technol. 2023, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Yamada, S.; Tabuchi, S. Handbook of Revegetation with Native Herbaceous Species: Restoration of Familiar Nature Vegetation; Asakura Shoten: Tokyo, Japan, 2020; ISBN 978-4-254-42042-5. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagase, A.; Dunnett, N. Drought Tolerance in Different Vegetation Types for Extensive Green Roofs: Effects of Watering and Diversity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Nemoto, M.; Koyanagi, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yatsuki, H. “Biodiversity-Conscious Vegetation Management in Riverdikes” Vegetation and Environmental Attributes in Species-Rich Semi-Natural Grassland in Riverbanks. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveg. Technol. 2016, 42, 428–432. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guidi, M.; Bousselot, J. Earlier Flowering Phenology and Pollinator Visitation on Urban Green Roofs Compared to Ground-Level Gardens. Land 2024, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnett, N. Naturalistic Planting Design: The Essential Guide; Filbert Pr: Bath, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-9933892-6-9. [Google Scholar]
- Buffam, I.; Mitchell, M.E.; Durtsche, R.D. Environmental Drivers of Seasonal Variation in Green Roof Runoff Water Quality. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S. What Happens to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrient Contributions from Green Roofs as They Age? A Review. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.B.; Monterusso, M.A.; Rugh, C.L. Assessment of Heat-Expanded Slate and Fertility Requirements in Green Roof Substrates. HortTechnology 2006, 16, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, A.; Dunnett, N. The Relationship between Percentage of Organic Matter in Substrate and Plant Growth in Extensive Green Roofs. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.E.; Emilsson, T.; Buffam, I. Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Variation along a Green Roof Chronosequence: Implications for Green Roof Ecosystem Development. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 164, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Umeki, K. Assessing the Performance of Native Grassland Species on Extensive Green Roofs Under Japanese Climatic Conditions. In Proceedings of the International Conference 2025 on Spatial Planning and Sustainable Development (SPSD 2025), Hankyong, Republic of Korea, 7–9 August 2025; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A Probabilistic Programming Language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
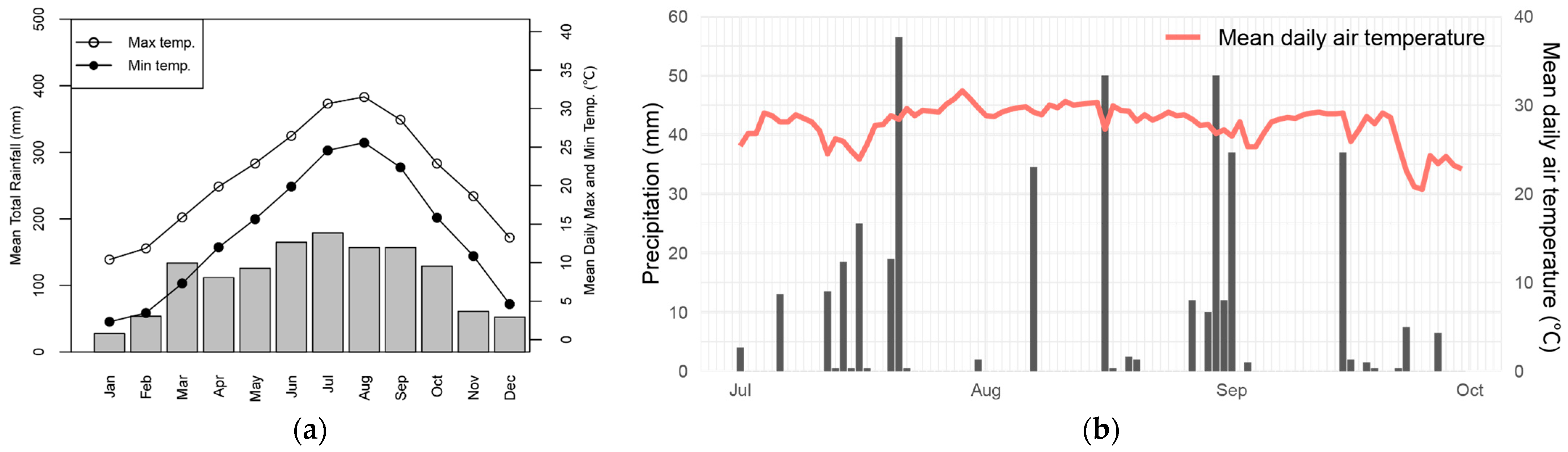









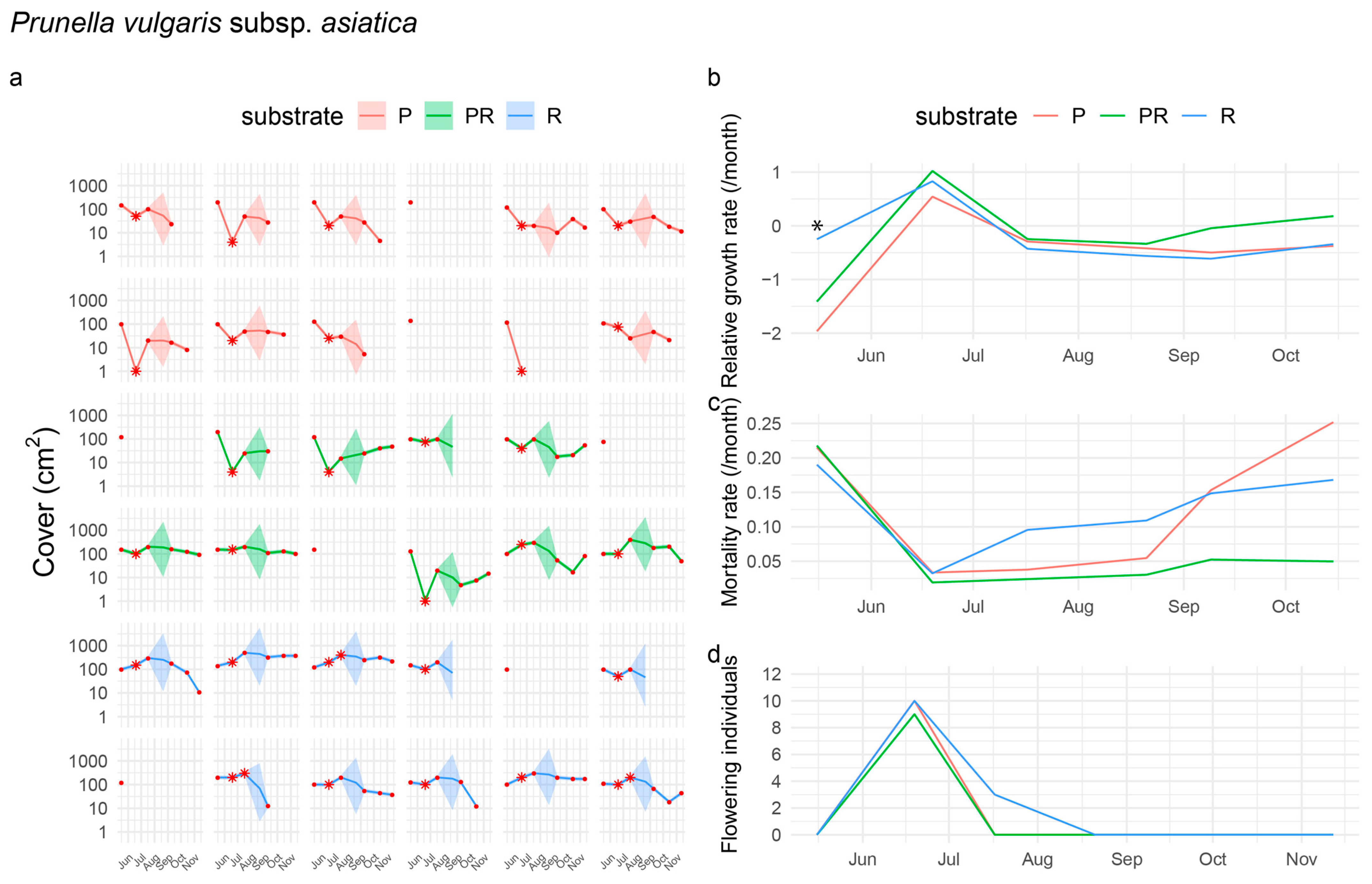


| Species | Family | Habitat | Distribution in Japan | Flowering Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imperata cylindrica | Poaceae | Open fields and embankments | Hokkaido to Kyushu | May to June | Kitamura et al. [42] |
| Patrinia scabiosifolia | Valerianaceae | Sunny place | Hokkaido to Kyushu | August to October | Iwatsuki et al. [43] |
| Dianthus superbus var. longicalycinus | Caryophyllaceae | Grassland | Honshu to Kyushu | June to September | Kitamura and Murata [44] |
| Sanguisorba officinalis | Rosaceae | Grassland | Hokkaido to Kyushu | July to October | Kitamura and Murata [44] |
| Prunella vulgairis susp. asiatica | Lamiaceae | Sunny grassland | Hokkaido to Kyushu | June to August | Iwatsuki et al. [43] |
| Adenophora triphylla var. japonica | Campanulaceae | Grassland | Hokkaido to Kyushu | July to November | Iwatsuki et al. [43] |
| Electrical Conductivity | pH | NH4-N | NO3-N | P2O5 | Dry Bulk Density | Saturated Bulk Density | WHC | C:N Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mS/m | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | g/cm3 | g/cm3 | % | |||
| R | 17.84 | 5.6 | 31.6 | 17.1 | 1096 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 74.0 | 10.05 |
| PR | 15.67 | 6.0 | 9.3 | 9.2 | 871 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 69.3 | 10.93 |
| P | 4.11 | 6.6 | 1.2 | <0.5 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 65.3 | |
| FLL guideline | 6.0–8.5 | <80 as N | <80 as N | <200 | 35–65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwata, T.; Shimoda, R.; Takahashi, T.; Umeki, K. Evaluating Native Grassland Species for Application in Extensive Green Roofs in Japan. Environments 2025, 12, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100345
Iwata T, Shimoda R, Takahashi T, Umeki K. Evaluating Native Grassland Species for Application in Extensive Green Roofs in Japan. Environments. 2025; 12(10):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100345
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwata, Tsukasa, Ryosuke Shimoda, Terumasa Takahashi, and Kiyoshi Umeki. 2025. "Evaluating Native Grassland Species for Application in Extensive Green Roofs in Japan" Environments 12, no. 10: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100345
APA StyleIwata, T., Shimoda, R., Takahashi, T., & Umeki, K. (2025). Evaluating Native Grassland Species for Application in Extensive Green Roofs in Japan. Environments, 12(10), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100345







