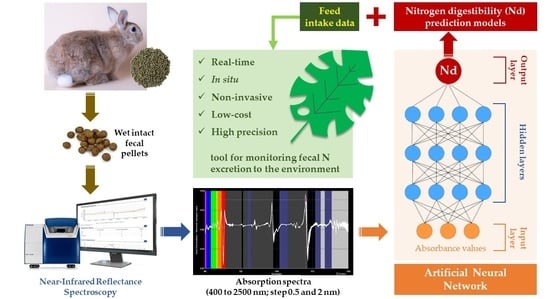
Real-Time Monitoring of Fecal Nitrogen Excretion to the Environment Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study in Rabbits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Digestibility Trial
| Diet A | Diet F | |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | ||
| Dehydrated alfalfa meal | 420 | 180 |
| Barley grain | 250 | 350 |
| Wheat bran | 100 | 150 |
| Sugar beet pulp | 100 | 190 |
| Sunflower meal, 280 g CP/kg | 80 | 20 |
| Soybean meal, 440 g CP/kg | 20 | 80 |
| Monocalcium phosphate | 7 | 7 |
| Arbocel ® 1 | 6 | 5 |
| Mineral + vitamin premix 2 | 5 | 5 |
| Ultrafed ® (binder) 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Sodium chloride | 4 | 4 |
| DL-Methionine, 990 g methionine/kg | 2 | 2 |
| L-Lysine HCl, 800 g lysine/kg | 1 | 1 |
| Calcium carbonate | - | 1 |
| Analyzed chemical composition | ||
| Digestible energy 4, MJ | 10.0 | 10.9 |
| Nitrogen (N)/Crude protein (N × 6.25) | 24.0/150 | 23.7/148 |
| aNDF 5 | 345 | 303 |
| ADF 5 | 215 | 153 |
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. NIRS Analysis and Modified Partial Least Squares
2.4. Artificial Neural Networks
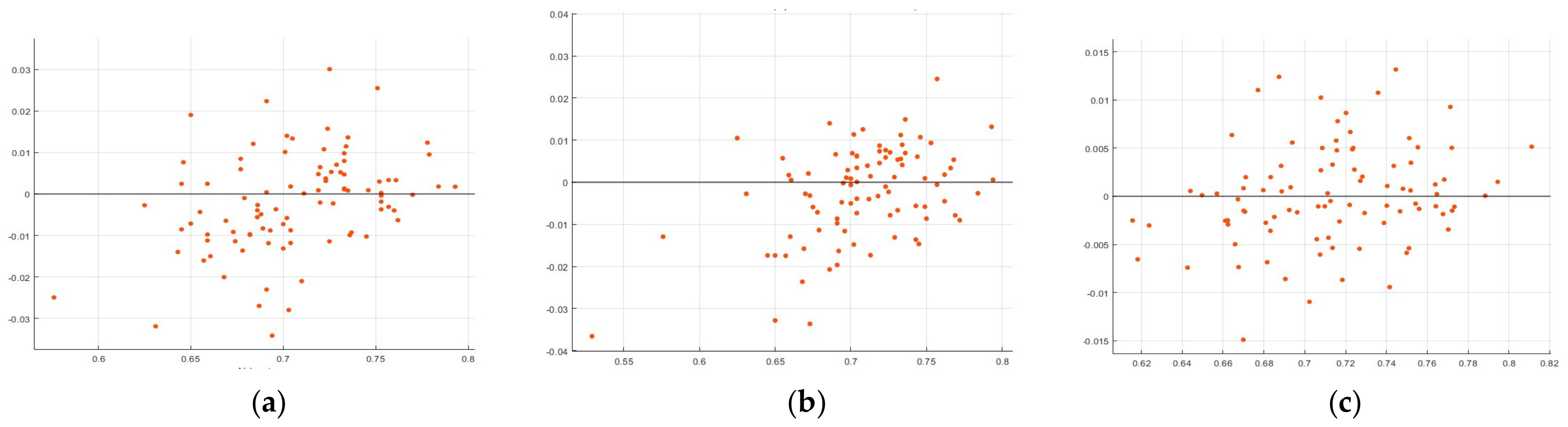
3. Results
3.1. Modified Partial Least Squares (MPLS) Methodology
3.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Methodology
4. Discussion
4.1. MPLS Methodology
4.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Methodology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beeckman, F.; Motte, H.; Beeckman, T. Nitrification in agricultural soils: Impact, actors and mitigation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weerden, T.J.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Podolyan, A.; Phillips, R.L.; Saggar, S.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Cox, N.; Ettema, P.; Rys, G. Nitrous oxide emissions from urea fertiliser and effluent with and without inhibitors applied to pasture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, D.R.; Zhang, X.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Malyshev, S.; Shevliakova, E. The importance of climate change and nitrogen use efficiency for future nitrous oxide emissions from agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. A review of methods to improve nitrogen use efficiency in agriculture. Sustain. Times 2017, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapaspongsa, T.; Christensen, P.; Schmidt, J.H.; Thrane, M. LCA of comprehensive pig manure management incorporating integrated technology systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, F.X.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Nicks, B. Ammonia emissions from pig houses: Influencing factors and mitigation techniques. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Powers, W.; Mukhtar, S. A review of practices and technologies for odor control in swine production facilities. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2014, 30, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, I.; Kyriazakis, I. How can we improve the environmental sustainability of poultry production? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, N. Life cycle assessment of Canadian egg products, with differentiation by hen housing system type. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asem-Hiablie, S.; Battagliese, T.; Stackhouse-Lawson, K.R.; Alan Rotz, C. A life cycle assessment of the environmental impacts of a beef system in the USA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Sánchez, N.; Martínez Marín, A.L.; Hernández, M.P.; Carrion, D.; Castro, G.G.; Pérez Alba, L.M. Faecal near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) as a tool to asses rabbit’s feed digestibility. Livest. Sci. 2012, 150, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patience, J.F.; Rossoni-Serão, M.C.; Gutiérrez, N.A. A review of feed efficiency in swine: Biology and application. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternostre, L.; Baeten, V.; Ampe, B.; Millet, S.; De Boever, J. The usefulness of NIRS calibrations based on feed and feces spectra to predict nutrient content, digestibility and net energy of pig feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 281, 115091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufrère, J.; Graviou, D.; Demarquilly, C.; Perez, J.M.; Andrieu, J. Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy to predict energy value of compound feeds for swine and ruminants. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 62, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, V.; Dardenne, P. Application of NIR in agriculture. In Near-Infrared Spectroscopy; Ozaki, Y., Huck, C., Tsuchikawa, S., Engelsen, S.B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Bastianelli, D.; Carré, B.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Bonnal, L.; Davrieux, F. Direct prediction of energy digestibility from poultry faeces using near infrared spectroscopy-Agritrop. In Near Infrared Spectroscopy, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–15 April 2005; Burling-Claridge, G.R., Holroyd, S.E., Sumner, R.M.W., Eds.; NZ NIRS Society Inc.: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2007; pp. 626–629. [Google Scholar]
- Coulibaly, I.; Métayer, J.P.; Chartrin, P.; Mahaut, B.; Bouvarel, I.; Hogrel, P.; Bastianelli, D. La combinaison des informations issues des aliments et des fientes améliore la prédiction par SPIR de la digestibilité chez le poulet: JRA-JRFG. In Proceedings of the Dixièmes Journées de la Recherche Avicole et Palmipèdes à Foie Gras (JRFG), La Rochelle, France, 26–28 March 2013; p. 165. [Google Scholar]
- Bastianelli, D.; Bonnal, L.; Jaguelin-Peyraud, Y.; Noblet, J. Predicting feed digestibility from NIRS analysis of pig faeces. Animal 2015, 9, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiborra, A.; Bulang, M.; Berk, A.; Susenbeth, A.; Schlecht, E. Using faecal near-infrared spectroscopy (FNIRS) to estimate nutrient digestibility and chemical composition of diets and faeces of growing pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 210, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirea, K.G.; de Nanclares, M.P.; Skugor, A.; Afseth, N.K.; Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Hansen, J.; Mydland, L.T.; Øverland, M. Assessment of fecal near-infrared spectroscopy to predict feces chemical composition and apparent total-tract digestibility of nutrients in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decruyenaere, V.; Lecomte, P.; Demarquilly, C.; Aufrere, J.; Dardenne, P.; Stilmant, D.; Buldgen, A. Evaluation of green forage intake and digestibility in ruminants using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS): Developing a global calibration. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 148, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meineri, G.; Peiretti, P.G.; Masoero, G. Appraisal of ingestion and digestibility in growing rabbits using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) of feeds and faeces. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Márín, D.; Garrido-Varo, A.; Guerrero, J.E. Non-linear regression methods in NIRS quantitative analysis. Talanta 2007, 72, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Rodehutscord, M. Application of artificial neural network and support vector machines in predicting metabolizable energy in compound feeds for pigs. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roush, W.B.; Cravener, T.L. Artificial neural network prediction of amino acid levels in feed ingredients. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravener, T.L.; Roush, W.R. Prediction of amino acid profiles in feed ingredients: Genetic algorithm calibration of artificial neural networks. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2001, 90, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Golian, A.; Mottaghitalab, M.; Nariman Zadeh, N. Prediction model for true metabolizable energy of feather meal and poultry offal meal using group method of data handling-type neural network. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1909–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.M.; Lebas, F.; Gidenne, T.; Maertens, L.; Xiccato, G.; Parigi-Bini, R.; Dalle Zotte, A.E.; Carazzolo, A.; Villamide, M.J.; Carabaño, R.; et al. European reference method for in vivo determination of diet digestibility in rabbits. World Rabbit Sci. 1995, 3, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidenne, T. Dietary fibres in the nutrition of the growing rabbit and recommendations to preserve digestive health: A review. Animal 2015, 9, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fundación Española para el Desarrollo de la Nutrición Animal. Tablas FEDNA de Composición y Valor Nutritivo de Alimentos Para la Fabricación de Piensos, 2nd ed.; De Blas, C., Mateos, G.G., Rebollar, P.G., Eds.; FEDNA: Madrid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 14th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and non starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Dardenne, P.; Flinn, P. Tutorial: Items to be included in a report on a near infrared spectroscopy project. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2017, 25, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. Released, IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 23.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB, Version: 9.14.0 (R2023a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.mathworks.com (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Gojun, M.; Valinger, D.; Šalíc, A.; Zelíc, B. Development of NIR-Based ANN models for on-line monitoring of glycerol concentration during biodiesel production in a microreactor. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancewicz, L.J.; Swift, M.L.; Penner, G.B.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Koenig, K.M.; Chibisa, G.E.; He, M.L.; McKinnon, J.J.; Yang, W.Z.; McAllister, T.A. Development of near-infrared spectroscopy calibrations to estimate fecal composition and nutrient digestibility in beef cattle. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 97, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehtiö, T.; Rinne, M.; Nyholm, L.; Mäntysaari, P.; Sairanen, A.; Mäntysaari, E.A.; Pitkänen, T.; Lidauer, M.H. Cow-specific diet digestibility predictions based on near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy scans of faecal samples. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2016, 133, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Conesa, A.; Ferré, J.; Pérez-Vendrell, A.M.; Callao, M.P.; Rui Sánchez, I. Use of visible-near infrared spectroscopy to predict nutrient composition of poultry excreta. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 283, 115169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidenne, T.; Garreau, H.; Drouilhet, L.; Aubert, C.; Maertens, L. Improving feed efficiency in rabbit production, a review on nutritional, technico-economical, genetic and environmental aspects. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 225, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiccato, G.; Trocino, A.; De Boever, J.L.; Maertens, L.; Carabaño, R.; Pascual, J.J.; Perez, J.M.; Gidenne, T.; Falcao-E-Cunha, L. Prediction of chemical composition, nutritive value and ingredient composition of European compound feeds for rabbits by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2003, 104, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.C. Implementation of near-infrared technology. In Near-Infrared Technology in the Agricultural and Food Industries; Williams, P.C., Norris, K.H., Eds.; AACC Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001; pp. 145–169. ISBN 978-1891127243. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Why you don’t need to use RPD. Pedometron 2013, 33, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, W.; Nakai, S. Artificial neural network-based predictive model for bacterial growth in a simulated medium of modified-atmosphere-packed cooked meat products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, E.; Blanco, M.; Maspoch, S.; Ortiz, M.C.; Sánchez, M.S.; Sarabia, L.A. Handling intrinsic non-linearity in near-infrared reflectancespectroscopy. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1999, 49, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stordrange, L.; Kvalheim, O.M.; Hazle, P.A.; Malthe-Srenssen, D.; Libnau, F.O. A comparison of techniques for modelling data with non-linear structure. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2003, 11, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ahumada, E.; Fearn, T.; Gomez, A.; Vallesquino, P.; Guerrero, J.E.; Pérez-Márín, D.; Garrido-Varo, A. Reducing NIR prediction errors with nonlinear methods and large populations of intact compound feedstuffs. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 085601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Marín, D.; Garrido-Varo, A.; Guerrero, J.E.; Gutiérrez-Estrada, J.C. Use of artificial neural networks in near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy calibrations for predicting the inclusion percentages of wheat and sunflower meal in compound feedingstuffs. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Calibration Set 1 | Validation Set 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range (Min–Max) | CV, % | Mean ± SD | Range (Min–Max) | CV, % | SEL | |
| Dietary N | 23.73 ± 1.42 | 21.07–29.49 | 6.0 | 23.6 ± 1.07 | 21.02–25.86 | 4.6 | 0.12 |
| Fecal N | 20.22 ± 2.05 | 21.07–41.18 | 10.1 | 20.00 ± 2.18 | 14.06–24.69 | 10.9 | 0.16 |
| Nd | 0.70 ± 0.040 | 0.56–0.81 | 5.8 | 0.70 ± 0.040 | 0.61–0.82 | 5.7 | - |
| Physical Form of Samples | Calibration and Cross-Validation 1 | Validation 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEC | R2cal | SECV | Mean ± SD | SEP | R2val | Bias | Slope | RPD | |
| Intact feed pellets | |||||||||
| Dietary N | 0.18 | 0.93 | 0.27 | 23.58 ± 0.93 | 0.23 | 0.88 | 0.010 | 1.07 | 2.5 |
| Ground feed pellets | |||||||||
| Dietary N | 0.13 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 23.39 ± 1.06 | 0.15 | 0.96 | 0.017 | 1.06 | 4.5 |
| Wet unground feces | |||||||||
| Fecal N | 0.41 | 0.89 | 0.47 | 19.47 ± 2.048 | 0.44 | 0.88 3 | −0.153 | 0.88 | 3.2 |
| Nd | 0.020 | 0.59 | 0.030 | 0.709 ± 0.029 | 0.018 | 0.70 | 0.002 | 0.94 | 2.3 |
| Dried unground feces | |||||||||
| Fecal N | 0.46 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 20.13 ± 2.141 | 0.53 | 0.88 3 | 0.026 | 1.06 | 2.4 |
| Nd | 0.020 | 0.72 | 0.020 | 0.705 ± 0.034 | 0.017 | 0.81 | 0 | 1.004 | 2.4 |
| Dried ground | |||||||||
| Fecal N | 0.28 | 0.95 | 0.30 | 19.22 ± 1.888 | 0.35 | 0.92 | −0.02 | 1.02 | 3.9 |
| Nd | 0.014 | 0.86 | 0.017 | 0.710 ± 0.034 | 0.017 | 0.85 | 0.071 | 0.962 | 2.7 |
| Physical Form of Samples | Calibration and Cross-Validation 1 | Validation 2 | Activation Function 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SECV | R2CV | SEP | R2val | ||
| Wet unground feces | |||||
| Fecal N | 0.237 | 0.988 | 0.246 | 0.984 | Tanh |
| Nd | 0.010 | 0.923 | 0.012 | 0.914 | Tanh |
| Dried unground feces | |||||
| Fecal N | 0.170 | 0.995 | 0.177 | 0.994 | ReLU |
| Nd | 0.009 | 0.941 | 0.011 | 0.932 | Tanh |
| Dried ground feces | |||||
| Fecal N | 0.176 | 0.961 | 0.190 | 0.968 | ReLU |
| Nd | 0.009 | 0.948 | 0.010 | 0.943 | Sigmoid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortatos, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Papadomichelakis, G. Real-Time Monitoring of Fecal Nitrogen Excretion to the Environment Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study in Rabbits. Environments 2023, 10, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120210
Fortatos E, Hadjigeorgiou I, Mountzouris KC, Papadomichelakis G. Real-Time Monitoring of Fecal Nitrogen Excretion to the Environment Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study in Rabbits. Environments. 2023; 10(12):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120210
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortatos, Efstathios, Ioannis Hadjigeorgiou, Konstantinos C. Mountzouris, and George Papadomichelakis. 2023. "Real-Time Monitoring of Fecal Nitrogen Excretion to the Environment Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study in Rabbits" Environments 10, no. 12: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120210
APA StyleFortatos, E., Hadjigeorgiou, I., Mountzouris, K. C., & Papadomichelakis, G. (2023). Real-Time Monitoring of Fecal Nitrogen Excretion to the Environment Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study in Rabbits. Environments, 10(12), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120210