Effects of Substituting Activated Carbon with Titanium-Dioxide-Coated Cenospheres in Conventional Aquarium Filters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
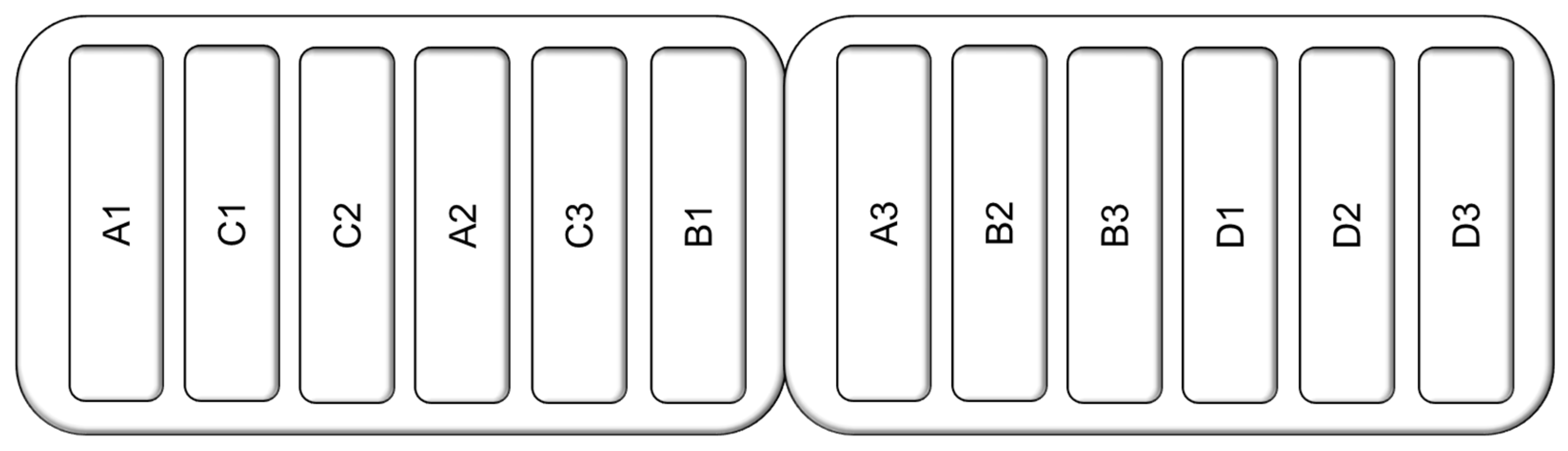
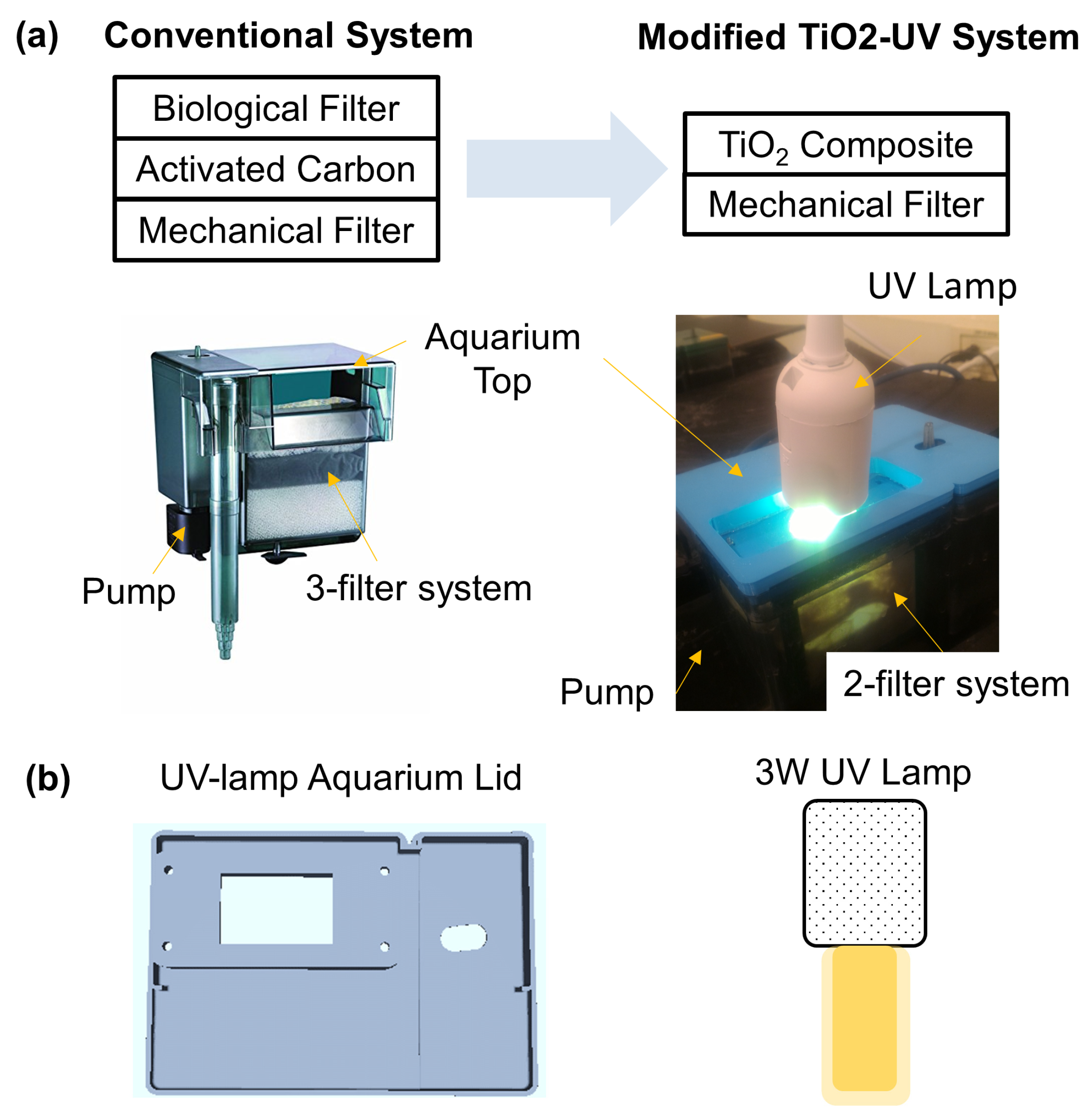
Experimental Design
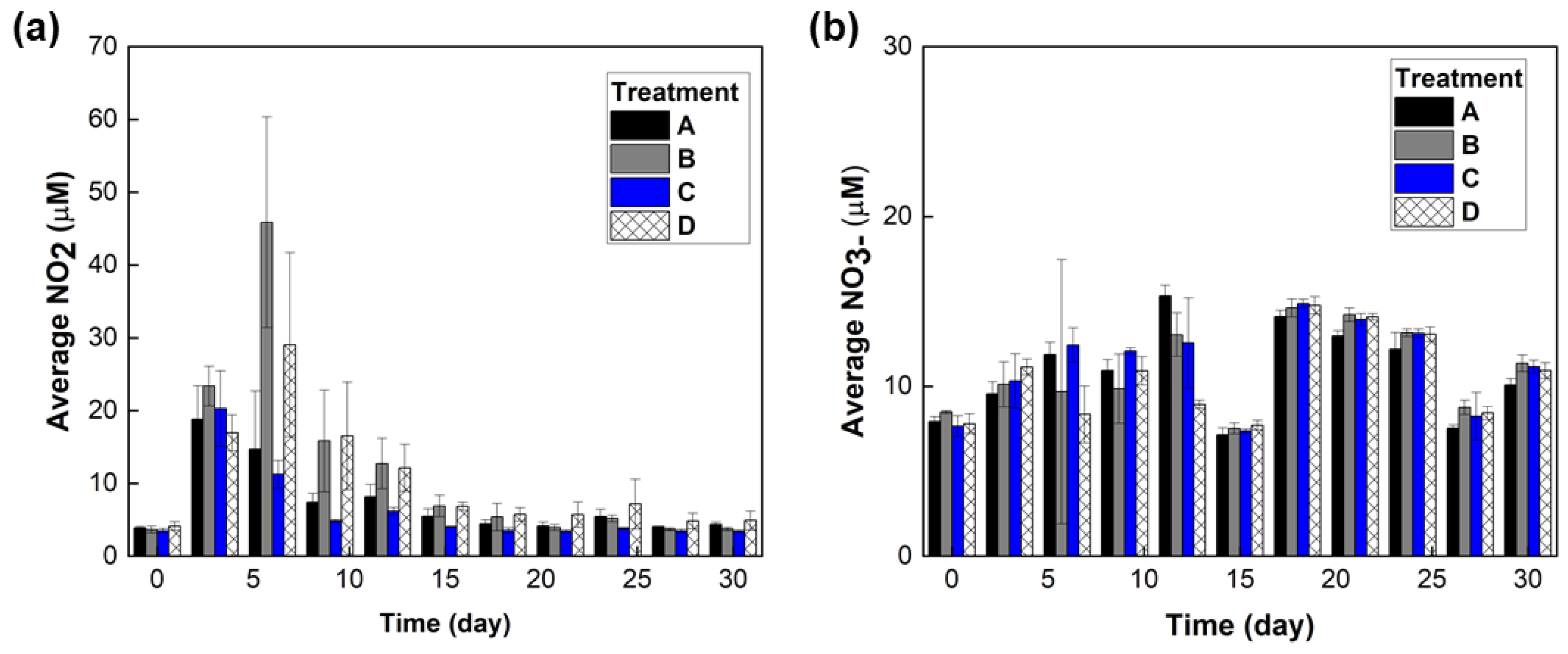
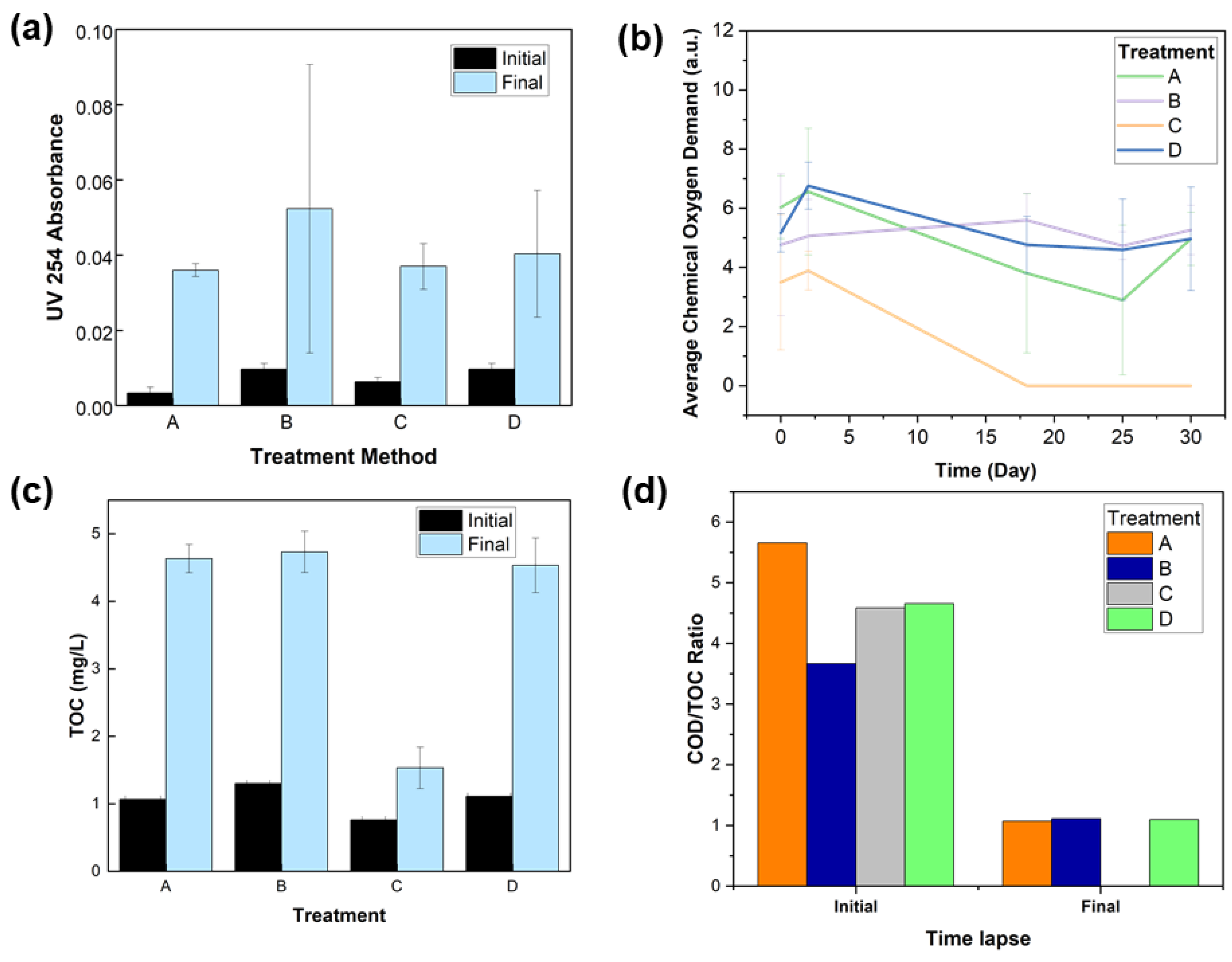
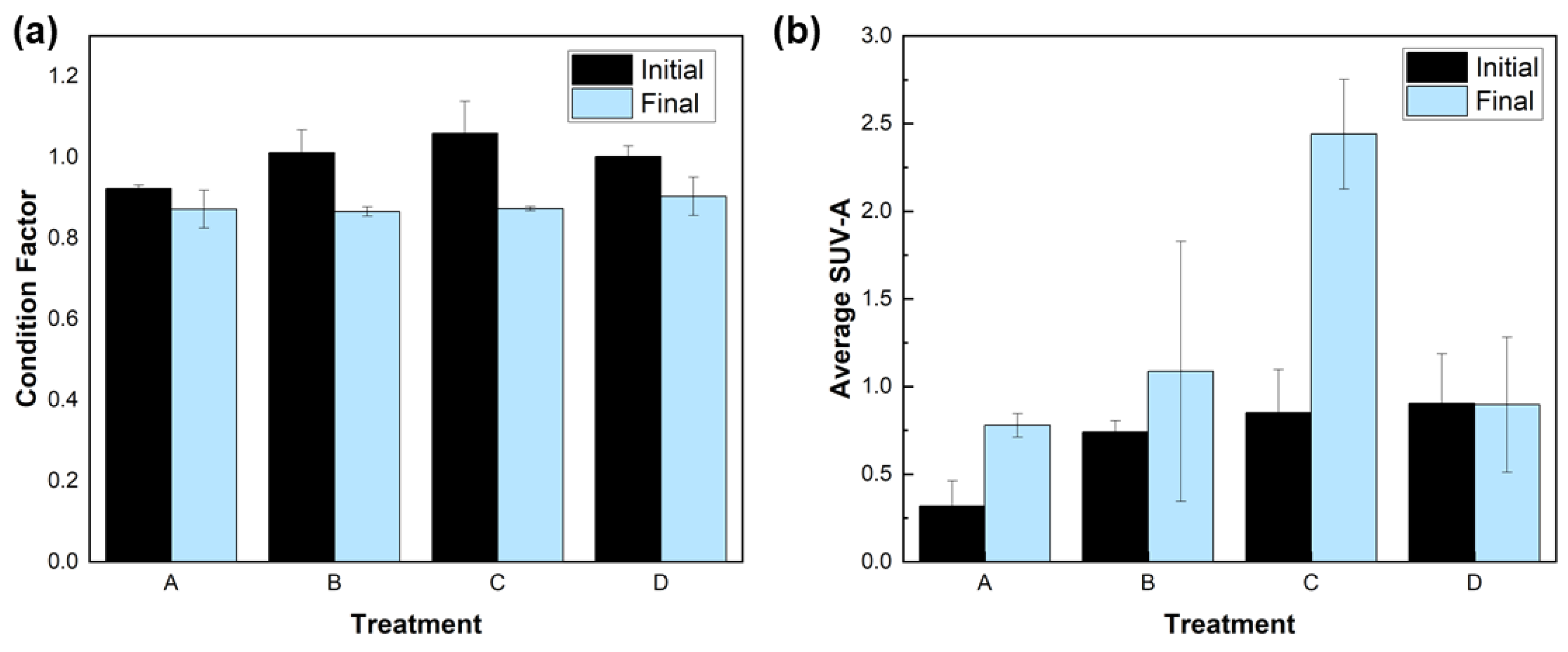
3. Results
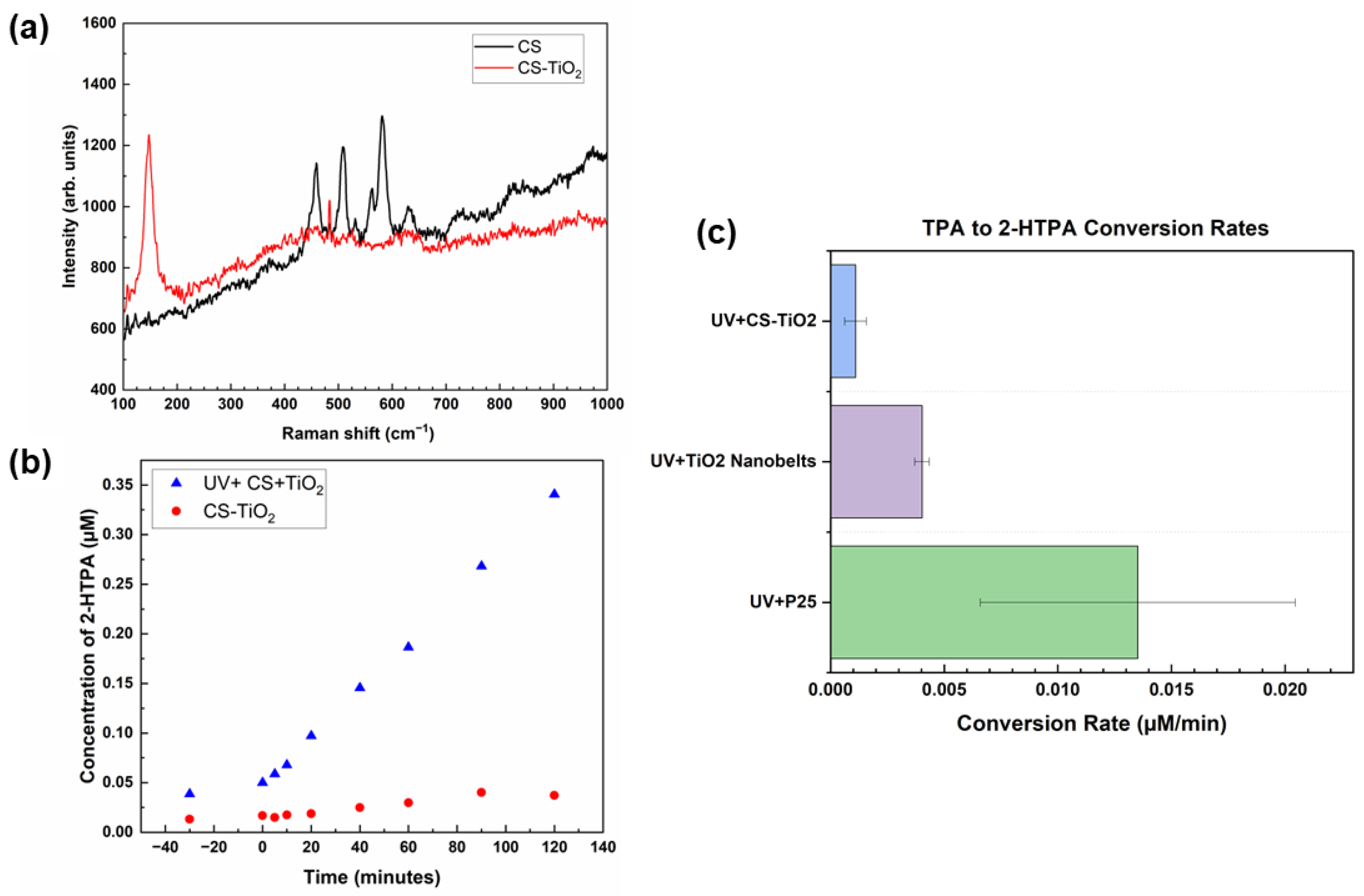
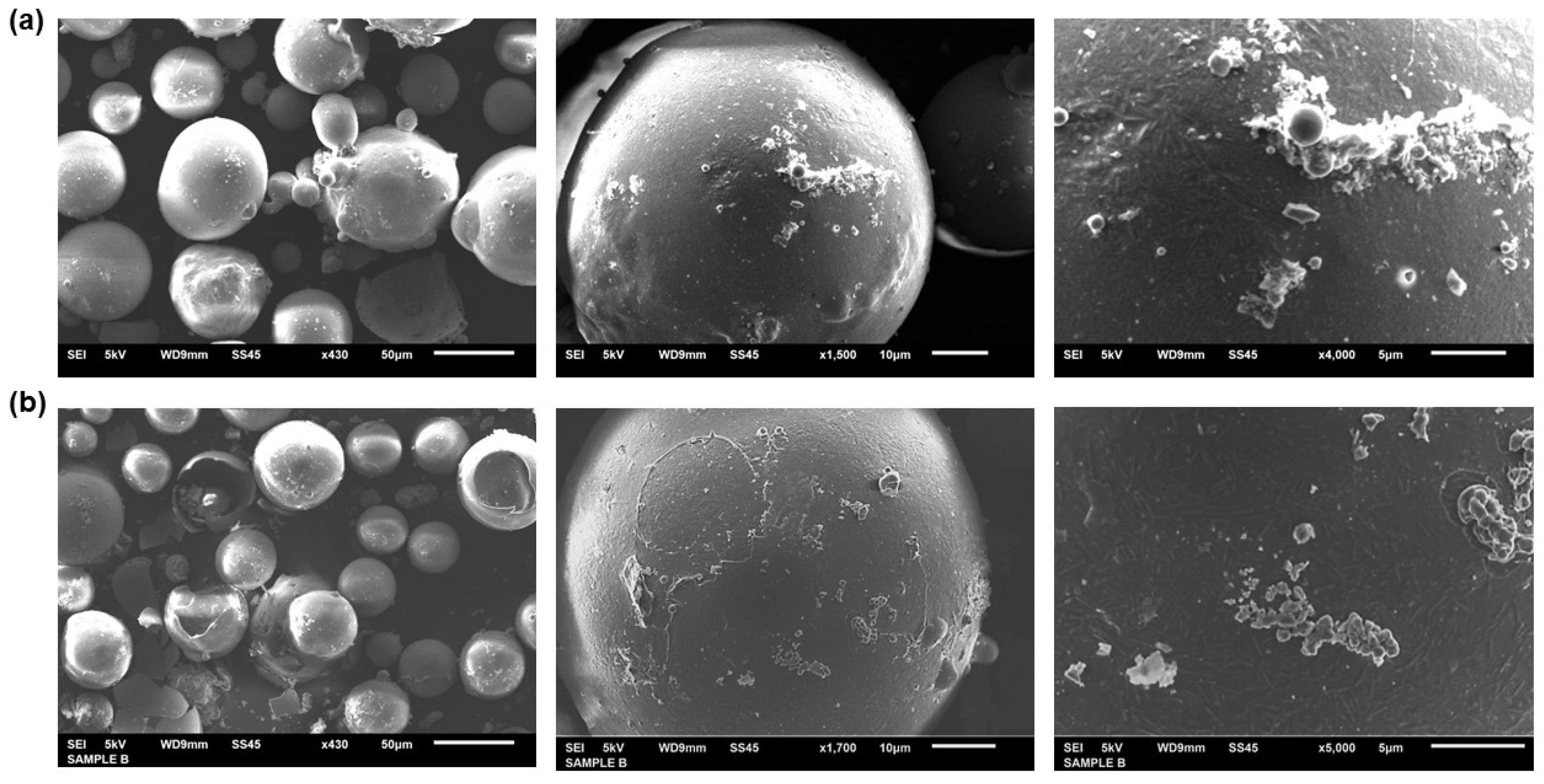
3.1. Materials Characterization
3.2. Minnow Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, P.J. The importance of Green Chemistry in Process Research and Development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Kuenzel, C. Cenospheres: A review. Fuel 2017, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żyrkowski, M.; Neto, R.C.; Santos, L.F.; Witkowski, K. Characterization of fly-ash cenospheres from coal-fired power plant unit. Fuel 2016, 174, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, P.J.; Porwal, M.; Vinoy, K.J.; Kishore; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Madras, G. Industrial waste fly ash cenosphere composites based broad band microwave absorber. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 134, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.; Shukla, A.; Bose, A. Processing and characterization of a lightweight concrete using cenospheres. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, P.; Garg, A.; Lin, P.; Hong, M.; Yi, Z.; Sreedeep, S. Exploring Potential of Fly Ash–Bentonite Mix as a Liner Material in Waste Containment Systems Under Concept of Sponge City. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.S.; Rowson, N.A. A review of the multi-component utilisation of coal fly ash. Fuel 2012, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losordo, T.; Masser, M.; Rakocy, J. Recirculating aquaculture tank production systems an overview of critical considerations. SRAC 1998, 451, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Annan, E.; Mustapha, K.; Odusanya, O.; Malatesta, K.; Soboyejo, W. Statistics of Flow and the Scaling of Ceramic Water Filters. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surolia, P.K.; Tayade, R.J.; Jasra, R.V. TiO2-Coated Cenospheres as Catalysts for Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue, p-Nitroaniline, n-Decane, and n-Tridecane under Solar Irradiation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8908–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Li Chun Fong, L.C.M.; Arlos, M.J.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Shahnam, E.; Peng, P.; Servos, M.R.; Zhou, Y.N. Photocatalytic degradation using one-dimensional TiO2 and Ag-TiO2 nanobelts under UV-LED controlled periodic illumination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4365–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlos, M.J.; Liang, R.; Hatat-Fraile, M.M.; Bragg, L.M.; Zhou, N.Y.; Servos, M.R.; Andrews, S.A. Photocatalytic decomposition of selected estrogens and their estrogenic activity by UV-LED irradiated TiO2 immobilized on porous titanium sheets via thermal-chemical oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowdon, M.; Liang, R.; Van Leeuwen, J.C.; Schneider, O.; Khan, A.; Li Chun Fong, L.C.M.; Zhou, N.Y.; Servos, M.R. Pharmaceutical Micropollutant Treatment with UV–LED/TiO2 Photocatalysis under Various Lighting and Matrix Conditions. Photochem 2022, 2, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorzano, L. Determination of Ammonia in Natural Waters by the Phenolhypochlorite Method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 799–801. [Google Scholar]
- SvobodovÁ, Z.; Máchová, J.; Poleszczuk, G.; Hůda, J. Nitrite Poisoning of Fish in Aquaculture Facilities with Water-recirculating Systems. Acta Vet. Brno 2005, 74, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sérodes, J.-B.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Li, H.; Bouchard, C. Occurrence of THMs and HAAs in experimental chlorinated waters of the Quebec City area (Canada). Chemosphere 2003, 51, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshin, G.V.; Wu, W.W.; Benjamin, M.M.; Hemingway, O. Correlations between differential absorbance and the formation of individual DBPs. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, A.K.; Gagnon, G.A. Application of photoelectrochemical chemical oxygen demand to drinking water. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2014, 106, E383–E390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.L.; Eller, J.M.; Gloyna, E.F. Analytical Parameters of Petrochemical and Refinery Wastewaters. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1971, 43, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefian, S. Identification of Types of Compounds Responsible for COD, TOC, and Colour in Bleached Kraft Pulp Mill Effluents; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, J. Impact of Increased Production on TOC to the Waste Water Treatment Plant: Piteå 750. Master’s Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, N.; Komatsu, K.; Kohzu, A.; Tomioka, N.; Shinohara, R.; Satou, T.; Watanabe, F.N.; Tada, Y.; Hamasaki, K.; Kushairi, M.R.M.; et al. Bacterial contribution to dissolved organic matter in eutrophic Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7160–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagi, T. Aerobic microbial transformation of pesticides in surface water. J. Pestic. Sci. 2013, 38, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; Blust, R. Metal concentrations in water, sediment and gudgeon (Gobio gobio) from a pollution gradient: Relationship with fish condition factor. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 126, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagenal, T. Methods for assessment of fish production in fresh waters. J. Anim. Ecol. 1979, 48, 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, T.; Connolly, P.L. The selection of suitable indices for the measurement and analysis of fish condition. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, C.; Leshuk, T.M.C.; Gu, F. Mild Photocatalysis Removes Microbial Inhibition and Enables Effective Biological Treatment of Naphthenic Acids. Chem. Eng. Ind. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snowdon, M.R.; Liang, R.F.L.; Kaur, A.; Burton, E.A.; Rathod, S.; Fang, W.; Dhiyebi, H.A.; Bragg, L.M.; Zhou, N.Y.; Servos, M.R.; et al. Effects of Substituting Activated Carbon with Titanium-Dioxide-Coated Cenospheres in Conventional Aquarium Filters. Environments 2023, 10, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10110188
Snowdon MR, Liang RFL, Kaur A, Burton EA, Rathod S, Fang W, Dhiyebi HA, Bragg LM, Zhou NY, Servos MR, et al. Effects of Substituting Activated Carbon with Titanium-Dioxide-Coated Cenospheres in Conventional Aquarium Filters. Environments. 2023; 10(11):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10110188
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnowdon, Monika R., Robert F. L. Liang, Avneet Kaur, Erika A. Burton, Shasvat Rathod, Wenkai Fang, Hadi A. Dhiyebi, Leslie M. Bragg, Norman Y. Zhou, Mark R. Servos, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Substituting Activated Carbon with Titanium-Dioxide-Coated Cenospheres in Conventional Aquarium Filters" Environments 10, no. 11: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10110188
APA StyleSnowdon, M. R., Liang, R. F. L., Kaur, A., Burton, E. A., Rathod, S., Fang, W., Dhiyebi, H. A., Bragg, L. M., Zhou, N. Y., Servos, M. R., & Freire-Gormaly, M. (2023). Effects of Substituting Activated Carbon with Titanium-Dioxide-Coated Cenospheres in Conventional Aquarium Filters. Environments, 10(11), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10110188







