Using Free Internet Videogames in Upper Extremity Motor Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
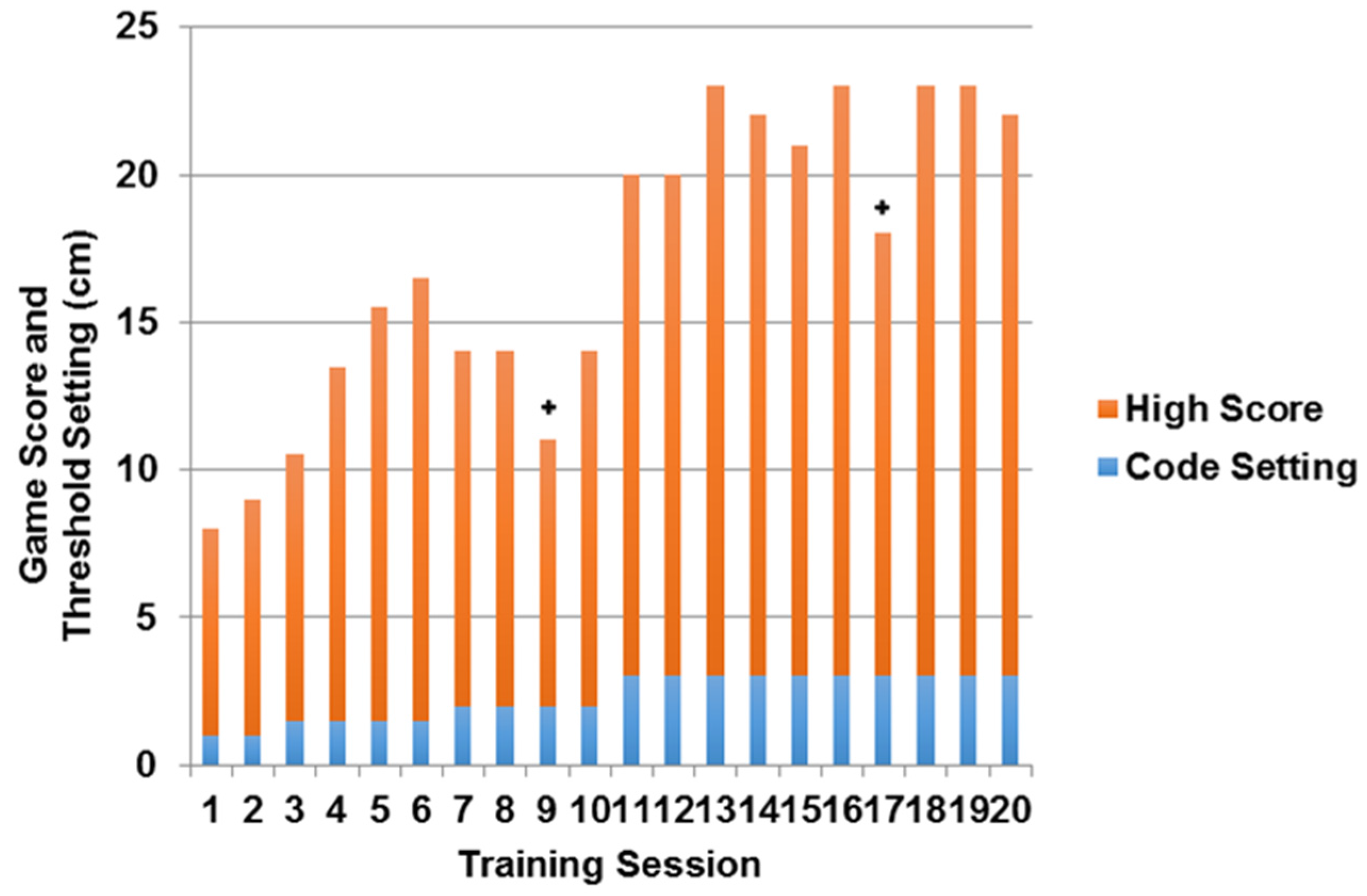
2.1. Feasibility of Intervention Delivery
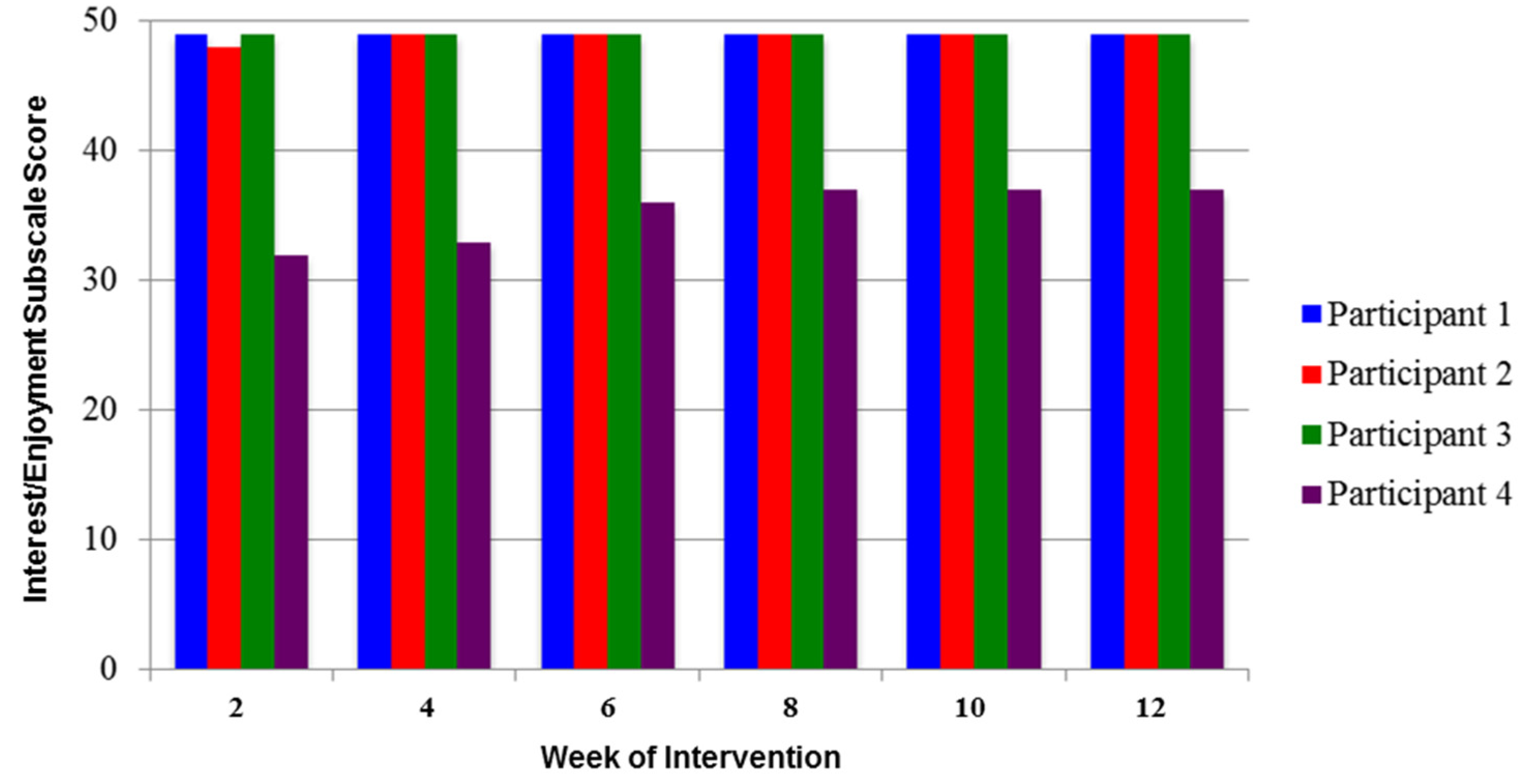
2.2. Level of Intrinsic Motivation during Training
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
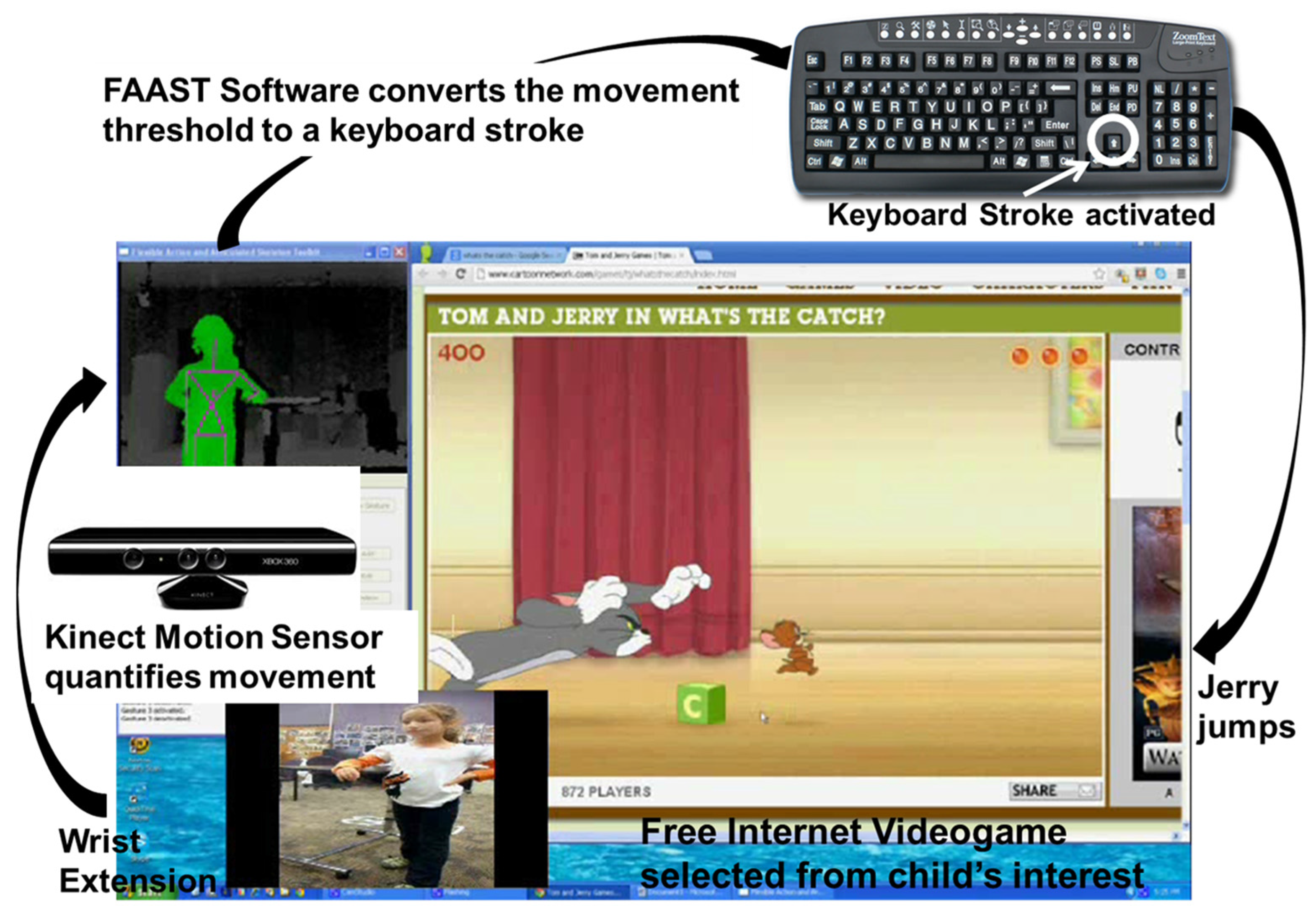
4.2. Intervention
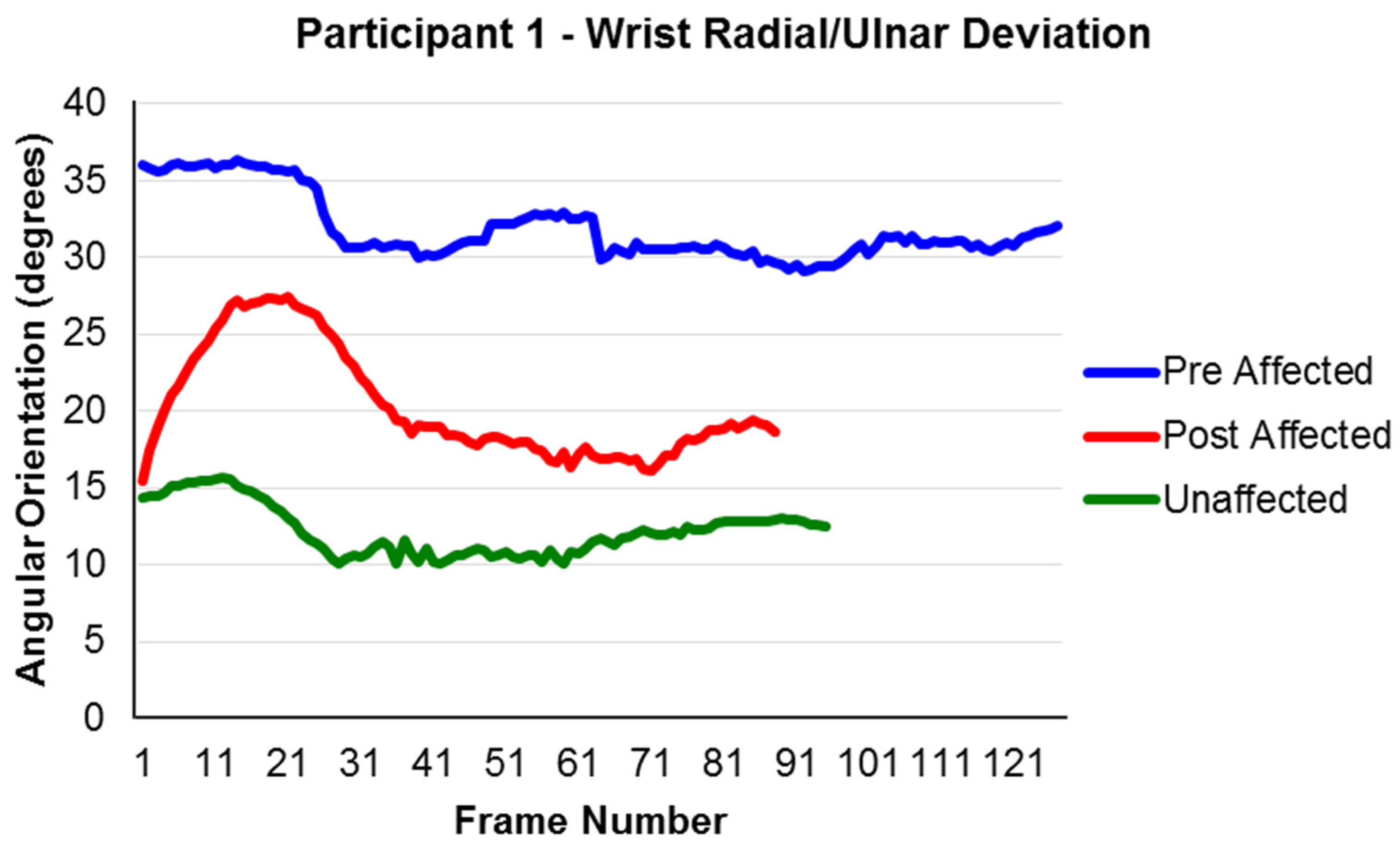
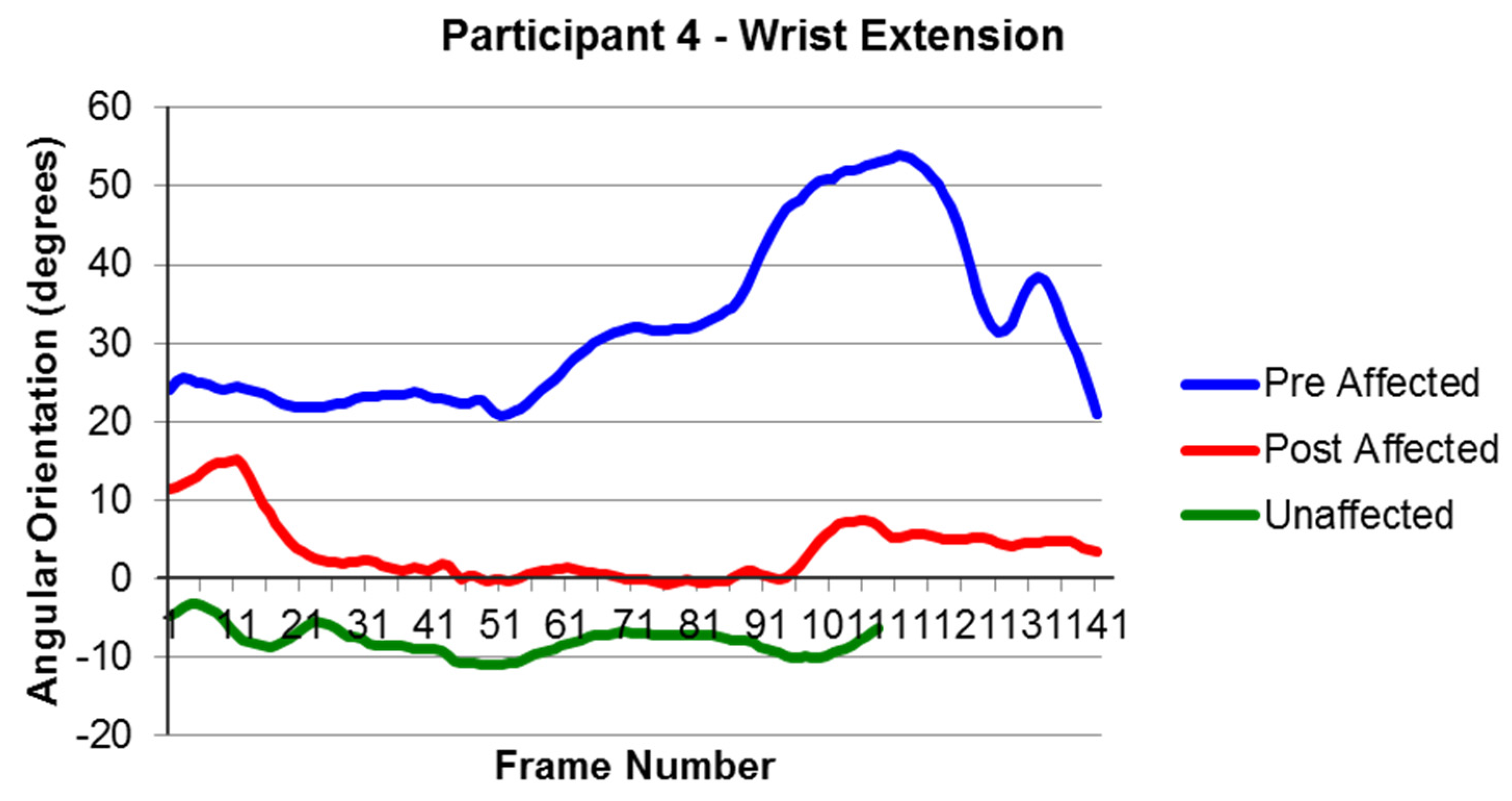
4.3. Feasibility of Intervention Delivery
4.4. Level of Intrinsic Motivation during Training
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AROM | active range of motion |
| BOT-2 | Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency |
| CP | cerebral palsy |
| FAAST | Flexible Action and Articulated Skeleton Toolkit software |
| IMI | Intrinsic Motivation Inventory |
| ROM | range of motion |
| UE | upper extremity |
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What you need to know about cerebral palsy. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/Features/CerebralPalsy/ (accessed on 3 March 2013).
- Chen, Y.P.; Kang, L.J.; Chuang, T.Y.; Doong, J.L.; Lee, S.J.; Tsai, M.W.; Jeng, S.F.; Sung, W.H. Use of virtual reality to improve upper-extremity control in children with cerebral palsy: A single-subject design. Phys. Ther. 2007, 87, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.; Rosie, J.A. Virtual reality games for movement rehabilitation in neurological conditions: How do we meet the need and expectations of the users? Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.; Ziviani, J.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N. Randomized controlled trial of web-based multimodal therapy for unilateral cerebral palsy to improve occupational performance. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochard, S.; Robertson, J.; Médée, B.; Rémy-Néris, O. What’s new in new technologies for upper extremity rehabilitation? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvin, J.; McDonald, R.; Catroppa, C.; Anderson, V. Does intervention using virtual reality improve upper limb function in children with neurological impairment: A systematic review of the evidence. Brain Inj. 2011, 25, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.; Wilson, P.H. Use of virtual reality in rehabilitation of movement in children with hemiplegia—A multiple case study evaluation. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryanton, C.; Bosse, J.; Brien, M.; McLean, J.; McCormick, A.; Sveistrup, H. Feasibility, motivation, and selective motor control: Virtual reality compared to conventional home exercise in children with cerebral palsy. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, D.; Boian, R.; Merians, A.S.; Tremaine, M.; Burdea, G.C.; Adamovich, S.V.; Recce, M.; Poizner, H. Virtual reality-enhanced stroke rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2001, 9, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, D.T. Benefits of a virtual play rehabilitation environment for children with cerebral palsy on perceptions of self-efficacy: A pilot study. Pediatr. Rehabil. 2002, 5, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proffitt, R.M.; Alanjus, G.; Kelleher, C.L.; Engsberg, J.R. Use of computer games as an intervention for stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2011, 18, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borern, J.; Bjorkhahl, A.; Claesson, L.; Goude, D.; Lundgren-Nilsson, A.; Samuelsson, H.; Blomstrand, C.; Sunnerhagen, K.S.; Rydmark, M. Virtual rehabilitation after stroke. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2008, 136, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cioi, D.; Kale, A.; Burdea, G.; Engsberg, J.; Janes, W.; Ross, S. Ankle Control and Strength Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy Using Rutgers Ankle CP. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011.
- Fluet, G.G.; Qui, Q.; Kelly, D.; Parikh, H.D.; Ramirez, D.; Saleh, S.; Adamovich, S.V. Interfacing a haptic robotic system with complex virtual environments to treat impaired upper extremity motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2010, 13, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, M.R.; McDonald, B.C.; Warden, S.J.; Yonkman, J.; Saykin, A.J.; Shirley, B.; Huber, M.; Rabin, B.; Abdelbaky, M.; Nwosu, M.E.; et al. In-home virtual reality videogame telerehabilitation in adolescents with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.; Rabin, B.; Docan, C.; Burdea, G.C.; AbdelBaky, M.; Golomb, M.R. Feasibility of modified remotely monitored in-home gaming technology for improving hand function in adolescents with cerebral palsy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weightman, A.; Preston, N.; Levesley, M.; Holt, R.; Mon-Williams, M.; Clarke, M.; Cozens, A.J.; Bhakta, B. Home-based computer-assisted upper extremity limb exercise for young children with cerebral palsy: A feasibility study investigating impact on motor control and functional outcome. J. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 43, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winkels, D.G.; Kottink, A.; Temmink, R.A.; Nijlant, J.M.; Buurke, J.H. Wii™-habilitation of upper extremity function in children with cerebral palsy: An explorative study. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2013, 16, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbach, S.A.; Foreman, M.H.; Engsberg, J.R. Computer games as therapy for persons with stroke. Games Health 2013, 2, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New xbox 360, kinect sensor and ‘‘kinect adventures’’—Get all your controller-free entertainment in one complete package. Available online: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/news/press/2010/jul10/07–20kinectpackagepr.aspx (accessed on 3 March 2013).
- Suma, E.A.; Krum, D.M.; Lange, B.; Sebastian, K.; Rizzo, A.; Bolas, M. Adapting user interfaces for gestural interaction with the flexible action and articulated skeleton toolkit. Comput. Gr. 2013, 37, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtleff, T.L.; Standeven, J.W.; Engsberg, J.R. Changes in dynamic trunk/head stability and functional reach after hippotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.M.; Lang, C.E.; Sahrmann, S.A.; Edwards, D.F.; Dromerick, A.W. Sensorimotor impairments and reaching performance in subjects with post stroke hemiparesis during the first few months of recovery. Phys. Ther. 2007, 87, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhart, A.; Kahne, J.; Middaugh, E.; Macgill, A.; Evans, C.; Vitak, J. Teens, video games and civics. Pew Internet and American Life Project, 16 September 2008; 2. [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp, J. 91 Percent of Kids Play Video Games, Says Study. Available online: http://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/91-percent-of-kids-play-video-games-says-study/ (accessed on 3 March 2013).
- Nudo, R.J.; Wise, B.M.; SiFuentes, F.; Milliken, G.W. Neural substrates for the effects of rehabilitative training on motor recovery after ischemic infarct. Science 1996, 27, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrinsic motivation inventory (imi). Available online: http://www.psych.rochester.edu/SDT/measures/IMI_description.php (accessed on 3 March 2013).
- Burdea, G.C.; Cioi, D.; Kale, A.; Janes, W.E.; Ross, S.A.; Engsberg, J.R. Robotics and gaming to improve ankle strength, motor control and function in children with cerebral palsy—Case study series. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross Motor Function Classification System-Expanded & Revised (GMFCS-E&R); McMaster University: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2016.
- Eliasson, A.C.; Krumlinde-Sundhold, L.; Rösblad, B.; Beckung, E.; Arner, M.; Orvall, A.M.; Rosenbaum, P. The manual ability classification system (macs) for children with cerebral palsy: Scale development and evidence of validity and reliability. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Performance Laboratory. CP Game Process. Available online: http://youtu.be/eM2cAMgMbzU (accessed on 14 February 2013).
- Gajdosik, R.L.; Bohannon, R.W. Clinical measurement of range of motion: Review of goniometry emphasizing reliability and validity. J. Am. Phys. Ther. Assoc. 1987, 67, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar]
- Deitz, J.C.; Kartin, D.; Kopp, K. Review of the bruininks-oseretsky test of motor proficiency, second edition (bot-2). Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2007, 27, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, E.; Duncan, T.; Tammen, V.V. Psychometric properties of the intrinsic motivation inventory in a competitive sport setting: A confirmatory factor analysis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1989, 60, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Game Name | Game Genre | Sub-genre | Goal of Game | Movement | Particpant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refriger-Raiders (Jerry) | Cartoon | Object Collection | Move to cheese and pick it up, drop it to nibbles. Avoid getting hit by pool balls. | Wrist Extension | 1, 2 |
| Refriger-Raiders (Tom) | Cartoon | Throwing | Throw balloons to hit the target as Jerry passes through it | Wrist Extension | 2 |
| What's the Catch (Jerry) | Cartoon | Chase | Help Jerry reach his mouse hole before Tom catches him while avoiding objects | Shoulder Flexion; Wrist Extension; Shoulder Abduction | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Robot Unicorn Attack | Cartoon | Jumping | Jump to catch the ferries and stay on the platform. Avoid stars. | Shoulder Abduction; Elbow Extension | 4 |
| Fruit Ninja | Cartoon | Slicing Fruit | Using of sword to slice through fruit that fly up into screen | Elbow Flexion, Shoulder Flexion | 1, 2 |
| Tower-Inator | Cartoon | Sling Shot | Sling shot of bowling balls at structures to knock them over | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 1 |
| Angry Birds | Cartoon | Sling Shot | Sling Shot of pigs at structures to knock them over | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 1 |
| GrumbleGum | Cartoon | Object Collection | Take character along path in order to collect items | Shoulder Flexion | 3 |
| Star Wars: Jedi vs. Jedi | Cartoon | Fighting | Jedi fight against computer Jedi | Shoulder Fexion; Shoulder External Rotation | 3 |
| Shotgun vs. Zombie | Cartoon | Fighting | Character fighting and shooting zombies | Shoulder Flexion; Shoulder Abduction | 4 |
| Lateral Collateral 2 | Sports | Football | Get the ball to the endzone without being tackled. Pass the ball back and forth to teamates and move up and down the field. | Bilateral Elbow Flexion; Shoulder Abduction | 2, 3, 4 |
| Highway Madness | Sports | Car Racing | Drive down the road avoiding traffic and collecting bonuses to complete the mission. | Shoulder Flexion, Shoulder External Rotation | 3 |
| Penalty Shootout | Sports | Soccer | Aim and shoot the ball into the net. Avoid the goalie. | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 3 |
| Hoops Mania | Sports | Basketball | Make as many baskets in a row as possible. | Elbow Flexion; Shoulder Abduction; Shoulder External Rotation; Shoulder Internal Rotation | 1, 3, 4 |
| Air Hockey | Sport | Hockey | Move hand around to defend goal and shoot puck | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 1, 3 |
| Marathon Runner | Sport | Running | Jump over obstacles while running | Elbow Flexion | 1 |
| Upstream Kayaking | Sport | Kyaking | Direct kayaker around obstacle | Elbow Flexion | 1 |
| G-Switch | Sport | Running | Move character while running to avoid obstacles | Elbow Flexion | 1 |
| Basket Shot | Sport | Basketball | Make as many baskets in a row as possible. | Elbow Flexion, Wrist extension | 1, 2, 4 |
| Harry Potter Quiddithch | Sport | Quidditch | Blocking computer player from scoring in goals | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 1, 3 |
| Cyclomaniacs | Sport | Bicycling | Guiding bike along path | Shoulder Abduction; Shoulder Flexion | 3 |
| Spiderman Racing | Sport | Bicycling | Guiding bike along path | Shoulder Abdcution; Shoulder External Rotation | 4 |
| Ulitmate Baseball | Sport | Baseball | Batting within baseball game | Wrist Extension | 4 |
| 1 on 1 Soccer | Sport | Soccer | Playing Soccer against computer person | Shoulder Abduction; Wrist Extension | 4 |
| Guitar Geek | Music | Guitar | Hit the notes at the right time to play the guitar | shoulder external rotation; shoulder flexion | 1 |
| Music Catch 2 | Music | Object Collection | Move select hand around the screen in order to catch the falling music notes | Combination Reaching Movement (Shoulder circumduction) | 1 |
| Participant (#) | Shoulder Flexion | Shoulder Extension | Shoulder Abduction | Shoulder Internal Rotation | Shoulder External Rotation | Elbow Flexion | Elbow Extension | Wrist Flexion | Wrist Extension | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| 1 | 155 | 150 | 50 | 50 | 155 | 146 | 75 | 80 | 45 | 50 | 140 | 145 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 67 | 0 | 7 |
| 2 | 160 | 150 | 60 | 52 | 150 | 158 | 75 | 68 | 55 | 50 | 140 | 140 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 25 | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 127 | 140 | 50 | 33 | 134 | 145 | 54 | 72 | 57 | 70 | 145 | 136 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 69 | 0 | 9 |
| 4 | 147 | 160 | 55 | 47 | 140 | 144 | 40 | 53 | 67 | 88 | 160 | 152 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 35 |
| Participant (#) | Manual Dexterity | Upper-Limb Coordination | Manual Coordination | % Rank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 28 | 29 | 1% | 2% |
| 4 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 15 | 34 | 40 | 6% | 16% |
| Participant (#) | Age (y) | Gender | Affected Side | * GMFCS Level | ** MACS Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | Female | Right | I | II |
| 2 | 8 | Female | Right | I | II |
| 3 | 10 | Male | Right | I | II |
| 4 | 9 | Male | Left | I | II |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sevick, M.; Eklund, E.; Mensch, A.; Foreman, M.; Standeven, J.; Engsberg, J. Using Free Internet Videogames in Upper Extremity Motor Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Behav. Sci. 2016, 6, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs6020010
Sevick M, Eklund E, Mensch A, Foreman M, Standeven J, Engsberg J. Using Free Internet Videogames in Upper Extremity Motor Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Behavioral Sciences. 2016; 6(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs6020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSevick, Marisa, Elizabeth Eklund, Allison Mensch, Matthew Foreman, John Standeven, and Jack Engsberg. 2016. "Using Free Internet Videogames in Upper Extremity Motor Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy" Behavioral Sciences 6, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs6020010
APA StyleSevick, M., Eklund, E., Mensch, A., Foreman, M., Standeven, J., & Engsberg, J. (2016). Using Free Internet Videogames in Upper Extremity Motor Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Behavioral Sciences, 6(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs6020010






