Burnout Risk Profiles in Psychology Students: An Exploratory Study with Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. Sociodemographic and Clinical Questionnaire
2.2.2. Maslach Burnout Inventory—Student Survey (MBI-SS; Schaufeli et al., 2002; Portuguese Version by Marôco & Tecedeiro, 2009)
2.2.3. Psychological General Well-Being Index (QGBEP; Grossi et al., 2006; Portuguese Version by Barroso et al., 2018)
2.2.4. Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale (DASS21; Lovibond & Lovibond, 1995; Portuguese Version by Pais-Ribeiro et al., 2004)
2.2.5. Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS; Gratz & Roemer, 2004; Portuguese Version by Coutinho et al., 2010)
2.2.6. International Physical Activity Questionnaire—Short Version (IPAQ; Craig et al., 2003; Portuguese Version by Campaniço, 2016)
2.2.7. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI; Buysee et al., 1989; Portuguese version by Del Rio João et al., 2017)
2.2.8. Food Frequency Questionnaire (QFA; Willett, 1998; Portuguese Version by C. M. d. M. Lopes, 2000; C. Lopes et al., 2007)
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Relationship Between Psychological and Lifestyle Variables with Academic Burnout
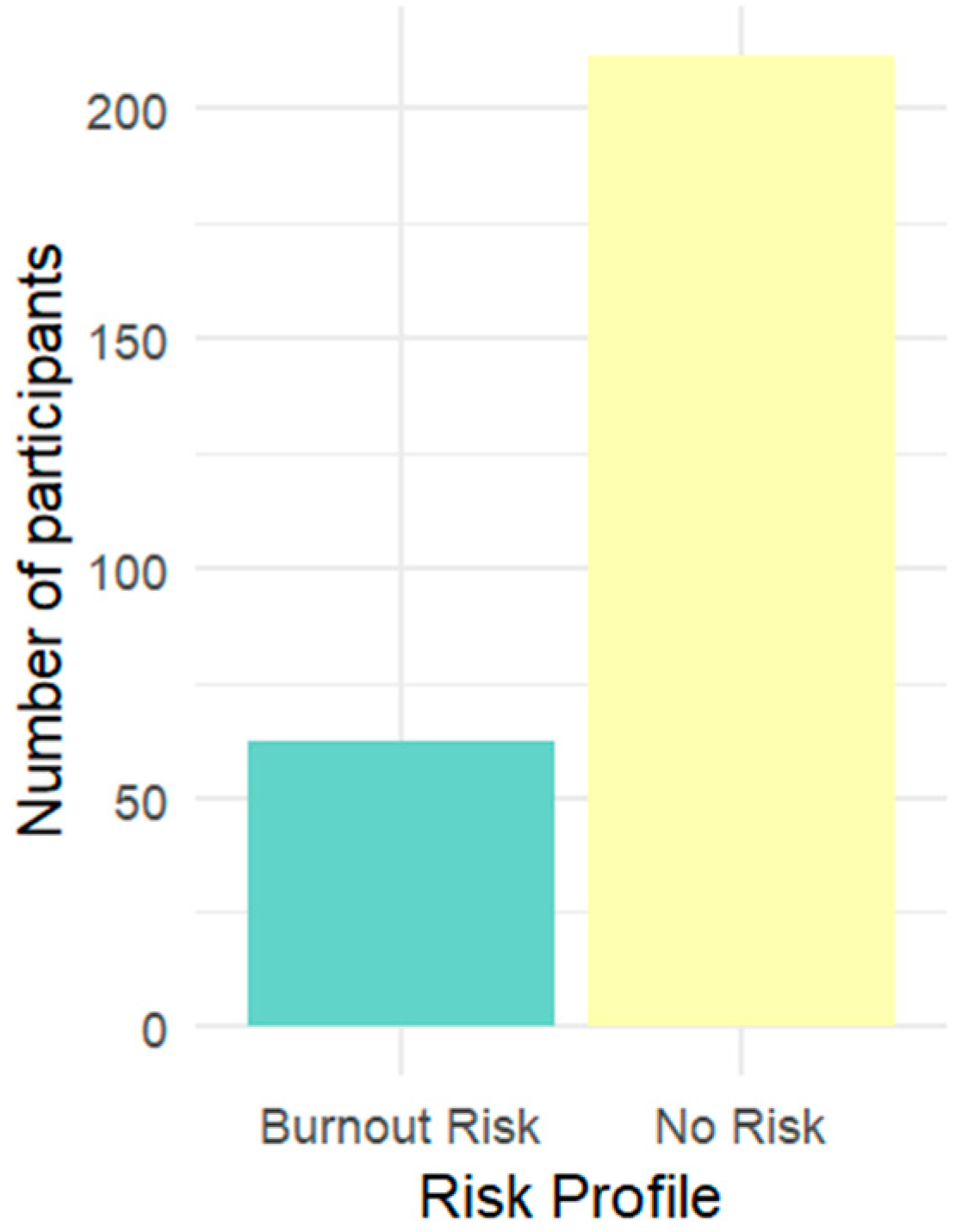
3.2. Cluster Analysis
3.3. Prediction of Burnout Risk Profiles
4. Discussion
Implications for Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DASS21 | Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale |
| DERS | Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale |
| DII | Dietary Inflammatory Index |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activity Questionnaire—Short Version |
| MBI-SS | Maslach Burnout Inventory—Student Survey |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| QFA | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| QGBEP | Psychological General Well-being Index |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEM | Structural Equation Modeling |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
References
- Abraham, A., Chaabna, K., Sheikh, J. I., Mamtani, R., Jithesh, A., Khawaja, S., & Cheema, S. (2024). Burnout increased among university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, H. K., Barrall, A. L., Vincent, K. B., & Arria, A. M. (2020). Stress and burnout among graduate students: Moderation by sleep duration and quality. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 28(1), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, K. V., Galdino, M. J. Q., & Martins, J. T. (2021). Burnout, daytime sleepiness and sleep quality among technical-level Nursing students. Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem, 29, e3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbabisarjou, A., Mehdi, H. S., Sharif, M. R., Alizadeh, K. H., Yarmohammadzadeh, P., & Feyzollahi, Z. (2015). The relationship between sleep quality and social intimacy, and academic burn-out in students of medical sciences. Global Journal of Health Science, 8(5), 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2017). Job demands–resources theory: Taking stock and looking forward. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 22(3), 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, I., Antunes, M., Barroso, I., Correia, T., Brito, I., & Monteiro, M. (2018). Adaptation and validation of the psychological general well-being index: Confirmatory factor analysis of the short version. Revista de Enfermagem Referência, 4(18), 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, R. S., & Malecki, K. M. (2017). The association of dietary inflammatory potential with depression and mental well-being among U.S. adults. Preventive Medicine, 99, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicalho, C. C. F., Carvalho, M. V., Andrade, N. C. L., & Guimarães, J. B. (2019). Lifestyle influences burnout indexes in teachers. Brazilian Journal of Development, 5(10), 19160–19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysee, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). Pittsburgh sleep quality index. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings, 28(2), 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaniço, H. (2016). Validade simultânea do questionário internacional de actividade física através da medição objectiva da actividade física por actigrafia proporcional [Master’s thesis, University of Lisbon]. Publication No. 28802867, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z., Xu, C., Zhang, P., & Wang, Y. (2022). Associations of sedentary time and physical activity with adverse health conditions: Outcome-wide analyses using isotemporal substitution model. EClinicalMedicine, 48, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalikkandy, S., Alhifzi, R. S. A., Asiri, M. A. Y., Alshahrani, R. S. A., Saeed, W. N. A., & Alamri, S. G. (2022). Burnout and its relation to emotion dysregulation and social cognition among female interns and undergraduate dental students at King Khalid University. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Q., Peng, C.-L., Lian, Y., Wang, B.-W., Chen, P.-Y., & Wang, G.-P. (2021). Association between dietary inflammatory index and mental health: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8, 662357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H. L., Wang, H. Y., Lai, S. F., & Ye, Z. J. (2022). The associations between psychological distress and academic burnout: A mediation and moderation analysis. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 15, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A. N., Seibert, G. S., May, R. W., Fitzgerald, M. C., & Fincham, F. D. (2017). School burnout and intimate partner violence: The role of self-control. Personality and Individual Differences, 112, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, J., Ribeiro, E., Ferreirinha, R., & Dias, P. (2010). Versão portuguesa da escala de dificuldades de regulação emocional e sua relação com sintomas psicopatológicos. Archives of Clinical Psychiatry, 37(4), 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C. L., Marshall, A. L., Sjöström, M., Bauman, A. E., Booth, M. L., Ainsworth, B. E., Pratt, M., Ekelund, U., Yngve, A., Sallis, J. F., & Oja, P. (2003). International physical activity questionnaire: 12-Country reliability and validity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 35(8), 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C. C. G., Bolognani, C. V., Amorim, F. F., & Imoto, A. M. (2023). Effectiveness of training programs based on mindfulness in reducing psychological distress and promoting well-being in medical students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Systematic Reviews, 12(1), 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio João, K. A., Becker, N. B., de Neves Jesus, S., & Isabel Santos Martins, R. (2017). Validation of the Portuguese version of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI-PT). Psychiatry Research, 247, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Nachreiner, F., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2001). The job demands-resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(3), 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L., Gualtieri, P., & De Lorenzo, A. (2021). Diet, nutrition and chronic degenerative diseases. Nutrients, 13(4), 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrbye, L. N., Thomas, M. R., Massie, F. S., Power, D. V., Eacker, A., Harper, W., Durning, S., Moutier, C., Szydlo, D. W., Novotny, P. J., Sloan, J. A., & Shanafelt, T. D. (2008). Burnout and Suicidal Ideation among U.S. Medical Students. Annals of Internal Medicine, 149(5), 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, D. J., Hair, J. F., Jr., & Smith, K. J. (2023). Psychological distress, burnout, and business student turnover: The role of resilience as a coping mechanism. Research in Higher Education, 64(2), 228–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada Araoz, E. G. (2024). Burnout académico y hábitos alimentarios en estudiantes universitarios: Un estudio transversal. Gaceta Médica de Caracas, 132(3), 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, E. F., Kleiman, E. M., Bentley, K. H., & Bernstein, E. E. (2024). Helpful for all? Examining the effects of psychotherapy treatment history on outcomes of single session, transdiagnostic cognitive behavioral interventions for university students. Psychological Services, 21(2), 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberger, H. J. (1974). Staff burn-out. Journal of Social Issues, 30(1), 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, J., Andrade, M., Martins, M., Cunha, O., Soares, S., Santos, T., Macedo, M., Nora, R., Pereira, J., & Martinho, S. (2023). Programa para a promoção de saúde mental no ensino superior [Program for the promotion of mental health in higher education] (Report). Presidência do Conselho de Ministros. Available online: https://wwwcdn.dges.gov.pt/sites/default/files/ppsmes_acces_2023-vf.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- Graça, L., & Brandão, T. (2024). Religious/spiritual coping, emotion regulation, psychological well-being, and life satisfaction among university students. Journal of Psychology and Theology, 52(3), 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26(1), 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, E., Groth, N., Mosconi, P., Cerutti, R., Pace, F., Compare, A., & Apolone, G. (2006). Development and validation of the short version of the Psychological General Well-Being Index (PGWB-S). Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzek, D., Skolmowska, D., & Głąbska, D. (2021). Associations between food preferences, food approach, and food avoidance in a Polish adolescents’ COVID-19 experience (PLACE-19) study population. Nutrients, 13(7), 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, H., Hosseinkhani, Z., Taherkhani, O., & Momeni, M. (2024). Association between chronotype, social jetlag, sleep quality, and academic burnout among nursing students: A cross-sectional study. Chronobiology international, 41(9), 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M. J., Torres, S. J., McNaughton, S. A., & Milte, C. M. (2021). Dietary patterns and associations with biomarkers of inflammation in adults: A systematic review of observational studies. Nutrition Journal, 20(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, B., Wright, B., & Bennett, P. (2019). Increasing student engagement and reducing exhaustion through the provision of demanding but well-resourced training. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 43(3), 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuga, I. A., & David, O. A. (2024). Emotion regulation and academic burnout among youth: A quantitative meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 36(4), 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodics, B., & Szabó, É. (2022). Student burnout in higher education: A demand-resource model approach. Trends in Psychology, 31(4), 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaggwa, M. M., Kajjimu, J., Sserunkuma, J., Najjuka, S. M., Atim, L. M., Olum, R., Tagg, A., & Bongomin, F. (2021). Prevalence of burnout among university students in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 16(8), e0256402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L. (2024). Relationship between anxiety and academic burnout in college students: The mediating role of emotion regulation strategy. In Addressing global challenges-exploring socio-cultural dynamics and sustainable solutions in a changing world (pp. 315–320). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L. N., Yao, Y., Chen, S. Z., & Zhu, J. L. (2023). Prevalence and associated factors of burnout among nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Education Today, 121, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjarski, M., Murray, G., Lee, V. V., & Jackson, M. L. (2018). Reciprocal relationships between daily sleep and mood: A systematic review of naturalistic prospective studies. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 42, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laher, S., Bain, K., Bemath, N., de Andrade, V., & Hassem, T. (2021). Undergraduate psychology student experiences during COVID-19: Challenges encountered and lessons learnt. South African Journal of Psychology, 51(2), 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H., Jang, G., Park, G., Lee, H., & Lee, S. M. (2024). Impact of state and trait emotion regulation on daily emotional exhaustion among Korean school counsellors. Stress and Health, 40(5), e3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H., & Lee, S. M. (2025). The reciprocal relationship between emotion regulation and emotional exhaustion among Korean school counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 103(2), 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H., Lee, T., Weng, C., & Lee, S. M. (2025). Effects of surface acting on exhaustion of Korean school counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 103(1), 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., Xie, Y., Sun, Z., Liu, D., Yin, H., & Shi, L. (2023). Factors associated with academic burnout and its prevalence among university students: A cross-sectional study. BMC Medical Education, 23(1), 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A. R., & Nihei, O. K. (2020). Burnout among nursing students: Predictors and association with empathy and self-efficacy. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, 73(1), e20180280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C., Aro, A., Azevedo, A., Ramos, E., & Barros, H. (2007). Intake and adipose tissue composition of fatty acids and risk of myocardial infarction in a male Portuguese community sample. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 107(2), 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C. M. d. M. (2000). Alimentação e enfarte agudo do miocárdio: Estudo caso-controlo de base comunitária [Doctoral’s dissertation, University of Porto]. Repositório Aberto da Universidade do Porto. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10216/9938 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Lovibond, P., & Lovibond, S. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33(3), 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, D. J., & Curran, T. (2021). Does burnout affect academic achievement? A meta-analysis of over 100,000 students. Educational Psychology Review, 33(2), 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March-Amengual, J.-M., Cambra Badii, I., Casas-Baroy, J.-C., Altarriba, C., Comella Company, A., Pujol-Farriols, R., Baños, J.-E., Galbany-Estragués, P., & Comella Cayuela, A. (2022). Psychological distress, burnout, and academic performance in first year college students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(6), 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marôco, J., & Assunção, H. (2020). Envolvimento e burnout no ensino superior em Portugal [Engagement and burnout in higher education in Portugal]. In H. Pereira, S. Monteiro, G. Esgalhado, & I. Leal (Eds.), 13º Congresso nacional de psicologia da saúde—Actas (pp. 399–407). Edições ISPA. [Google Scholar]
- Marôco, J., Assunção, H., Harju-Luukkainen, H., Lin, S.-W., Sit, P.-S., Cheung, K., Maloa, B., Ilic, I. S., Smith, T. J., & Campos, J. A. D. B. (2020). Predictors of academic efficacy and dropout intention in university students: Can engagement suppress burnout? PLoS ONE, 15(10), e0239816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marôco, J., & Tecedeiro, M. M. V. (2009). Inventário de burnout de maslach para estudantes portugueses [Maslach burnout inventory for portuguese students]. Psicologia, Saúde & Doenças, 10, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M., Caetano, S., Xavier, S., Melo, A., Ferreira, A., Martins, J., Lavaredas, C., Silva, B., Morais, S., Moura, D., Madeira, N., Queirós, A., & Martins, M. J. (2024). Improving access to mental health care through a stepped care approach: Preliminary results from a university students’ sample. Portuguese Journal of Public Health, 42(3), 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rubio, D., Martínez-Brotons, C., Monreal-Bartolomé, A., Barceló-Soler, A., Campos, D., Pérez-Aranda, A., Colomer-Carbonell, A., Cervera-Torres, S., Solé, S., Moreno, Y., & Montero-Marín, J. (2021). Protective role of mindfulness, self-compassion and psychological flexibility on the burnout subtypes among psychology and nursing undergraduate students. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 77(8), 3398–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslach, C., & Jackson, S. E. (1981). The measurement of experienced burnout. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 2(2), 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (2001). Job burnout. Annual Review of Psychology, 52(1), 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N., Harvey, A. G., Lockley, S. W., & Dijk, D.-J. (2022). Circadian rhythms and disorders of the timing of sleep. The Lancet, 400(10357), 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolajczak, M., Gross, J. J., Stinglhamber, F., Lindahl Norberg, A., & Roskam, I. (2020). Is parental burnout distinct from job burnout and depressive symptoms? Clinical Psychological Science, 8(4), 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, H., Dehghan, H., Dehrouyeh, S., & Tajik, E. (2021). Academic burnout among undergraduate nursing students: Predicting the role of sleep quality and healthy lifestyle. Research and Development in Medical Education, 10(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nteveros, A., Kyprianou, M., Artemiadis, A., Charalampous, A., Christoforaki, K., Cheilidis, S., Germanos, O., Bargiotas, P., Chatzittofis, A., & Zis, P. (2020). Burnout among medical students in Cyprus: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 15(11), e0241335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özhan, M. B., & Boyaci, M. (2022). Adjustment to school as the predictor of school burnout in university students. Acta Educationis Generalis, 12(2), 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnin, D., de Queiroz, V., Carvalho, Y. T. M. S., Dutra, A. S. S., Amaral, M. B., & Queiroz, T. T. (2014). The relation between burnout and sleep disorders in medical students. Academic Psychiatry, 38, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais-Ribeiro, J. L., Honrado, A. A. J. D., & Leal, I. (2004). Contribuição para o estudo da adaptação portuguesa das escalas de ansiedade, depressão e stress (EADS) de 21 itens de Lovibond e Lovibond [Contribution to the study of the portuguese adaptation of the 21-item anxiety, Depression and Stress Scales (EADS) by Lovibond and Lovibond]. Psicologia, Saúde & Doenças, 5(2), 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Paloș, R., Maricuţoiu, L. P., & Costea, I. (2019). Relations between academic performance, student engagement, symptoms, anxiety and student burnout: A cross-lagged analysis of a two-wave study. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 60, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M. G., Fraga, J., Santos, M., Ferraz, A., & Vilaça, M. (2024). Parental burnout during COVID-19: The moderating role of anxiety and family functioning. Stress and Health, 40(5), e3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlis, M. L., Posner, D., Riemann, D., Bastien, C. H., Teel, J., & Thase, M. (2022). Insomnia. The Lancet, 400(10357), 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C. M., Shivappa, N., Hébert, J. R., & Perry, I. J. (2018). Dietary inflammatory index and mental health: A cross-sectional analysis of the relationship with depressive symptoms, anxiety and well-being in adults. Clinical Nutrition, 37(5), 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, R., & Caguana Telenchana, L. M. (2023). Regulación emocional y bienestar psicológico en estudiantes universitarios. LATAM Revista Latinoamericana de Ciencias Sociales y Humanidades, 4(1), 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portoghese, I., Leiter, M. P., Maslach, C., Galletta, M., Porru, F., D’Aloja, E., Finco, G., & Campagna, M. (2018). Measuring burnout among university students: Factorial validity, invariance, and latent profiles of the Italian version of the Maslach burnout inventory student survey (MBI-SS). Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proper, K. I., & Van Oostrom, S. H. (2019). The effectiveness of workplace health promotion interventions on physical and mental health outcomes—A systematic review of reviews. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health, 45(6), 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A. U., Bhuttah, T. M., & You, X. (2020). Linking burnout to psychological well-being: The mediating role of social support and learning motivation. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 13, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S., Addas, A., Rahman, M. A., Shahiman, M. A., & Li, Z. (2024). Sequential mediation analysis of physical activity, healthy diet, BMI, and academic burnout in the Pakistani educational landscape. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A. C., Saheb, R., Moyo, T., Smith, C., & Sperandei, S. (2021). the impact of mental health literacy training programs on the mental health literacy of university students: A systematic review. Prevention Science, 23(4), 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Risquez, M. I., García-Izquierdo, M., Sabuco-Tebar, E. de los Á., Carrillo-Garcia, C., & Solano-Ruiz, C. (2018). Connections between academic burnout, resilience, and psychological well-being in nursing students: A longitudinal study. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 74(12), 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, N. (2019). Stress and inflammation—The need to address the gap in the transition between acute and chronic stress effects. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 105, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Ricardo, Y., & Ferreira, J. P. (2022). Effects of physical exercise on burnout syndrome in university students. MEDICC Review, 24(1), 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Ricardo, Y., Rizzo-Chunga, F., Mocha-Bonilla, J., & Ferreira, J. P. (2021). Prevalence of burnout syndrome in university students: A systematic review. Salud Mental, 44(2), 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, W. (2012). Stress, burnout, and job dissatisfaction in mental health workers. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 262(S2), 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabagh, Z., Hall, N. C., & Saroyan, A. (2018). Antecedents, correlates and consequences of faculty burnout. Educational Research, 60(2), 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela-Aro, K., & Upadyaya, K. (2014). School burnout and engagement in the context of demands—Resources model. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(1), 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, H. M., Sanchez, E. G. d. M., Barbosa, M. A., Guimarães, E. C., & Porto, C. C. (2019). Impacto da saúde na qualidade de vida e trabalho de docentes universitários de diferentes áreas de conhecimento [Impact of health on the quality of life and work of university professors from different areas of knowledge]. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva, 24(11), 4111–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A. S., Fagundes, J., & Zaffalon Junior, J. R. (2019). Lifestyle’s impact on the realized effort stress of hypertensive and normotensive teachers. SALUSVITA, 38(2), 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Satinsky, E. N., Kimura, T., Kiang, M. V., Abebe, R., Cunningham, S., Lee, H., Lin, X., Liu, C. H., Rudan, I., Sen, S., Tomlinson, M., Yaver, M., & Tsai, A. C. (2021). Systematic review and meta-analysis of depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among Ph.D. students. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 14370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W. B., Martínez, I. M., Pinto, A. M., Salanova, M., & Bakker, A. B. (2002). Burnout and Engagement in University Students. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 33(5), 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R., Selvamani, T. Y., Zahra, A., Malla, J., Dhanoa, R. K., Venugopal, S., Shoukrie, S. I., Hamouda, R. K., & Hamid, P. (2022). Association Between Dietary Habits and Depression: A Systematic Review. Cureus, 14(12), e32359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppälä, E. M., Bradley, C., Moeller, J., Harouni, L., Nandamudi, D., & Brackett, M. A. (2020). Promoting Mental Health and Psychological Thriving in University Students: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Three Well-Being Interventions. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, 534776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N., Steck, S. E., Hurley, T. G., Hussey, J. R., & Hébert, J. R. (2013). Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutrition, 17(8), 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N., Steck, S. E., Hussey, J. R., Ma, Y., & Hebert, J. R. (2015). Inflammatory potential of diet and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Study. European Journal of Nutrition, 56(2), 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P., Taliscas, T., & Paiva, C. (2024). Saúde mental nas IES Portuguesas: Explorando a saúde psicológica e recursos de apoio entre estudantes do ensino superior [Mental health in Portuguese HEIs: Exploring psychological health and support resources among higher education students]. Departamento de Ação Política—ANEP. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C. E., Scott, E. J., & Owen, K. (2022). Physical activity, burnout and quality of life in medical students: A systematic review. The Clinical Teacher, 19(6), e13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhavert, Y., De Martelaer, K., Van Hoof, E., Van Der Linden, E., Zinzen, E., & Deliens, T. (2020). The association between energy balance-related behavior and burn-out in adults: A systematic review. Nutrients, 12(2), 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, C., Arias-Gundín, O., & Rodríguez, C. (2019). Exploring coping and optimism as predictors of academic burnout and performance among university students. Educational Psychology, 39(6), 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Sun, M., Wang, L., Li, J., Xie, Z., Guo, R., Wang, Y., & Li, B. (2023). The role of dietary inflammatory index and physical activity in depressive symptoms: Results from NHANES 2007–2016. Journal of Affective Disorders, 335, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, S.-R., Amarasekara, N. A., Bartonicek, A., & Conner, T. S. (2020). The big three health behaviors and mental health and well-being among young adults: A cross-sectional investigation of sleep, exercise, and diet. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 579205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. (1998). Food frequency methods. In J. L. Kelsey, M. G. Marmot, P. D. Stolley, & M. P. Vessey (Eds.), Nutritional epidemiology (pp. 74–100). Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., & Chae, S. (2020). The mediating effect of resilience on the relationship between the academic burnout and psychological well-being of medical students. Korean Journal of Medical Education, 32(1), 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., Wang, Y., & Liu, F. (2022). Language learning motivation and burnout among English as a foreign language undergraduates: The moderating role of maladaptive emotion regulation strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 808118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M. S. B., Hadie, S. N. H., & Yasin, M. A. M. (2021). The roles of emotional intelligence, neuroticism, and academic stress on the relationship between psychological distress and burnout in medical students. BMC Medical Education, 21(1), 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Participants Characteristics | n (%) | Mean (SD) | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 274 | 22.05 (5.82) | 18–49 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 29 (10.6) | ||
| Female | 245 (89.4) | ||
| Marital status | |||
| Single or divorced | 253 (92.3) | ||
| Dating or married | 21 (7.7) | ||
| Educational level | |||
| Undergraduate | 199 (72.6) | ||
| Graduate | 75 (27.4) | ||
| Course satisfaction | |||
| Dissatisfied | 8 (2.9) | ||
| Neutral | 19 (6.9) | ||
| Satisfied | 18 (6.6) | ||
| Very satisfied | 229 (83.6) | ||
| Chronic illness | |||
| Yes | 62 (22.6) | ||
| No | 212 (77.4) | ||
| Medication | |||
| Yes | 74 (27.0) | ||
| No | 200 (73.0) | ||
| Perceived health status | |||
| Bad | 5 (1.8) | ||
| Fair | 65 (23.7) | ||
| Good | 154 (56.2) | ||
| Very good | 50 (18.2) | ||
| Tobacco use | |||
| Yes | 36 (13.1) | ||
| No | 238 (86.9) | ||
| Substance use | |||
| Yes | 18 (6.6) | ||
| No | 256 (93.4) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | |||
| Yes | 165 (60.2) | ||
| No | 109 (39.8) | ||
| Psychological support | |||
| Yes | 42 (15.3) | ||
| No | 232 (84.7) |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Psychological distress | - | 0.678 ** | −0.749 ** | 0.084 | 0.522 ** | −0.068 | 0.560 ** |
| 2. Difficulties in emotional regulation | - | −0.539 ** | 0.017 | 0.352 ** | −0.049 | 0.457 ** | |
| 3. Psychological well-being | - | −0.012 | −0.486 ** | −0.006 | −0.610 ** | ||
| 4. Physical activity | - | 0.033 | −0.127 * | −0.024 | |||
| 5. Sleep quality | - | 0.011 | 0.336 ** | ||||
| 6. Dietary inflammatory index | - | 0.169 | |||||
| 7. Academic burnout | - | ||||||
| Mean | 16.87 | 83.51 | 16.53 | 1.95 | 6.46 | −0.198 | 2.33 |
| SD | 11.820 | 21.471 | 5.218 | 0.705 | 2.868 | 2.159 | 0.936 |
| Profile | Psychological Distress | Psychological Well-Being | Difficulties in Emotional Regulation | Sleep Quality | Physical Activity | Dietary Inflammatory Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burnout Risk | 24.6 | 12.9 | 96.9 | 8.10 | 1.79 | 1.69 |
| No Risk | 14.7 | 17.6 | 79.6 | 6 | 2 | −0.774 |
| Profile | Psychological Distress | Psychological Well-Being | Difficulties in Emotional Regulation | Sleep Quality | Physical Activity | Dietary Inflammatory Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | |
| Burnout Risk | 11–53 | 3–20 | 72–132 | 4–15 | 1–3 | 0.07–3.39 |
| No Risk | 0–50 | 6–29 | 36–137 | 0–13 | 1–3 | 4.20–3.56 |
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 95.06% | 88.89% | 88.89% | 88.89% |
| SVM | 93.82% | 93.34% | 77.78% | 84.85% |
| XGBoost | 97.53% | 90.00% | 99.99% | 94.73% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, M.G.; Santos, M.; Magalhães, R.; Rodrigues, C.; Araújo, O.; Durães, D. Burnout Risk Profiles in Psychology Students: An Exploratory Study with Machine Learning. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15040505
Pereira MG, Santos M, Magalhães R, Rodrigues C, Araújo O, Durães D. Burnout Risk Profiles in Psychology Students: An Exploratory Study with Machine Learning. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(4):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15040505
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, M. Graça, Martim Santos, Renata Magalhães, Cláudia Rodrigues, Odete Araújo, and Dalila Durães. 2025. "Burnout Risk Profiles in Psychology Students: An Exploratory Study with Machine Learning" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 4: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15040505
APA StylePereira, M. G., Santos, M., Magalhães, R., Rodrigues, C., Araújo, O., & Durães, D. (2025). Burnout Risk Profiles in Psychology Students: An Exploratory Study with Machine Learning. Behavioral Sciences, 15(4), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15040505






