Degraded Visibility Body-Specifically Affects Mental Rotation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Conditions and Stimuli
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
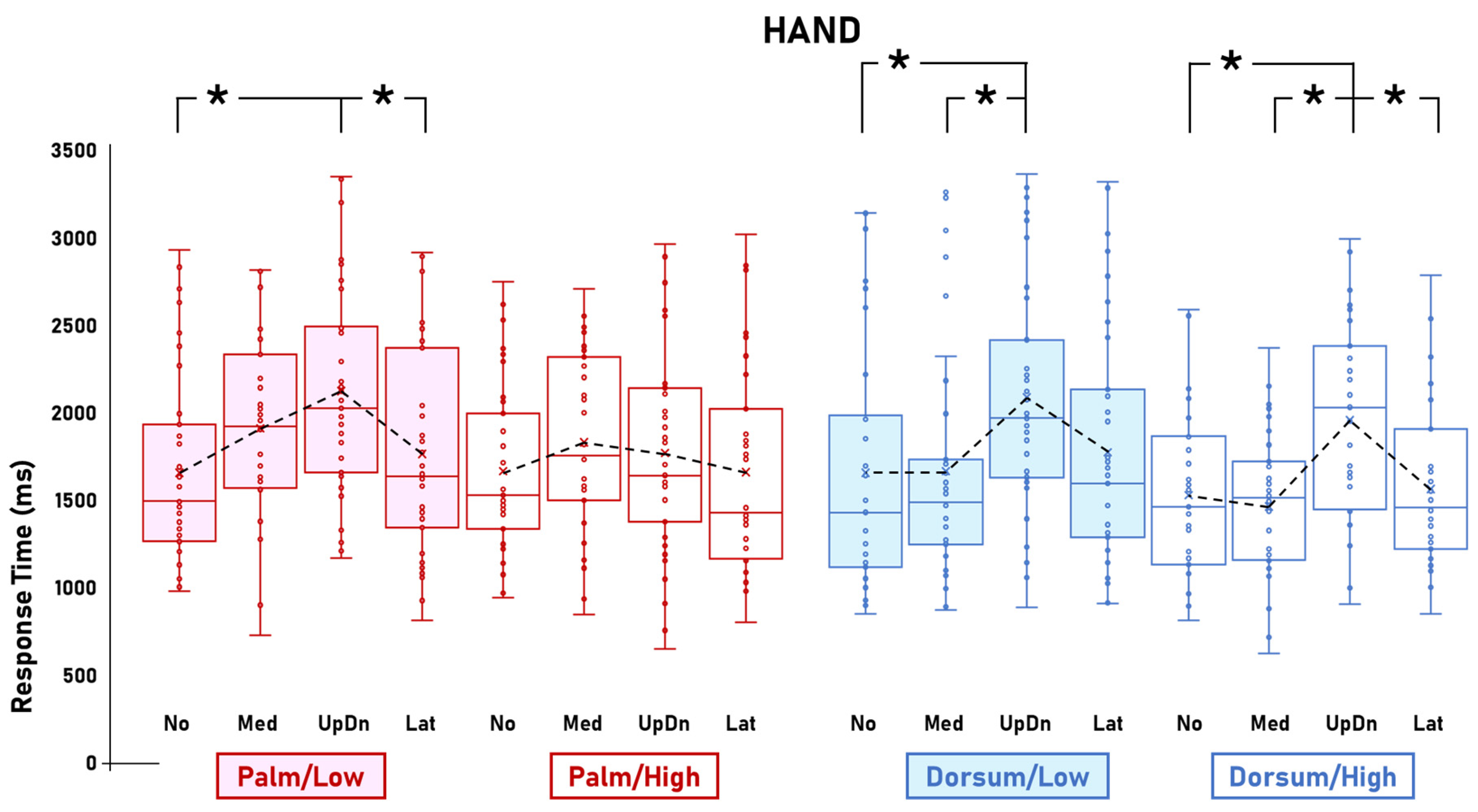
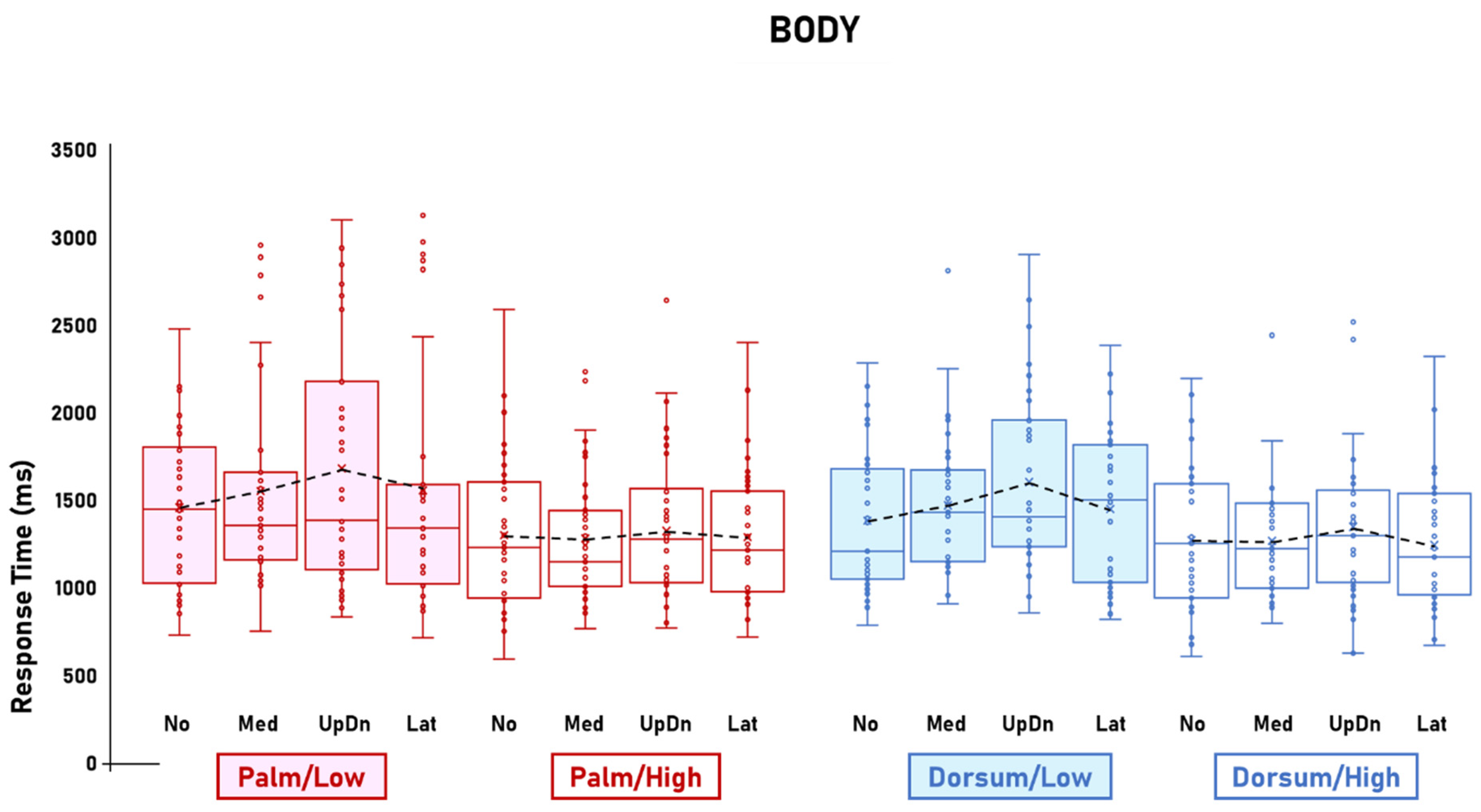
3. Results
3.1. Visibility Effects
3.2. Other Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Body-Specific Visual-to-Motor Shifts
4.1.1. Stimuli-Related Effects
4.1.2. Palm-View-Related Inter-Stimulus Comparisons
4.1.3. Dorsum-View-Related Inter-Stimulus Comparisons
4.2. Visual Perturbation and Body Representation
4.3. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jeannerod, M. Neural simulation of action: A unifying mechanism for motor cognition. Neuroimage 2001, 14, S103–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmich, I.; Meyer, C.; Voelk, M.; Coenen, J.; Mueller, S.; Schepmann, J.; Lausberg, H. The pantomime of mental rotation: Left-handers are less lateralized. Neuropsychologia 2022, 176, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vastano, R.; Widerstrom-Noga, E. Event-related potentials during mental rotation of body-related stimuli in spinal cord injury population. Neuropsychologia 2023, 179, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugin, D.; Notter, M.P.; Knebel, J.F.; Ionta, S. Temporo-parietal contribution to mental representations of self/other face. Brain Cogn. 2020, 143, 105600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, D.; Richert, B.; Weigelt, M. Neurophysiology of embodied mental rotation: Event-related potentials in a mental rotation task with human bodies as compared to alphanumeric stimuli. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 5384–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.S.; Pegna, A.J.; Mayer, E.; Hauert, C.A. Representation of anatomical constraints in motor imagery: Mental rotation of a body segment. Brain Cogn. 2003, 51, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.M. Imagined spatial transformations of one’s hands and feet. Cogn. Psychol. 1987, 19, 178–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegelke, C.; Hughes, C.M. The influence of action possibility and end-state comfort on motor imagery of manual action sequences. Brain Cogn. 2015, 101, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapparoli, L.; Invernizzi, P.; Gandola, M.; Berlingeri, M.; De Santis, A.; Zerbi, A.; Banfi, G.; Paulesu, E. Like the back of the (right) hand? A new fMRI look on the hand laterality task. Exp. Brain Res. 2014, 232, 3873–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, H.; Suzuki, M.; Sekiyama, K. Advanced aging effects on implicit motor imagery and its links to motor performance: An investigation via mental rotation of letters, hands, and feet. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1025667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicky, V.; Fialova, J.; Stella, D.; Sterbova, Z.; Kleisner, K.; Havlicek, J. 360 Degrees of Facial Perception: Congruence in Perception of Frontal Portrait, Profile, and Rotation Photographs. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeugin, D.; Arfa, N.; Notter, M.; Murray, M.M.; Ionta, S. Implicit self-other discrimination affects the interplay between multisensory affordances of mental representations of faces. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 333, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.M.; Causby, R.S.; Stewart, H.; Stanton, T.R. Differential influence of habitual third-person vision of a body part on mental rotation of images of hands and feet. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandola, M.; Dodoni, L.; Lazzeri, G.; Arcangeli, C.A.; Avesani, R.; Moro, V.; Ionta, S. Neurocognitive Benefits of Physiotherapy for Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, A.L.; Wilson, P.H. Adult age differences in the ability to mentally transform object and body stimuli. Neuropsychol. Dev. Cogn. B Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2010, 17, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habacha, H.; Lejeune-Poutrain, L.; Molinaro, C. Realistic stimuli reveal selective effects of motor expertise during a mental body rotation task. Am. J. Psychol. 2017, 130, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bek, J.; Humphries, S.; Poliakoff, E.; Brady, N. Mental rotation of hands and objects in ageing and Parkinson’s disease: Differentiating motor imagery and visuospatial ability. Exp. Brain Res. 2022, 240, 1991–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionta, S.; Perruchoud, D.; Draganski, B.; Blanke, O. Body context and posture affect mental imagery of hands. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.R.; Giovanola, Y.; Ionta, S. Social Touch Somatotopically Affects Mental Body Representations. Neuroscience 2022, 494, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perruchoud, D.; Michels, L.; Piccirelli, M.; Gassert, R.; Ionta, S. Differential neural encoding of sensorimotor and visual body representations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionta, S.; Villiger, M.; Jutzeler, C.R.; Freund, P.; Curt, A.; Gassert, R. Spinal cord injury affects the interplay between visual and sensorimotor representations of the body. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ní Choisdealbha, Á.; Brady, N.; Maguinness, C. Differing roles for the dominant and non-dominant hands in the hand laterality task. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 211, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovaola, Y.; Rojo Martinez, V.; Ionta, S. Degraded vision affects mental representations of the body. Vis. Cogn. 2022, 30, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fang, H.; Li, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, B.-m.; Wang, C. Sex differences in large-scale brain network connectivity for mental rotation performance. NeuroImage 2024, 298, 120807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzo, F.; Moe, A.; Cadinu, M.; Bertolli, C. The role of implicit gender spatial stereotyping in mental rotation performance. Acta Psychol. 2019, 194, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Segura, C.; Aguirre, N.; Cruz-Gomez, A.J.; Solozano, N.; Forn, C. Do Gender-Related Stereotypes Affect Spatial Performance? Exploring When, How and to Whom Using a Chronometric Two-Choice Mental Rotation Task. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L.; Jansen, P. The influence of the design of mental rotation trials on performance and possible differences between sexes: A theoretical review and experimental investigation. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2024, 77, 1250–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Braithwaite, F.A.; Edwards, L.M.; Causby, R.S.; Conson, M.; Stanton, T.R. The effect of handedness on mental rotation of hands: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Res. 2021, 85, 2829–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hegarty, M.; Chrastil, E.R. Telling right from right: The influence of handedness in mental rotation of hands. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2020, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P.; Jost, L.; Jansen, P. Embodied Mental Rotation—Does It Affect Postural Stability? J. Mot. Behav. 2023, 55, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Choi, S.H.; Noh, E.; Lee, W.J.; Jang, J.H.; Moon, J.Y.; Kang, D.H. Impaired Performance in Mental Rotation of Hands and Feet and Its Association with Social Cognition in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionta, S.; Fourkas, A.D.; Fiorio, M.; Aglioti, S.M. The influence of hands posture on mental rotation of hands and feet. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 183, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ye, H. Postural Effects on mental Rotation of Body-Related Pictures: An fMRI Study. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusa, F.; Erden, M.S.; Sedda, A. More implicit and more explicit motor imagery tasks for exploring mental representation of hands and feet in action. Exp. Brain Res. 2023, 241, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, S.; van Schie, H.T.; Cross, E.S.; de Lange, F.P.; Wigboldus, D.H. Disentangling neural processes of egocentric and allocentric mental spatial transformations using whole-body photos of self and other. Neuroimage 2015, 116, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, O.; Ionta, S.; Fornari, E.; Mohr, C.; Maeder, P. Mental imagery for full and upper human bodies: Common right hemisphere activations and distinct extrastriate activations. Brain Topogr. 2010, 23, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cona, G.; Panozzo, G.; Semenza, C. The role of dorsal premotor cortex in mental rotation: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Brain Cogn. 2017, 116, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasing, B.; Brugger, P.; Weigelt, M.; Schack, T. Does thumb posture influence mental rotation of hands? Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 534, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionta, S.; Fourkas, A.D.; Aglioti, S.M. Egocentric and object-based transformations in the laterality judgement of human and animal faces and of non-corporeal objects. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, M.; Brugger, P. Mental rotation of congenitally absent hands. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2008, 14, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Horst, A.C.; van Lier, R.; Steenbergen, B. Mental rotation task of hands: Differential influence number of rotational axes. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 203, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamplona, G.S.P.; Hardmeier, M.; Younes, S.; Goy, I.; Fornari, E.; Ionta, S. Vision- and touch-dependent brain correlates of body-related mental processing. Cortex 2022, 157, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionta, S.; Sforza, A.; Funato, M.; Blanke, O. Anatomically plausible illusory posture affects mental rotation of body parts. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 13, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.M. Temporal and kinematic properties of motor behavior reflected in mentally simulated action. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1994, 20, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.; Firestone, C. Visual cognition: A new perspective on mental rotation. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R1281–R1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, M.; Raab, M.; Jansen, P.; Klatt, S. Embodied mental rotation ability in open- and closed-skill sports: Pilot study with a new virtual paradigm. Exp. Brain Res. 2024, 242, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, S.J.; Klatzky, R.L. Haptic perception: A tutorial. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2009, 71, 1439–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, V.; Corbella, M.; Ionta, S.; Ferrari, F.; Scandola, M. Cognitive Training Improves Disconnected Limbs’ Mental Representation and Peripersonal Space after Spinal Cord Injury. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmor, G.S.; Zaback, L.A. Mental rotation by the blind: Does mental rotation depend on visual imagery? J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1976, 2, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, B.; Celik, S.; Ilci, C. Representation of haptic objects during mental rotation in congenital blindness. Percept. Mot. Skills 2014, 118, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, S. Body image and body schema: A conceptual clarification. J. Mind Behav. 1986, 7, 541–554. [Google Scholar]
- Head, H. Studies in Neurology II; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1920. [Google Scholar]
- Berlucchi, G.; Aglioti, S. The body in the brain: Neural bases of corporeal awareness. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghez, C.; Gordon, J.; Ghilardi, M.F. Impairments of reaching movements in patients without proprioception. II. Effects of visual information on accuracy. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 73, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainburg, R.L.; Poizner, H.; Ghez, C. Loss of proprioception produces deficits in interjoint coordination. J. Neurophysiol. 1993, 70, 2136–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilder, P. The Image and Appearance of the Human Body; International Universities Press: New York, NY, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, D.D.; Johnson, T.C.; Cole, S.P. Physical fitness, body image, and locus of control in college freshman men and women. Percept. Mot. Skills 1989, 68, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adame, D.D.; Radell, S.A.; Johnson, T.C.; Cole, S.P. Physical fitness, body image, and locus of control in college women dancers and nondancers. Percept. Mot. Skills 1991, 72, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.M.; Moncrieff, C. Body image distortion in anorexics as a non-sensory phenomenon: A signal detection approach. J. Clin. Psychol. 1988, 44, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S.; Cole, J. Body Image and Body Schema in a Deafferented Subject. J. Mind Behav. 1995, 16, 369–390. [Google Scholar]
- Ungar, S.; Blades, M.; Spencer, C. Mental rotation of a tactile layout by young visually impaired children. Perception 1995, 24, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, B.; Rosler, F.; Hennighausen, E. Different cortical activation patterns in blind and sighted humans during encoding and transformation of haptic images. Psychophysiology 1997, 34, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.F.; Bartholomew, A.N. Blindness enhances tactile acuity and haptic 3-D shape discrimination. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2011, 73, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, K.; Deschamps, L.; Baena-Gomez, D. Mental rotation in blind and sighted adolescents: The effects of haptic strategies. Rev. Eur. Psychol. Appliquée/Eur. Rev. Appl. Psychol. 2011, 61, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Manga, D.; Reales, J.M. Haptic discrimination of bilateral symmetry in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional unfamiliar displays. Percept. Psychophys. 1997, 59, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, M.W.; Van Lienen, T.; Verstijnen, I.M.; Kappers, A.M. Look what I have felt: Unidentified haptic line drawings are identified after sketching. Acta Psychol. 2008, 128, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinter, A.; Fernandes, V.; Orlandi, O.; Morgan, P. Exploratory procedures of tactile images in visually impaired and blindfolded sighted children: How they relate to their consequent performance in drawing. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, A.; Paolieri, D. The influence of estradiol and progesterone on neurocognition during three phases of the menstrual cycle: Modulating factors. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 417, 113593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, A.; Mateo-Martínez, R.; Paolieri, D. Influence of sex, menstrual cycle, and hormonal contraceptives on egocentric navigation with or without landmarks. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 120, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuringer, A.; Pletzer, B. Sex differences and menstrual cycle dependent changes in cognitive strategies during spatial navigation and verbal fluency. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, C.; Nicholls, I.; Lavale, A.; Kulkarni, J. Oral contraceptives and cognition: A systematic review. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 69, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotach, Z.; Beazley, C.; Ionta, S. Degraded Visibility Body-Specifically Affects Mental Rotation. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090784
Rotach Z, Beazley C, Ionta S. Degraded Visibility Body-Specifically Affects Mental Rotation. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(9):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090784
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotach, Zoé, Claude Beazley, and Silvio Ionta. 2024. "Degraded Visibility Body-Specifically Affects Mental Rotation" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 9: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090784
APA StyleRotach, Z., Beazley, C., & Ionta, S. (2024). Degraded Visibility Body-Specifically Affects Mental Rotation. Behavioral Sciences, 14(9), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090784





