When Games Influence Words: Gaming Addiction among College Students Increases Verbal Aggression through Risk-Biased Drifting in Decision-Making
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Game Addiction and Game Violence
1.2. Verbal Aggression
1.3. Inhibitory Control
1.4. Risk Preference
1.5. Mediation Model
1.6. The Present Study
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Research Instruments
2.2.1. Questionnaires
2.2.2. Antisaccade Task
2.2.3. Go/No-Go Task
2.2.4. The Cup Task
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Validity Analysis
2.4.2. The Hierarchical Drift Diffusion Model
2.4.3. Mediation Model
3. Results
3.1. Correlational Analysis and the Cut-Off Point for Gaming Addiction
3.2. Validity Analysis
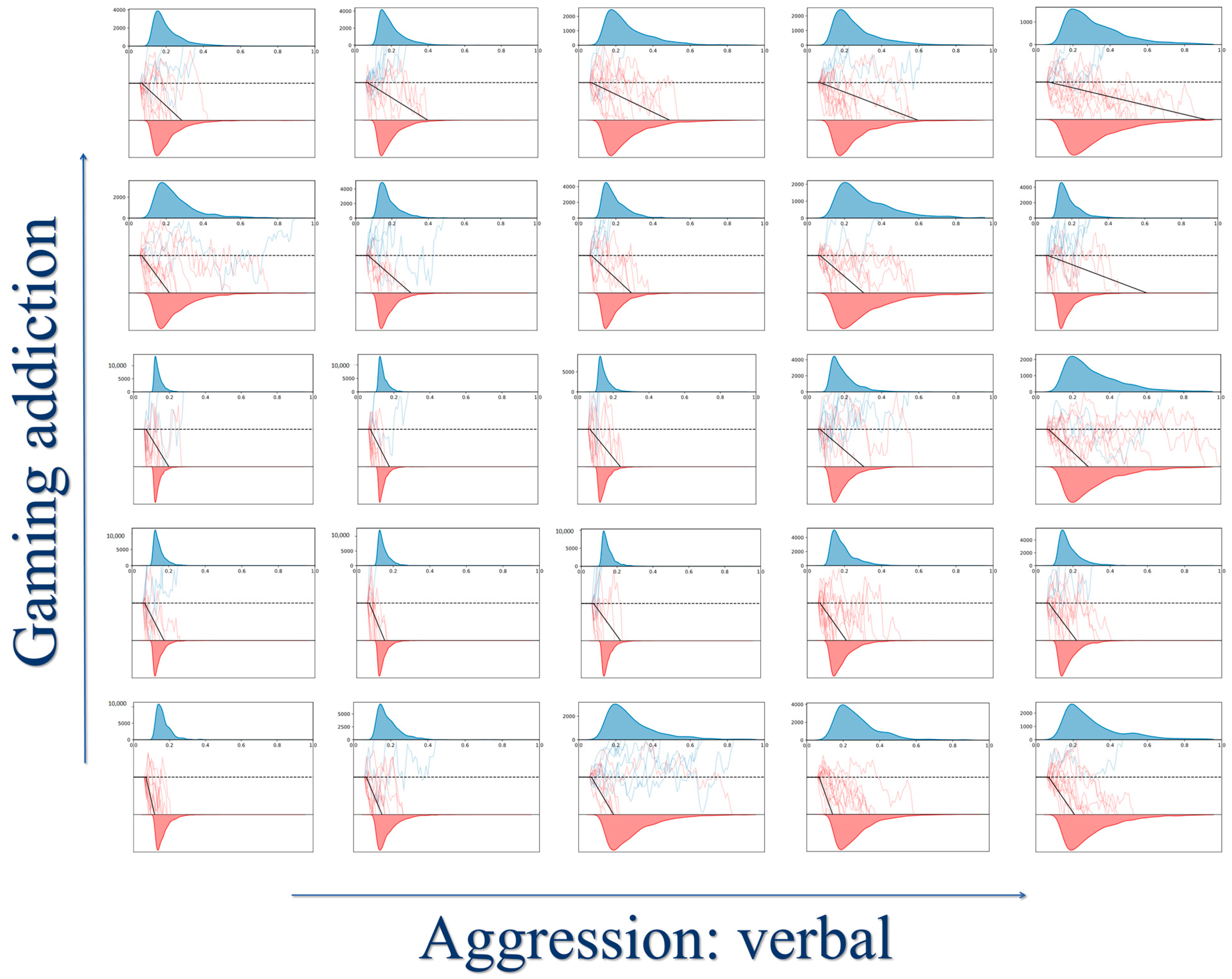
3.3. Hierarchical Drift Diffusion Model
3.4. Mediation Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Mediation Model
4.2. Risk Preference
4.3. Inhibitory Control
4.4. Contribution of the Present Study
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statista. Number of Video Gamers Worldwide in 2021, by Region. 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/293304/number-video-gamers/#:~:text=Figures%20in%202020%20showed%20that,across%20the%20globe%20in%202020 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Statista. Number of Video Gamers in the United States in 2022, by Engagement Level. 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/300942/number-core-gamers-usa/ (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Bickham, D.S. Current Research and Viewpoints on Internet Addiction in Adolescents. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Yim, H.; Lee, T.-H. Negative Impact of Daily Screen Use on Inhibitory Control Network in Preadolescence: A Two-Year Follow-up Study. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2023, 60, 101218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-P.; Chen, K.-L.; Chou, W.; Yuan, K.-S.; Yen, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chow, J.C. Prolonged Touch Screen Device Usage Is Associated with Emotional and Behavioral Problems, but Not Language Delay, in Toddlers. Infant Behav. Dev. 2020, 58, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederhold, B.K. Kids Will Find a Way: The Benefits of Social Video Games. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.A.; Collignon, A.; Bieler-Aeschlimann, M. Serious Video Games and Virtual Reality for Prevention and Neurorehabilitation of Cognitive Decline Because of Aging and Neurodegeneration. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Bushman, B.J. Human Aggression. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.E.; Anderson, C.A. A Theoretical Model of the Effects and Consequences of Playing Video Games. In Playing Video Games: Motives, Responses, and Consequences; Vorderer, P., Bryant, J., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, A.; Sauer, J.D.; Ferguson, C.J. Do Longitudinal Studies Support Long-Term Relationships between Aggressive Game Play and Youth Aggressive Behaviour? A Meta-Analytic Examination. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, T.E.; Gouveia, V.V.; Pimentel, C.E. The Effect of Video Games on Positive and Negative Cognitions. RPI 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshani, A.; Braverman, S.; Meirow, G. Video Games and Close Relations: Attachment and Empathy as Predictors of Children’s and Adolescents’ Video Game Social Play and Socio-Emotional Functioning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 114, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, P.; Gao, F. The Effects of Violent Video Games and Shyness on Individuals’ Aggressive Behaviors. Aggress. Behav. 2020, 46, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S. Violent Video Games and Aggression: Stimulation or Catharsis or Both? Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, R.; Behr, K.M.; Fisher, J.T.; Lonergan, C.; Quebral, C. Video Game Violence and Interactivity: Effect or Equivalence? J. Commun. 2020, 70, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, X. Internet Gaming Disorder and Aggression: A Meta-Analysis of Teenagers and Young Adults. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1111889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tian, J. Effects of violent video games on players’ and observers’ aggressive cognitions and aggressive behaviors. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2021, 203, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, S.S.; Yang, H. Smartphone Addiction and Checking Behaviors Predict Aggression: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. IJERPH 2021, 18, 13020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, P.C.; Fang, J.; Kulbo, N.B.; Gumah, B.; Dagadu, J.C.; Li, L. Violent Video Games and Aggression Among Young Adults: The Moderating Effects of Adverse Environmental Factors. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Guo, T.; Cheng, J.; Wang, M.; Rong, F.; Zhang, S.; Tan, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y. Sex Differences in Association between Internet Addiction and Aggression among Adolescents Aged 12 to 18 in Mainland of China. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 312, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Bushman, B.J.; Bartholow, B.D.; Cantor, J.; Christakis, D.; Coyne, S.M.; Donnerstein, E.; Brockmyer, J.F.; Gentile, D.A.; Green, C.S.; et al. Screen Violence and Youth Behavior. Pediatrics 2017, 140 (Suppl. 2), S142–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, O.; Sleczka, P.; Pontes, H.M.; Urbán, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Demetrovics, Z. Validation of the Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10) and evaluation of the nine DSM-5 Internet Gaming Disorder criteria. Addict. Behav. 2017, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Jan, R.A.; Alsaedi, S.L. Symptoms, Mechanisms, and Treatments of Video Game Addiction. Cureus 2023, 15, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, S.; Higuchi, S. Cross-sectional and longitudinal epidemiological studies of Internet gaming disorder: A systematic review of the literature. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 71, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, P.J.; Willoughby, T. The Longitudinal Association between Competitive Video Game Play and Aggression among Adolescents and Young Adults. Child Dev. 2016, 87, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Qi, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, X. Enhanced neural responses in specific phases of reward processing in individuals with Internet gaming disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuji, K.; Yoshida, F. The influences of interaction during online gaming on sociability and aggression in real life. Shinrigaku Kenkyu Jpn. J. Psychol. 2010, 80, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducharme, P.; Kahn, J.; Vaudreuil, C.; Gusman, M.; Waber, D.; Ross, A.; Rotenberg, A.; Rober, A.; Kimball, K.; Peechatka, A.L.; et al. A “Proof of Concept” Randomized Controlled Trial of a Video Game Requiring Emotional Regulation to Augment Anger Control Training. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 591906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wei, M.; Wang, X.; Liao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Competitive Video Game Exposure Increases Aggression through Impulsivity in Chinese Adolescents: Evidence from a Multi-Method Study. J. Youth Adolesc. 2024; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Turel, O.; Bechara, A.; He, Q. A Tripartite Neurocognitive Model of Internet Gaming Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, W. Does Early Adversity Predict Aggression Among Chinese Male Violent Juvenile Offenders? The Mediating Role of Life History Strategy and the Moderating Role of Meaning in Life. BMC Psychol. 2023, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glascock, J. Contribution of Verbally Aggressive TV Exposure and Perceived Reality to Trait Verbal Aggression. Commun. Rep. 2021, 34, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.; Boland, A.; Murphy, S.; Cooney, C. Vocally Disruptive Behavior: A Case Report and Literature Review. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2022, 39, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poling, D.V.; Smith, S.W. Perceptions about Verbal Aggression: Survey of Secondary Students with Emotional and Behavioral Disorders. J. Emot. Behav. Disord. 2023, 31, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.A.; Chandler, T.A.; Rudd, J.E. Test of an Argumentative Skill Deficiency Model of Interpersonal Violence. Commun. Monogr. 1989, 56, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Sharma, K.; Sigdel, D.; Thapa, T.; Mehta, R. Internet Gaming Disorder and Aggression among Students on School Closure during COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2022, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Columb, D.; Wong, M.C.; O’Mahony, V.; Harrington, C.; Griffiths, M.D.; O’Gara, C. Gambling Advertising during Live Televised Male Sporting Events in Ireland: A Descriptive Study. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2023, 40, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, P.; Mendolia, S.; Yerokhin, O. Social Media Use and Emotional and Behavioural Outcomes in Adolescence: Evidence from British Longitudinal Data. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2021, 41, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, K.H.; Smith, M.R.; Moran, L.; Ruberry, E.J.; Lengua, L.J. Tests of Bidirectional Relations of TV Exposure and Effortful Control as Predictors of Adjustment in Early Childhood in the Context of Family Risk Factors. Infant Child Dev. 2022, 31, e2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtrakul, N.; Louthrenoo, O.; Narkpongphun, A.; Boonchooduang, N.; Chonchaiya, W. Media Use and Psychosocial Adjustment in Children and Adolescents. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 54, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, N.E.; Santoro, E.; Lugo, A.; Madrid-Valero, J.J.; Ghislandi, S.; Torbica, A.; Gallus, S. The Role of Technology and Social Media Use in Sleep-Onset Difficulties among Italian Adolescents: Cross-sectional Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e20319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Wegmann, E.; Stark, R.; Müller, A.; Wölfling, K.; Robbins, T.W.; Potenza, M.N. The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) Model for Addictive Behaviors: Update, Generalization to Addictive Behaviors beyond Internet-Use Disorders, and Specification of the Process Character of Addictive Behaviors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, E.; Davison, C.B.; Lee, T.T.C. Response Inhibition and Internet Gaming Disorder: A Meta-analysis. Addict. Behav. 2017, 71, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounoua, N.; Spielberg, J.M.; Sadeh, N. Clarifying the Synergistic Effects of Emotion Dysregulation and Inhibitory Control on Physical Aggression. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 5358–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.-H.; Potenza, M.N. Considering Gender Differences in the Study and Treatment of Internet Gaming Disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 153, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W. Short-Term Touch-Screen Video Game Playing Improves the Inhibition Ability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.; Volkow, N. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Drug Addiction: Updating Actions to Habits to Compulsions Ten Years On. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlung, M.; Vedelago, L.; Acker, J.; Balodis, I.; MacKillop, J. Steep delay discounting and addictive behavior: A meta-analysis of continuous associations. Addiction 2017, 112, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turel, O.; He, Q.; Brevers, D.; Bechara, A. Delay discounting mediates the association between posterior insular cortex volume and social media addiction symptoms. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 18, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Pérez-García, M.; Bechara, A. Emotion, decision-making and substance dependence: A somatic-marker model of addiction. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, D.; Shim, M.S. Factors influencing smartphone overdependence among adolescents. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R. Using decision tree to predict non-suicidal self-injury among young adults: The role of depression, childhood maltreatment and recent bullying victimization. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2024, 15, 2322390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooren, M.M.M.V.; Visch, V.T.; Spijkerman, R. The Design and Application of Game Rewards in Youth Addiction Care. Information 2019, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, J.; Fan, L.; Qiu, Y. Reduction of Symptom after a Combined Behavioral Intervention for Reward Sensitivity and Rash Impulsiveness in Internet Gaming Disorder: A Comparative Study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 153, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Osso, B.; Di Bernardo, I.; Vismara, M.; Piccoli, E.; Giorgetti, F.; Molteni, L.; Fineberg, N.A.; Virzì, C.; Bowden-Jones, H.; Truzoli, R.; et al. Managing Problematic Usage of the Internet and Related Disorders in an Era of Diagnostic Transition: An Updated Review. CPEMH 2021, 17, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.M.; Antons, S.; Wegmann, E.; Ioannidis, K.; King, D.L.; Potenza, M.N.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Brand, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Risky Decision-making in Specific Domains of Problematic Use of the Internet: Evidence across Different Decision-making Tasks. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 152, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lim, J.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.N.; Kim, D.J.; Ha, J.E.; Kwon, J.S.; Choi, J.-S. Impulsivity and Compulsivity in Internet Gaming Disorder: A Comparison with Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kräplin, A.; Scherbaum, S.; Kraft, E.-M.; Rehbein, F.; Bühringer, G.; Goschke, T.; Mößle, T. The Role of Inhibitory Control and Decision-making in the Course of Internet Gaming Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 9, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.; Cabello, R.; Megías-Robles, A.; Gómez-Leal, R.; Fernández-Berrocal, P. Emotional Intelligence and Aggressive Behaviors in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trauma Violence Abus. 2022, 23, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.S.; Chen, R.T.; Liu, M.M.; Zheng, D.H. Monetary Reward Discounting, Inhibitory Control, and Trait Impulsivity in Young Adults with Internet Gaming Disorder and Nicotine Dependence. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 628933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, X.; Brevers, D.; Bechara, A. A neurocognitive approach to understanding the neurobiology of addiction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Feng, T. Lateralization of self-control over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in decision-making: A systematic review and meta-analytic evidence from noninvasive brain stimulation. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 24, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laino Chiavegatti, G.; Floresco, S.B. Acute stress differentially alters reward-related decision making and inhibitory control under threat of punishment. Neurobiol. Stress 2024, 30, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, H.M.; Király, O.; Demetrovics, Z.; Griffiths, M.D. The Conceptualisation and Measurement of DSM-5 Internet Gaming Disorder: The Development of the IGD-20 Test. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlo, G.; Randall, B.A. The Development of a Measure of Prosocial Behaviors for Late Adolescents. J. Youth Adolesc. 2002, 31, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, A.H.; Perry, M. Personality Processes and Individual Differences. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 63, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Friedman, N.P.; Emerson, M.J.; Witzki, A.H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T.D. The Unity and Diversity of Executive Functions and Their Contributions to Complex “Frontal Lobe” Tasks: A Latent Variable Analysis. Cogn. Psychol. 2000, 41, 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosek, B.A.; Greenwald, A.G.; Banaji, M.R. Understanding and Using the Implicit Association Test: II. Method Variables and Construct Validity. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2005, 31, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, I.P.; Hart, S.S. Risk Preferences in Young Children: Early Evidence of Individual Differences in Reaction to Potential Gains and Losses. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2003, 16, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods in Biostatistics. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1996, 5, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, Y.; Jarratt-Barnham, I.; Petitet, P.; Fernandez-Egea, E.; Manohar, S.G.; Husain, M. Negative symptoms and cognitive impairment are associated with distinct motivational deficits in treatment resistant schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W. A Study on the Cause Analysis of Cyberbullying in Korean Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, L. The Association between Violent Video Game Exposure and Sub-Types of School Bullying in Chinese Adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1026625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.P.; Samp, J.A. Stoicism and Verbal Aggression in Serial Arguments: The Roles of Perceived Power, Perceived Resolvability, and Frequency of Arguments. J. Interpers. Violence 2022, 37, NP11836–NP11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Huang, J.; Du, X. Enhanced reward sensitivity and decreased loss sensitivity in Internet addicts: An fMRI study during a guessing task. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Hawes, S.W.; Waller, R.; Delgado, M.R.; Sutherland, M.T.; Dick, A.S.; Trucco, E.M.; Riedel, M.C.; Pacheco-Colón, I.; Laird, A.R.; et al. Neural response to monetary loss among youth with disruptive behavior disorders and callous-unemotional traits in the ABCD study. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tian, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, X. Reduced Loss Aversion and Inhibitory Control in Adolescents with Internet Gaming Disorder. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2020, 34, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bediou, B.; Adams, D.M.; Mayer, R.E.; Tipton, E.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Meta-Analysis of Action Video Game Impact on Perceptual, Attentional, and Cognitive Skills. Psychol. Bull. 2018, 144, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichon, S.; Bediou, B.; Antico, L.; Jack, R.; Garrod, O.; Sims, C.; Green, C.S.; Schyns, P.; Bavelier, D. Emotion perception in habitual players of action video games. Emotion 2021, 21, 1324–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foland-Ross, L.C.; Buckingam, B.; Mauras, N.; Arbelaez, A.M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Tsalikian, E.; Cato, A.; Tong, G.; Englert, K.; Mazaika, P.K.; et al. Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet). Executive task-based brain function in children with type 1 diabetes: An observational study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamp, G.; Sola Molina, R.M.; Hugrass, L.; Beaton, R.; Crewther, D.; Crewther, S.G. Kinematic Studies of the Go/No-Go Task as a Dynamic Sensorimotor Inhibition Task for Assessment of Motor and Executive Function in Stroke Patients: An Exploratory Study in a Neurotypical Sample. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabedo-Peris, J.; González-Sala, F.; Merino-Soto, C.; Pablo, J.Á.C.; Toledano-Toledano, F. Decision Making in Addictive Behaviors Based on Prospect Theory: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiebener, J.; Zamarian, L.; Delazer, M.; Brand, M. Executive functions, categorization of probabilities, and learning from feedback: What does really matter for decision making under explicit risk conditions? J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplak, M.E.; Sorge, G.B.; Benoit, A.; West, R.F.; Stanovich, K.E. Decision-making and cognitive abilities: A review of associations between Iowa Gambling Task performance, executive functions, and intelligence. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 562–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, A.D.; Shulkin, J.; Lac, A.; Rapp, T. A meta-analysis of cognitive reappraisal and personal resilience. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2024, 110, 102428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxandi, M.; Baenas, I.; Mora-Maltas, B.; Granero, R.; Fernández-Aranda, F.; Tovar, S.; Solé-Morata, N.; Lucas, I.; Casado, S.; Gómez-Peña, M.; et al. Are Signals Regulating Energy Homeostasis Related to Neuropsychological and Clinical Features of Gambling Disorder? A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riek, H.C.; Brien, D.C.; Coe, B.C.; Huang, J.; Perkins, J.E.; Yep, R.; McLaughlin, P.M.; Orange, J.B.; Peltsch, A.J.; Roberts, A.C.; et al. Cognitive correlates of antisaccade behaviour across multiple neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.; Cameron, I.G.M.; Van der Kolk, N.M.; de Vries, N.M.; Klimars, E.; Toni, I.; Bloem, B.R.; Helmich, R.C. Aerobic Exercise Alters Brain Function and Structure in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, K.E.; McClaine, R.; Laurianti, V.; Connell, A.M. Effects of binge drinking and depression on cognitive-control processes during an emotional Go/No-Go task in emerging adults. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 162, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, P. Impact of Social Media Use on Executive Function. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2023, 141, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Jia, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D. Inhibitory Control in Excessive Social Networking Users: Evidence From an Event-Related Potential-Based Go-Nogo Task. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.J.; Jones, R.M.; Hare, T.A. The Adolescent Brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1124, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, A.; Hare, T.A.; Parra, C.E.; Penn, J.; Voss, H.; Glover, G.; Casey, B.J. Earlier Development of the Accumbens Relative to Orbitofrontal Cortex Might Underlie Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescents. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 6885–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, A.; Hare, T.; Voss, H.; Glover, G.; Casey, B. Risk-Taking and the Adolescent Brain: Who Is at Risk? Dev. Sci. 2007, 10, F8–F14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, A.A.; Floresco, S.B.; Goto, Y.; Lodge, D.J. Regulation of Firing of Dopaminergic Neurons and Control of Goal-Directed Behaviors. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larche, C.J.; Chini, K.; Lee, C.; Dixon, M.J. To Pay or Just Play? Examining Individual Differences Between Purchasers and Earners of Loot Boxes in Overwatch. J. Gambl. Stud. 2023, 39, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendle, D.; Flick, C.; Halgarth, D.; Ballou, N.; Cutting, J.; Drachen, A. The Relationship Between Lockdowns and Video Game Playtime: Multilevel Time-Series Analysis Using Massive-Scale Data Telemetry. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e40190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenberg, K.; Holtmann, M. Einzug der Computerspielstörung als Verhaltenssucht in die ICD-11. Z. Kinder-Jugendpsychiatr. Psychother. 2022, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenberg, K.; Kindt, S.; Szász-Janocha, C. Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy–Based Intervention in Preventing Gaming Disorder and Unspecified Internet Use Disorder in Adolescents: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2148995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zack, M.; St. George, R.; Clark, L. Dopaminergic signaling of uncertainty and the aetiology of gambling addiction. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 99, 109853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Dai, J.; Potenza, M.N. Ten years of research on the treatments of internet gaming disorder: A scoping review and directions for future research. J. Behav. Addict. 2024, 13, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, T. Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Version of the Internet Gaming Disorder Scale among College Students. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 28, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Hong, H.; Tan, C.; Li, L. Revision of the Prosocial Tendency Scale for Adolescents. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 2007, 1, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yang, S. Revision and Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Version of the Buss and Perry Aggression Questionnaire. Chin. J. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2011, 10, 607–613. [Google Scholar]


| Recreation Program | M | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Video game | 59.29 | 70.77 |
| TV | 40.96 | 48.10 |
| Short video | 78.02 | 72.62 |
| Card game | 4.61 | 17.68 |
| Text-based media | 38.77 | 48.52 |
| Webcast | 7.00 | 25.30 |
| Terms | Explanations |
|---|---|
| awin & advantage | The threshold in the risk advantage condition when winning money is used as feedback. |
| awin& disadvantage | The threshold in the risk disadvantage condition when winning money is used as feedback. |
| awin& neutral | The threshold in the neutral condition when winning money is used as feedback. |
| aloss & advantage | The threshold in the risk advantage condition when losing money is used as feedback. |
| aloss & disadvantage | The threshold in the risk disadvantage condition when losing money is used as feedback. |
| aloss & neutral | The threshold in the neutral condition when losing money is used as feedback. |
| vwin & advantage | The drift rates in the risk advantage condition when winning money are used as feedback. |
| vwin& disadvantage | The drift rates in the risk disadvantage condition when winning money are used as feedback. |
| vwin& neutral | The drift rates in the neutral condition when winning money are used as feedback. |
| vloss & advantage | The drift rates in the risk advantage condition when losing money are used as feedback. |
| vloss & disadvantage | The drift rates in the risk disadvantage condition when losing money are used as feedback. |
| vloss & neutral | The drift rates in the neutral condition when losing money are used as feedback. |
| twin | The non-decision time when winning money is used as feedback. |
| tloss | The non-decision time when losing money is used as feedback. |
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gaming addiction | 42.595 | 13.131 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Prosocial tendencies measure | 100.754 | 11.558 | −0.031 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. Aggression: Physical | 13.627 | 4.318 | 0.201 ** | −0.075 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4. Aggression: Verbal | 11.599 | 3.332 | 0.175 ** | −0.054 | 0.499 *** | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5. Aggression: Anger | 13.643 | 5.063 | 0.156 * | −0.107 | 0.488 *** | 0.638 *** | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6. Aggression: Hostility | 16.837 | 4.986 | 0.221 *** | −0.261 *** | 0.373 *** | 0.412 *** | 0.578 *** | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||
| 7. Aggression: Self-aggression | 9.996 | 3.981 | 0.248 *** | −0.098 | 0.421 *** | 0.360 *** | 0.598 *** | 0.603 *** | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||
| 8. Overall score of Aggression | 65.702 | 16.863 | 0.257 *** | −0.162 ** | 0.711 *** | 0.724 *** | 0.864 *** | 0.789 *** | 0.773 *** | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||
| 9. Antisaccade task | 0.939 | 0.076 | 0.076 | 0.015 | −0.031 | 0.043 | 0.060 | −0.015 | −0.014 | 0.011 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||
| 10. Go/No-go task | 0.779 | 0.188 | 0.034 | 0.006 | 0.021 | −0.004 | 0.028 | 0.044 | 0.017 | 0.030 | 0.321 *** | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| 11.%Choicewin & advantage | 0.735 | 0.223 | 0.039 | 0.023 | 0.051 | 0.106 | −0.015 | −0.036 | −0.048 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.092 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| 12.%Choicewin & disadvantage | 0.070 | 0.165 | −0.048 | 0.108 | −0.020 | −0.116 | −0.101 | −0.081 | 0.045 | −0.072 | 0.062 | −0.016 | 0.118 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| 13.%Choicewin & neutral | 0.275 | 0.242 | −0.005 | 0.098 | 0.041 | 0.004 | −0.017 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.468 *** | 0.582 *** | 1.000 | |||||||||
| 14.%Choiceloss & advantage | 0.874 | 0.187 | 0.005 | 0.014 | 0.055 | 0.072 | −0.006 | −0.044 | −0.096 | −0.009 | 0.008 | 0.049 | 0.349 *** | −0.236 *** | 0.013 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| 15.%Choiceloss & disadvantage | 0.168 | 0.216 | −0.140 * | −0.002 | 0.013 | −0.117 | −0.052 | 0.002 | 0.073 | −0.018 | −0.098 | −0.149 * | −0.126 * | 0.319 *** | 0.185 ** | 0.182 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| 16.%Choiceloss & neutral | 0.589 | 0.286 | −0.112 | −0.016 | 0.015 | −0.059 | −0.008 | −0.002 | −0.011 | −0.013 | −0.016 | 0.038 | 0.159 * | 0.030 | 0.164 ** | 0.624 *** | 0.509 *** | 1.000 | ||||||
| 17.Gaming addiction: Salience | 6.119 | 2.869 | 0.893 *** | 0.024 | 0.218 *** | 0.154 ** | 0.123 | 0.180 ** | 0.181 ** | 0.219 *** | 0.079 | 0.052 | −0.016 | −0.026 | −0.016 | −0.010 | −0.116 | −0.0127 * | 1.000 | |||||
| 18.Gaming addiction: Mood | 8.786 | 2.340 | 0.473 *** | −0.025 | 0.163 ** | 0.103 | 0.021 | 0.154 * | 0.153 * | 0.150 * | −0.003 | 0.050 | 0.048 | −0.001 | 0.038 | −0.017 | −0.043 | −0.059 | 0.432 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| 19.Gaming addiction: Tolerance | 6.623 | 2.745 | 0.845 *** | 0.019 | 0.148* | 0.126* | 0.107 | 0.170 ** | 0.203 ** | 193** | 0.072 | 0.026 | 0.036 | −0.026 | 0.007 | 0.049 | −0.094 | −0.048 | 0.771 *** | 0.389 *** | 1.000 | |||
| 20.Gaming addiction: Withdrawal | 5.254 | 2.249 | 0.838 *** | −0.091 | 0.231 *** | 0.167 *** | 0.106 * | 0.245 *** | 0.244 *** | 270 *** | 0.059 | −0.020 | −0.006 | −0.017 | −0.053 | 0.007 | −0.072 | −0.082 | 0.673 *** | 0.368 *** | 0.643 *** | 1.000 | ||
| 21.Gaming addiction: Conflict | 10.190 | 2.853 | 0.703 *** | −0.003 | 0.163 ** | 0.203 ** | 0.109 | 0.157 * | 0.210 *** | 0.210 *** | 0.023 | −0.062 | 0.023 | −0.012 | −30.774 × 10−4 | 0.006 | −5.784 × 10−4 | −0.082 | 0.631 *** | 0.393 *** | 0.573 *** | 0.644 *** | 1.000 | |
| 22.Gaming addiction: Relapse | 5.774 | 2.802 | 0.835 *** | 0.025 | 0.165 ** | 0.149 * | 0.156 * | 0.135 * | 0.220 ** | 210 *** | 0.033 | 0.019 | 0.079 | −0.009 | 0.068 | 0.010 | −0.099 | −0.114 | 0.727 *** | 0.347 *** | 0.641 *** | 0.643 *** | 0.579 *** | 1.000 |
| Variable | 11.awin & advantage | 12.awin & disadvantage | 13.awin & neutral | 14.vwin & advantage | 15.vwin & disadvantage | 16.vwin & neutral | 17.twin | 18.aloss & advantage | 19.aloss & disadvantage | 20.aloss & neutral | 21.vloss & advantage | 22.vloss & disadvantage | 23.vloss & neutral | 24.tloss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gaming addiction | −0.042 | −0.053 | −0.022 | 0.041 | −0.108 | −0.052 | −0.009 | −0.076 | 0.004 | −0.058 | 0.025 | −0.25 *** | −0.106 | −0.037 |
| 2. Antisaccade task | −0.033 | −0.054 | 0.037 | 0.024 | 0.054 | 0.052 | −0.008 | −0.018 | 0.059 | 0.038 | 0.025 | −0.078 | −0.022 | −0.023 |
| 3. Go/No-go task | 0.076 | 0.05 | 0.097 | 0.059 | 0.009 | 0.047 | 0.091 | 0.091 | 0.191 ** | 0.142 * | −0.029 | −0.125 * | −0.01 | 0.143 * |
| 4. Prosocial tendencies measure | −0.114 | −0.089 | −0.116 | 0.046 | 0.062 | 0.091 | −0.105 | −0.152 * | −0.125 * | −0.168 ** | 0.055 | −0.002 | 0.029 | −0.035 |
| 5. Aggression: Physical | −0.099 | −0.115 | −0.123 | 0.04 | −0.105 | −0.016 | −0.028 | −0.08 | −0.062 | −0.094 | 0.075 | −0.052 | 0.024 | −0.082 |
| 6. Aggression: Verbal | −0.016 | −0.056 | −0.046 | 0.088 | −0.126 * | −0.015 | −0.004 | −0.034 | −0.026 | −0.049 | 0.067 | −0.164 * | −0.074 | −0.129 * |
| 7. Aggression: Anger | −0.033 | −0.047 | −0.038 | −0.024 | −0.130 * | −0.052 | 0.024 | −0.049 | −0.031 | −0.038 | −0.011 | −0.086 | −0.048 | −0.045 |
| 8. Aggression: Hostility | 0.019 | 0.031 | −0.009 | −0.043 | −0.136 * | −0.03 | 0.015 | −0.006 | −0.008 | −0.022 | −0.033 | −0.091 | −0.035 | −0.007 |
| 9. Aggression: Self-aggression | −0.064 | −0.093 | −0.08 | −0.038 | −0.041 | −0.026 | 0.04 | −0.139 * | −0.108 | −0.121 | −0.037 | −0.03 | −0.016 | −0.019 |
| 10. Overall score of Aggression | −0.048 | −0.067 | −0.074 | −0.001 | −0.141 * | −0.038 | 0.013 | −0.076 | −0.058 | −0.08 | 0.01 | −0.105 | −0.037 | −0.066 |
| Variable | M | SD |
|---|---|---|
| awin & advantage | 1.783 | 0.030 |
| awin & disadvantage | 1.954 | 0.033 |
| awin & neutral | 1.812 | 0.030 |
| aloss & advantage | 2.203 | 0.043 |
| aloss & disadvantage | 2.454 | 0.044 |
| aloss & neutral | 2.178 | 0.041 |
| vwin & advantage | 0.842 | 0.070 |
| vwin & disadvantage | −1.959 | 0.072 |
| vwin & neutral | −0.810 | 0.070 |
| vloss & advantage | 1.347 | 0.065 |
| vloss & disadvantage | −1.095 | 0.064 |
| vloss & neutral | 0.276 | 0.063 |
| twin | 0.430 | 0.007 |
| tloss | 0.413 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, B. When Games Influence Words: Gaming Addiction among College Students Increases Verbal Aggression through Risk-Biased Drifting in Decision-Making. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080699
Teng H, Zhu L, Zhang X, Qiu B. When Games Influence Words: Gaming Addiction among College Students Increases Verbal Aggression through Risk-Biased Drifting in Decision-Making. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(8):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080699
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Huina, Lixin Zhu, Xuanyu Zhang, and Boyu Qiu. 2024. "When Games Influence Words: Gaming Addiction among College Students Increases Verbal Aggression through Risk-Biased Drifting in Decision-Making" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 8: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080699
APA StyleTeng, H., Zhu, L., Zhang, X., & Qiu, B. (2024). When Games Influence Words: Gaming Addiction among College Students Increases Verbal Aggression through Risk-Biased Drifting in Decision-Making. Behavioral Sciences, 14(8), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080699






