Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems in Chinese Children: The Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation in a Multi-Level Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Shyness and Internalizing Problems in China
1.2. Shyness and Internalizing Problems: Mediating Role of Sport Engagement
1.3. Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation
1.4. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Shyness
2.2.2. Sport Engagement and Class Sport Participation
2.2.3. Depression
2.2.4. Social Anxiety
2.2.5. Loneliness
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Plan of Data Analysis
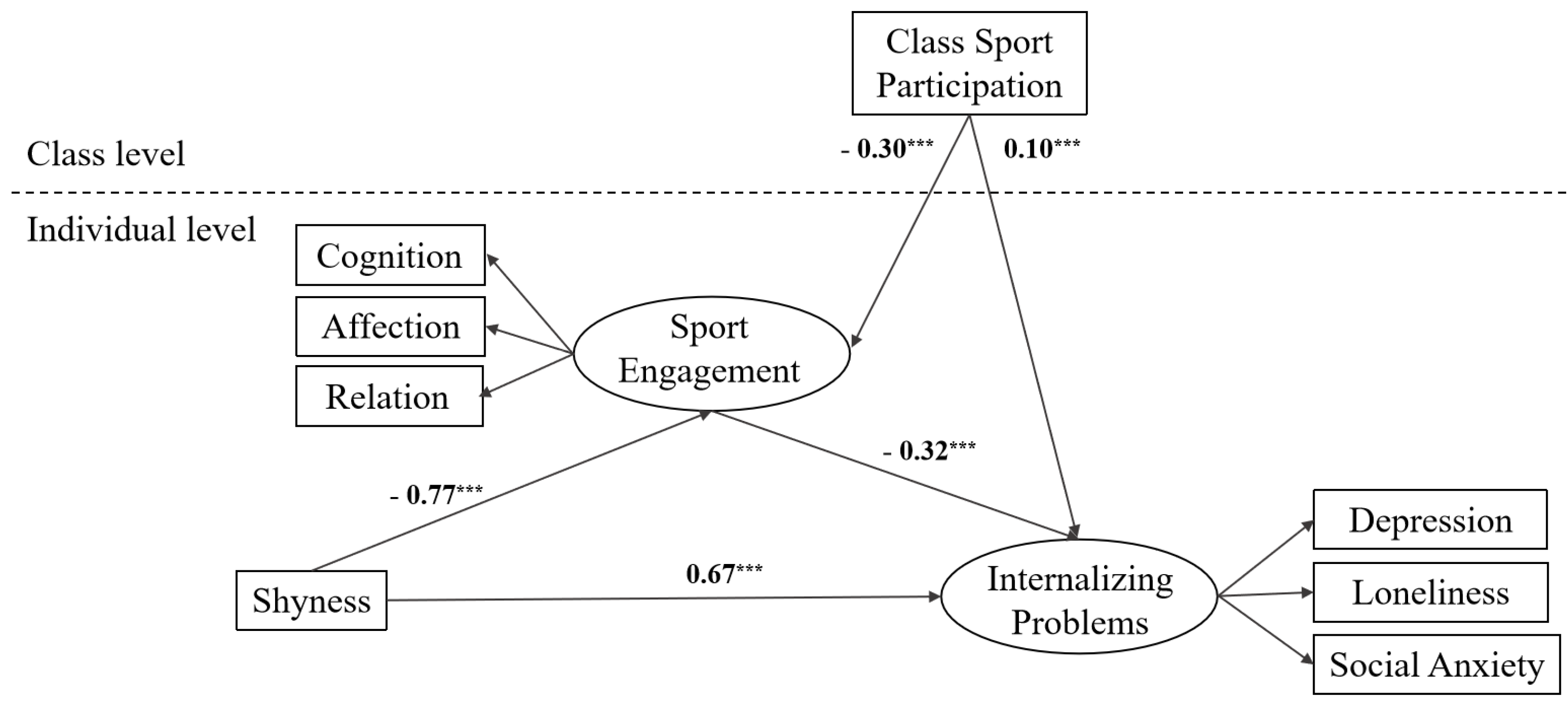
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
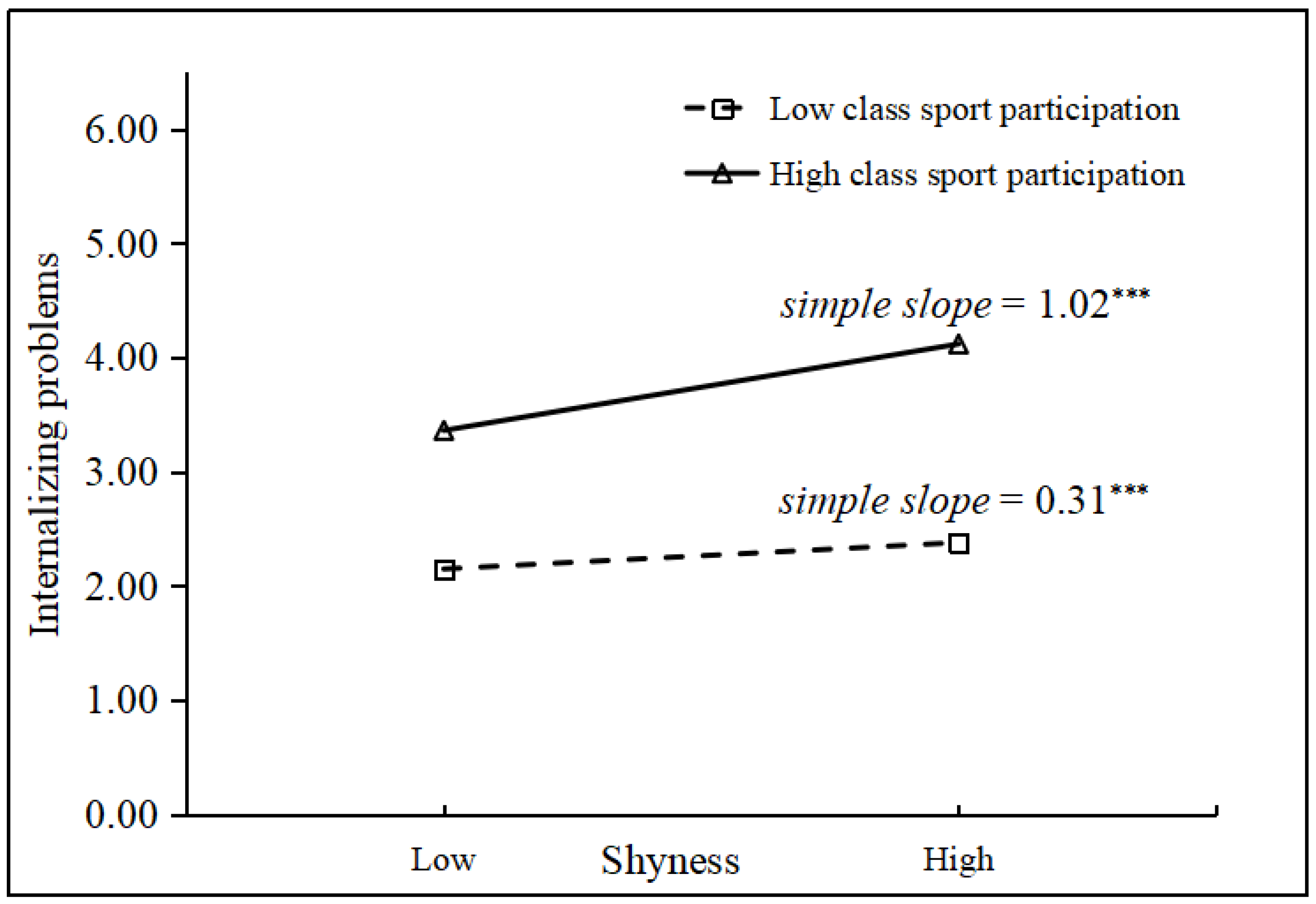
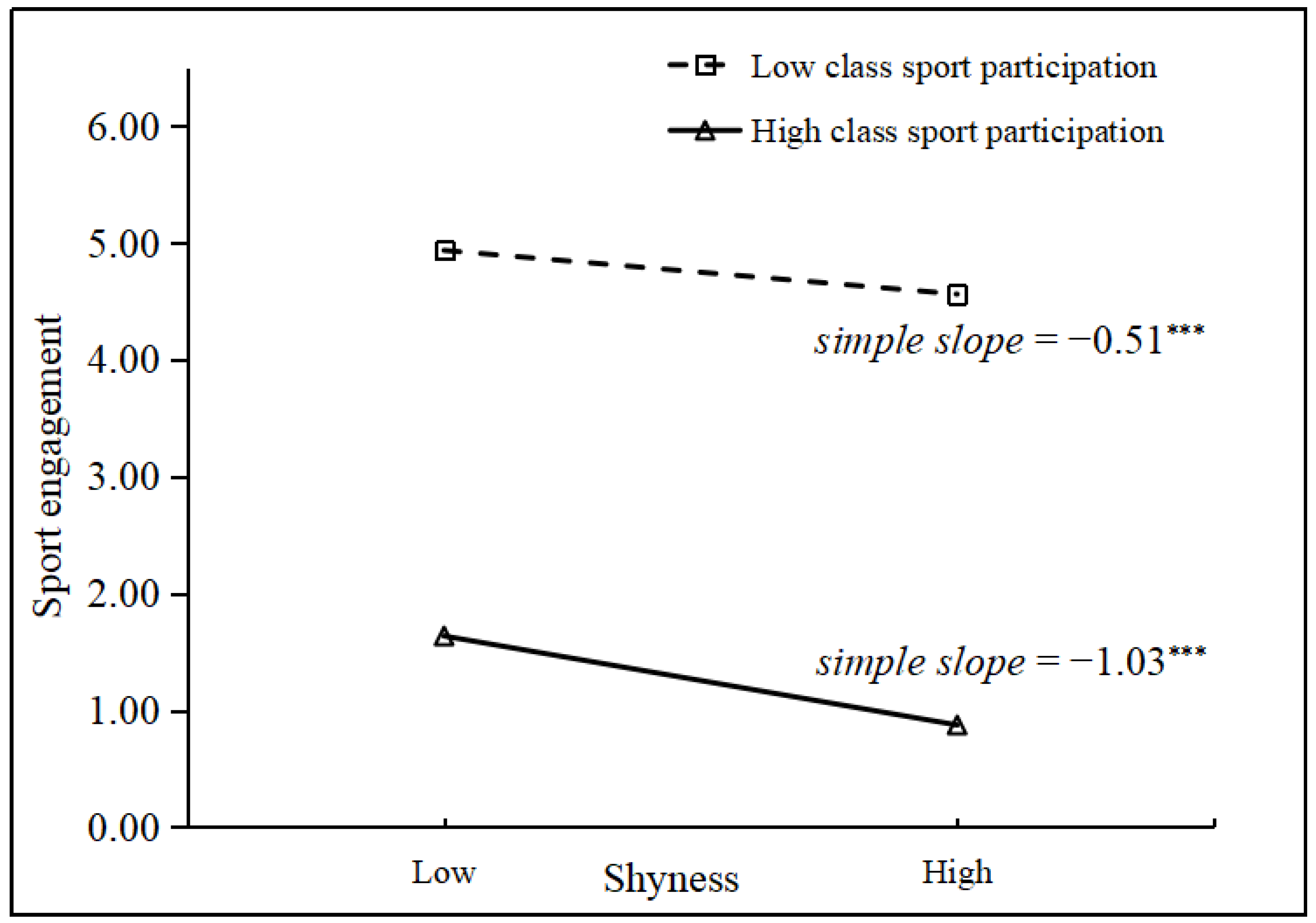
3.2. Testing Cross-Level Moderated Mediation Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems
4.2. Role of Class Sport Participation
4.3. Limitations and Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crozier, W.R. Shyness and self-esteem in middle childhood. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 1995, 65, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, H.H.; Lemery, K.S.; Aksan, N.; Buss, K.A. Temperamental substrates of personality development. In Temperament and Personality Development across the Life Span; Molfese, V.J., Molfese, D.L., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Asendorpf, J.B. Beyond social withdrawal: Shyness, unsociability, and peer avoidance. Hum. Dev. 1990, 33, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplan, R.J.; DeBow, A.; Schneider, B.H.; Graham, A.A. The social behaviors of extremely inhibited children in and out of preschool. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 2009, 27, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baardstu, S.; Coplan, R.J.; Karevold, E.B.; Laceulle, O.M.; von Soest, T. Longitudinal pathways from shyness in early childhood to personality in adolescence: Do peers matter? J. Res. Adolesc. 2020, 30, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Ooi, L.L.; Coplan, R.J.; Zhu, X.; Sang, B. Relations between social withdrawal subtypes and socio-emotional adjustment among Chinese children and early adolescents. J. Res. Adolesc. 2023, 33, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.H.; Coplan, R.J.; Bowker, J.C. Social withdrawal in childhood. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2009, 60, 141–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilmette, M.; Mulvihill, K.; Villemaire-Krajden, R.; Barker, E.T. Past and present participation in extracurricular activities is associated with adaptive self-regulation of goals, academic success, and emotional well-being among university students. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2019, 73, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, H.L.; Busseri, M.A.; Khanna, N.; Hamilton, Y.N.; Ottawa, Y.N.; Rose-Krasnor, L. Youth engagement and suicide risk: Testing a mediated model in a Canadian community sample. J. Youth Adolesc. 2010, 39, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Guo, H.; Yi, H. Use IoT in physical education and sport in China schools. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 8133279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busseri, M.A.; Rose-Krasnor, L.; Mark Pancer, S.; Pratt, M.W.; Adams, G.R.; Birnie-Lefcovitch, S.; Polivy, J.; Gallander Wintre, M. A longitudinal study of breadth and intensity of activity involvement and the transition to university. J. Adolesc. Res. 2011, 21, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, G.W.; Kochenderfer-Ladd, B.; Eggum, N.D.; Kochel, K.P.; McConnell, E.M. Characterizing and comparing the friendships of anxious-solitary and unsociable preadolescents. Child Dev. 2011, 82, 1434–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkley, L.C.; Capitanio, J.P. Perceived social isolation, evolutionary fitness and health outcomes: A lifespan approach. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollendick, T.H.; Hirshfeld-Becker, D.R. The developmental psychopathology of social anxiety disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, A.; Collishaw, S.; Pine, D.S.; Thapar, A.K. Depression in adolescence. Lancet 2012, 379, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, E.V.; Boivin, M.; Vitaro, F.; Bukowski, W.M. The power of friendship: Protection against an escalating cycle of peer victimization. Dev. Psychol. 1999, 35, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.H.; LeMare, L.J.; Lollis, S. Social withdrawal in childhood: Developmental pathways to peer rejection. In Peer Rejection in Childhood; Asher, S.R., Coie, J.D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; pp. 217–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bowker, J.C.; Raja, R. Social withdrawal sub-types during early adolescence in India. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2011, 39, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahng, K.E.; Kim, Y. Relationships between children’ s shyness, play disconnection, and loneliness: Moderating effect of children’ s perceived child-teacher intimate relationship. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2021, 52, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.E.; Lee, K.H. The mediating effect of friendship quality sub-factors on the relationship of shyness and loneliness: With a focus on 5th, 6th grade boys and girls. Stud. Korean Youth 2009, 53, 65–89. [Google Scholar]
- Coplan, R.J.; Rose-Krasnor, L.; Weeks, M.; Kingsbury, A.; Kingsbury, M.; Bullock, A. Alone is a crowd: Social motivations, social withdrawal, and socioemotional functioning in later childhood. Dev. Psychol. 2013, 49, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Liu, J. Relations of shyness and unsociability with adjustment in migrant and non-migrant children in urban China. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2020, 48, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, B.; Ding, X.; Coplan, R.J.; Liu, J.; Pan, T.; Feng, X. Assessment and implications of social avoidance in Chinese early adolescents. J. Early Adolesc. 2018, 38, 554–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, X. Shyness and psychological maladjustment in Chinese adolescents: Selection and influence processes in friendship networks. J. Youth Adolesc. 2021, 50, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Q.; Ding, X. Relation between social avoidance and loneliness in urban Chinese children: A moderated-mediation model. Eur. J. Dev. Psychol. 2024, 21, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, W. Relationship between shyness and loneliness among Chinese adolescents: Social support as mediator. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2016, 44, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, J.C.; Anderson, C.A. Loneliness, shyness, and depression: The etiology and interrelationships of everyday problems in living. In The Interactional Nature of Depression: Advances in Interpersonal Approaches; Joiner, T., Coyne, J.C., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 93–125. [Google Scholar]
- Coplan, R.J.; Prakash, K.; O’ Neil, K. Do you “want” to play? Distinguishing between conflicted shyness and social disinterest in early childhood. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coplan, R.J.; Arbeau, K.A.; Armer, M. Don’t fret, be supportive! Maternal characteristics linking child shyness to psychosocial and school adjustment in kindergarten. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2008, 36, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, L. Relations between shyness-sensitivity and internalizing problems in Chinese children: Moderating effects of academic achievement. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2013, 41, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggum-Wilkens, N.D.; Valiente, C.; Swanson, J.; Lemery-Chalfant, K. Children’ s shyness, popularity, school liking, cooperative participation, and internalizing problems in the early school years. Early Child. Res. Q. 2014, 29, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Coplan, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, Z. Assessment and implications of aloneliness in Chinese children and early adolescents. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2023, 85, 101514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.M.; Wells, A. A cognitive model of social phobia. In Social Phobia: Diagnosis, Assessment, and Treatment; Heimberg, R.G., Liebowitz, M., Hope, D., Scheier, F., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Weeks, M.; Ooi, L.L.; Coplan, R.J. Cognitive biases and the link between shyness and social anxiety in early adolescence. J. Early Adolesc. 2016, 36, 1095–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöte, A.W.; Miers, A.C.; Van den Bos, E.; Westenberg, P.M. Negative social self-cognitions: How shyness may lead to social anxiety. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2019, 63, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Coplan, R.J.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Sang, B. Self-reported shyness in Chinese children: Validation of the children’ s shyness questionnaire and exploration of its links with adjustment and the role of coping. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 68, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Brook, C.A.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Schmidt, L.A. Shyness sub-types and associations with social anxiety: A comparison study of Canadian and Chinese children. Dev. Sci. 2023, e13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, G.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, H. Behavioral inhibition system and self-esteem as mediators between shyness and social anxiety. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 270, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Culture and shyness in childhood and adolescence. New Ideas Psychol. 2019, 53, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, P.M.; Suzuki, L.K.; Rothstein-Fisch, C. Cultural pathways through human development. In Handbook of Child Psychology; Renninger, K.A., Sigel, I.E., Damon, W., Lerner, R.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 655–699. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Farver, J.A.M.; Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, L. Moving away or fitting in? Understanding shyness in Chinese children. Merrill. Palmer. Q. 2007, 53, 527–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Shyness-inhibition in childhood and adolescence: A cross-cultural perspective. In The Development of Shyness and Social Withdrawal; Rubin, K.H., Coplan, R.J., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 213–235. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bowker, J.C.; Coplan, R.J.; Yang, P.; Li, D.; Chen, X. Evaluating links among shyness, peer relations, and internalizing problems in Chinese young adolescents. J. Res. Adolesc. 2019, 29, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cen, G.; Li, D.; He, Y. Social functioning and adjustment in Chinese children: The imprint of historical time. Child Dev. 2005, 76, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; French, D. Shyness-sensitivity, aggression, and adjustment in urban Chinese adolescents at different historical times. J. Res. Adolesc. 2012, 22, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, H.L.; Rose-Krasnor, L.; Busseri, M.A.; Gadbois, S.; Bowker, A.; Findlay, L. Measuring psychological engagement in youth activity involvement. J. Adolesc. 2015, 45, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Bullock, A.; Coplan, R.J. Shyness, extracurricular activity engagement, and internalizing problems among emerging adults in university. Canadian J. Behav. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.H.; Younger, A.J.; Smith, T.; Freeman, P. A longitudinal exploration of the cross-contextual stability of social withdrawal in early adolescence. J. Early Adolesc. 1998, 18, 374–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.; Coplan, R.J. Shy skaters? Shyness, coping, and adjustment outcomes in female adolescent figure skaters. Athl. Insight 2003, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.R. I don’t want to get involved: Shyness, psychological control, and youth activities. J. Soc. Pers. Relat. 2012, 29, 908–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, L.C.; Coplan, R.J. Come out and play: Shyness in childhood and the benefits of organized sports participation. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 2008, 40, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.C.; Nickerson, P.; Wright, K.L. Structured leisure activities in middle childhood: Links to well-being. J. Community Psychol. 2003, 31, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, A.; Dimech, A.; Seiler, R. Extra-curricular sport participation: A potential buffer against social anxiety symptoms in primary school children. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2011, 12, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.M.; Frey, J.; Talbert, R.; Falk, C. Children’ s feelings of loneliness and social dissatisfaction: Relationship to measures of physical fitness and activity. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 1992, 11, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, S.M.; Crouter, A.C.; Tucker, C. Free-time activities in middle childhood: Links with adjustment in early adolescence. Child Dev. 2001, 72, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfebrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development: Experiments by Nature and Design; Harvard University Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L. The role of classroom norms in contextualizing the relations of children’ s social behaviors to peer acceptance. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, T.; Säfvenbom, R.; Ommundsen, Y. Sport participation and loneliness in adolescents: The mediating role of perceived social competence. Curr. Psychol. 2013, 32, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, A.; Denault, A.S.; Poulin, F. Organized activities during high school and adjustment one year post high school: Identifying social mediators. J. Youth Adolesc. 2015, 44, 1638–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmivalli, C. Peer victimization and adjustment in young adulthood: Commentary on the special section. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2018, 46, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmore, A.; Witkow, M.; Graham, S.; Juvonen, J. Beyond the individual: The impact of ethnic context and classroom behavioral norms on victims’ adjustment. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alden, L.E.; Phillips, N. An interpersonal analysis of social anxiety and depression. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1990, 14, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, M.A.; Belkin, D.K. Attributional style in shyness and depression: Shared and specific maladaptive patterns. Cognit. Ther. Res. 2001, 25, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkhus, M.; McVarnock, A.; Coplan, R.J.; Ulset, V.; Kraft, B. Developmental changes in the structure of shyness and internalizing symptoms from early to middle childhood: A network analysis. Child Dev. 2023, 94, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplan, R.J.; Ooi, L.L.; Baldwin, D. Does it matter when we want to be alone? Exploring developmental timing effects in the implications of unsociability. New Ideas Psychol. 2019, 53, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, K.H.; Bukowski, W.M.; Bowker, J.C. Children in peer groups. In Handbook of Child Psychology and Developmental Science; Lerner, R.M., Bornstein, M.H., Leventhal, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 175–222. [Google Scholar]
- Busseri, M.A.; Rose-Krasnor, L. Subjective experiences in activity involvement and perceptions of growth in a sample of first-year female university students. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2008, 49, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 2nd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, M. The Children’ s Depression Inventory (CDI) Manual, 1st ed.; Multi-Health Systems: Oppenheim, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Coplan, R.J.; Deng, X.; Ooi, L.L.; Li, D.; Sang, B. Sad, scared, or rejected? A short-term longitudinal study of the predictors of social avoidance in Chinese children. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2019, 47, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Greca, A.M.; Stone, W.L. Social Anxiety Scale for Children-Revised: Factor structure and concurrent validity. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 1993, 22, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Coplan, R.J.; Ooi, L.L.; Chen, X.; Li, D. Examining the implications of social anxiety in a community sample of Chinese mainland children. J. Clin. Psychol. 2015, 71, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, S.R.; Hymel, S.; Renshaw, P.D. Loneliness in children. Child Dev. 1984, 55, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jin, G.; Ren, T.; Haidabieke, A.; Chen, L.; Ding, X. Relations between Prosociality and Psychological Maladjustment in Chinese Elementary and Secondary School Students: Mediating Roles of Peer Preference and Self-Perceived Social Competence. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, A.S.; Raudenbush, S.W. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Coplan, R.J.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Y. Unsociability and shyness in Chinese children: Concurrent and predictive relations with indices of adjustment. Soc. Dev. 2014, 23, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualter, P.; Rouncefield-Swales, A.; Bray, L.; Blake, L.; Allen, S.; Probert, C.; Crook, K.; Carter, B. Depression, anxiety, and loneliness among adolescents and young adults with IBD in the UK: The role of disease severity, age of onset, and embarrassment of the condition. Qual. Life Res. 2021, 30, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, C.K.; Tofighi, D. Centering predictor variables in cross-sectional multilevel models: A new look at an old issue. Psychol. Methods 2007, 12, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Coplan, R.J.; Closson, L.; Arbeau, K. Gender differences in the behavioral associates of loneliness and social dissatisfaction in kindergarten. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Coplan, R.J. Exploring the processes linking shyness and academic achievement in childhood. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2010, 25, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volbrecht, M.M.; Goldsmith, H.H. Early temperamental and family predictors of shyness and anxiety. Dev. Psychol. 2010, 46, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.M.; Zarco, E.P. Shyness, physical activity, and sports team participation among Philippine high school students. Child Study J. 2001, 31, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.R.; Coll, E. From social withdrawal to social confidence: Evidence for possible pathways. Curr. Psychol. 2007, 26, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, A.M.; Aikins, J.W.; Edidin, J. The role of organized activities in facilitating social adaptation across the transition to college. J. Adolesc. Res. 2007, 22, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, C.; Menezes, M.; Sadikova, E.; Mazurek, M. Friendship and anxiety/depression symptoms in boys with and without autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2023, 128, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekauc, D.; Reimers, A.K.; Wagner, M.O.; Woll, A. Physical activity in sports clubs of children and adolescents in Germany: Results from a nationwide representative survey. Z. Gesundh. Wiss. 2013, 21, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.W.; Hansen, D.M.; Moneta, G. Differing profiles of developmental experiences across types of organized youth activities. Dev. Psychol. 2006, 42, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipson, W.E.; Coplan, R.J.; Séguin, D.G. Active emotion regulation mediates links between shyness and social adjustment in preschool. Soc. Dev. 2019, 28, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Brown, C. Susceptibility to peer pressure among adolescents: Biological, demographic, and peer-related determinants. J. Stud. Res. 2023, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.G. A Monte Carlo study of the effects of correlated method variance in moderated multiple regression analysis. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1985, 36, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemsen, E.; Roth, A.; Oliveira, P. Common method bias in regression models with linear, quadratic, and interaction effects. Organ. Res. Methods 2010, 13, 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Valente, M.J. Mediation from multilevel to structural equation modeling. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 65, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Beretvas, S.N. Sample size limits for estimating upper level mediation models using multilevel SEM. Struct. Equ. Model. 2013, 20, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.; Won, D.; Park, S. School engagement, self-esteem, and depression of adolescents: The role of sport participation and volunteering activity and gender differences. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 113, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Boys | Girls |
|---|---|---|
| Shyness | 1.44 (0.45) | 1.56 (0.41) |
| Cognitive engagement | 3.25 (0.77) | 2.87 (0.81) |
| Affective engagement | 3.28 (0.81) | 2.93 (0.92) |
| Relational engagement | 3.20 (0.84) | 2.97 (0.91) |
| Social anxiety | 1.99 (0.84) | 2.20 (0.91) |
| Depression | 1.40 (0.33) | 1.42 (0.38) |
| Loneliness | 1.92 (0.71) | 1.90 (0.75) |
| Individual sport participation | 24.28 (11.52) | 22.68 (12.08) |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Shyness | - | ||||||
| 2. Cognitive engagement | −0.31 ** | - | |||||
| 3. Affective engagement | −0.32 ** | 0.79 ** | - | ||||
| 4. Relational engagement | −0.30 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.77 ** | - | |||
| 5. Depression | 0.53 ** | −0.37 ** | −0.39 ** | −0.41 ** | - | ||
| 6. Loneliness | 0.47 ** | −0.35 ** | −0.36 ** | −0.40 ** | 0.64 ** | - | |
| 7. Social anxiety | 0.74 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.32 ** | −0.33 ** | 0.65 ** | 0.54 ** | - |
| 8. Class sport participation | 0.11 ** | −0.15 ** | −0.11 ** | −0.08 * | 0.14 ** | −0.02 | 0.14 ** |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internalizing Problems | Sport Engagement | Internalizing Problems | Sport Engagement | Internalizing Problems | |
| Individual level | |||||
| Gender | −0.03 (0.03) | −0.15 *** (0.03) | −0.08 ** (0.03) | 0.35 *** (0.08) | 0.28 *** (0.07) |
| ISP | −0.09 *** (0.03) | 0.26 *** (0.04) | −0.03 (0.03) | 0.04 *** (0.01) | −0.01 ** (0.01) |
| Shyness | 0.79 *** (0.02) | −0.31 *** (0.03) | 0.71 *** (0.03) | −0.77 *** (0.12) | 0.67 *** (0.26) |
| Sport engagement | −0.24 *** (0.04) | −0.32 *** (0.07) | |||
| Class level | |||||
| Class size | −0.01 (0.14) | −0.03 (0.09) | |||
| CSP | −0.30 *** (0.03) | 0.10 *** (0.03) | |||
| Shyness × CSP | −0.06 ** (0.03) | 0.09 * (0.04) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; Kong, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Ding, X. Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems in Chinese Children: The Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation in a Multi-Level Model. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080661
Zhao R, Kong X, Li M, Zhu X, Wang J, Ding W, Ding X. Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems in Chinese Children: The Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation in a Multi-Level Model. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(8):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080661
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Rumei, Xiaoxue Kong, Mingxin Li, Xinyi Zhu, Jiyueyi Wang, Wan Ding, and Xuechen Ding. 2024. "Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems in Chinese Children: The Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation in a Multi-Level Model" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 8: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080661
APA StyleZhao, R., Kong, X., Li, M., Zhu, X., Wang, J., Ding, W., & Ding, X. (2024). Shyness, Sport Engagement, and Internalizing Problems in Chinese Children: The Moderating Role of Class Sport Participation in a Multi-Level Model. Behavioral Sciences, 14(8), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080661







