Evaluating Two Brief Motivational Interventions for Excessive-Drinking University Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Baseline Assessment
2.3. Computer Software
2.4. Follow-Up Assessment
2.5. Procedure
2.6. Interventions
2.6.1. Computerized Brief Intervention
2.6.2. Enhanced Computerized Brief Intervention
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
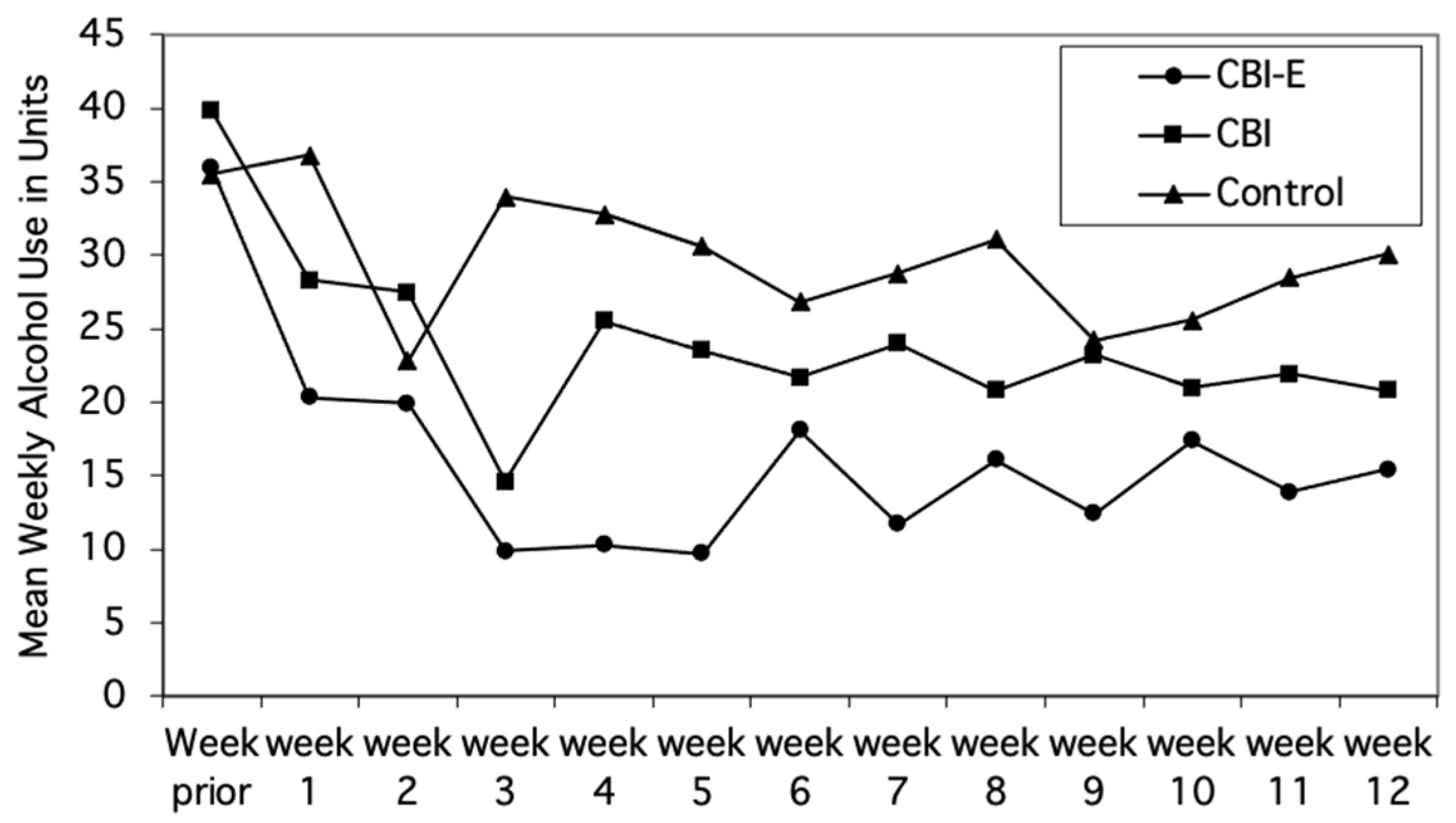
3.2. Changes in Drinking at Follow-Up
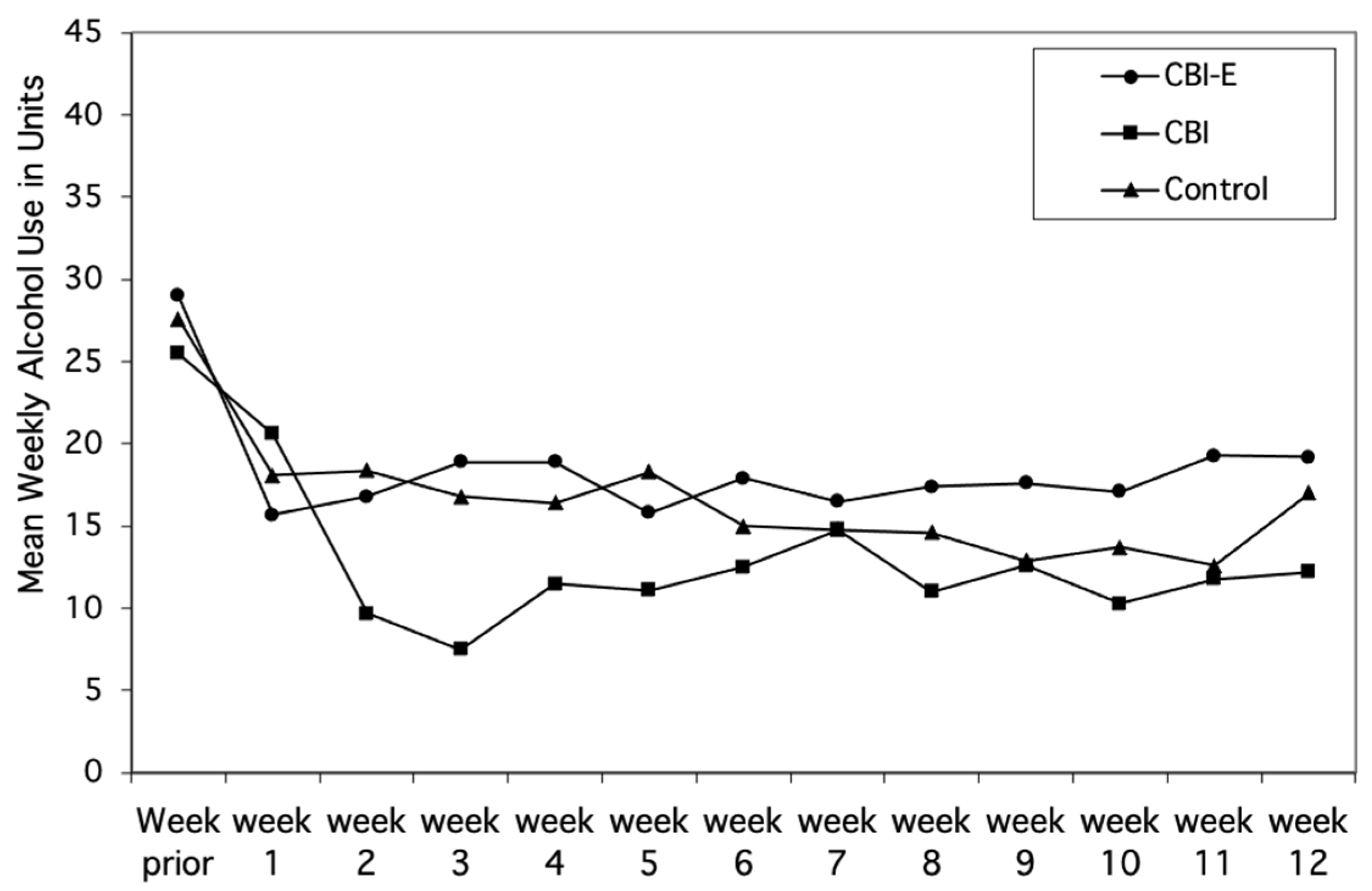
3.3. Reductions in Binge Drinking
4. Discussion
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagheri, M.; Cox, W.M. Self-regulation, adaptive motivation, and alcohol consumption: Understanding university students’ motivation for drinking. J. Subst. Use 2024, 29, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Hosier, S.G.; Crossley, S.; Kendall, B.; Roberts, K.L. Motives for drinking, alcohol consumption, and alcohol-related problems among British secondary-school and university students. Addict. Behav. 2006, 31, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helle, A.C.; Boness, C.L.; Sher, K.J. College students’ receptiveness to intervention approaches for alcohol and cannabis use. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2022, 36, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moagi, M.M.; van der Wath, A.E. Demand for alcohol use among students at higher education institutions: An integrative literature review. J. Subst. Use 2023, 28, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.K.; Pearson, M.R.; Field, C.A. A comprehensive examination of alcohol-related motivations among college students: Unique relations of drinking motives and motivations for drinking responsibly. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 30, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Alcohol and its effects on the body. In Why People Drink; How People Change: A Guide to Alcohol and People’s Motivation for Drinking It; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gajda, M.; Sedlaczek, K.; Szemik, S.; Kowalska, M. Determinants of Alcohol Consumption among Medical Students: Results from POLLEK Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiClemente, C.C.; Corno, C.M.; Graydon, M.M.; Wiprovnick, A.E.; Knoblach, D.J. Motivational interviewing, enhancement, and brief interventions over the last decade: A review of reviews of efficacy and effectiveness. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2017, 31, 862–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimer, M.E.; Kilmer, J.R.; Cronce, J.M.; Hultgren, B.A.; Gilson, M.S.; Lee, C.M. Thirty years of BASICS: Dissemination and implementation progress and challenges. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2022, 36, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, A.W.; Marlatt, G.A. Motivational enhancement as a brief intervention for college student drinkers. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems, 2nd ed.; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 531–547. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.R.; Rollnick, S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People to Change Addictive Behavior; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 1991.
- Miller, W.R.; Rollnick, S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change, 2nd ed.; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2002.
- Miller, W.R.; Rollnick, S. Motivational Interviewing: Helping People Change, 3rd ed.; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Resnicow, K.; Rollnick, S. Motivational interviewing in health promotion and behavioral medicine. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems, 2nd ed.; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 591–605. [Google Scholar]
- Demmel, R. Motivational Interviewing: A Review. Addict. J. Sci. Pract. 2001, 47, 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, B.L.; Arkowitz, H.; Menchola, M. The efficacy of motivational interviewing: A meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2003, 71, 843–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.; Campbell, P.; Maxwell, M.; O’Carroll, R.E.; Dombrowski, S.U.; Williams, B.; Cheyne, H.; Coles, E.; Pollock, A. Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on adult behaviour change in health and social care settings: A systematic review of reviews. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundahl, B.; Burke, B.L. The effectiveness and applicability of motivational interviewing: A practice-friendly review of four meta-analyses. J. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 65, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magill, M.; Gaume, J.; Apodaca, T.R.; Walthers, J.; Mastroleo, N.R.; Borsari, B.; Longabaugh, R. The technical hypothesis of motivational interviewing: A meta-analysis of MI’s key causal model. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 82, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilaki, E.I.; Hosier, S.G.; Cox, W.M. The efficacy of motivational interviewing as a brief intervention for excessive drinking: A meta-analytic review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006, 41, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, A.S.; Rosenbaum, L.; Sheperis, D. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of motivational enhancement therapy for reducing substance use. J. Addict. Offender Couns. 2016, 37, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Leffingwell, T.; Claborn, K.; Meier, E.; Walters, S.; Neighbors, C. Personalized feedback interventions for college alcohol misuse: An update of Walters & Neighbors (2005). Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2013, 27, 909–920. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Systematic Motivational Counseling: From motivational assessment to motivational change. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems, 2nd ed.; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 275–302. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. A motivational model of alcohol use. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1988, 97, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Incentive motivation, affective change, and alcohol use: A model. In Why People Drink: Parameters of Alcohol as a Reinforcer; Cox, W.M., Ed.; Psychology Press: Gardner, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. A motivational model of alcohol use: Determinants of use and change. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Concepts, Approaches, and Assessment; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. A motivational model of alcohol use: Determinants of use and change. In Handbook of Motivational Counselling. Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 131–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Why People Drink; How People Change: A Guide to Alcohol and People’s Motivation for Drinking It; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Fadardi, J.S.; Hosier, S.G.; Pothos, E.M. Differential effects and temporal course of attentional and motivational training on excessive drinking. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 23, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, Z.V.; Shamloo, Z.S.; Fadardi, J.S. Comparing the effectiveness of the Life Enhancement and Advancement Program and reality therapy on improving in-treatment substance abusers’ recovery indices. Res. Clin. Psychol. Couns. 2013, 3, 99–118. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Measuring motivation: The Motivational Structure Questionnaire, Personal Concerns Inventory, and their variants. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 161–204. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, W.M.; Klinger, E. Motivational structure: Relationships with substance use and processes of change. Addict. Behav. 2002, 27, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Schippers, G.M.; Klinger, E.; Skutle, A.; Stuchlíková, I.; Man, F.; King, A.L.; Inderhaug, I. Motivational structure and alcohol use of university students with consistency across four nations. J. Stud. Alcohol 2002, 63, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, S.T.; Neighbors, C. Feedback interventions for college alcohol misuse: What, why and for whom? Addict. Behav. 2005, 30, 1168–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hogan, L.; Patterson, C.W.; Cox, M. Accurately estimating alcohol consumption: A comparison of self-administrated and interview methods. Subst. Use Misuse 2020, 55, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, C.; Hogan, L.; Cox, M. A comparison between two retrospective alcohol consumption measures and the daily drinking diary method with university students. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2019, 45, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B. Timeline Follow-Back: A technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biochemical Methods; Litten, R.Z., Allen, J.P., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.R.; Tonigan, J.S.; Longabaugh, R. The Drinker Inventory of Consequences (DrInC): An Instrument for Assessing Adverse Consequences of Alcohol Abuse; Project MATCH Monograph Series, Vol. 4. DHHS Publication No. 95-3911; National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995.
- Davidson, R.; Raitrick, D. The validity of the Short Alcohol Dependence Data (SADD) questionnaire: A short self-report questionnaire for the assessment of alcohol dependence. Br. J. Addict. 1986, 81, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.; Bunting, B.; Raitrick, D. The homogeneity of the alcohol dependence syndrome: A factor analysis of the SADD questionnaire. Br. J. Addict. 1989, 84, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heather, N.; Gold, R.; Rollnick, S. Readiness to Change Questionnaire: User’s Manual. Technical Report 15; National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales: Kensington, Australia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Heather, N.; Rollnick, S.; Bell, A. Predictive validity of the Readiness to Change Questionnaire. Addiction 1993, 88, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollnick, S.; Heather, N.; Gold, R.; Hall, W. Development of a short ‘readiness to change’ questionnaire for use in brief, opportunistic interventions among excessive drinkers. Addiction 1992, 87, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, K.J.; Wood, P.K.; Crews, T.M.; Vandiver, P.A. The Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire: Reliability and validity studies and short derivation of a short form. Psychol. Assess. 1995, 7, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Excel. 2018. Available online: https://office.microsoft.com/excel (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Klinger, E.; Cox, W.M. The Motivational Structure Questionnaire, Personal Concerns Inventory, and their variants: Psychometric properties. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 204–232. [Google Scholar]
- House of Commons Health Committee. Alcohol. 2010. Available online: https://www.ias.org.uk/uploads/pdf/News%20stories/hchc-report-080110.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Feather, N.T.; Newton, J.W. Values, expectations, and the prediction of social action: An expectancy-valence analysis. Motiv. Emot. 1982, 6, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, E.; Cox, W.M. Motivation and the goal theory of current concerns. In Handbook of Motivational Counseling: Goal-Based Approaches to Assessment and Intervention with Addiction and Other Problems; Cox, W.M., Klinger, E., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 3–47. [Google Scholar]
- van Eerde, W.; Thierry, H. Vroom’s expectancy models and work-related criteria: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 1996, 81, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braitman, A.L.; Linden-Carmichael, A.; Henson, J.M. Protective behavioral strategies as a context-specific mediator: A multilevel examination of within- and between-person associations of daily drinking. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 25, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierski, F.; Benzerouk, F.; De Wever, E.; Duka, T.; Kaladjian, A.; Quaglino, V.; Naassila, M. Cloninger’s temperament and character dimensions of personality and binge drinking among college students. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, K.B.; DiBello, A.M.; Orazio, E.E.; Hatch, M.R.; Mastroleo, N.R. Predictors of receptivity to an alcohol intervention among mandated students. Addict. Behav. 2021, 112, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, M.E.; Fried-Somerstein, A.; Flori, J.N.; Hall, T.V.; Dvorak, R.D. Reducing alcohol use in mandated college students: A comparison of a Brief Motivational Intervention (BMI) and the Expectancy Challenge Alcohol Literacy Curriculum (ECALC). Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 28, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babor, T.; Grant, M. (Eds.) Project on Identification and Management of Alcohol-Related Problems. Report on Phase II: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Brief Interventions in Primary Health Care; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, G. Brief interventions for problem drinking and women. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2002, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.E.; Carey, K.B.; Sliwinski, M.J. Mailed personalized normative feedback as a brief interention for at-risk college drinkers. J. Stud. Alcohol 2002, 63, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.G.; Benson, T.A.; Vuchinich, R.E.; Deskins, M.M.; Eakin, D.; Flood, A.M.; McDevitt-Murphy, M.; Torrealday, O. A Comparison of Personalized Feedback for College Student Drinkers Delivered with and without a Motivational Interview. J. Stud. Alcohol 2004, 65, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Control | CBI | CBI-E | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n = 12) | Female (n = 14) | Male (n = 11) | Female (n = 16) | Male (n = 7) | Female (n = 15) | |||||||
| Variable | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD |
| Weekly units, t1 | 37.3 | 33.1 | 23.3 | 12.1 | 35.1 | 17.1 | 25.3 | 20.9 | 37.4 | 13.0 | 23.0 | 9.9 |
| Weekly units, t2 | 29.3 | 18.3 | 15.7 | 8.2 | 22.7 | 14.4 | 12.1 | 7.2 | 14.6 | 7.4 | 17.6 | 12.6 |
| Binge † total, t1 | 20.1 | 13.5 | 19.7 | 9.0 | 25.0 | 12.8 | 23.4 | 21.0 | 27.7 | 12.8 | 20.2 | 8.1 |
| Binge † total, t2 | 18.9 | 12.7 | 15.1 | 10.3 | 17.5 | 10.7 | 10.4 | 9.0 | 9.8 | 6.5 | 16.0 | 13.3 |
| DrInC total, t1 | 20.8 | 14.9 | 25.3 | 14.5 | 18.4 | 7.8 | 22.9 | 19.0 | 23.3 | 13.5 | 21.4 | 12.4 |
| DrInC total, t2 | 20.3 | 13.3 | 15.4 | 8.2 | 19.4 | 11.5 | 14.6 | 11.6 | 19.1 | 10.6 | 18.8 | 12.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hogan, L.M.; Cox, W.M. Evaluating Two Brief Motivational Interventions for Excessive-Drinking University Students. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050381
Hogan LM, Cox WM. Evaluating Two Brief Motivational Interventions for Excessive-Drinking University Students. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(5):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050381
Chicago/Turabian StyleHogan, Lee M., and W. Miles Cox. 2024. "Evaluating Two Brief Motivational Interventions for Excessive-Drinking University Students" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 5: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050381
APA StyleHogan, L. M., & Cox, W. M. (2024). Evaluating Two Brief Motivational Interventions for Excessive-Drinking University Students. Behavioral Sciences, 14(5), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050381




