Suicidal Behaviour among School-Going Adolescents in Saint Lucia: Analysis of Prevalence and Associated Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Theoretical Framework: Interpersonal Theory of Suicide
1.2. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Sampling Procedure
2.3. Study Measures
2.3.1. Dependent Variables
2.3.2. Independent Variables
2.3.3. Ethical Statement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
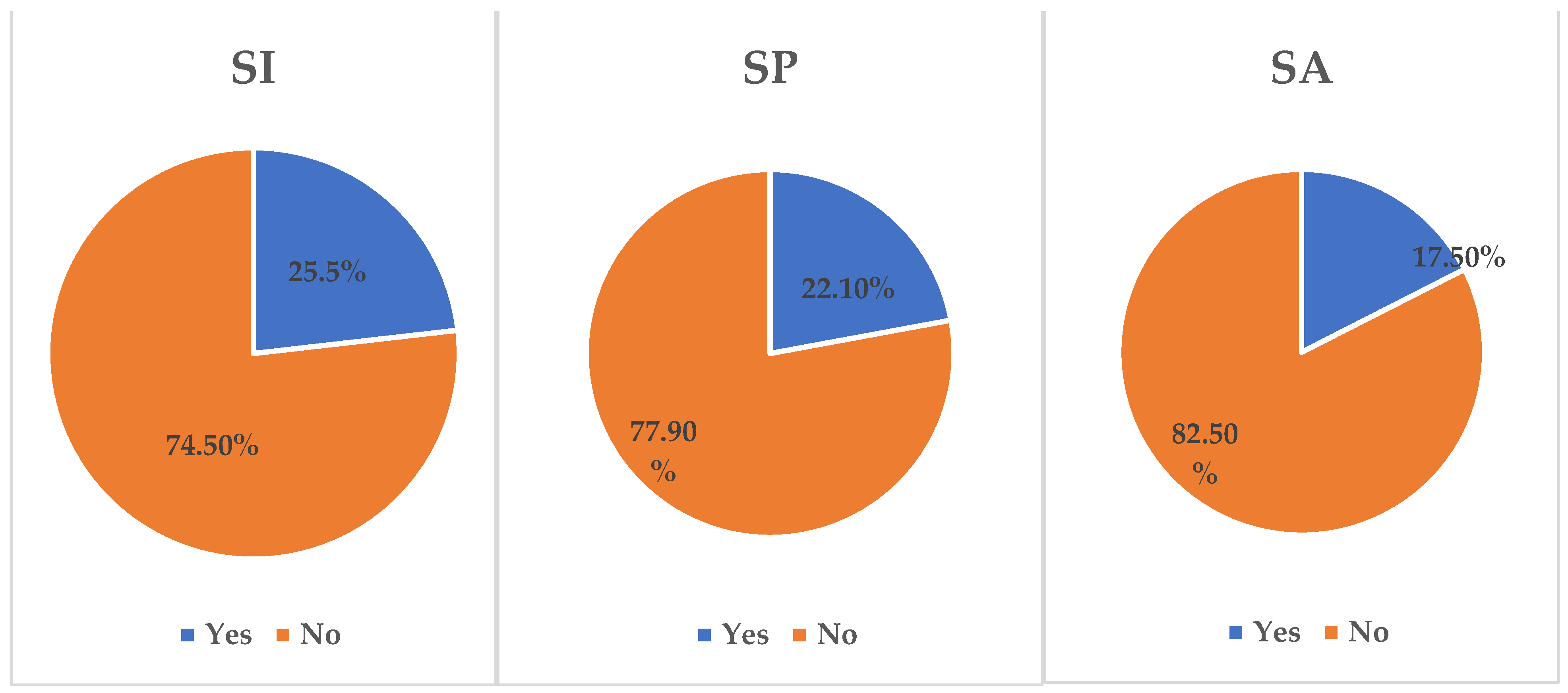
3.1. Background Characteristics of Adolescents in Saint Lucia
3.2. Bivariate Analysis on the Association between Independent Variables and Suicidal Behaviour (SI, SP, and SA)
3.3. Multivariate Regression Analysis on the Predictors of Suicidal Ideation, Planning, and Attempts
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
4.2. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Suicide 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/suicide (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Wong, S.M.Y.; Ip, C.H.; Hui, C.L.M.; Suen, Y.N.; Wong, C.S.M.; Chang, W.C.; Chan, S.K.W.; Lee, E.H.M.; Lui, S.S.Y.; Chan, K.T.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of suicidal behaviours in a representative epidemiological youth sample in Hong Kong: The significance of suicide-related rumination, family functioning, and ongoing population-level stressors. Psychol. Med. 2022, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecki, G.; Brent, D.A. Suicide and suicidal behaviour. Lancet 2016, 387, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, S.C.; Carducci, B.; Akseer, N.; Zasowski, C.; Szatmari, P.; Bhutta, Z.A. Suicidal behaviours among adolescents from 90 countries: A pooled analysis of the global school-based student health survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppong-Asante, K.; Kugbey, N.; Osafo, J.; Quarshie, E.N.B.; Sarfo, J.O. The prevalence and correlates of suicidal behaviours (ideation, plan and attempt) among adolescents in senior high schools in Ghana. SSM Popul. Health 2017, 3, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, R.; Burton, N.W.; Maple, M.; Khan, S.R.; Khan, A. Suicidal ideation, suicide planning, and suicide attempts among adolescents in 59 low-income and middle-income countries: A population-based study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2019, 3, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, T. Why People Die by Suicide; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cero, I.; Zuromski, K.L.; Witte, T.K.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Joiner, T.E. Perceived burdensomeness, thwarted belongingness, and suicide ideation: Re-examination of the Interpersonal-Psychological Theory in two samples. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Orden, K.A.; Witte, T.K.; Gordon, K.H.; Bender, T.W.; Joiner, T.E. Suicidal Desire and the Capability for Suicide: Tests of the Interpersonal-Psychological Theory of Suicidal Behavior Among Adults. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2008, 76, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Orden, K.A.; Lynam, M.E.; Hollar, D.; Joiner, T.E. Perceived burdensomeness as an indicator of suicidal symptoms. Cognit. Ther. Res. 2006, 30, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Orden, K.A.; Cukrowicz, K.C.; Witte, T.K.; Joiner, T.E. Thwarted belongingness and perceived burdensomeness: Construct validity and psychometric properties of the Interpersonal Needs Questionnaire. Psychol. Assess 2012, 24, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.M. The effects of parental abuse and peer victimisation on adolescent’s suicidal ideation-the mediating pathway of interpersonal needs and hopelessness. Korean J. Soc. Welf. 2012, 64, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, K.; Pengpid, S. Alcohol misuse prevalence and correlates among school adolescents from national surveys in Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. J. Psychol. Afr. 2022, 32, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfo, J.O.; Obeng, P.; Debrah, T.P.; Gbordzoe, N.I.; Fosu, A.K. Suicidal behaviours (ideation, plan and attempt) among school-going adolescents: A study of prevalence, predisposing, and protective factors in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Dialogues Health 2022, 1, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahumud, R.A.; Dawson, A.J.; Chen, W.; Biswas, T.; Keramat, S.A.; Morton, R.L.; Renzaho, A.M.N. The risk and protective factors for suicidal burden among 251 763 school-based adolescents in 77 low- and middle-income to high-income countries: Assessing global, regional and national variations. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, B.; Gariépy, G.; Sentenac, M.; Elgar, F.J. Adolescent suicidal behaviours in 32 low- and middle-income countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2016, 94, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, A.; Oh, H.; Carvalho, A.F.; Smith, L.; Haro, J.M.; Vancampfort, D.; Stubbs, B.; De Vylder, J.E. Bullying Victimisation and Suicide Attempt Among Adolescents Aged 12–15 Years From 48 Countries. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 58, 907–918.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global School-Based Student Health Survey 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/noncommunicable-diseases/surveillance/systems-tools/global-school-based-student-health-survey (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Lindsey, M.A.; Sheftall, A.H.; Xiao, Y.; Joe, S. Trends of suicidal behaviors among high school students in the United States: 1991–2017. Pediatrics 2019, 144, 20191187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, M.K.; Green, J.G.; Hwang, I.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Sampson, N.A.; Zaslavsky, A.M.; Kessler, R.C. Prevalence, Correlates, and Treatment of Lifetime Suicidal Behavior Among Adolescents: Results From the National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thi Khanh, H.; Nguyen Thanh, L.; Pham Quoc, T.; Pham Viet, C.; Duong Minh, D.; le Thi Kim, A. Suicidal behaviors and depression “among adolescents in Hanoi, Vietnam: A multilevel analysis of data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey 2019. Health Psychol. Open 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidu, A.A.; Amu, H.; Dadzie, L.K.; Amoah, A.; Ahinkorah, B.O.; Ameyaw, E.K.; Acheampong, H.Y.; Kissah-Korsah, K. Suicidal behaviours among in-school adolescents in Mozambique: Cross-sectional evidence of the prevalence and predictors using the Global School-Based Health Survey data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Jia, C.X. Prevalence of suicidal behaviour and associated factors in a large sample of Chinese adolescents. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 28, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canetto, S.S.; Sakinofsky, I. The Gender Paradox in Suicide. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 1998, 28, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, D.; Liu, X.; Zheng, R.; Mao, X.; Chen, T.; He, W. Prevalence of suicide attempts among Chinese adolescents: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Compr. Psychiatry 2015, 61, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, R.S.; Gobinath, A.R.; Galea, L.A. Sex differences in depression: Insights from clinical and preclinical studies. Progress Neurobiol. 2019, 176, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.P.; Asnaani, A.; Litz, B.T.; Hofmann, S.G. Gender differences in anxiety disorders: Prevalence, course of illness, comorbidity and burden of illness. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryba, M.M.; Hopko, D.R. Gender differences in depression: Assessing mediational effects of overt behaviors and environmental reward through daily diary monitoring. Depress. Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 865679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, E.R.; Canetto, S.S. The role of gender and suicide precipitant in attitudes toward non-fatal suicidal behavior. Death Stud. 2010, 26, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canetto, S.S.; Lester, D. Gender, Culture, and Suicidal Behavior. Transcult. Psychiatry 1998, 35, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.; Cho, H.J. Associations between the Type of Tobacco Products and Suicidal Behaviors: A Nationwide Population-Based Study among Korean Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, K. Electronic cigarette use and suicidal behaviors among adolescents. J. Public Health 2021, 43, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, K.; Pengpid, S.; Wasserman, D.; Carli, V.; Hadlaczky, G. Early Substance Use Initiation and Suicide Ideation and Attempts among School-Aged Adolescents in Four Pacific Island Countries in Oceania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12291–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfy, K.; Brown, M.C.; Nerio, N.; Aimiuwu, O.; Tran, B.; Anghel, A.; Friedman, T.C. Repeated stress alters the ability of nicotine to activate the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, N.; Kirschbaum, C. The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis in habitual smokers. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 59, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amare, T.; Meseret Woldeyhannes, S.; Haile, K.; Yeneabat, T. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Suicide Ideation and Attempt among Adolescent High School Students in Dangila Town, Northwest Ethiopia. Psychiatry J. 2018, 2018, 7631453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, H.L. Is Emotional Abuse As Harmful as Physical and/or Sexual Abuse? J. Child Adolesc. Trauma 2019, 13, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolke, D.; Lereya, S.T. Long-term effects of bullying. Arch. Dis. Child 2015, 100, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gournellis, R.; Tournikioti, K.; Touloumi, G.; Thomadakis, C.; Michalopoulou, P.G.; Christodoulou, C.; Papadopoulou, A.; Douzenis, A. Psychotic (delusional) depression and suicidal attempts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2018, 137, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqueras, J.A.; Soto-Sanz, V.; Rodríguez-Marín, J.; García-Oliva, C. What is the Role of Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms in Adolescent Suicide Behaviors? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Sanz, V.; Castellví, P.; Piqueras, J.A.; Rodríguez-Marín, J.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, T.; Miranda-Mendizábal, A.; Parés-Badell, O.; Almenara, J.; Alonso, I.; Blasco, M.J.; et al. Internalising and externalising symptoms and suicidal behaviour in young people: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 140, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockenberry, J.M.; Timmons, E.J.; vander Weg, M. Smoking, parent smoking, depressed mood, and suicidal ideation in teens. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2010, 12, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, T.; Tripathy, J.P.; Thinley, S.; Rani, M.; Dhendup, T.; Laxmeshwar, C.; Tenzin, K.; Gurung, M.S.; Tshering, T.; Subba, D.K.; et al. Suicidal ideation and attempt among school going adolescents in bhutan- A secondary analysis of a global school-based student health survey in Bhutan 2016. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K. Single and Multiple Suicide Attempts: Prevalence and Correlates in School-Going Adolescents in Liberia in 2017. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2020, 13, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, L.K.; Kawachi, I.; Barbeau, E.M.; Subramanian, S.V. Exposure to domestic violence associated with adult smoking in India: A population based study. Tob. Control 2007, 16, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.C.; Chang, O.D.; Lucas, A.G.; Li, M.; Beavan, C.B.; Eisner, R.S.; McManamon, B.M.; Rodriguez, N.S.; Katamanin, O.M.; Bourke, E.C.; et al. Depression, loneliness, and suicide risk among Latino College Students: A test of a Psychosocial Interaction Model. Soc. Work 2019, 64, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.J.; Cullen, B.; Graham, N.; Lyall, D.M.; Mackay, D.; Okolie, C.; Pearsall, R.; Ward, J.; John, A.; Smith, D.J. Living alone, loneliness and lack of emotional support as predictors of suicide and self-harm: A nine-year follow up of the UK Biobank cohort. J. Affect Disord. 2021, 279, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkley, L.C.; Cacioppo, J.T. Loneliness Matters: A Theoretical and Empirical Review of Consequences and Mechanisms. Ann. Behav. Med. 2010, 40, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.C.; Tucker, R.P. Repetitive negative thinking and suicide: A burgeoning literature with need for further exploration. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2018, 22, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Monteagudo, M.C.; Delgado, B.; Díaz-Herrero, Á.; García-Fernández, J.M. Relationship between suicidal thinking, anxiety, depression and stress in university students who are victims of cyberbullying. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 286, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, I.H.; Boffa, J.W.; Rogers, M.L.; Hom, M.A.; Albanese, B.J.; Chu, C.; Capron, D.W.; Schmidt, N.B.; Joiner, T.E. Anxiety Sensitivity and Suicidal Ideation/Suicide Risk: A Meta-Analysis. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 86, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosidou, K.; Dalman, C.; Fredlund, P.; Lee, B.K.; Galanti, R.; Isacsson, G.; Magnusson, C. School performance and the risk of suicide attempts in young adults: A longitudinal population-based study. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, R.F.; Brewer, L.E.; Tice, D.M.; Twenge, J.M. Thwarting the Need to Belong: Understanding the Interpersonal and Inner Effects of Social Exclusion. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass. 2007, 1, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, I.; Bawdekar, M. Mental Health Issues of Young Females in Mumbai: Case Studies. Int. J. Indian Psychol. 2019, 7, 2349–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.M.; Kissane, D.W. Demoralisation: Its phenomenology and importance. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2002, 36, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, A.; Vasileios, C.; Ambrosetti, J.; Shah, S.; Amerio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Serafini, G.; Piguet, V.; Luthy, C.; Cedraschi, C.; et al. Demoralisation in suicide: A systematic review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2022, 157, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaniang, S.; Klongdee, K.; Jompaeng, Y. Suicide prevention: A qualitative study with Thai secondary school students. Belitung Nurs. J. 2022, 8, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, A.; Ambrosetti, J.; Wyss, K.; Bondolfi, G.; Sarasin, F.; Khan, R. Prévenir le suicide aux urgences : De la Théorie Interpersonnelle du Suicide à la connectedness Prevention of suicide at Emergency Room: From the Interpersonal Theory of Suicide to the connectedness. Rev. Med. Suisse 2018, 14, 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, A.P.; Hendin, H.; Mann, J.J. Suicide in College Students. Am. Behav. Sci. 2016, 46, 1224–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Explanatory Variables | Questions |
|---|---|
| Sex | What is your sex? |
| Age | How old are you? |
| Grade | What grade are you in? |
| School truancy | In the past 30 days, did you miss classes or school without permission? |
| Hunger | Were you hungry most of the time, or did you always go hungry? |
| Missed PE classes | Did you miss the recent physical education classes? |
| Physical attack | Have you been attacked physically before? |
| Suicidal ideation | In the past 12 months, did you ever seriously consider attempting suicide? |
| Suicide attempt | In the past 12 months, did you attempt suicide? |
| Suicide plan | In the past 12 months, did you make a plan about how you would attempt suicide? |
| School truancy | In the past 30 days, did you miss classes or school without permission? |
| Amphetamine use | In your life, did you use amphetamine or methamphetamine (also called ice or yellow)? |
| Current use of alcohol | In the past 30 days, did you have at least one drink containing alcohol? |
| Ever got drunk after consuming alcohol | Have you ever drunk so much alcohol that you were really drunk? |
| Marijuana smoking | In the past 30 days, did you use marijuana? |
| Cigarette smoking | Do you currently smoke cigarettes? |
| Use of tobacco products other than cigarette | Do you use any other tobacco product apart from cigarettes? |
| Parental use of tobacco | Do you have parents or guardians who use any form of tobacco? |
| Physical fight | Have you engaged in a physical fight before? |
| Bullied | Have you been bullied at school in the past 12 months? |
| Attended physical education classes on ≥3 days | Did you attend physical education classes on three or more days? |
| Attended physical education classes on ≥5 days | Did you attend physical education classes on five or more days? |
| Close friends | Do you have close friends? |
| Loneliness | Do you feel lonely most of the time or always? |
| Worry | Do you most of the time or always worry about something that you could not study? |
| Sex with multiple sexual partners | Have you slept with two or more partners before? |
| Variables | Suicidal Ideation (N = 1864) | Suicide Plan (N = 1864) | Suicide Attempt (N = 1864) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Chi-Square (χ2) | Yes | No | Chi-Square (χ2) | Yes | No | Chi-Square (χ2) | ||
| Demographic | ||||||||||
| Age (years) | 12–14 | 247 (13.3%) | 740 (39.7%) | 0.29 | 219 (11.7%) | 768 (41.2%) | 0.01 | 180 (9.7%) | 807 (43.3%) | 0.70 |
| 15–17 | 229 (12.3%) | 648 (34.8%) | 684 (36.7%) | 193 (10.4%) | 147 (7.9%) | 730 (39.2%) | ||||
| Sex | Male | 133 (7.1%) | 732 (39.3%) | 87.63 *** | 129 (6.9%) | 736 (39.5%) | 48.46 *** | 121 (6.5%) | 744 (39.9%) | 14.08 *** |
| Female | 343 (18.4%) | 656 (35.2%) | 283 (15.2%) | 716 (38.4%) | 206 (11.1%) | 793 (42.5%) | ||||
| Grade | 1–3 | 237 (12.7%) | 728 (39.1%) | 1.00 | 210 (11.3%) | 755 (40.5%) | 0.135 | 183 (9.8%) | 782 (42.0%) | 2.79 |
| 4–6 | 239 (12.8%) | 660 (35.4%) | 202 (10.8%) | 697 (37.4%) | 144 (7.7%) | 755 (40.5%) | ||||
| Personal | ||||||||||
| Truancy | Yes | 104 (5.6%) | 254 (13.6%) | 2.88 | 101 (5.4%) | 257 (13.8%) | 9.61 ** | 94 (5.0%) | 264 (14.2% | 23.26 *** |
| No | 372 (20.0%) | 1134 (60.8%) | 311 (16.7%) | 1195 (64.1%) | 233 (12.5%) | 1273 (68.3%) | ||||
| Hunger | Yes | 58 (3.1%) | 120 (6.4%) | 5.14 * | 46 (2.5%) | 132 (7.1%) | 1.60 | 44 (2.4%) | 134 (7.2%) | 7.01 * |
| No | 418 (22.4%) | 1268 (68.0%) | 366 (19.6%) | 1320 (70.8%) | 283 (15.2%) | 1403 (75.3%) | ||||
| Missed PE classes | Yes | 218 (11.7%) | 563 (30.2%) | 3.99 * | 180 (9.7%) | 601 (32.2%) | 0.70 | 130 (7.0%) | 651 (34.9%) | 0.75 |
| No | 258 (13.8%) | 825 (44.3%) | 232 (12.4%) | 851 (45.7%) | 197 (10.6%) | 886 (47.5%) | ||||
| Drug and substance use | ||||||||||
| Amphetamine or methamphetamines use | Yes | 48 (2.6%) | 93 (5.0%) | 5.80 * | 49 (2.6%) | 92 (4.9%) | 14.17 *** | 55 (3.0%) | 86 (4.6%) | 48.58 *** |
| No | 428 (23.0%) | 1295 (69.5%) | 363 (19.5%) | 1360 (73.0%) | 272 (14.6%) | 1451 (77.8%) | ||||
| Marijuana use | Yes | 81 (4.3%) | 179 (9.6%) | 5.01 * | 80 (4.3%) | 180 (9.7%) | 13.18 ** | 87 (4.7%) | 173 (9.3%) | 52.93 *** |
| No | 395 (21.2%) | 1209 (64.9%) | 332 (17.8%) | 1272 (68.2%) | 240 (12.9%) | 1364 (73.2%) | ||||
| Drunk alcohol | Yes | 274 (14.7%) | 598 (32.1%) | 29.85 *** | 246 (13.2%) | 626 (33.6%) | 35.50 *** | 203 (10.9%) | 669 (35.9%) | 37.28 *** |
| No | 202 (10.8%) | 790 (42.4%) | 166 (8.9%) | 826 (44.3%) | 124 (6.7%) | 868 (46.6%) | ||||
| Ever got drunk after consuming alcohol | Yes | 160 (8.6%) | 324 (17.4%) | 19.45 *** | 152 (8.2%) | 332 (17.8%) | 32.85 *** | 128 (6.9%) | 356 (19.1%) | 35.83 *** |
| No | 316 (17.0%) | 316 (17.0%) | 260 (13.9%) | 1120 (60.1%) | 199 (10.7%) | 1181 (63.4%) | ||||
| Smoke cigarettes | Yes | 57 (3.1%) | 92 (4.9%) | 13.78 *** | 59 (3.2%) | 90 (4.8%) | 28.79 *** | 68 (3.6%) | 81 (4.3%) | 88.37 *** |
| No | 419 (22.5%) | 1296 (69.5%) | 353 (18.9%) | 1362 (73.1%) | 259 (13.9%) | 1456 (78.1%) | ||||
| Use of tobacco products other than cigarette | Yes | 46 (2.5%) | 75 (4.0%) | 10.60 ** | 47 (2.5%) | 74 (4.0%) | 21.06 *** | 61 (3.3%) | 60 (3.2%) | 96.65 *** |
| No | 430 (23.1%) | 430 (23.1%) | 365 (19.6%) | 1378 (73.9%) | 266 (14.3%) | 1477 (79.2%) | ||||
| Psychosocial | ||||||||||
| Physically attacked | Yes | 181 (9.7%) | 449 (24.1%) | 22.87 *** | 166 (8.9%) | 393 (21.1%) | 26.74 *** | 142 (7.6%) | 417 (22.4%) | 34.10 *** |
| No | 295 (15.8%) | 939 (50.4%) | 246 (13.2%) | 1059 (56.8%) | 185 (9.9%) | 1120 (60.1%) | ||||
| Physical fight | Yes | 181 (9.7%) | 449 (24.1%) | 5.10 * | 162 (8.7%) | 468 (25.1%) | 7.21 ** | 152 (8.2%) | 478 (25.6%) | 28.52 *** |
| No | 295 (15.8%) | 939 (50.4%) | 250 (13.4%) | 984 (52.8%) | 175 (9.4%) | 1059 (56.8%) | ||||
| Bullied | Yes | 188 (10.1%) | 283 (15.2%) | 68.52 *** | 170 (9.1%) | 301 (16.1%) | 71.65 *** | 147 (7.9%) | 324 (17.4%) | 81.39 *** |
| No | 288 (15.5%) | 1105 (59.3%) | 242 (13.0%) | 1151 (61.7%) | 180 (9.7%) | 1213 (65.1%) | ||||
| Loneliness | Yes | 189 (10.1%) | 177 (9.5%) | 163.18 *** | 167 (9.0%) | 199 (10.7%) | 146.39 *** | 140 (7.5%) | 226 (12.1%) | 135.02 *** |
| No | 287 (15.4%) | 177 (9.5%) | 245 (13.1%) | 1253 (67.2%) | 187 (10.0%) | 1311 (70.3%) | ||||
| Close friends | Yes | 64 (3.4%) | 150 (8.0%) | 2.43 | 68 (3.6%) | 146 (7.8%) | 13.14 *** | 76 (4.1%) | 138 (7.4%) | 53.98 *** |
| No | 412 (22.1%) | 1238 (66.4%) | 344 (18.5%) | 1306 (70.1%) | 251 (13.5%) | 1399 (75.1%) | ||||
| Parents/guardians’ use of tobacco | Yes | 104 (5.6%) | 158 (8.5%) | 32.14 **** | 83 (4.5%) | 179 (9.6%) | 16.24 *** | 79 (4.2%) | 183 (9.8%) | 33.51 *** |
| No | 372 (20.0%) | 1230 (66.0%) | 329 (17.7%) | 1273 (68.3%) | 248 (13.3%) | 1354 (72.6%) | ||||
| Understanding parents | Yes | 113 (6.1%) | 554 (29.7%) | 40.35 *** | 98 (5.3%) | 569 (30.5%) | 33.13 *** | 81 (4.3%) | 586 (31.4%) | 20.93 *** |
| No | 363 (19.5%) | 834 (44.7%) | 314 (16.8%) | 883 (47.4%) | 246 (13.2%) | 951 (51.0%) | ||||
| Multiple sexual partners | Yes | 107 (5.7%) | 266 (14.3%) | 2.43 | 104 (5.6%) | 269 (14.4%) | 9.05 ** | 96 (5.2%) | 277 (14.9%) | 21.65 *** |
| No | 369 (19.8%) | 1122 (60.2%) | 308 (16.5%) | 1183 (63.5%) | 231 (12.4%) | 1260 (67.6%) | ||||
| Attended PE classes on ≥3 days | Yes | 101 (5.4%) | 373 (20.0%) | 5.98 * | 95 (5.1%) | 379 (20.3%) | 1.57 | 82 (4.4%) | 392 (21.0%) | 0.03 |
| No | 375 (20.1%) | 1015 (54.5%) | 317 (17.0%) | 1073 (57.6%) | 245 (13.1%) | 1145 (61.4%) | ||||
| Attended PE classes on ≥5 days | Yes | 64 (3.4%) | 246 (13.2%) | 4.68 * | 56 (3.0%) | 254 (13.6%) | 3.52 | 44 2.4%) | 266 (14.3%) | 2.88 |
| No | 412 (22.1%) | 1142 (61.3%) | 356 (19.1%) | 1198 (64.3%) | 283 (15.2%) | 1271 (68.2%) | ||||
| Worried | Yes | 152 (8.2%) | 138 (7.4%) | 130.47 *** | 126 (6.8%) | 164 (8.8%) | 90.88 *** | 118 (6.3%) | 172 (9.2%) | 127.20 *** |
| No | 324 (17.4%) | 1250 (67.1%) | 286 (15.3%) | 1288 (69.1%) | 209 (11.2%) | 1365 (73.2%) | ||||
| Variable | Suicidal Ideation | Suicide Plan | Suicide Attempt |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOR (95%CI) | AOR (95%CI) | AOR (95%CI) | |
| Demographic | |||
| Sex | 0.324(0.248–0.422) *** | 0.365(0.276–0.483) *** | 0.453(0.330–0.621) *** |
| Personal | |||
| Truancy | – | 1.181(0.866–1.611) | 1.249(0.891–1.751) |
| Hunger | 0.879(0.593–1.303) | – | 0.713(0.454–1.119) |
| Missed PE classes | 0.995(0.763–1.296) | – | – |
| Drug and substance use | |||
| Amphetamine or methamphetamines use | 1.151(0.698–1.899) | 1.247(0.767–2.028) | 1.380(0.830–2.295) |
| Marijuana use | 1.063(0.727–1.554) | 1.030(0.699–1.516) | 1.325(0.881–1.992) |
| Alcohol | 1.358(1.057–1.744) | 1.371(1.056–1.781) | 1.339(0.997–1.799) |
| Ever got drunk after consuming alcohol | 1.146(0.855–1.534) | 1.266(0.940–1.705) | 0.953(0.683–1.330) |
| Smoke cigarettes | 1.226(0.764–1.968) | 1.504(0.948–2.386) | 2.092(1.297–3.374) ** (0.002) |
| Currently used any tobacco products other than cigarettes | 1.002(0.593–1.695) | 1.052(0.630–1.755) | 2.055(1.226–3.443) ** (0.006) |
| Psychosocial | |||
| Physically attacked | 1.425(1.087–1.868) * | 1.367(1.039–1.800) * | 1.245(0.919–1.689) |
| Physical fight | 1.080(0.823–1.416) | 1.043(0.790–1.378) | 1.261(0.929–1.711) |
| Bullied | 1.671(1.287–2.169) *** | 1.716(1.315–2.240) *** | 1.758(1.308–2.363) *** |
| Parents/guardians’ use of tobacco | 1.637(1.195–2.244) ** | 0.308(1.188–0.853) | 1.412(0.987–2.019) |
| Understanding parents | 0.627(0.482–0.816) *** | 0.662(0.504–0.869) ** | 0.800(0.588–1.089) |
| Multiple sexual partners | – | 1.336(0.959–1.860) | 1.402(0.978–2.009) |
| Close friends | – | 1.587(1.118–2.253) * | 3.021(2.102–4.341) *** |
| Loneliness | 2.634(1.999–3.471) *** | 2.649(2.006–3.498) *** | 2.669(1.961–3.632) *** |
| Attended PE classes on ≥3 days | 0.764(0.503–1.159) | – | – |
| Attended PE classes on ≥5 days | 1.016(0.637–1.621) | – | – |
| Worry | 2.375(1.757–3.210) *** | 1.703(1.251–2.319) ** | 2.347(1.687–3.265) *** |
| Constant | 0.056 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarfo, J.O.; Amoadu, M.; Obeng, P.; Gbordzoe, N.I.; Debrah, T.P.; Ofori, C.O.B.; Hagan, J.E. Suicidal Behaviour among School-Going Adolescents in Saint Lucia: Analysis of Prevalence and Associated Factors. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070535
Sarfo JO, Amoadu M, Obeng P, Gbordzoe NI, Debrah TP, Ofori COB, Hagan JE. Suicidal Behaviour among School-Going Adolescents in Saint Lucia: Analysis of Prevalence and Associated Factors. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(7):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarfo, Jacob Owusu, Mustapha Amoadu, Paul Obeng, Newton Isaac Gbordzoe, Timothy Pritchard Debrah, Crescens Osei Bonsu Ofori, and John Elvis Hagan. 2023. "Suicidal Behaviour among School-Going Adolescents in Saint Lucia: Analysis of Prevalence and Associated Factors" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 7: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070535
APA StyleSarfo, J. O., Amoadu, M., Obeng, P., Gbordzoe, N. I., Debrah, T. P., Ofori, C. O. B., & Hagan, J. E. (2023). Suicidal Behaviour among School-Going Adolescents in Saint Lucia: Analysis of Prevalence and Associated Factors. Behavioral Sciences, 13(7), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070535






