Teacher Burnout in Saudi Arabia: The Catastrophic Role of Parental Disengagement
Abstract
1. Teacher Burnout: Consequences and Predictors
2. Why a Nonlinear Framework?
3. Goals of the Present Study
4. Method
4.1. Participants and Procedures
4.2. Measures
4.2.1. Teacher Burnout
4.2.2. Teacher Efficacy and Parental Engagement and Involvement
4.2.3. Teacher Satisfaction and Experience
4.2.4. Student Achievement
4.3. Data Analyses
4.3.1. Construct Composition: Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Omega Reliability
4.3.2. Cusp Catastrophe Model
5. Results
5.1. Prerequisite Psychometric Analyses of the Measured Constructs
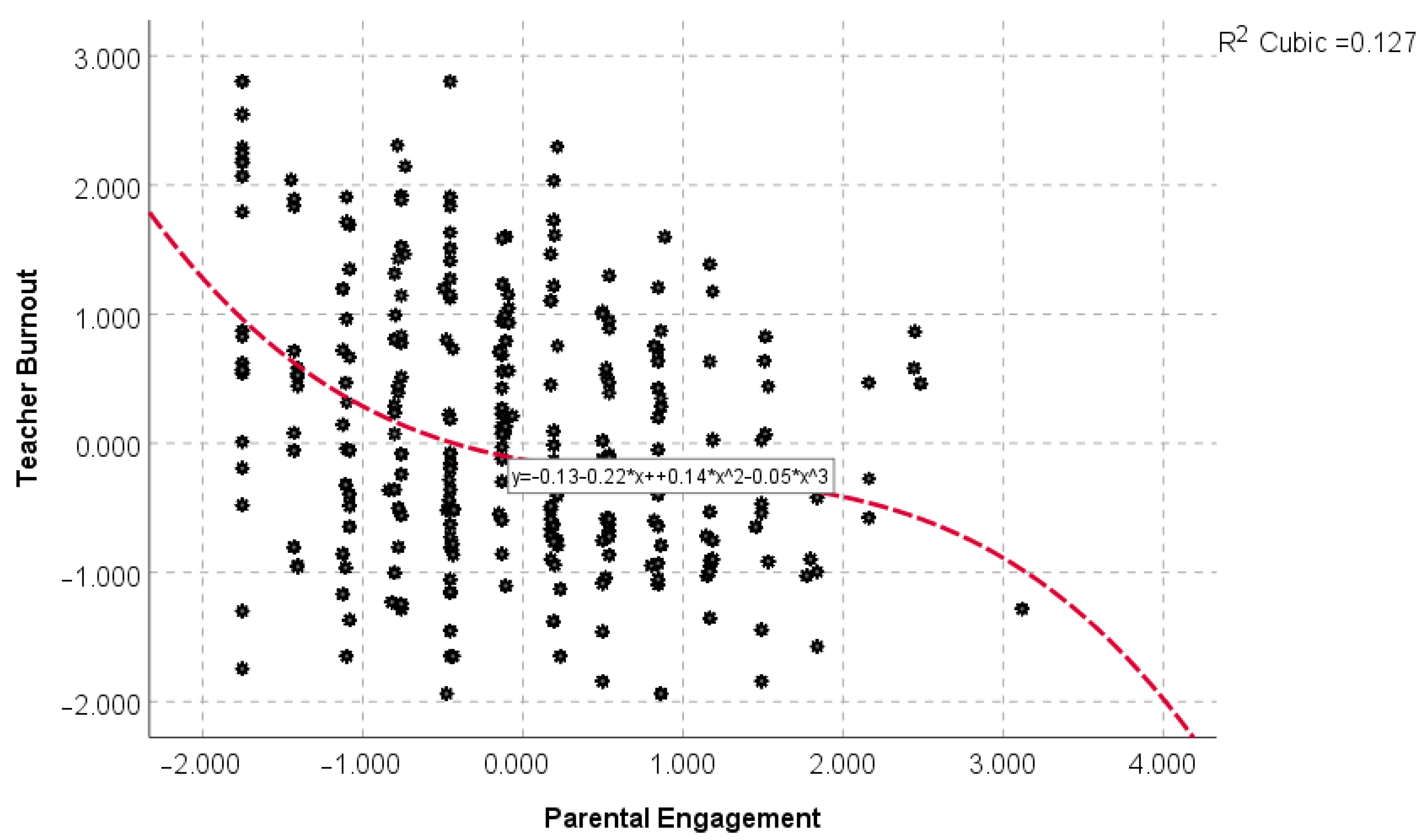
5.2. Preliminary Results on the Relationship between Parental Engagemetn and Teacher Burnout
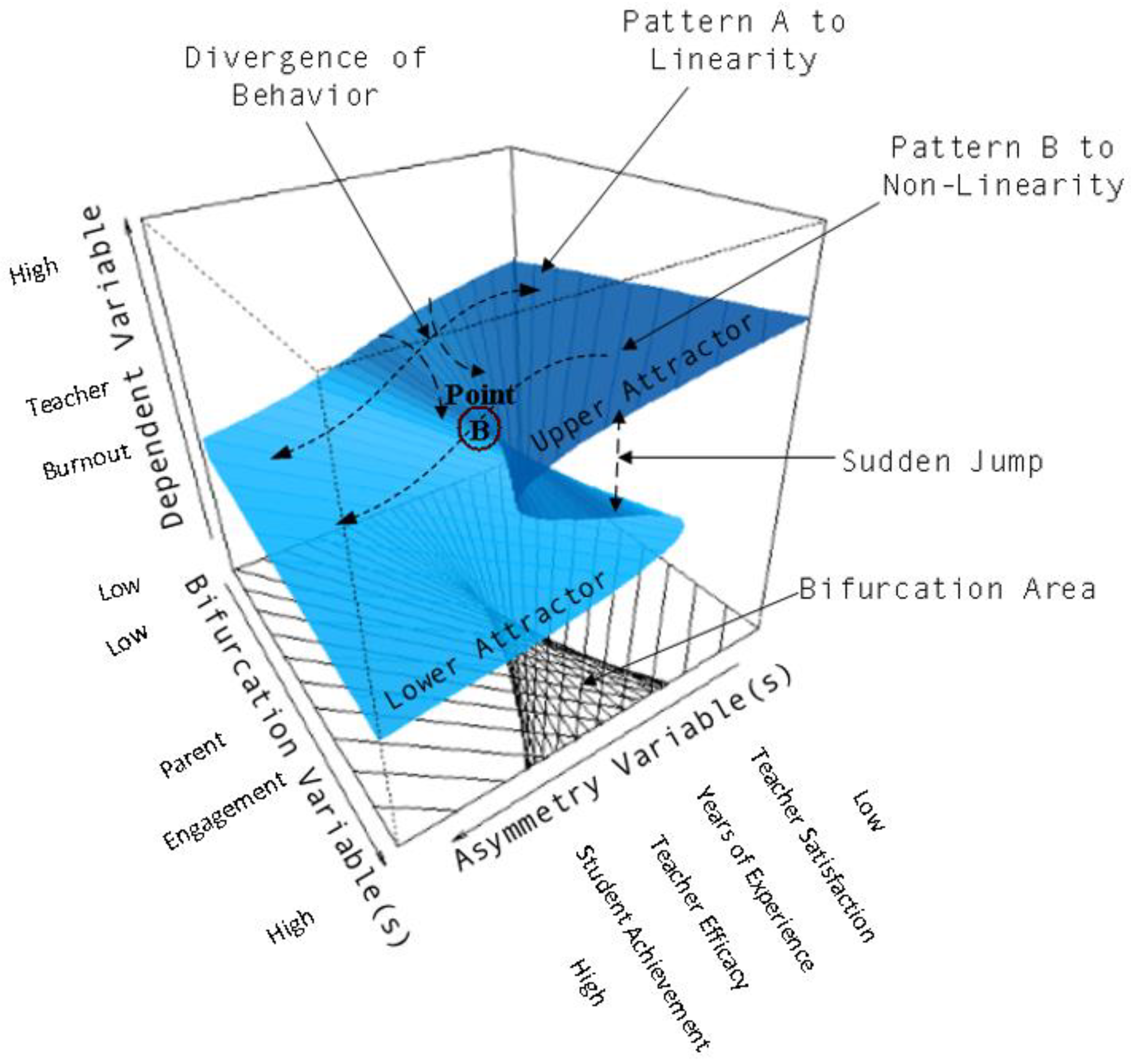
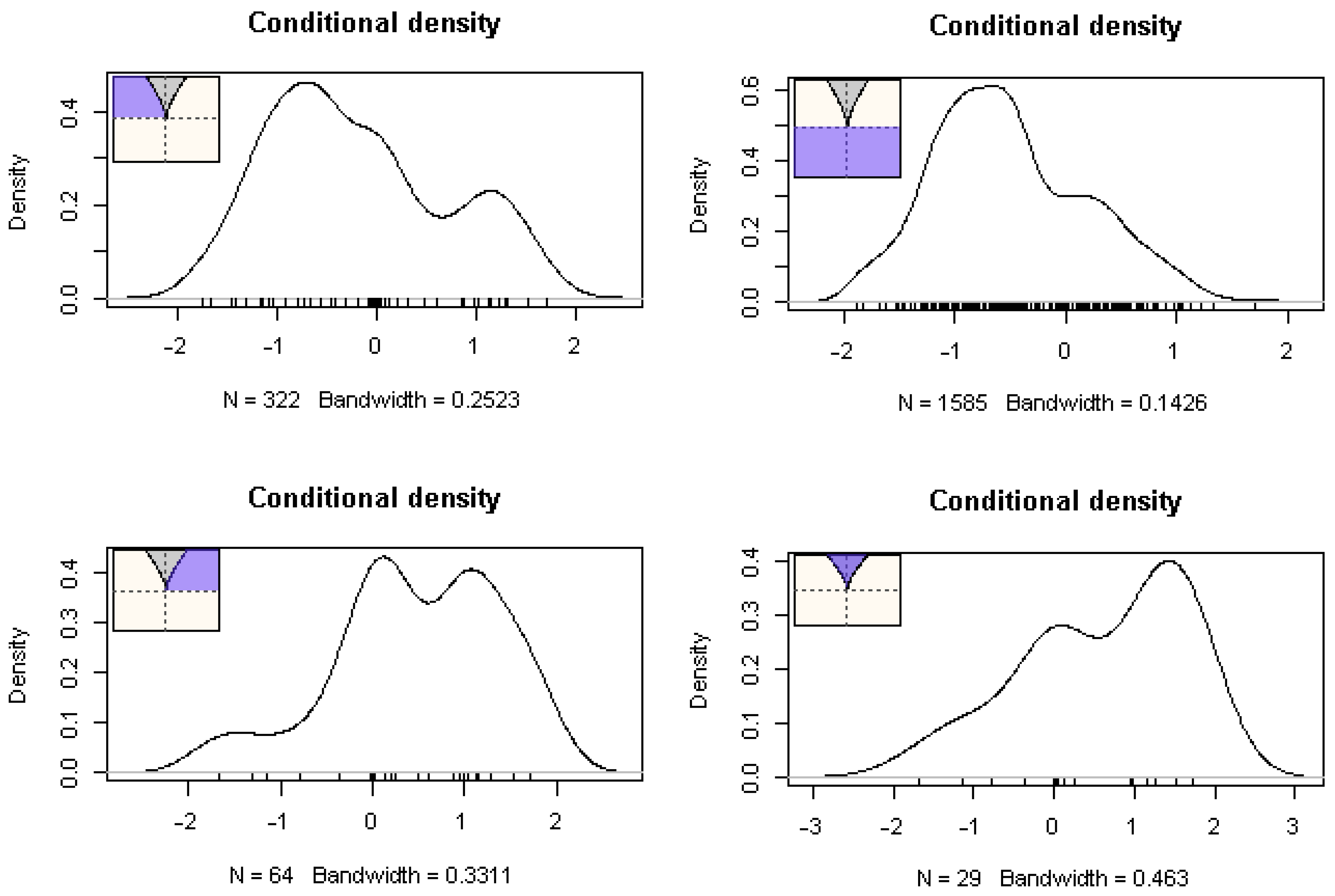
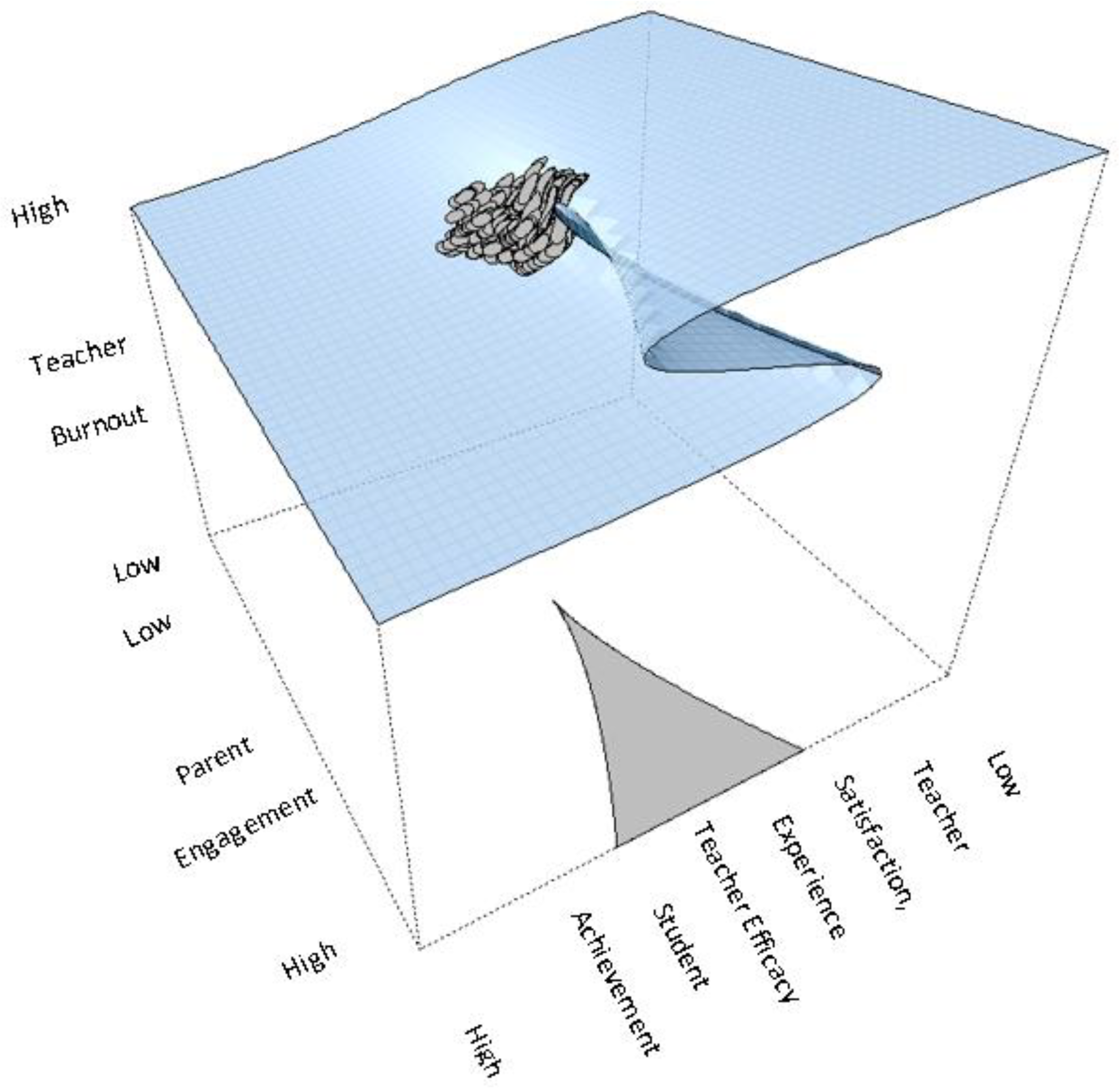
5.3. Parental Engagement and Teacher Burnout: A Cusp Catastrophe Modeling Approach
6. Discussion
6.1. Cusp Model Interpretation
6.2. Implications of the Findings for Educational Policy
6.3. Study Limitations and Directions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| TIMSS 2019 Number | TIMSS 2019 Variable Name | Domains/Constructs |
|---|---|---|
| Teacher Burnout | ||
| TQG-09a | ATBG09A | There are too many students in the classes |
| TQG-09b | ATBG09B | I have too much material to cover in class |
| TQG-09c | ATBG09C | I have too many teaching hours |
| TQG-09d | ATBG09D | I need more time to prepare for class |
| TQG-09e | ATBG09E | I need more time to assist individual students |
| TQG-09f | ATBG09F | I feel too much pressure from parents |
| TQG-09g | ATBG09G | I have difficulty keeping up with all of the changes to the curriculum |
| TQG-09h | ATBG09H | I have too many administrative tasks |
| School Emphasis on Academic Success—Teachers’ Efficacy | ||
| TQG-06a | ATBG06A | Teachers’ understanding of the school’s curricular goals |
| TQG-06b | ATBG06B | Teachers’ degree of success in implementing the school’s curriculum |
| TQG-06c | ATBG06C | Teachers’ expectations for student achievement |
| TQG-06d | ATBG06D | Teachers’ ability to inspire students |
| School Emphasis on Academic Success: Parental Engagement/Involvement | ||
| TQG-06e | ATBG06E | Parental involvement in school activities |
| TQG-06f | ATBG06F | Parental commitment to ensure that students are ready to learn |
| TQG-06g | ATBG06G | Parental expectations for student achievement |
| TQG-06h | ATBG06H | Parental support for student achievement |
| Teachers’ Job Satisfaction | ||
| ATDGTJS | Teachers’ Job Satisfaction | |
| Teachers’ Teaching Experience | ||
| ATBG01 | Years teaching | |
| Mathematics Achievement (8th Grade) | ||
| ASMMAT01 | Mathematics 1st plausible value (the correlation between plausible values was 0.99) | |
References
- Almatrafi, M.; Alsulami, E.; Saleh, R.; Sadaqa, G.; Alamoudi, R.; Althagafi, J.; Alghamdi, F.; Goweda, R. The prevalence and severity of burnout syndrome among school teachers in Makkah city, Saudi Arabia: A cross sectional study. Med. Sci. 2022, 26, ms466e2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslach, C.; Schaufeli, W.B.; Leiter, M.P. Job burnout. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsouloupas, C.N.; Carson, R.L.; Matthews, R.; Grawitch, M.J.; Barber, L.K. Exploring the Association between Teachers’ Perceived Student Misbehaviour and Emotional Exhaustion: The Importance of Teacher Efficacy Beliefs and Emotion Regulation. Educ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, V.; Joshanloo, M.; Park, M.S.A. Burnout, Depression, Efficacy Beliefs, and Work-Related Variables among School Teachers. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 95, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, G.; Nikdel, F.; Labbafi, A. Exploring the Consequences of Teachers’ Self-Efficacy: A Case of Teachers of English as a Foreign Language. Asian-Pac. J. Second Foreign Lang. Educ. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernet, C.; Guay, F.; Senecal, C.; Austin, S. Predicting Intraindividual Changes in Teacher Burnout: The Role of Perceived School Environment and Motivational Factors. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2012, 28, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauermann, F.; Konig, J. Teachers’ Professional Competence and Wellbeing: Understanding the Links between General Pedagogical Knowledge, Self-Efficacy and Burnout. Learn. Instr. 2016, 45, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, D.A. Demoralized: Why Teachers Leave the Profession They Love and How They Can Stay; Harvard Education Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marvel, J.; Lyter, D.M.; Peltola, P.; Strizek, G.A.; Morton, B.A. Teacher Attrition and Mobility: Results from the 2004–2005 Follow up Teacher Survey; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, WA, USA, 2006.
- Whipp, P.R.; Tan, G.; Yeo, P.T. Experienced physical education teachers reaching their “use-by date” powerless and disrespected. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2007, 78, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, I.S. Stress in First-Year Women Teachers: The Context of Social Support and Coping. Genet. Soc. Gen. Psychol. Monogr. 2001, 127, 133–168. [Google Scholar]
- Klusmann, U.; Kunter, M.; Trautwein, U.; Ludtke, O.; Baumert, J. Teachers’ occupational well-being and quality of instruction: The important role of self-regulatory patterns. J. Educ. Psychol. 2008, 100, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, R.M.; Chiu, M.M. Effects on Teachers’ Self-Efficacy and Job Satisfaction: Teacher Gender, Years of Experience, and Job Stress. J. Educ. Psychol. 2010, 102, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; McCaughtry, N.; Martin, J.; Garn, A.; Kulik, N.; Fahlman, M. The Relationship between Teacher Burnout and Student Motivation. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 85, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, L.N.; Nickerson, A.B. Bullying Participant Roles and Gender as Predictors of Bystander Intervention: Predictors of Bystander Intervention. Aggress. Behav. 2017, 43, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschannen-Moran, M.; Woolfolk Hoy, A. The Differential Antecedents of Self-Efficacy Beliefs of novice and experienced teachers. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2007, 23, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, D.; Kim, L. Does Teacher Burnout Affect Students? A Systematic Review of Its Association with Academic Achievement and Student-Reported Outcomes. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 105, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaalvik, E.M.; Skaalvik, S. Dimensions of Teacher Self-Efficacy and Relations with Strain Factors, Perceived Collective Teacher Efficacy, and Teacher Burnout. J. Educ. Psychol. 2007, 99, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, T.; Parker, P.D.; Marsh, H.W.; Kunter, M.; Schmeck, A.; Leutner, D. Self-Efficacy in Classroom Management, Classroom Disturbances, and Emotional Exhaustion: A Moderated Mediation Analysis of Teacher Candidates. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 106, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, T.; Parker, P.D.; Holzberger, D.; Kunina-Habenicht, O.; Kunter, M.; Leutner, D. Beginning Teachers’ Efficacy and Emotional Exhaustion: Latent Changes, Reciprocity, and the Influence of Professional Knowledge. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 41, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, R.; O’Brien, P.; Goddard, M. Work Environment Predictors of Beginning Teacher Burnout. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2006, 32, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigaard, R.; Giske, R.; Sundsli, K. Newly Qualified Teachers’ Work Engagement and Teacher Efficacy Influences on Job Satisfaction, Burnout, and the Intention to Quit. Eur. J. Teach. Educ. 2012, 35, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serow, R.C. Called to Teach: A Study of Highly Motivated Preservice Teachers. J. Res. Dev. Educ. 1994, 27, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zakriveska, M. The Differences between Special Education Teachers Professional Burnout Levels for 10 and 25 Work Experience. In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Conference on Social Sciences & Arts SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 2–7 September 2014; pp. 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, E.W.; Shapard, L. Employee Burnout: A Meta-analysis of the Relationship between Age or Years of Experience. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2004, 3, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Job Demands and Resources as Antecedents of University Teachers’ Exhaustion, Engagement and Job Satisfaction. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 40, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swider, B.W.; Zimmerman, R.D. Born to Burnout: A Meta-Analytic Path Model of Personality, Job Burnout, and Work Outcomes. J. Vocat. Behav. 2010, 76, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klusmann, U.; Richter, D.; Lüdtke, O. Teachers’ Emotional Exhaustion Is Negatively Related to Students’ Achievement: Evidence from a Large-Scale Assessment Study. J. Educ. Psychol. 2016, 108, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, A.; Evers, W.; Tomic, W. A Longitudinal Study of Teacher Burnout and Perceived Self-Efficacy in Classroom Management. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2000, 16, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschannen-Moran, M.; Woolfolk Hoy, A.W. Teacher Efficacy: Capturing an Elusive Construct. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2001, 17, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, I.A.; Kass, E. Teacher Self-Efficacy: A Classroom-Organization Conceptualization. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2002, 18, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfolk, A. Educational Psychology, 10th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaith, G.; Yaghi, M. Relationships among Experience, Teacher Efficacy, and Attitudes toward the Implementation of Instructional Innovation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 1997, 13, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinder, R.M. The Relationship between Efficacy and the Instructional Practices of Special education teachers and consultants. Teach. Educ. Spec. Educ. 1994, 17, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimmieson, N.L.; Hannam, R.L.; Yeo, G.B. Teacher Organizational Citizenship Behaviors and Job Efficacy: Implications for Student Quality of School Life. Br. J. Psychol. 2010, 101, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Cawthon, S.; Dawson, K. Elementary and Secondary Teacher Self-Efficacy for Teaching and Pedagogical Conceptual Change in a Drama-Based Professional Development Program. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2013, 30, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfolk, A.; Rosoff, B.; Hoy, W.K. Teachers’ Sense of Efficacy and Their Beliefs about managing students. Teach. Teach. Educ. 1990, 6, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, A.D.; Yan, N. Classroom Race/Ethnic Composition, Family-School Connections, and the Transition to School. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2015, 19, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Expósito-Casas, E.; López-Martín, E.; Lizasoain, L.; Navarro-Asencio, E.; Gaviria, J. Parental Involvement on Student Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis. Educ. Res. Rev. 2015, 14, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Kwok, O. Influence of Student-Teacher and Parent-Teacher Relationships on Lower Achieving Readers’ Engagement and Achievement in the Primary Grades. J. Educ. Psychol. 2007, 99, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Lo, M.; Bai, H. Recommended Practices: Cultivating a Culturally Responsive Learning Environment for Chinese Immigrants and Chinese American Students. Prev. Sch. Fail. Altern. Educ. Child. Youth 2013, 57, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilli, C.; Albanese, O.; Gabola, P.; Pepe, A. Teachers’ Emotional Competence and Social Support: Assessing the Mediating Role of Teacher Burnout. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 61, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolnick, W.S.; Slowiaczek, M.L. Parents’ Involvement in Children’s Schooling: A Multidimensional Conceptualization and Motivational Model. Child Dev. 1994, 65, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons-Morton, B.; Chen, R. Peer and Parent Influences on School Engagement among Early Adolescents. Youth Soc. 2009, 41, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, W.H. The Relationship between Parental Involvement and Urban Secondary School Student Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis. Urban Educ. 2007, 42, 82–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, M. Parental Involvement and Students’ Academic Achievement: A Metaanalysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; McCartney, C.; Richard, V.; Johnson, S.; Kwon, K. Associations between Parent-Teacher and Teacher-Child Relationships and Children’s Socioemotional Functioning. Early Child Dev. Care 2021, 191, 2407–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpell, Z.N.; Mashburn, A.J. Family-School Connectedness and Children’s Early Social Development. Soc. Dev. 2012, 21, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.T.; Sheikh-Khalil, S. Does parental involvement matter for student achievement and mental health in high school? Child Dev. 2014, 85, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.N.; Tolbert, A.R.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.J.; Bonomi, A.E. A Cocaring Framework for Infants and Toddlers: Applying a Model of Coparenting to Parent-Teacher Relationships. Early Child. Res. Q. 2016, 34, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minke, K.M.; Sheridan, S.M.; Kim, E.M.; Ryoo, J.H.; Koziol, N.A. Congruence in Parent-Teacher Relationships: The Role of Shared Perceptions. Elem. Sch. J. 2014, 114, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iruka, I.U.; Winn, D.C.; Kingsley, S.J.; Orthodoxou, Y.J. Links between Parent-Teacher Relationships and Kindergartners’ Social Skills: Do Child Ethnicity and Family Income Matter? Elem. Sch. J. 2011, 111, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkovich, I.; Eyal, G. I’m Caught in the Middle’: Preschool Teachers’ Perspectives on Their Work with Divorced Parents. Int. J. Early Years Educ. 2021, 29, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrooks, M.A.; Raskin, M.; McBrian, S.F. Father Involvement and Toddlers’ Behavior Regulation: Evidence from a High Social Risk Sample. Father. J. Theory Res. Pract. Men Father. 2014, 12, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, R.; Garbacz, A.; Beattie, T.; Moore, C. Parent-teacher relationships in elementary school: An examination of parent-teacher trust. Psychol. Sch. 2016, 53, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, S.A.; Herman, K.C.; Thompson, A.M.; Reinke, W.M. Family engagement in education and intervention: Implementation and evaluation to maximize family, school, and student outcomes. J. Sch. Psychol. 2017, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, S.D.; Park, S. Broken Compass or Broken System? Questioning the Role of Parent Involvement in Promoting Student Achievement. Hum. Dev. 2014, 57, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilton, R.; Jackson, A.; Hymer, B. Cooperation, Conflict and Control: Parent–Teacher Relationships in an English Secondary School. Educ. Rev. 2018, 70, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasky, S. The cultural and emotional politics of teacher–parent interactions. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2000, 16, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Harris, A. The Broken Compass: Parental Involvement with Children’s Education; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dicke, T.; Stebner, F.; Linninger, C.; Kunter, M.; Leutner, D. A Longitudinal Study of Teachers’ Occupational Well-Being: Applying the Job Demands-Resources Model. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2018, 23, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.G.; McCarthy, C.; O’Donnell, M.; Wang, C. Measuring elementary teacher stress and coping in the classroom: Validity evidence for the classroom appraisal of resources and demands. Psychol. Sch. 2009, 46, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, R. Structural Stability and Morphogenesis; Benjamin, W.A.: Reading, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Maslach, C. Burnout, the Cost of Caring; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Badri, M. School Emphasis on Academic Success and TIMSS Science/Math Achievements. Int. J. Res. Educ. Sci. IJRES 2019, 5, 176–189. [Google Scholar]
- Skaalvik, E.M.; Skaalvik, S. Teacher Job Satisfaction and Motivation to Leave the Teaching Profession: Relations with School Context, Feeling of Belonging, and Emotional Exhaustion. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2011, 27, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastello, S.J. Managing Emergent Phenomena: Non-Linear Dynamics in Work Organizations; Lawrence: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grasman, R.P.; Maas, H.L.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Fitting the Cusp Catastrophe in R: A Cusp-Package Primer. J. Stat. Softw. 2009, 32, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, L. An Introduction to Cusp Surface Analysis; Technical Report; Aetheling Consultants: Louisville, CO, USA, 1998; Available online: http://www.aetheling.com/models/cusp/Intro (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Hartelman, P.A.I. Stochastic Catastrophe Theory. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zabel, R.H.; Zabel, M.K. Revisiting Burnout among Special Education Teachers: Do Age, Experience, and Preparation Still Matter. Teach. Educ. Spec. Educ. 2001, 24, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Garbacz, S.A.; Dishion, T.J.; Gau, J.M.; Brown, K.L.; Stormshak, E.A.; Seeley, J.R. Proactive Parent Engagement in Public Schools: Using a Brief Strengths and Needs Assessment in a Multiple-Gating Risk Management Strategy. J. Posit. Behav. Interv. 2016, 18, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, E.; Stanley, L.; Kemple, K.M. Opening Doors: Understanding School and Family Influences on Family Involvement. Early Child. Educ. J. 2005, 33, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, K.C.; Hickmon-Rosa, J.; Reinke, W.M. Empirically Derived Profiles of Teacher Stress, Burnout, Self-Efficacy, and Coping Associated Student Outcomes. J. Posit. Behav. Interv. 2018, 20, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedmont, R.L. A Longitudinal Analysis of Burnout in the Health Care Setting: The Role of Personal Dispositions. J. Pers. Assess. 1993, 61, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, S.A.; Santiago, R.; Kosty, D.; Zahn, M.; Stormshak, E.A.; Smolkowski, K.; Seeley, J.R. Examining Congruence in Parent-Teacher Perceptions of Middle School Supports for Students and Families. Psychol. Sch. 2020, 58, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiani, J.; Duran, C.; Pas, E.; Bradshaw, C. Teacher Stress and Burnout in Urban Middle Schools: Associations with Job Demands, Resources, and Effective Classroom Practices. J. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 77, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Terms in Cusp Model | B | C.I. B95% Low | C.I. B95% High | S.E. | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Intercept of asymmetry var.) | −0.123 | −0.356 | 0.111 | 0.119 | −1.031 | 0.303 |
| a1 (Teacher’s Efficacy) | −0.332 | −0.387 | −0.276 | 0.028 | −11.729 | 0.001 ** |
| a2 (Teacher’s Satisfaction) | −0.557 | −0.752 | −0.361 | 0.100 | −5.585 | 0.001 ** |
| a3 (Teacher’s Years of Experience) | −0.243 | −0.290 | −0.196 | 0.024 | −10.034 | 0.001 ** |
| a4 (Student’s Math Achievement) | 0.224 | 0.188 | 0.260 | 0.018 | 12.356 | 0.001 ** |
| b (Intercept of bifurcation vars.) | −0.375 | −0.454 | −0.295 | 0.041 | −9.255 | 0.001 ** |
| b (Parental Involvement) | −0.418 | −0.459 | −0.376 | 0.021 | −19.919 | 0.001 ** |
| w (Intercept of outcome variable) | −0.418 | −0.452 | −0.385 | 0.017 | −24.426 | 0.001 ** |
| w (Teacher Burnout) | 0.762 | 0.743 | 0.781 | 0.010 | 78.646 | 0.001 ** |
| Model Tested | Loglikelihood | Npar | AIC | AICc | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Linear | −2706.65 | 7 | 5427.302 | 5427.358 | 5466.508 |
| 2. Logistic | −2629.42 | 8 | 5274.830 | 5274.902 | 5319.637 |
| 3. Cusp | −2600.25 | 9 | 5218.505 | 5218.596 | 5268.913 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sideridis, G.; Alghamdi, M.H. Teacher Burnout in Saudi Arabia: The Catastrophic Role of Parental Disengagement. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050367
Sideridis G, Alghamdi MH. Teacher Burnout in Saudi Arabia: The Catastrophic Role of Parental Disengagement. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(5):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050367
Chicago/Turabian StyleSideridis, Georgios, and Mohammed H. Alghamdi. 2023. "Teacher Burnout in Saudi Arabia: The Catastrophic Role of Parental Disengagement" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 5: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050367
APA StyleSideridis, G., & Alghamdi, M. H. (2023). Teacher Burnout in Saudi Arabia: The Catastrophic Role of Parental Disengagement. Behavioral Sciences, 13(5), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050367





