The Influence of Emotion Induced by Accidents and Incidents on Pilots’ Situation Awareness
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Human Factors in Aviation Accidents and Influence on Pilot Emotions
1.2. Influence of Pilot Emotion on Aviation Security and SA
1.3. Influence of Emotions on Cognitive Abilities and Regulating Effects of Emotional Intelligence
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
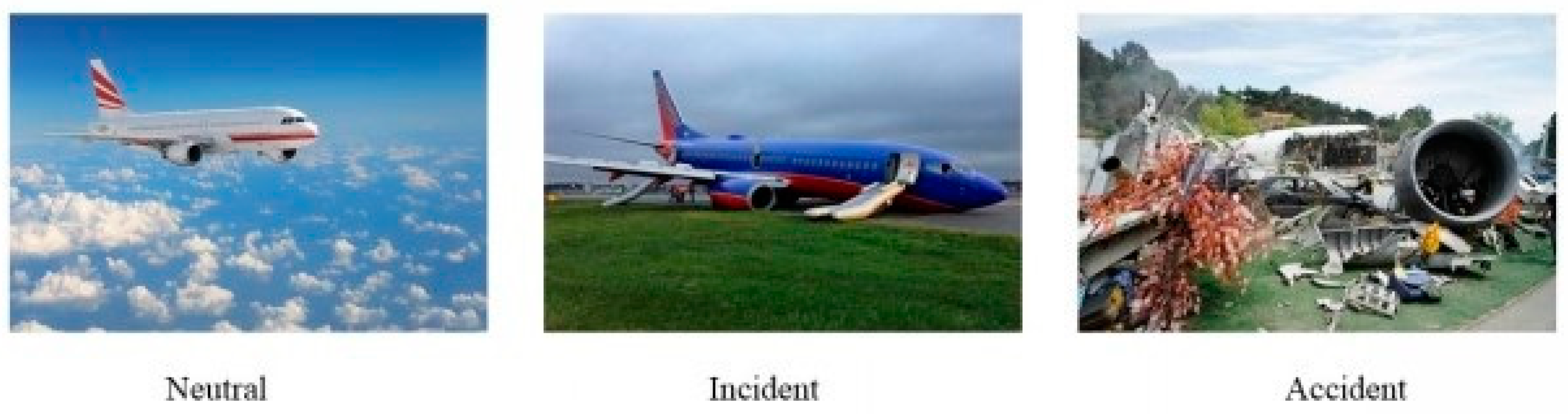
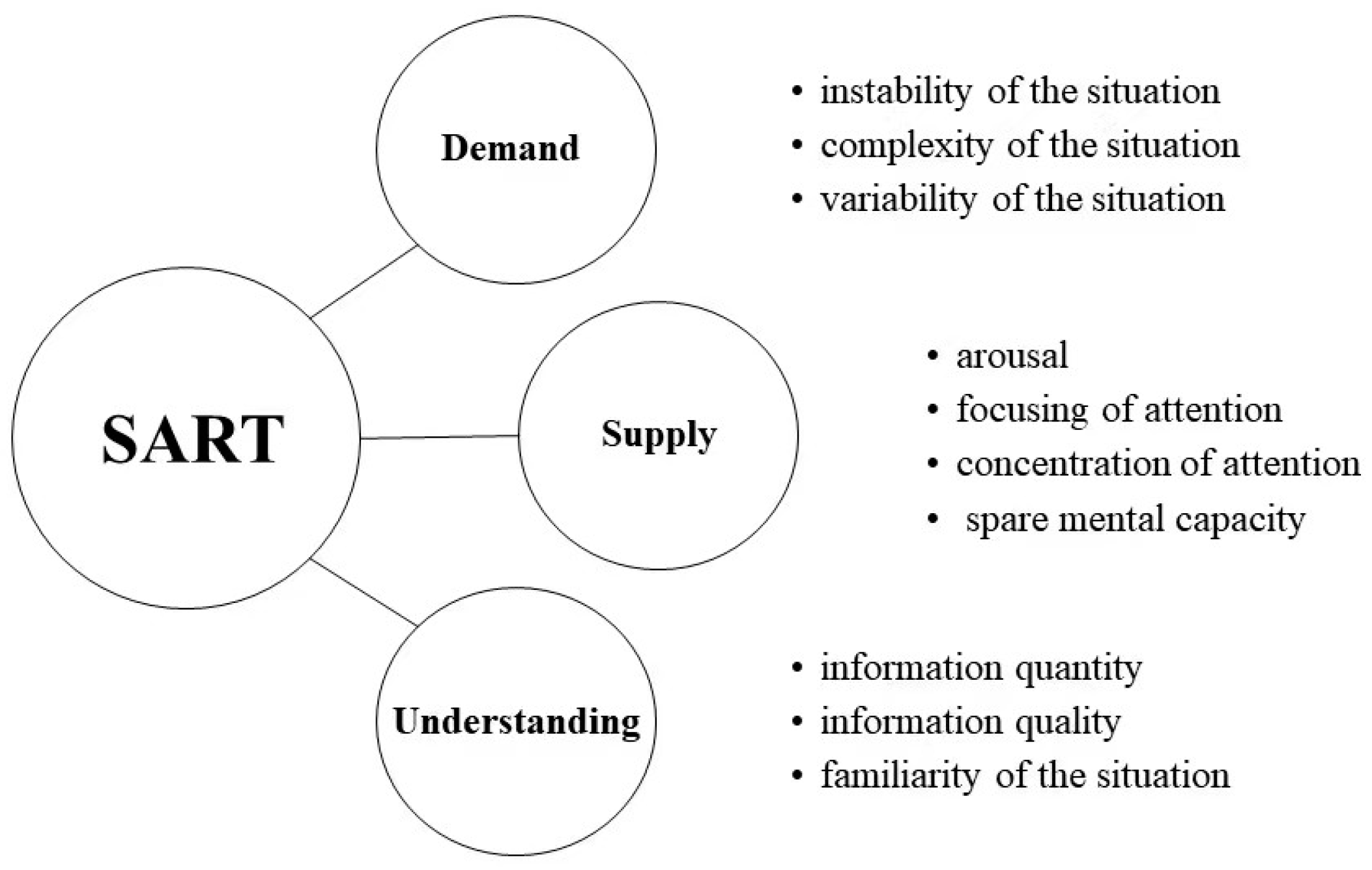
2.2. Materials
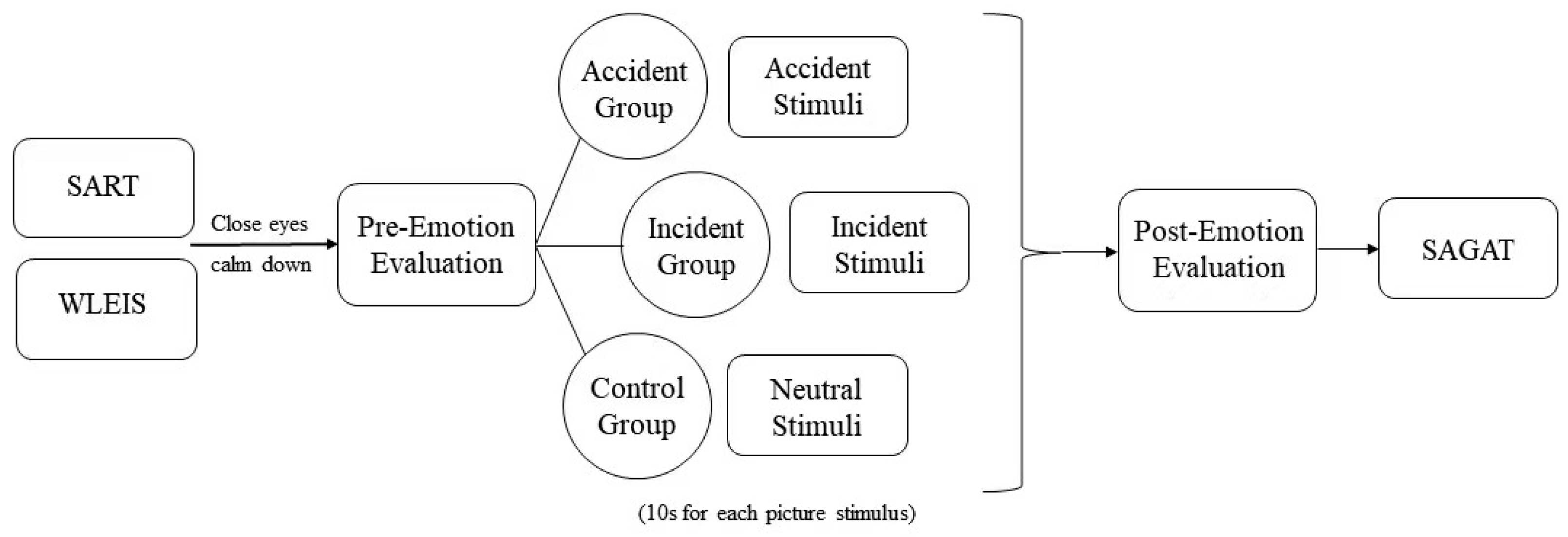
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Pilot’s Emotional State of Various Dimensions under Different Induction Conditions
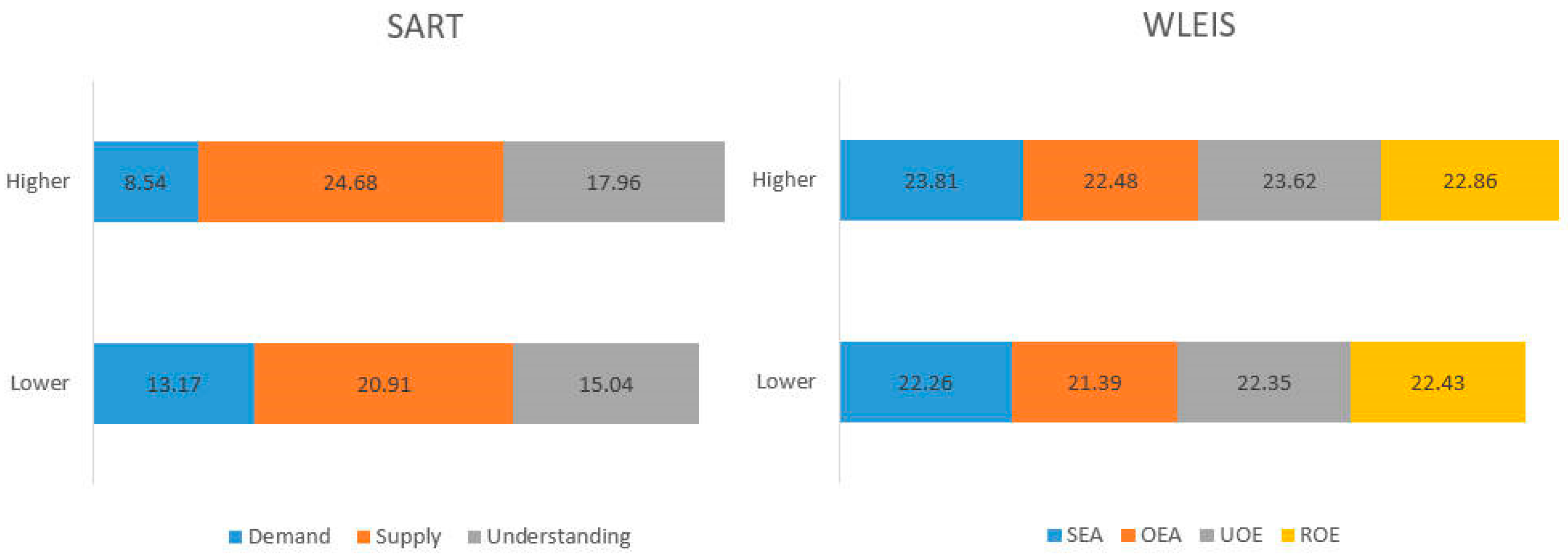
3.2. Differences of Emotional Intelligence between Groups under Clustering of SART
3.3. The Effect of Pilot’s Emotional Intelligence on the Rate of Emotional Change after Induction
3.4. The Effects of SART and the Rate of Emotional Change on SAGAT after Induction
3.5. A Conditional Process Model of Evoked Pilots’ SA: Mediating Effect of Emotion and Moderating Effect of Emotional Intelligence
4. Discussion
4.1. The Difference in Pilots’ Emotional Change Rate Is Insignificant under Accident and Incident Induction Conditions
4.2. Emotional Intelligence Mediates the Effects of Accidents and Incidents’s on Pilot Emotions and Baseline SA Level
4.3. Accidents and Incidents and Post-Induction Emotional Changes Follow Different Functional Mechanisms on Pilots’ Post-SA Emotional Induction
4.4. Accidents and Incidents’ Influence on Pilots’ Post-Induction Emotions, Self-Regulation, and Post-Induction SA Is Regulated by Pilot SA Level and Induction Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noroozi, A.; Khakzad, N.; Khan, F.; MacKinnon, S.; Abbassi, R. The Role of Human Error in Risk Analysis: Application to Pre- and Post-Maintenance Procedures of Process Facilities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 119, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endsley, M.R. Errors in Situation Assessment: Implications for System Design. In Human Error and System Design and Management; Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences; Springer: London, UK, 2000; Volume 253, pp. 15–26. ISBN 978-1-85233-234-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.G.; Endsley, M.R. Sources of Situation Awareness Errors in Aviation. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1996, 67, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orasanu, J.; Davison, J.; Ciavarelli, A.; Cohen, M.; Fischer, U.; Slovic, P. The Many Faces of Risk in Aviation Decision Making. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2001, 45, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasvári, T. Risk, Risk Perception, Risk Management—A Review of the Literature. Public Financ. Q. 2015, 60, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sarter, N.B.; Woods, D.D. Situation Awareness: A Critical But Ill-Defined Phenomenon. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1991, 1, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J.; Tenney, Y.J.; Pew, R.W. Situation Awareness and the Cognitive Management of Complex Systems. Hum. Factors 1995, 37, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, C.E. Situation Awareness Measurement and Analysis: A Commentary. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Experimental Analysis and Measurement of Situation Awareness; Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University Press: Daytona Beach, FL, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.M. Situational Awareness Rating Technique (SART): The Development of a Tool for Aircrew Systems Design. In Situational Awarenes; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 111–128. ISBN 978-1-315-08792-4. [Google Scholar]
- Endsley, M.R. Toward a Theory of Situation Awareness in Dynamic Systems. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 1995, 37, 32–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endsley, M.R.; Garland, D.J. Situation Awareness Analysis and Measurement; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Endsley, M.R.; Robertson, M.M. Situation Awareness in Aircraft Maintenance Teams. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2000, 26, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.W.; Doane, S.M. Memory Processes of Flight Situation Awareness: Interactive Roles of Working Memory Capacity, Long-Term Working Memory, and Expertise. Hum. Factors 2004, 46, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Mathna, E.K. Metacognitive Strategy Training Improves Driving Situation Awareness. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2009, 37, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, C.D.; McCarley, J.S.; Alexander, A.L.; Thomas, L.C.; Ambinder, M.; Zheng, S. Attention-Situation Awareness (A-SA) Model of Pilot Error. In Human Performance Modeling in Aviation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; Volume 9, pp. 213–239. ISBN 978-0-8058-5964-5. [Google Scholar]
- Endsley, M.R.; Bolstad, C.A. Individual Differences in Pilot Situation Awareness. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1994, 4, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ling, L.; Liang, Z.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Y. Survey and Analysis of Mental Health in Civil Pilots. J. Trop. Med. 2004, 4, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xuan, Y.; Wei, D.; Ge, Q. Dynamic Research of Mental Health of Pilots Exposed to Aviation Accident. J. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 39, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathne, D.J. Modelling of Situation Awareness with Perception, Attention, and Prior and Retrospective Awareness. Biol. Inspired Cogn. Archit. 2015, 12, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharoufah, H.; Murray, J.; Baxter, G.; Wild, G. A Review of Human Factors Causations in Commercial Air Transport Accidents and Incidents: From to 2000–2016. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2018, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Weiner, M.; Neylan, T. Regional Cerebral Volumes in Veterans with Current versus Remitted Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2013, 213, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, J.K.; Lamke, J.-P.; Gaebler, M.; Walter, H.; Scheel, M. White matter integrity and its relationship to ptsd and childhood trauma-a systematic review and meta-analysis: White matter integrity. Depress. Anxiety 2013, 30, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Killgore, W.D.S.; Rosso, I.M.; Britton, J.C.; Schwab, Z.J.; Weiner, M.R.; Simon, N.M.; Pollack, M.H.; Rauch, S.L. Voxel-Based Morphometric Gray Matter Correlates of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. J. Anxiety Disord. 2013, 27, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Shen, C.; Shi, X.; Ma, W. Investigation on the Psychological Health Situation of the Pilots after Crush. Med. J. Air Force 2014, 30, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, S.; de Rooy, D. Pilot Mental Health, Negative Life Events, and Improving Safety with Peer Support and a Just Culture. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2018, 89, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. On the Application of Sketch Engine in Teaching Civil Aviation Terms: Taking Accident and Incident as Examples. Coll. Foreign Lang. Teach. Res. 2016, 1, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, M.W.; Moser, R. Aviators at Risk. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1995, 66, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiegmann, D.A.; Shappell, S.A. A Human Error Analysis of Commercial Aviation Accidents Using the Human Factors Analysis and Classification System (HFACS); Office of Aviation Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Catherwood, D.; Edgar, G.K.; Nikolla, D.; Alford, C.; Brookes, D.; Baker, S.; White, S. Mapping Brain Activity During Loss of Situation Awareness: An EEG Investigation of a Basis for Top-Down Influence on Perception. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2014, 56, 1428–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, N.; Clore, G.L. Mood, Misattribution, and Judgments of Weil-Being: Informative and Directive Functions of Affective States. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1983, 45, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, G.; Lerner, J.S. The Role of Affect in Decision Making. In Handbook of Affective Sciences; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 31, pp. 619–642. ISBN 0-19-512601-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, J.S.; Keltner, D. Beyond Valence: Toward a Model of Emotion-Specific Influences on Judgement and Choice. Cogn. Emot. 2000, 14, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunathan, R.; Pham, M.T. All Negative Moods Are Not Equal: Motivational Influences of Anxiety and Sadness on Decision Making. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1999, 79, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.J.; Tversky, A. Affect, Generalization, and the Perception of Risk. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1983, 45, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D. Emotional Intelligence. Imagin. Cogn. Personal. 1990, 9, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, E.H.; Humphrey, R.H.; Pollack, J.M.; Hawver, T.H.; Story, P.A. The Relation between Emotional Intelligence and Job Performance: A Meta-Analysis. J. Organ. Behav. 2011, 32, 788–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Wickens, C. Eye-Tracking and Individual Differences in Off-Normal Event Detection When Flying with a Synthetic Vision System Display. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2004; Volume 48, pp. 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, E.; Blättler, C.; Camachon, C.; Hurter, C. Eye Movements Data Processing for Ab Initio Military Pilot Training. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Decision Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 39, pp. 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- van de Merwe, K.; van Dijk, H.; Zon, R. Eye Movements as an Indicator of Situation Awareness in a Flight Simulator Experiment. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 2012, 22, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Gugerty, L. Development of a Novel Measure of Situation Awareness: The Case for Eye Movement Analysis. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2010, 54, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, F.; Zhou, S. Analysis on Eye Movement Indexes Based on Simulated Flight Task. In Proceedings of the Engineering Psychology and Cognitive Ergonomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8532, pp. 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.-S.; Law, K.S. The Effects of Leader and Follower Emotional Intelligence on Performance and Attitude. Leadersh. Q. 2002, 13, 243–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Bandalos, D.L. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis, 2nd ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017; p. 714. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, L.C.; Miller, M.R.; Ree, M.J. Structured Interviews for Pilot Selection: No Incremental Validity. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1993, 3, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Sussman, T.J. Top-down Modulation of Attention by Emotion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeters, K.-M.; Timmermann, B.; Maschke, P. The Construction of Personality Questionnaires for Selection of Aviation Personnel. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1993, 3, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.R.; Angela, S.; Tom, J. (Eds.) Appraisal Processes in Emotion: Theory, Methods, Research; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-19-513007-3. [Google Scholar]
- Izard, C.E. The Structure and Functions of Emotions: Implications for Cognition, Motivation, and Personality. In The G. Stanley Hall Lecture Series; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 9, pp. 39–73. [Google Scholar]
- Izard, C.E. Basic Emotions, Natural Kinds, Emotion Schemas, and a New Paradigm. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 2, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.A.; King, L.M.; Howard, J.A. Inducing Affect about Self or Other: Effects on Generosity in Children. Dev. Psychol. 1979, 15, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, B.; Olatunji, B.O. Specificity of Disgust Sensitivity in the Prediction of Behavioral Avoidance in Contamination Fear. Behav. Res. Ther. 2007, 45, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, L. On the Formation and Regulation of Anger and Aggression. Am. Psychol. 1990, 45, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: Volume II—Separation, Anxiety and Anger; The Hogarth Press: London, UK, 1973; ISBN 978-0-14-021870-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.; Daly, M. Competitiveness, Risk Taking, and Violence: The Young Male Syndrome. Ethol. Sociobiol. 1985, 6, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, M.G.; Tesser, A. The Effects of Affective-Cognitive Consistency an on the Attitude-Behavior Relation. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1989, 25, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.A.; Papa, A.; Lalande, K.; Westphal, M.; Coifman, K. The Importance of Being Flexible: The Ability to Both Enhance and Suppress Emotional Expression Predicts Long-Term Adjustment. Psychol. Sci. 2004, 15, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.J. Antecedent- and Response-Focused Emotion Regulation: Divergent Consequences for Experience, Expression, and Physiology. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 74, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, R.J.; Roessingh, J.J.M. An Evaluation of Cognitive Models for Surprise and Situation Awareness in a Flight Simulator with Fighter Pilots; National Aerospace Laboratory NLR: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.; Talone, A.B.; Boesser, C.T.; Jentsch, F.; Yeh, M. Startle and Surprise on the Flight Deck: Similarities, Differences, and Prevalence. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 58, pp. 1047–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Frijda, N.H. The Emotions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1986; ISBN 0-521-30155-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, R.S. Emotion and Adaptation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 0-19-506994-3. [Google Scholar]
- Finucane, A.M.; Whiteman, M.C.; Power, M.J. The Effect of Happiness and Sadness on Alerting, Orienting, and Executive Attention. J. Atten. Disord. 2010, 13, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joormann, J.; Gotlib, I.H. Updating the Contents of Working Memory in Depression: Interference from Irrelevant Negative Material. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2008, 117, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolen-Hoeksema, S.; Wisco, B.E.; Lyubomirsky, S. Rethinking Rumination. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 3, 400–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, N.; Schweitzer, K.; Chai, C.A.; Myers, B. Negative Emotions Felt During Trial: The Effect of Fear, Anger, and Sadness on Juror Decision Making: Negative Emotions and Decision Making. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2015, 29, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanska, G.; Murray, K.T.; Harlan, E.T. Effortful Control in Early Childhood: Continuity and Change, Antecedents, and Implications for Social Development. Dev. Psychol. 2000, 36, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


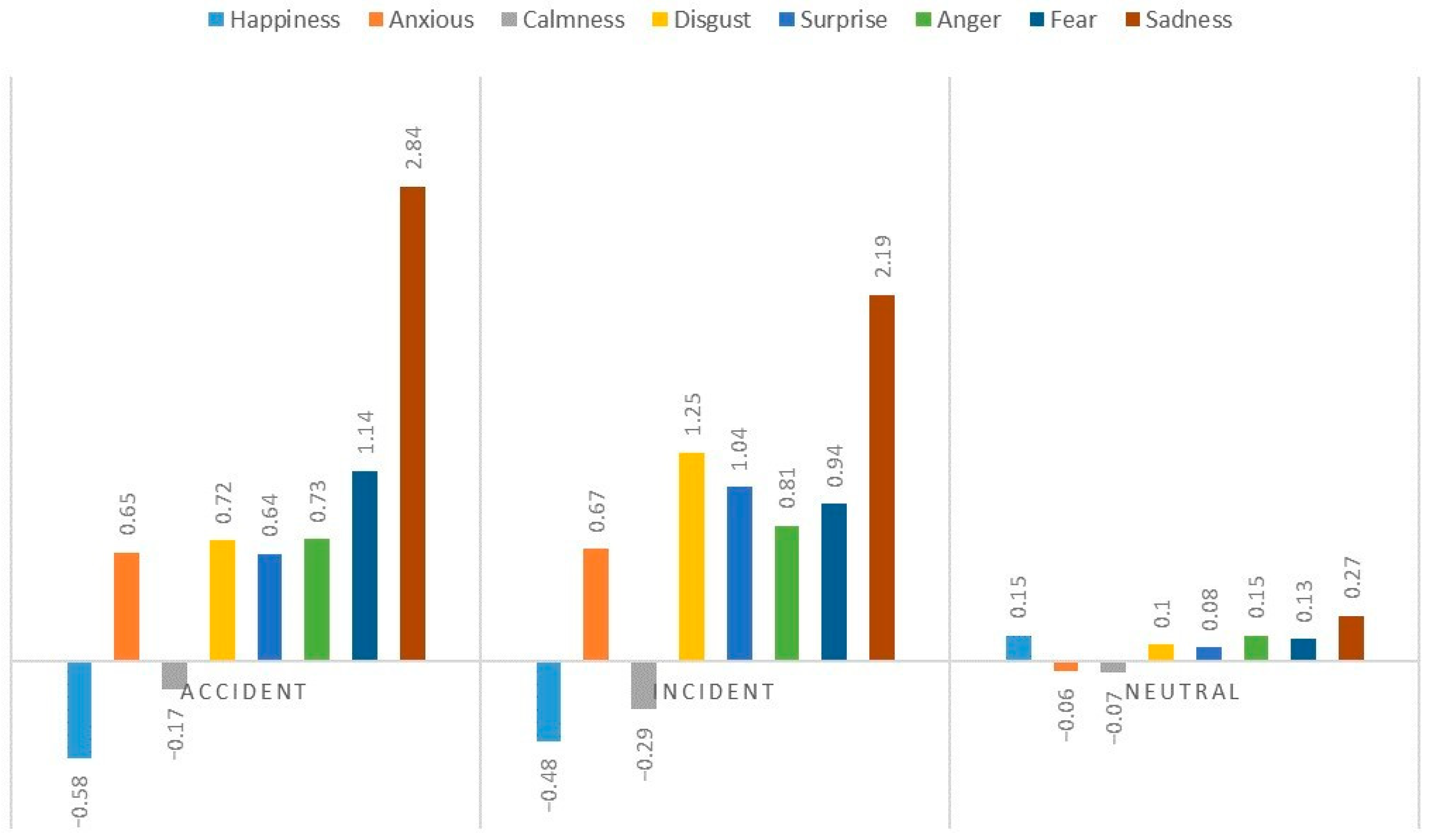

| SA | Happiness | Anxiety | Calmness | Disgust | Surprise | Anger | Fear | Sadness | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | F | p | Eta | ||
| High | Accident | 6.18 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 3.59 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 1.15 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 2.24 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 1.07 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 1.50 | 0.24 | 0.09 |
| Incident | 9.35 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 3.98 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 6.74 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 2.71 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 2.07 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 2.93 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 6.83 | 0.02 | 0.31 | |
| WLEIS | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 3.77 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 7.82 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 4.87 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 7.05 | 0.02 | 0.32 | |
| Int 1 | 0.08 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 2.60 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 4.97 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 5.22 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 6.98 | 0.02 | 0.32 | |
| Int 2 | 1.59 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 6.30 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.86 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 13.14 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 2.26 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 2.77 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.02 | |
| Low | Accident | 9.63 | 0.01 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.86 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.57 | 0.03 | 1.02 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 1.26 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 1.28 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 5.01 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| Incident | 3.08 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 0.96 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 3.03 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 1.39 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.76 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.70 | 0.41 | 0.04 | |
| WLEIS | 0.10 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 3.53 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.86 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.00 | |
| Int 1 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 1.03 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 0.00 | |
| Int 2 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1.81 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.00 | |
| Condition | Items | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | SE | Beta | |||||
| Accident | Level1 | surprise | 0.47 | 0.14 | 0.67 | 3.38 | 0.00 |
| Level2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Level3 | Sadness | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.55 | 2.44 | 0.03 | |
| SAGAT | Sadness | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 2.77 | 0.02 | |
| Incident | Level1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Level2 | demand | −0.18 | 0.08 | −0.55 | 2.38 | 0.03 | |
| Level3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SAGAT | demand | −0.28 | 0.12 | −0.56 | 2.41 | 0.03 | |
| Regression Equation | R | R2 | SE | F | p | β | se | t | p | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Variable | Predictor Variable | ||||||||||
| Calmness | 0.66 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 6.63 | 0.00 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| WLEIS | - | - | - | - | - | −0.18 | 0.05 | −3.52 | 0.00 | [−0.29, −0.07] | |
| SART (information processing) | - | - | - | - | - | −0.02 | 0.05 | −0.45 | 0.66 | [−0.14, 0.09] | |
| WLEIS × SART | - | 0.19 | 8.58 | - | 0.14 | 0.05 | 2.93 | 0.01 | [0.04, 0.24] | ||
| Anger | 0.36 | 0.13 | 1.09 | 4.13 | 0.05 | ||||||
| Calmness | - | - | - | - | - | −1.14 | 0.56 | −2.03 | 0.05 | [−2.29, 0.01] | |
| SAGAT | 0.63 | 0.39 | 2.38 | 4.04 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Anger | - | - | - | - | - | −0.20 | 0.27 | −0.70 | 0.49 | [−0.75, 0.37] | |
| Incident | - | - | - | - | - | −0.66 | 0.59 | −1.12 | 0.27 | [−1.88, 0.56] | |
| Anger × Incident | - | 0.17 | - | 7.05 | - | −1.40 | 0.53 | −2.65 | 0.01 | [−2.49, −0.31] | |
| SART (Demand) | - | - | - | - | - | −0.17 | 0.08 | −2.22 | 0.04 | [−0.32, −0.01] | |
| Path | Condition | SART | Effect | SE | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLEIS → Calmness → Anger → SAGAT | Accident | High | 0.02 | 0.06 | [−0.09, 0.16] |
| Moderate | 0.47 | 0.08 | [−0.10, 0.28] | ||
| Low | 0.19 | 0.20 | [−0.22, 0.58] | ||
| Incident | High | −0.04 | 0.10 | [−0.26, 0.12] | |
| Moderate | 0.53 | −0.17 | [−0.47, −0.00] | ||
| Low | −0.38 | 0.24 | [−0.93, −0.01] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, M.; You, X. The Influence of Emotion Induced by Accidents and Incidents on Pilots’ Situation Awareness. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030231
Lu T, Li Y, Zhou C, Tang M, You X. The Influence of Emotion Induced by Accidents and Incidents on Pilots’ Situation Awareness. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(3):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030231
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Tianjiao, Yuan Li, Chenchen Zhou, Menghan Tang, and Xuqun You. 2023. "The Influence of Emotion Induced by Accidents and Incidents on Pilots’ Situation Awareness" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 3: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030231
APA StyleLu, T., Li, Y., Zhou, C., Tang, M., & You, X. (2023). The Influence of Emotion Induced by Accidents and Incidents on Pilots’ Situation Awareness. Behavioral Sciences, 13(3), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030231





