The Effects of Visual Complexity and Task Difficulty on the Comprehensive Cognitive Efficiency of Cluster Separation Tasks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Observers
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Design
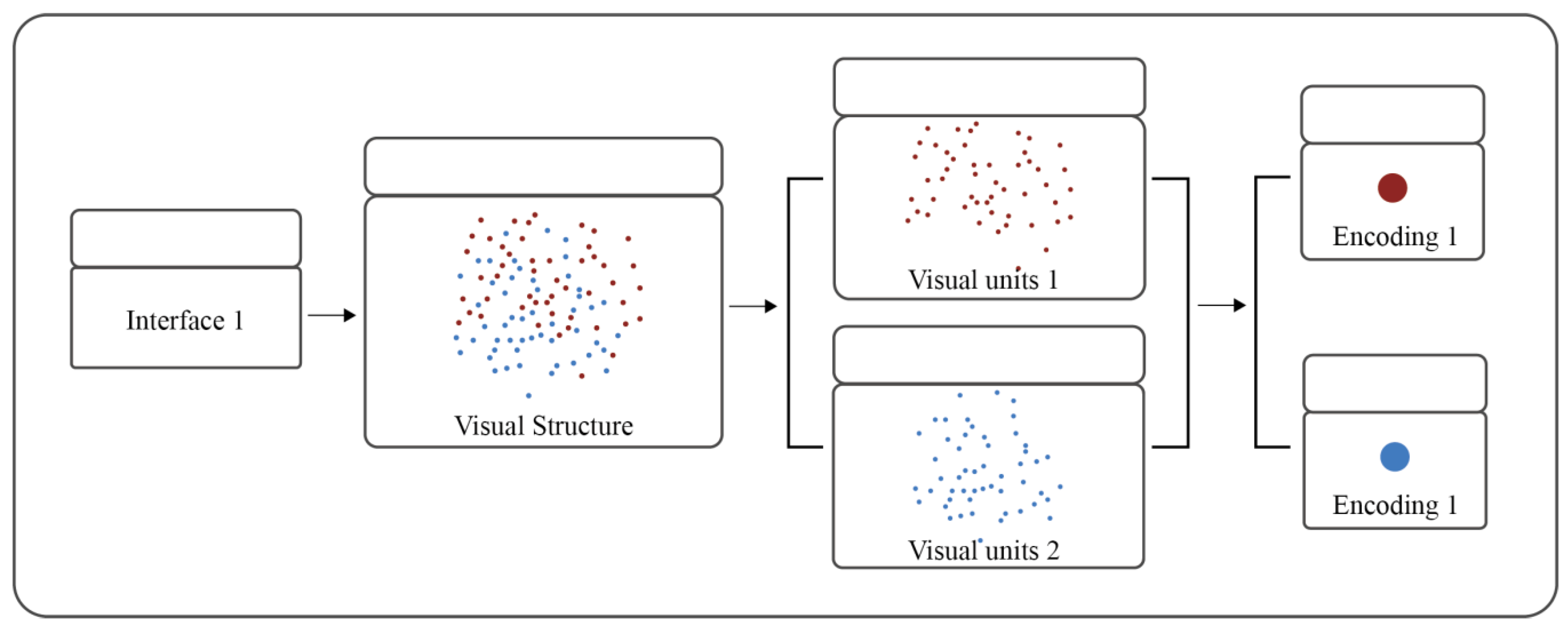
2.3.1. The Visual Complexity Level Classification
Calculation of Visual Complexity
The Visual Complexity Level Classification Results
2.3.2. Task Difficulty Level Classification
The Discrimination Method
Task Difficulty Level Classification Results
2.4. Experimental Hypotheses
- (1)
- In the visual statistics task, the greater the task difficulty, the lower the overall cognitive efficiency;
- (2)
- The greater the task complexity, the lower the comprehensive cognitive efficiency;
- (3)
- Visual complexity and task difficulty significantly affect comprehensive cognitive efficiency;
- (4)
- Different visualization interfaces of the same complexity differ from each other in terms of cognitive efficiency due to their different encoding forms.
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Data Collection and Analysis
3. Experimental Results
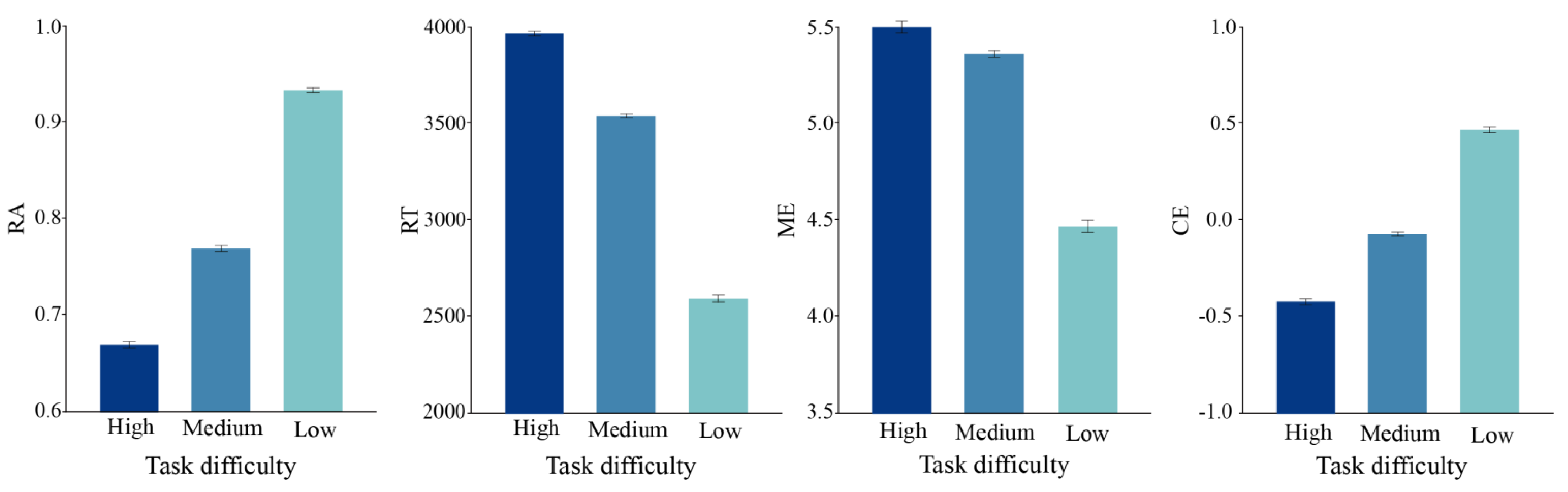
3.1. Visual Complexity
3.2. Task Difficulty
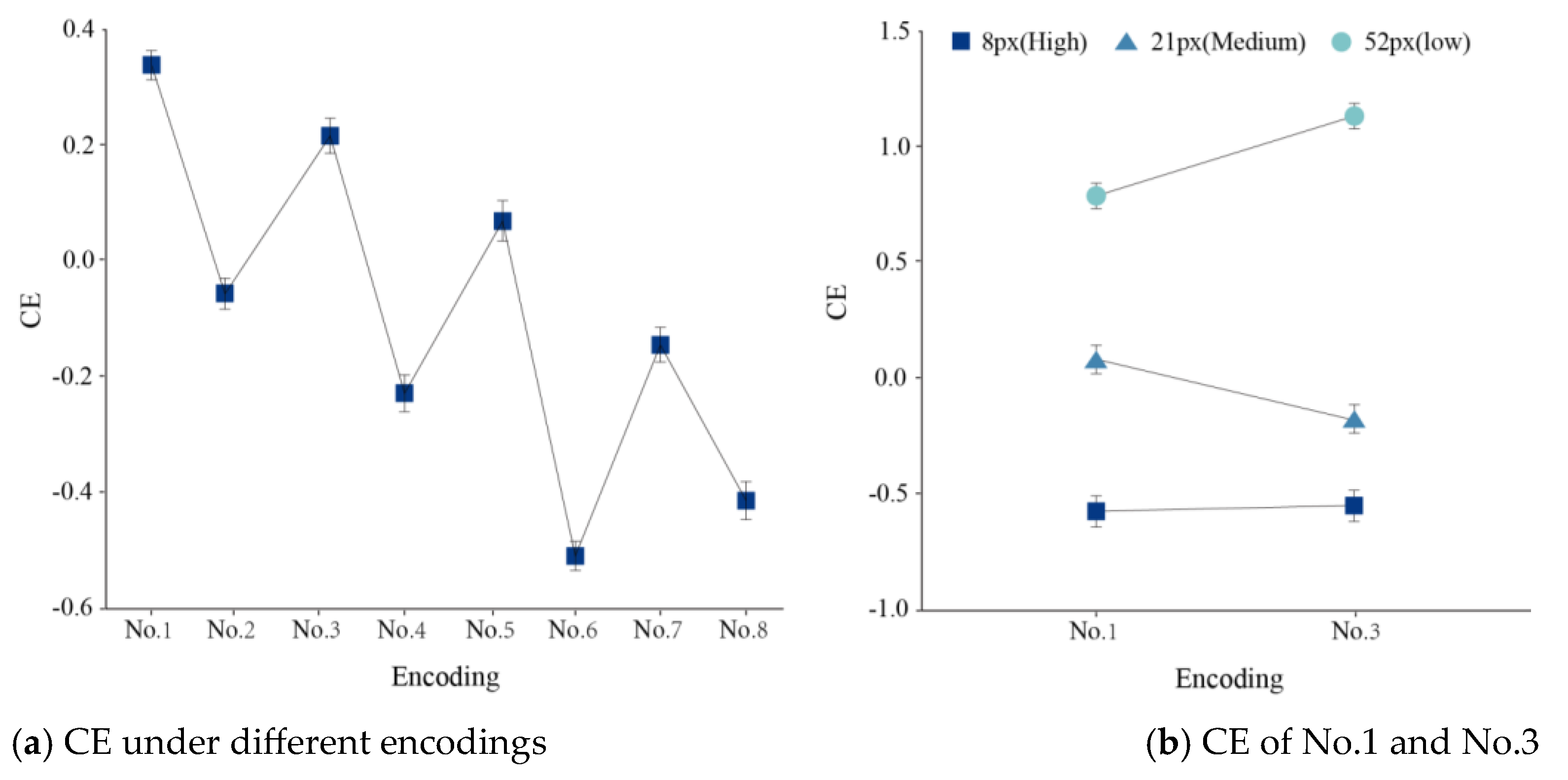
3.3. Differences in Cognitive Efficiency between Different Encodings and Task Difficulty
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boulhic, L.; Bignon, A.; Silone, F.; Morineau, T.; Rechard, J.; Bouillon, J.F. Effects of color codes used on marine supervision HMI on mental workload and information retrieval: Experimentations with novices and experts. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 67, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyan, X.; Zhuang, D.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Song, J.W. Influence of mental workload on detecting information varieties revealed by mismatch negativity during flight simulation. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 64, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, J.R.; Gast, D.L. (Eds.) Single subject research methodology in behavioral sciences. In Applications in Special Education and Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: England, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikaya, A.; Gleicher, M. Scatterplots: Tasks, data, and designs. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, J. Semiology of Graphics; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, W.S.; McGill, R. Graphical perception: Theory, experimentation, and application to the development of graphical methods. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1984, 79, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, I.; Lewandowsky, S. Displaying proportions and percentages. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 1991, 5, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensink, R.A.; Baldridge, G. The perception of correlation in scatterplots. In Computer Graphics; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010; Volume 29, pp. 1203–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Szafir, D.A. Modeling color difference for visualization design. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Hou, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, W. The effects of color combinations, luminance contrast, and area ratio on icon visual search performance. Displays 2021, 67, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, G.L. A cognitive model for understanding graphical perception. Hum. Comput. Interact. 1993, 8, 353–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, D.D. An integrated model of eye movements and visual encoding. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2001, 1, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya-Feng, N.; Jin, L.; Jia-Qi, C.; Wen-Jun, Y.; Hong-Rui, Z.; Jia-Xin, H.; Tao, J. Research on visual representation of icon colour in eye-controlled systems. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, J.T. Locating information in documents: Examination of a cognitive model. Read. Res. Q. 1988, 23, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.E.; Anderson, R.B.; Angott, A.M.; Klopfer, D.S. The perception of scatterplots. Percept. Psychophys. 2007, 69, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byström, K.; Järvelin, K. Task complexity affects information seeking and use. Inf. Process. Manag. 1995, 31, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaps, C.; Handel, S. Similarity and features of natural textures. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1999, 25, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, L.; Ogden, R.; Makin, A.D.; Bertamini, M. Examining visual complexity and its influence on perceived duration. J. Vis. 2014, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Poole, M.S. Affect in web interfaces: A study of the impacts of web page visual complexity and order. Mis Q. 2010, 34, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.; Wedel, M.; Batra, R. The stopping power of advertising: Measures and effects of visual complexity. J. Mark. 2010, 74, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Research on the Complexity of Big Data Visualization Based on User Perception; Southeast University: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass, J.G.; Vanderwart, M. A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Learn. Mem. 1980, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuch, A.N.; Presslaber, E.E.; Stöcklin, M.; Opwis, K.; Bargas-Avila, J.A. The role of visual complexity and prototypicality regarding first impression of websites: Working towards understanding aesthetic judgments. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2012, 70, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwenberg, E.L. A perceptual coding language for visual and auditory patterns. Am. J. Psychol. 1971, 84, 307–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanarayanan, G.; Bala, K.; Ferwerda, J.A.; Walter, B. Dimensionality of visual complexity in computer graphics scenes. Hum. Vis. Electron. Imaging XIII 2008, 6806, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Olivia, A.; Mack, M.L.; Shrestha, M.; Peeper, A. Identifying the perceptual dimensions of visual complexity of scenes. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 4–7 August 2004; Volume 26, pp. 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, M.L.; Oliva, A. The perceptual dimensions of visual simplicity. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniukovich, A.; De Angeli, A. Quantification of interface visual complexity. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 May 2014; pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Moshagen, M.; Thielsch, M.T. Facets of visual aesthetics. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2010, 68, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemerien, K.; Magel, K. GUIEvaluator: A Metric-tool for Evaluating the Complexity of Graphical User Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering, Vancouver, Canada, 1–3 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zen, M.; Vanderdonckt, J. Towards an evaluation of graphical user interfaces aesthetics based on metrics. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Eighth International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science (RCIS), Marrakesh, Morocco, 28–30 May 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Donderi, D.C. Visual complexity: A review. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 132, 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onel, M.; Beykal, B.; Ferguson, K.; Chiu, W.A.; McDonald, T.J.; Zhou, L.; House, J.S.; Wright, F.A.; Sheen, D.A.; Rusyn, I.; et al. Grouping of complex substances using analytical chemistry data: A framework for quantitative evaluation and visualization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purchase, H.C.; Freeman, E.; Hamer, J. An exploration of visual complexity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Theory and Application of Diagrams, Canterbury, UK, 5 July 2012; pp. 200–213. [Google Scholar]
- Michailidou, E.; Harper, S.; Bechhofer, S. Visual complexity and aesthetic perception of web pages. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual ACM International Conference on Design of Communication, New York, NY, USA, 22–24 September 2008; pp. 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, U.R.; Wirtz, J. Consumer processing of interior service environments: The interplay among visual complexity, processing fluency, and attractiveness. J. Serv. Res. 2014, 17, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.H. Contributions to Information Integration Theory: Volume 1: Cognition; Psychology Press: England, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, X. A Task-Centered Visualization Design Environment and A Method for Measuring the Complexity of Visualization Designs; Georgia State University: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Paas, F.G.; Van Merriënboer, J.J. Instructional control of cognitive load in the training of complex cognitive tasks. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 1994, 6, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweller, J.; Van Merrienboer, J.J.; Paas, F.G. Cognitive architecture and instructional design. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 1998, 10, 251–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paas, F.; Tuovinen, J.E.; Van Merrienboer, J.J.; Aubteen Darabi, A. A motivational perspective on the relation between mental effort and performance: Optimizing learner involvement in instruction. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2005, 53, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, A.; Capra, R.; Arguello, J. Time pressure, user satisfaction and task difficulty. Proc. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Cole, M.; Belkin, N.J.; Zhang, X. Task difficulty and domain knowledge effects on information search behaviors. Proc. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleicher, M.; Correll, M.; Nothelfer, C.; Franconeri, S. Perception of average value in multiclass scatterplots. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2013, 19, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rensink, R.A. Visual features as carriers of abstract quantitative information. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2022, 151, 1793–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Viegut, A.A.; Matthews, P.G. More than the sum of its parts: Exploring the development of ratio magnitude versus simple magnitude perception. Dev. Sci. 2021, 24, e13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlmair, M.; Tatu, A.; Munzner, T.; Tory, M. A taxonomy of visual cluster separation factors. In Computer Graphics Forum; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 31, pp. 1335–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Coltheart, M.; Humphreys, G.W.; Darwin, C.J.; Mitchell, D.C.; Frith, C.D.; Monsell, S.; Sutherland, N.S. The quarterly journal of experimental psychology. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. Sect. A 1985, 37, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill, D.; Grimsen, C.; Fahle, M.; Wegener, D. Human feature-based attention consists of two distinct spatiotemporal processes. J. Vis. 2015, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Corbetta, M.; Miezin, F.M.; Dobmeyer, S.; Shulman, G.L.; Petersen, S.E. Attentional modulation of neural processing of shape, color, and velocity in humans. Science 1990, 248, 1556–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, J.M. Guided search 2.0 a revised model of visual search. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 1994, 1, 202–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberman, J.; Whitney, D. Ensemble perception: Summarizing the scene and broadening the limits of visual processing. Percept. Conscious. Search. Anne Treisman 2012, 33, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Giannouli, V. Visual symmetry perception. Encephalos 2013, 50, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, P.J.; Clarke, A.D.F. The human visual system preserves the hierarchy of two-dimensional pattern regularity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafir, D.A.; Haroz, S.; Gleicher, M.; Franconeri, S. Four types of ensemble coding in data visualizations. J. Vis. 2016, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.C.; Treisman, A. Representation of statistical properties. Vis. Res. 2003, 43, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masry, E. Poisson sampling and spectral estimation of continuous-time processes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1978, 24, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecham, R.; Dykes, J.; Meulemans, W.; Slingsby, A.; Turkay, C.; Wood, J. Map lineups: Effects of spatial structure on graphical inference. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 23, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, G. Weber’s law and related functions. J. Psychol. 1959, 47, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paas, F.G.; Van Merriënboer, J.J. The efficiency of instructional conditions: An approach to combine mental effort and performance measures. Hum. Factors 1993, 35, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, R.; Lei, J.; Fu, H.; Cheng, M.M.; Lin, W.; Huang, Q. Review of visual saliency detection with comprehensive information. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 29, 2941–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luder, C.B.; Barber, P.J. Redundant color coding on airborne CRT displays. Hum. Factors 1984, 26, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbers, I.G.; Collier, G.D. Coding techniques for process plant VDU formats. Appl. Ergon. 1990, 21, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhengre, S.; Mathur, J.; Oghazian, F.; Tan, X.; McComb, C. Towards Enhanced Creativity in Interface Design through Automated Usability Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Creativity_ICCC20, Coimbra, Portugal, 7–11 September 2020; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Soui, M.; Chouchane, M.; Mkaouer, M.W.; Kessentini, M.; Ghedira, K. Assessing the quality of mobile graphical user interfaces using multi-objective optimization. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 7685–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniukovich, A.; Sulpizio, S.; De Angeli, A. Visual complexity of graphical user interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces, New York, NY, USA, 29 May 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, Y.W.; Ji, Y.G. Effects of visual complexity of in-vehicle information display: Age-related differences in visual search task in the driving context. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 81, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, E.D.; Bowman, D.A.; Kopper, R.; Stinson, C.; Scerbo, S.; McMahan, R.P. Effects of field of view and visual complexity on virtual reality training effectiveness for a visual scanning task. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2015, 21, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Degree of Understanding (Refers to the Degree to Which the Evaluators Are Clear about the Logic of the Information Encoded in the Interface) | Degree of Familiarity (Refers to the Evaluators’ Familiarity with the Form of Information Encoded in the Interface) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Very well understood | 5 | Very familiar | 5 |
| Well understood | 4 | Familiar | 4 |
| Relatively well understood | 3 | Relatively familiar | 3 |
| Generally well understood | 2 | Generally familiar | 2 |
| Not understood | 1 | Unfamiliar | 1 |
| Display No. | Encoding Forms | Target 1 | Target 2 | Interference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Color encoding |  | 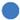 | |
| 2 | Shape encoding |  | 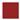 | |
| 3 | Color * Shape (redundancy encoding) |  |  | |
| 4 | Interference color encoding |  |  | 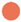 |
| 5 | Color * Shape (orthogonal encoding) |   |   | |
| 6 | Color * Shape (orthogonal and interference encoding) |   |   |  |
| 7 | Shape * Color (orthogonal encoding) |   |   | |
| 8 | Shape * Color (interference encoding) |   |   |  |
| Display No. | K | V | ω | Mean | Complexity Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.02 | 0.71 | 0.22 | 0.81 | 2.71 | Low level |
| 2 | 4.87 | 0.76 | 0.31 | 0.80 | 2.79 | |
| 3 | 4.98 | 0.89 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 2.81 | |
| 4 | 4.97 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 0.79 | 6.89 | Medium level |
| 5 | 5.01 | 0.83 | 0.31 | 0.76 | 12.31 | High level |
| 6 | 4.93 | 0.92 | 0.29 | 0.80 | 13.37 | |
| 7 | 5.07 | 0.72 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 13.29 | |
| 8 | 4.90 | 0.86 | 0.25 | 0.79 | 13.14 |
| Steady-State Accuracy | 55% | 75% | 95% |
|---|---|---|---|
| The mean Δy | 8 px ± 1 | 21 px ± 2 | 52 px ± 2 |
| Task difficulty level | High | Middle | Low |
| Sources | Variable | Sum of Squares (SS) | df | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected model | RA | 72.854 a | 23 | 18.590 | 0.000 |
| RT | 2,810,590,074.445 b | 23 | 18.022 | 0.000 | |
| ME | 2202.952 c | 23 | 43.141 | 0.000 | |
| CE | 1274.590 d | 23 | 62.271 | 0.000 | |
| Task difficulty | RA | 64.428 | 3 | 126.042 | 0.000 |
| RT | 1,861,806,572.850 | 3 | 91.528 | 0.000 | |
| ME | 1454.553 | 3 | 218.383 | 0.000 | |
| CE | 982.542 | 3 | 368.024 | 0.000 | |
| Complexity | RA | 3.970 | 5 | 4.660 | 0.000 |
| RT | 786,042,613.761 | 5 | 23.185 | 0.000 | |
| ME | 627.285 | 5 | 56.507 | 0.000 | |
| CE | 251.201 | 5 | 56.454 | 0.000 | |
| Task difficulty * Complexity | RA | 4.456 | 15 | 1.743 | 0.037 |
| RT | 162,740,887.834 | 15 | 1.600 | 0.066 | |
| ME | 121.115 | 15 | 3.637 | 0.000 | |
| CE | 40.847 | 15 | 3.060 | 0.000 | |
| Error | RA | 445.736 | 2616 | 0.000 | |
| RT | 17,737,760,706.191 | 2616 | |||
| ME | 5808.011 | 2616 | |||
| CE | 2328.048 | 2616 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Chen, Y. The Effects of Visual Complexity and Task Difficulty on the Comprehensive Cognitive Efficiency of Cluster Separation Tasks. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100827
Guo Q, Chen Y. The Effects of Visual Complexity and Task Difficulty on the Comprehensive Cognitive Efficiency of Cluster Separation Tasks. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(10):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100827
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qi, and Yan Chen. 2023. "The Effects of Visual Complexity and Task Difficulty on the Comprehensive Cognitive Efficiency of Cluster Separation Tasks" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 10: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100827
APA StyleGuo, Q., & Chen, Y. (2023). The Effects of Visual Complexity and Task Difficulty on the Comprehensive Cognitive Efficiency of Cluster Separation Tasks. Behavioral Sciences, 13(10), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100827






