Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Honey in Learning and Memory—Evidence from Human Studies
3. Honey in Learning and Memory—Evidence from Animal Studies
4. Possible Mechanisms of Tualang Honey in Learning and Memory
4.1. Oxidative Stress and Tualang Honey
4.2. Cholinergic System and Tualang Honey
4.3. BDNF and Tualang Honey
4.4. Anti-Inflammatory and Tualang Honey
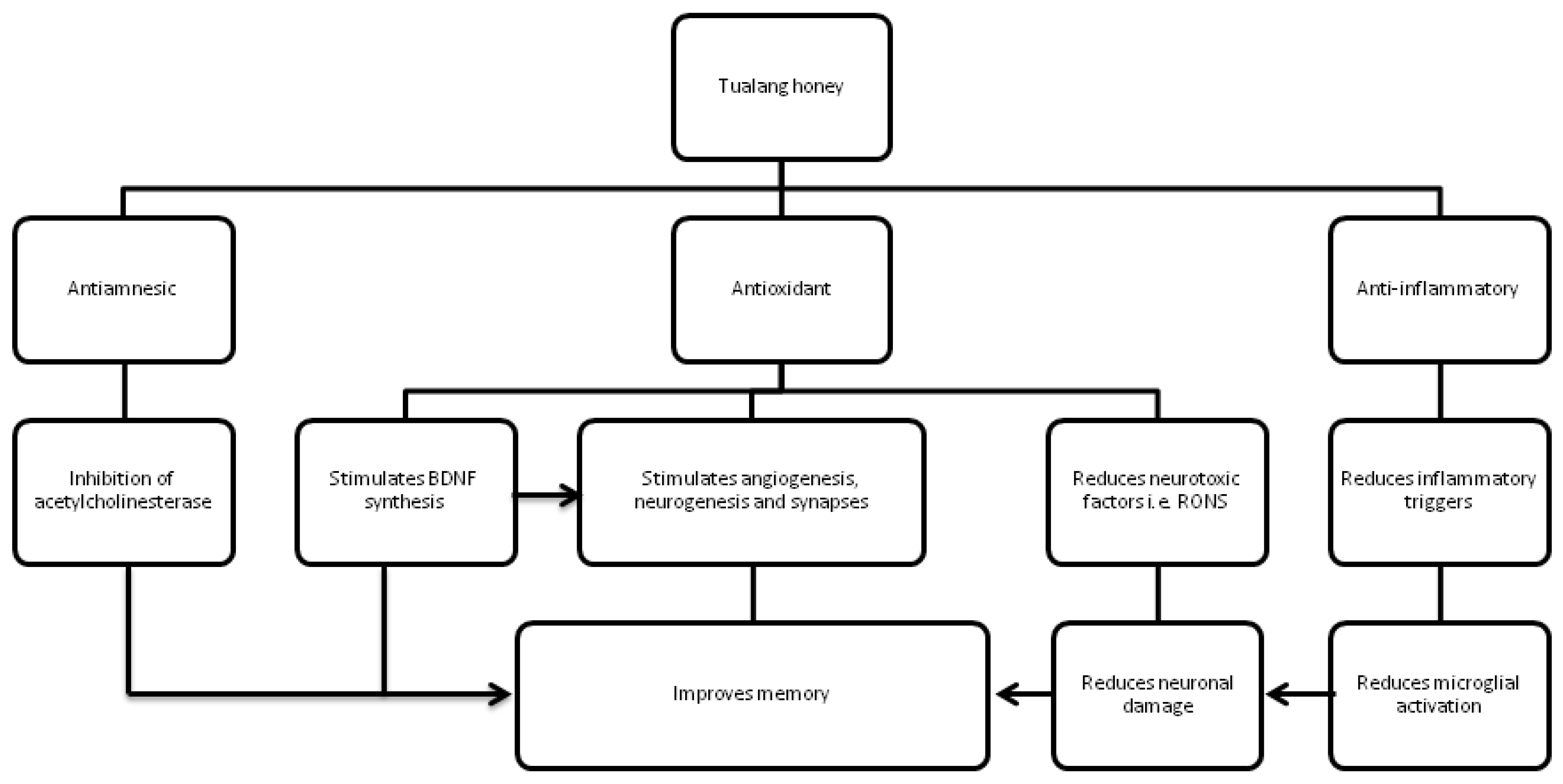
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rainforest Journal. The tualang tree or Koompassia excelsa. Available online: http://www.rainforestjournal.com/the-tualang-tree-or-koompassia-excelsa/ (accessed on 1 September 2014).
- Ahmed, S.; Othman, H. Review of the medicinal effects of Tualang honey and a comparison with Manuka honey. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 20, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghazali, F.C. Morphological characterization study of Malaysian honey—A VPSEM, EDX randomised attempt. Ann. Microsc. 2009, 9, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.T.; Rahman, R.A.; Gan, S.H.; Halim, A.S.; Hassan, S.A.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Kirnpal-Kaur, B. The antibacterial properties of Malaysian tualang honey against wound and enteric microorganisms in comparison to manuka honey. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. High 5-hydroxymethylfurfural concentrations are found in Malaysian honey samples stored for more than one year. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.I.; Alam, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Phenolic Acid Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Malaysian Honeys. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C921–C928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, R.K.; Halim, A.S.; Syazana, M.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N. Tualang honey has higher phenolic content and greater radical scavenging activity compared with other honey sources. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.I.; Mahaneem, M.; Jamalullail, S.M.S.; Alam, N.; Sulaiman, S.A. Evaluation of Radical Scavenging Activity and Colour Intensity of Nine Malaysian Honeys of Different Origin. J. ApiProd. ApiMed. Sci. 2011, 3, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syazana, M.S.N.; Halim, A.S.; Gan, S.H.; Shamsuddin, S. Antiproliferative effect of methanolic extraction of tualang honey on human keloid fibroblasts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Himyari, F.A. The use of honey as a natural preventive therapy of cognitive decline and dementia in the Middle East. Alzheimers Dement. 2009, 5, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, H.A.; Denenberg, V.H. Estradiol facilitates performance as working memory load increases. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1999, 24, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, J.M.; Roberts, S.L.; Dohanich, G.P. Effects of ovarian hormones and environment on radial maze and water maze performance of female rats. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohanich, G.P. Gonadal steroids, learning, and memory. In Hormones, Brain and Behavior; Pfaff, D.W., Arnold, A.P., Etgen, A., Fahrbach, S.E., Rubin, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press (Elsevier Science): San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 265–327. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin, B.B. Estrogen and cognitive aging in women. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, Z.; Shafin, N.; Zakaria, R.; Hussain, N.H.N.; Mohammad, W.M.Z.W. Improvement in immediate memory after 16 weeks of tualang honey (Agro Mas) supplement in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause 2011, 18, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akuchekian, S.; Layegh, E.; Najafi, M.; Barekatein, M.; Maracy, M.R.; Zomorodi, M.H. Effects of herbal medicine on memory impairment in electroconvulsive therapy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2012, S59–S64. [Google Scholar]
- Chepulis, L.M.; Starkey, N.J.; Waas, J.R.; Molan, P.C. The effects of long-term honey, sucrose or sugar-free diets on memory and anxiety in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanmu, M.A.; Olowookere, T.A.; Atunwa, S.A.; Ibrahim, B.O.; Lamidi, O.F.; Adams, P.A.; Ajimuda, B.O.; Adeyemo, L.E. Neuropharmacological effects of Nigerian honey in mice. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 8, 230–249. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Shin, B.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, S.J.; Park, C.S.; Won, D.H.; Hong, N.D.; Kang, D.H.; Yutaka, Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of a traditional herbal prescription on transient cerebral global ischemia in gerbils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rahbi, B.; Zakaria, R.; Othman, Z.; Hassan, A.; Mohd Ismail, Z.I.; Muthuraju, S. Tualang honey supplement improves memory performance and hippocampal morphology in stressed ovariectomized rats. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warad, V.B.; Shastri, R.; Habbu, P.; Katti, P.; Jagannath, A.B.; Kulkarni, V.H.; Chakraborty, M. Preparation and screening of Swarnaprashana for nootropic activity. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2014, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, B.N.; Shigenaga, M.K.; Hagen, T.M. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7915–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohal, R.S.; Weindruch, R. Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science 1996, 273, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, S.A.; Poon, H.F.; Dogrukol-Ak, D.; Drake, J.; Banks, W.A.; Eyerman, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Morley, J.E. The antioxidants α-lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine reverse memory impairment and brain oxidative stress in aged SAMP8 mice. J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmijn, S.; Feskens, E.; Launer, L.J.; Kromhout, D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, and cognitive function in very old men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.S. Free radicals in the genesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 695, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, C.R.; Martyn, C.N.; Cooper, C. Cognitive impairment and mortality in a cohort of elderly people. Biomed. J. 1996, 312, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, R.M.; Requejo, A.M.; Andres, P.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Quintas, M.E.; Redondo, M.R.; Navia, B.; Rivas, T. Dietary intake and cognitive function in a group of elderly people. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brownbill, R.A.; Ilich, J.Z. Cognitive function in relation with bone mass and nutrition: Cross-sectional association in postmenopausal women. BMC Women’s Health 2004, 4, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devore, E.E.; Kang, J.H.; Stampfer, M.J.; Grodstein, F. The association of antioxidants and cognition in the Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafin, N.; Othman, Z.; Zakaria, R.; Nik Hussain, N.H. Tualang Honey Supplementation Reduces Blood Oxidative Stress Levels/Activities in Postmenopausal Women. ISRN Oxid. Med. 2014, 2014. Article ID 364836. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rahbi, B.; Zakaria, R.; Othman, Z.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, A.H. Protective effects of Tualang honey against oxidative stress and anxiety-like behaviour in stressed ovariectomized rats. ISRN 2014, 2014. Article ID 521065. [Google Scholar]
- Oyefuga, O.H.; Ajani, E.O.; Salau, B.A.; Agboola, F.; Adebawo, O.O. Honey consumption and its anti-ageing potency in White Wister albino rats. Sch. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mansouri, A.S.; Lorke, D.E.; Nurulain, S.M.; Ashoor, A.; Keun-Hang, S.Y.; Petroianu, G.; Isaev, D.; Oz, M. Methylene blue inhibits the function of a7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 11, 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Farbood, Y.; Sameri, M.J.; Sarkaki, A.; Naghizadeh, B. Neuroprotective effects of oral gallic acid against oxidative stress induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in rats. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Roghani, M. Effect of naringenin on intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive deficits in rat: A behavioral analysis. Pharmacology 2006, 78, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.B.; Khan, M.M.; Khan, A.; Ahmed, M.E.; Ishrat, T.; Tabassum, R.; Vaibhav, K.; Ahmad, A.; Islam, F. Naringenin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-type neurodegeneration with cognitive impairment (AD-TNDCI) caused by the intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin in rat model. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, L.R.; Zhu, S-T.; Harris, P.J. Antioxidant and antigenotoxic effects of plant cell wall hydroxycinnamic acids in cultured HT-29 cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, M.H.; El-Mahdy, M.A.; Abd-Ellah, M.F.; Helal, G.K.; Khalifa, F.; Hamada, F.M.A. Influence of pcoumaric acid on doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress in rat’s heart. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pu, X-P. Neuroprotective effect of kaempferol against a 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridineinduced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.S.; Cheng, H.Y.; Hsieh, M.T.; Wu, C.R.; Lin, Y.C.; Peng, W.H. The ameliorating effects of luteolin on beta-amyloid-induced impairment of water maze performance and passive avoidance in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, K.W. Protection of apigenin against kainate-induced excitotoxicity by anti-oxidative effects. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rahbi, B.; Zakaria, R.; Othman, Z.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, A.H. The effects of Tualang Honey Supplement on Medial Prefrontal Cortex Morphology and Cholinergic System in Stressed Ovariectomised Rats. IJARNP 2014, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sastry, B.V.R.; Janson, V.; Jaiswal, N.; Tayeb, O. Changes in enzymes of the cholinergic system and acetylcholine release in the cerebra of aging male Fischer rats. Pharmacology 1983, 26, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, A.V., Jr.; Buccafusco, J.J. The cholinergic hypothesis of age and Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits: Recent challenges and their implications for novel drug development. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maelicke, A. The pharmacological rationale for treating vascular dementia with galantamine (Reminyl). Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2001, 120, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Curtis, M.; Dick, D.; Candy, J.; Atack, J.; Bloxham, C.; Blessed, G.; Fairbairn, A.; Tomlinson, B.E.; Perry, R.H. Cholinergic correlates of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Comparisons with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1985, 48, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T.; Perry, E.K. Cholinergic and other neurotransmitter mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease, Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, S351–S357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitkamp, K. Pro and contra honey. Are statements on the effects of honey’scientifically sufficient reliable. Oecotrophologie 1984, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.H.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.A.; Hong, S.I.; Kim, H.C.; Jo, T.H.; Park, Y.I.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid on scopolamine-induced amnesia via anti-acetylcholinesterase and anti-oxidative activities in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, W.J.; Alonso, M.; Bramham, C.R.; Pozzo-Miller, L.D. From acquisition to consolidation: On the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in hippocampal-dependent learning. Learn. Mem. 2002, 9, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, P.T.; Lu, B. Regulation of late phase LTP in normal and aging hippocampus: Role of secreted protein tPA and BDNF. Ageing Res. Rev. 2004, 3, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, E.R. The molecular biology of memory storage: A dialog between genes and synapses. Science 2001, 294, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Katche, C.; Slipczuk, L.; Gonzalez, C.; Dorman, G.; Cammarota, M.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Persistence of long-term memory storage: New insights into its molecular signatures in the hippocampus and related structures. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 18, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igaz, L.M.; Bekinschtein, P.; Vianna, M.M.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Gene expression during memory formation. Neurotox. Res. 2004, 6, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athos, J.; Impey, S.; Pineda, V.V.; Chen, X.; Storm, D.R. Hippocampal CRE mediated gene expression is required for contextual memory formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1119–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Memory formation: The sequence of biochemical events in the hippocampus and its connection to activity in other brain structures. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 1997, 68, 285–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaugh, J.L. Memory—A century of consolidation. Science 2000, 287, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Igaz, L.M.; Bevilaqua, L.R.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. Persistence of long-term memory storage requires a late protein synthesisand BDNF- dependent phase in the hippocampus. Neuron 2007, 53, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Katche, C.; Slipczuk, L.; Rossato, J.I.; Goldin, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poo, M.M. Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rahbi, B.; Zakaria, R.; Othman, Z.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, A.H. Enhancement of the brain BDNF concentration and restoration of HPA axis reduce depressive-like behaviour in stressed ovariectomised rat treated with Tualang honey. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.M.; El Mohsen, M.A.; Vauzour, D.; Rendeiro, C.; Butler, L.T.; Ellis, J.A.; Whiteman, M.; Spencer, J.P. Blueberry-induced changes in spatial working memory correlate with changes in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) levels. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Pei, X.R.; Wang, J.B.; Cai, M.Y.; Li, Y. Long-term administration of green tea catechins prevents age-related spatial learning and memory decline in C57BL/6 J mice by regulating hippocampal cyclic amp-response element binding protein signaling cascade. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Pei, X.R.; Wang, J.B.; Li, Y. Long-term green tea catechin administration prevents spatial learning and memory impairment in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 mice by decreasing Aβ1–42 oligomers and upregulating synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Aboukhatwa, M.A.; Lei, D.L.; Manaye, K.; Khan, I.; Luo, Y. Anti-depressant natural flavonols modulate BDNF and beta amyloid in neurons and hippocampus of double TgAD mice. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendeiro, C.; Vauzour, D.; Rattray, M.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Mérillon, J.M.; Butler, L.T.; Williams, C.M.; Spencer, J.P. Dietary levels of pure flavonoids improve spatial memory performance and increase hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.L.; Bi, C.W.C.; Choi, R.C.Y.; Zhu, K.Y.; Miernisha, A.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Flavonoids induce the synthesis and secretion of neurotrophic factors in cultured rat astrocytes: A signaling responsemediated by estrogen receptor. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 127075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Cannon, T.C.; Alto, L.T.; McAlpine, F.E.; Tansey, M.G. Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.J.; Thrash, J.C.; Walter, B. The cellular response in neuroinflammation: The role of leukocytes, microglia and astrocytes in neuronal death and survival. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 6, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur Azida, M.N.; Dorai, A.A.; Halim, A.S.; Norimah, Y. A comparative pilot study using tualang honey with aquacel and aquacel dressing on superficial burn wounds. Malays J. Medic. Sci. 2008, 15 (Suppl. 1), 204. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharil, M.S.A.; Sulaiman, W.A.W.; Halim, A.S.; Jumaat, M.Y.S.; Hasnan, J. The Efficacy of Tualang Honey in Comparison to Silver in Dressing Wounds in Rats. J. ApiPro. ApiMed. Sci. 2011, 3, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, F.H.; Dorai, A.A.; Halim, A.S.; Sulaiman, W.A.W. Tualang Honey Hydrogel in the Treatment of Split- Skin Graft Donor Sites. J. ApiPro. ApiMed. Sci. 2011, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.T.; Halim, A.S.; Singh, K.K.; Mohamad, N.A. Wound contraction effects and antibacterial properties of Tualang honey on full-thickness burn wounds in rats in comparison to hydrofibre. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppannan, B.; Embong, Z.; Shaharuddin, B.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S.; Naik, V. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Tualang honey in alkali injury on the eyes of rabbits: Experimental animal study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Othman, Z.; Zakaria, R.; Hussain, N.H.N.; Hassan, A.; Shafin, N.; Al-Rahbi, B.; Ahmad, A.H. Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci3020003
Othman Z, Zakaria R, Hussain NHN, Hassan A, Shafin N, Al-Rahbi B, Ahmad AH. Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory. Medical Sciences. 2015; 3(2):3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci3020003
Chicago/Turabian StyleOthman, Zahiruddin, Rahimah Zakaria, Nik Hazlina Nik Hussain, Asma' Hassan, Nazlahshaniza Shafin, Badriya Al-Rahbi, and Asma Hayati Ahmad. 2015. "Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory" Medical Sciences 3, no. 2: 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci3020003
APA StyleOthman, Z., Zakaria, R., Hussain, N. H. N., Hassan, A., Shafin, N., Al-Rahbi, B., & Ahmad, A. H. (2015). Potential Role of Honey in Learning and Memory. Medical Sciences, 3(2), 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci3020003




