Efficacy and Safety of VMAT-2 Inhibitors and Dopamine Stabilizers for Huntington’s Chorea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Types of Study
2.2. Types of Participants
2.3. Types of Intervention
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Searching Methods
2.6. Selection of Studies
2.7. Data Extraction
2.8. Assessment of Risk of Bias
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics and Participants
3.3. Risk of Bias Within Studies
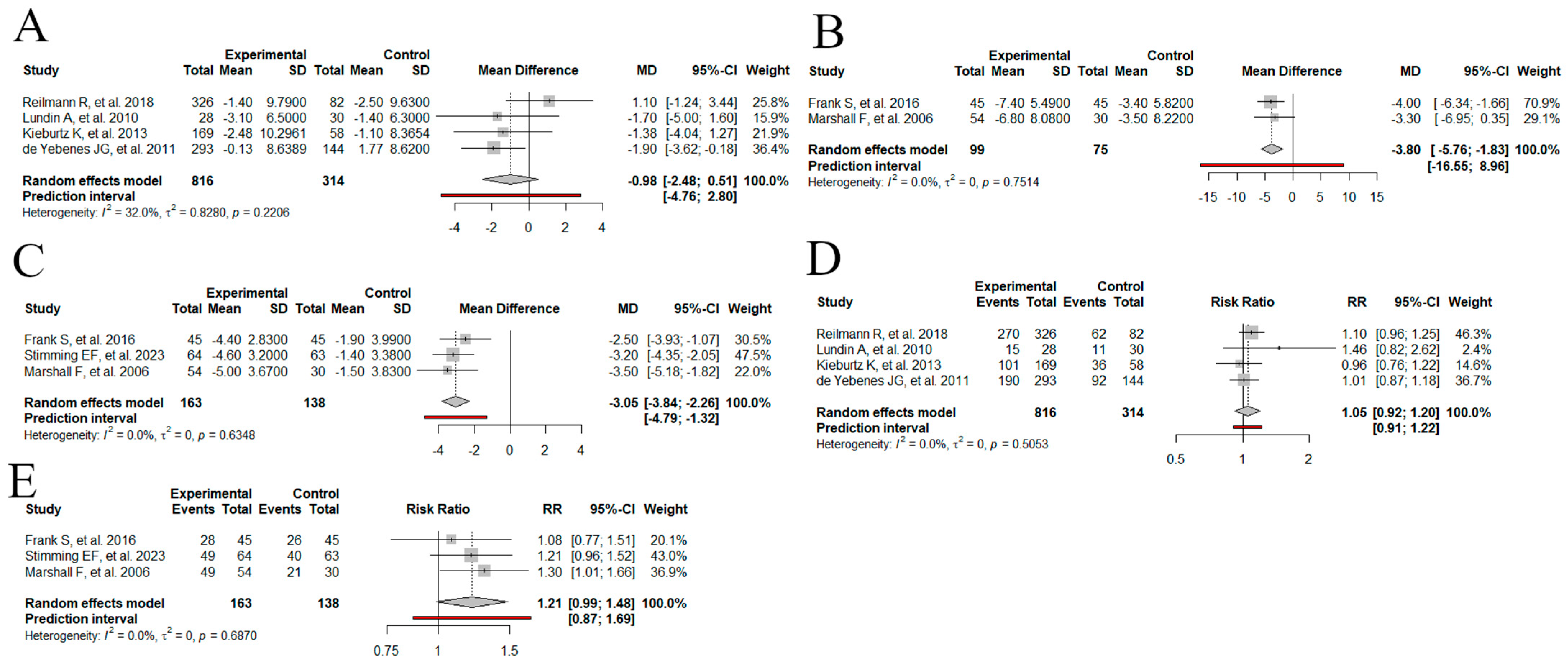
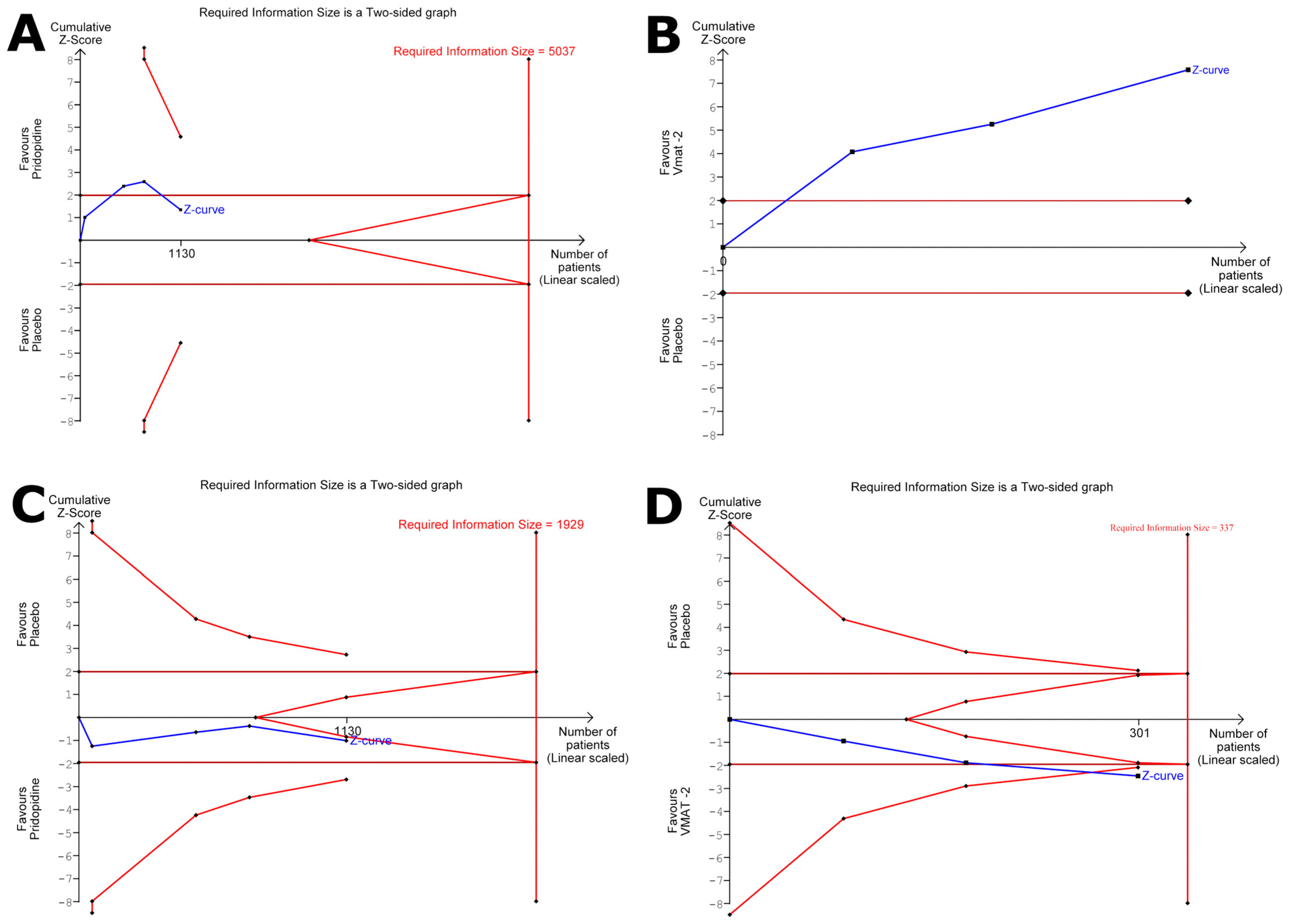
3.4. Meta Analysis
3.4.1. Change in the UHDRS TMS from the Baseline: Dopamine Stabilizers
3.4.2. Change in the UHDRS TMS from the Baseline: VMAT-2
3.4.3. Change in the UHDRS TMC from the Baseline: VMAT-2
3.4.4. Total Adverse Events: Dopamine Stabilizers
3.4.5. Total Adverse Events: VMAT-2
4. Discussion
Limitations and Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachoud-Lévi, A.C.; Ferreira, J.; Massart, R.; Youssov, K.; Rosser, A.; Busse, M.; Craufurd, D.; Reilmann, R.; De Michele, G.; Rae, D.; et al. international guidelines for the treatment of Huntington’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Mahjoub, Y.; Shaver, L.; Pringsheim, T. Prevalence and Incidence of Huntington’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.S.; Strong, M.; Quarrell, O.W. The global prevalence of Huntington’s disease: A systematic review and discussion. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2016, 6, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-M.; Ramos, E.M.; Lee, J.H.; Gillis, T.P.; Mysore, J.S.; Hayden, M.R.; Warby, S.C.; Morrison, P.J.; A Nance, M.; A Ross, C.; et al. CAG repeat expansion in Huntington disease determines age at onset in a fully dominant fashion. Neurology 2012, 78, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.M.; Rego, A.C. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2803–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lalonde, K.; Truesdell, A.; Gomes Welter, P.; Brocardo, P.S.; Rosenstock, T.R.; Gil-Mohapel, J. New Avenues for the Treatment of Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liang, T.; Xue, T.; Xue, S.; Xue, Q. Pridopidine for the Improvement of Motor Function in Patients With Huntington’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 658123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geva, M.; Kusko, R.; Soares, H.; Fowler, K.D.; Birnberg, T.; Barash, S.; Wagner, A.M.; Fine, T.; Lysaght, A.; Weiner, B.; et al. Pridopidine activates neuroprotective pathways impaired in Huntington Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3975–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachev, I.D.; Meyer, P.M.; Becker, G.A.; Bronzel, M.; Marsteller, D.; Pastino, G.; Voges, O.; Rabinovich, L.; Knebel, H.; Zientek, F.; et al. Sigma-1 and dopamine D2/D3 receptor occupancy of pridopidine in healthy volunteers and patients with Huntington disease: A [18F] fluspidine and [18F] fallypride PET study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Shi, W.X.; Dashtipour, K. VMAT2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 212, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, S.; Ponten, H.; Edling, M.; Svanberg, B.; Klamer, D.; Waters, N. The dopaminergic stabilizers pridopidine and ordopidine enhance cortico-striatal Arc gene expression. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Testa, C.; Edmondson, M.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kayson, E.; Leavitt, B.R.; Oakes, D.; O’neill, C.; Vaughan, C.; Whaley, J.; et al. The Safety of Deutetrabenazine for Chorea in Huntington Disease: An Open-Label Extension Study. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadlamani, N.; Ibrahimli, S.; Khan, F.A.; A Castillo, J.; Amaravadi, K.S.S.; Nalisetty, P.; Khan, S. Efficacy and Safety of Tetrabenazine in Reducing Chorea and Improving Motor Function in Individuals With Huntington’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e71476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimming, E.F.; O Claassen, D.; Kayson, E.; Goldstein, J.; Mehanna, R.; Zhang, H.; Liang, G.S.; Haubenberger, D.; Adams, J.; Beck, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of valbenazine for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease (KINECT-HD): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) Tool|Cochrane Methods. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/risk-bias-2 (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Harrer, M.; Cuijpers, P.; Furukawa, T.A.; Ebert, D.D. Doing Meta-Analysis with R; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.; White, I.R.; Thompson, S.G. Extending DerSimonian and Laird’s methodology to perform multivariate random effects meta-analyses. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 1282–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlund, K.; Engstrøm, J.; Wetterslev, J.; Brok, J.; Imberger, G.; Gluud, S. User Manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA); Copenhagen Trial Unit Centre for Clinical Intervention Research Department: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, F.J. Tetrabenazine as antichorea therapy in Huntington disease: A randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2006, 66, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Reilmann, R.; McGarry, A.; Grachev, I.D.; Savola, J.-M.; Borowsky, B.; Eyal, E.; Gross, N.; Langbehn, D.; Schubert, R.; Wickenberg, A.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pridopidine in patients with Huntington’s disease (PRIDE-HD): A phase 2, randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre, dose-ranging study. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Yebenes, J.G.; Landwehrmeyer, B.; Squitieri, F.; Reilmann, R.; Rosser, A.; Barker, R.A.; Saft, C.; Magnet, M.K.; Sword, A.; Rembratt, A.; et al. Pridopidine for the treatment of motor function in patients with Huntington’s disease (MermaiHD): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, A.; Dietrichs, E.; Haghighi, S.; Göller, M.-L.; Heiberg, A.; Loutfi, G.; Widner, H.; Wiktorin, K.; Wiklund, L.; Svenningsson, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the dopaminergic stabilizer pridopidine (ACR16) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieburtz, K.; McGarry, A.; McDermott, M.P.; The Huntington Study Group HART Investigators. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pridopidine in Huntington’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Huntington Study Group; Frank, S.; Testa, C.M.; Stamler, D.; Kayson, E.; Davis, C.; Edmondson, M.C.; Kinel, S.; Leavitt, B.; Oakes, D.; et al. Effect of Deutetrabenazine on Chorea Among Patients with Huntington Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, K.; McCusker, E.; Loy, C.; Griffith, J.; Mills, J.; Paulsen, J. Poster 18: Lack of Awareness of Motor and Cognitive Phenoconversion in Huntington’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asla, M.M.; Nawar, A.A.; Abdelsalam, A.; Elsayed, E.; Rizk, M.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Kamel, W.A. The Efficacy and Safety of Pridopidine on Treatment of Patients with Huntington’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Wallman, P.; Dzahini, O.; Howes, O.; Taylor, D. Meta-analysis and systematic review of vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT-2) inhibitors in schizophrenia and psychosis. Psychopharmacology 2024, 241, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, S.M. Mechanism of action of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors in tardive dyskinesia: Reducing dopamine leads to less ‘go’ and more ‘stop’ from the motor striatum for robust therapeutic effects. CNS Spectr. 2018, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y.P.; Navon-Perry, L.; Cruz-Herranz, A.; Chen, K.; Hecker-Barth, G.; Spiegel, K.; Cohen, Y.; Niethammer, M.; Tan, A.M.; Schuring, H.; et al. The Safety Profile of Pridopidine, a Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Huntington’s Disease. CNS Drugs 2025, 39, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

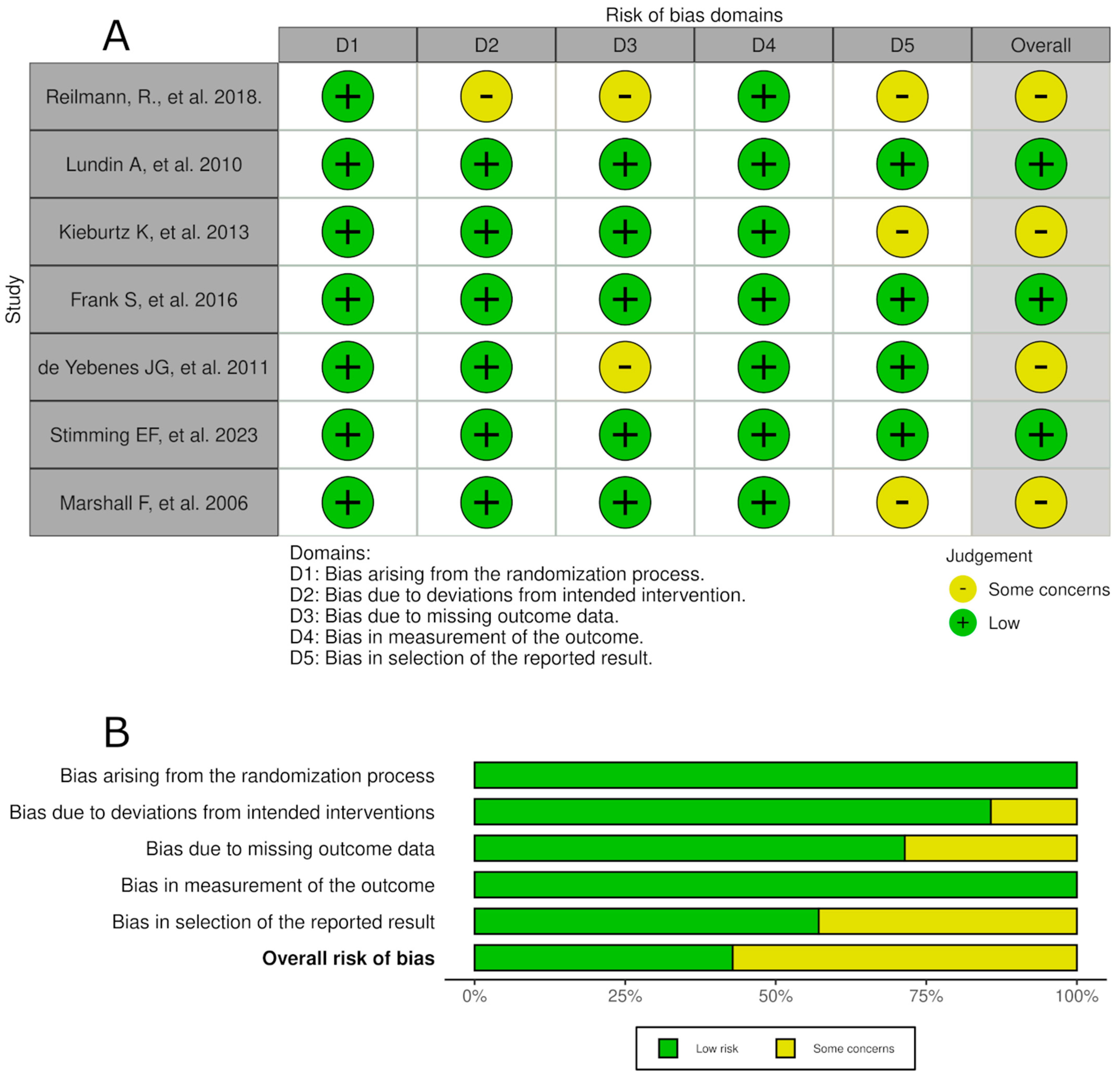

| Author, Year | Risk of Bias | Median Age, Years | Sample Size | Follow-Up Period (Weeks) | Intervention Group and Dosage | Primary Outcomes Measured | Most Common Adverse Event | Most Common Serious Adverse Event | Treatment Discontinuation Because of ADR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reilmann R, et al., 2018 [22] | Low | Cases: 51.9 (11.8) Control: 50.3 (11.3) | 164 | 54 | Dopamine stabilizer (pridopidine) 45 mg, 67.5 mg, 90 mg, and 112.5 | UHDRS- TMS; Q-test; CGI | Falls Cases: 19 (23%) Controls: 17 (21%) | Cases: Suicidal ideation: 1 (1.2%) and aspiration pneumonia: 1 (1.2%) | Yes |
| Lundin A, et al., 2010 [24] | Low | Cases: 50.2 (7) Control: 56 (10) | 58 | NA | Dopamine stabilizer (pridopidine) 50 mg | UHDRS TMS and mMS; Raitan Trail-Making Test; Stroop Test;HADS, CGIC | Cases: tiredness: 5 (17.8%), and falls and injuries: 5 (21%) Control: infections 5 (21%). | Cases: pneumonia 1 (3.3%) | No |
| Kieburtz K, et al., 2013 [25] | Low | Cases: 54.3 (11) Control: 50.4 (10.5) | 114 | 14 | Dopamine stabilizer (pridopidine) 10 mg, 22.5 mg, and 45 mg initial dose 20 mg, 45 mg, and 90 mg target dose | UHDRS TMS; TFC | Falls 10 mg: Cases: 9 (16.1%) Control: 7 (12.1%) 22.5 mg: Cases: 8 (14.5%) Control: 7 (12.1%) 45 mg: Cases: 8 (13.8%) Control: 7 (12.1%). | Cases: Seizures: 2 (3% in treated with 22.5 mg at initial dose | Yes |
| Frank S, et al., 2016 [26] | Low | Cases: 55.4 (10.3) Control: 52.1 (13.4) | 90 | 13 | VMAT-2 (deutetrabenazine 6 mg, mg initial dose 48 mg target dose | UHDRS-TMC and TMS; PGIC; CGIC; SF-36; Berg Balance test | Cases: somnolence 5 (11.1) Control: irritability 6 (13.3%) | Cases: cholecystitis: 1 (2.2%), and agitated depression: 1 (2.2%) Control: COPD: 1 (2.2%) | Yes |
| de Yebenes JG, et al., 2011 [23] | Low | Cases: 51 (10.7) Control: 49.1 (9.6) | 292 | 26 | Dopamine stabilizer (pridopidine) 45 mg and 90 mg | UHDRS -mMS; CGI; UHDRS, Stroop test | 45 mg: Cases: dizziness 11 (7%) Control: falls, chorea and nauseas: 8 (5.5%) 90 mg: Cases: falls 13 (9%) Control: falls, chorea, and nausea: 8 (5.5%) | NA | Yes |
| Stimming EF, et al., 2023 [14] | Low | Cases: 54.1 (10.1) Control: 53.3 (11.4) | 125 | 14 weeks | VMAT-2 (deutetrabenazine 40 mg, mg initial dose 80 mg target dose | UHDRS- TMC; CGIC; PGI; Neuro-Qol | Cases: somnolence: 5 (16%) Control: falls: 8 (13%) | Angioedema: 1 (2%) in cases group, colon cancer: 1 (2%), and psychosis: 1 (2%) in control group | Yes |
| Marshall F, et al., 2006 [21] | Low | Cases: 49.4 (12.4) Control: 48.8 (10.5) | 84 | 12 weeks | VMAT-2 (deutetrabenazine) 12.5 mg, mg initial dose 100 mg target dose | UHDRS, HAM-D, CGI, UPDRS, Stroop test, TE, | Fatigue Cases: 7 (14.3%) Control: 2 (6.9%) | Multiples: 4 (7.4%) in cases group | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Floridia Rietmann, L.M.; Romano, C.; Beltrán Covarrubias, S.A.; Gomez Miranda, J.A.; Briceño Cardeña, O.E.; Shenod, S.; Marrero Peralta, A.V.; Ferrer Zavala, G.M.; Hanumanthu, P.; Borges Sosa, O.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of VMAT-2 Inhibitors and Dopamine Stabilizers for Huntington’s Chorea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030201
Floridia Rietmann LM, Romano C, Beltrán Covarrubias SA, Gomez Miranda JA, Briceño Cardeña OE, Shenod S, Marrero Peralta AV, Ferrer Zavala GM, Hanumanthu P, Borges Sosa O, et al. Efficacy and Safety of VMAT-2 Inhibitors and Dopamine Stabilizers for Huntington’s Chorea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(3):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030201
Chicago/Turabian StyleFloridia Rietmann, Lautaro Manuel, Candela Romano, Salma Alejandra Beltrán Covarrubias, Jose Antonio Gomez Miranda, Omar Enrique Briceño Cardeña, Shwetha Shenod, Ada Victoria Marrero Peralta, Genesis Mariana Ferrer Zavala, Prasanth Hanumanthu, Omar Borges Sosa, and et al. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety of VMAT-2 Inhibitors and Dopamine Stabilizers for Huntington’s Chorea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis" Medical Sciences 13, no. 3: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030201
APA StyleFloridia Rietmann, L. M., Romano, C., Beltrán Covarrubias, S. A., Gomez Miranda, J. A., Briceño Cardeña, O. E., Shenod, S., Marrero Peralta, A. V., Ferrer Zavala, G. M., Hanumanthu, P., Borges Sosa, O., & Calderon Martinez, E. (2025). Efficacy and Safety of VMAT-2 Inhibitors and Dopamine Stabilizers for Huntington’s Chorea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis. Medical Sciences, 13(3), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030201










