Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
3. Challenges of the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) in CNS Drug Delivery
4. Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted TKIs in Brain Metastases
Combination Strategies: EGFR-TKIs with Radiotherapy
5. Efficacy of ALK-Targeted TKIs in Brain Metastases
Combination Strategies: ALK-TKIs with Radiotherapy
6. Comparative Efficacy and Clinical Implications
6.1. Cross-Generational and Cross-Mutation Efficacy Comparisons
6.2. Impact of BBB Penetration on Clinical Outcomes
6.3. Guiding Treatment Decisions for NSCLC Brain Metastases
7. Safety Profile and Adverse Events of TKIs in Brain Metastases
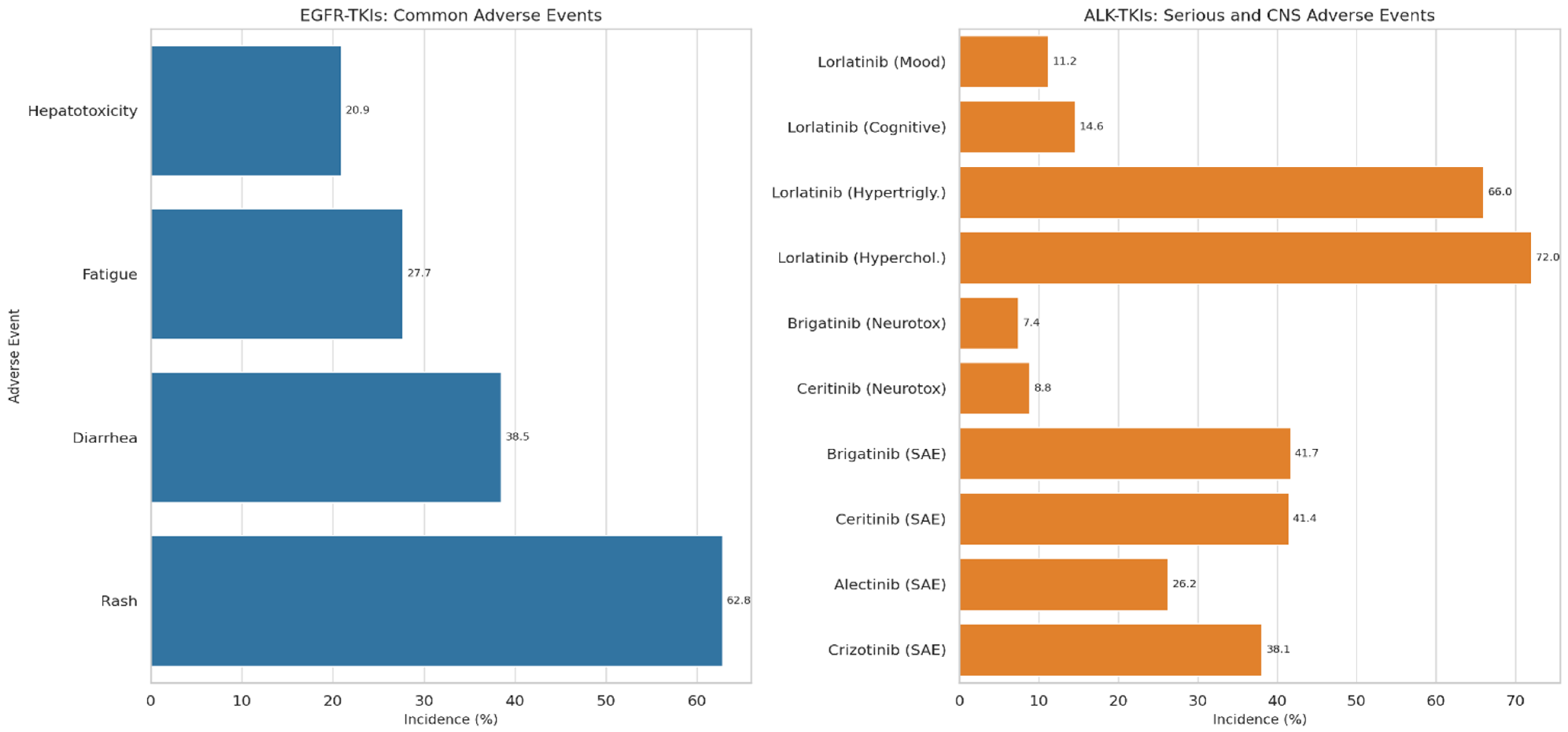
7.1. Adverse Events Associated with EGFR-TKIs
7.2. Adverse Events Associated with ALK-TKIs
7.3. Safety Considerations for TKI-Radiotherapy Combinations
8. Drug Resistance Mechanisms and Challenges in CNS Metastases of Lung Cancer
- 1.
- Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) and Blood–Tumor Barrier (BTB):The BBB restricts the entry of most chemotherapeutic agents and targeted therapies into the CNS through tight endothelial junctions, efflux pumps such as P-glycoprotein, and enzymatic degradation. Even in established brain metastases, the BTB remains heterogeneous, creating areas of poor drug penetration [82,83].
- 2.
- Tumor Cell–Intrinsic Mechanisms:Secondary mutations (e.g., EGFR T790M, C797S; ALK G1202R) reduce the binding affinity of TKIs [84].Bypass signaling activation (e.g., MET amplification, HER2 alterations, KRAS mutations) can restore downstream signaling despite receptor inhibition [85].Intratumoral and interlesional heterogeneity between CNS and extracranial disease leads to variable treatment responses [86].
- 3.
- Microenvironmental Resistance:The CNS microenvironment, including astrocytes and microglia, can secrete cytokines such as IL-6 and TGF-β, promoting tumor survival, stemness, and drug tolerance. Hypoxia and metabolic reprogramming further impair drug sensitivity [87].
- 4.
- Immune-Mediated Resistance:The CNS is relatively immune-privileged, with reduced T-cell infiltration and impaired antigen presentation. PD-L1 expression and T-cell exhaustion within brain metastases limit the efficacy of ICIs [88].
- 5.
- Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Barriers:Inadequate solubility, rapid clearance, or efflux-mediated exclusion of drugs prevents therapeutic concentrations from being sustained within intracranial lesions, even when systemic disease remains controlled [89].
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BMs | Brain metastases |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DCR | Disease control rate |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| IC-ORR | Intracranial objective response rates |
| iDCR | Intracranial disease control rate |
| iORR | Intracranial objective response rate |
| iPFS | Intracranial progression-free survival |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| SRS | Stereotactic radiosurgery |
| TKIs | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
References
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakobson, A.; Brenner, R.; Gothelf, I.; Rabinovich, N.M.; Cohen, A.Y.; Abu Jama, A.; Abu Yasin, N.; Abu Ghalion, F.; Agbarya, A.; Shalata, W. Exploring the Impact of TP53 Mutation and Wild-Type Status on the Efficacy of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, X.; Huang, S.; Xiao, H.; Zeng, S.; Liu, J.; Ran, Z.; Xiong, B. Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 plus CTLA-4 antibodies ± other therapies in lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2021, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Liang, S.; Yu, Y.; Han, Y. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant immunotherapy protocols and cycles for non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1276549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parr, N.J.; Anderson, J.A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and EGFR-TKIs as Adjuvant/Neoadjuvant Therapies for Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review; Department of Veterans Affairs (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sidrak, M.M.A.; De Feo, M.S.; Frantellizzi, V.; Marongiu, A.; Caponnetto, S.; Filippi, L.; Nuvoli, S.; Spanu, A.; Schillaci, O.; De Vincentis, G. First-, Second-, and Third-Generation Radiolabeled Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Positron Emission Tomography: State of the Art, a Systematic Review. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharm. 2023, 38, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filetti, M.; Lombardi, P.; Falcone, R.; Giusti, R.; Giannarelli, D.; Carcagnì, A.; Altamura, V.; Scambia, G.; Daniele, G. Comparing efficacy and safety of upfront treatment strategies for anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2023, 4, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doherty, M.K.; Korpanty, G.J.; Tomasini, P.; Alizadeh, M.; Jao, K.; Labbé, C.; Mascaux, C.M.; Martin, P.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Tsao, M.S.; et al. Treatment options for patients with brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-driven lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Soejima, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Brain metastases in oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, S298–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petrelli, F.; Lazzari, C.; Ardito, R.; Borgonovo, K.; Bulotta, A.; Conti, B.; Cabiddu, M.; Capitanio, J.F.; Brighenti, M.; Ghilardi, M.; et al. Efficacy of ALK inhibitors on NSCLC brain metastases: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 21 studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mobley, J.M.; Phillips, K.I.; Chen, Q.; Reusch, E.; Reddy, N.; Magsam, J.B.; McLouth, L.E.; Huang, B.; Villano, J.L. Outcomes of Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzhu, G.; Chen, L.; Ning, J.; Xue, W.; Wang, C.; Xiao, G.; Yang, J.; Zhou, R. Metastatic brain tumors: From development to cutting-edge treatment. Medcomm 2024, 6, e70020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boire, A.; Brastianos, P.K.; Garzia, L.; Valiente, M. Brain metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 20, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, C.S.; Mustafa, M.A.; Richardson, G.E.; Alam, A.M.; Lee, K.S.; Hughes, D.M.; Escriu, C.; Zakaria, R. Genomic Alterations and the Incidence of Brain Metastases in Advanced and Metastatic NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Pang, Q.; Wang, P. Brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with uncommon EGFR mutations: A report of seven cases and literature review. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Dang, J.; Li, G.; Ma, Y. First-line treatments in EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Xie, T.; Xing, P.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Front-line therapy for brain metastases and non-brain metastases in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nelson, T.A.; Wang, N. Targeting lung cancer brain metastases: A narrative review of emerging insights for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive disease. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gil, M.; Knetki-Wróblewska, M.; Niziński, P.; Strzemski, M.; Krawczyk, P. Effectiveness of ALK inhibitors in treatment of CNS metastases in NSCLC patients. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, R.; Lehrer, E.J.; Ko, S.; Peterson, J.; Lou, Y.; Porter, A.B.; Kotecha, R.; Brown, P.D.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Trifiletti, D.M. Brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR or ALK mutations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of multidisciplinary approaches. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 144, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, W.-L.; Han, P.-L.; Yan, W.-F.; Yang, Z.-G. Enhancing intracranial efficacy prediction of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer: A novel approach through brain MRI radiomics. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1399983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, H.; Perez-Soler, R. Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e43–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, F.; Pellerino, A.; Soffietti, R.; Rudà, R. Blood–Brain Barrier in Brain Tumors: Biology and Clinical Relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patil, S.; Rathnum, K. Management of leptomeningeal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J. Cancer 2019, 56, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldig, C.; Boldig, K.; Mokhtari, S.; Etame, A.B. A Review of the Molecular Determinants of Therapeutic Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’BRien, F.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Griffin, B.T.; Cryan, J.F. Interactions between antidepressants and P-glycoprotein at the blood–brain barrier: Clinical significance of in vitro and in vivo findings. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Davis, T.P.; Sanchez-Covarubias, L.; Tome, M.E. P-glycoprotein trafficking as a therapeutic target to optimize CNS drug delivery. Adv. Pharmacol. 2014, 71, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Bian, Z.; Fei, B.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Z. An Integrated Three-Long Non-coding RNA Signature Predicts Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bai, H.; Xiong, L.; Han, B. The effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs against brain metastases in EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Batra, U.; Lokeshwar, N.; Gupta, S.; Shirsath, P. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the management of central nervous system metastases in epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive nonsmall cell lung cancer patients. Indian J. Cancer 2017, 54, S37–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.A.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K.; Sun, J.-M. The different central nervous system efficacy among gefitinib, erlotinib and afatinib in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hui, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Intracranial Outcomes of De Novo Brain Metastases Treated with Osimertinib Alone in Patients with Newly Diagnosed EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Kniep, H.C.; Madesta, F.; Schneider, T.; Hanning, U.; Schönfeld, M.H.; Schön, G.; Fiehler, J.; Gauer, T.; Werner, R.; Gellissen, S. Radiomics of Brain MRI: Utility in Prediction of Metastatic Tumor Type. Radiology 2019, 290, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. This update meta-analysis aimed to derive a more precise estimation of radiotherapy plus epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in NSCLC patients with BM. PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library were searched to identify any relevant publications. Oncotargets Ther. 2016, 9, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, L. First-line treatment for advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2025, 14, 1498518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Ho, H.-L.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Shen, C.-I.; Luo, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chou, T.-Y. Prognosticators of osimertinib treatment outcomes in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer and leptomeningeal metastasis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hyak, J.; Rashdan, S. The Landscape and Management of Brain Parenchymal and Leptomeningeal Metastases in EGFR Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, C.; Shi, X.; Zou, Y.; Chen, J.; Jia, X.; Su, L. The advance of the third-generation EGFR-TKI in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2024, 51, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liam, C.-K. The role of osimertinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S448–S452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tatineni, V.; O’shea, P.J.; Ozair, A.; Khosla, A.A.; Saxena, S.; Rauf, Y.; Jia, X.; Murphy, E.S.; Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; et al. First- versus Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases. Cancers 2023, 15, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-X.; He, H.; Ruan, Z.-H.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Li, R.-Q.; He, X.; Lan, B.-H.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Liu, G.-D.; Xiao, H.-L.; et al. Central nervous system progression in advanced non–small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations in response to first-line treatment with two EGFR-TKIs, gefitinib and erlotinib: A comparative study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ricciuti, B.; Baglivo, S.; De Giglio, A.; Chiari, R. Afatinib in the first-line treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical evidence and experience. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12, 1753466618808659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Xing, P.; Li, J. Efficacy of dacomitinib in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC and brain metastases. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Park, S.; Baldry, R.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; et al. Phase II Efficacy and Safety of 80 mg Osimertinib in Patients with Leptomeningeal Metastases Associated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (BLOSSOM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2747–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, W.; Shen, Y.; Chien, C.; Liao, W.; Chen, C.; Hsia, T.; Tu, C.; Chen, H. The optimal therapy strategy for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A real-world study from Taiwan. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, T.N.H.; Van, Q.L.; Thi Bich, P.N.; Thi, H.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Minh, T.D.; Duc, L.N.; Thanh, D.P.; Le, L.N.; Van, C.N.; et al. Therapeutic Outcomes of Osimertinib in EGFR—Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: Results from a Retrospective Study at Vietnam National Cancer Hospital. Cancer Control 2025, 32, 10732748251348429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, T.; Min, W.; Li, Y.; Yue, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhou, C. Radiotherapy plus EGFR TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: An update meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nepote, A.; Poletto, S.; Bertaglia, V.; Carnio, S.; Piumatti, C.; Lanzetta, C.; Cantale, O.; Saba, G.; Bironzo, P.; Novello, S.; et al. Role of osimertinib plus brain radiotherapy versus osimertinib single therapy in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2025, 205, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, J.; Ma, S.; Xia, B.; Zhu, L. Efficacy analysis of brain radiotherapy in EGFR mutation non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastasis: A retrospective study. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qian, J.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Analysis of the efficacy of upfront brain radiotherapy versus deferred radiotherapy for EGFR/ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zeng, Z.; Feng, S.; Gao, T.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Lian, Y. Efficacy and Safety of EGFR-TKI Combined with Early Brain Radiotherapy Versus TKI Alone in Patients with EGFR-Mutated NSCLC with Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2025, 26, e391–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.-Y.; Li, M.-F.; Lin, J.-H.; Lin, D.; Lin, R.-J. Comparing the efficacy of concurrent EGFR-TKI and whole-brain radiotherapy vs EGFR-TKI alone as a first-line therapy for advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, M.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Yi, G.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, R.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z. Effects of EGFR-TKIs combined with intracranial radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A retrospective multi-institutional analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tao, X.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cai, N.; Hao, C. Efficacy and toxicity of stereotactic radiotherapy combined with third-generation EGFR-TKIs and immunotherapy in patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2025, 201, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, S.; Xu, S.; Li, L.; Xue, Z.; He, L. Efficacy and safety of EGFR-TKI combined with WBRT vs. WBRT alone in the treatment of brain metastases from NSCLC: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1362061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hong, X.; Chen, Q.; Ding, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Fang, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, H. Clinical benefit of continuing crizotinib therapy after initial disease progression in Chinese patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41631–41640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y.; Hao, W.; Han, L. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Felip, E.; Blackhall, F.H.; Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Mekhail, T.; Paolini, J.; et al. Intracranial Efficacy of Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from PROFILE 1014. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical Experience with Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mok, T.; Camidge, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Rosell, R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Kim, D.-W.; Pérol, M.; Ou, S.-H.; Ahn, J.; Shaw, A.; et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Fu, Y.; Guo, J.; Fu, C.; Tang, N.; Zhang, C.; Han, X.; Wang, Z. Efficacy and survival outcomes of alectinib vs. crizotinib in ALK-positive NSCLC patients with CNS metastases: A retrospective study. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 27, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zou, Z.; Xing, P.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ma, K.; Dong, G.; et al. Intracranial efficacy of alectinib in ALK-positive NSCLC patients with CNS metastases—A multicenter retrospective study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, D. Efficacy and safety of first-line treatments for patients with advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutated, non–small cell cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancer 2023, 129, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Lorlatinib and Alectinib for ALK-Rearrangement Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Asian and Non-Asian Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chow, L.Q.; Barlesi, F.; Bertino, E.M.; Bent, M.J.v.D.; Wakelee, H.A.; Wen, P.Y.; Chiu, C.-H.; Orlov, S.; Chiari, R.; Majem, M.; et al. ASCEND-7: Efficacy and Safety of Ceritinib Treatment in Patients with ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastatic to the Brain and/or Leptomeninges. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Liu, G.; Felip, E.; Mok, T.S.; Soo, R.A.; Mazieres, J.; Shaw, A.T.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Wu, Y.-L.; et al. Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced ALK -Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes from the Phase III CROWN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3400–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Kim, H.R.; Soo, R.A.; Zhou, Q.; Akamatsu, H.; Chang, G.-C.; Chiu, C.-H.; Hayashi, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Goto, Y.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in Asian Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC: Five-Year Outcomes from the CROWN Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, 20, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Jassem, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated analysis of data from the phase 3, randomised, open-label CROWN study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Iadeluca, L.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from the randomized phase 3 CROWN study of first-line lorlatinib versus crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2022, 174, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, S.A.; Camidge, D.R. PROFILE 1014: Lessons for the new era of lung cancer clinical research. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK -positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.J.; Kim, H.R.; Yang, J.C.; Han, J.-Y.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Hochmair, M.J.; Chang, G.-C.; Delmonte, A.; Lee, K.H.; Campelo, R.G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Brigatinib Compared with Crizotinib in Asian vs. Non-Asian Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic ALK–Inhibitor-Naive ALK+ Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Final Results from the Phase III ALTA-1L Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Noel, G. Combining Radiation Therapy with ALK Inhibitors in Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Clinical and Preclinical Overview. Cancers 2021, 13, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, S.; Hu, P.; Geng, D.; Zheng, R.; Li, X. Alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer and comparison of next-generation TKIs after crizotinib failure: Real-world evidence. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 4491–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Georgakopoulos, I.; Kouloulias, V.; Ntoumas, G.; Desse, D.; Koukourakis, I.; Kougioumtzopoulou, A.; Charpidou, A.; Syrigos, K.N.; Zygogianni, A. Combined use of radiotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the management of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A literature review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2024, 204, 104520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Shi, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alectinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer and blood markers for prognosis and efficacy: A retrospective cohort study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 2521–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Hui, Z. Treatment Optimization for Brain Metastasis from Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2019, 42, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agbarya, A.; Raphael, A.; Sorotsky, H.G.; Rottenberg, Y.; Šebek, V.; Radonjic, D.; Yakobson, A.; Arnon, J.; Shalata, W. Real-World Data on Osimertinib-Associated Cardiac Toxicity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shalata, W.; Abu Jama, A.; Dudnik, Y.; Abu Saleh, O.; Shalata, S.; Tourkey, L.; Sheva, K.; Meirovitz, A.; Yakobson, A. Adverse Events in Osimertinib Treatment for EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Unveiling Rare Life-Threatening Myelosuppression. Medicina 2024, 60, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arvanitis, C.D.; Ferraro, G.B.; Jain, R.K. The blood–brain barrier and blood–tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Aoyama, H.; Barani, I.J.; Barboriak, D.P.; Baumert, B.G.; Bendszus, M.; Brown, P.D.; Camidge, D.R.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: Proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e270–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Sriuranpong, V.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; Okamoto, I.; Zhou, C.; et al. Osimertinib versus Standard of Care EGFR TKI as First-Line Treatment in Patients with EGFRm Advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Asian Subset. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Carter, S.L.; Santagata, S.; Cahill, D.P.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Jones, R.T.; Van Allen, E.M.; Lawrence, M.S.; Horowitz, P.M.; Cibulskis, K.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Brain Metastases Reveals Branched Evolution and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xing, F.; Kobayashi, A.; Okuda, H.; Watabe, M.; Pai, S.K.; Pandey, P.R.; Hirota, S.; Wilber, A.; Mo, Y.Y.; Moore, B.E.; et al. Reactive astrocytes promote the metastatic growth of breast cancer stem-like cells by activating Notch signalling in brain. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sznol, M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Cohen, J.; Vortmeyer, A.; Jilaveanu, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: Early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mittapalli, R.K.; Vaidhyanathan, S.; Dudek, A.Z.; Elmquist, W.F. Mechanisms Limiting Distribution of the Threonine-Protein Kinase B-RaFV600E Inhibitor Dabrafenib to the Brain: Implications for the Treatment of Melanoma Brain Metastases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, W.; Vallega, K.A.; Sun, S.-Y. Managing Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Through Co-Targeting MEK/ERK Signaling. Lung Cancer Targets Ther. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, X.; Zeng, L.; Huang, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Yan, H.; Zou, C.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y. Strategies Beyond 3rd EGFR-TKI Acquired Resistance: Opportunities and Challenges. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| TKI Generation/Drug | Blood–Brain Barrier Penetration (CSF/Plasma Ratio) | Intracranial Objective Response Rate | Median Intracranial Progression-Free Survival | Median Overall Survival | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Generation (Gefitinib/Erlotinib) | 1.1–3.3% | ~50–60% (51.8%) | ~7.4 months | ~11.9 months | [42] |
| Second Generation (Afatinib/Dacomitinib) | ~1.7% | Variable/Limited | Not consistently reported | Not consistently reported | [43,44] |
| Third Generation (Osimertinib) | 2.5–16.0% | 54–100% (commonly ~76%) | ~8–15 months (varies by study) | Not reached (especially in de novo brain metastases) | [45,46] |
| TKI Generation/Drug | Blood–Brain Barrier Penetration | Intracranial Objective Response Rate | Median Intracranial Progression-Free Survival | Median Overall Survival | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Generation (Crizotinib) | Poor | ~40% (no prior radiotherapy), ~70% (with prior radiotherapy) | ~10.8 months | ~58.7 months (selected subgroups) | [72] |
| Second Generation (Alectinib) | Improved | ~78.6% (no prior radiotherapy), ~85.7% (with prior radiotherapy) | ~36.0 months | Not reached | [61,73] |
| Second Generation (Brigatinib) | Good | ~78% (treatment-naïve patients) | ~24.0 months | Not reached | [67,74] |
| Third Generation (Lorlatinib) | Excellent | ~60%, ~49% complete response | Not reached (in first line) | Not evaluable/immature data | [68,69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalata, W.; Naamneh, R.; Najjar, W.; Abu Amna, M.; Asla, M.; Agbarya, A.; Brenner, R.; Abu Jama, A.; Abu Yasin, N.; Abu Juda, M.; et al. Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030200
Shalata W, Naamneh R, Najjar W, Abu Amna M, Asla M, Agbarya A, Brenner R, Abu Jama A, Abu Yasin N, Abu Juda M, et al. Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(3):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030200
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalata, Walid, Rashad Naamneh, Wenad Najjar, Mahmoud Abu Amna, Mohnnad Asla, Abed Agbarya, Ronen Brenner, Ashraf Abu Jama, Nashat Abu Yasin, Mhammad Abu Juda, and et al. 2025. "Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases" Medical Sciences 13, no. 3: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030200
APA StyleShalata, W., Naamneh, R., Najjar, W., Abu Amna, M., Asla, M., Agbarya, A., Brenner, R., Abu Jama, A., Abu Yasin, N., Abu Juda, M., Abu Zeid, E. E. D., Rouvinov, K., & Yakobson, A. (2025). Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases. Medical Sciences, 13(3), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030200









