Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment of Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Data Visualization and Tabulation
2.7. Software and Statistical Packages
3. Results
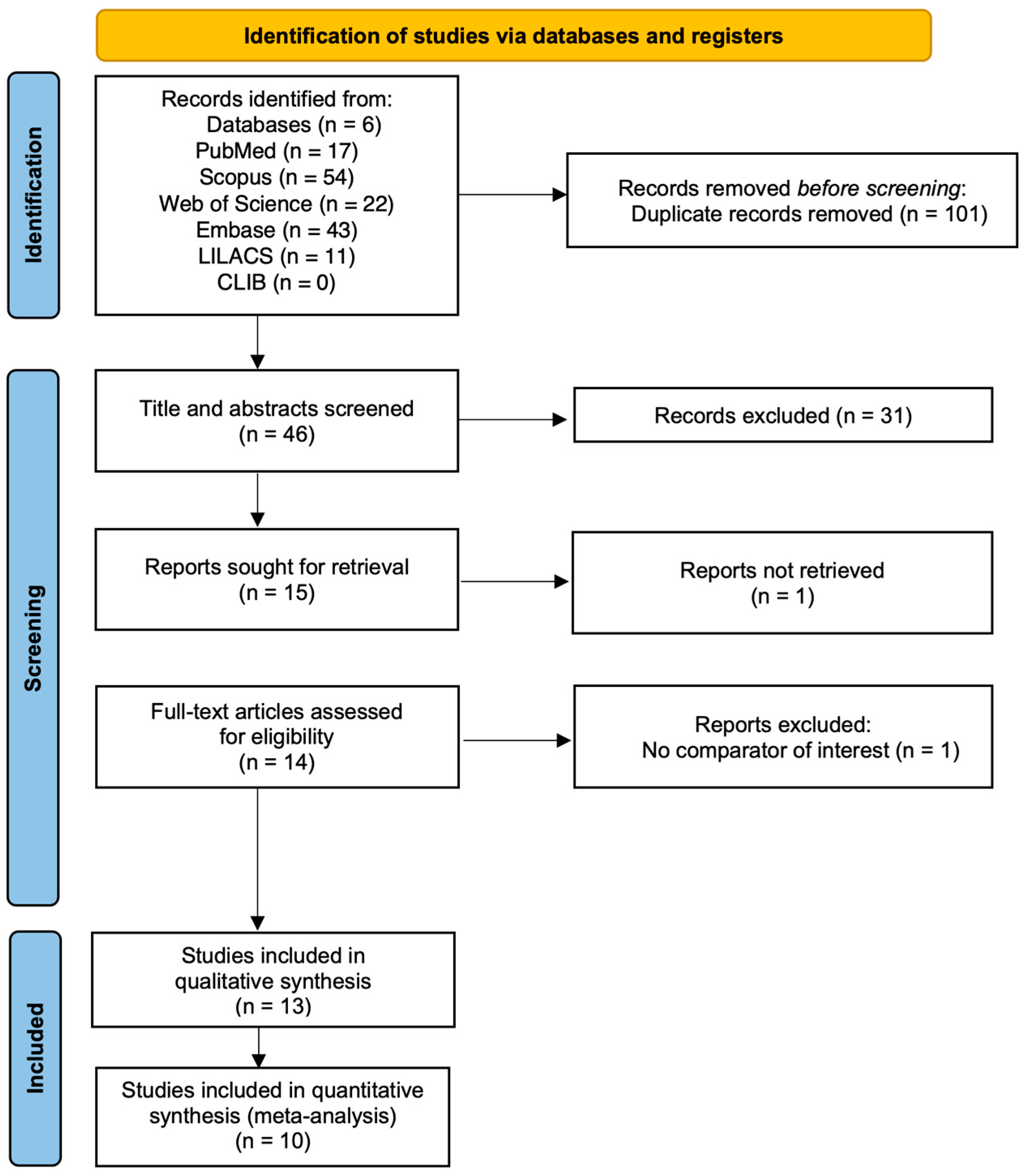
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
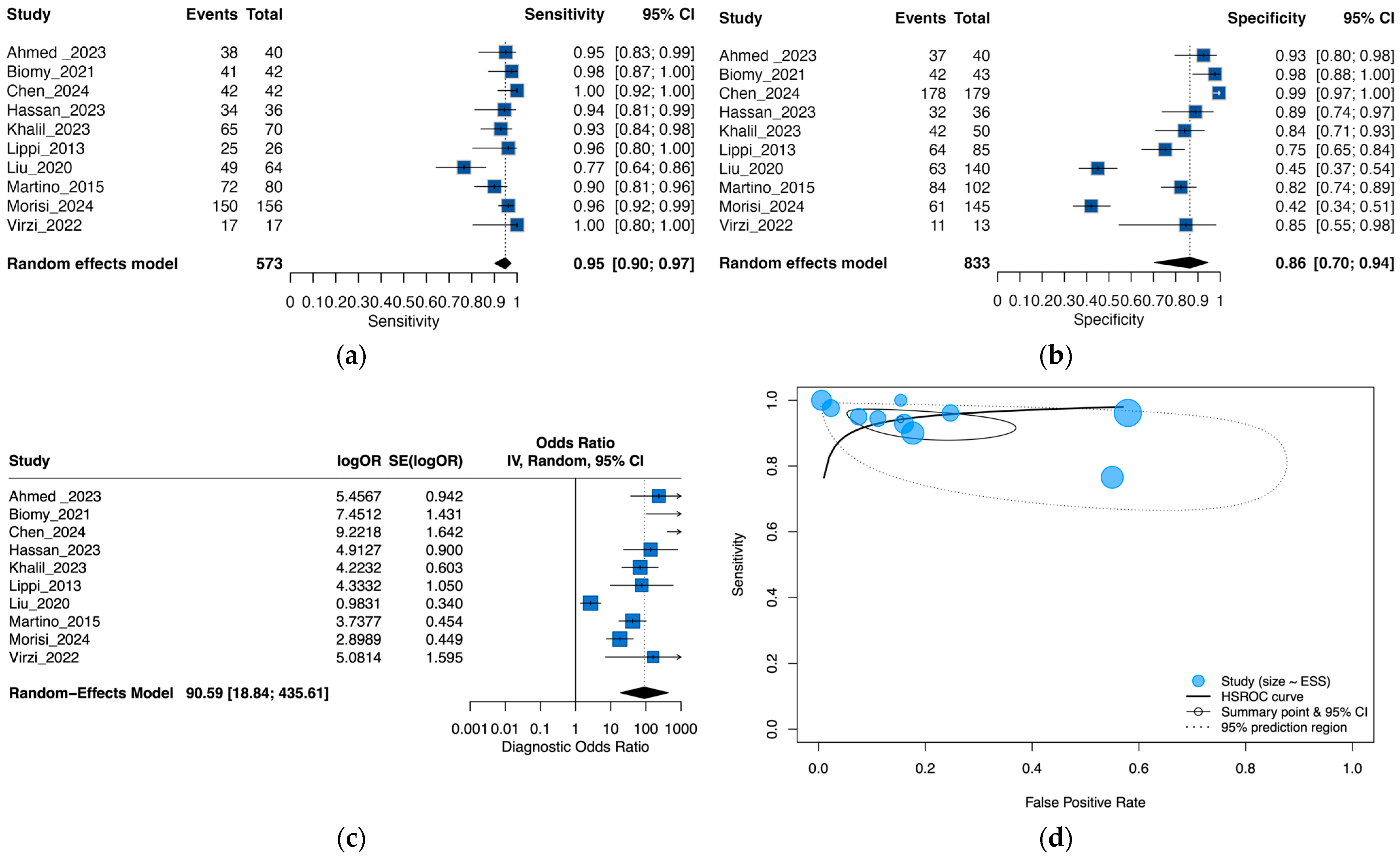
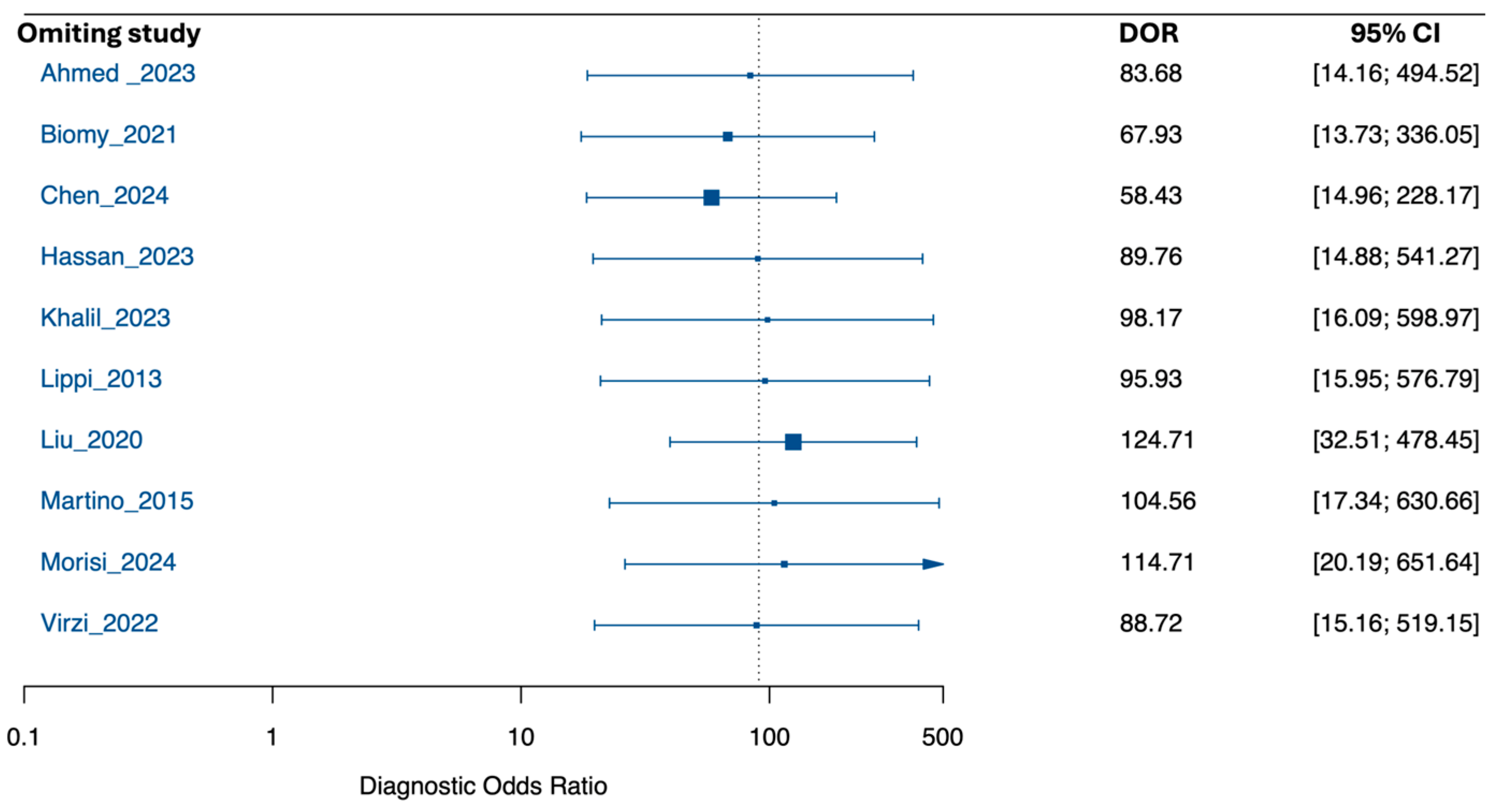
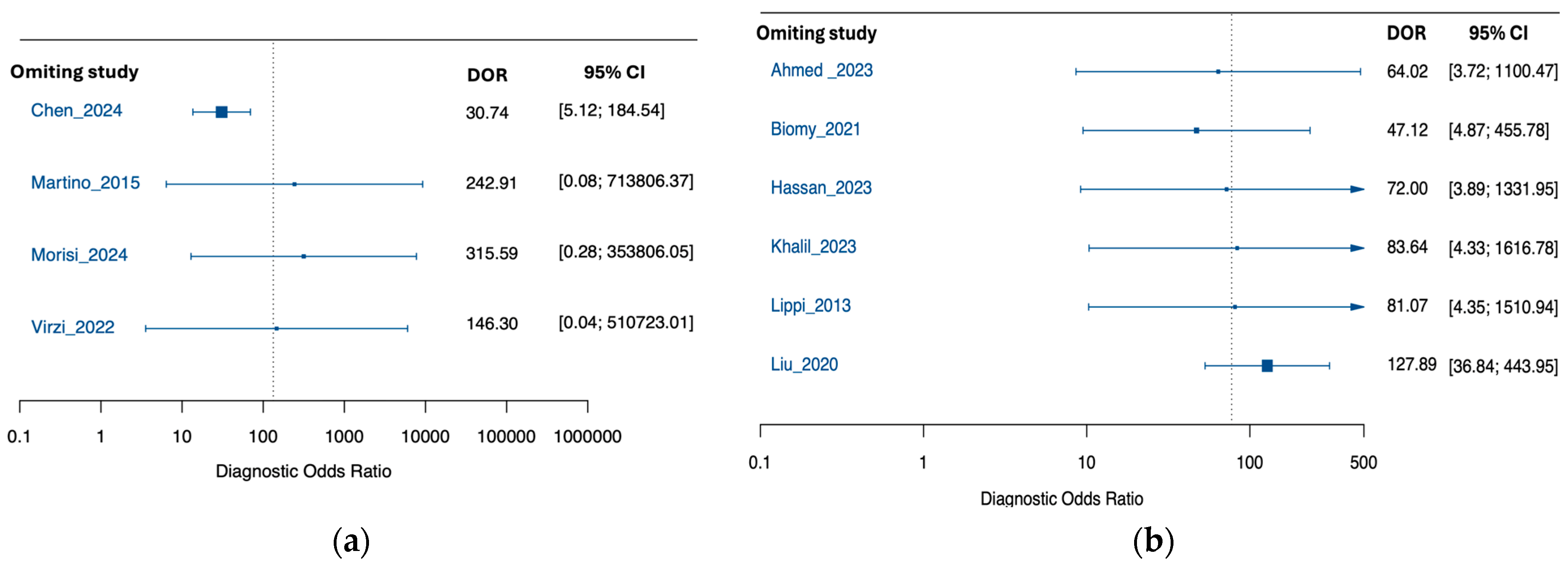
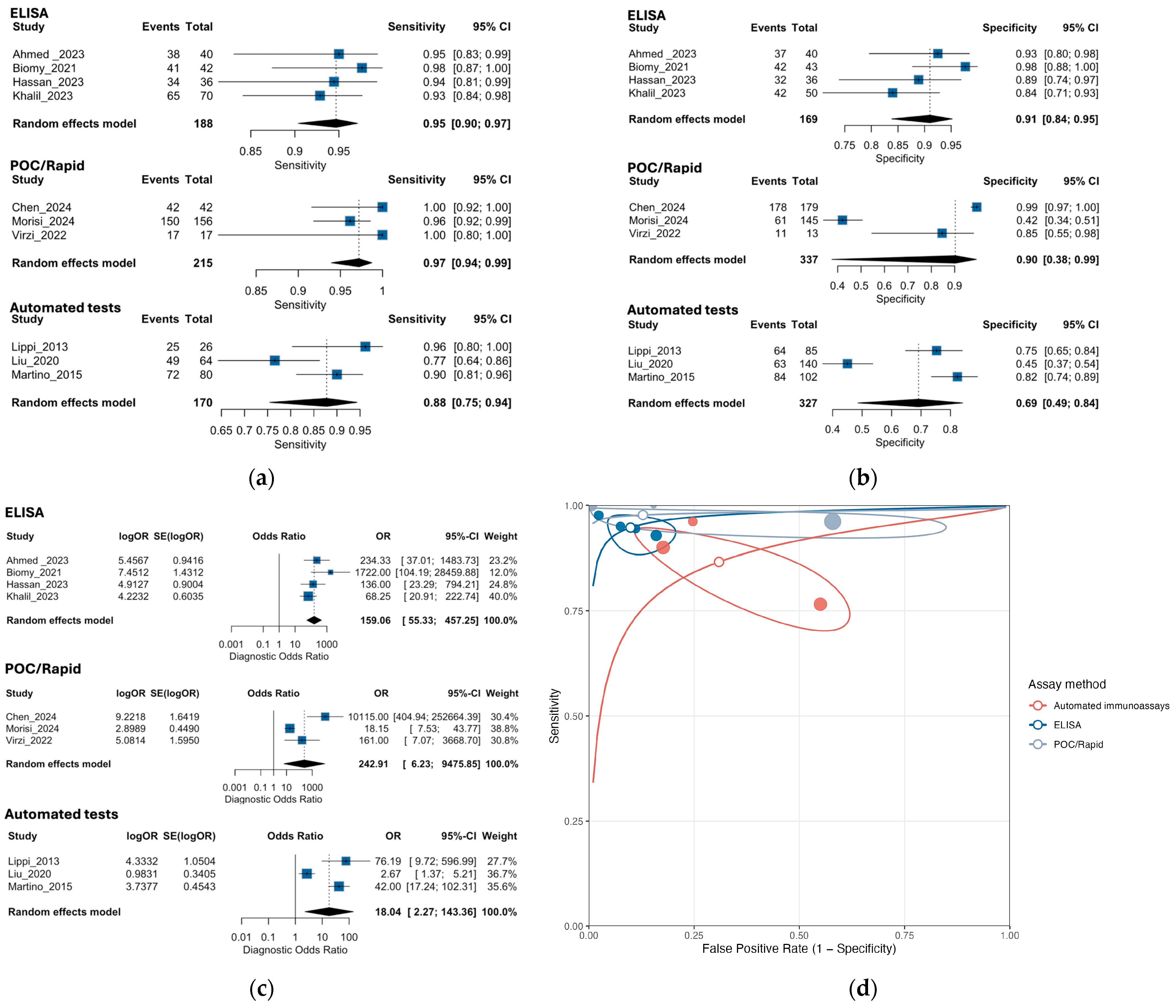
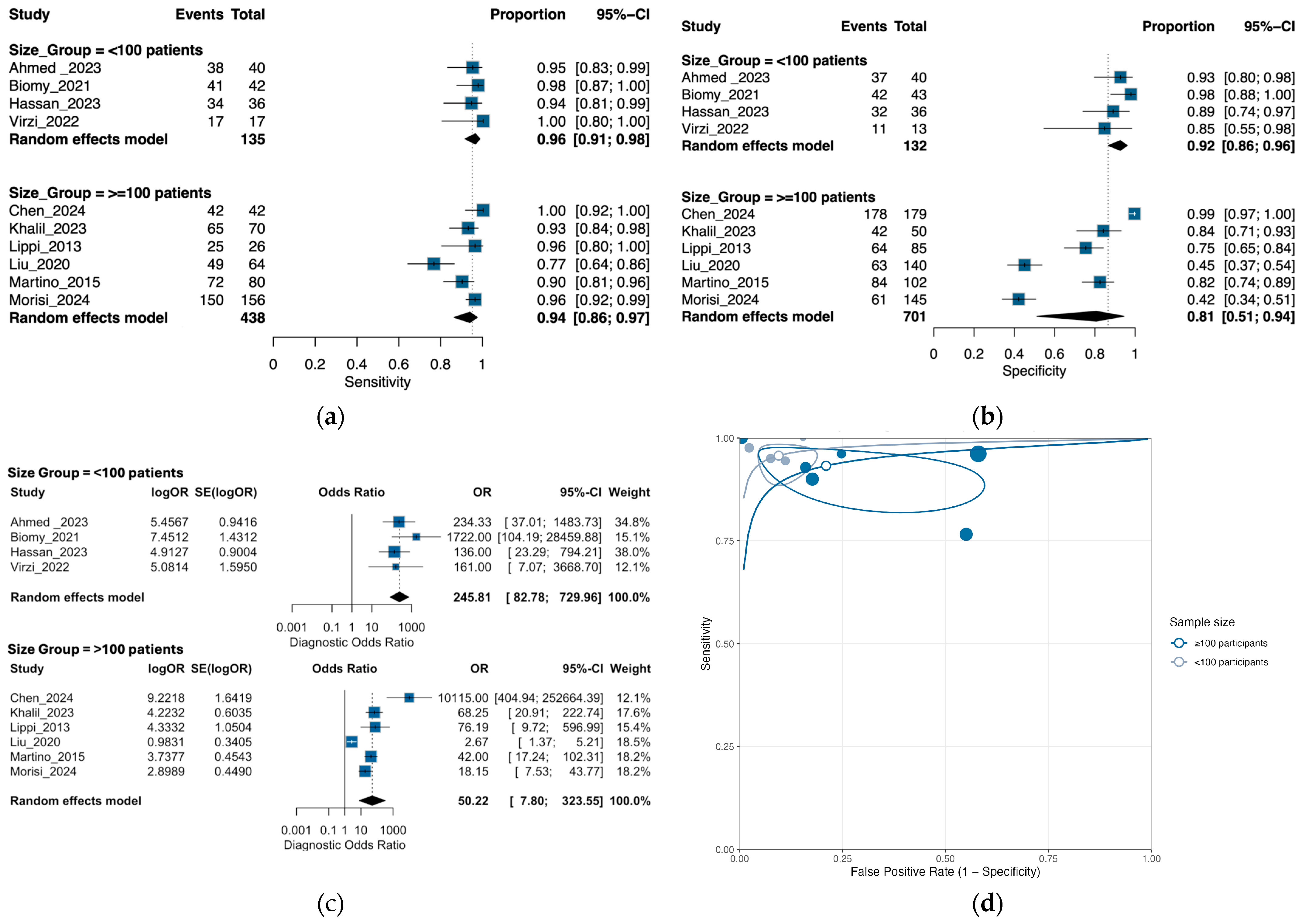
3.3. Performance of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Detection of SBP and PDAP
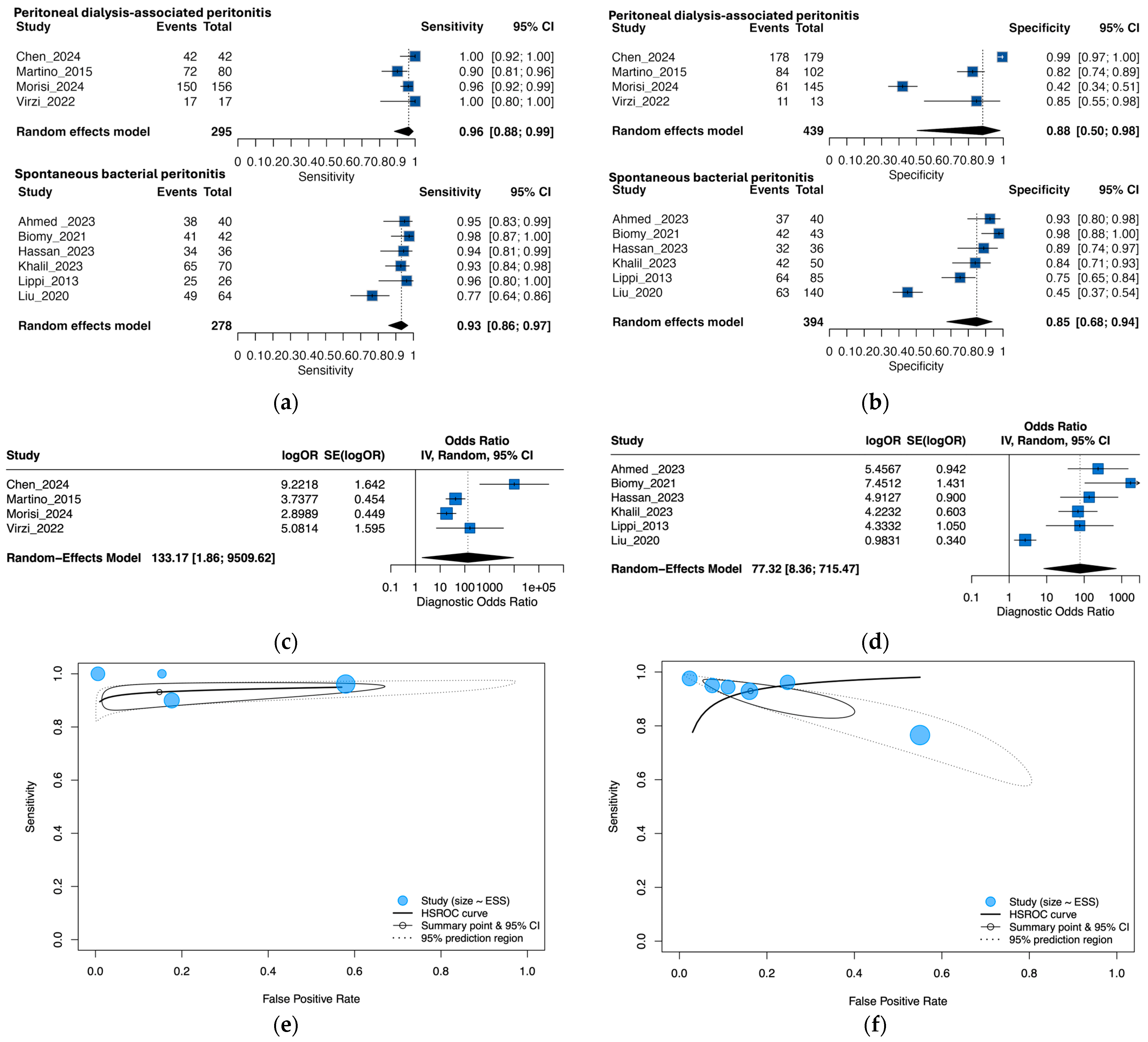
3.4. Exploratory Subgroup Analysis by Peritonitis Type
3.5. Exploratory Subgroup Analysis by NGAL Assay Method
3.6. Exploratory Subgroup Analysis by Sample Size
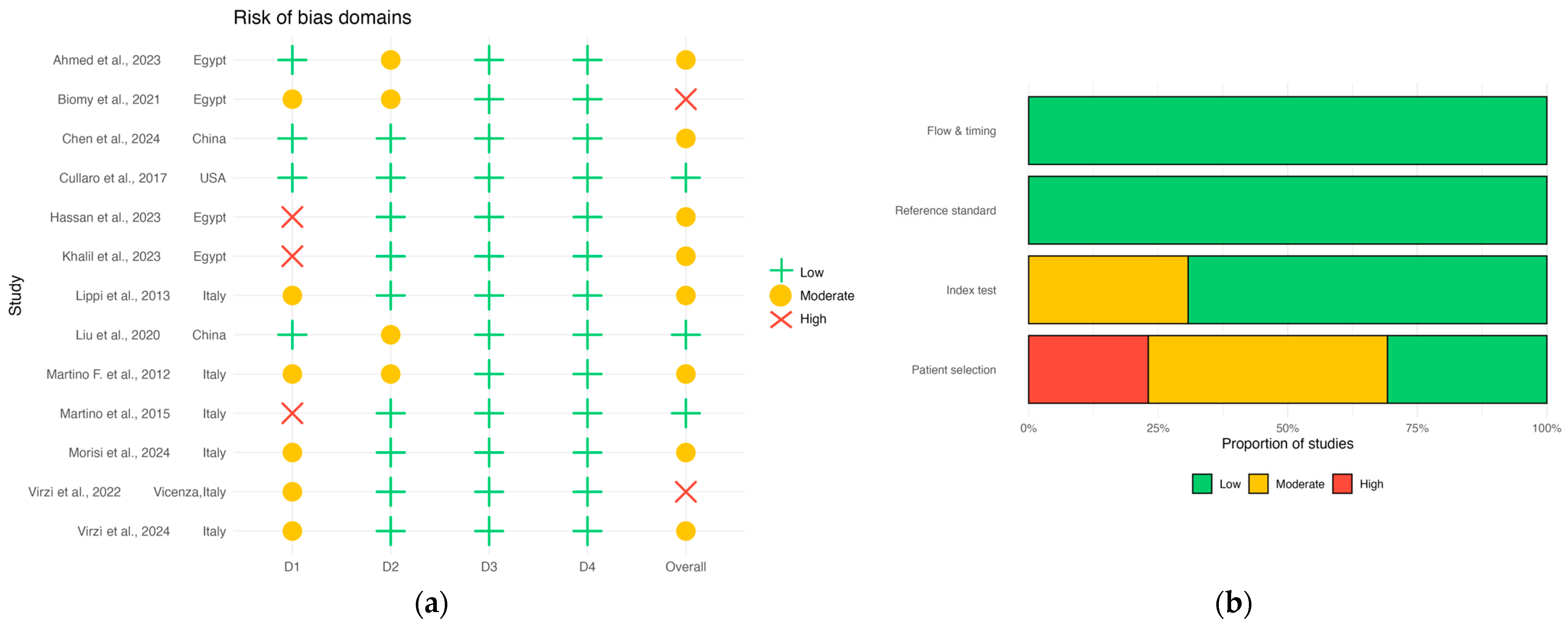
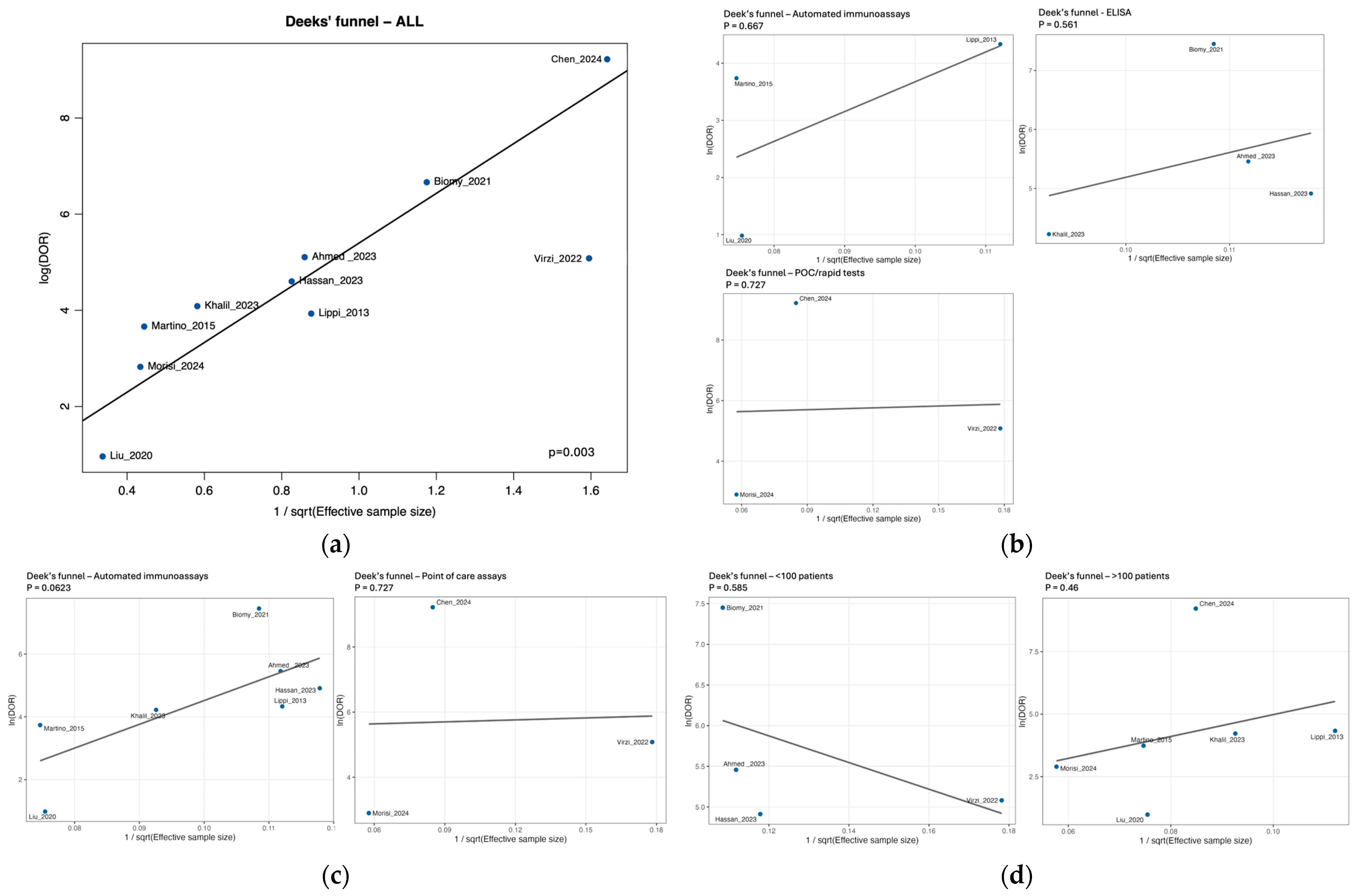
3.7. Risk of Bias
3.8. Certainty of the Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AASLD | American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
| ANC | Absolute Neutrophil Count |
| APD | Automated Peritoneal Dialysis |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CAPD | Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis |
| CBC | Complete Blood Count |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CNNA | Culture-Negative Neutrocytic Ascites |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| DOR | Diagnostic odds ratio |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| HSROC | Hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| ISPD | International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| NGALds | NGAL Dipstick Test |
| NGALlab | Laboratory-based NGAL Test |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PD | Peritoneal Dialysis |
| PDAP | Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis |
| PMN | Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils |
| PMNL | Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes |
| POC | Point-of-care |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| QUADAS-2 | Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SBP | Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis |
| SROC | Summary receiver operating characteristic |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
References
- Teitelbaum, I. Peritoneal Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, P.W.L.; Xiao, J.; Tan, D.J.H.; Ng, C.; Lye, Y.N.; Lim, W.H.; Teo, V.X.Y.; Heng, R.R.Y.; Yeow, M.W.X.; Lum, L.H.W.; et al. An Epidemiological Meta-Analysis on the Worldwide Prevalence, Resistance, and Outcomes of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 693652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Freha, N.; Michael, T.; Poupko, L.; Estis-Deaton, A.; Aasla, M.; Abu-Freha, O.; Etzion, O.; Nesher, L. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis among Cirrhotic Patients: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.W.; Zhao, J.; Pisoni, R.L.; Piraino, B.M.; Shen, J.I.; Boudville, N.; Schreiber, M.J.; Teitelbaum, I.; Perl, J.; McCullough, K. Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis Trends Using Medicare Claims Data, 2013–2017. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flythe, J.E.; Watnick, S. Dialysis for Chronic Kidney Failure: A Review. JAMA 2024, 332, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, L.; Scalamogna, A.; Ponzano, F.; Sikharulidze, A.; Tripodi, F.; Vettoretti, S.; Alfieri, C.; Castellano, G. Peritoneal Dialysis Related Peritonitis: Insights from a Long-Term Analysis of an Italian Center. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A. Peritonitis Remains the Major Clinical Complication of Peritoneal Dialysis: The London, UK, Peritonitis Audit 2002–2003. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 29, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Fontan, M.; Rodríguez-Carmona, A.; García-Naveiro, R.; Rosales, M.; Villaverde, P.; Valdés, F. Peritonitis-Related Mortality in Patients Undergoing Chronic Peritoneal Dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2005, 25, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kamath, P.S.; Reddy, K.R. The Evolving Challenge of Infections in Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lee, H.-F. Short and Long-Term Mortality of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhotic Patients. Medicine 2024, 103, e40851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoiemma, P.P.; Dakwar, O.; Angarone, M.P. A Retrospective Analysis of Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhosis Patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekraksakit, P.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Miao, J.; Leelaviwat, N.; Thongpiya, J.; Qureshi, F.; Craici, I.M.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Outcomes of Peritoneal Dialysis in Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2025, 45, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullaro, G.; Kim, G.; Pereira, M.R.; Brown, R.S.; Verna, E.C. Ascites Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Identifies Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3487–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virzì, G.M.; Mattiotti, M.; Milan Manani, S.; Gnappi, M.; Tantillo, I.; Corradi, V.; de Cal, M.; Giuliani, A.; Carta, M.; Giavarina, D.; et al. Peritoneal NGAL: A Reliable Biomarker for PD-Peritonitis Monitoring. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 2139–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, J.R.; Borregaard, N.; Cowland, J.B. Induction of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Expression by Co-Stimulation with Interleukin-17 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Is Controlled by IkappaB-Zeta but Neither by C/EBP-Beta nor C/EBP-Delta. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14088–14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaberi, S.A.; Cohen, A.; D’Souza, C.; Abdulrazzaq, Y.M.; Ojha, S.; Bastaki, S.; Adeghate, E.A. Lipocalin-2: Structure, Function, Distribution and Role in Metabolic Disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasioudis, D.; Witkin, S.S. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Innate Immune Responses to Bacterial Infections. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Adolph, T.E.; Gerner, R.R.; Wieser, V.; Tilg, H. Lipocalin-2: A Master Mediator of Intestinal and Metabolic Inflammation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Hassan, R.; Abd Elghafar Salem, G.; Mohamed ALsayed Refaat Mohamed, B.; Ahmed Zidan, A.; El-Gebaly, A.M. Prognostic Value of Ascitic Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Patients. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 91, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Caleffi, A.; Pipitone, S.; Elia, G.; Ngah, A.; Aloe, R.; Avanzini, P.; Ferrari, C. Assessment of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Lactate Dehydrogenase in Peritoneal Fluids for the Screening of Bacterial Peritonitis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 418, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, P.; Nie, C.; Ye, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Pang, G.; Han, T. The Value of Ascitic Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.; Scalzotto, E.; Giavarina, D.; Rodighiero, M.P.; Crepaldi, C.; Day, S.; Ronco, C. The Role of NGAL in Peritoneal Dialysis Effluent in Early Diagnosis of Peritonitis: Case-Control Study in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2015, 35, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Chirico, V.; Mondello, S.; Buemi, A.; Lupica, R.; Fazio, M.R.; Buemi, M.; Aloisi, C. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Dialysis Reflects Status of Peritoneum. J. Nephrol. 2013, 26, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.C.K.; Lam, M.F.; Tang, S.C.W.; Chan, L.Y.Y.; Tam, K.Y.; Yip, T.P.S.; Lai, K.N. Roles of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; the QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies|Annals of Internal Medicine. Available online: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Li, P.K.-T.; Chow, K.M.; Cho, Y.; Fan, S.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Harris, T.; Kanjanabuch, T.; Kim, Y.-L.; Madero, M.; Malyszko, J.; et al. ISPD Peritonitis Guideline Recommendations: 2022 Update on Prevention and Treatment. Perit. Dial. Int. 2022, 42, 110–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggins, S.W.; Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ginès, P.; Ling, S.C.; Nadim, M.K.; Wong, F.; Kim, W.R. Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis, and Hepatorenal Syndrome in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Abd El Wahed, M.R.; Elgohary, M.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Ateya, R.M. Value of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Serum and Peritoneal Fluids in the Diagnosis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and the Prediction of In-Hospital Mortality. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, e934–e955. Available online: https://jptcp.com/index.php/jptcp/article/view/2659/2680 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Biomy, H.A.; Ramadan, N.E.; Ameen, S.G.; Kandil, A.E.D.I.; Galal, Z.W. Evaluation of Ascitic Fluid Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin in Patients with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Benha Med. J. 2021, 38, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kong, G.; Lyu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Q. Utility of Homodimer Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Rapid Test Kit for the Diagnosis of Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis. Chin. J. Nephrol. 2024, 40, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, F.O.; Mandour, S.S.M.S.; Bedira, I.S.; Elkhadry, S.; Ibrahim, A.R.; Abdelmageed, N.; El-shemy, E.; El-refai, H.A. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin-2 and Macrophage Antigen -1 in Cirrhotic Patients Infected with Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisi, N.; Virzì, G.M.; Manani, S.M.; Alfano, G.; Castiglione, C.; De Cal, M.; Tantillo, I.; Donati, G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. NGAL Dipstick for Peritonitis: Bridging the Gap between Rapid Assessment and Clinical Efficiency in Peritoneal Dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, gfae069-0926-758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Milan Manani, S.; Marcello, M.; Costa, E.; Marturano, D.; Tantillo, I.; Lerco, S.; Corradi, V.; De Cal, M.; Martino, F.K.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in Peritoneal Dialytic Effluent: Preliminary Results on the Comparison between Two Different Methods in Patients with and without Peritonitis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.K.; Filippi, I.; Giavarina, D.; Kaushik, M.; Rodighiero, M.P.; Crepaldi, C.; Teixeira, C.; Nadal, A.F.; Rosner, M.H.; Ronco, C. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in the Early Diagnosis of Peritonitis: The Case of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin. Contrib. Nephrol. 2012, 178, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzi, G.M.; Morisi, N.; Manani, S.M.; de Cal, M.; Tantillo, I.; Donati, G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. #996 Validation of Peritoneal NGAL as a Biomarker for Peritonitis: A Comparison between Laboratory-Base Method and Rapid Stick Test. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, 39, gfae069-0927-0996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisi, N.; Virzì, G.M.; Barajas, J.D.G.; Diaz-Villavicencio, B.; Manani, S.M.; Zanella, M. Validation of Peritoneal Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker for Peritonitis: A Comparison between Laboratory-Base Method and Rapid Stick Test. J. Transl. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 5, e00006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.-H. Lipocalin2 Expressions Correlate Significantly With Tumor Differentiation in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuk, C.; Kulasingam, V.; Gunawardana, C.G.; Smith, C.R.; Batruch, I.; Diamandis, E.P. Mining the Ovarian Cancer Ascites Proteome for Potential Ovarian Cancer Biomarkers. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kaur, S.; Muddana, V.; Sharma, N.; Wittel, U.A.; Papachristou, G.I.; Whitcomb, D.; Brand, R.E.; Batra, S.K. Elevated Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Is an Early Predictor of Severity and Outcome in Acute Pancreatitis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2010, 105, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, B.-I.; Sagstad, S.J.; Karlsen, T.V.; Wiig, H. Isolation of Interstitial Fluid and Demonstration of Local Proinflammatory Cytokine Production and Increased Absorptive Gradient in Chronic Peritoneal Dialysis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F198–F206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innico, G.; Gobbi, L.; Bertoldi, G.; Rigato, M.; Basso, A.; Bonfante, L.; Calò, L.A. Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Peritoneal Dialysis: A Molecular Biology Approach. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Angeli, P.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Clària, J.; Trebicka, J.; Fernández, J.; Gustot, T.; Caraceni, P.; Bernardi, M.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Hypothesis: Towards a New Paradigm of Acute Decompensation and Multiorgan Failure in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed/MEDLINE | (“neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin”[Title/Abstract] OR “NGAL”[Title/Abstract] OR “lipocalin-2”[Title/Abstract]) AND (“peritoneal dialysis”[Title/Abstract] OR “dialysis effluent”[Title/Abstract] OR “peritoneal fluid”[Title/Abstract] OR “ascites”[Title/Abstract]) AND (“peritonitis”[Title/Abstract] OR “spontaneous bacterial peritonitis”[Title/Abstract] OR “secondary bacterial peritonitis”[Title/Abstract] OR “infection”[Title/Abstract]) |
| Embase | (‘neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin’:ab,ti OR ‘NGAL’:ab,ti OR ‘lipocalin 2’:ab,ti) AND (‘peritoneal dialysis’:ab,ti OR ‘dialysis effluent’:ab,ti OR ‘peritoneal fluid’:ab,ti OR ‘ascites’:ab,ti) AND (‘peritonitis’:ab,ti OR ‘spontaneous bacterial peritonitis’:ab,ti OR ‘secondary bacterial peritonitis’:ab,ti OR ‘infection’:ab,ti) |
| Cochrane Library | (“neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin” OR NGAL OR “lipocalin-2”) AND (“peritoneal dialysis” OR “dialysis effluent” OR “peritoneal fluid” OR “ascites”) AND (peritonitis OR “spontaneous bacterial peritonitis” OR “secondary bacterial peritonitis” OR infection) |
| LILACS | (“neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin” OR NGAL OR “lipocalin-2”) AND (“diálisis peritoneal” OR “efluente peritoneal” OR “líquido peritoneal” OR ascitis) AND (peritonitis OR “peritonitis bacteriana espontánea” OR “peritonitis bacteriana secundaria” OR infección) |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY(“neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin” OR NGAL OR “lipocalin-2”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“peritoneal dialysis” OR “dialysis effluent” OR “peritoneal fluid” OR ascites) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(peritonitis OR “spontaneous bacterial peritonitis” OR “secondary bacterial peritonitis” OR infection) |
| WoS 1 | TS = (“neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin” OR NGAL OR “lipocalin-2”) AND TS = (“peritoneal dialysis” OR “dialysis effluent” OR “peritoneal fluid” OR ascites) AND TS = (peritonitis OR “spontaneous bacterial peritonitis” OR “secondary bacterial peritonitis” OR infection) |
| Study (Year, Country; Context) | Design | NGAL Method | Threshold Used in Primary Study | TP | FP | TN | FN | Diagnostic Performance Metrics Reported | QUADAS-2 (Overall) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed et al., 2023 [30] (Egypt); SBP † | Case–control | ELISA (SunRed); laboratory | 297.80 ng/mL | 38 | 3 | 37 | 2 | -Sensitivity: 95.6% -Specificity: 92.5% -Positive Predictive Value: 95% -Negative Predictive Value: 95% -AUC: 0.845 -Accuracy: 95% | Moderate |
| Biomy et al., 2021 [31], (Egypt); SBP | Cross-sectional | ELISA (Bioassay Science Lab E1719Hu); laboratory | 100.80 ng/mL | 41 | 1 | 42 | 1 | -Sensitivity: 97.62% -Specificity: 97.67% -Positive predictive value: 97.62% -Negative predictive value: 97.67% -AUC: 0.974 | High |
| Chen et al., 2024 [32], (China); PDAP | Prospective diagnostic | Rapid immunochromatographic POC | Positive/negative per kit ‡ | 42 | 1 | 178 | 0 | -Sensitivity: 100% (95% CI 91.62–100%) -Specificity: 99.44% (95% CI 96.90–99.90%) -Accuracy: 99.55% (95% CI 97.48–99.92%) -Positive Predictive Value: 97.67% (95% CI 87.94–99.59%) -Negative Predictive Value: 100% (95% CI 97.89–100%) -Kappa value: 0.985 (95% CI 0.956–1.000) | Moderate |
| Hassan et al., 2023 [19], (Egypt); SBP | Case–control | ELISA (SunRed); laboratory | 230.05 ng/mL | 34 | 4 | 32 | 2 | -Sensitivity: 94.4% -Specificity: 88.9% -Positive Predictive Value: 89.5% -Negative Predictive Value: 94.1% -AUC: 0.989- Accuracy: 91.7% | Moderate |
| Khalil et al., 2023 [33], (Egypt); SBP | Case–control | ELISA (DRG GmbH); laboratory | 110.72 ng/mL | 65 | 8 | 42 | 5 | -Sensitivity: 92.7% (CI: [0.82, 0.98]) -Specificity: 84% (CI: [0.75, 0.91]) -Positive Predictive Value: 0.77 (CI: [0.65, 0.86]) -Negative Predictive Value: 0.95 (CI: [0.88, 0.98]) -Area under the ROC curve (AUC): 0.899 (CI: [0.848, 0.951]) | Moderate |
| Lippi et al., 2013 [20], (Italy); SBP | Cross-sectional | Immunoturbidimetric (BioPorto NGAL Test™); laboratory | 120.0 ng/mL | 25 | 21 | 64 | 1 | -Sensitivity: 96% (95% CI: 80–100%) -Specificity: 75% (95% CI: 65–84%) -Positive Predictive Value: Not reported -Negative Predictive Value: Not reported -AUC: 0.89 (95% CI: 0.82–0.95) | Moderate |
| Liu et al., 2020 [21], (China); SBP † | Prospective cohort | Immunoturbidimetric (BSBE); laboratory | 108.95 ng/mL | 49 | 77 | 63 | 15 | -Sensitivity: 76.9% (for mortality prediction) -Specificity: 45.1% (for mortality prediction) -Positive Predictive Value: Not reported -Negative Predictive Value: Not reported | Low |
| Martino et al., 2015 [22], (Italy); PDAP | Case–control | CMIA (Abbott Architect); laboratory | 85.00 ng/mL | 72 | 18 | 84 | 8 | -Sensitivity: Not reported -Specificity: Not reported -Positive Predictive Value: Not reported -Negative Predictive Value: Not reported -AUC peritoneal NGAL 0.99 | Low |
| Morisi et al., 2024 [34], (Italy); PDAP | Retrospective diagnostic | POC dipstick (NGALds) | 100 ng/mL | 150 | 84 | 61 | 6 | -Sensitivity: 96% -Specificity: Not reported -Positive predictive value: 0.64 -Negative predictive value: 0.87 -Area under the ROC curve (AUC): 0.82 | Moderate |
| Virzì et al., 2022 [35], (Italy); PDAP | Case–control | POC dipstick (BioPorto NGALds) + lab comparator | 300 ng/mL | 17 | 2 | 11 | 0 | Spearman’s ρ between NGALds and lab NGAL = 0.88 (p < 0.01), Spearman’s ρ between NGALds and effluent WCC = 0.82 (p < 0.01), Inter-operator reproducibility: ρ = 0.847 (p < 0.001), κ = 0.786 (p < 0.001). | High |
| Study | Design/Context | NGAL Method/Platform | Threshold as Reported | Diagnostic Performance Metrics Reported | QUADAS-2 (Overall) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cullaro et al., 2017 [13], (USA) | Prospective cohort; SBP | ELISA (laboratory; AntibodyShop) | Diagnostic cut-off for SBP not prespecified (AUC reported) | -For SBP diagnosis: -c-statistic (AUC): 0.68 | Low |
| Martino et al., 2012 [36], (Italy) | Case–control; PDAP | Chemiluminescent immunoassay (Abbott Architect) | Threshold not specified (ROC performed) | -AUC peritoneal NGAL 0.99 | Moderate |
| Virzì et al., 2024 [37], (Italy) | Retrospective; PDAP | Laboratory turbidimetric (NGALlab) and rapid dipstick (NGALds) | Lab: >100 µg/L; Dipstick categories 25–600 µg/L | -Spearman’s Rs = 0.876 (p = 10−96) -Sensitivity: 96% (150/156) | Moderate |
| Study (Year) | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication Bias | Overall Certainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed et al. [30], 2023 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Biomy et al. [31], 2021 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Chen et al. [32], 2024 | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | High |
| Cullaro et al. [13], 2017 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Hassan et al. [19], 2023 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Khalil et al. [33], 2023 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Lippi et al. [20], 2013 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Liu et al. [21], 2020 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Martino et al. [36], 2012 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Martino et al. [22], 2015 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Morisi et al. [34], 2024 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Virzì et al. [35], 2022 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
| Virzì et al. [37], 2024 | Moderate | Not serious | Not serious | Serious | Undetected | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prieto-Magallanes, M.L.; González-Barajas, J.D.; Camarena-Arteaga, V.A.; Díaz-Villavicencio, B.; Gómez-Fregoso, J.A.; López-Yáñez, A.M.; Rodríguez-Montaño, R.; De Arcos-Jiménez, J.C.; Briseno-Ramírez, J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030175
Prieto-Magallanes ML, González-Barajas JD, Camarena-Arteaga VA, Díaz-Villavicencio B, Gómez-Fregoso JA, López-Yáñez AM, Rodríguez-Montaño R, De Arcos-Jiménez JC, Briseno-Ramírez J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(3):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030175
Chicago/Turabian StylePrieto-Magallanes, Manuel Luis, José David González-Barajas, Violeta Aidee Camarena-Arteaga, Bladimir Díaz-Villavicencio, Juan Alberto Gómez-Fregoso, Ana María López-Yáñez, Ruth Rodríguez-Montaño, Judith Carolina De Arcos-Jiménez, and Jaime Briseno-Ramírez. 2025. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Medical Sciences 13, no. 3: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030175
APA StylePrieto-Magallanes, M. L., González-Barajas, J. D., Camarena-Arteaga, V. A., Díaz-Villavicencio, B., Gómez-Fregoso, J. A., López-Yáñez, A. M., Rodríguez-Montaño, R., De Arcos-Jiménez, J. C., & Briseno-Ramírez, J. (2025). Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medical Sciences, 13(3), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030175







