Twice as Effective? Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy: New Frontiers in Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
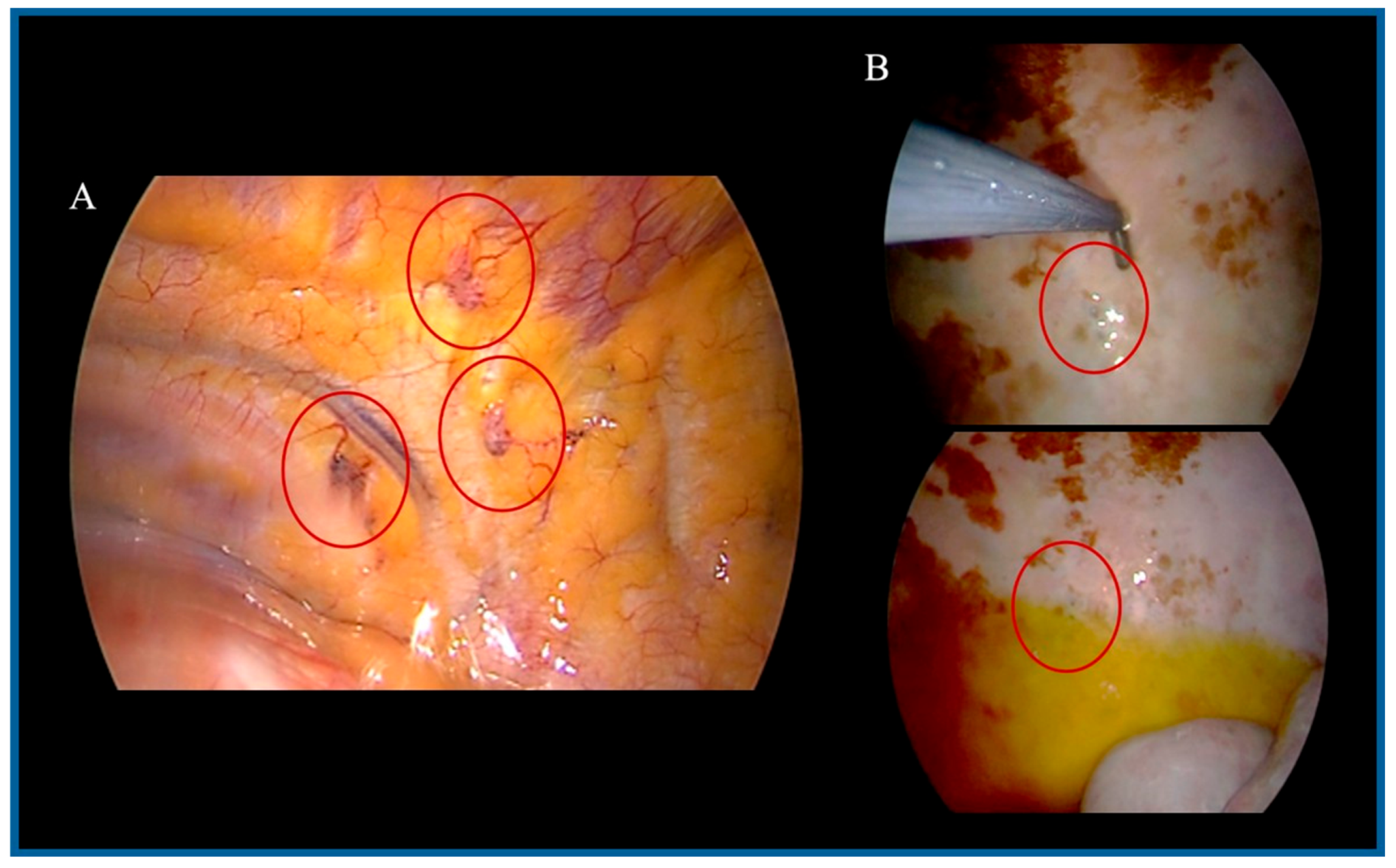
2.1. PITAC Procedure
2.2. Chemotherapy Regimen
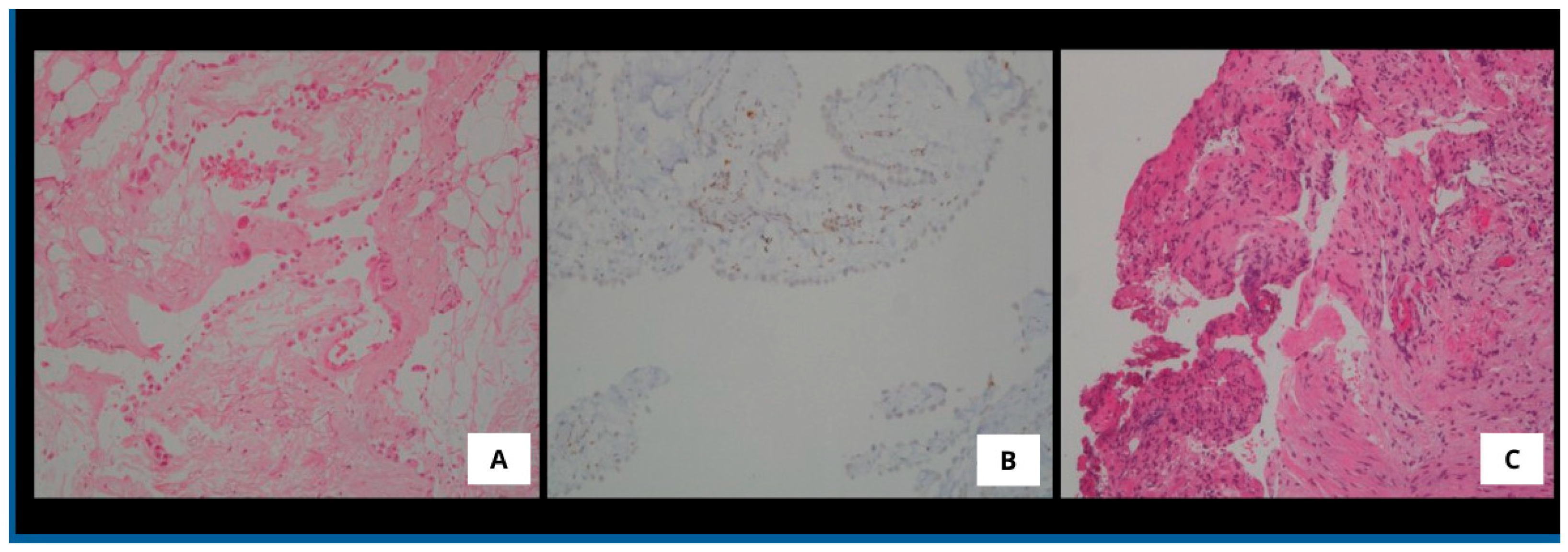
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clive, A.O.J.; Bhatnagar, R.; Preston, N.J.; Maskell, N. Interventions for the management of malignant pleural effusions: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, CD010529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, A.C.; Dorn, P.; Psallidas, I.; Porcel, J.M.; Janssen, J.; Froudarakis, M.; Subotic, D.; Astoul, P.; Licht, P.; Schmid, R.; et al. ERS/EACTS statement on the management of malignant pleural effusions. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 55, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, A.; Binazzi, A.; Marzio, D.D.; Scarselli, A.; Verardo, M.; Mirabelli, D.; Gennaro, V.; Mensi, C.; Riboldi, L.; Merler, E.; et al. Pleural malignant mesothelioma epidemic: Incidence, modalities of asbestos exposure and occupations involved from the Italian National Register. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridda, A.; Padoan, I.; Mencarelli, R.; Frego, M. Peritoneal mesothelioma: A review. MedGenMed 2007, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scherpereel, A.; Wallyn, F.; Albelda, S.M.; Munck, C. Novel therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, S.J.; Larson, T.C.; Wu, M.; Antao, V.C.; Lewis, M.; Pinheiro, G.A.; Eheman, C. Mesothelioma incidence in 50 states and the District of Columbia, United States, 2003–2008. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2013, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, A.S.; Wistuba, I.; Roth, J.A.; Kindler, H.L. Malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Stevenson, J.P. Current issues in malignant pleural mesothelioma evaluation and management. Oncologist 2014, 19, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I.; Carbone, M. Current status of screening for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 21, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Lenzini, A.; Aprile, V.; Alì, G.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. New Insights in Pleural Mesothelioma Classification Update: Diagnostic Traps and Prognostic Implications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enewold, L.; Sharon, E.; Thomas, A. Patterns of care and survival among patients with malignant mesothelioma in the United States. Lung Cancer 2017, 112, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.B.; Rice, D.C.; Niu, J.; Atay, S.; Vaporciyan, A.A.; Antonoff, M.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Walsh, G.L.; Swisher, S.G.; Roth, J.A.; et al. Long-term survival outcomes of cancer-directed surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Propensity score matching analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail-Khan, R.; Robinson, L.A.; Williams, C.C.J.; Garrett, C.R.; Bepler, G.; Simon, G.R. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: A comprehensive review. Cancer Control 2006, 13, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Perrot, M.; Feld, R.; Cho, B.C.; Bezjak, A.; Anraku, M.; Burkes, R.; Roberts, H.; Tsao, M.S.; Leighl, N.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. Trimodality therapy with induction chemotherapy followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and adjuvant high-dose hemithoracic radiation for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, V.; Lenzini, A.; Lococo, F.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Mastromarino, M.G.; Guglielmi, G.; Palmiero, G.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemo-therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: The Forefront of Surgery-Based Multimodality Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.; Davies, A.M.; Evans, W.K.; Haynes, A.E.; Lloyd, N.S. The use of chemotherapy in patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review and practice guideline. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2006, 1, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386, Erratum in Lancet 2021, 397, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Aprile, V.; Lucchi, M. Editorial: Advances in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Diagnosis, treatment, and molecular mechanisms. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1158416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Opitz, I.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bölükbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaro, V.; Montanaro, F.; Lazzarotto, A.; Bianchelli, M.; Celesia, M.V.; Canessa, P.A. Mesothelioma registry of the Liguria region. Incidence and occupational etiology in a high risk area. Epidemiol. Prev. 2000, 24, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Spella, M.; Giannou, A.D.; Stathopoulos, G.T. Switching off malignant pleural effusion formation-fantasy or future? J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zocchi, L. Physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid turnover. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Aprile, V.; Elia, G.; Bacchin, D.; Lenzini, A.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Lucchi, M.; et al. Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy (PITAC): Preliminary results in malignant pleural effusion. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, OA1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Aprile, V.; Elia, G.; Bacchin, D.; Lenzini, A.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Lucchi, M. Safety and Efficacy of Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Pleural Carcinomatosis: Preliminary Results of a Pilot Study. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solass, W.; Hetzel, A.; Nadiradze, G.; Sagynaliev, E.; Reymond, M.A. Description of a novel approach for intraperitoneal drug delivery and the related device. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempfer, C.B.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Seebacher, V.; Petersen, M.; Dogan, A.; Rezniczek, G.A. A phase I, single-arm, open-label, dose escalation study of intraperitoneal cisplatin and doxorubicin in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer and peritoneal carcinomatosis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solass, W.; Kerb, R.; Mürdter, T.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Strumberg, D.; Tempfer, C.; Zieren, J.; Schwab, M.; Reymond, M.A. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy of peritoneal carcinomatosis using pressurized aerosol as an alternative to liquid solution: First evidence for efficacy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger-Pabst, U.; Demtröder, C.; Falkenstein, T.A.; Ouaissi, M.; Götze, T.O.; Rezniczek, G.A.; Tempfer, C.B. Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) for the treatment of malignant mesothelioma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchen, N.; Cereser, T.; Hailemariam, S.; Schoeb, O. Safety and efficacy of pressurized intraperitoneal/intrathoracic aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC/PITAC) in patients with peritoneal and/or pleural carcinomatosis: A preliminary experience. J. Med. Therap. 2018, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Drevet, G.; Maury, J.M.; Bakrin, N.; Tronc, F. Technique of pressurized intrathoracic aerosol chemotherapy (PITAC) for malignant pleural effusion. Pleura Peritoneum 2020, 5, 20200129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solass, W.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Zieren, J.; Reymond, M.A. Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC): Occupational health and safety aspects. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, K.; Homma, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Kawabata, M.; Tsuboi, E.; Nakata, K.; Yoshimura, K. Efficacious pleurodesis with OK-432 and doxorubicin against malignant pleural effusions. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, P.S.; Graversen, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Ainsworth, A.P.; Mortensen, M.B. Pressurized IntraThoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy (PITAC) directed therapy of patients with malignant pleural effusion and pleural metastasis. Pleura Peritoneum 2024, 9, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Ainsworth, A.P.; Fristrup, C.W.; Mortensen, M.B.; Pfeiffer, P.; Tarpgaard, L.S. Importance of biopsy site selection for peritoneal regression grading score (PRGS) in peritoneal metastasis treated with repeated pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC). Pleura Peritoneum 2022, 7, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, M.; Toon, C.W.; Clarkson, A.; Sioson, L.; Watson, N.; Andrici, J.; Gill, A.J. Loss of expression of BAP1 predicts longer survival in mesothelioma. Pathology 2015, 47, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, I.; Alì, G.; Poma, A.M.; Bruno, R.; Proietti, A.; Niccoli, C.; Zirafa, C.C.; Melfi, F.; Mastromarino, M.G.; Lucchi, M.; et al. New Immunohistochemical Markers for Pleural Mesothelioma Subtyping. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.L.; Dacic, S.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Attanoos, R.L.; Butnor, K.J.; Churg, A.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Khoor, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances Since the 2015 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Patients (n) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 8 |
| Female | 1 |
| Median Age (years, IQR) | 74 (8) |
| ECOG score | |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| Comorbidities | |
| Hypertensive heart disease | 7 |
| Heavy smoking | 2 |
| Diabetes | 2 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 4 |
| Occupational exposure to asbestos | 6 |
| Histology | |
| Mesothelioma in situ | 1 |
| Epithelioid | 4 |
| Biphasic | 4 |
| Sarcomatoid | 0 |
| BAP-1 status | |
| Positive | 1 |
| Negative | 4 |
| Not tested | 4 |
| Post-operative treatment | |
| None | 2 |
| Pemetrexed + Cisplatin | 3 |
| Pemetrexed + Carboplatin | 1 |
| Nivolumab + ipilimumab | 3 |
| Absence of MPE recurrence | |
| at 1 month | 9 |
| at 3 months | 7 |
| at 6 months | 7 |
| Re-PITAC | 2 |
| 1 patient (M, mesothelioma in situ) after one year * | |
| 1 patient (F, biphasic) after 9 months * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastromarino, M.G.; Guerrini, E.; Guerrieri, R.; Elia, G.; Lenzini, A.; Aprile, V.; Alì, G.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. Twice as Effective? Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy: New Frontiers in Pleural Mesothelioma. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020072
Mastromarino MG, Guerrini E, Guerrieri R, Elia G, Lenzini A, Aprile V, Alì G, Korasidis S, Ambrogi MC, Lucchi M. Twice as Effective? Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy: New Frontiers in Pleural Mesothelioma. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(2):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastromarino, Maria Giovanna, Elena Guerrini, Raffaele Guerrieri, Gianmarco Elia, Alessandra Lenzini, Vittorio Aprile, Greta Alì, Stylianos Korasidis, Marcello Carlo Ambrogi, and Marco Lucchi. 2025. "Twice as Effective? Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy: New Frontiers in Pleural Mesothelioma" Medical Sciences 13, no. 2: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020072
APA StyleMastromarino, M. G., Guerrini, E., Guerrieri, R., Elia, G., Lenzini, A., Aprile, V., Alì, G., Korasidis, S., Ambrogi, M. C., & Lucchi, M. (2025). Twice as Effective? Pressurized Intra-Thoracic Aerosol Chemotherapy: New Frontiers in Pleural Mesothelioma. Medical Sciences, 13(2), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020072








