Effectiveness of Stress Shielding Prevention Using a Low Young’s Modulus Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn Stem: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Characteristics of the TNS Stem
2.4. Surgery and Rehabilitation
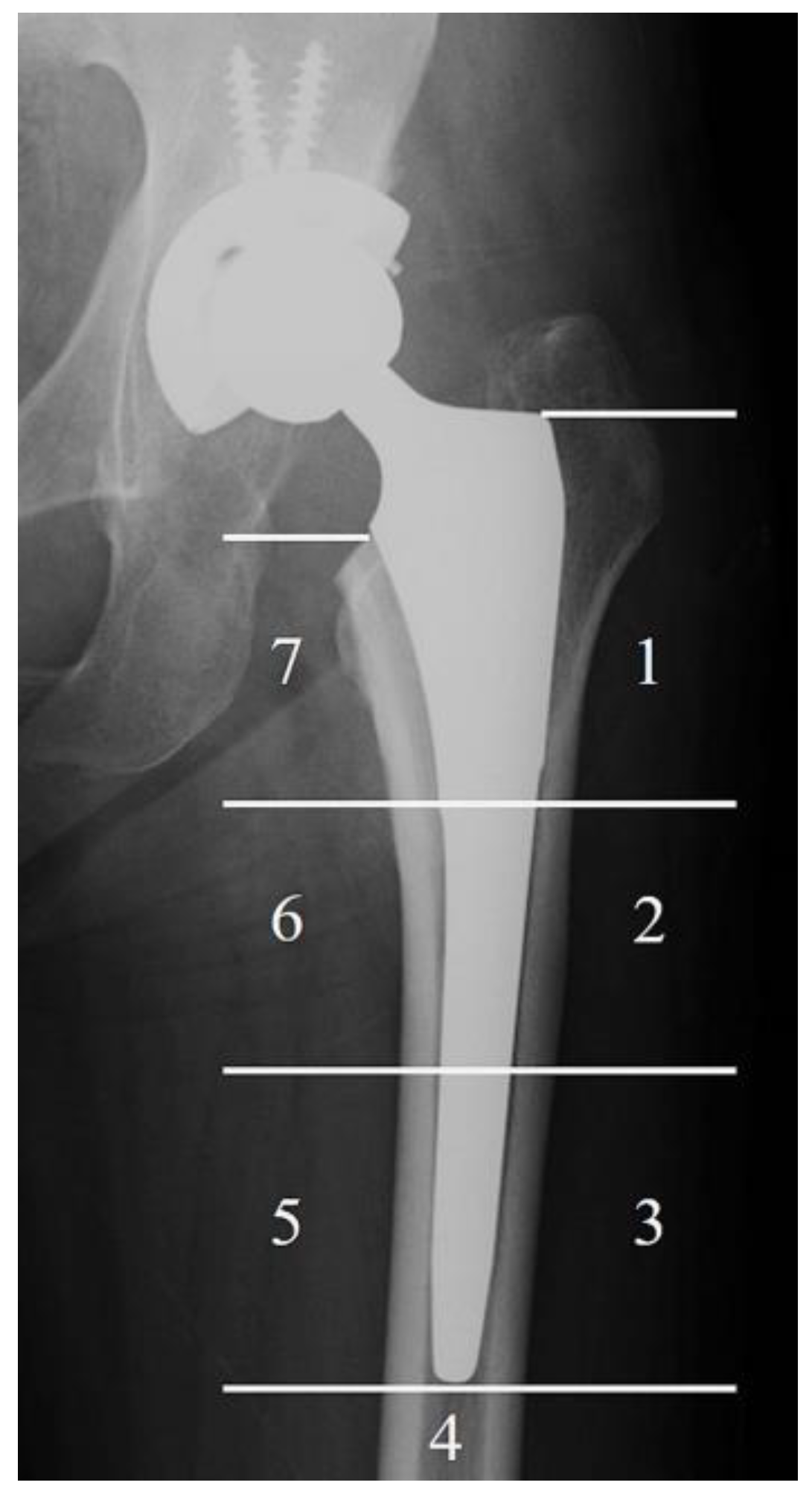
2.5. Radiographic Evaluation
2.6. Clinical Assessments
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Radiographic Evaluation
3.3. Clinical Assessment
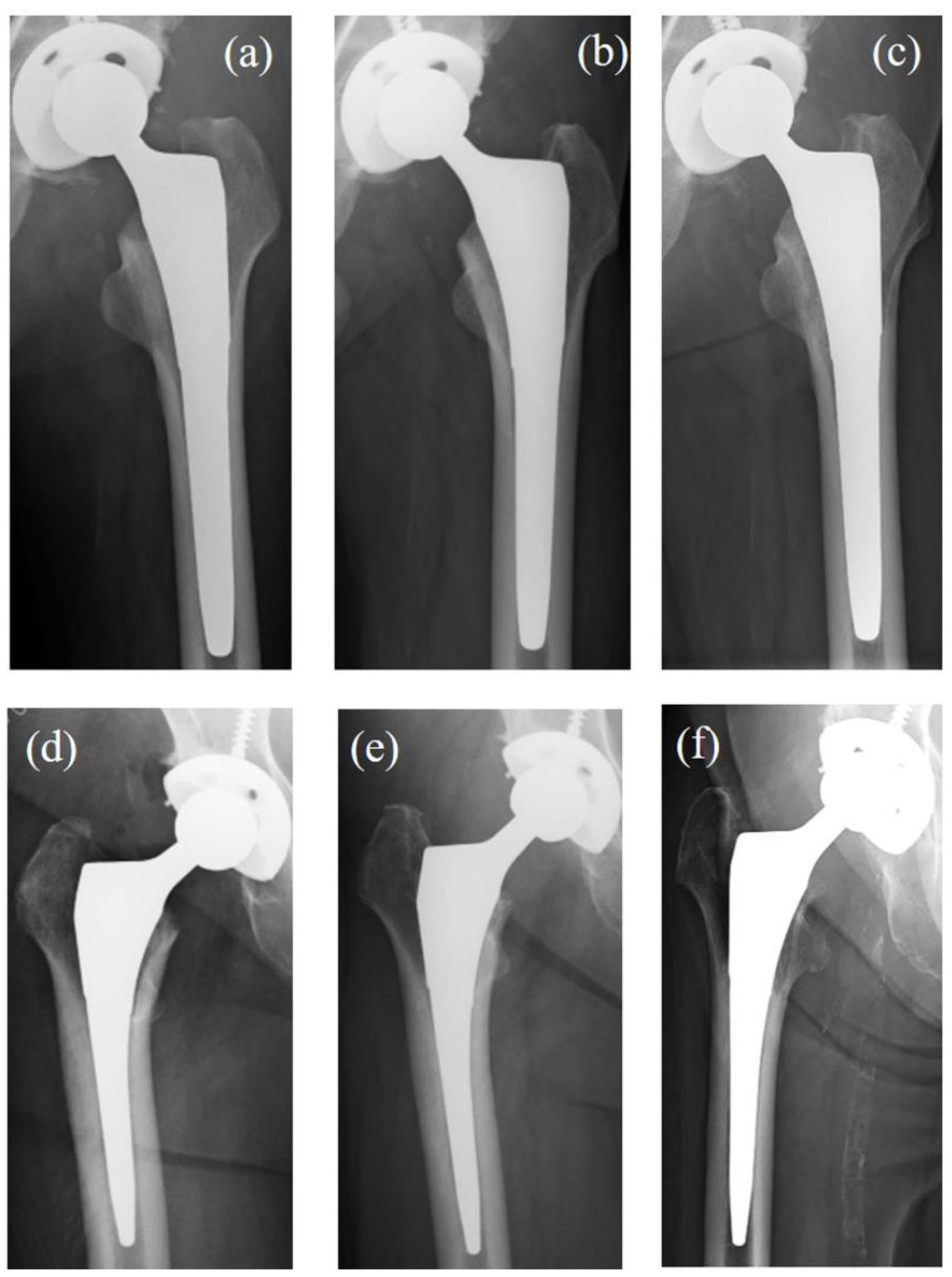
3.4. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THA | total hip arthroplasty |
| SS | Stress shielding |
| TNS | β-type Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn |
| JOA | Japanese Orthopaedic Association |
References
- Pallante, G.D.; Statz, J.M.; Milbrandt, T.; Trousdale, R. Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients 20 Years Old and Younger. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Cleveland, J.D. Rates of Total Joint Replacement in the United States: Future Projections to 2020–2040 Using the National Inpatient Sample. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, A.; Pfluger, D.H.; Gramlich, Y.; Hoffmann, R.; Drees, P.; Kutzner, K.P. Future Burden of Primary and Revision Hip Arthroplasty in Germany: A Socio-Economic Challenge. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2021, 141, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.M.; Farley, K.X.; Guild, G.N.; Bradbury, T.L., Jr. Projections and Epidemiology of Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States to 2030. J. Arthroplasty 2020, 35, S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, G.; Mileti, I.; Nalli, F.; Palermo, E.; Cortese, L. Additive Manufacturing Structural Redesign of Hip Prostheses for Stress-Shielding Reduction and Improved Functionality and Safety. Mech. Mater. 2022, 165, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The Relationship between Stress Shielding and Bone Resorption around Total Hip Stems and the Effects of Flexible Materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostu, D.; Lucaciu, O.; Berce, C.; Lucaciu, D.; Cosma, D. Current Methods of Preventing Aseptic Loosening and Improving Osseointegration of Titanium Implants in Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, A.; Mori, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kamimura, M.; Masahashi, N.; Hanada, S.; Itoi, E. Effects of Elastic Intramedullary Nails Composed of Low Young’s Modulus Ti-Nb-Sn Alloy on Healing of Tibial Osteotomies in Rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Mori, Y.; Kamimura, M.; Koguchi, M.; Kurishima, H.; Koyama, T.; Mori, N.; Masahashi, N.; Hanada, S.; Itoi, E.; et al. Β-Type TiNbSn Alloy Plates with Low Young Modulus Accelerates Osteosynthesis in Rabbit Tibiae. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, R.; Mathys, R. Cementless Isoelastic RM Total Hip Prosthesis. J. R. Soc. Med. 1982, 75, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamako, G.; Janssen, D.; Hanada, S.; Anijs, T.; Ochiai, K.; Totoribe, K.; Chosa, E.; Verdonschot, N. Improving Stress Shielding Following Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Femoral Stem Made β Type Ti-33.6 Nb-4Sn Young’s Modulus Gradation. J. Biomech. 2017, 63, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, J.H.; Huiskes, R. Mathematical Optimization of Elastic Properties: Application to Cementless Hip Stem Design. J. Biomech. Eng. 1997, 119, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, S.; Masahashi, N.; Jung, T.-K.; Yamada, N.; Yamako, G.; Itoi, E. Fabrication of a High-Performance Hip Prosthetic Stem Using β Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 30, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, K.; Mori, Y.; Chiba, D.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kurishima, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kogure, A.; Kamimura, M.; Yamada, N.; Ohtsu, S.; et al. TiNbSn Stems with Gradient Changes of Young’s Modulus and Stiffness Reduce Stress Shielding Compared to the Standard Fit-and-Fill Stems. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, D.; Yamada, N.; Mori, Y.; Oyama, M.; Ohtsu, S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Baba, K.; Tanaka, H.; Aizawa, T.; Hanada, S.; et al. Mid-Term Results of a New Femoral Prosthesis Using Ti-Nb-Sn Alloy with Low Young’s Modulus. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnley, J. The Long-Term Results of Low-Friction Arthroplasty of the Hip Performed as a Primary Intervention. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1972, 54-B, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamako, G.; Chosa, E.; Totoribe, K.; Hanada, S.; Masahashi, N.; Yamada, N.; Itoi, E. In-Vitro Biomechanical Evaluation Stress Shielding Initial Stability Low-Modulus Hip Stem Made β Type Ti-33.6 Nb-4Sn Alloy. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaelli, M.; Buchalter, D.B.; Mont, M.A.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Hepinstall, M.S. A New Classification System for Cementless Femoral Stems in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplasty 2023, 38, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A. The Self-Locking Metal Hip Prosthesis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1957, 39-A 4, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, C.A.; Bobyn, J.D.; Glassman, A.H. Porous-Coated Hip Replacement: Factors Governing Bone Ingrowth, Stress Shielding, Clinical Results. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1987, 69, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, T.; Mcneice, G.; Amstutz, H. “Modes of Failure” of Cemented Stem-Type Femoral Components: A Radiographic Analysis of Loosening. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1979, 141, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imura, S. Japanese Orthopaedic Association: Evaluation Chart Hip Joint Functions. J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 1995, 69, 864–867. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobyn, J.D.; Glassman, A.H.; Goto, H.; Krygier, J.J.; Miller, J.E.; Brooks, C.E. The Effect of Stem Stiffness on Femoral Bone Resorption after Canine Porous-Coated Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1990, 261, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, S.J.; Hurst, J.A.; Sanders, M.S.; Turner, C.H.; Burr, D.B.; Li, J. Bone Adaptation to a Mechanical Loading Program Significantly Increases Skeletal Fatigue Resistance. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Mori, Y.; Kamimura, M.; Tanaka, H.; Tome, R.; Ito, K.; Koguchi, M.; Mori, N.; Aizawa, T. TiNbSn Alloy Plates with Low Young’s Modulus Modulates Interfragmentary Movement and Promote Osteosynthesis in Rat Femur. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 161, 106820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Castellani, C.M.; Popp, K.L.; Guerriere, K.I.; Matheny, R.W., Jr.; Nindl, B.C.; Bouxsein, M.L. The Central Role of Osteocytes in the Four Adaptive Pathways of Bone’s Mechanostat. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2020, 48, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerry, T.M. One Mechanostat or Many? Modifications of the Site-Specific Response of Bone to Mechanical Loading by Nature and Nurture. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2006, 6, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Arabnejad, S.; Johnston, B.; Tanzer, M.; Pasini, D. Fully Porous 3D Printed Titanium Femoral Stem to Reduce Stress-Shielding Following Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Masahashi, N.; Aizawa, T. A Review of Anodized TiNbSn Alloys for Improvement in Layer Quality and Application to Orthopedic Implants. Materials 2022, 15, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.O.; Blake, V.; Hing, C.B. Minimally Invasive versus Conventional Exposure for Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical and Radiological Outcomes. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Feng, J.G.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.L. Minimally Invasive Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xing, Z.; Moon, B.S.; Satcher, R.L.; Lin, P.P.; Lewis, V.O. A Long Femoral Stem Is Not Always Required in Hip Arthroplasty for Patients with Proximal Femur Metastases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahk, J.H.; Han, S.-B.; Rhyu, K.H.; Yoo, J.J.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, K.K.; Kim, S.-M.; Lim, Y.W. Identification of Essential Features in Developing a Novel Femoral Stem Reflecting Anatomical Features of East Asian Population: A Morphological Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, C.; Grappiolo, G.; Engh, C.A., Jr.; Vidalain, J.-P.; Chen, A.-F.; Boehler, N.; Matta, J.; Vendittoli, P.-A. Long-Term Bone Remodelling around “legendary” Cementless Femoral Stems. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauch, M.; Brecht, H.; Clauss, M.; Stoffel, K. Use of Short Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Observational Study of 31 Patients. Medicina 2023, 59, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solou, K.; Solou, A.V.; Tatani, I.; Lakoumentas, J.; Tserpes, K.; Megas, P. Increased Stability of Short Femoral Stem through Customized Distribution of Coefficient of Friction in Porous Coating. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kurishima, H.; Kanabuchi, R.; Mori, N.; Sasagawa, K.; Aizawa, T. Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TNS Group | Control Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (hips) | 35 | 21 | |
| Gender, female: male, n (%) | 32 (91): 3 (9) | 18 (86): 3 (14) | p = 0.66 |
| Mean age at surgery (years) | 65.4 ± 7.7 | 62.6 ± 10.6 | p = 0.26 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.7 ± 4.1 | 24.4 ± 2.8 | p = 0.78 |
| Follow-up period (months) | 87 (84–96) | 91.8 ± 4.4 | p = 0.27 |
| Implant | |||
| Stem, n | TNS stem, 35 | Versys Taper, 13 | |
| Synergy Select II, 8 | |||
| Cup, n | ARC HA Cup, 35 | Trilogy, 13 | |
| Reflection, 8 | |||
| Preoperative diagnosis, n (%) | |||
| Osteoarthritis | 31 (89) | 17 (81) | p = 0.45 |
| Osteonecrosis of the femoral head | 4 (11) | 4 (19) |
| SS Grade | TNS Group | Control Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0, n (%) | 3 (9) | 0 (0) | 0.03 * |
| 1, n (%) | 9 (27) | 5 (24) | |
| 2, n (%) | 11 (32) | 6 (28) | |
| 3, n (%) | 11 (32) | 5 (24) | |
| 4, n (%) | 0 (0) | 5 (24) |
| Gruen Zone | TNS Group | Control Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 1, n (%) | 15 (44) | 10 (48) | 1 |
| Zone 2, n (%) | 5 (15) | 9 (43) | 0.02 * |
| Zone 3, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (19) | 0.01 * |
| Zone 4, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Zone 5, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0.38 |
| Zone 6, n (%) | 3 (9) | 11 (52) | 0.001 ** |
| Zone 7, n (%) | 27 (79) | 17 (81) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baba, K.; Mori, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kanabuchi, R.; Kuriyama, Y.; Kurishima, H.; Ito, K.; Kamimura, M.; Chiba, D.; Aizawa, T. Effectiveness of Stress Shielding Prevention Using a Low Young’s Modulus Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn Stem: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020051
Baba K, Mori Y, Tanaka H, Kanabuchi R, Kuriyama Y, Kurishima H, Ito K, Kamimura M, Chiba D, Aizawa T. Effectiveness of Stress Shielding Prevention Using a Low Young’s Modulus Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn Stem: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaba, Kazuyoshi, Yu Mori, Hidetatsu Tanaka, Ryuichi Kanabuchi, Yasuaki Kuriyama, Hiroaki Kurishima, Kentaro Ito, Masayuki Kamimura, Daisuke Chiba, and Toshimi Aizawa. 2025. "Effectiveness of Stress Shielding Prevention Using a Low Young’s Modulus Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn Stem: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study" Medical Sciences 13, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020051
APA StyleBaba, K., Mori, Y., Tanaka, H., Kanabuchi, R., Kuriyama, Y., Kurishima, H., Ito, K., Kamimura, M., Chiba, D., & Aizawa, T. (2025). Effectiveness of Stress Shielding Prevention Using a Low Young’s Modulus Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn Stem: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study. Medical Sciences, 13(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020051






