Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients
3. Methods
Statistical Analysis
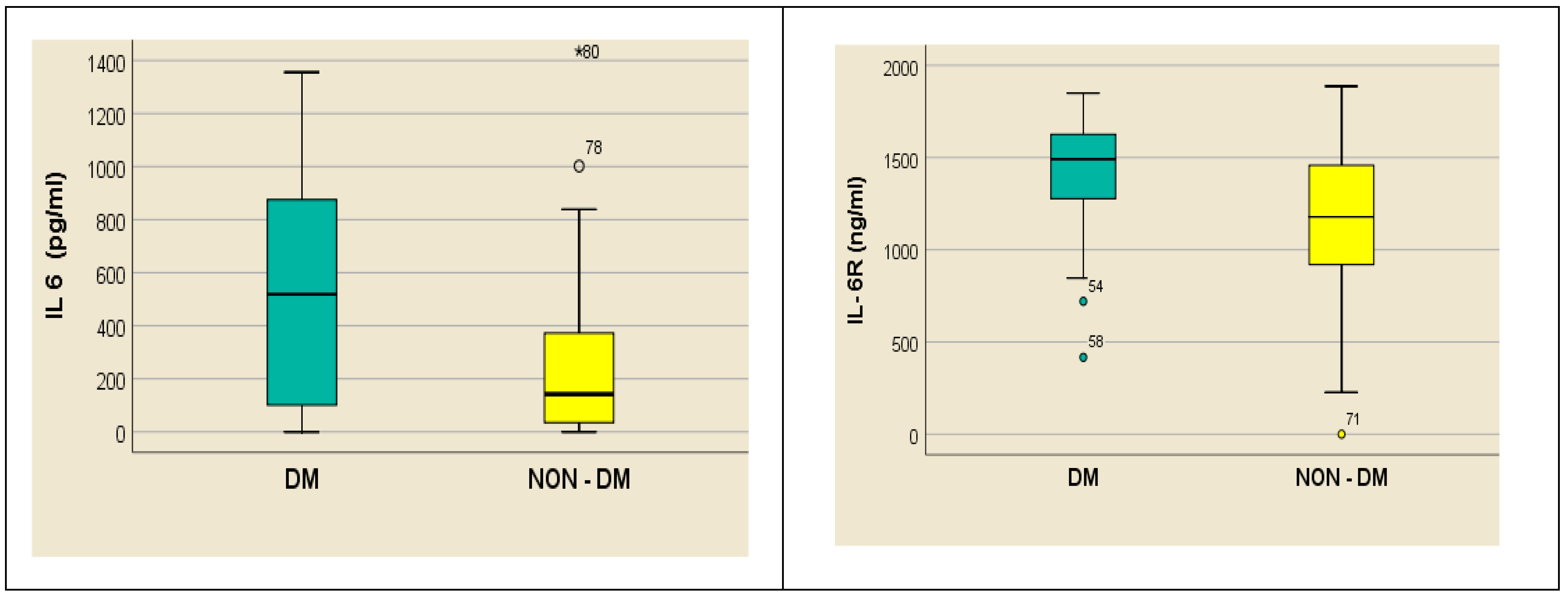
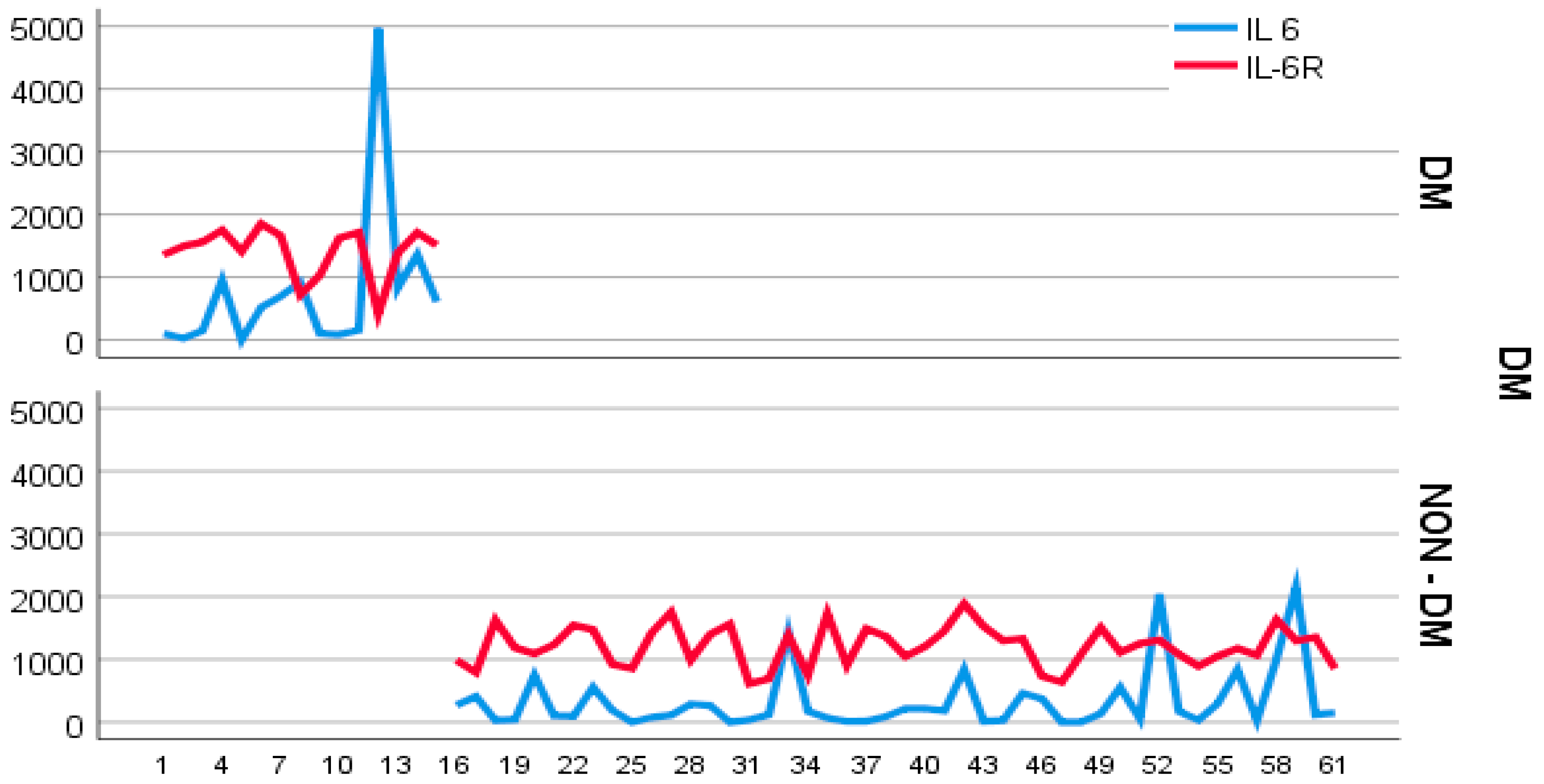
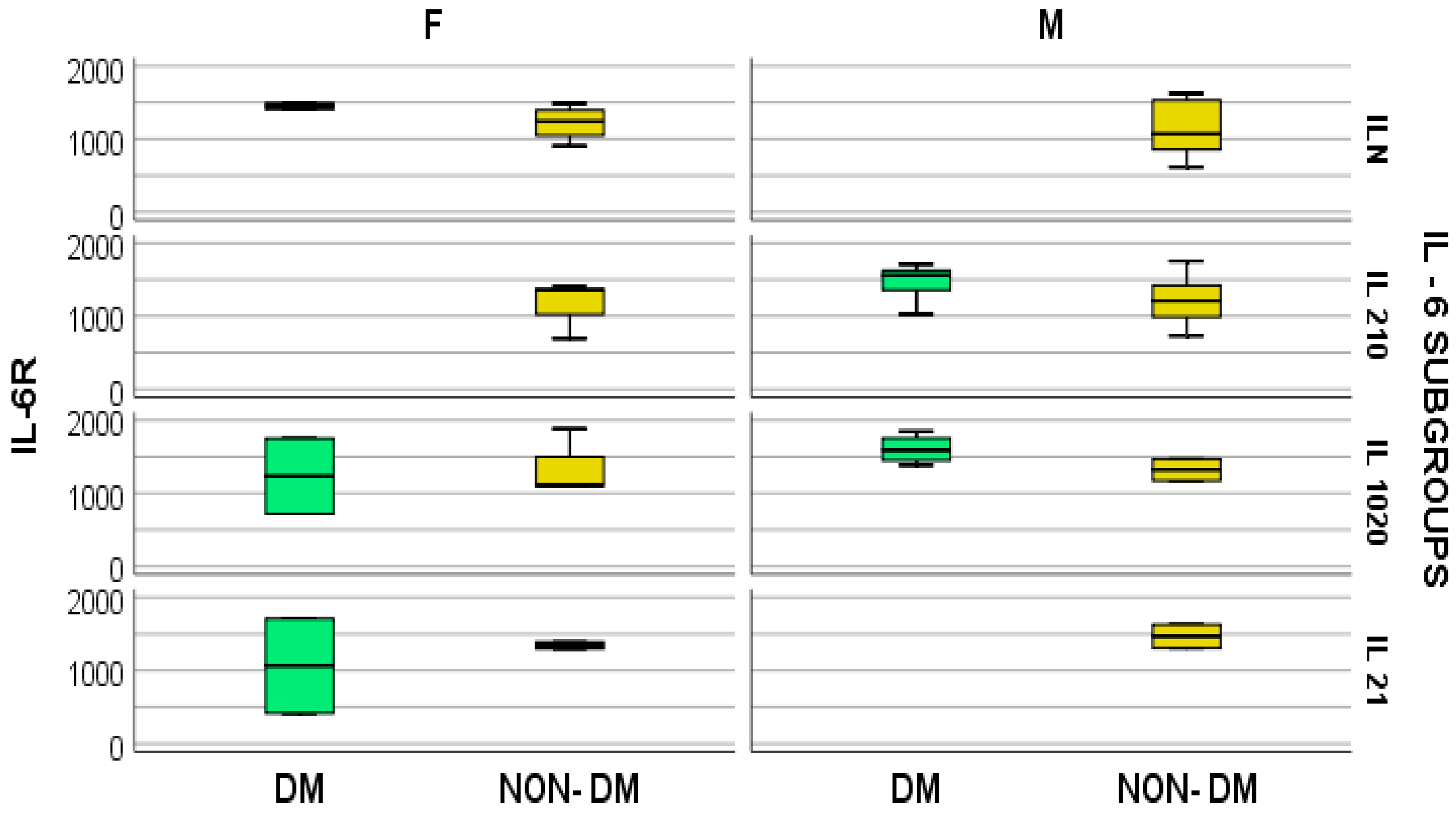
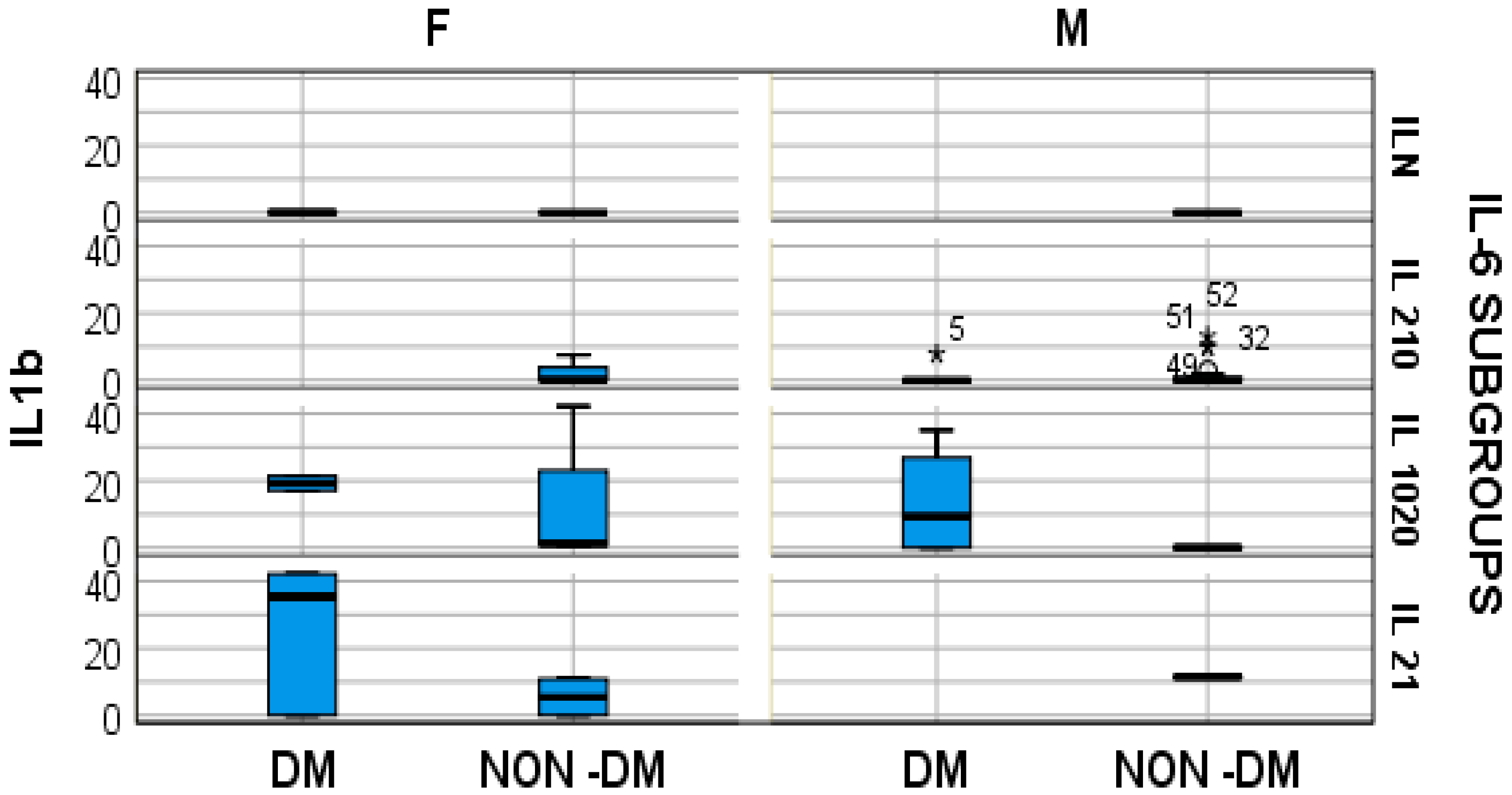
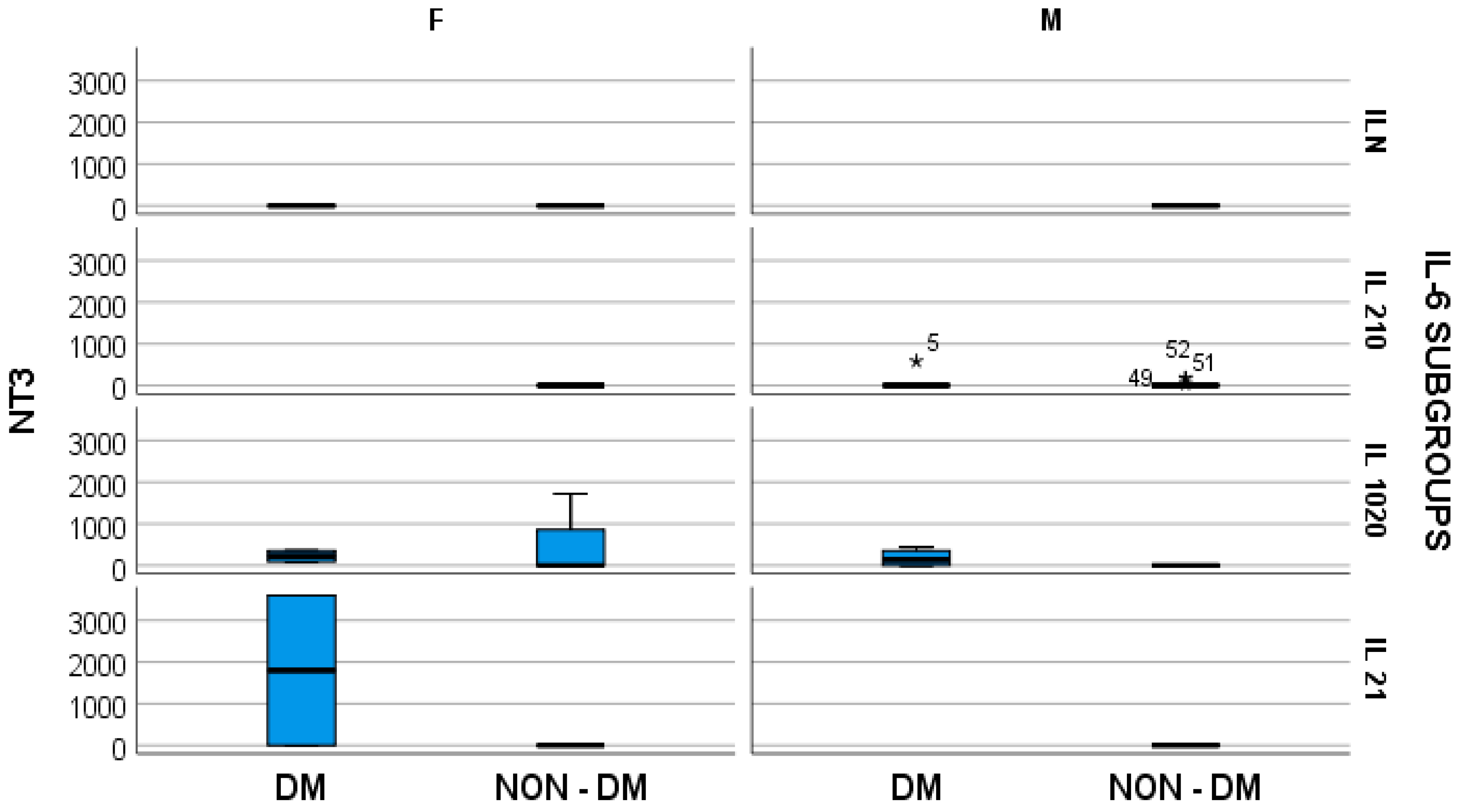
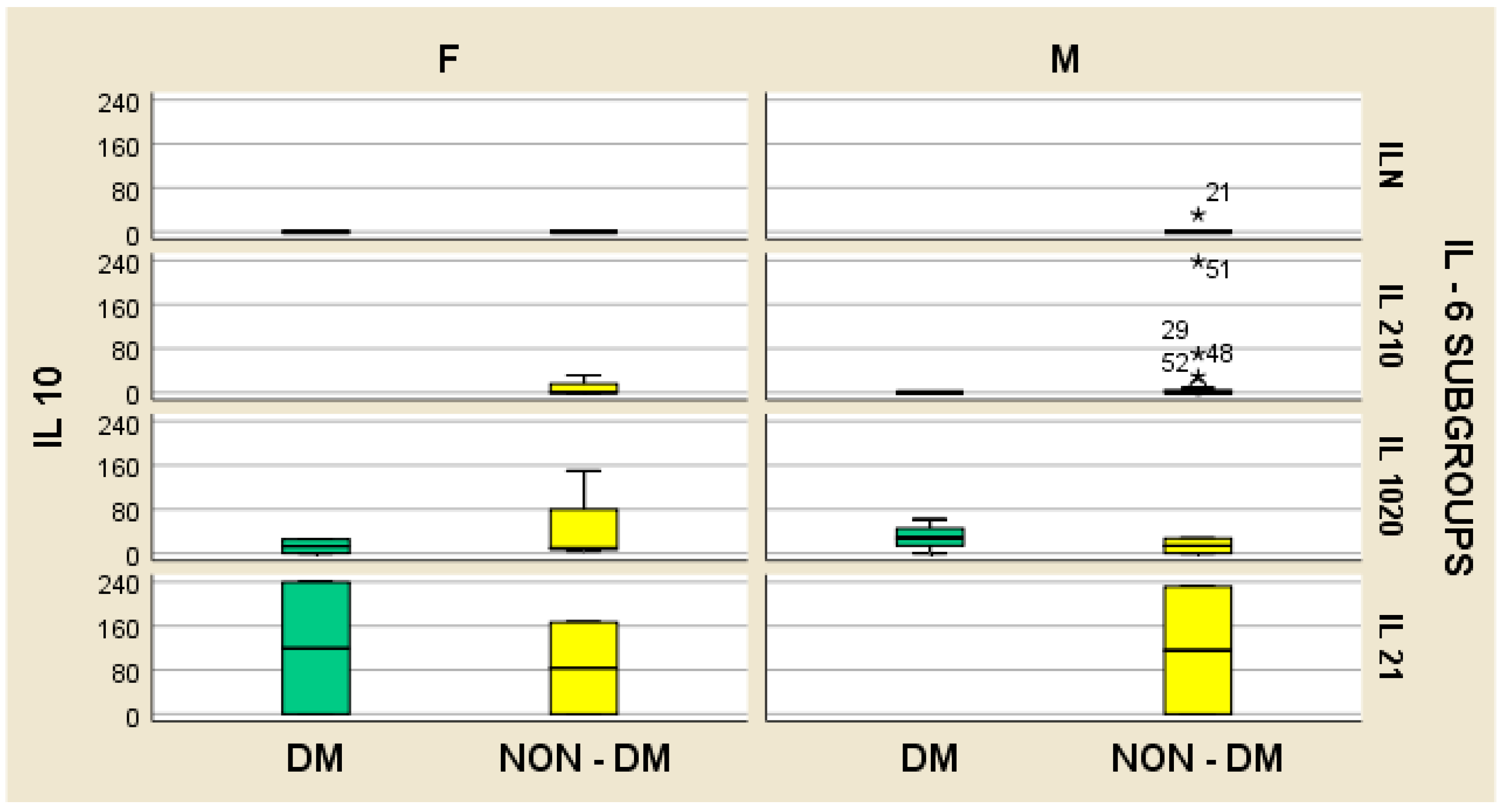
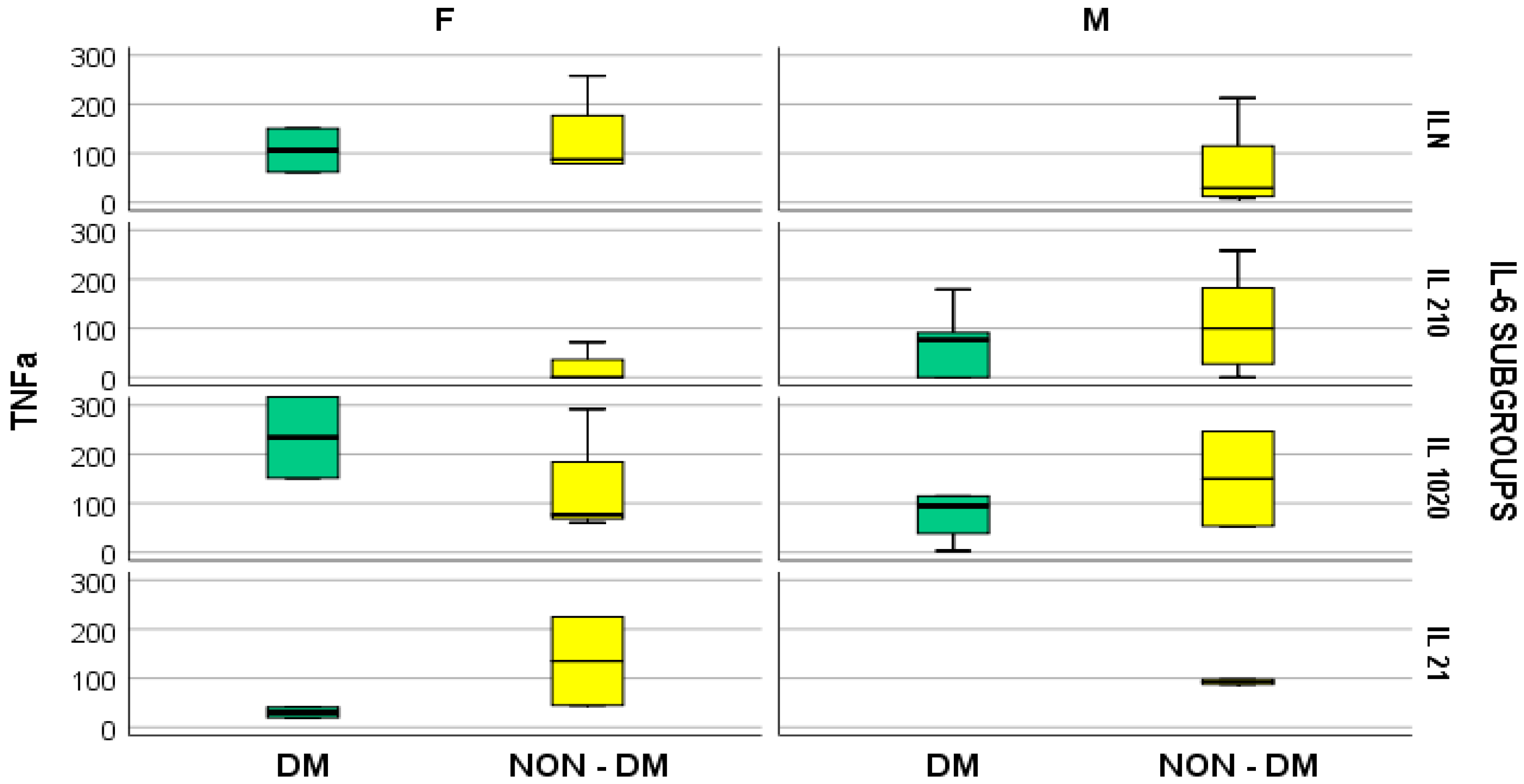
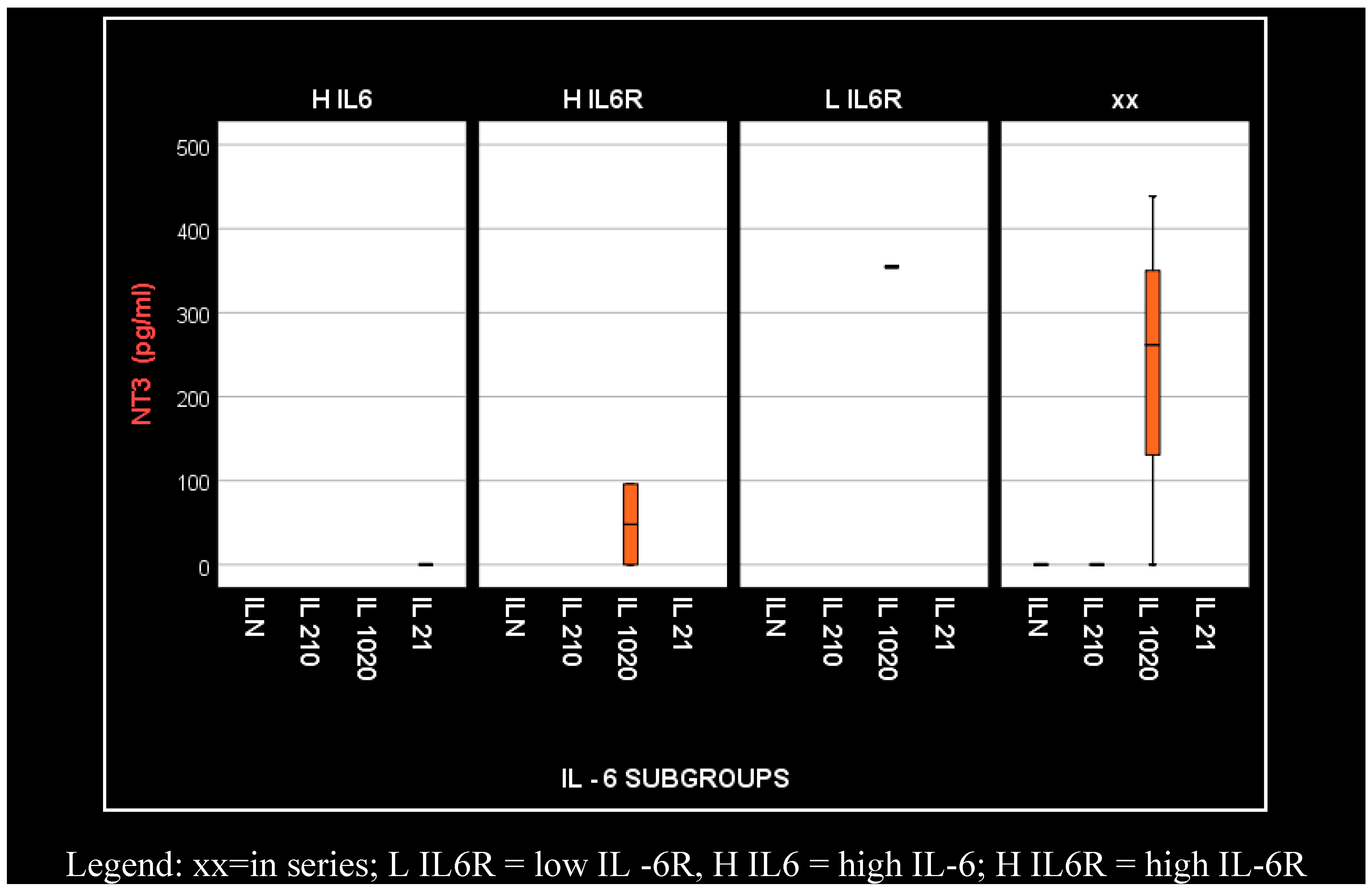
4. Results
- -
- Regular IL-6 (under 50 pg/mL) = ILN (2 patients with diabetes and 13 without);
- -
- IL-6 increased by 2–10 times the regular value (100–500 pg/mL) = IL 2–10; (4 patients with diabetes and 19 without);
- -
- IL-6 increased by 10–20 times the regular value (500–1000 pg/mL) = IL 10–20 (7 patients with diabetes and 11 without);
- -
- IL-6 increased by over 20 times the regular value, so a minimum of 21 times (over 1000 pg/mL) = IL 21 (7 patients with diabetes and 13 without).
- -
- In hemodialyzed diabetes patients, there were no statistically significant differences in parameters relating to general IL-6 determination;
- -
- In hemodialyzed patients without diabetes, we obtained statistically significant differences (p = 0.05) in parameters relating to the general IL-6 level, as follows: IL1-β vs. IL-6, p = 0.034 (Figure 4); TNF-β vs. IL6, p = 0.036 (Figure 5); NT-3 vs. IL-6 p = 0.046 (Figure 6); VEGFβ vs. IL-6 p = 0.034 (Figure 7); IL-10 vs. IL6 p = 0.018 (Figure 8).
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The International Nephrology Society Website. New Global Kidney Health Report Sheds Light on Current Capacity around the World to Deliver Kidney Care. Available online: https://www.theisn.org/blog/2023/03/30/new-global-kidney-health-report-sheds-light-on-current-capacity-around-the-world-to-deliver-kidney-care/ (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Monardo, P.; Lacquaniti, A.; Campo, S.; Bucca, M.; Casuscelli di Tocco, T.; Rovito, S.; Ragusa, A.; Santoro, A. Updates on hemodialysis techniques with a common denominator: The personalization of the dialytic therapy. Semin. Dial. 2021, 34, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, L. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease Associated with Hemodialysis for End-Stage Renal Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 800950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jofré, R.; Rodriguez-Benitez, P.; López-Gómez, J.M.; Pérez-Garcia, R. Inflammatory syndrome in patients on hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17 (Suppl. 3), S274–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; De Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging: An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, X.; Zou, J.; Shen, B. Decreased Peripheral Naïve T Cell Number and Its Role in Predicting Cardiovascular and Infection Events in Hemodialysis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 644627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, S.; Codrici, E.; Popescu, I.D.; Enciu, A.M.; Albulescu, L.; Necula, L.G.; Mambet, C.; Anton, G.; Tanase, C. Inflammation-Related Mechanisms in Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction, Progression, and Outcome. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2180373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Popolo, A.; Autore, G.; Pinto, A.; Marzocco, S. Oxidative stress in patients with cardiovascular disease and chronic renal failure. Free. Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hoedt, C.H.; Bots, M.L.; Grooteman, M.P.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Penne, E.L.; Mazairac, A.H.; Levesque, R.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Nubé, M.J.; ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Clinical predictors of decline in nutritional parameters over time in ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Inflammation Markers, Adhesion Molecules, and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with ESRD: Searching for the Best Risk Marker by Multivariate Modeling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16 (Suppl. 1), S83–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, J.; Arana, C.; Ureña, P.; Torres, A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Fayos, L.; Coll, V.; Lloret, M.J.; Ochoa, J.; Almadén, Y.; et al. Hyporesponsiveness or resistance to the action of parathyroid hormone in chronic kidney disease. Nefrología (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 41, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewczas, M.A.; Pavkov, M.E.; Skupien, J.; Smiles, A.; Md Dom, Z.I.; Wilson, J.M.; Park, J.; Nair, V.; Schlafly, A.; Saulnier, P.J.; et al. A signature of circulating inflammatory proteins and development of end-stage renal disease in diabetes. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sakai, N.; Wada, T. Revisiting inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: The role of the Nlrp3 inflammasome in glomerular resident cells. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, M.; Acikgoz, S.B.; Genc, A.B.; Yaylaci, S.; Dheir, H.; Sipahi, S.S. The levels of inflammatory biomarkers in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2021, 67, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oncel, M.; Akbulut, S.; Toka Ozer, T.; Kiyici, A.; Keles, M.; Baltaci, B.; Turk, S. Cytokines, adipocytokines and inflammatory markers in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borazan, A.; Ustün, H.; Ustundag, Y.; Aydemir, S.; Bayraktaroglu, T.; Sert, M.; Yilmaz, A. The effects of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and C-reactive-protein levels. Mediat. Inflamm. 2004, 13, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, V.; Shelton, E.L.; Pitzer, A.; Yang, H.C.; Kirabo, A. Inflammation, Lymphatics, and Cardiovascular Disease: Amplification by Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gallo, G.; Volpe, M.; Savoia, C. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension: Current Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 798958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brady, M.C.; Ali, M.; VandenBerg, K.; Williams, L.J.; Williams, L.R.; Abo, M.; Becker, F.; Bowen, A.; Brandenburg, C.; Breitenstein, C.; et al. Complex Speech-Language Therapy Interventions for Stroke-Related Aphasia: The Release Study Incorporating a Systematic Review and Individual Participant Data Network Meta-Analysis; National Institute for Health and Care Research: Southampton, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Carmone, C.; Keijer, J.; Zhang, D. Role of Oxidative DNA Damage and Repair in Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Heart Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westheimer, G. Visual science and investigative ophthalmology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1978, 17, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Wellmer, A.; Facer, P.; Saldanha, G.; Kopelman, P.; Lindsay, R.M.; Anand, P. Neurotrophin-3 is increased in skin in human diabetic neuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Sheu, W.H.; Lee, I.T. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor associated with kidney function. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rysz, J.; Banach, M.; Cialkowska-Rysz, A.; Stolarek, R.; Barylski, M.; Drozdz, J.; Okonski, P. Blood serum levels of IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 3, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canaud, B.; Kooman, J.P.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W.; Francis, S.; Maierhofer, A.; Kopperschmidt, P.; Collins, A.; Kotanko, P. Dialysis-Induced Cardiovascular and Multiorgan Morbidity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsukao, H.; Kobayashi, H. Evaluation of the Biocompatibility of Dialysis Membranes. Blood Purif. 2015, 40, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Agrawal, D.K. Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with Vascular Cuffing and Chronic Inflammation Mediating Early Thrombosis in Arteriovenous Fistula. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, B.; Chan, M.R.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Gardezi, A.; Astor, B.C. Arteriovenous Access Type and Risk of Mortality, Hospitalization, and Sepsis Among Elderly Hemodialysis Patients: A Target Trial Emulation Approach. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennankore, K.K.; d’Gama, C.; Faratro, R.; Fung, S.; Wong, E.; Chan, C.T. Adverse technical events in home hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchior, P.; Erlenkötter, A.; Zawada, A.M.; Delinski, D.; Schall, C.; Stauss-Grabo, M.; Kennedy, J.P. Complement activation by dialysis membranes and its association with secondary membrane formation and surface charge. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepniewska, J.; Dolegowska, B.; Golembiewska, E.; Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Domanski, M.; Ciechanowski, K.; Zair, L. The activation of complement system in different types of renal replacement therapy. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.L.; Pilely, K.; Lund, K.P.; Warming, P.E.; Plesner, L.L.; Iversen, K.K.; Garred, P. Hemodialysis leads to plasma depletion of lectin complement pathway initiator molecule ficolin-2. Hemodial. Int. 2021, 25, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, J.; Richtrova, P.; Hricinova, A.; Tuma, Z.; Moravec, J.; Lysak, D.; Matejovic, M. Proteomic profiling of blood-dialyzer interactome reveals involvement of lectin complement pathway in hemodialysis-induced inflammatory response. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, S.; Bohorquez, L.; Gutiérrez-Calabrés, E.; García-Ayuso, D.; Miguel, V.; Griera, M.; Calle, Y.; de Frutos, S.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate- and P-cresol-induced monocyte adhesion and migration is mediated by integrin-linked kinase-dependent podosome formation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Ancuta, P.; Crowe, S.; Dalod, M.; Grau, V.; Hart, D.N.; Leenen, P.J.; Liu, Y.J.; MacPherson, G.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 2010, 116, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, A.; Agüera, M.L.; Luna-Ruiz, C.; Buendía, P.; Calleros, L.; García-Jerez, A.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M.; Arias, M.; Arias-Guillen, M.; de Arriba, G.; et al. Markers of endothelial damage in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 312, F673–F681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Johnson, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.F.; Lu, Y.; Nanayakkara, G.; Fu, H.; Shao, Y.; Sanchez, C.; et al. Uremic toxins are conditional danger- or homeostasis-associated molecular patterns. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 348–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addi, T.; Poitevin, S.; McKay, N.; El Mecherfi, K.E.; Kheroua, O.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; de Macedo, A.; Gondouin, B.; Cerini, C.; Brunet, P.; et al. Mechanisms of tissue factor induction by the uremic toxin indole-3 acetic acid through aryl hydrocarbon receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akbari, M.; Hassan-Zadeh, V. IL-6 signalling pathways and the development of type 2 diabetes. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 signalling in health and disease. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumertl, T.; Lokau, J.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Function and proteolytic generation of the soluble interleukin-6 receptor in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, P.; Nitz, R.; Grötzinger, J.; Scheller, J.; Garbers, C. Minimal interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor stalk composition for IL-6 receptor shedding and IL-6 classic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14756–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalaris, A.; Rabe, B.; Paliga, K.; Lange, H.; Laskay, T.; Fielding, C.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Apoptosis is a natural stimulus of IL6R shedding and contributes to the proinflammatory trans-signaling function of neutrophils. Blood 2007, 110, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizawa, S. Subchapter 41C—Neurotrophin-3. In Handbook of Hormones, 2nd ed.; Ando, H., Ukena, K., Nagata, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 483–485. ISBN 9780128206492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, T.; Oliveira, Á.; Sardà-Arroyo, L.; Ulrich, H. Chapter 7—Growth and Neurotrophic Factor Receptors in Neural Differentiation and Phenotype Specification. In Neural Surface Antigens; Pruszak, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 77–90. ISBN 9780128007815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.L.; Peglau, L.; Moon, L.D.F.; Groß, S.; Schulze, J.; Ruhnau, J.; Vogelgesang, A. Neurotrophin-3 attenuates human peripheral blood T cell and monocyte activation status and cytokine production post stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.I.; Zheng, J.; Kong, W.; Ye, X.; Gou, L.; Regmi, A.; Chen, L.L. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor-B in metabolic homoeostasis: Current evidence. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20171089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lee, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Arjunan, P.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Kumar, A.; Dong, L. VEGF-B: A survival, or an angiogenic factor? Cell Adhes. Migr. 2009, 3, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Nagai, N.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Scotney, P.; Lennartsson, J.; Zhu, C.; Qu, Y.; Fang, C.; et al. VEGF-B inhibits apoptosis via VEGFR-1-mediated suppression of the expression of BH3-only protein genes in mice and rats. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robciuc, M.R.; Kivelä, R.; Williams, I.M.; de Boer, J.F.; van Dijk, T.H.; Elamaa, H.; Tigistu-Sahle, F.; Molotkov, D.; Leppänen, V.M.; Käkelä, R.; et al. VEGFB/VEGFR1-Induced Expansion of Adipose Vasculature Counteracts Obesity and Related Metabolic Complications. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, Z.; Hou, X.; Lennartsson, J.; Li, Y.; Koch, A.W.; Scotney, P.; Lee, C.; Arjunan, P.; Dong, L.; et al. VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6152–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.K.; Baldwin, M.E.; Peale, F.; Fuh, G.; Liang, W.C.; Lowman, H.; Meng, G.; Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P. Redundant roles of VEGF-B and PlGF during selective VEGF-A blockade in mice. Blood 2006, 107, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olofsson, B.; Korpelainen, E.; Pepper, M.S.; Mandriota, S.J.; Aase, K.; Kumar, V.; Gunji, Y.; Jeltsch, M.M.; Shibuya, M.; Alitalo, K.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) binds to VEGF receptor-1 and regulates plasminogen activator activity in endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11709–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, R.W.; Litjens, N.H.; de Wit, E.A.; Langerak, A.W.; van der Spek, A.; Baan, C.C.; Weimar, W.; Betjes, M.G. Uremia causes premature ageing of the T cell compartment in end-stage renal disease patients. Immun. Ageing 2012, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, N.H.; van Druningen, C.J.; Betjes, M.G. Progressive loss of renal function is associated with activation and depletion of naive T lymphocytes. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crépin, T.; Legendre, M.; Carron, C.; Vachey, C.; Courivaud, C.; Rebibou, J.M.; Ferrand, C.; Laheurte, C.; Vauchy, C.; Gaiffe, E.; et al. Uraemia-induced immune senescence and clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; Borges, M.; Fernandes, J.; Nascimento, H.; Sameiro-Faria, M.; Miranda, V.; Reis, F.; Belo, L.; Costa, E.; Santos-Silva, A. Apoptosis of peripheral CD4(+) T-lymphocytes in end-stage renal disease patients under hemodialysis and rhEPO therapies. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisowska, K.A.; Pindel, M.; Pietruczuk, K.; Kuźmiuk-Glembin, I.; Storoniak, H.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Witkowski, J.M. The influence of a single hemodialysis procedure on human T lymphocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Chung, B.H.; Jeon, E.J.; Kim, B.M.; Choi, B.S.; Park, C.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, S.G.; Cho, M.L.; Yang, C.W. B cell-associated immune profiles in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, P.; Rampino, T.; Gregorini, M.; Gabanti, E.; Bianzina, S.; Dal Canton, A. Mechanisms underlying sCD40 production in hemodialysis patients. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 278, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Clemont, A.; Feener, E.P.; Hein, K.D.; Igarashi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; White, M.F.; King, G.L. Characterization of selective resistance to insulin signaling in the vasculature of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Moffat, B.; Harkins, R.N. Human lymphotoxin. Production by a lymphoblastoid cell line, purification, and initial characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 2012, 119, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Eessalu, T.E.; Hass, P.E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature 1985, 318, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kohr, W.J.; Hass, P.E.; Moffat, B.; Spencer, S.A.; Henzel, W.J.; Bringman, T.S.; Nedwin, G.E.; Goeddel, D.V.; Harkins, R.N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramaglia, I.; Mauri, D.N.; Miner, K.T.; Ware, C.F.; Croft, M. Lymphotoxin alphabeta is expressed on recently activated naive and Th1-like CD4 cells but is down-regulated by IL-4 during Th2 differentiation. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, C.F. Network communications: Lymphotoxins, LIGHT, and TNF. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 787–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Subjects on Hemodialysis (n) | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | CKD Duration (Years) | Time on Hemodialysis (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NON DM (62) | 61.5 ± 15.1 | 33/28 | 8.26 ± 6.99 years. | 5.29 ± 4.71 |
| DM (21) | 63 ± 11.8 | 9 M, 12 F | 5.23 ± 4.34 years. | 2.53 ± 2.69 |
| Value Range | IL-6 (pg/mL) | IL-6R (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM (n) | NON-DM (n) | DM (n) | NON-DM (n) | |
| <50 | 2 | 13 | 0 | 1 |
| 50–100 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 100–500 | 4 | 19 | 1 | 2 |
| 500–1000 | 7 | 11 | 3 | 17 |
| ≥1000 | 7 | 13 | 17 | 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trandafir, M.-F.; Savu, O.; Pasarica, D.; Bleotu, C.; Gheorghiu, M. Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci12020031
Trandafir M-F, Savu O, Pasarica D, Bleotu C, Gheorghiu M. Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients. Medical Sciences. 2024; 12(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci12020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrandafir, Maria-Florina, Octavian Savu, Daniela Pasarica, Coralia Bleotu, and Mihaela Gheorghiu. 2024. "Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients" Medical Sciences 12, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci12020031
APA StyleTrandafir, M.-F., Savu, O., Pasarica, D., Bleotu, C., & Gheorghiu, M. (2024). Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients. Medical Sciences, 12(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci12020031







