The Association of Toxoplasma gondii with the Combination of Cardiovascular Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hypothesis
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Indicators for Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Liver
2.3.1. Cardiovascular Disease
2.3.2. CKD
- Stage 1: eGFR ≥ 90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and estimated persistent albuminuria;
- Stage 2: eGFR 60–89 mL/min/1.73 m2 and estimated persistent albuminuria;
- Stage 3: eGFR 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2;
- Stage 4: eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m2;
- Stage 5: eGFR < 15 mL/min/1.73 m2.
2.3.3. CLD
- Men: ALT > 40 U/L or AST > 37 U/L
- Women: ALT or AST > 31 U/L
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. Holistic Assessment
4. Discussion
Limitaitons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Innes, E. A brief history and overview of Toxoplasma gondii. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.-L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular Diseases-PAHO/WHO|Pan American Health Organization. 2023. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/topics/cardiovascular-diseases (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Babekir, A.; Mostafa, S.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. The Association of Toxoplasma gondii IgG and Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Lopez, H.I.A.O.; Pérez, G.E.; Burgos, L.M.; Farina, J.M.; Saldarriaga, C.; Lopez-Santi, R.; Cotella, J.I.; Pérez, A.L.S.; Baranchuk, A. Toxoplasmosis and the Heart. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, A.I.; Converse, R.R.; Griffin, S.M.; Styles, J.N.; Sams, E.; Hudgens, E.; Wade, T.J. Latent Toxoplasma gondii infections are associated with elevated biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.B.; Jensen, K.D.; Saeij, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii effectors are master regulators of the inflammatory response. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, J. Chronic kidney disease: Overview. In Chronic Kidney Disease; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Kanso, A.; Sedor, J.R. Chronic kidney disease and its complications. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2008, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babekir, A.; Mostafa, S.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. The Association of Toxoplasma gondii IgG Antibody and Chronic Kidney Disease Biomarkers. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Angulo, P.; Lindor, K.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 172, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babekir, A.; Mostafa, S.; Minor, R.C.; Williams, L.L.; Harrison, S.H.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. The Association of Toxoplasma gondii IgG and Liver Injury in US Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Wan, B.; Velani, B.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, S. Is Toxoplasma gondii infection correlated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?—A population-based study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, V.P.; Wright, G.A.; Banaji, M.; Mukhopadhya, A.; Mookerjee, R.; Moore, K.; Jalan, R. Relationship between activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renal blood flow autoregulation in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 111–119.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuche, C. The cardiovascular system and associated disorders. Br. J. Nurs. 2022, 31, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozougwu, J.C. Physiology of the liver. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biosci. 2017, 4, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wadei, H.M.; Textor, S.C. The role of the kidney in regulating arterial blood pressure. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, B.C. Hepatic function. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 327–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hankins, J. The role of albumin in fluid and electrolyte balance. J. Infus. Nurs. 2006, 29, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, H.J. Hepatotoxicity: The Adverse Effects of Drugs and Other Chemicals on the Liver; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States, 2019; US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/pdf/2019_National-Chronic-Kidney-Disease-Fact-Sheet.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Himmelfarb, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hakim, R.M. The elephant in uremia: Oxidant stress as a unifying concept of cardiovascular disease in uremia. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Plutzky, J. Management of Low Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol. Circulation 2013, 128, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ridker, P.M. Cardiology Patient Page. C-reactive protein: A simple test to help predict risk of heart attack and stroke. Circulation 2003, 108, e81–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttmann, E.; Brant, L.J.; Concin, H.; Diem, G.; Rapp, K.; Ulmer, H. γ-Glutamyltransferase as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. Circulation 2005, 112, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Golabi, P.; Mishra, A.; Rafiq, N.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of chronic liver diseases in the USA in the past three decades. Gut 2020, 69, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, A.; Lupu, M.A.; Lighezan, R.; Paduraru, A.A.; Olariu, T.R. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases from Western Romania: A Case–Control Study. Life 2023, 13, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.M.; Ramadan, M.E.; Ramadan, M.E. Toxoplasma gondii infection and chronic liver diseases: Evidence of an association. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2016, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Lin, C.; Tona, F.; Osto, E. The crosstalk between the cardiovascular and the immune system. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 1, H83–H88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems; Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG): Cologne, Germany, 2020.
- Noor, M.T.; Manoria, P. Immune Dysfunction in Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Mueller, S.H.; Chung, S.-C.; Foster, G.R.; Lai, A.G. Increased burden of cardiovascular disease in people with liver disease: Unequal geographical variations, risk factors and excess years of life lost. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, S.; Hernandez, G.T. The link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. J. Nephropathol. 2014, 3, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espi, M.; Koppe, L.; Fouque, D.; Thaunat, O. Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Immune Dysfunctions: Impact of Protein-Bound Uremic Retention Solutes on Immune Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoult, E.; Georges, E.; Biava, M.-F.; Hulin, C.; Frimat, L.; Hestin, D.; Kessler, M. Toxoplasmosis in kidney transplant recipients: Report of six cases and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M. Innate, adaptive, and cell-autonomous immunity against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Parise, M.E.; Fiore, A.E. Neglected parasitic infections in the United States: Toxoplasmosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Khanna, P. Development of Toxoplasma gondii vaccine: A global challenge. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opsteegh, M.; Kortbeek, T.M.; Havelaar, A.H.; van der Giessen, J.W. Intervention strategies to reduce human Toxoplasma gondii disease burden. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cardiovascular Biomarker | Biomarker Value Assigned Index Value (1) | Biomarker Value Assigned Index Value (0) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) | ≤80 | >80 | [26] |
| Systolic blood pressure (SBP) | ≤120 | >120 | [26] |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) | ≥50 mg/dL | <50 mg/dL | [27] |
| Triglycerides (TG) | ≤199 mg/dL | >199 mg/dL | [26] |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | ≤1 mg/dL | >1 mg/dL | [28] |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) | ≤40 U/L | >40 U/L | [29] |
| Total cholesterol (TC) | <200 mg/dL | >200 mg/dL | [26] |
| Glucose (FG) | <100 mg/dL | >100 mg/dL | [26] |
| Overall Biomarkers Index | Sum of the index values | [26] | |
| Variables | Description | n | Weighted Percentage/Mean (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T. gondii IgG Antibody | <33 IU/mL (IgG−) | 1662 | 85.1 |
| ≥33 IU/mL (IgG+) | 399 | 15.1 | |
| Gender | Male | 984 | 47.2 |
| Female | 1077 | 52.8 | |
| Age | 2061 | 48.12 (0.56) | |
| Race/ethnicity | Mexican American | 412 | 9.4 |
| Other Hispanic | 236 | 5.5 | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 1006 | 69.8 | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 314 | 9.6 | |
| Other Race | 93 | 5.8 | |
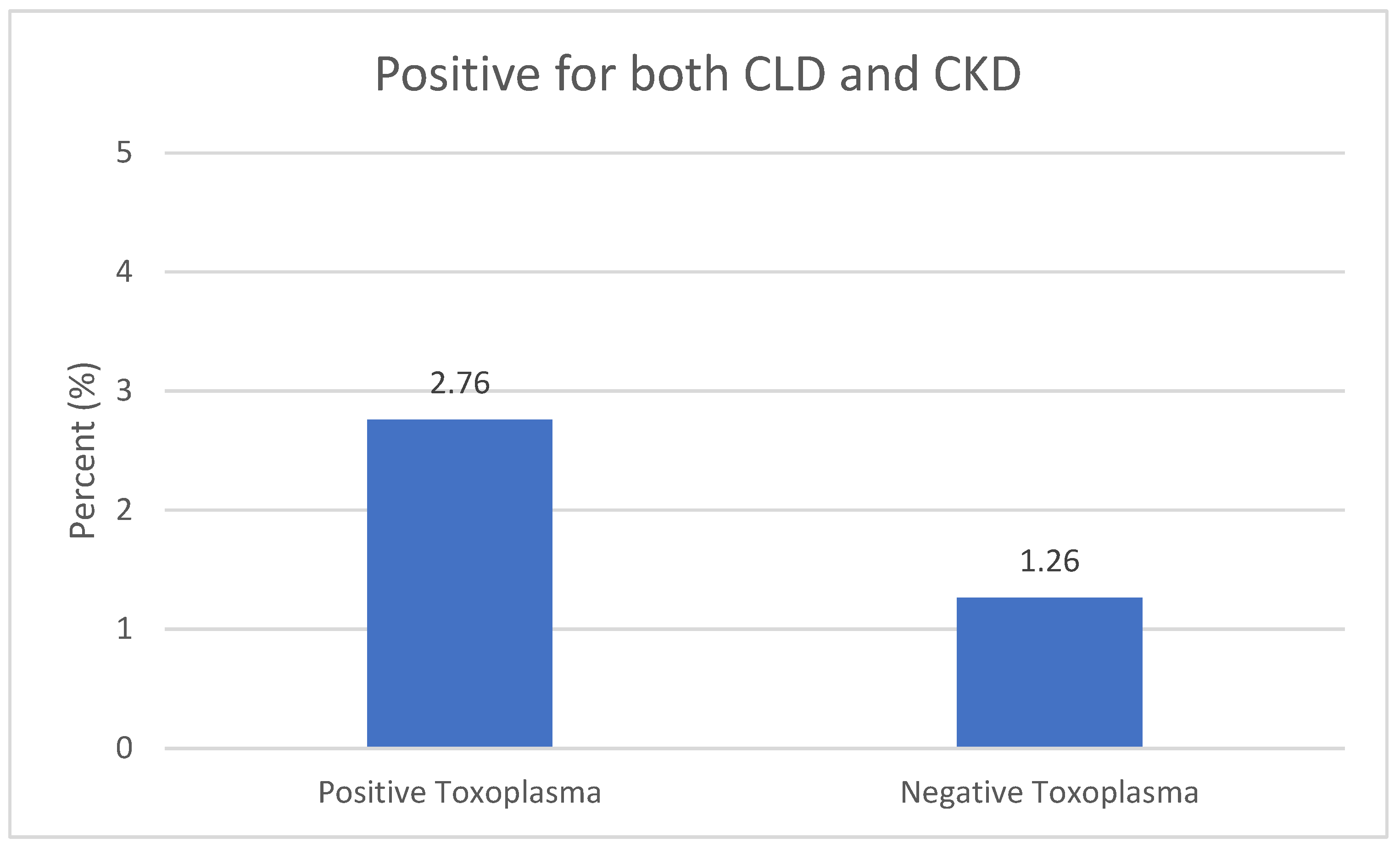
| Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) | Negative | 1730 | 83.8 |
| Positive | 331 | 16.2 | |
| Chronic Kidney Disease CKD | Negative | 1790 | 89.7 |
| Positive | 271 | 10.3 | |
| Overall Cardiovascular Biomarker Index (OCBI) median | 2061 | 5.0 |
| T. gondii (Positive) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size = 2061 | Odds Ratio | OR 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| OCBI | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 0.0448 |
| CLD (positive) | 1.42 | 1.07 | 1.90 | 0.0149 |
| CKD (negative) | 1.06 | 0.87 | 1.46 | 0.7347 |
| Constant Pseudo R-Square = 0.01 | 0.37 | 0.22 | 0.55 | 0.0001 |
| T. gondii (Positive) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size = 2061 | Odds Ratio | OR 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| OCBI | 0.99 | 0.91 | 1.08 | 0.9310 |
| CLD (positive) | 1.72 | 1.28 | 2.31 | 0.0001 |
| CKD (negative) | 0.64 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.0119 |
| Age | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 0.0001 |
| Constant Pseudo R-Square = 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.0001 |
| CLD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size = 2061 | Odds Ratio | OR 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| OCBI | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.0001 |
| Toxoplasma (positive) | 1.68 | 1.25 | 2.26 | 0.0006 |
| CKD (negative) | 0.84 | 0.54 | 1.30 | 0.4445 |
| Age | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.08 | 0.0001 |
| Constant Pseudo R-Square = 0.09 | 7.17 | 3.81 | 13.51 | 0.0001 |
| CKD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size = 2061 | Odds Ratio | OR 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| OCBI | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 0.0353 |
| CLD (positive) | 1.01 | 0.67 | 1.56 | 0.9557 |
| Toxoplasma (positive) | 1.50 | 1.60 | 2.13 | 0.0221 |
| Age | 1.01 | 1.0 | 1.02 | 0.0001 |
| Constant Pseudo R-Square = 0.22 | 579.59 | 226.54 | 1482.81 | 0.0001 |
| OCBI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size = 2061 | Odds Ratio | OR 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| CKD (negative) | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.0006 |
| CLD (positive) | 1.10 | 0.51 | 2.30 | 0.8117 |
| Toxoplasma (positive) | 1.70 | 0.70 | 4.02 | 0.2345 |
| Age | 1.03 | 1.0 | 1.05 | 0.0225 |
| Constant Pseudo R-Square = 0.06 | 1.03 | 0.30 | 3.48 | 0.9360 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babekir, A.; Mostafa, S.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. The Association of Toxoplasma gondii with the Combination of Cardiovascular Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Preliminary Study. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11040065
Babekir A, Mostafa S, Obeng-Gyasi E. The Association of Toxoplasma gondii with the Combination of Cardiovascular Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Preliminary Study. Medical Sciences. 2023; 11(4):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11040065
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabekir, Amani, Sayed Mostafa, and Emmanuel Obeng-Gyasi. 2023. "The Association of Toxoplasma gondii with the Combination of Cardiovascular Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Preliminary Study" Medical Sciences 11, no. 4: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11040065
APA StyleBabekir, A., Mostafa, S., & Obeng-Gyasi, E. (2023). The Association of Toxoplasma gondii with the Combination of Cardiovascular Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Preliminary Study. Medical Sciences, 11(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11040065








