Abstract
Quantitative acoustic marine habitat mapping needs to consider the impact of macrobenthic organisms on backscatter data. However, the sensitivity of hydroacoustic systems to epibenthic life is poorly constrained. This study explores the impact of a benthic community with sparse abundance on seafloor microroughness and acoustic backscatter at a sandy seafloor in the German North Sea. A multibeam echo sounder survey was ground-truthed by lander measurements combining a laser line scanner with sub-mm resolution and broad-band acoustic transducers. Biotic and abiotic features and spatial roughness parameters were determined by the laser line scanner. At the same locations, acoustic backscatter was measured and compared with an acoustic scatter model utilizing the small-roughness perturbation approximation. Results of the lander experiments show that a coverage with epibenthic features of 1.6% increases seafloor roughness at spatial wavelengths between 0.005–0.03 m, increasing both spectral slope and intercept. Despite the fact that a strong impact on backscatter was predicted by the acoustic model based on measured roughness parameters, only a minor (1.1 dB) change of backscatter was actually observed during both the lander experiments and the ship-based acoustic survey. The results of this study indicate that benthic coverage of less than 1.6% is insufficient to be detected by current acoustic remote sensing.
1. Introduction
Habitat mapping using acoustic remote sensing has become an important topic for marine spatial management and research purposes [1,2,3,4], increasingly including the detection of benthic life. Multibeam and sidescan sonar systems provide information about seafloor characteristics based on the intensity of the acoustic signal backscattered from the seafloor. The acoustic backscatter intensity is affected by the sensor geometry relative to the seafloor and physical characteristics of the sediment–water interface, the water column characteristics such as stratification, the applied acoustic frequency, and the shallow subsurface [5]. The physical properties of the seafloor interface are influenced by the presence of benthic life. Benthic life, including macrofauna [6,7] and macroflora [8], are biological activities that change physical sediment properties [9,10,11]. The impact of benthic life on acoustic backscatter is both a challenge and an opportunity for environmental remote sensing. Benthic life has an impact on both lander-based [6,7,12,13] and ship-based [14,15,16,17,18,19] acoustic remote sensing tools. Conversely, these technologies have an unrealized potential to determine spatial and temporal dynamics of biologically impacted seafloor. Recent research activities to provide calibrated, multi-frequency acoustic scatter data from the seafloor [20,21,22] allow us to compare acoustic surveys undertaken at different seasons and with different systems and improve the spatial and temporal discrimination power of acoustic surveys. Improved knowledge on the impact of benthic life on seafloor properties would allow an improved understanding of the potential discrimination of acoustic techniques. Ideally, acoustic backscatter would be predicted by a forward model, which is based on geophysical seafloor parameters derived from physical sampling. As most of the required geophysical parameters (including sediment type, mean grain size, porosity, permeability, particle type, pore fluid, and pore space characteristics) are difficult to measure, especially for seafloor impacted by benthic organisms [11], seafloor interface parameters are commonly reduced to seafloor roughness [9,23,24]. Especially for well-sorted sand environments with limited penetration of a few centimeters for high-frequency (>100 kHz) acoustic waves [25], interface roughness strongly controls the intensity of the backscatter with minor contributions of volume scatter. Natural interface roughness is caused by sediment composition, hydrodynamic forces, presence of benthic life and small-scale bioturbation processes [9]. Seafloor roughness magnitudes vary with spatial scale. Applied to seafloor morphology on scales relevant to high-frequency acoustic wavelengths in the mm to cm scale, roughness is dominated by hydrodynamic ripple structures with wavelengths >0.1 m and amplitudes of few centimeters [26]. On smaller scales, roughness is controlled by biological structures and activities, causing small-scale sediment transport and redeposition in the mm to cm scale [26]. In the past, field experiments have been conducted to record acoustic backscatter data on extensively ground-truthed sandy environments with the aim to compare measured scatter intensities with various types of model predictions [27]. The comparison of recorded backscatter intensities and acoustic model results at frequencies <100 kHz and above the critical angle (~30° for sand) show good correlation if both the surface roughness and subsurface volume scatter mechanism are taken into account [28,29]. However, for high-frequency backscatter data (>100 kHz) above critical angles, significant model/data disparities were observed, indicating the need for further experimental studies. These disparities were related to biological fragments primarily responsible for acoustic scatter [6,9,30].
The objective of this study is to assess the impact a sparse cover of benthic organisms exerts on mm-scale seafloor interface roughness and high-frequency (200 kHz) acoustic scatter in a sand environment. Toward this aim, we use an underwater laser line scanner in combination with an acoustic transducer and underwater video images to record a concurrent dataset of local small-scale seafloor morphology, benthic life, and acoustic scatter. The long-term aim is to utilize the backscatter data recorded by the lander transducer units to calibrate ship-based high-resolution imaging sonar system within a research area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regional Setting
The study area is located 17.5 km offshore Sylt island in the German Bight (Figure 1) at a water depth of approximately 15 m. The region is exposed to storm events from the west and influenced by semidiurnal tides that are flood dominated. The seafloor surface and subsurface of the area have been described as homogenous sandy surfaces by [14,31,32]. A backscatter map of the study site reveals numerous patchy features. The benthic community is mainly characterized by endobenthic species with few structures protruding from the sediment surface. The most prominent structures are tubes constructed by the sand mason Lanice conchilega. The endobenthic community inhabiting the fine sands can be assigned as Tellina-fabula assemblage [33], whereas medium and coarse sands are colonized by a typical Goniadella-Spisula assemblage [34]. While attached epifauna is scarce, mobile epifauna is dominated by echinoderms (mainly starfish and brittlestars). Mostly due to high wave energy frequently reaching the seabed, density and species richness are reduced compared to deeper parts of this area [34].
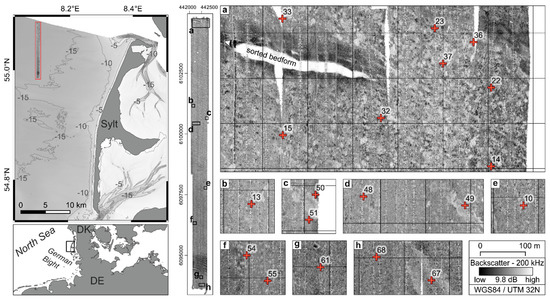
Figure 1.
Left hand side: Overview and bathymetry map offshore Sylt. Middle: A ship-based backscatter intensity map of the investigation area. Right hand side: Close up of the study area and the lander deployment stations (red cross), with Norbit multibeam echosounder backscatter data recorded at a frequency of 200 kHz. The dynamic range of the shown uncalibrated backscatter values is approx. 10 dB.
2.2. Field Measurements
During the research cruise HE486 onboard FS Heincke in May 2017, a total of 76 optical surface scans and 1900 acoustic traces were recorded at 19 different stations (Figure 1). Three previously available optical surface scans measured in 2016 onboard FS Mya [7] that showed higher abundances of benthic organisms were included in the analysis. A ship-based background backscatter mosaic of 8 km2 was recorded during the HE486 survey utilizing a roll-stabilized NORBIT iWBMSe multibeam echo sounder operating at a frequency of 200kHz. Multibeam echo sounder raw data is available for download in the Pangea database (refer to the section Supplementary Materials). Hypack 2016 (Hypack / Xylem Inc., Middeltown, CT, USA) was used as a recording software. Data processing was involved the application of sound velocity corrections, the interpolation of asynchronous navigation records, and tidal effects. Backscatter mosaics were subsequently created using Hypack Geocoder with a resolution of 0.5 m, correcting for the insonified area and the effects beam pattern by applying an angle varied gain.
The autonomous operating lander system is equipped with a rotating laser line scanner (ULS200 2G Robotics Inc., Waterloo, ON, Canada) and five acoustic transmitter/receiver units (Figure 2). The effective optical surface coverage is 0.16 m2 at a resolution of 0.001 m. The scan resolution is controlled by the attachment height of 0.5 m above the seafloor, the rotation range of 60°, the rotation step size of 0.09°, and the fixed opening swath width of 50° with 480 equidistant capture points. At each deployment location, four surface scans were performed, with each scan lasting, on average, 110 seconds. To mitigate the impact of particle flow within the water column and rapidly changing light conditions in a shallow water environment, two digital filters were applied during data recording, provided by 2G Robotics. The ambient light filter performs multiple line scans to measure and subtract background noise. A defined recording window of ± 0.1 m above and below the seafloor reduces reflection from particles close to the laser head.
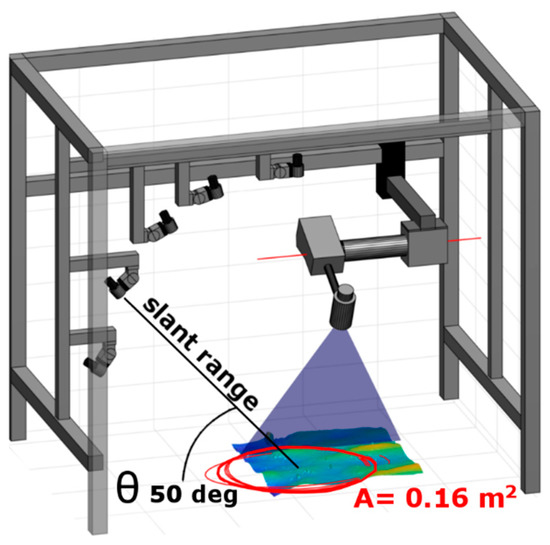
Figure 2.
Setup of the lander frame. The size of the lander frame is 120 cm × 80 cm × 100 cm. Displayed are the slant range and the grazing angle θ of the selected profiler, which is defined as the angle between the wavefield motion and the zero mean seafloor surface. The red circles mark the areas of the acoustic footprint. In blue the laser swath is highlighted. The ULS200 mid-range laser scan system is manufactured by 2G Robotics, and the acoustic transducer units by Benthowave Instruments Inc.
For the acoustic experiment, five planar transducers (Benthowave Instruments Inc., Collingwood, ON, Canada) were fixed to the lander frame (Figure 2). The transducers have different incidence angles and slant ranges with a common footprint center and a constant acoustic footprint of ~0.25 m2. For this study, we focus on the transducer mounted at a grazing angle of 50° because backscatter intensities recorded at grazing angles between 30° to 60° are less responsive to slight changes in grazing angle [21]. The chosen footprint size of 0.16 m2 at an angle of 50 degrees corresponds approximately to the footprint size of a single beam of a multibeam system. The acoustic footprint is located within the area captured by the laser scanner. Recording windows of the transducers were adjusted to avoid multiple reflections, system reverberation, and nearfield effects. To improve the signal-to-noise ratio at each shot, 20 time series were logged and stacked during post-processing. For transmitting, a driving voltage of 80 V generated a 102 µs linear chirp pulse signal with a bandwidth range of 80 to 310 kHz. For receiving, the sampling rate was set to 10 MHz. The time-varying response function (TVR) and the oscillation circuit voltage (OCV) were provided by the manufacturer to convert the recorded voltage into an acoustic signal. The TVR describes the frequency-dependent relationship between the transmitted signal amplitude at a 1 V driving voltage and the pressure change at a one-meter distance in µPa. The OCV describes the frequency-dependent amplitude conversion of a 1 µPa pressure field into a voltage response. TVR and OCV are defined for the transducer center frequency at 194 kHz (wavelength 7.73 mm), with amplitudes strongly decreasing for both higher and lower frequencies. Because the transducer-specific response function could not be accurately measured, a constant transducer configuration ensures a comparable signal between the stations for each grazing angle. To ensure no reflection or scattering effects caused by the lander frame or optic unit occurred, the system was tested while elevated in the water column.
A Van-Veen-grab sampler was used for sediment recovery at each lander station. To evaluate the grain size distribution, sediment subsamples in the depth range of 0 to 0.02 m of the undisturbed surface were analyzed by a particle laser sizer (Cilas 1180). Due to the low organic content, no chemical pretreatment of the samples was required. For additional ground-truthing, two GoPro cameras were mounted on the lander frame, and an underwater towed camera system was used to image the local geological framework.
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Optical Data
As a first data processing step, stacking of the point clouds from multiple measurements at each station was performed to remove outliers caused by particle reflection close to the seafloor surface. Scrips used for data evaluation are provided for download in the Pangea database (refer to the section Supplementary Materials). The point clouds were measured with the exact same geometry and center points, and the stacking was performed by computing the mean point cloud from repeated measurements. The remaining outliers were removed by applying a 2D high-pass filter with a cut off wavelength of 0.0025 m in combination with a density probability function to eliminate values outside the 3σ confidence interval, were σ is the standard variation. The variance of the surface roughness was tested to follow a Gaussian distribution [7]. Previous studies [7] showed that this outlier removal procedure affects less than 2% of the total dataset but is crucial for comparing the results of spectral analysis between the different deployment locations. Following the outlier correction, the datasets were gridded using Matlabs’s griddata function with linear data interpolation based on the largest horizontal point spacing, resulting in a width (Δx) and height (Δy) of a square pixel of 0.001 m. A mean plane surface was subtracted, so the mean of each surface grid (Sx,y) is zero. An example of a gridded surface is demonstrated in Figure 3a. Each surface contains a spatial wavelength range between 0.002 to 0.17 m. The gridded surfaces were used to derive interface roughness parameters in the form of the root-mean-square roughness (RMS roughness). The RMS roughness was computed according to Equation (1) and describes the mean height variation of the zero mean surface grid.
M, N: number of grid points in the x,y direction.
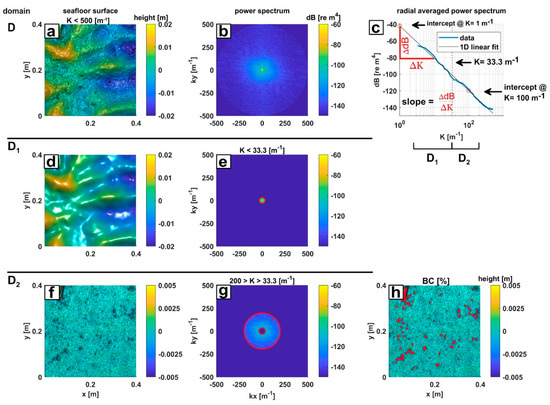
Figure 3.
An example of a measured surface by the laser line scanner is displayed in (a), while (b) shows the corresponding power spectral density (PSD) containing the wavelength interval D (0.002–0.17 m). The blue line in (c) shows the radial averaging PSD of (b). The black line in (c)represents the linear fit of the radial averaged PSD required to derive the spectral slope and the spectral intercepts at the wavelengths 0.01 m and 1 m. The vertical dashed line in (c) indicates the separation of the spectrum D into the intervals D1 and D2, which is equivalent to separation of the PSD demonstrated in (d)–(g). The inverse transform of the low-pass filtered PSD D1 interval is shown in (d) with the corresponding spectrum in (e). The inverse transform of the PSD D2 covering wavelength <0.03 m is shown in (f), with the corresponding high-pass filtered spectrum in (g). The red circles in (e) and (g) indicate the cutoff wavelength. The red markers in (h) highlight the detected objects from (f), which were used to compute the benthic coverage (BC).
The 2D power spectral density (PSD) is a directional characterization of surface roughness and reflects spatial height variations of distinct wavelengths (Figure 3c). For PSD computation, the measured surface was transformed into the frequency domain by the application of a 2D fast Fourier transformation (FFT) [24,35,36]. To avoid spectral leakage during the FFT, the surface edges were tapered to smoothly approach zero. This has been achieved by multiplying the gridded surface by an equal size 2D Tukey window with a flank interval of 20% of the grid length. Based on the transformed surface, the 2D PSD was computed (Figure 3b) according to reference [36] by Equation (2). The transformed surface (Wkx,ky) in Equation (2) is obtained by applying the FFT routine onto the windowed surface Sx,y and shifting the zero-frequency component to the center [36]. By radially averaging the amplitudes of a given spatial wavelength of the 2D power spectrum following the method described in reference [36], an average radial power spectrum (PSD) was computed using Equation (3) and is displayed in Figure 3c.
- PSD: 2D power spectral density [m4]
- W: Fourier transformed windowed surface, given by fft2(winSx,y) [m]
- A: area of the surface grid, given by MΔxNΔy [m2]
- kx: the wave number in the x direction [m−1],
- ky: the wave number in the y direction [m−1],
- fs: sampling frequency = =
- PSD: 2D radial averaged power spectral density [m4]
- Nr: total number of points, which lie upon a circle with radius K
- K: 2D wave vector length [m−1], given by
Computed amplitude values in the frequency domain are displayed as their common logarithm multiplied by ten. The radial averaged psdK is used to derive interface roughness parameters in the form of the spectral slope (γ2) and spectral intercept (ω2). The parameters “spectral slope,” which describes the slope of a linear fit, and “spectral strength,” which describes the intercept of the linear fit at a certain spatial wavelength, were calculated as described by references [24,37] and are outlined in Figure 3c. For acoustic modeling, the spectral strength is extrapolated to a spatial wavenumber of K = 1 m−1 [5], which corresponds to a wavelength of 1 m. Details on the used acoustic model are given in Appendix A. Additionally, for comparison with past studies of seafloor roughness [6], the spectral strength was computed at a spatial wavenumber of K = 100 m−1, which corresponds to a wavelength of 0.01 m.
To investigate the spatial effect of benthic organisms on seafloor roughness, the PSDkx,ky and PSDK were divided into two intervals (Figure 3c–g). The wavelength ranges for the subdivision were set according to the information gathered from the surface scans and video footage. The D1 roughness domain encompasses the spatial wavelength range 0.03–0.17 m (Figure 3c,e) corresponding to hydrodynamic bedforms (Figure 3d). The D2 domain contains the spatial wavelength range 0.005–0.03 m (Figure 3c,g) corresponding to the size of observed biological features (Figure 3f). An inverse FFT algorithm was applied onto the two PSDkx,ky intervals D1 (Figure 3e) and D2 (Figure 3g), to visualize the corresponding seafloor structures (Figure 3d,f) and to derive the RMS roughness values for the D1 and D2 intervals by utilizing Equation (1). Considering the prefactor “A” and the squared amplitude of “W” in Equation (2), the RMS roughness values computed from Sx,y and PSDkx,ky by Equation (1) are equivalent within each interval [37]. Further, the RMS roughness is also directly related to the psdK by a summation of the radial averaged spatial height variations (blue line in Figure 3c) [37].
An automated differentiation between abiotic and biotic surface structures is challenging, due to natural texture and shape variation between individuals of taxonomic groups and due to a variation in view perspective. However, for the purpose of this study, a quantitative interpretation of biological structures is not required. Therefore, a simple approach using the object size was utilized to obtain a biological feature coverage percentage per scan area. The observed bedforms are much larger than biological objects and abiotic objects (like gravel), which may have a similar size to biological structures, were not observed. Features like larger shell fragments, which can significantly impact acoustic backscatter, have been rarely observed on video data of the seafloor surface but frequently below the seabed in the grab samples. Therefore, the seafloor surface of the D2 domain could be utilized to obtain the small-scale structures (0.005–0.03 m) of the seafloor surface. A threshold level of 0.001 m was found to best isolate benthic structures, and a particle counter was then used to cluster and count the biotic objects. The benthic coverage (BC) was computed by dividing the number of grid cells covered by the detected objects by the total number of grid cells (Figure 3h).
2.3.2. Acoustic Data
To remove noise in the recorded data, a cosine (0-pi) bandpass filter (60 to 330 kHz) with a filter flank of ± 20 kHz was applied. The transmitted (Tx) and received (Rx) energy was calculated by integrating over the voltage amplitudes of the recorded time series. To transfer the computed voltage energy into the corresponding sound pressure level in dB [V/µa @1m], Rx and Tx values are transferred into the logarithmic domain and corrected by the applied system gains. Rx is required to compute the acoustic source level (SL) and Tx to obtain the acoustic echo level (EL) by
with TVR: 149 dB [µPa/V] @ 1 m @ 194 kHz
with OCV = −189 dB [V/µPa] @ 1 m @ 194 kHz
SL = 20 × log(Tx) + TVR
EL = 20 × log(Rx) − OCV
The sonar equation can be utilized to derive the backscatter target strength (BS) by
where A (0.16 m2) is the insonified area in m2, and TL the transmission loss defined by
with R (0.66 m) being the slant range in and α being the absorption coefficient in dB/m. For this study, the insonified area and the slant ranges were already known in advance, due to the lander geometry. Assuming the absorption coefficient is a constant factor for the observed and the predicted backscatter over all stations, Equation (7) is further simplified to
BS = EL − SL + 2TL + 10 log(A)
TL = 20 log(R) + α × R
BS = EL − SL + 40 log(R)
2.3.3. Acoustic Scatter Model
To relate the measured surface roughness to the measured backscatter response, an acoustic scatter model was computed to predict backscatter data based on the interface roughness by utilizing the small-roughness perturbation approximation (APL-UW 9407). This scatter model assumes a homogeneous sediment subsurface with no stratification [6,28]. To predict the interaction between the acoustic wavefield and the seafloor surface, the model combines geophysical and acoustic parameters. Geophysical parameters describe the physical properties of the sediment and include the sediment–water density ratio and the surface roughness. Acoustic parameters describe the propagation of the acoustic wave field and include the acoustic frequency, the acoustic wave speed in the water, the sediment–water sound speed ratio, and the attenuation coefficient. Additionally, the model is a function of the grazing angles of the incoming and scattered acoustic wavefield. The input parameters for the surface roughness and the sound speed in water were directly measured during the field experiments. For the sediment–water density ratio, the sediment–water sound speed ratio and the attenuation coefficient literature values [9] were used according to areas with fine to medium sand sediment composition. With the grazing angle and literature values kept constant, the surface scatter was modeled for the center frequency of the transducer unit at 194 kHz. Following [6,38], a detailed summary of the model is provided in Appendix A. Calculated from the model, for this study the predicted backscatter is only depending upon the changing surface roughness parameters.
3. Results
3.1. Ship-Based Acoustic Survey and Ground Truthing
The dominant feature in the ship-based background backscatter mosaics (Figure 1) are several sorted bedforms composed of coarse sand and gravel, which show high backscatter intensities. Sorted bedforms in the northern part of the investigation site (Figure 1) are surrounded by a halo of intermediate to high backscatter intensities with little internal structure. Several SE–NW–elongated stripes of intermediate to high backscatter intensities can be recognized throughout the investigation site, which may be interpreted as remnants of bottom trawling activities. The remainder of the mosaic shows a featureless to patchy appearance of low to intermediate backscatter intensities. The typical diameter of the patches is 10 to 25 m at maximum. Generally, the seafloor appears more chaotic towards the southern and especially, the northern part of the research site, while the central part appears more homogeneous. At the lander sites, ship-based uncalibrated backscatter values have been retrieved at a frequency of 200 kHz (Figure 1). The values were averaged over m2 to account for position inaccuracies and the resulting intensities are displayed in Figure 4. Between all lander stations, the difference in the ship-based backscatter strength is 6.6 dB.
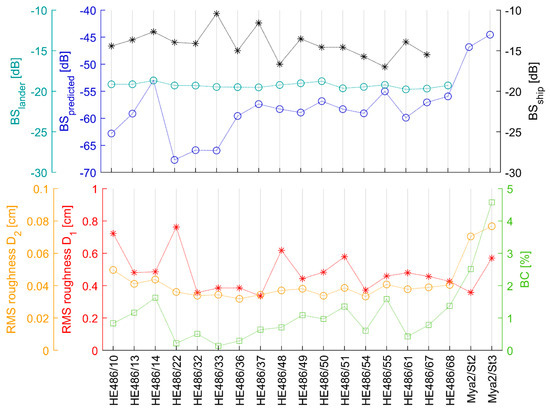
Figure 4.
Predicted backscatter strength using the small-roughness perturbation approximation (blue), the measured backscatter strength (BS) from the lander (cyan), the measured backscatter strength from the ship-based system (black), root-mean-square roughness (RMS roughness) for the D1 interval (red), RMS roughness for the D2 interval (yellow), and benthic coverage (BC) at the seafloor for the lander stations (green). The last two station digits correspond to the position of the lander stations displayed in Figure 1.
Based on the backscatter data in the study site, a total of 30 grab samples were taken and 21 underwater camera surveys were performed. Grab samples revealed an oxic-sediment zone without any notable hydrogen sulfide, and no free gas was observed within the sediment echo sounder data in prior studies [19]. There was no stratification in the upper 0.1 m of the subsurface sediments and no anoxic transgression boundary. The top 0.02 m of the sediment recovered by the grab sampler was used for grain size analysis. Laser diffraction grain-size analysis (CILAS 1180) showed homogeneous well-sorted fine sand with a mode of about 2.6 phi. Biological ground-truthing by the camera and grab samples generally revealed an increased coverage of the sand mason Lanice conchilega (a tubeworm, annelids) in the northern and southern end of the study site. Further, the onboard screening revealed bivalve shells including Tellinidae, Spisula spp., Ensis spp., Donax vittatus and Mactra stultorum, as well as a few brittlestars (Ophiuroidea) and the heart urchin Echinocardium cordatum. Abundant shell hash (diameter << 0.01 m) was present in all grab samples.
Despite the homogeneous sediment composition, video footage revealed three different sedimentary facies within a distance of 20 m, dominant ripple structures with absent to sparse benthic coverage (Figure 5a), higher benthic coverage with reworked ripple structures (Figure 5d), and a reworked ripple structure with sparse benthic coverage (Figure 5e). Considering Figure 5a,e, no relationship is visually recognized between the occurrence of bedforms and the presence of benthic life. Further, no relationship between benthic life and backscatter variation (Figure 5f) was visually recognized.
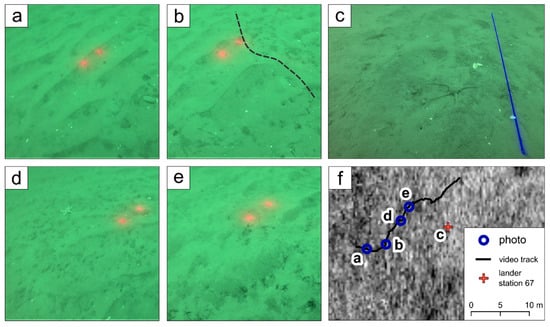
Figure 5.
Video footage from a survey near station 63_1 (a), (b), (d), (e) (red dots have a 10 cm distance), from the lander station 67 (c) and the corresponding position in the ship-based backscatter mosaic (f). (a) reveals asymmetrical straight to sinusoidal ripples with sparse benthic coverage and organic fluff located inside the ripple troughs. (b) indicates the transition is between the ripple-dominated and the benthic-dominated seafloor type. In (c), degenerate ripple structures were observed with few tubeworm structures, shell fragments, and brittlestars (Ophiuroidea). (d) reveals degraded ripple residuals and a higher coverage of tubeworm structures, few starfish, and larger shell fragments. The morphology in (e) shows no ripple structures and very few visible epibenthic features besides some organic fluff. The ship-based backscatter mosaic in (f) shows a corresponding change from low to high backscatter along the video track. However, the positioning is not sufficiently accurate to relate video snapshots directly to the backscatter mosaic.
3.2. Lander Experiment
3.2.1. Seafloor Roughness
The location of the individual lander experiments in the larger geological framework is displayed in Figure 1. Most lander stations show a weak ripple pattern with ripple wavelengths of approx. 0.06–0.10 m (Figure 3a and Figure 5a). Ripple amplitudes vary between 0.025 and 0.043 m. The slope of observed ripple features ranges from 6.5° to 13°. The RMS roughness between the stations varies between 0.004 to 0.008 m. Different biogenic components observed in the video images could be recognized in the bathymetric grids (including worm tubes and shells of Ensis). The number of observed benthic objects varied between 15 and 122, resulting in a BC between 0.1% and 4.6% (Figure 4).
The impact of benthic objects on roughness is focused on the spatial domain D2 (Figure 3). Here, elevated magnitudes in the roughness spectra are observed with increasing biological presence (Figure 6). The curves of roughness magnitudes converge at the larger boundary of this interval, while convergence at the smaller boundary is incomplete. The maximum difference in roughness magnitude is observed at spatial wavelengths of 0.01 m. Correspondingly, there is no correlation found between the BC and the RMS roughness of the D and D1 interval (both R = 0.06), but a strong correlation for the smaller-scale roughness features in the domain D2 (R = 0.73) exists (Table 1). The mean spectral intercept at K = 100 m−1 (equal to a wavelength of 0.01 m) for the complete roughness spectrum is 0.00012 ± 0.00012 over all stations, while the spectral exponent is −4.1 ± 0.27 (Figure 6). Generally, a strong correlation is observed between the benthic abundance and the spectral intercept @ K = 100 m−1 (R = 0.91), while the relationship to the spectral slope is moderate (R = 0.64). No significant correlation is found between the spectral slope and the RMS roughness of any interval. The spectral intercept at K = 1 m−1 contains the extrapolated spatial roughness parameters of seafloor features at 1 m wavelength and is primarily affected by the trend of the roughness spectrum over all wavelengths. Correspondingly, the spectral intercept shows a moderate correlation with the RMS roughness. The spectral intercept at K = 100 m−1 is affected by the roughness spectrum with wavelengths <0.01 m and only correlates with the RMS roughness of the D2 interval.
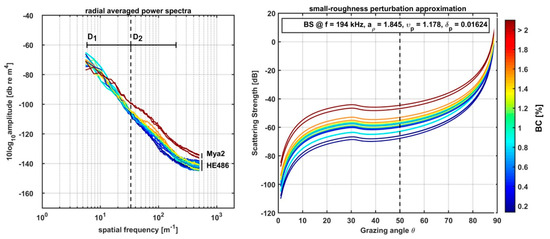
Figure 6.
Left hand side psdK over all lander stations. The vertical dashed line indicates the cutoff frequency (K = 33 m−1) between the D1 and D2 domain. The color shows the corresponding benthic coverage. High RMS roughness values in the D2 domain correlate with high benthic coverage. Right hand side, backscatter strength predicted by the small-roughness perturbation approximation given by reference [6] for the lander sites with acoustic data.

Table 1.
Correlation matrix of the studied parameters. Entries highlighted show a probability value << 0.05.
3.2.2. Acoustic Scatter
Backscatter strength data recorded by the lander system at 50° show a range of 1.1 dB with a mean value of −19.3 dB (σ ± 0.3 dB). The amplitude values are displayed in Figure 4. No lander-based backscatter data exist for the Mya cruise 2016 because the system was not fully operational at that time. The lander backscatter values recorded during the HE486 cruise show no correlation with the RMS roughness and a moderate correlation with the traced benthos parameters (Table 1). The backscatter values predicted by the small-roughness perturbation approximation are displayed in Figure 4 and were used for a model/data comparison. Between all stations, the predicted backscatter strength shows a range of 23.2 dB with a mean value of −58.0 dB (σ ± 5.7 dB). Excluding stations with unavailable lander backscatter data, the difference in backscatter strength decreases to a range of 14.7 dB with a mean strength of −59.7 dB (σ ± 4.0 dB). The predicted backscatter during the HE486 cruise shows an insignificant weak correlation with the RMS roughness of any domain and a strong correlation with the traced benthos parameters (Table 1). No correlation was observed between the ship-based BS values and the parameter obtained by the lander system (Table 1).
4. Discussion
Laser scanner–based bathymetry indicates a benthic coverage (Figure 3) ranging from 0.14% to 1.63% during the Heincke cruise and up to 4.6% during the earlier Mya cruise [7]. The combined dataset allows for further investigation of the impact of low to medium abundant benthic life on seafloor interface roughness parameters. The low abundances during the Heincke cruise of normally widespread tubeworms, confirmed during the video transects, are chiefly attributed to seasonal effects. In the early spring season, the worm tubes are poorly developed, and the settlement coverage of the specimen is lower compared to the summer season, although major changes between years have also been reported [14,39]. The high mean of spectral slope values (>4) derived from the Heincke data also indicate a lack of high-frequency roughness and suggest a low recent modification of the seafloor surface by biological processes [6]. In comparison, spectral slope values derived from the Mya2 data, recorded during the summer season in the same area, increase up to −3.6, which demonstrates the high impact of benthic structures on high-frequency spatial roughness [7].
For a seafloor composed of well-sorted fine sand (2.6 phi), the calculated RMS roughness [29] spectral slope and intercept values are within the range of previously reported values [6]. Due to the very homogeneous sediment composition at the lander stations, the remaining variability of roughness parameters (slope and intercept) is not related to changes in sedimentological composition. Based on video observations, the occurrence of benthic life is also not related to the presence of sedimentary bedforms for most of the observed sedimentary facies (Figure 5a,d,e). Correspondingly, no correlation is found for the RMS roughness of the D and D1 interval, which are dominated by larger hydrodynamic bedforms and the BC (Table 1) in the available laser scanner–derived data. While high abundances of deposit feeders may increase large-scale seafloor roughness due to the local presence of larger mounds [6,7,40], the impact of benthic life on seafloor roughness is usually focused on higher spatial frequencies [19]. A further possibility for benthic life to impact large-scale roughness is the deconstruction of hydrodynamic bedforms [41], which decreases large-scale roughness. This is rarely observed in the video data (an eventual example is shown in Figure 5a) and depends both on the abundance of benthic life and the present hydrodynamic conditions. However, a clear positive correlation exists between BC and roughness derived from higher spatial frequencies (Figure 6), despite the lower limit of the BC being much less than in previously reported studies [7,41,42]. Because the substrate type does not differ between the stations and the present hydrodynamic bedforms are not expressed at high spatial frequencies (Figure 3), the strong correlation is caused by biological presence with a peak impact at spatial wavelengths of 0.01 m. This can also be observed in older 1D power spectra derived from stereo-photogrammetry [43]. Due to this peak, the presence of the local benthic life has a marked control on both spectral slope and intercept (Figure 7a). While both spectral slope and intercept increase, the spectral intercept at K = 100 m−1 was more clearly impacted (Figure 7). The reason for the reduced correlation with spectral slope is the remaining scatter in large-scale roughness caused by variable ripple amplitudes and wavelengths, which changes the slope of the linear regression of the psdK. At higher benthic abundances above 2%, the two available data points may indicate the presence of a threshold effect limiting spectral slope and intercept. To constrain this effect, additional surface models are required.
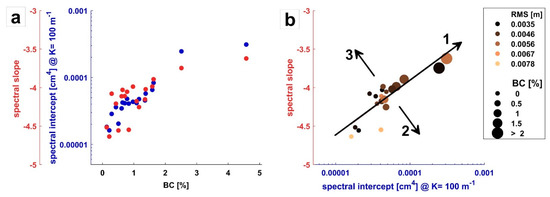
Figure 7.
(a) Spectral slopes and intercepts displayed against the benthic coverage. Grain size is constant at 2.6 phi. (b) A slope vs. intercept diagram for the study site. Symbol color denotes RMS roughness, symbol size denotes the benthic coverage in percent. Arrow 1: Effect of increasing high-frequency roughness due to benthic life (this study). Arrow 2: Effect of relative decrease of low-frequency roughness [9]. Arrow 3: Effect of the relative increase of low-frequency roughness [9].
No clear trend perpendicular to the slope-intercept line exists (Figure 7b), which would be expected due to relative changes in low-frequency to high-frequency roughness. Such trends were found for seafloors with different sedimentological composition or more contrasting bedforms [6,7] (arrow 2 and 3 in Figure 7b). Related to the presence of benthic organisms, such behavior can be caused by the increased presence of biological objects causing degradation of ripples (e.g., observed by [14]), thus reducing low-spatial-frequency roughness. However, due to the relatively low abundances of benthic life present in this study, this effect could not be observed. In contrast, the increasing high-spatial-frequency variability caused by changes in benthic coverage shifts stations up the slope-intercept line (Figure 7b, Arrow 1). While this also represents a relative decrease in low-frequency roughness, in this case, the spectral intercept increases because it is defined at spatial wavelengths of 0.01 m, where the maximum of the biology-induced roughness is situated.
Spectral slopes and intercepts are frequently required for modeling high-frequency acoustic scattering. Generally, at low grazing angles, acoustic scatter is typically controlled by roughness features of about half the acoustic wavelength [26]. For the available 80 to 310 kHz data, this corresponds to spatial wavelengths of ~0.003 to 0.01 m (Figure 3). As the observed small differences in benthic densities already produce an effect on small-scale roughness at these scales, it is interesting to compare the impact of benthic life on the effects on seafloor backscatter. Backscatter strengths were calculated using the small-roughness perturbation approximation for interface roughness, ignoring the (unknown) volume scatter or vertical gradient components and the only difference between the stations being the spectral slope and intercept. However, interface scatter appears as the dominant mechanism already at frequencies as low as 50 kHz for sand-dominated environments with negligible mud and silt content [44]. In addition, grab samples did not reveal sediment layering or lenses of coarser or finer material in the upper centimeters of the subsurface. This is in line with the ship-based surveys in the investigation area [19]—finding volume scatter impact chiefly in areas with increased clay and silt content, which was not encountered during the lander experiments reported here. The model results show a backscatter increase of 14 dB between the Heincke data (−59.7 dB) with an observed sparse benthic coverage of <1.5% and the Mya data (−45.7 dB), in which local mounds and a high coverage of polychaetas could be observed with a corresponding benthic coverage >2.5%. Unfortunately, no sufficient acoustic data was available to confirm the results of the model.
Comparing backscatter variations with benthic densities for lander stations with available acoustic data (BC = 0.8% ± 0.4%), a strong correlation is predicted (R = 0.74, Table 1) for the modeled backscatter (σ = 4.0 dB), whereas the observed backscatter by the lander (σ = 0.3 dB) shows a moderate correlation (R = 0.51, Table 1). No correlation was found for the ship-based backscatter (σ = 1.7 dB). While absolute values of the measured and modeled data cannot be compared, due to the unknown transducer source level and the lack of precise geoacoustic parameters, measured and modeled backscatter strengths are only very weakly correlated (R = 0.27). Hence, by comparing the observed backscatter variations with the seafloor interface-roughness parameter (RMS roughness, slope and intercept) no significant relationships were found (Table 1). In fact, the observed lander backscatter difference (1.1 dB) may be within a natural time-varying fluctuation in sand environments [45,46] and is less than 4 dB for small patches with increased abundance of benthic life in the investigation area based on a 200 kHz ship-based multibeam echo sounder survey reported by reference [19]. The lander data-model comparison showed no correlation. It is unlikely that volume scatter, including scatter by subsurface free gas for which no indication was found during survey and sampling, or vertical gradients in homogeneous sand deposits play a decisive role in the environment of this study. Therefore, the small-roughness perturbation approximation (computed for surface scatter) is likely not applicable to predict backscatter strength at high frequencies for seafloor covered with sparse benthic macrofauna. Spectral slope and intercept, which are primary input parameters for the acoustic model, seemed more sensitive to BC changes than the recorded backscatter.
One reason for the missing relationship between the observed and measured acoustic backscatter may be introduced by deriving the spectral slope and intercept from the linear regression of the power spectrum. The linear fit is based on the assumption, that seafloor morphology alteration in a sandy environment is a constant process and occurs as a dynamic balance between hydrodynamics forces and benthic activities [5,6]. This means, in a highly energetic regime (e.g., during storm events), hydrodynamic forces dominate over benthic activities, which destroy benthic structures and form distinct ripple fields. With decreasing energy, benthic activities dominate over hydrodynamic forces, which continuously alter ripple structures until an isotropic roughness regime is reached [5,6,47]. As discussed earlier, a spatial impact of epibenthos on seafloor roughness was demonstrated, while an interaction with hydrodynamic bedforms was rarely observed. The lack of interaction between the two roughness domains indicates an imbalanced seafloor alteration process. Following reference [5], a roughness spectrum with two roughness components (D1 and D2 RMS roughness), which differ over a limited spatial frequency domain (D1 or D2 interval) without being related by a continuous alteration process, is referred to follow a scale-free, power-law behavior. A scale-free, power-law behavior is not applicable to derive input parameters for high-frequency acoustic modeling [5]. Therefore, slope and intercept values derived by the Heincke data with benthic coverage <2% must be considered to introduce error associated with the backscatter prediction. Unfortunately, no lander-based acoustic data was available for the Mya data [7] with benthic coverage >2.5%, where an interaction between epibenthos and hydrodynamic bedforms was demonstrated.
Moreover, benthic structures, which do not form a continuous cover and approach the size of the acoustic wavelengths, must be considered as discrete objects [9,23]. A previously performed data/model comparison for sandy site demonstrated that for frequencies of about 200 kHz, shell fragments and benthic structures act as discrete objects. Scattering from discrete objects can become the dominant scatter mechanism [23,29,30]. This scatter mechanism may affect the lander backscatter measurement; however, it has not been considered by the model.
5. Conclusions
The results of an optical–acoustic lander experiment in a sand environment offshore Sylt island (German North Sea) show that sparse benthic life dominated by tubeworms, shell fragments, and brittlestars (1–5% seafloor coverage) impacts seafloor roughness at spatial wavelengths of 0.005 to 0.03 m and increases both the spectral slope and intercept. In turn, backscatter strengths modeled by the small-roughness perturbation approximation are strongly influenced by sparse benthic organism abundance. However, measured acoustic data do not agree with the modeled data or correlate with benthic coverage (backscatter difference of 1.1 dB). This suggests that sparse benthic life cannot be reliably detected by each acoustic scatter data set. While a clear impact of local benthic habitats on backscatter data has been demonstrated in the past, the lower limit of biological abundance that can be detected in the studied sandy environment remains to be determined. In addition, for this study, the small-roughness perturbation approximation for interface scatter was not suitable to predict backscatter values for the sedimentary facies, including low abundance of benthic organisms at frequencies typically utilized during ship-based acoustic surveys. In addition, the non-linearity in the power spectra introduced by benthic life must be considered when modeling backscatter strengths of lower frequencies.
Supplementary Materials
The ship-based survey data, acoustic and optic lander data, and code developed for this study can be found within the PANGEA database (https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.907370; Schönke et al. (2019) “ Impact of sparse benthic life on seafloor roughness and high-frequency acoustic scatter.”).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F., M.S., D.W., and S.P.; methodology, M.S., P.F., and D.W.; software, M.S. and L.W.; validation, L.W. and I.S.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, M.S., P.F., D.W., S.P., and L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S. and P.F.; writing—review and editing, I.S., L.W., A.D. and S.P.; visualization, M.S. and I.S.
Funding
Part of this work resulted from the BONUS ECOMAP project, supported by BONUS (Art 185), funded jointly by the EU and the Federal Ministry of Education and Research of Germany (BMBF), the National Centre for Research and Development of Poland (NCBR), and the Innovation Fund Denmark (Innovationsfonden).
Acknowledgments
We thank the master and crew of FS Heincke for their support during our research survey HE486. The helpful comments of the reviewers and the editors are highly appreciated. We thank Philipp Held, Arne Lohrberg, and our student assistants for their assistance during the fieldwork. A very special thanks goes to Gerald Nickel for the development of the acoustic system hardware and its control software.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
For backscatter strength modeling, the small-roughness perturbation approximation was applied considering the fluid seafloor model, using the method described by [5]. The small-roughness perturbation approximation describes the physical interaction between the acoustic wavefield and the sediment interface via partial equations. The three central components are (1) the surface roughness (slope and intercept) of the scattering cross sections, (2) the 2D wave vector ( of the wavefield, and (3) the constrain of the applied seafloor model (). The model was computed based on the following assumptions, moderate grazing angle (50°), homogeneous sediment composition, homogeneous subsurface without layering or gradient, sandy seafloor, surface scatter as dominant scatter mechanism, and the surfaces roughness is given by a power law form. Volume scatter was neglected. All parameters, except those related to surface roughness, are assumed to be constant. The model approach is performed to estimate the relative backscatter variation caused by surface roughness.
Values given by field measurements: wavenumber , slope , intercept , sound speed in water , frequency f
Literature values listed by reference [38]: Density ratio, = 1.85, sound speed ratio = 1.18, absorption coefficient = 0.016
Determination of the angles for the incoming and scattered acoustic wavefield:
: scattering angle, for monostatic, scatter geometry = 50 deg
: angle describing the direction of the receiving wavefield = 180 deg
: angle describing the direction of transmitted wavefield = 360 deg;
Computation of the acoustic wavelength in water (λ) and the acoustic wavenumber in water ):
, with λ = .
The 2D wavevector defined at the scattering cross section, which combines the movement direction between the incidence wave and the wave direction toward the receiver:
The complex sound speed ratio :
Factor B to describe the subseafloor stratification for a fluid–fluid boundary layer:
The imaginary angle , required to describe the angle between the seafloor surface and the moment direction of the p-wave within the sediment layer:
Computing the impedance contrast () at the water-sediment interface:
Determination of the reflection coefficient for the transmitted and received wave field:
The green’s function G gives the special solution for the movement of the wave field:
A dimensionless factor , according to the seafloor model (fluid theory):
Predicted backscatter for scattering cross section:
Correction for the footprint (A) for the scattering cross section:
References
- Lyons, B.P.; Thain, J.E.; Stentiford, G.D.; Hylland, K.; Davies, I.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Using biological effects tools to define Good Environmental Status under the European Union Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report of the Working Group on Acoustic and Egg Surveys for Sardine and Anchovy in ICES Areas VIII and IX (WGACEGG); ICES: Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 2007; p. 163.
- Bouwma, I.; Schleyer, C.; Primmer, E.; Winkler, K.J.; Berry, P.; Young, J.; Carmen, E.; Jana, Š.; Bezák, P.; Preda, E. Adoption of the ecosystem services concept in EU policies. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roadmap for Maritime Spatial Planning: Achieving Common Principles in the EU; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008; pp. 1–11.
- Jackson, D.R.; Richardson, M. High-Frequency Seafloor Acoustics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9780387369457. [Google Scholar]
- Self, R.F.L.; A’Hearn, P.; Jumars, P.A.; Jackson, D.R.; Richardson, M.D.; Briggs, K.B. Effects of macrofauna on acoustic backscatter from the seabed: Field manipulations in West Sound, Orcas Island, Washington, U.S.A. J. Mar. Res. 2001, 59, 991–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönke, M.; Feldens, P.; Wilken, D.; Papenmeier, S.; Heinrich, C.; von Deimling, J.S.; Held, P.; Krastel, S. Impact of Lanice conchilega on seafloor microtopography off the island of Sylt (German Bight, SE North Sea). Geo-Marine Lett. 2016, 37, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, T.; Jenkins, C. Physik biologisch besiedelter Meeresböden. J. Appl. Hydrogr. 2017, 106, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, K.B.; Williams, K.L.; Richardson, M.D.; Jackson, D.R. Effects of Changing Roughness on Acoustic Scattering: (1) Natural Changes. Proc. Inst. Acoust. 2001, 23, 343–390. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.D.; Briggs, K.B.; Bentley, S.J.; Walter, D.J.; Orsi, T.H. The effects of biological and hydrodynamic processes on physical and acoustic properties of sediments off the Eel River, California. Mar. Geol. 2002, 182, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, M.S.; Lee, K.M. The Acoustics of Marine Sediments. Acoust. Today 2017, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.D.; Jaffe, J.S. Time-evolution of high-resolution topographic measurements of the sea floor using a 3-D laser line scan mapping system. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 27, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.D.; Briggs, K.B.; Bibee, L.D.; Jumars, P.A.; Sawyer, W.B.; Albert, D.B.; Bennett, R.H.; Berger, T.K.; Buckingham, M.J.; Chotiros, N.P.; et al. Overview of SAX99: Environmental considerations. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 26–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, C.; Feldens, P.; Schwarzer, K. Highly dynamic biological seabed alterations revealed by side scan sonar tracking of Lanice conchilega beds offshore the island of Sylt (German Bight). Geo-Marine Lett. 2017, 37, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, C.; Grabowski, J.H.; Brown, C.J.; Weber, T.C.; Quinn, R. Detection of deep water benthic macroalgae using image-based classification techniques on multibeam backscatter at Cashes Ledge, Gulf of Maine, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, C.; Brown, C.; Quinn, R.; Grabowski, J. Evaluation of image-based multibeam sonar backscatter classification for benthic habitat discrimination and mapping at Stanton Banks, UK. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Hasan, R.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Laurenson, L. Combining angular response classification and backscatter imagery segmentation for benthic biological habitat mapping. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 97, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bas, T.P.P.; Huvenne, V.A.I. Acquisition and processing of backscatter data for habitat mapping—Comparison of multibeam and sidescan systems. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldens, P.; Schulze, I.; Papenmeier, S.; Schönke, M.; Schneider von Deimling, J. Improved Interpretation of Marine Sedimentary Environments Using Multi-Frequency Multibeam Backscatter Data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Degrendele, K.; Vrignaud, C.; Loyer, S.; Le Bas, T.; Augustin, J.M.; Lurton, X. Control of the repeatability of high frequency multibeam echosounder backscatter by using natural reference areas. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, X.; Lamarche, G.; Brown, C.; Lucieer, V.; Rice, G.; Schimel, A.; Weber, T. Backscatter Measurements by Seafloor—Mapping Sonars. In Guidelines and Recommendations; Lurton, X., Lamarche, G., Eds.; 2015; p. 200. Available online: http://geohab.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/BWSG-REPORT-MAY2015.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Wendelboe, G. Backscattering from a sandy seabed measured by a calibrated multibeam echosounder in the 190–400 kHz frequency range. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Briggs, K.; Williams, K.; Tang, D.; Jackson, D.; Thorsos, E. The effects of seafloor roughness on acoustic scattering: Manipulative experiments. In Boundary Influences in High Frequency Shallow Water Acoustics; Pace, N., Blondel, P., Eds.; University of Bath: Bath, UK, 2005; Volume 298, pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Buscombe, D.; Grams, P.E.; Kaplinski, M.A. Characterizing riverbed sediment using high-frequency acoustics: 1. Spectral properties of scattering. J. Geophys. Res. F Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 2674–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, L. Acoustic Remote Sensing as a Tool for Habitat Mapping in Alaska Waters. Mar. Habitat Mapp. Technol. Alaska 2008, 10, 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D. Fine-scale measurements of sediment roughness and subbottom variability. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiros, N.P.; Isakson, M.J. The evolution of sediment acoustic models. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1495, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.R.; Briggs, K.B. High-frequency bottom backscattering: Roughness versus sediment volume scattering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 92, 962–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivakin, A.N. High frequency scattering from sandy sediments: Roughness vs. discrete inclusions. In Proceedings of the Boundary Influences in High Frequency Shallow Water Acoustics, Bath, UK, 5–9 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ivakin, A.N. Scattering from discrete inclusions in marine sediments. In Proceedings of the Seventh European Conference on Underwater Acoustics, ECUA 2004, Delft, The Netherlands, 5–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Valerius, J.; Kösters, F.; Zeiler, M. Erfassung von Sandverteilungsmustern zur großräumigen Analyse der Sedimentdynamik auf dem Schelf der Deutschen Bucht. Die Küste 2015, 83, 39–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.; Schwarzer, K.; Ricklefs, K. Seabed morphology and sediment dynamics. Kuste 2008, 74, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Salzwedel, H.; Eike, R.; Dieter, G. Benthic macrofauna communities in the German Bight. In Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven; Salzwedel, H., Eike, R., Dieter, G., Eds.; Institute for Marine Research in Bremerhaven: Bremerhaven, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Benthosuntersuchungen im Rahmen des Beweissicherungsverfahrens für den Ausbau des Hafenbecken IV in Büsum. Available online: https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/44126/ (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Panda, S.; Panzade, A.; Sarangi, M.; Chowdhury, S.K.R. Spectral Approach on Multiscale Roughness Characterization of Nominally Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidick, E. Power spectral density specification and analysis of large optical surfaces. Model. Asp. Opt. Metrol. II 2009, 7390, 73900L. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, K.B.; Lyons, A.P.; Pouliquen, E.; Mayer, L.A.; Richardson, M.D. Seafloor roughness, sediment grain size, and temporal stability. Nav. Res. LAB STENNIS Sp. Cent. MS SEAFLOOR Sci. Dir. 2005, 298, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørnø, L. Applied Underwater Acoustics; Neighbors, T., Bradley, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-811240-3. [Google Scholar]
- Degraer, S.; Moerkerke, G.; Rabaut, M.; Van Hoey, G.; Du Four, I.; Vincx, M.; Henriet, J.P.; Van Lancker, V. Very-high resolution side-scan sonar mapping of biogenic reefs of the tube-worm Lanice conchilega. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peine, F.; Friedrichs, M.; Graf, G. Potential influence of tubicolous worms on the bottom roughness length z 0 in the south-western Baltic Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2009, 374, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.R.; Richardson, M.D.; William, K.L.; Lyons, A.P.; Jones, C.D.; Briggs, K.B.; Tang, D. Acoustic observation of the time dependence of the roughness of sandy seafloors. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 34, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Davies, G.; Bellettini, A.; Pinto, M. Multipath Effect on DPCA Micronavigation of a Synthetic Aperture Sonar. In Impact of Littoral Environmental Variability of Acoustic Predictions and Sonar Performance; Pace, N.G., Jensen, F.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, K.L.; Jackson, D.R.; Thorsos, E.I.; Tang, D.; Briggs, K.B. Acoustic backscattering experiments in a well characterized sand sediment: Data/model comparisons using sediment fluid and Biot models. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 27, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, A.P.; Fox, W.L.J.; Hasiotis, T.; Pouliquen, E. Characterization of the two-dimensional surface roughness of a wave-rippled sea floor using digital photography. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 27, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Roche, M.; Lurton, X.; Degrendele, K.; Terseleer, N.; Van Lancker, V. Seafloor change detection using multibeam echosounder backscatter: Case study on the Belgian part of the North Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Roche, M.; Degrendele, K.; Lurton, X.; Terseleer, N.; Baeye, M.; Francken, F.; Van Lancker, V. Insights into the Short-Term Tidal Variability of Multibeam Backscatter from Field Experiments on Different Seafloor Types. Geosciences 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, K.B.; Tang, D.; Williams, K.L. Characterization of interface roughness of rippled sand off fort Walton Beach, Florida. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 27, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).