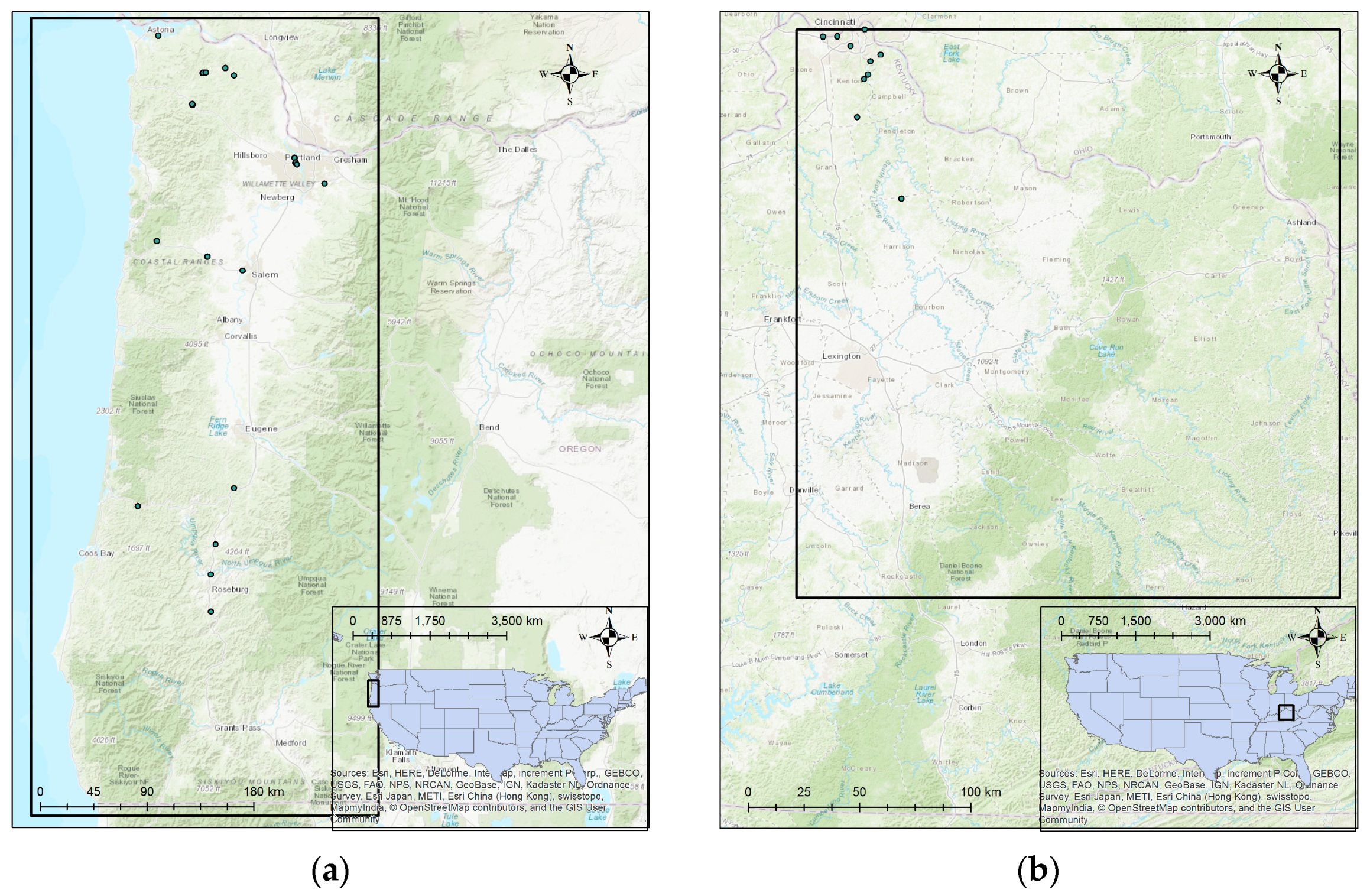
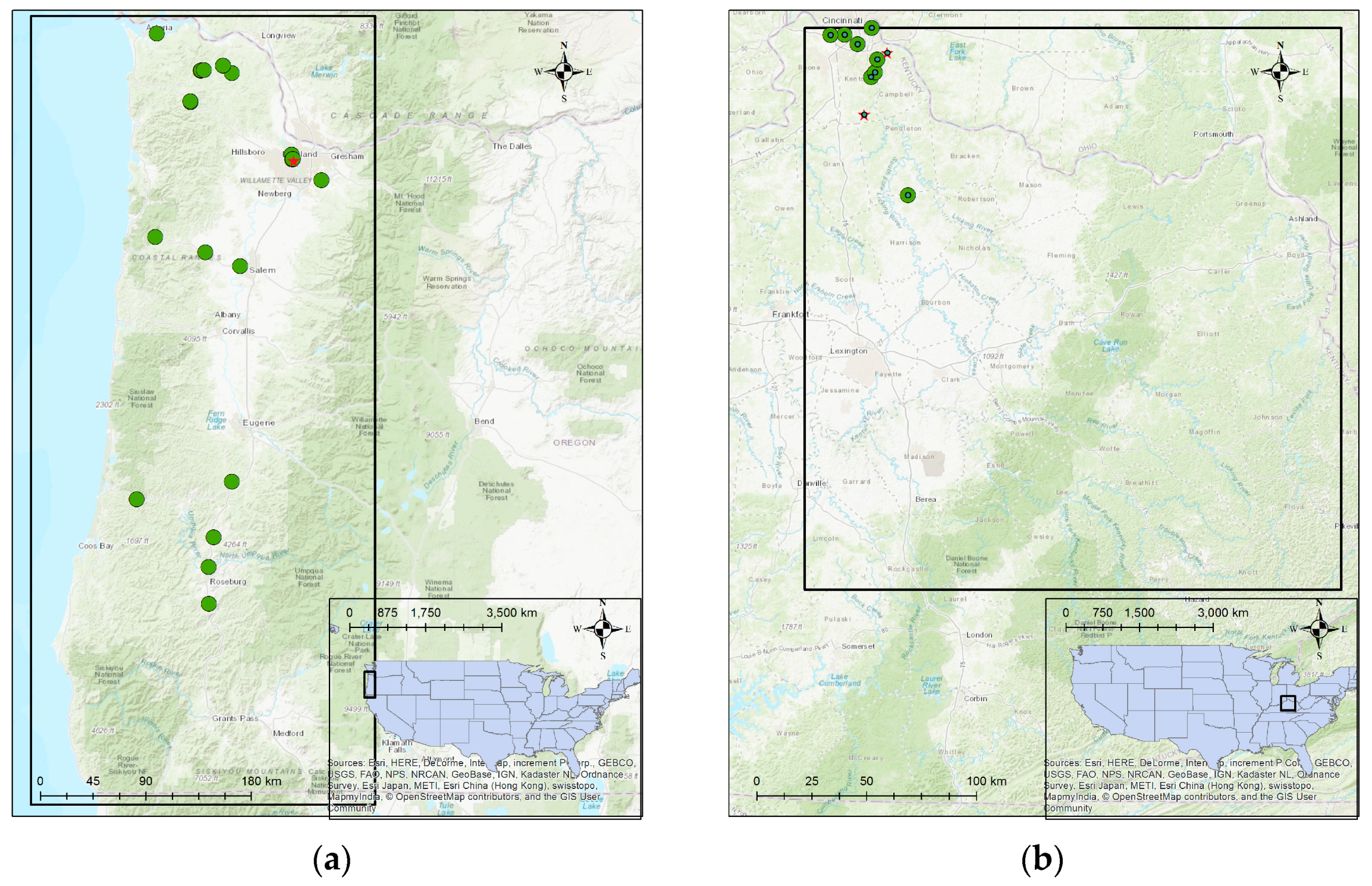
Figure 1.
Selected soil slide sites from (a) Oregon, United States (USA) and (b) Kentucky, USA.
Figure 1.
Selected soil slide sites from (a) Oregon, United States (USA) and (b) Kentucky, USA.
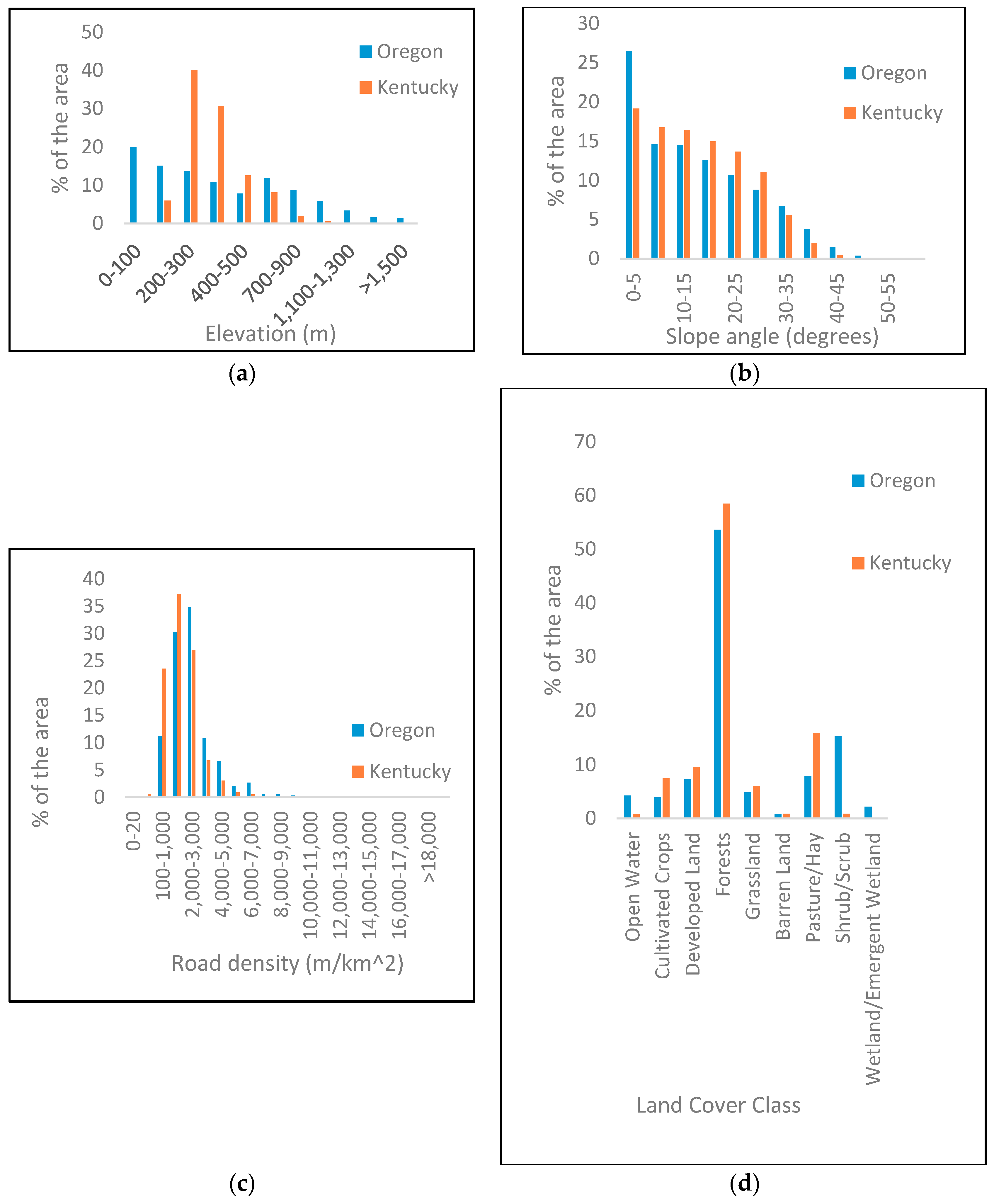
Figure 2.
Frequency distributions of (a) elevation; (b) slope angle; (c) road density; and (d) land cover in the two study areas.
Figure 2.
Frequency distributions of (a) elevation; (b) slope angle; (c) road density; and (d) land cover in the two study areas.
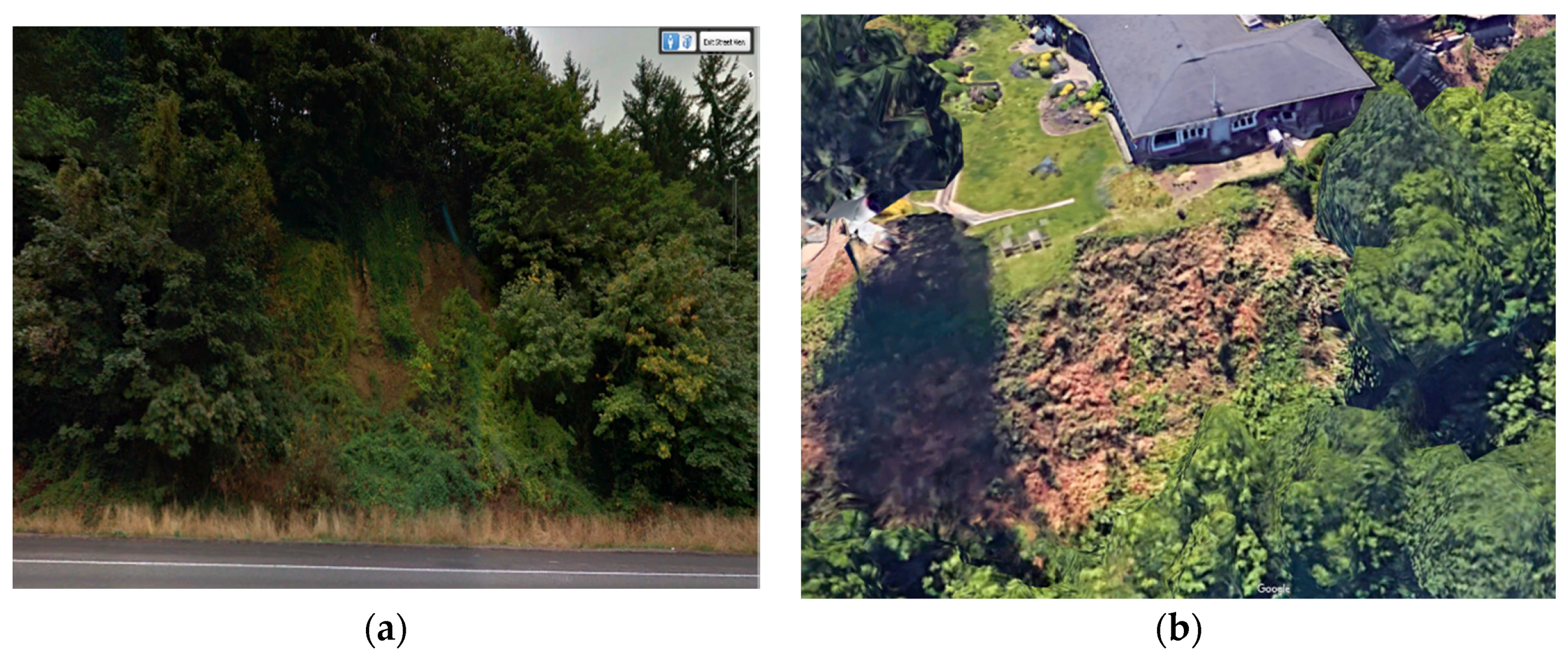
Figure 3.
(a,b) Images of two sample locations that were excluded from the study due to the presence of exposed rock (Google Earth, 2018).
Figure 3.
(a,b) Images of two sample locations that were excluded from the study due to the presence of exposed rock (Google Earth, 2018).
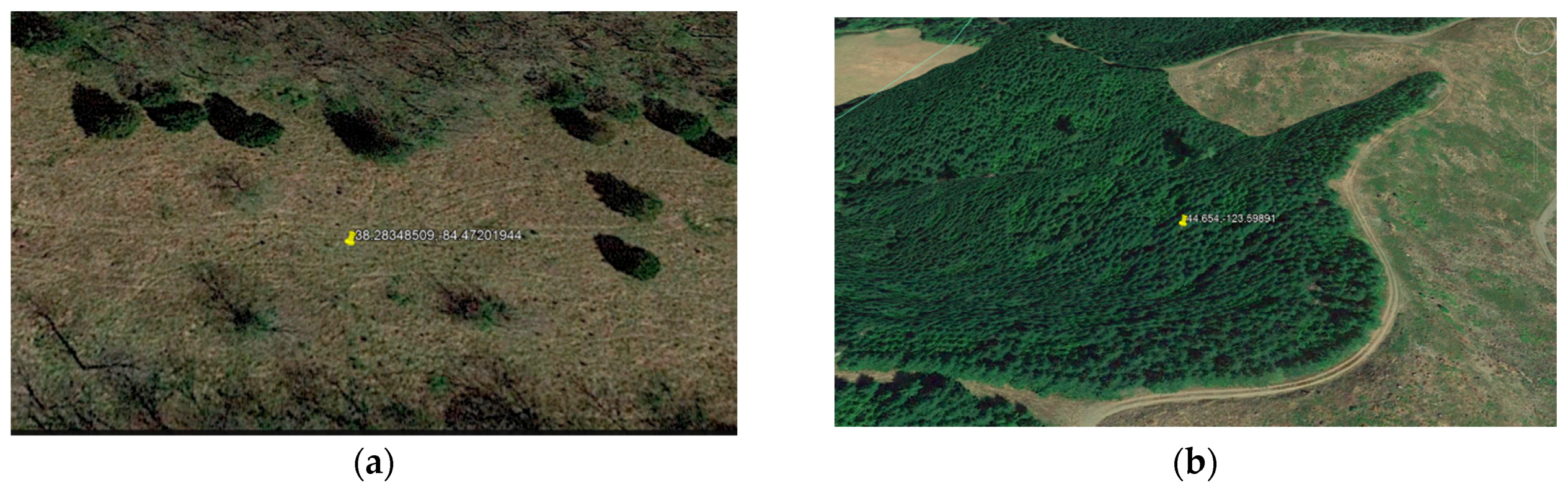
Figure 4.
(a,b) May 2018 images of two selected soil slide sites (Google Earth, 2018).
Figure 4.
(a,b) May 2018 images of two selected soil slide sites (Google Earth, 2018).
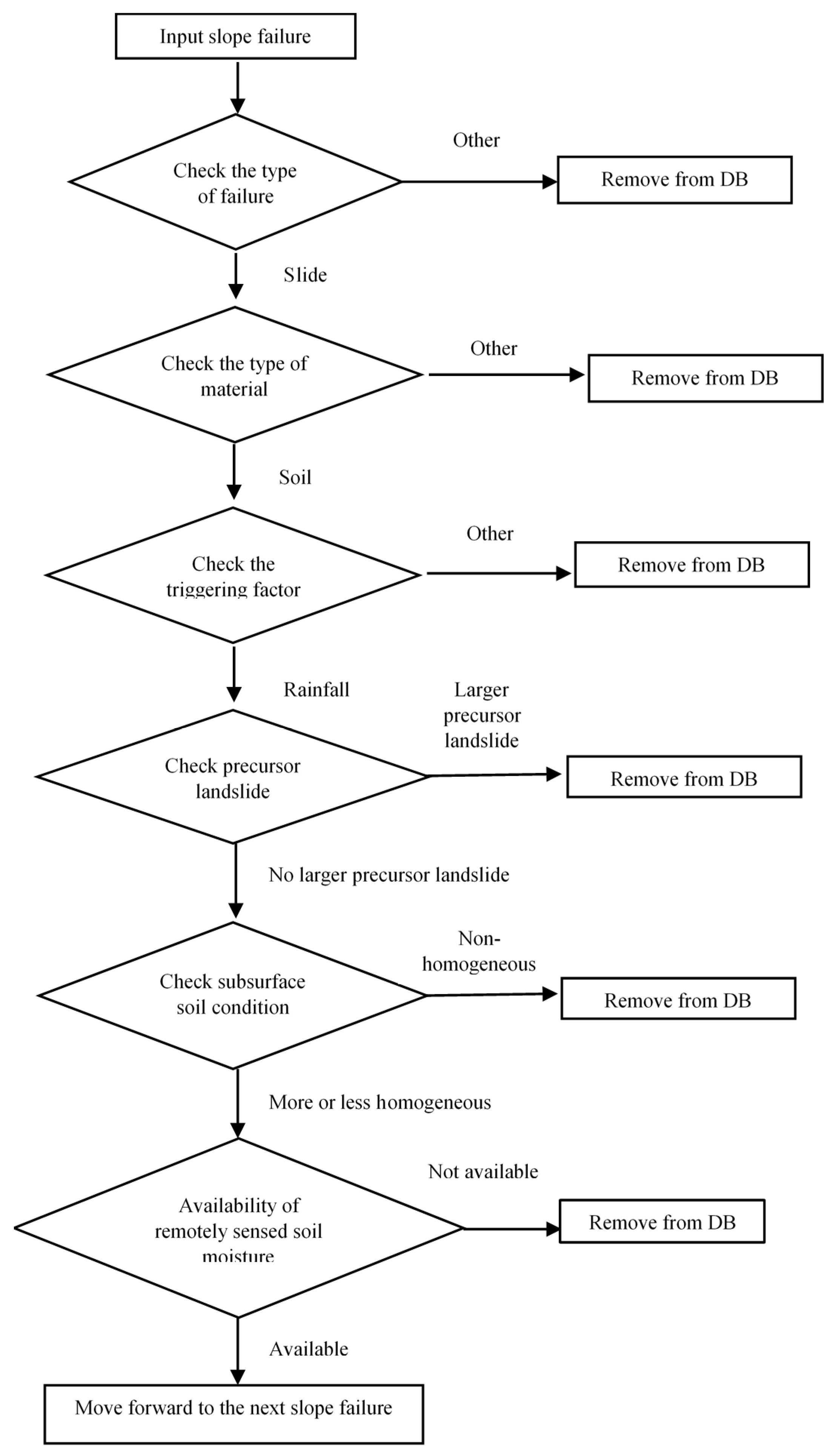
Figure 5.
Procedure for selecting soil slide sites for this study.
Figure 5.
Procedure for selecting soil slide sites for this study.
Figure 6.
(a,b) Two randomly selected non-soil slide locations used in the study (Google Earth, 2018).
Figure 6.
(a,b) Two randomly selected non-soil slide locations used in the study (Google Earth, 2018).
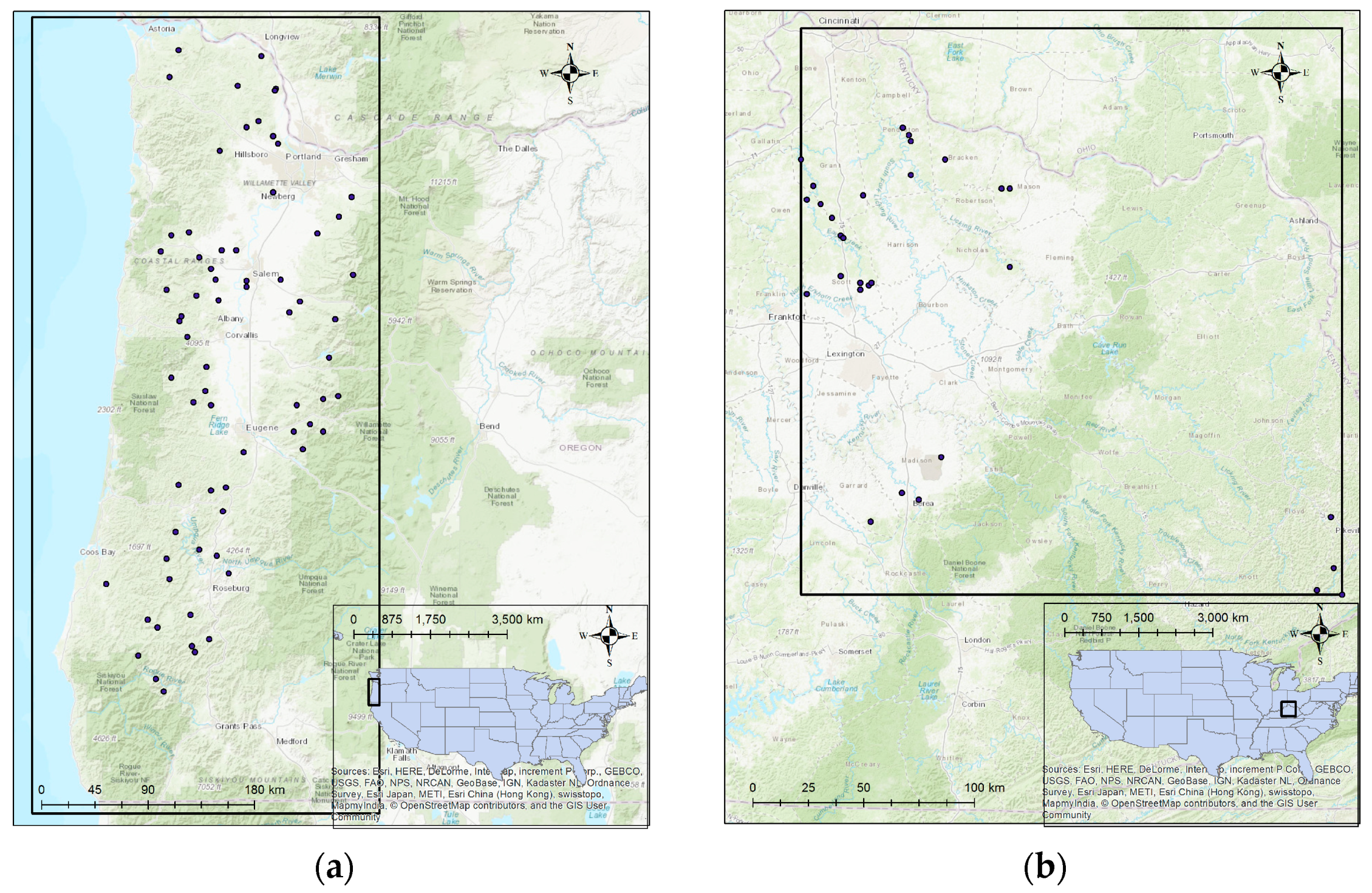
Figure 7.
Selected non-soil slides from (a) Oregon, USA, and (b) Kentucky, USA.
Figure 7.
Selected non-soil slides from (a) Oregon, USA, and (b) Kentucky, USA.
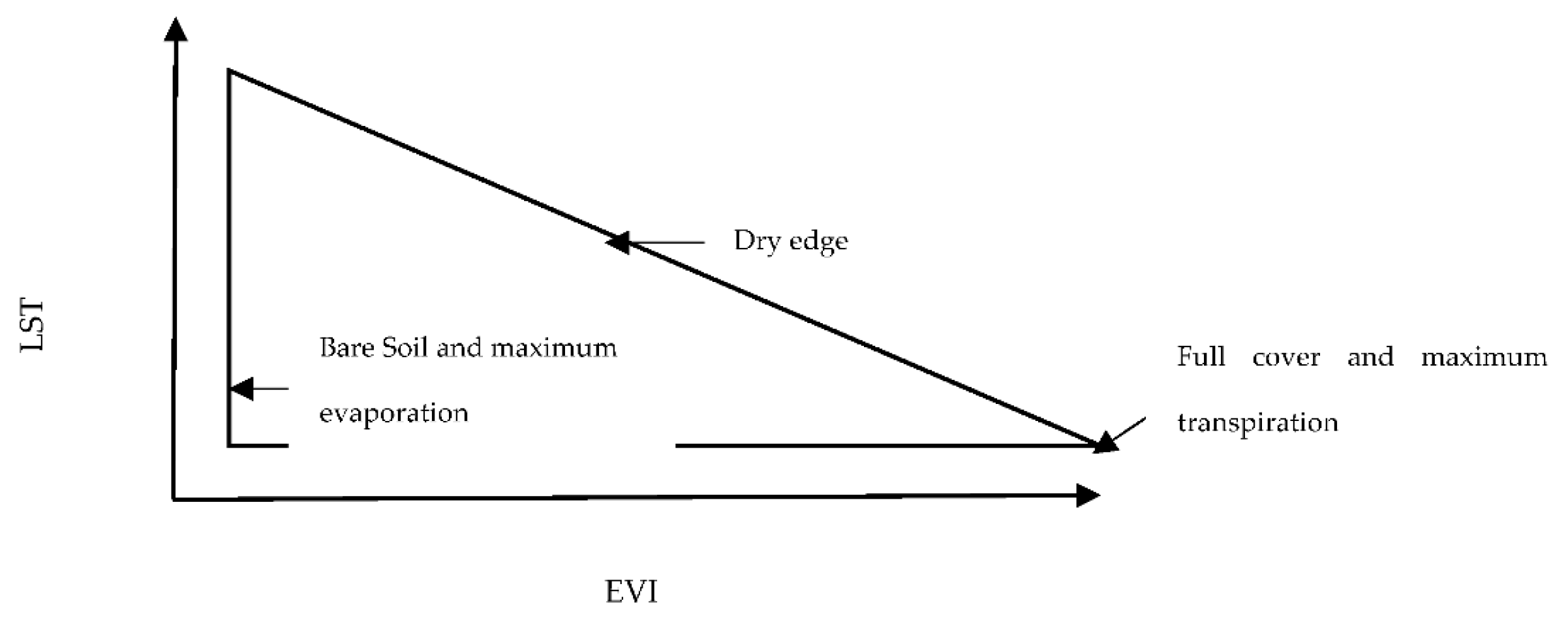
Figure 8.
Triangular relationship between land surface temperature (LST) and the enhanced vegetation index (EVI).
Figure 8.
Triangular relationship between land surface temperature (LST) and the enhanced vegetation index (EVI).
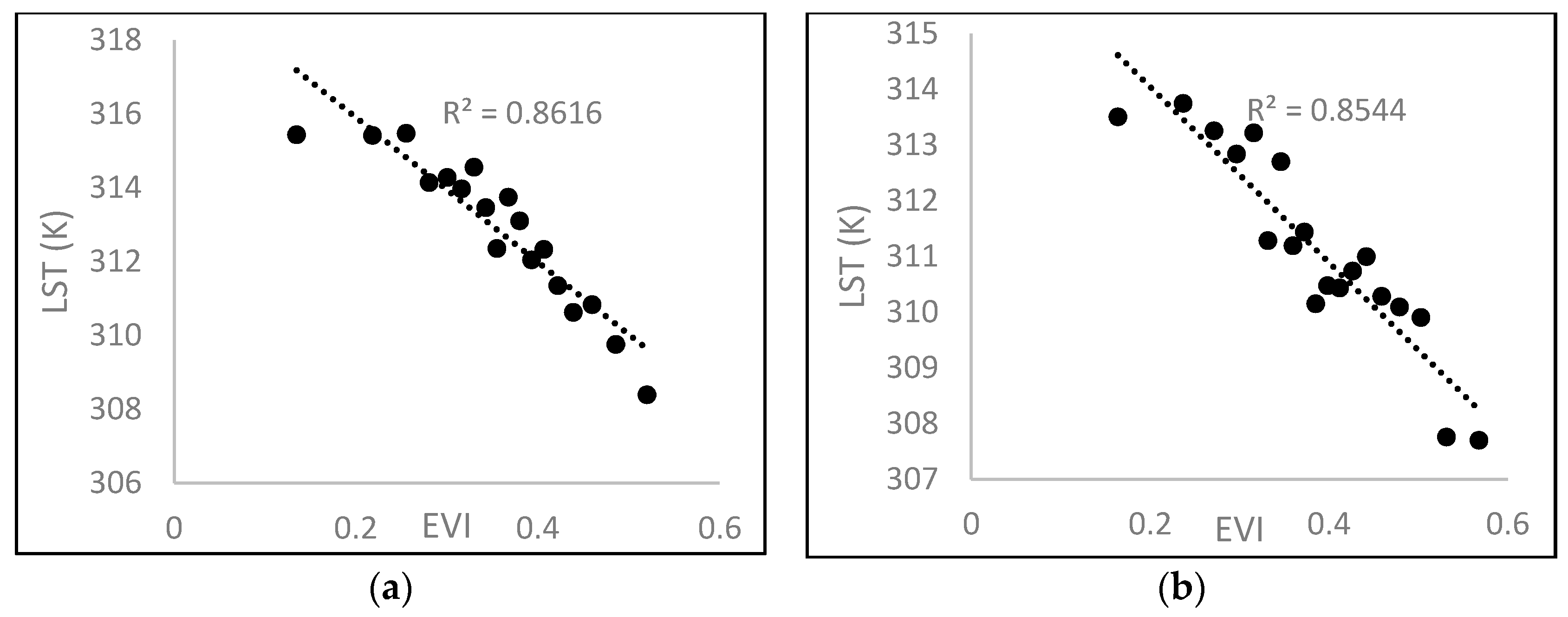
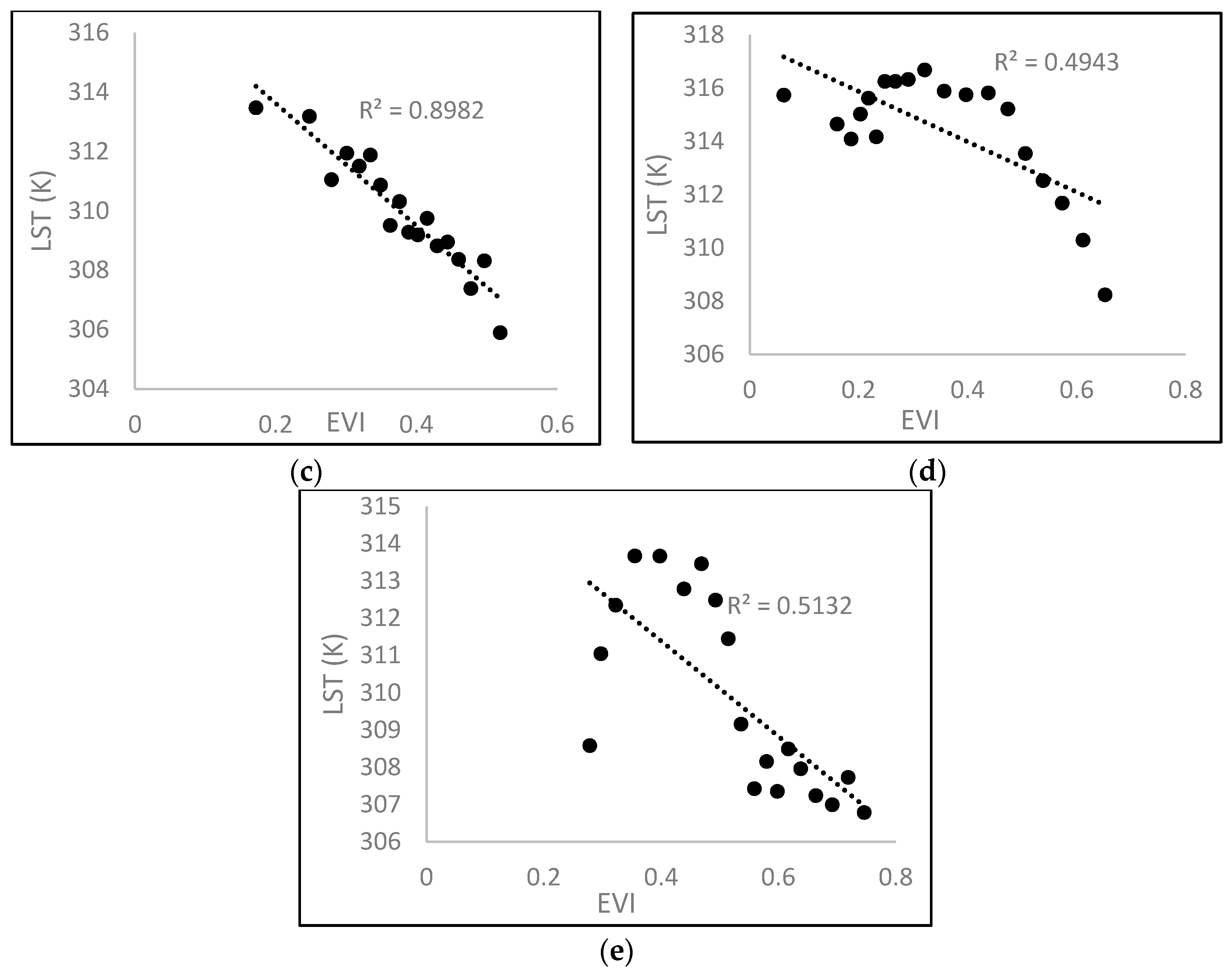
Figure 9.
Dry edge parameters of (a) the top window of Oregon; (b) the middle window of Oregon; (c) the bottom window of Oregon; (d) the top window of Kentucky; and (e) the bottom window of Kentucky.
Figure 9.
Dry edge parameters of (a) the top window of Oregon; (b) the middle window of Oregon; (c) the bottom window of Oregon; (d) the top window of Kentucky; and (e) the bottom window of Kentucky.
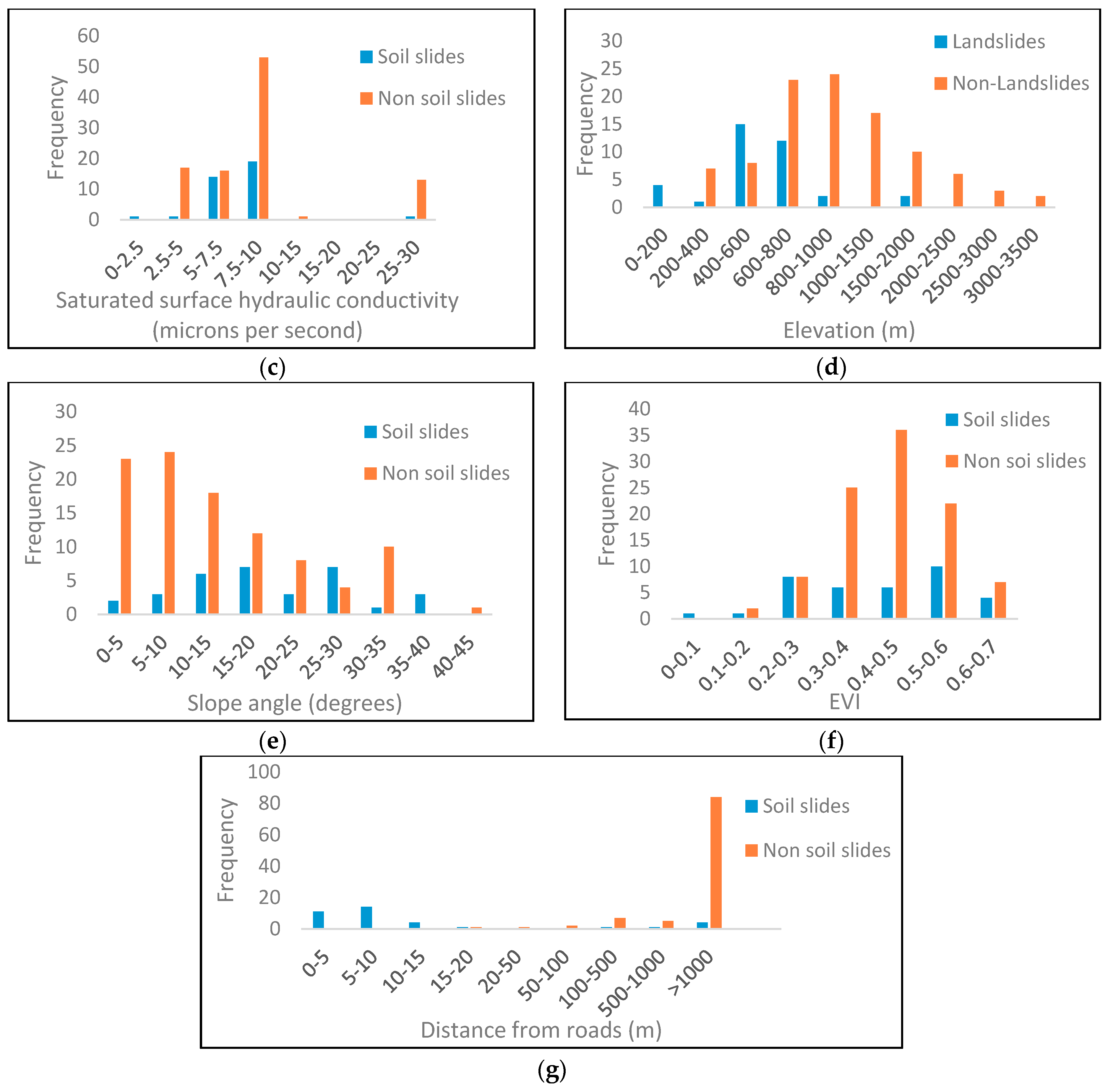
Figure 10.
Frequency distribution of (a) downscaled soil moisture; (b) undownscaled soil moisture; (c) saturated surface hydraulic conductivity; (d) elevation; (e) slope angle; (f) EVI; and (g) distance from roads.
Figure 10.
Frequency distribution of (a) downscaled soil moisture; (b) undownscaled soil moisture; (c) saturated surface hydraulic conductivity; (d) elevation; (e) slope angle; (f) EVI; and (g) distance from roads.
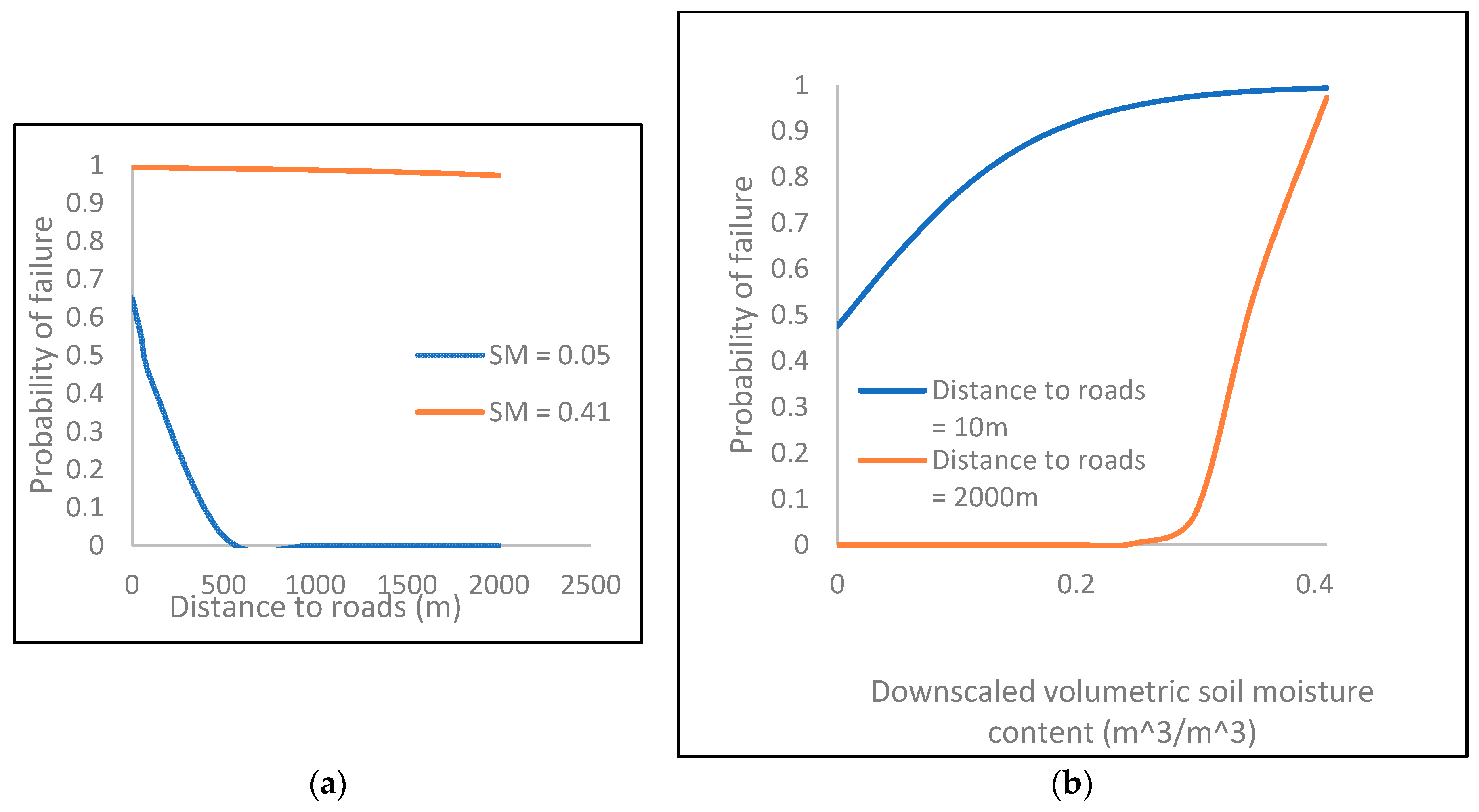
Figure 11.
Variation of probability of failure with distance to roads (a) under low and high soil moisture contents; and (b) at low and high distances from roads.
Figure 11.
Variation of probability of failure with distance to roads (a) under low and high soil moisture contents; and (b) at low and high distances from roads.
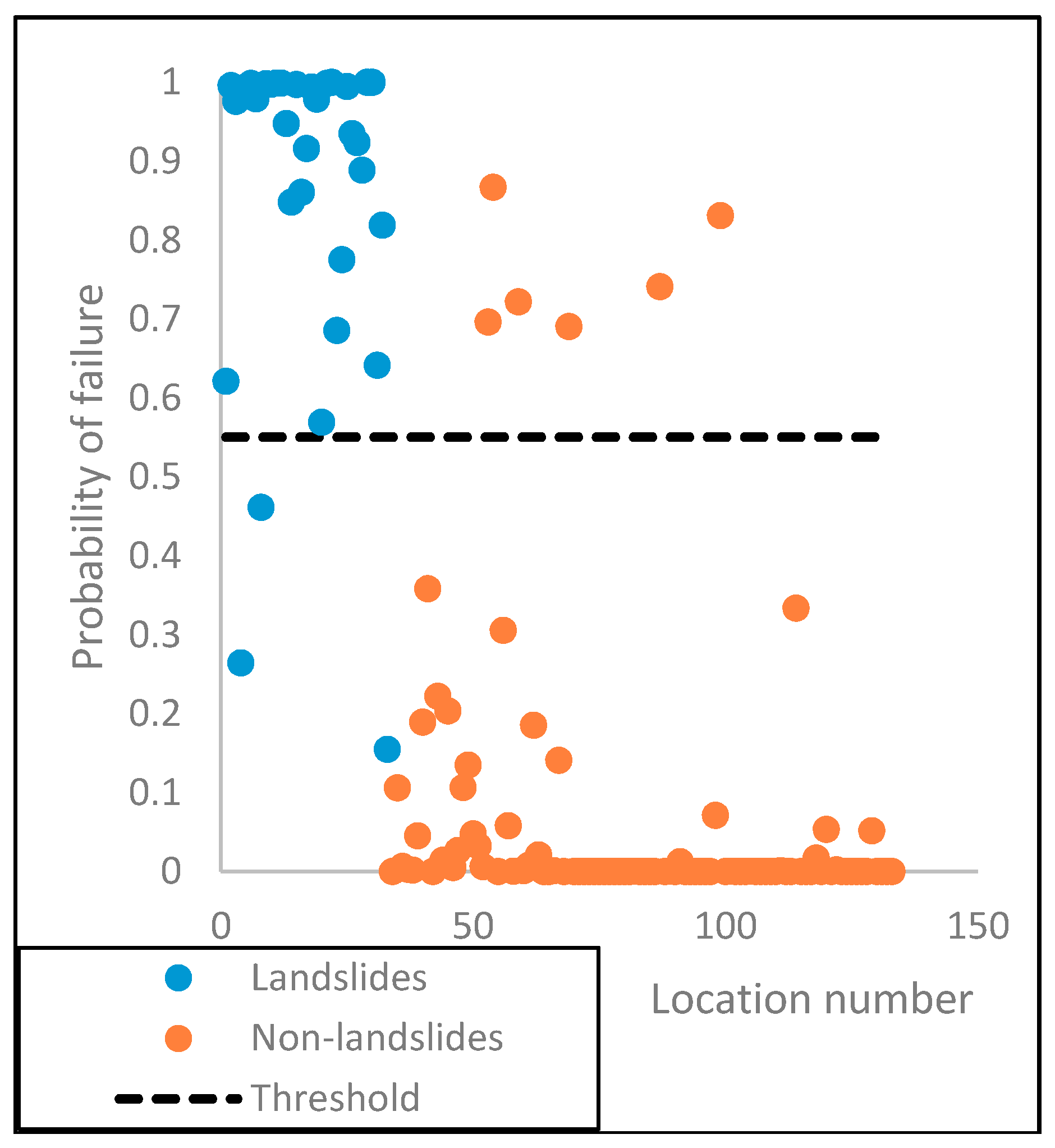
Figure 12.
Distribution of the predicted probability of failure at the soil slide and non-soil slide locations.
Figure 12.
Distribution of the predicted probability of failure at the soil slide and non-soil slide locations.
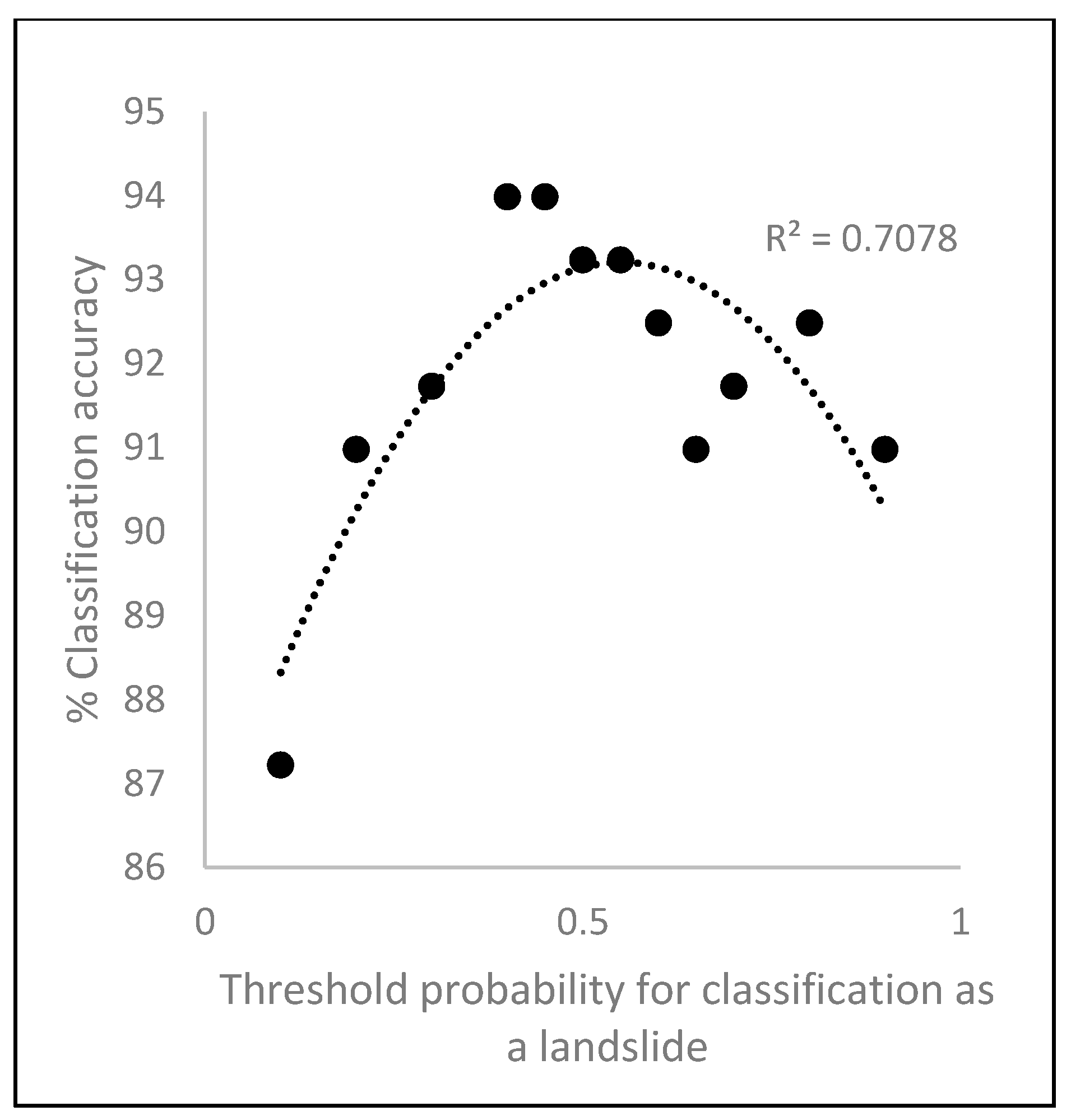
Figure 13.
Selection of the failure probability threshold by maximizing the classification accuracy.
Figure 13.
Selection of the failure probability threshold by maximizing the classification accuracy.
Figure 14.
Classification of soil slides in (a) Oregon and (b) Kentucky.
Figure 14.
Classification of soil slides in (a) Oregon and (b) Kentucky.
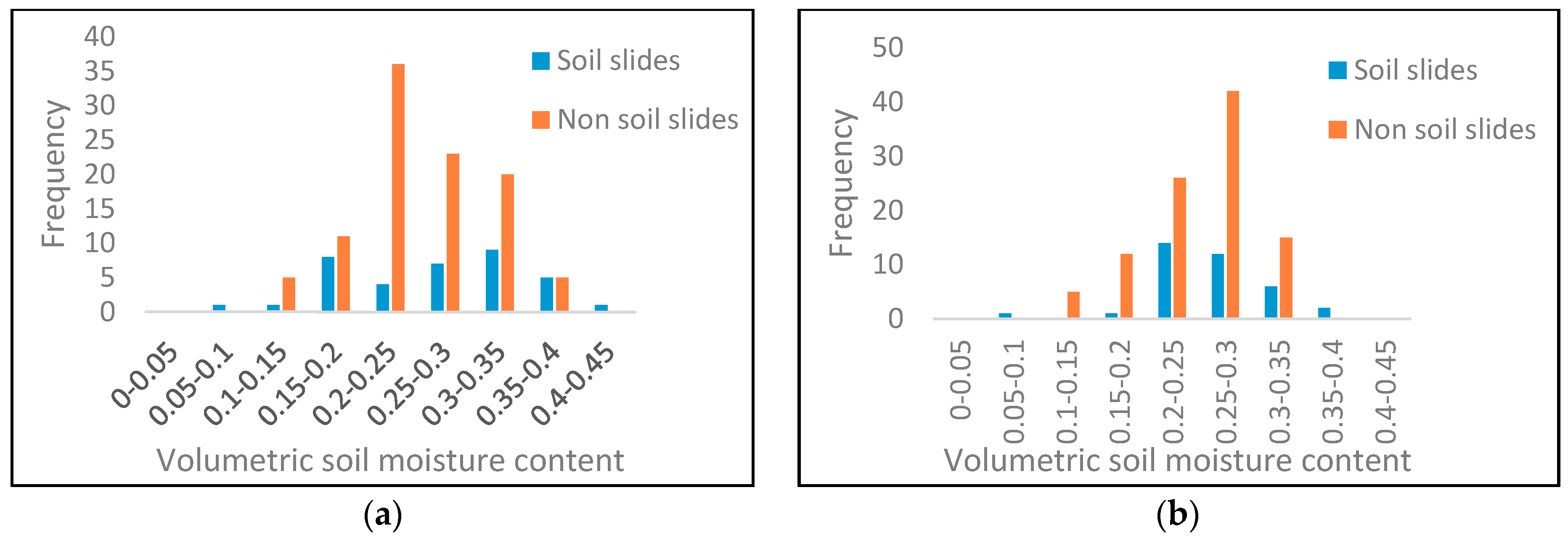
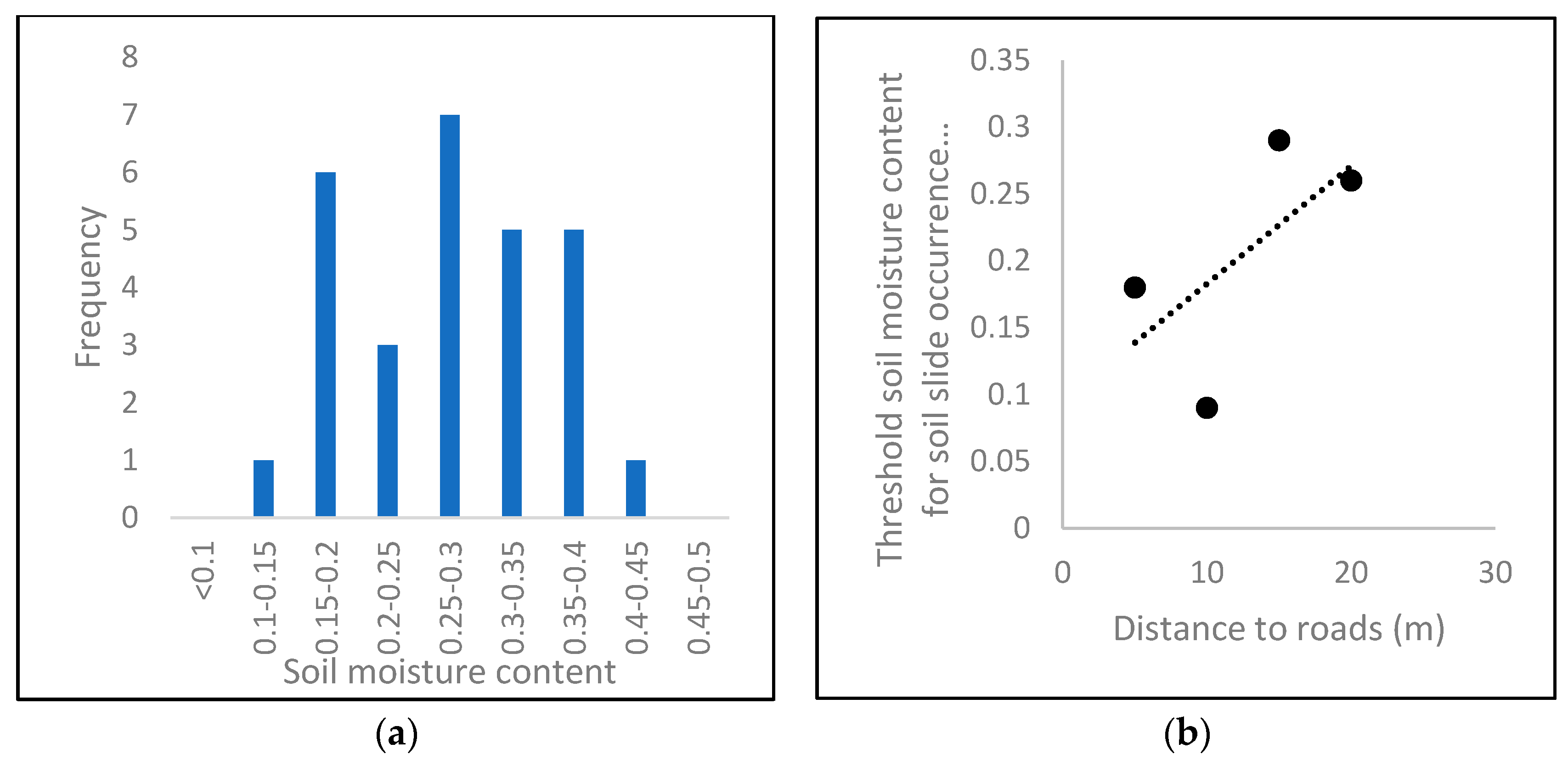
Figure 15.
(a) Frequency distribution of soil moisture at a 20-m distance from roads and (b) the variation of soil moisture thresholds for soil slide occurrence with distance from roads within a 20-m influence zone.
Figure 15.
(a) Frequency distribution of soil moisture at a 20-m distance from roads and (b) the variation of soil moisture thresholds for soil slide occurrence with distance from roads within a 20-m influence zone.
Table 1.
Correlation matrix of the explanatory variables.
Table 1.
Correlation matrix of the explanatory variables.
| Variable | Elevation (m) | Slope | Presence of Clay Soil Type (Categorical Variable) | Presence of Silt Soil Type (Categorical Variable) | Presence of Gravel Soil Type (Categorical Variable) | Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) | Downscaled Soil Moisture |
| Elevation (m) | - | 0.17 | −037 | 0.03 | 0.46 | −0.002 | −0.03 |
| Slope | 0.17 | - | −0.28 | −0.03 | 0.41 | −0.04 | 0.07 |
| Presence of clay soil type (categorical variable) | −0.37 | −0.28 | - | −0.70 | −0.50 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Presence of silt soil type (categorical variable) | 0.03 | −0.03 | −0.70 | - | −0.28 | −0.03 | −0.04 |
| Presence of gravel soil type (categorical variable) | 0.46 | 0.41 | −0.50 | −0.28 | - | 0 | −0.02 |
| EVI | −0.002 | −0.04 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0 | - | −0.23 |
| Downscaled soil moisture | −0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 | −0.04 | −0.02 | −0.23 | - |
| Undownscaled soil moisture | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0 | −0.11 | −0.16 | 0.83 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | 0.42 | 0.42 | −0.44 | −0.15 | 0.77 | 0.02 | −0.09 |
| Distance from roads (m) | 0.67 | 0.19 | −0.44 | 0.06 | 0.52 | −0.02 | −0.19 |
| Proximity to drainage (m) | −0.05 | −0.14 | 0.18 | −0.08 | −0.14 | 0.26 | 0.01 |
| Drainage density (m−1) | 0.32 | 0.36 | −0.31 | 0.12 | 0.27 | −0.17 | −0.02 |
| TWI | −0.19 | −0.60 | 0.09 | 0.08 | −0.21 | 0.04 | −0.06 |
| Variable | Un-Downscaled Soil Moisture | Saturated Surface Hydraulic Conductivity | Distance from Roads (m) | Distance to Drainage (m) | Drainage Density (m−1) | Topographic Wetness Index (TWI) |
| Elevation (m) | −0.02 | 0.42 | 0.67 | −0.05 | 0.32 | −0.19 |
| Slope | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.19 | −0.14 | 0.36 | −0.60 |
| Presence of clay soil type (categorical variable) | 0.07 | −0.44 | −0.44 | 0.18 | −0.31 | 0.09 |
| Presence of silt soil type (categorical variable) | 0 | −0.15 | 0.06 | −0.08 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| Presence of gravel soil type (categorical variable) | −0.11 | 0.77 | 0.52 | −0.14 | 0.27 | −0.21 |
| EVI | −0.16 | 0.02 | −0.02 | 0.26 | −0.17 | 0.04 |
| Downscaled soil moisture | 0.83 | −0.09 | −0.19 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.06 |
| Undownscaled soil moisture | - | −0.16 | −0.21 | −0.05 | 0 | −0.05 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.16 | - | 0.57 | −0.09 | −0.19 | −0.20 |
| Distance from roads (m) | −0.21 | 0.57 | - | −0.18 | −0.16 | −0.10 |
| Proximity to drainage (m) | −0.05 | −0.09 | −0.18 | - | −0.06 | −0.07 |
| Drainage density (m−1) | 0 | −0.19 | −0.16 | −0.06 | 1 | −0.21 |
| TWI | −0.05 | −0.20 | −0.10 | −0.07 | −0.21 | - |
Table 2.
Statistics of the explanatory variables. EVI: Enhanced Vegetation Index.
Table 2.
Statistics of the explanatory variables. EVI: Enhanced Vegetation Index.
| Variable | Soil Slide Locations | Non-Soil Slide Locations |
|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|
| Downscaled soil moisture (m3/m3) | 0.2787 | 0.0750 | 0.2523 | 0.0585 |
| Undownscaled soil moisture (m3/m3) | 0.2682 | 0.0519 | 0.2503 | 0.0478 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | 7.84 | 4.15 | 10.04 | 7.39 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 20.93 | 12.29 | 13.34 | 9.68 |
| Elevation (m) | 189 | 100 | 335 | 200 |
| EVI | 0.4020 | 0.1568 | 0.4403 | 0.1105 |
| Distance from roads (m) | 257 | 637 | 6676 | 7511 |
Table 3.
The distribution of soil types at soil slide and non-soil slide locations.
Table 3.
The distribution of soil types at soil slide and non-soil slide locations.
| Soil Type | % Soil Slide Locations | % Non-Soil Slide Locations |
|---|
| GM (silty gravel) | 3.03 | 5 |
| GC (clayey gravel) | 0 | 16 |
| ML (low plasticity silt) | 27.27 | 14 |
| MH (high plasticity silt) | 0 | 14 |
| CL (low plasticity clay) | 27.27 | 29 |
| CH (high plasticity clay) | 42.42 | 22 |
Table 4.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the logistic regression model with all of the explanatory variables.
Table 4.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the logistic regression model with all of the explanatory variables.
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | −2.54 | – | −0.42 | 0.67 |
| Downscaled soil moisture | 17.47 | 1.05 | 2.44 | 0.01 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.01 | −1.92 | −2.01 | 0.04 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.18 | 1.92 | 2.76 | 0.01 |
| Distance from roads (m) | −0.003 | −19.86 | −3.30 | 0.001 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.38 | −2.55 | −1.71 | 0.09 |
| Presence of silt soil type (ML and MH) | 5.80 | 2.55 | 1.51 | 0.13 |
| Presence of clay soil type (CL and CH) | 3.35 | 1.65 | 0.90 | 0.37 |
| EVI | −2.42 | −0.29 | −0.59 | 0.56 |
Table 5.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with downscaled soil moisture content.
Table 5.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with downscaled soil moisture content.
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | 2.38 | - | 1.03 | 0.30 |
| Downscaled soil moisture | 12.48 | 0.72 | 1.71 | 0.09 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.01 | −2.03 | −2.32 | 0.02 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.17 | 1.79 | 2.98 | 0.003 |
| Distance from roads (m) | −0.009 | −65.37 | −2.44 | 0.01 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.52 | −3.43 | −2.61 | 0.009 |
| Presence of silt soil type (ML and MH) | 3.32 | 1.44 | 1.97 | 0.05 |
| Downscaled soil moisture × Distance to roads | 0.02 | 35.67 | 1.96 | 0.05 |
Table 6.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with undownscaled soil moisture content.
Table 6.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with undownscaled soil moisture content.
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | 0.54 | - | 0.20 | 0.84 |
| Undownscaled soil moisture | 12.15 | 0.57 | 1.48 | 0.14 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.007 | −1.48 | −1.98 | 0.05 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.14 | 1.47 | 2.99 | 0.003 |
| Distance from roads (m) | −0.002 | −16.24 | −3.64 | 0.0003 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.36 | −2.46 | −2.35 | 0.02 |
| Presence of silt soil type (ML and MH) | 2.12 | 0.94 | 1.77 | 0.08 |
Table 7.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with proximity to drainage accessories.
Table 7.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with proximity to drainage accessories.
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | 6.85 | - | 2.27 | 0.02 |
| Distance to drainage accessories (m) | −0.009 | −1.52 | −1.39 | 0.16 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.026 | −5.21 | −2.62 | 0.01 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.16 | 1.69 | 3.06 | 0.002 |
| Distance from roads (m) | −0.002 | −13.41 | −3.49 | 0.0005 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.37 | −2.49 | −1.81 | 0.07 |
| Distance to drainage × Elevation | 1.68 × 10−5 | 3.16 | 1.81 | 0.07 |
Table 8.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with drainage density.
Table 8.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with drainage density.
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | 0.81 | - | 1.00 | 0.32 |
| Drainage density (m−1) | −0.48 | −0.60 | −1.90 | 0.06 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.013 | −2.46 | −3.86 | 0.0001 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.15 | 1.67 | 4.08 | 0 |
Table 9.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with Topographic Wetness Index (TWI).
Table 9.
Parameter estimates, standardized parameter estimates, t-statistics, and p-values of the best performing logistic regression model with Topographic Wetness Index (TWI).
| Variable | Parameter Estimate | Standardized Parameter Estimate | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|
| Intercept | −0.75 | - | −0.24 | 0.81 |
| Topographic Wetness Index | 0.44 | 0.81 | 1.64 | 0.1 |
| Elevation (m) | −0.007 | −1.35 | −1.85 | 0.06 |
| Slope angle (degrees) | 0.18 | 2.01 | 2.99 | 0.003 |
| Distance to roads (m) | −0.002 | −15.62 | −3.77 | 0.0002 |
| Saturated surface hydraulic conductivity (microns per second) | −0.39 | −2.63 | −2.60 | 0.01 |
| Presence of silt soil type (ML and MH) | 1.70 | 0.76 | 1.48 | 1.40 |
Table 10.
Comparison of the performance of logistic regression models. AIC: Akaike information criterion; BIC: Bayesian information criterion.
Table 10.
Comparison of the performance of logistic regression models. AIC: Akaike information criterion; BIC: Bayesian information criterion.
| Hydrological Variable in the Model | Log Likelihood | AIC | BIC |
|---|
| Downscaled soil moisture content | −17.90 | 51.8 | 74.92 |
| Undownscaled soil moisture content | −23.33 | 60.6 | 80.89 |
| Distance to drainage accessories (m) | −22.30 | 58.6 | 78.89 |
| Drainage density (m−1) | −49.71 | 107.4 | 118.98 |
| Topographic Wetness Index | −23.28 | 60.6 | 80.79 |
Table 11.
Classification accuracies of soil slide and non-soil slides for Oregon and Kentucky.
Table 11.
Classification accuracies of soil slide and non-soil slides for Oregon and Kentucky.
| Dataset | Classification Accuracy % |
|---|
| All data | 93.2 |
| Oregon data | 95.7 |
| Kentucky data | 80.5 |
Table 12.
Classification accuracies of soil slide and non-soil slides for Oregon and Kentucky.
Table 12.
Classification accuracies of soil slide and non-soil slides for Oregon and Kentucky.
| | Oregon % | Kentucky % |
|---|
| Soil slides | 81.8 | 95.5 |
| Non-soil slides | 90 | 95.7 |
Table 13.
Confusion matrix for the results obtained with the soil slide classification model.
Table 13.
Confusion matrix for the results obtained with the soil slide classification model.
| Predicted Class |
|---|
| True class | | Soil Slides | Non-Soil Slides |
| Soil slides | 30 | 3 |
| Non-soil slides | 6 | 94 |