Abstract
Accurate precipitation measurements for high magnitude rainfall events are of great importance in hydrometeorology and climatology research. The focus of the study is to assess the performance of satellite-based precipitation products against a gauge adjusted Next-Generation Radar (NEXRAD) Stage IV product during high magnitude rainfall events. The assessment was categorized across three spatial scales using watershed ranging from ~200–10,000 km2. The propagation of the errors from rainfall estimates to runoff estimates was analyzed by forcing a hydrologic-model with the satellite-based precipitation products for nine storm events from 2004 to 2015. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Climate Prediction Center (CPC) Morphing Technique (CMORPH) products showed high correlation to the NEXRAD estimates in all spatial domains, and had an average Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of 0.81. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Early product was inconsistent with a very high variance of Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient in all spatial domains (from −0.46 to 0.38), however, the variance decreased as the watershed size increased. Surprisingly, Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) also showed a very high variance in all the performance statics. In contrast, the un-corrected product of the TRMM showed a relatively better performance. The errors of the precipitation estimates were amplified in the simulated hydrographs. Even though the products provide evenly distributed near-global spatiotemporal estimates, they significantly underestimate strong storm events in all spatial scales.
1. Introduction
Accurate precipitation measurements for high magnitude events are of key importance to a number of areas in hydrometeorology and climatology research. In addition to research pursuits, these measurements have great value to public well-being by providing the backbone of rainfall-runoff prediction systems aimed at forecasting floods [1,2]. Over the past couple of decades in operational settings, these datasets have primarily been generated with radar and rain gauge networks [3]. Radar networks have the advantage of providing near real-time information over a continuous region at very fine scales, mostly unattainable with ground-based gauge networks. Numerous validation studies showed good performance of radar measurements, especially when combined with gauge networks for bias adjustments/quality control (e.g., Wang, Xie [4], Habib, Larson [5]). However, lack of even global distribution of radar network and problems such as beam blockage in complex terrain introduced significant gaps in radar coverage that pushed researchers to explore robust solution [6].
Satellite precipitation estimates provide a means for timely, near-global precipitation estimates, and much of the recent effort has been put into their validation and verification [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Several products, including those provided by the recently launched Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission, now provide the spatiotemporal resolution needed to forecast or conduct post-event analysis of flash floods. Even though the potential of satellite-based products was highly regarded, their poor performances were reported widely across the globe, especially, in their ability to accurately capture high magnitude precipitation events. Nikolopoulos, Anagnostou [14] demonstrated mean areal precipitation is consistently underestimated in their satellite ensemble analysis of a high magnitude precipitation event in Italy. AghaKouchak, Behrangi [15] examined several operational satellite precipitation products across the southern Great Plains with respect to precipitation thresholds and demonstrated the detection skill reduces as the choice of extreme threshold decreases. Mehran and AghaKouchak [16] reported similar findings when comparing three operational satellite products across the conterminous United States. Mei, Anagnostou [17] showed that satellite precipitation estimates are more biased for frontal events than for short-duration events. However, the error statistics of the products showed higher variability for the latter. Moreover, the products showed high inconsistency across different terrain [12] and climatic conditions [11]. These and other studies stress the need for more analysis and evaluation of the accuracy and performance of recent satellite products in capturing the behavior of extreme precipitation events by comparing them against products from ground-based measurement networks (radar or rain gauges).
Satellite-based precipitation products were found to be more accurate in a dry season and in wet tropical and dry zones than in semi-arid and mountainous regions. The uncertainty amongst the products was higher in estimating heavy rainfall storms in a semi-arid area. Moreover, the products, in general, overestimate the number of rainy days and underestimate the heavy rainfall storms [11]. Amongst the highly cited satellite-based products in the literature, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Climate Prediction Center (CPC) Morphing Technique (CMORPH) and Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks (PERSIANN)were reported to be spatially inconsistent [10,11,12,18,19,20]. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) and its continuation mission GPM were found in many studies to be relatively consistent and more accurate but overestimated the average rainfall events and underestimated the heavy storm events in general [11,12,13,19,21].
The potential of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates in hydrological applications is supported by the facts that satellite measurements are not inhibited by local topography and are available at a global scale. Forcing hydrological models with high-resolution satellite-based precipitation products can provide a streamflow forecast for ungauged, complex terrain basins. The manner in which rainfall errors propagate through a hydrologic model has important implications for building operational flow forecasts for such basins. Propagation of errors is influenced by spatial and temporal resolution of the satellite estimate, basin scale, and complexity of the physical interactions represented by the watershed model, among others. Presently, the majority of detailed error propagation studies were forced with radar rainfall data (e.g., Sharif, Ogden [22], Sharif, Ogden [23,24], Vivoni, Entekhabi [25]) with comparatively less work done for satellite-based precipitation (e.g., Nikolopoulos, Anagnostou [14], Gebregiorgis, Tian [26], Maggioni, Vergara [27], Chintalapudi, Sharif [28]). Moreover, most of the studies forced by satellite-based precipitation on propagation error into hydrologic predictions were focused on grid-based evaluation or long-term basin-averaged runoff response (e.g., Su, Gao [29], Wu, Adler [30]).
Spatial scale (with respect to both satellite resolution and basin size) is an important aspect in rainfall-to-runoff error propagation for satellite precipitation, and a more comprehensive understanding of it plays a vital role in mitigation of natural disasters. Nikolopoulos, Anagnostou [14] developed satellite rainfall ensembles for a single flood event and showed error propagation is strongly related to the size and characteristics of the watershed and the satellite product resolution. A rainfall-runoff process reduces the satellite-precipitation error variance in a mild-sloped catchment, and this effect exhibits the basin-scale dependence [31]. However, many other factors also have a significant impact, such as precipitation type, magnitude, and spatiotemporal pattern, and basin characteristics interact with the scale effect [31,32,33].
The Gridded Surface Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis (GSSHA) model, which is fully distributed and physically-based, was developed by the Department of Defense in order to simulate surface flows in non-Hortonian watersheds and watersheds with diverse characteristics of runoff production [34]. The model employs a mass-conserving solution of partial differential equations to produce the different components of hydrologic processes. The model was able to reproduce stream flows from a very diverse watershed with reasonable accuracy [35]. Moreover, the grid size can be used to optimize the required accuracy with the required computational power [36].
In the present study, the performance of several satellite precipitation products with respect to gauge corrected ground-based radar estimations for nine moderate to high magnitude events across the Guadalupe River system in south Texas was investigated. The analysis was conducted across three nested watersheds (ranging from 200 to 10,000 km2 in area) to capture and quantify the effect of the scale on the propagation of the error. Satellite-based precipitation data sets were used to force a fully distributed physics-based Gridded Surface Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis (GSSHA) model to examine error propagation through the hydrologic model. Both gauge-corrected and uncorrected satellite products were used, encompassing a variety of latency times, spatial resolutions, and temporal resolutions. Satellite-based precipitation datasets used in the study include various products from GPM, PERSIANN system, CMORPH, and TRMM.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Watershed
The Guadalupe River originates in south-central Texas and flows southeasterly until emptying into the Guadalupe estuary/Gulf of Mexico. In this study, the testbed is the middle and upper portions of the basin, with the watershed outlet taken near Gonzales, TX past the confluence of the Guadalupe and San Marcos rivers (herein referred to as Guadalupe basin). At the outlet, the basin drains approximately 9000 km2. Two additional catchments within the watershed were delineated for scale effect analysis: Little Blanco River (178 km2) and the Blanco River (1130 km2). The spatial extent of the Guadalupe watershed along with the two nested watersheds is shown in Figure 1. Canyon Lake reservoir is formed by an impoundment along the Guadalupe River and contains significant flood storage, thus, we removed the dam from our watershed model to simulate a naturally flowing river for the analysis of hydrograph error propagation.
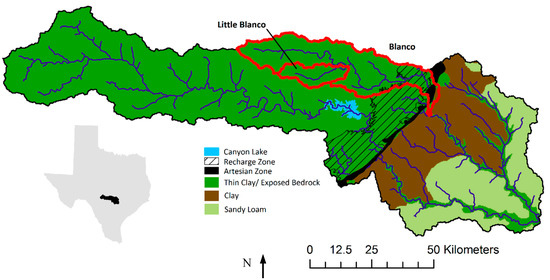
Figure 1.
Location and area map of the study watersheds along with a generalized soil map. Each of the three interior watersheds are outlined, and the Edwards Aquifer recharge and artesian zones are displayed.
The Guadalupe River flows across distinct landscapes with varying hydrological characteristics. The upper portion of the watershed is located in an area known as the Texas Hill Country. This region is comprised of a karstic landscape with steep surfaces, exposed bedrock, and very thin clayey soils. As the river passes through the Balcones Escarpment, it encounters the Edwards Aquifer recharge and artesian zones. In these regions, soils are permeable and there is much groundwater-surface water interaction. The lower portion of the river crosses the Blackland Prairies before entering the Coastal Plain. A generalized soil map of the study area including the recharge and artesian areas of the Edwards Aquifer is displayed in Figure 1. There are a number of studies available describing the surface characteristics of the watershed in detail along with its flood hydrology [36,37,38].
2.2. Storm Events
The Texas Hill Country is one of the most flash flood-prone areas of the entire United States due to its flood-prone physiography and susceptibility to extreme precipitation [38,39]. Although not considered among the very humid regions of the U.S., proximity to the Gulf of Mexico allows for extremely moist tropical air masses to reach the Balcones Escarpment where they can be subjected to orographic lift [40]. The region holds or has held several precipitation world records on time scales less than 24 h (USGS 2014). The precipitation envelope curve for Texas is comprised mostly from events in this region with others from the coastal plain. Once precipitation falls, the availability of steep slopes, high drainage density, exposed bedrock, and clay-rich soils have the ability to produce extremely high runoff coefficients with short lag times [41].
Here, nine large precipitation events from 2004–2015 across the middle Guadalupe basin were selected to examine satellite precipitation estimate performance and hydrologic model error propagation. All of the storm event accumulations from the Stage IV precipitation record are presented in Figure 2. The hydrometeorology of several of these events has been examined in detail including Furl, Sharif [42] (May 2015 event), Furl, Sharif [40] (September 2010 event), and Sharif, Sparks [36] (November 2004 events).
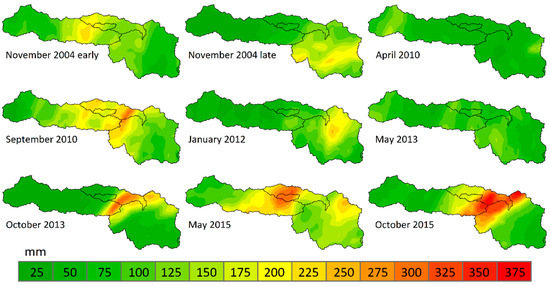
Figure 2.
Total accumulations from stage IV data for individual storm events used in the analysis (mm). The month and year in which the storm occurred is displayed along with outlines of the interior watersheds. Numbers along the legend represent the maximum value from each category.
2.3. Precipitation Datasets
In total, ten satellite precipitation products were examined, encompassing a variety of spatiotemporal resolutions. Moreover, the examined products include gauge corrected and uncorrected products to assess the impact of the adjustment. A brief description of the precipitation products is included below.
2.3.1. NEXRAD Stage IV
Each of the satellite precipitation datasets was compared to the National Weather Service (NWS) and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) stage IV Quantitative Precipitation Estimate (herein Stage IV) [43]. The precipitation estimate is a quality controlled multi-sensor product (radar and gauges) produced by NCEP from the NEXRAD Precipitation Processing System [44] and the NWS River Forecast Center precipitation processing [45]. Precipitation bins are 4 km × 4 km and have an hourly temporal resolution. The primary radar operating across the study area is National Weather Service in Austin/San Antonio (KEWX) station approximately 70 km from the watershed outlet.
The authors acknowledge the inherent biases that accompany radar-based precipitation estimates. However, the relatively fine space-time scales of the dataset provide the best means to describe the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of the rainfall across the basin and make satellite comparisons. Moreover, previous studies by the authors demonstrated that Stage IV products were more suitable than observations by typical rain gauge networks as inputs to physically based distributed-parameter models (e.g., [28,36]).
2.3.2. GPM
The GPM core observatory was launched on 27 February 2014 providing a new means of satellite global precipitation measurement. The GPM consists of a core-satellite and numerous others in its constellation. The GPM mission is based on a constellation of microwave radiometers and integrated IR sensors to cover the blind spot of the microwave sensors. The Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) is the precipitation product developed by the GPM network. The core GPM satellite carries a dual-frequency precipitation radar along with multichannel microwave imagers and is used for calibration of the constellation satellites. Additionally, GPM can integrate infrared (IR) measurements from geostationary data to cover areas not seen by constellation satellites. The data produces a near global precipitation product with a spatial resolution of 0.1° and 30-min temporal resolution [46,47].
IMERG output is available in Early, Late, and Final runs, with a latency of approximately 4 h, 18 h, and 4 months, respectively. The Final IMERG run is calibrated by monthly gauge precipitation data following a certain procedure (Huffman, Bolvin [46]). In the present study, version 3 processing algorithms were used, and each of the three IMERG products were examined.
2.3.3. PERSIANN
The PERSIANN system estimates rainfall from infrared image data provided by geostationary satellites. PERSIANN data are calibrated in real time from independent microwave precipitation estimates. The calibration process is based on an adaptive training technique which updates neural network parameters when microwave data are available [48]. The data are available in 0.25°, 30-min resolution approximately 2 days after the gridded IR images are collected. The rainfall product covers tropical and middle latitudes from 50 S to 50 N [48,49].
PERSIANN-Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) allows for precipitation estimates at the same temporal resolution and a finer spatial resolution (0.04°). Additionally, the data are available in near real-time. The system allows for the discernment and classification of cloud patch features based on height, areal extent, and variable texture. These classifications are used to further refine the assignment rainfall within each cloud. The product with a latency of two days was used for PERSIANN-CCS in this study.
2.3.4. CMORPH
CMORPH estimates precipitation from microwave-based precipitation images advected in time using infrared images from geosynchronous satellites. The product combines the positive side of the two satellites: estimated precipitation from low orbited satellites using microwave images and transportation of the estimated precipitation in time using the IR from the geosynchronous satellites. Microwave images are much better in estimating precipitation but they are not continuous, and IR from geosynchronous satellites are available and are continuous in time. The precipitation product is available at 30 min intervals with 8 km resolution as well as 3-h, 0.25° resolution. Precipitation estimates are available approximately 18 h past instrument measurement [50]. CMORPH products used in this study include the raw satellite-only precipitation product (CMORPH_RAW), the climate data record (CDR) version (CMORPH CDR) and the published 8 KM resolution product CMORPH 8KM.
2.3.5. TRMM
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) employs a combination of microwave and IR data to estimate precipitation at 0.25° every 3 h. The TRMM product is produced by combining microwave estimates which are used to calibrate IR estimates from geosynchronous satellites. The IR estimates are used to fill gaps left by the microwave sensors. TRMM 3B42 V7 and TRMM-RT 3B42 V7 were used in the study. Gridded monthly rain gauge values are used to adjust the TRMM 3B42 V7 estimates [51]. The TRMM-RT (Real-Time) product is a near real-time dataset with no gauge adjustments. An overview of the availability of the entire dataset is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of satellite precipitation dataset availability.
2.4. Hydrologic Model
Precipitation datasets were used to force the fully distributed physics-based GSSHA model [34,52]. Hydrological processes simulated included infiltration, landscape retention, overland flow, and stream routing. Evapotranspiration and deep aquifer contributions were assumed to be insignificant relative to the processes since the simulation is event based. Model preprocessing was conducted using ArcGIS and Aquaveo’s Watershed Modeling System. Watershed terrain was constructed from USGS 10 m digital elevation models (DEM) filled using the Cleandam algorithm distributed with the GSSHA model. Land use and land cover data were extracted from the National Land Cover Database 2011 (NLCD 2011) dataset. Soils data were prepared from SSURGO datasets along with maps from the Edwards Aquifer Authority defining the Edwards Aquifer recharge zone.
Infiltration calculations were conducted using Green and Ampt with redistribution [53] and pre-calibrated saturated hydraulic conductivity values taken from Rawls, Brakensiek [54]. Grid cells were assigned to one of four land use classes for retention and overland roughness. Stream channels were modeled using irregular cross sections for the main channel and large tributaries. The irregular channel and floodplain geometry were extracted from a triangular irregular network constructed from the DEM allowing for control of floodplain simulation. Upland tributaries were modeled as a uniform trapezoidal profile. Reach specific Manning’s n values were assigned based on field observations and prior modeling experience in this region of Texas. Routing was calculated using the diffusive wave equation in 1D for streams and 2D for overland flow. The hydrological model was run on a 150-m grid cell size with a 1-min simulation time step.
Distributed models have the distinct advantage of allowing examination of hydrologic properties at any point in the basin. In this study, three watershed models were constructed: Blanco watershed, Upper Guadalupe watershed, and Middle Guadalupe watershed. Results from the Little Blanco watershed were harvested from the proper interior node of the Blanco River watershed model. The Middle Guadalupe model (i.e., implementation of the hydrologic model over Middle Guadalupe) used streamflow from the outlets of the Blanco and Upper Guadalupe as boundary condition inflows, thereby allowing a very fine gridded distributed model over a 9000 km2 basin. The Upper Guadalupe model discharge hydrograph was input into the Middle Guadalupe at the outlet of Canyon Lake, bypassing the reservoir.
The Blanco watershed model was the primary model calibrated. Furl et al. [42] calibrated the model to the November 2004 “early” event used here and achieved r2, Nash-Sutcliffe model efficiency (NSE), and percent bias (PBIAS) values of 0.91, 0.90, and 10.2%, respectively for the calibration run. Similar model parameter values were used for the Upper Guadalupe model. The setup for the Middle Guadalupe followed hydrologic parameters described by Sharif, Sparks [36], which described the November 2004 “late” event. It should be noted that our main objective with model calibration is to provide realistic rainfall-runoff mechanisms such that error propagation analysis can be conducted. Surface properties for the Blanco River watershed are shown in Table 2. The readers are directed to Sharif, Sparks [36] and Furl et al. [42] for detailed descriptions of the watershed models and their comparisons with measured flows.

Table 2.
Gridded Surface Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis (GSSHA) infiltration and overland flow parameters for the Blanco watershed model.
2.5. Evaluation Criteria
Satellite precipitation results were analyzed by comparing mean areal precipitation hyetographs with those generated from the Stage IV precipitation record. Here, the reference hydrographs were those driven by the reference precipitation product (radar). It will not be appropriate to use observed hydrographs as a reference since we do not have a precipitation product that will perfectly produce the observed hydrographs. A weighting method was used in the averaging routine to account for rainfall bins only partially covering a portion of the basin. For comparisons, satellite hyetographs were scaled to a one-hour time step using a simple linear transformation in order to match the Stage IV record. The comparison period was confined to when the Stage IV record indicated 1 mm of precipitation had fallen across the basin until rainfall ceased. Streamflow hydrograph comparisons were conducted in a similar manner by comparing satellite generated model output with the hydrograph generated by the Stage IV record. The analysis period was determined by visually examining the Stage IV generated hydrographs and capturing from just before the rising limb of the hydrograph until after the falling limb. The comparisons for hyetographs and hydrographs were completed using the percent bias (PBIAS), normalized root-mean-square-error (nRMSE), and Nash-Sutcliffe model efficiency (NSE) statistics. Simple relative error in precipitation, peak flow, and volume of flow was calculated for error propagation analysis. Calculations were completed using the hydroGOF package [55] in R environment as follows:
where:
- is the simulated rainfall (estimated by the product),
- is the estimated rainfall by NEXRAD stage IV,
- is the estimated rainfall by the product/precipitation/simulated peak flow with the product, and
- is the estimated rainfall NEXRAD stage IV/simulated peak flow with NEXRAD stage IV rainfall.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Precipitation
Precipitation from the Stage IV record averaged over the entire watershed ranged from approximately 50–150 mm, and storm durations lasted from just a few hours to approximately 72 h. Among the 27 isolated storm event and watershed size combinations (9 storm events × 3 watersheds), the satellite-based precipitation products showed a wide range level of accuracy when compared to the Stage IV estimates. As shown in Figure 3, for the largest spatial domain, satellite precipitation estimates showed the ability to very closely match radar results (November 2004 (late), May 2013), and consistently overestimate (November 2004, early) and also systematically underestimate precipitation (October 2015). The products tended to significantly underestimate in four events and only once overestimated when compared to NEXRAD Stage IV estimates. In addition to the inherent errors in the satellite products due to calibration and the rainfall estimation technique (i.e., microwave or infrared), the relatively coarse resolution of the products may have contributed to the underestimations errors. Underestimation is more pronounced for the large events where satellite underestimates the high intensity periods. Interestingly, the Final GPM product underestimates rainfall more than the earlier products. This can also be attributed to the nature of the events where climatology and gauge adjustments did not capture the localized intensity of the events. In the rest of the four storm events, the NEXRAD product seemed to fit the average of all the satellite-based products (Figure 3). The satellite-based products failed to capture the storm events that occurred in the Fall (September, October) with the exception of the 2004 storm where they tended to overestimate the storm. In contrast, the margin of error was very low in storm events that occurred in May.
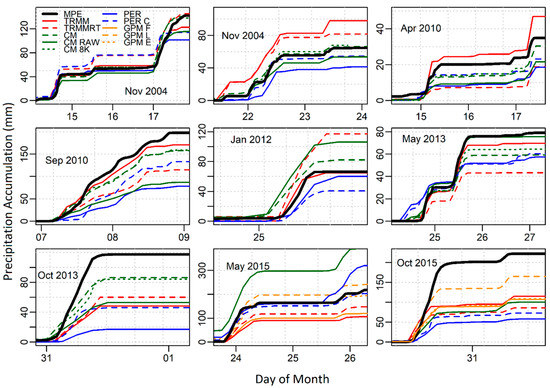
Figure 3.
Storm event rainfall accumulations averaged over the Blanco watershed. Legend labels are abbreviated as follows: MPE—Stage IV, TRMM—TRMM 3B42, CM—CMORPH CDR, GPM F—GPM IMERG FINAL, CM 8K—CMORPH 8KM, PER C—PERSIANN CCS, GPM E—GPM IMERG EARLY, GPM L—GPM IMERG LATE, CM RAW—CMORPH RAW, TRMM-RT—TRMM-RT 3B42, and PER—PERSIANN.
In general, the satellite products (adjusted and unadjusted) underestimated the storm events from the stage IV record at all spatial scales with the exception of some storm events. This is not surprising given the small sample size focused on events on the tail side of the distribution. Other researchers have noted similar satellite underestimations for high magnitude events [14,15,16,56]. However, it should be noted there was no strong correlation between percent bias and total accumulated precipitation for any of the three spatial domains. Moreover, satellite-based products underestimated heavy storm events in larger spatial domains (0.4 to 1.3 million km2) in several regions of Africa [11].
Generally, the satellite-based precipitation products showed less variability in the case of the Guadalupe basin (Large) relative to the two smaller watersheds (Figure 4). This could be mainly because of the smoothing power of mean value over the large spatial domain (filtering the noise introduced by the products). Both products from CMOPRH (labeled as CM and CM 8K) showed very high correlation with the stage IV product in all spatial domains with very high Nash coefficient. GPM Early was found to be inconsistent with a very high variance of Nash coefficient in all spatial domains, however, the variance was decreased as the watershed size increase. Surprisingly, TRMM showed a very high variance in all the performance statics, especially in the two small watersheds. In contrast, the TRMM-RT product showed relatively better performance. As described above, the performance of GPM Final product was inferior to the earlier ones. The whole distribution of the performance statistics is provided in Figure 4.
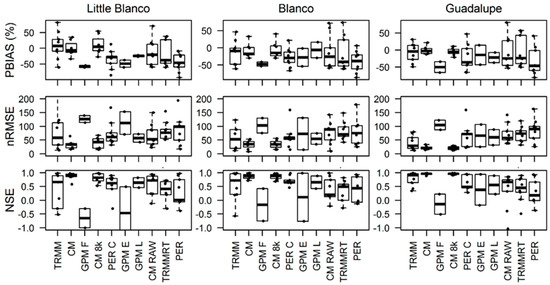
Figure 4.
Boxplots for hyetograph performance statistics for all spatial domains. X-axis labels are abbreviated as follows: TRMM—TRMM 3B42, CM—CMORPH CDR, GPM F—GPM IMERG FINAL, CM 8K—CMORPH 8KM, PER C—PERSIANN CCS, GPM E—GPM IMERG EARLY, GPM L—GPM IMERG LATE, CM RAW—CMORPH RAW, TRMM-RT—TRMM-RT 3B42, and PER—PERSIANN. Boxplots display the lower and upper quartiles and median. Whiskers extend to the data point nearest ± 1.5 * interquartile range.
In order to provide some comparison between satellites products, performance statistic results were pooled from all spatial domains for each individual satellite product. Table 3 displays the median, average, and range of the statistics after this aggregation. For the 0.25° uncorrected products, performance statistics indicated CMORPH RAW > TRMM-RT > PERSIANN for the nine events examined. Sapiano and Arkin [10] found that correlations were highest with CMORPH in an inter-comparison and validation study on sub-daily satellite precipitation data. For the gauge corrected products at 0.25°, there was very little difference between TRMM and CMORPH when the same events were compared (2015 events unavailable for CMORPH). It is difficult to draw conclusions about the performance of GPM given that only two events were measured. GPM results are compared to the other products for the 2015 events below.

Table 3.
Satellite hyetograph performance statistics aggregated across the three spatial domains.
3.2. Impact of Spatial Resolution
Several papers have noted a scale dependence of error caused by the inability of coarse-resolution products to adequately represent mean areal precipitation in smaller basins because their sampling involves an area much larger than the basin (e.g., Nikolopoulos, Anagnostou [14]). Here, we investigate the scale dependence of rainfall error first by comparing the CMORPH and PERSIANN products with their fine-scale counterparts and then by examining changes in PBIAS as a function of watershed size.
The PERSIANN CCS product has a spatial resolution of 0.04 degrees and has a similar size to stage IV bins across the study area. When compared to PERSIANN, the PERSIANN CCS product consistently performed better in each of the three watersheds for all performance statistics. However, the gap in performance statistics did not grow as watershed size decreased, as may be expected if scale issues were the root cause of the discrepancy. It is difficult to identify the primary causes for the differing performance given PERSIANN CCS uses different processing algorithms.
Unlike the PERSIANN products, there was virtually no difference between CMORPH and the CMORPH 8KM product with regard to performance statistics. This suggests the downscaling techniques employed by the CMORPH 8KM product are not adequate if their intent is to provide a more detailed spatial representation of rainfall.
3.3. GPM Rainfall Events
The two largest rain events from the dataset occurred in May and October of 2015, and both resulted in significant flash flood events along the Blanco River [42]. These events were captured by GPM and offer an initial look at GPM performance for short duration high magnitude storms. Figure 5 shows performance statistic results for each of the real-time products (PERSIANN, PERSIANN-CCS, TRMM-RT, and CMORPH RAW) along with the Early and Late GPM runs. Generally, the GPM products performed better than did the other real-time satellite products. For the May 2015 event, the Early product produced better estimates than the Late run, with the opposite pattern for the October 2015 event. Gauge corrected estimates (Table 3) showed a significant underestimation of the events, which is not surprising given it is adjusted to monthly values. The Early GPM product failed to capture the storm event of October 2015 showed by the negative value of Nash coefficient (Figure 5).
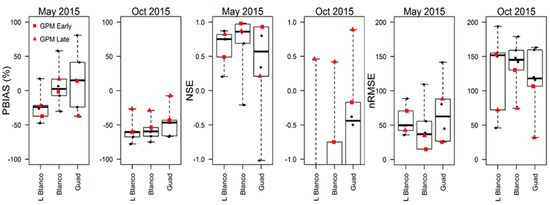
Figure 5.
Performance statistic results for the non-gauge adjusted satellite results for the May and October 2015 storms that included the GPM products.
As anticipated, hydrograph results closely mimic the rainfall fields with respect to their ability to overestimate and underestimate the reference Stage IV forcing. The hydrographs driven by Stage IV rainfall along with satellite results for the nine storm events at the Guadalupe basin outlet are shown in Figure 6 (same as Figure 3). The hydrographs from the products were able to capture the bi-modal behavior of the hydrograph but with a high range of accuracy levels for November 2004 and May 2014 events. Some of the errors were quite high, indicating that the rainfall errors were amplified in the resulting runoff hydrograph. In the case of the events that have a one peak hydrograph, most of the products tend to underestimate the hydrograph by a considerable amount. As expected, the hydrographs driven by the GPM Early and Late products had less errors than those driven by the Final products due to the severe underestimation of rainfall by the latter as described above (see Figure 3 and Figure 4). In all the fall events, the pattern of the hydrograph was more or less captured, but with very significant underestimation of the precipitation. For the events that occurred in May, the magnitude and the pattern of the stage IV seem to be the mean value of the hydrographs from the satellite-based products.
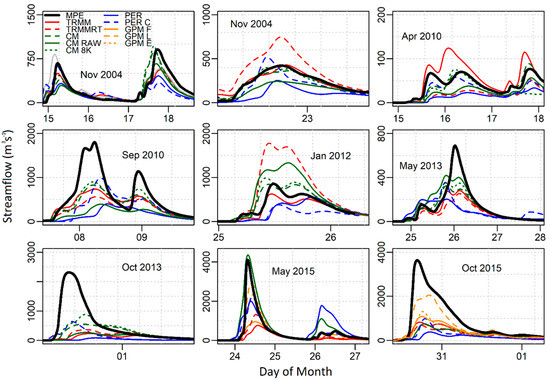
Figure 6.
Streamflow hydrographs at the Blanco watershed outlet. Legend labels are abbreviated as follows: MPE—Stage IV, TRMM—TRMM 3B42, CM—CMORPH CDR, GPM F—GPM IMERG FINAL, CM 8K—CMORPH 8KM, PER C—PERSIANN CCS, GPM E—GPM IMERG EARLY, GPM L—GPM IMERG LATE, CM RAW—CMORPH RAW, TRMM-RT—TRMM-RT 3B42, and PER—PERSIANN.
The performance of the precipitation products in the simulated hydrograph followed a similar pattern as described in the precipitation analysis. However, the variability of the products seems to increase as the scale of the watershed increases. Boxplot results showing performance statistics at each of the three basins are displayed in Figure 7. The CMORPH product (labeled as CM) showed higher Nash coefficient in Little Blanco (the smallest basin) but as the size of the watershed increased, the performance was seen to plummet. A similar pattern was observed in most the products when moving from Little Blanco to Guadalupe. All evaluation criteria showed a very wide range and high variability and error magnitude in the case of the Guadalupe Basin (Figure 7). The accumulated effect of all the discrepancies in the products across the watershed caused a significant increase in variability at the outlet. However, the increase in spatial domain of the watershed improved the performance of the GPM Late product across all the criteria.
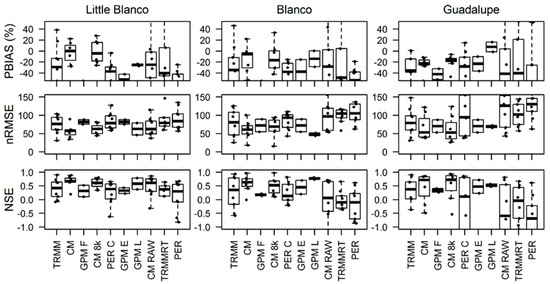
Figure 7.
Boxplots for hydrograph performance statistics for all spatial domains. X-axis labels abbreviations and boxplot representations are the same as those described in Figure 4.
3.4. GPM Model Simulations
GPM products showed a higher Nash Coefficient than their counterparts in both events in all spatial scales except in the case of Little Blanco for the May 2015 event. Moreover, the Late GPM product outclassed the Early GPM product in almost all the criteria and in all spatial domains. There is no clear pattern of the impact of scale effect on a single product but, in case of GPM products, the performance of the PBIAS was improved as the spatial domain increased. However, the variability of the performance of the non-gauge adjusted products increased as the spatial domain size increased (Figure 8).
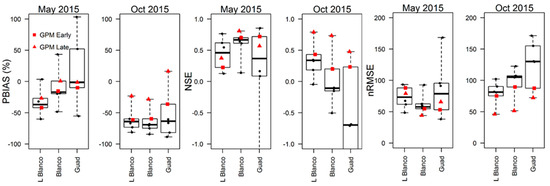
Figure 8.
Performance statistic results for the non-gauge adjusted satellite results for the May and October 2015 storms that included the GPM products (for the hydrographs).
3.5. Error Propagation
The error was seen to propagate from the precipitation dataset to the hydrograph at the outlet. The propagation was magnified in all of the criteria shown in Figure 9 except in the case of the streamflow PBIAS. Moreover, the pattern was seen across all the spatial domains in the same manner. The scale effect of the spatial domains does not seem to affect the error propagation, as they were very close in all the evaluation criteria (Figure 9).
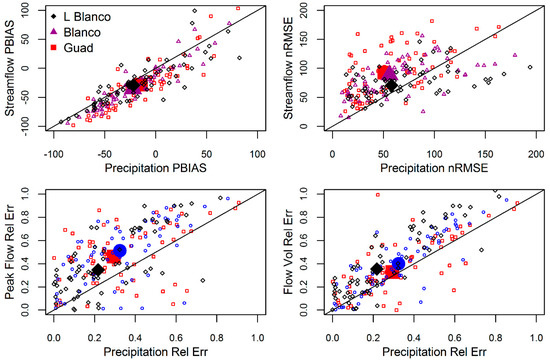
Figure 9.
Annual Error propagations descriptions comparing streamflow and precipitation percent bias (PBIAS) and normalized root-mean-square-error (nRMSE) (top left and top right, respectively) and relative error in precipitation versus peak flow relative error (bottom left) and streamflow volume relative error (bottom right) N.B. the big markers represent the mean value.
4. Conclusions
Precipitation is the main driver of all the hydrologic models that are used to predict/forecast the relationship between rainfall and runoff. Moreover, rainfall amount and distribution represent the major components of the floodplain analysis and water resource management practices. That is why it is a significant achievement to capture the spatial and temporal distribution of rainfall, since the accuracy of almost all hydrologic processes depends on the accuracy of the precipitation estimates. Rain gauges are only reliable for a very small area because of the intermittent behavior of precipitation. Radars have problems with beam blockage in complex terrain and lack even distribution across the globe. Satellite-based precipitation estimation with high spatiotemporal resolution has a potential to capture the spatiotemporal distribution of precipitation if the products and algorithms are improved to a reasonable accuracy.
The assessment of ten satellite-based precipitation products was carried in relation to the radar stage IV (NCEP product) over Guadalupe river basin with a drainage area of around 9000 km2. Moreover, the assessment was done in two smaller sub-watersheds of the Guadalupe river basin (Little Blanco River (178 km2) and the Blanco River (1130 km2)). This procedure was done to assess the scale impact on the accuracy of the products. Nine significantly large events with a wide spatial coverage were used in the analysis.
Furthermore, to understand the propagation of rainfall error into the predicted runoff, hydrologic model simulations were implemented. GSSHA, a physically-based fully distributed hydrologic model, forced with those ten satellite-based precipitation products, was used to simulate the rainfall-runoff relationship for the basins. The most widely used model evaluation criteria such as Nash-Sutcliffe, PBIAS, nRMSE, and relative error were used in the assessment of both precipitation and hydrographs of the outlet.
The products underestimated the storm events in relation to the radar product Stage IV. This pattern was seen in several other studies over various regions of the world [14,15,16,56]. Moreover, the satellite-based precipitation products showed a very compact distribution in all the evaluation criteria in the case of the largest basin. Both products of CMORPH showed a very high correlation in all spatial domains and was reflected with an average Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of 0.81. GPM Early was found to be inconsistent with a very high variance of Nash coefficient in all spatial domains (from −0.46 to 0.38), however, the variance was decreased as the watershed size increased. This is mainly due to the smoothing caused by averaging over a larger area. Among all GPM products, the Final product underestimated rainfall most, indicating that the methodology used to prepare the product (using climatology and rain gauges) probably was not able to capture the areas and/or periods of very intense localized rainfall. Surprisingly, TRMM also showed a very high variance in all the performance statics, especially in the two small watersheds (from −4.0 to 0.99 with an average of 0.16). In contrast, the TRMM RT (non-gauge corrected product of TRMM) product showed relatively better performance of Nash-Sutcliffe with an average of 0.39 and a range from 0.05 to 0.82.
The pattern of the precipitation estimates was also reflected on the simulated hydrograph forced by the precipitation products. The average Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient was reduced from 0.81 in precipitation to 0.58 in the runoff for CMORPH. CMORPH product showed higher Nash coefficient in Little Blanco (the smallest basin) but as the size of the watershed increased, the performance was seen to plummet. A similar pattern was observed in most of the products when moving from Little Blanco to Guadalupe. However, the increase in the spatial domain of the watershed improved the performance of the GPM Late product across all the criteria.
The error was seen to amplify as it propagated from the precipitation dataset to the hydrograph at the outlet. The propagation was magnified in all of the evaluation criteria except in the case of the streamflow PBIAS. Moreover, the pattern was seen across all the spatial domains in the same manner. The scale effect of the spatial domains does not seem to affect the error propagation as it was very close in all of the evaluation criteria.
In summary, the satellite-based precipitation products provide very high spatiotemporal resolution precipitation estimates. However, the estimates lack accuracy, especially at a local scale. The products underestimate heavy storm events significantly, and the errors were amplified in the runoff hydrographs generated.
Author Contributions
H.O.S. and C.F. designed the overall study. C.F. downloaded the remote sensing products and prepared and performed the hydrologic model simulations with input from H.O.S. D.G. helped C.F. with post-analysis of the model outputs and preparation of the first draft. C.F. and H.O.S. reviewed and revised the manuscript. H.O.S. did the final overall proofreading of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by U.S. Army Research Office (Grant W912HZ-14-P-0160).
Acknowledgments
This research funded in part by the U.S. Army Research Office (Grant W912HZ-14-P-0160). This support is cordially acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, A. Precipitation Characteristics in Eighteen Coupled climate models. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4605–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Todd, M.; Hulme, M.; Jones, P. Precipitation measurements and trends in the twentieth century. Int. J. Clim. 2001, 21, 1889–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.; Smith, J. Radar hydrology: Rainfall estimation. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Sharif, H.; Zeitler, J. Validating NEXRAD MPE and Stage III precipitation products for uniform rainfall on the Upper Guadalupe River Basin of the Texas Hill Country. J. Hydrol. 2008, 348, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Larson, B.F.; Graschel, J. Validation of NEXRAD multisensor precipitation estimates using an experimental dense rain gauge network in south Louisiana. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, R.A.; Zhang, J.; Gourley, J.J.; Howard, K.W. Weather radar coverage over the contiguous United States. Weather Forecast. 2002, 17, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Some, B.; McCollum, J.; Nelkin, E.; Klotter, D.; Berte, Y.; Diallo, B.M.; Gaye, I.; Kpabeba, G.; Ndiaye, O.; et al. Validation of TRMM and other rainfall estimates with a high-density gauge dataset for West Africa. Part II: Validation of TRMM rainfall products. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, J.R.; Krajewski, W.F.; Ferraro, R.R.; Ba, M.B. Evaluation of biases of satellite rainfall estimation algorithms over the continental United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.; Arkin, P. An intercomparison and validation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates with 3-hourly gauge data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemig, V.; Rojas, R.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Levizzani, V.; de Roo, A. Validation of satellite-based precipitation products over sparsely gauged African river basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1760–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Gebremichael, M.; Hopson, T. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over very complex terrain in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantas, V.; Liu, Z.; Caro, C.; Pereira, A.J.S.C. Validation of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) products in the Peruvian Andes. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Hossain, F.; Gebremichael, M.; Borga, M. Understanding the scale relationships of uncertainty propagation of satellite rainfall through a distributed hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Amitai, E. Evaluation of satellite-retrieved extreme precipitation rates across the central United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, A.; AghaKouchak, A. Capabilities of satellite precipitation datasets to estimate heavy precipitation rates at different temporal accumulations. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Borga, M. Error analysis of satellite precipitation products in mountainous basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1778–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernimmen, R.; Hooijer, A.; Mamenun; Aldrian, E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Evaluation and bias correction of satellite rainfall data for drought monitoring in Indonesia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, Y.; Ghebreyesus, D.; Temimi, M.; Milewski, A.; al Mandous, A. Assessment of the consistency among global precipitation products over the United Arab Emirates. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omranian, E.; Sharif, H.O. Evaluation of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Satellite Rainfall Products Over the Lower Colorado River Basin, Texas. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.O.; Ogden, F.L.; Krajewski, W.F.; Xue, M. Numerical simulations of radar rainfall error propagation. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 15-1–15-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.O.; Ogden, F.L.; Krajewski, W.F.; Xue, M. Statistical analysis of radar rainfall error propagation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M. Accuracy of radar rainfall estimates for streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivoni, E.R.; Entekhabi, D.; Hoffman, R.N. Error propagation of radar rainfall nowcasting fields through a fully distributed flood forecasting model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Hossain, F. Tracing hydrologic model simulation error as a function of satellite rainfall estimation bias components and land use and land cover conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Vergara, H.J.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Stampoulis, D. Investigating the applicability of error correction ensembles of satellite rainfall products in river flow simulations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1194–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintalapudi, S.; Sharif, H.O.; Xie, H. Sensitivity of distributed hydrologic simulations to ground and satellite based rainfall products. Water 2014, 6, 1221–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Gao, H.; Huffman, G.J.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential utility of the real-time TMPA-RT precipitation estimates in streamflow prediction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Adler, R.F.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Real-time global flood estimation using satellite-based precipitation and a coupled land surface and routing model. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2693–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, H.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Maggioni, V.; Stampoulis, D.; Kirstetter, Pi. Effects of resolution of satellite-based rainfall estimates on hydrologic modeling skill at different scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 593–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Evaluating satellite precipitation error propagation in runoff simulations of mountainous basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1407–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downer, C.W.; Ogden, F.L. GSSHA: Model to simulate diverse stream flow producing processes. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2004, 9, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, S.; Omranian, E.; Feng, D. Relative Sensitivity of Flood Inundation Extent by Different Physical and Semi-Empirical Models; CUAHSI Technical Report No. 13; The Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, H.O.; Sparks, L.; Hassan, A.A.; Zeitler, J.; Xie, H. Application of a distributed hydrologic model to the November 17, 2004, flood of Bull Creek watershed, Austin, Texas. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caran, S.C.; Baker, V.R. Flooding along the Balcones escarpment, central Texas. In The Balcones Escarpment-Geology, Hydrology, Ecology and Social Development in Central TEXAS; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1986; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, V.R. Flood Hazards along the Balcones Escarpment inCentral Texas Alternative Approaches to Their Recognition, Mapping, and Management; Bureau of Economic Geology Circular; Bureau of Economic Geology, University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Morrison, J.E.; Sturdevant-Rees, P. Catastrophic rainfall and flooding in Texas. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 1, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furl, C.; Sharif, H.O.; el Hassan, A.; Mazari, N.; Burtch, D.; Mullendore, G.L. Hydrometeorological Analysis of Tropical Storm Hermine and Central Texas Flash Flooding, September 2010. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, P.C.; Baker, V.R. Morphometry and floods in small drainage basins subject to diverse hydrogeomorphic controls. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furl, C.; Sharif, H.; Zeitler, J.W.; el Hassan, A.; Joseph, J. Hydrometeorology of the catastrophic Blanco river flood in South Texas, May 2015. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Mitchell, K.E. 1.2 the NCEP stage II/IV hourly precipitation analyses: Development and applications. In Proceedings of the 19th Conference Hydrology, American Meteorological Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, Do.; Miller, D.A.; O’Bannon, T. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P.; Seo, D.-J.; Habib, E. Assessment and implications of NCEP stage IV quantitative precipitation estimates for product intercomparisons. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) technical documentation. NASA/GSFC Code 2015, 612, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, B.; Liu, D.; Gourley, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y. Global view of real-time TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis: Implications for its successor global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, Ku.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite–based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downer, C.W.; Ogden, F.L. Gridded Surface Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis (GSSHA) User’s Manual; Version 1.43 for Watershed Modeling System 6.1.; Engineer Research and Development Center Coastal and Hydraulics Lab.: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, F.L.; Saghafian, B. Green and Ampt infiltration with redistribution. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1997, 123, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Miller, N. Green-Ampt infiltration parameters from soils data. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Bigiarini, M. Package ‘hydroGOF’: Goodness-of-Fit Functions for Comparison of Simulated and Observed Hydrological Time Series. R package Version 0.3-8. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/hydroGOF/hydroGOF.pdf (accessed on 8 February 2018).
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).