Selected Metal Content and Binding Behaviour in Riverbed Sediments of the Kavala–Philippi Area (Northern Greece)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
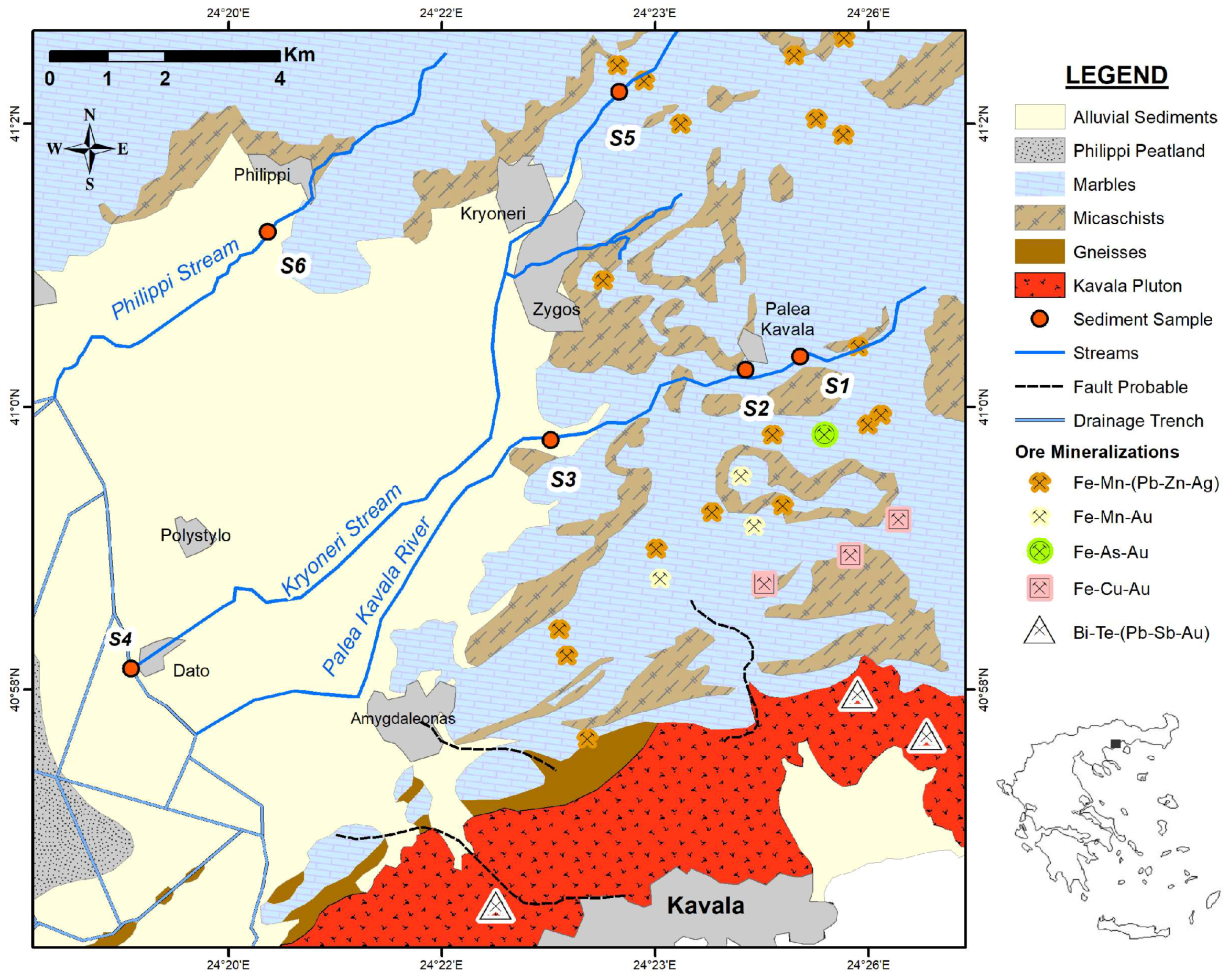
3.1. Study Area Description
3.2. Samples Collection
3.3. Samples Preparation
3.4. Samples Analysis
3.4.1. Metal Content
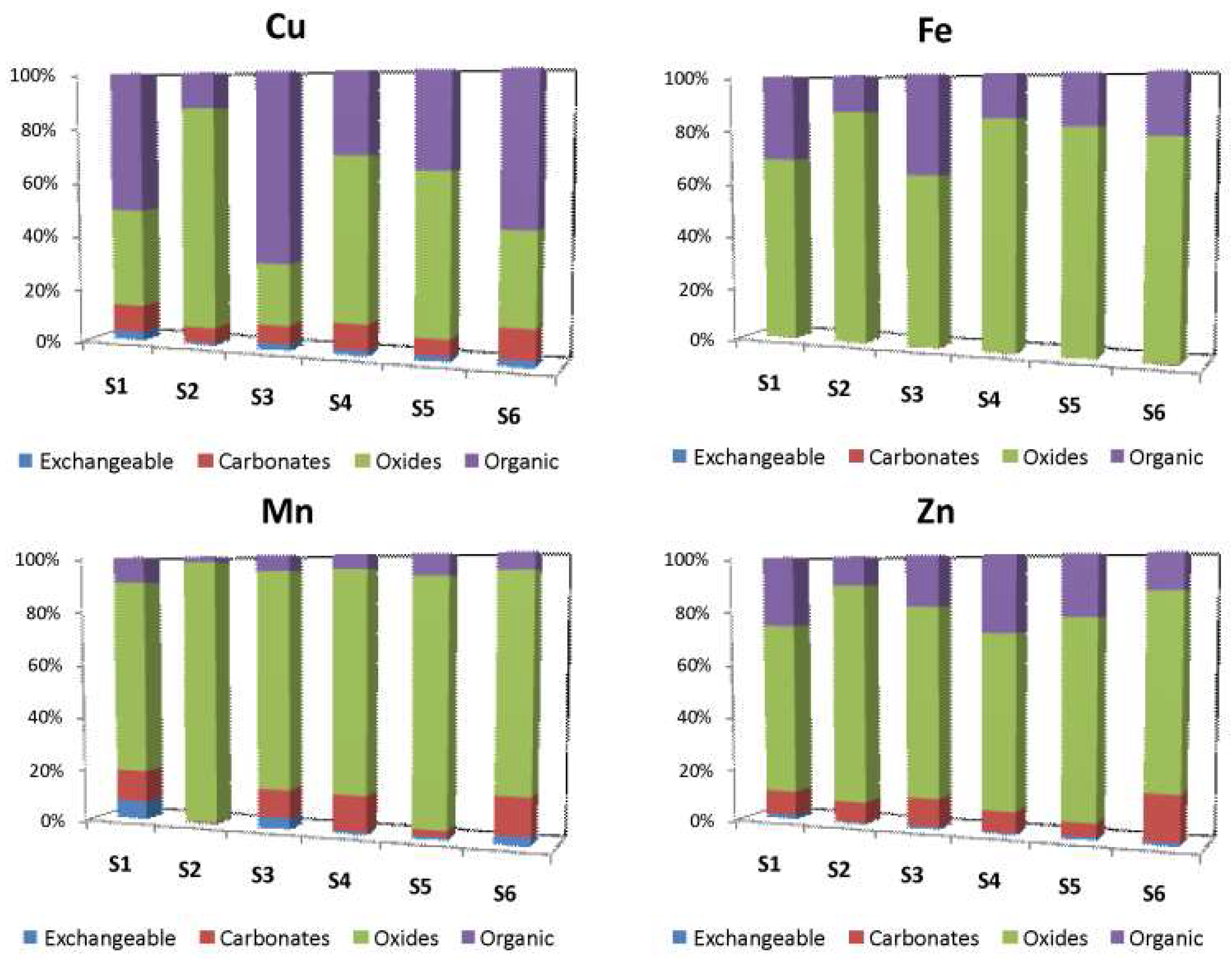
3.4.2. Metals Fractionation
- Exchangeable fraction: 1 g of the dried sediment sample was extracted with 8 mL of 1 M MgCl2 (pH = 7) for 1 h at room temperature (20–25 °C) with continuous agitation.
- Fraction bound to carbonates: the residue from the exchangeable fraction was extracted with 8 mL of 1 M NaOAc (adjusted to pH = 5 with HOAc) for 5 h at room temperature with continuous agitation.
- Fraction bound to Fe-Mn oxides: the residue from the carbonates fraction was extracted with 20 mL of 0.04 M NH2OH∙HCl in 25% (v/v) HOAc, for 6 h at 96 °C with occasional agitation.
- Fraction bound to organic matter: the residue from the Fe-Mn oxides fraction was extracted with 3 mL of 0.02 M HNO3 and 5 mL of 30% H2O2 (adjusted to pH = 2 with HNO3) for 2 h at 85 °C with occasional agitation. After cooling, 3 mL of H2O2 were added to the extracted solution and the sample was heated again to 85 °C for 3 h with occasional agitation. Finally, 5 mL of 3.2 M NH4OAc in 20% (v/v) HNO3 were added to the solution and agitated continuously for 30 min at room temperature.
3.5. Data Interpretation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Grain Size Distribution of Sediments
4.2. Elemental Content of Sediments
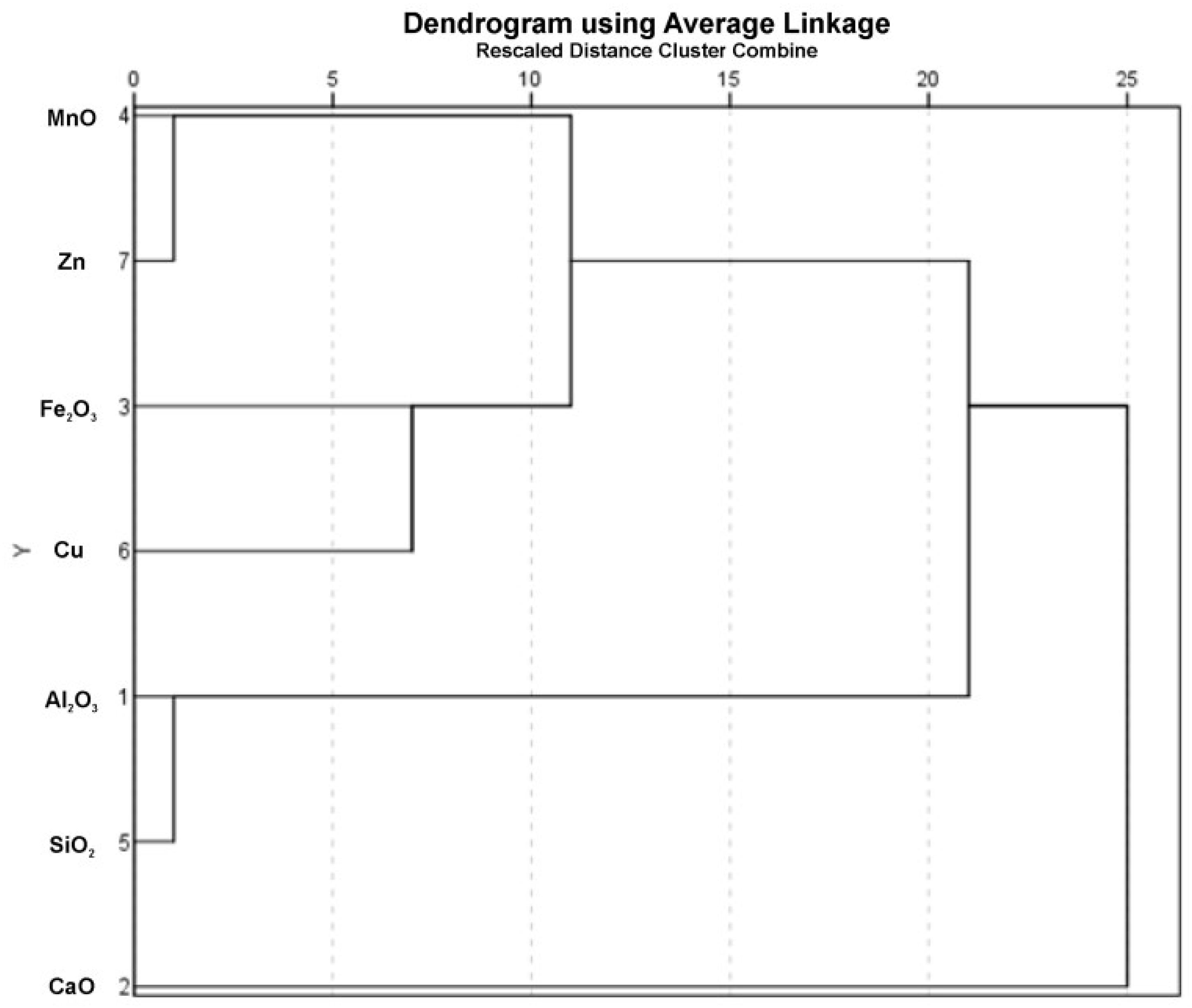
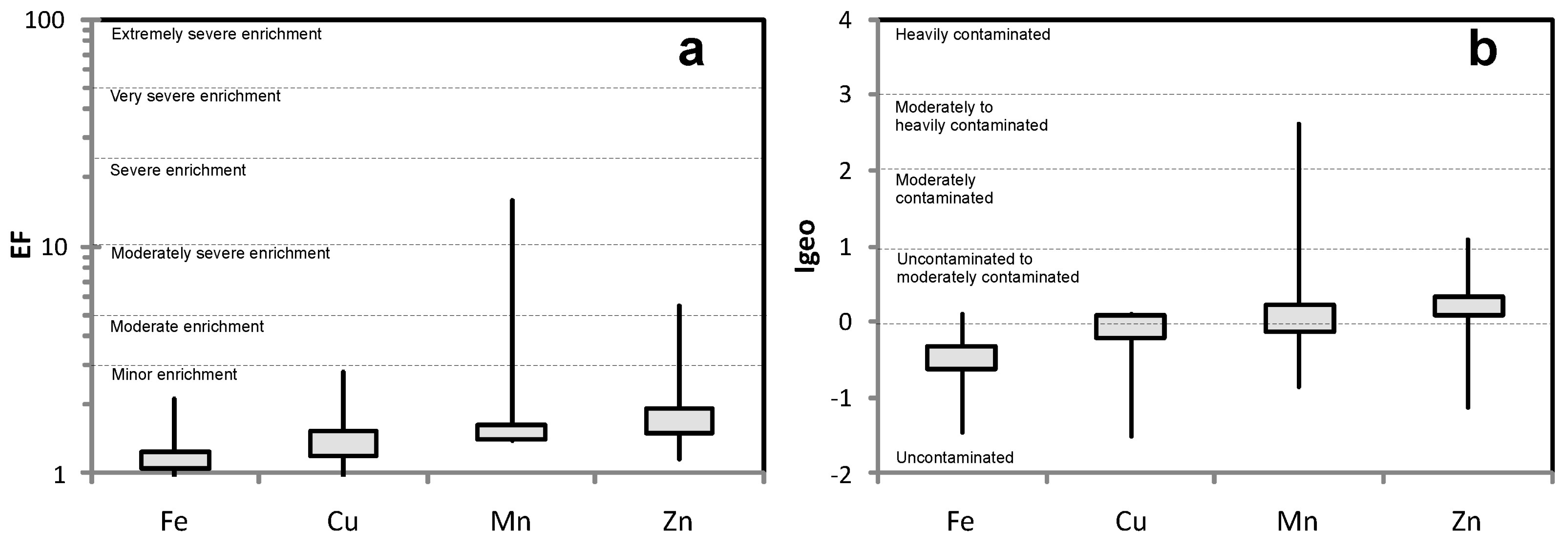
4.3. Metals Enrichment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—A tributary of the Ganges India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Nema, A.K.; Chabukdhara, M.; Gupta, S.K. Assessment of metals in water and sediments of Hindon River, India: Impact of industrial and urban discharges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Lin, C. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments: A reexamination into the offshore environment in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Y. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Metals in the Hydrocycle; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984; 349p. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, U.; Salomons, W. Mobilization of metals from sediment. In Metals and Their Compounds in the Environment; Merian, E., Ed.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1991; pp. 379–398. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.F.; Song, Y.H.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.Y.; Qiu, G.L. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, H.E. Partitioning of toxic metals in natural water-sediment systems. In Transport and Transformation of Contaminants near the Sediment Water Interface; De Pinto, J.V., Lick, W., Paul, J.F., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tokalioglu, S.; Kartal, S.; Elçi, L. Determination of heavy metals and their speciation in lake sediments by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after a four-stage sequential extraction procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 413, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Erratico, C.; Vigano, L. Assessment of the environmental significance of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments of the River Po. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, D.Z.R. Studies of the availability of toxic heavy metal elements in soil and sediments in the vicinity of lead smelting site (Germany). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1994, 78, 317–334. [Google Scholar]
- Baeyens, W.; Monteny, F.; Leermakers, M.; Bouillon, S. Evalution of sequential extractions on dry and wet sediments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förstner, U. Contaminated sediment. In Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences; Bhattacharij, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 1–157. [Google Scholar]
- Laws, E.A. Aquatic Pollution: An Introductory Text, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; 611p. [Google Scholar]
- Calmano, W.; Ahlf, W.; Förstner, U. Sediment quality assessment: Chemical and biological approaches. In Sediments and Toxic Substances; Calmano, W., Förstner, U., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; 548p. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Die Schwermetallbelstung der sedimente des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse: Eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemicer-Zeitung 1981, 105, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, P.; Arienzo, M.; Imperato, M.; Naimo, D.; Nardi, G.; Stanzione, D. Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and sub-surface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahim, G.; Parker, R. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophoridis, C.; Dedepsidis, D.; Fytianos, K. Occurrence and distribution of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of Thermaikos Gulf, N. Greece. Assessment using pollution indicators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D. Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Chang, J.; Qu, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, L. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: An assessment from different indexes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Bi, J.; Zhao, J.; Bu, R. Spatial distribution and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the southern Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melfos, V.; Voudouris, P. Cenozoic metallogeny of Greece and potential for precious, critical and rare metals exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 89, 1030–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christanis, K.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Fernandez-Turiel, J.L.; Bouzinos, A. Geological factors influencing the concentration of trace elements in the Philippi peatland, eastern Macedonia, Greece. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 36, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giouri, A.; Vavelidis, M.; Melfos, V. Primary Approach on the Evaluation of Total Arsenic Concentration in Palea Kavala River, NE Macedonia, Northern Greece. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference Protection and Restoration of the Environment XI (PREXI), Thessaloniki, Greece, 3–6 July 2012; Katsifarakis, K.L., Theodossiou, N., Christodoulatos, C., Koutsospyros, A., Mallios, Z., Eds.; pp. 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Giouri, A.; Vavelidis, M.; Melfos, V. Occurrence of Arsenic in waters and sediments of the Palea Kavala river, NE Macedonia, Northern Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2013, XLVII, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giouri, K.; Vavelidis, M.; Melfos, V.; Papadopoulou, L. Assessment of selected metals enrichment in sediments from Palea Kavala river, NE Macedonia, Northern Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2016, 50, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, A.; Fernandez-Turiel, J.L.; Gimeno, D.; Sikalidis, C. Natural and anthropogenic effects on the soil geochemistry of Kavala area, northern Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2010, 43, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergios, G.; Fernandez-Turiel, J.L.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Gimeno, D. Arsenic Background Concentrations in Surface Soils of Kavala Area, Northern Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 209, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, A.; Fernandez-Turiel, J.L.; Gimeno, D.; Sikalidis, C. Surface soil geochemistry for environmental assessment in Kavala area, northern Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohe, A.; Mposkos, E. Multiple generations of extensional detachments in the Rhodope Mountains (northern Greece): Evidence of episodic exhumation of high-pressure rocks. In The Timing and Location of Major Ore Deposits in an Evolving Orogen; Blundell, D.J., Neubauer, F., von Quadt, A., Eds.; Geological Society: London, UK, 2002; Volume 204, pp. 151–178. [Google Scholar]
- Brun, J.P.; Sokoutis, D. Kinematics of the Southern Rhodope Core Complex (North Greece). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 1079–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydonakis, K.; Gallagher, K.; Brun, J.P.; Jolivet, M.; Gueydan, F.; Kostopoulos, D. Upper Cretaceous exhumation of the western Rhodope Metamorphic Province (Chalkidiki Peninsula, northern Greece). Tectonics 2014, 33, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, G. Tertiary magmatism in the Greek Rhodope Massif, northern Greece: Granitic plutons. In Terranes of Serbia: The Formation of the Geologic Framework of Serbia and the Adjacent Regions; Knezevic, V., Krstic, B., Eds.; University of Belgrade: Belgrade, Serbia, 1996; pp. 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Kronberg, P. Kavala Sheet. In Geological Map of Greece, Scale 1:50.000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME): Athens, Greece, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kronberg, P.; Melidonis, N. Krinidhes Sheet. In Geological Map of Greece, Scale 1:50.000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME): Athens, Greece, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Vavelidis, M.; Melfos, V.; Eleftheriadis, G. Mineralogy and microthermometric investigations in the Au-bearing sulphide mineralization of Palea Kavala (Macedonia, Greece). In Mineral Deposits: Research and Exploration—Where Do They Meet; Papunen, H., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Fornadel, A.P.; Spry, P.G.; Melfos, V.; Vavelidis, M.; Voudouris, P. Is the Palea Kavala Bi–Te–Pb–Sb±Au district, northeastern Greece, an intrusion-related system? Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavelidis, M.; Christofides, G.; Melfos, V. The Au–Ag-bearing mineralization and placer gold of Palea Kavala (Macedonia, N. Greece). In Terranes of Serbia: The Formation of the Geologic Framework of Serbia and the Adjacent Regions; Knežević-Dorđević, V., Krstić, B., Eds.; University of Belgrade: Belgrade, Serbia, 1996; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Vavelidis, M.; Gialoglou, G.; Melfos, V.; Wagner, G.A. Goldgrube in Palea Kavala-Griechenland: Entdeckung von Skaptehyle? Erzmetall 1996, 49, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Melfos, V.; Voudouris, P.; Vavelidis, M.; Spry, P.G. Microthermometric Results and Formation Conditions of a New Intrusion-Related Bi–Te–Pb–Sb±Au Mineralization in the Kavala Pluton, Greece. In Proceedings of the 13th All-Russian Conference on Thermobarogeochemistry in Conjuction with the 4th Asian and Pacific International Fluid Inclusion Society Symposium, Moscow, Russia, 22–25 September 2008; Volume 2, pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Vavelidis, M.; Andreou, S. Gold and Gold Working in Late Bronze Age Northern Greece: The Evidence from Thessaloniki Toumba. Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C. Partitioning of Trace Metals in Sediments: Relationships with Bioavailability. Hydrobiologia 1987, 149, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, W. Environmental impact of metals derived from mining activities: Processes, predictions, preventions. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 52, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Cuia, R.; Li, J.; Weia, H.; Zhao, J.; Bai, F.; Song, W.; Ding, X. Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Changhua River Estuary and adjacent shelf (Hainan Island). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G.; Dutter, R. Statistical Data Analysis Explained; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; 343p. [Google Scholar]
- Grunsky, E.C. The interpretation of geochemical survey data. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2010, 10, 27–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.M.; Djordjević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Polic, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, R. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks; Hemphill Publishing Company: Austin, TX, USA, 1980; 184p. [Google Scholar]
- Egashira, S.; Ashida, K. Flow resistance and sediment transportation in streams with step-pool bed morphology. In Fluvial Hydraulics of Mountain Regions; Armanini, A., DiSilvio, G., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Armanini, A. Principles of River Hydraulics; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; 236p. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.J.; Mo, D.W.; Guo, Y.Y.; Fu, Q.; Yang, J.H.; Jia, Y.F. Multivariate analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, southern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Liu, Y. Study on heavy metal sand ecological risk assessment from Gansu, Ningxia and Inner Mongolia sections of the Yellow, China. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2013, 33, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar]
- Grim, R.E. Applied Clay Mineralogy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962; 422p. [Google Scholar]
- Blatt, H.; Middeleton, G.; Murray, R. Origin of Sedimentary Rocks, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA; 1980; 782p. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MS, USA, 1997; 378p. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, A.; Rapin, F.; Carignan, R. Trace metals in oxic lake sediments: Possible adsorption onto iron oxyhydroxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 47, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.W.; Hawkes, H.E.; Webb, J.S. Geochemistry in Mineral Exploration, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; 657p. [Google Scholar]
- Gambrell, R. Trace and toxic metals in wetlands—Review. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed.; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1995; 371p. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D. Trace elements in terrestrial environments. In Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability and Risks of Metals; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 867p. [Google Scholar]
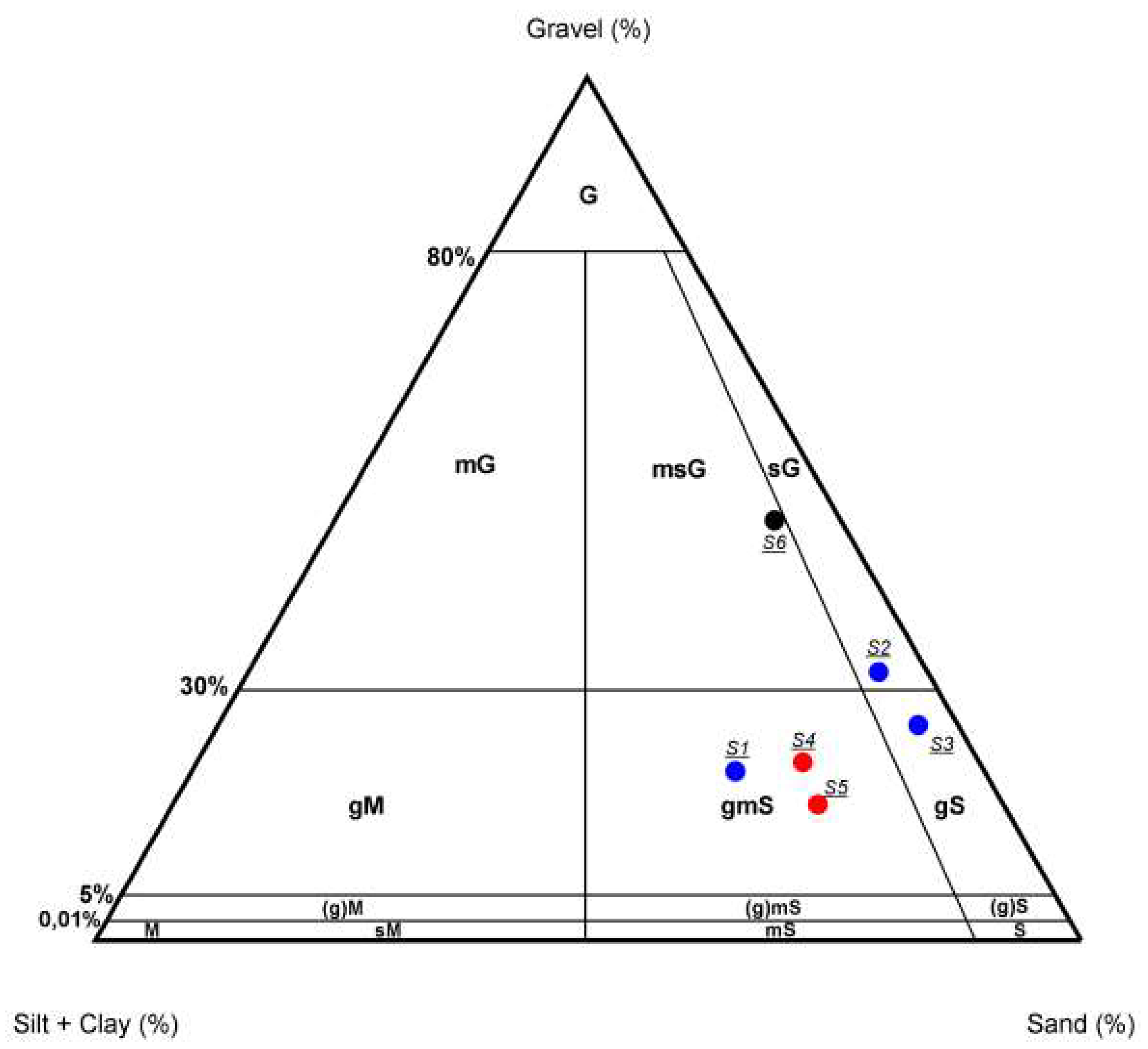
| Sample ID | Gravel (wt %) | Sand (wt %) | Silt+Clay (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 19.85 | 54.98 | 25.18 |
| S2 | 31.26 | 63.66 | 5.08 |
| S3 | 25.06 | 70.87 | 4.07 |
| S4 | 20.63 | 61.38 | 18.00 |
| S5 | 15.90 | 65.34 | 18.77 |
| S6 | 48.75 | 44.52 | 6.73 |
| Median | 22.84 | 62.52 | 12.36 |
| Mean ± SD | 26.91 ± 11.91 | 60.12 ± 9.24 | 12.97 ± 8.81 |
| Variation | 32.85 | 26.35 | 21.11 |
| Sample ID | Al2O3 (wt %) | CaO (wt %) | Fe2O3 (wt %) | MnO (wt %) | SiO2 (wt %) | Cu (μg∙g−1) | Zn (μg∙g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 15.90 | 5.70 | 7.30 | 0.16 | 50.35 | 73.20 | 151.00 |
| S2 | 8.74 | 27.69 | 8.40 | 1.01 | 21.03 | 73.31 | 302.80 |
| S3 | 12.65 | 11.78 | 6.42 | 0.15 | 40.44 | 56.97 | 154.40 |
| S4 | 14.61 | 6.46 | 7.27 | 0.18 | 50.97 | 66.58 | 171.50 |
| S5 | 18.78 | 1.22 | 10.87 | 0.20 | 47.68 | 61.23 | 181.70 |
| S6 | 9.03 | 25.72 | 3.63 | 0.09 | 31.22 | 23.54 | 65.10 |
| Median | 13.63 | 13.10 | 7.28 | 0.17 | 44.06 | 63.91 | 162.95 |
| Mean ± SD | 13.28 ± 3.95 | 9.12 ± 11.08 | 7.31 ± 2.38 | 0.30 ± 0.35 | 40.28 ± 12.03 | 59.14 ± 18.60 | 171.08 ± 76.65 |
| Variation | 10.04 | 26.47 | 7.24 | 0.92 | 29.94 | 49.77 | 237.70 |
| Average Shale | 8.00 | 4.72 | 0.085 | 45 | 95 |
| Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MnO | SiO2 | Cu | Zn | |
| Al2O3 | 1 | ||||||
| CaO | −0.999 | 1 | |||||
| Fe2O3 | 0.429 | −0.429 | 1 | ||||
| MnO | 0.086 | −0.086 | 0.886 | 1 | |||
| SiO2 | 0.771 | −0.771 | 0.086 | −0.029 | 1 | ||
| Cu | −0.029 | 0.029 | 0.657 | 0.771 | 0.086 | 1 | |
| Zn | −0.029 | 0.029 | 0.771 | 0.943 | −0.143 | 0.600 | 1 |
| Parameter | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 0.962 | 0.203 |
| CaO | −0.990 | −0.128 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.448 | 0.816 |
| MnO | −0.662 | 0.745 |
| SiO2 | 0.968 | −0.113 |
| Cu | 0.292 | 0.874 |
| Zn | −0.278 | 0.955 |
| Eigenvalues | 3.651 | 2.960 |
| % total variance | 52.04 | 42.39 |
| % cumulative variance | 52.04 | 94.43 |
| (a) | Cu exchangeable | Fe exchangeable | Mn exchangeable | Zn exchangeable |
| Cu exchangeable | 1 | |||
| Fe exchangeable | 0.261 | 1 | ||
| Mn exchangeable | 0.343 | 0.088 | 1 | |
| Zn exchangeable | 0.638 | 0.143 | 0.794 | 1 |
| (b) | Cu carbonates | Fe carbonates | Mn carbonates | Zn carbonates |
| Cu carbonates | 1 | |||
| Fe carbonates | −0.143 | 1 | ||
| Mn carbonates | −0.086 | 0.600 | 1 | |
| Zn carbonates | 0.600 | −0.771 | −0.143 | 1 |
| (c) | Cu oxides | Fe oxides | Mn oxides | Zn oxides |
| Cu oxides | 1 | |||
| Fe oxides | 0.714 | 1 | ||
| Mn oxides | 0.771 | 0.943 | 1 | |
| Zn oxides | 0.657 | 0.486 | 0.714 | 1 |
| (d) | Cu organic | Fe organic | Mn organic | Zn organic |
| Cu organic | 1 | |||
| Fe organic | −0.771 | 1 | ||
| Mn organic | −0.943 | 0.886 | 1 | |
| Zn organic | 0.143 | 0.086 | 0.086 | 1 |
| Sample ID | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF | Igeo | EF | Igeo | EF | Igeo | EF | Igeo | |
| S1 | 1.03 | −0.47 | 1.55 | 0.12 | 1.39 | −0.04 | 1.51 | 0.08 |
| S2 | 2.15 | −0.27 | 2.82 | 0.12 | 15.98 | 2.62 | 5.51 | 1.09 |
| S3 | 1.14 | −0.66 | 1.51 | −0.24 | 1.59 | −0.17 | 1.94 | 0.12 |
| S4 | 1.11 | −0.48 | 1.53 | −0.02 | 1.66 | 0.10 | 1.87 | 0.27 |
| S5 | 1.30 | 0.10 | 1.09 | −0.14 | 1.45 | 0.27 | 1.54 | 0.35 |
| S6 | 0.90 | −1.48 | 0.88 | −1.52 | 1.38 | −0.87 | 1.15 | −1.13 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giouri, K.; Melfos, V.; Papadopoulou, L.; Vavelidis, M.; Alifragkis, D. Selected Metal Content and Binding Behaviour in Riverbed Sediments of the Kavala–Philippi Area (Northern Greece). Geosciences 2018, 8, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050187
Giouri K, Melfos V, Papadopoulou L, Vavelidis M, Alifragkis D. Selected Metal Content and Binding Behaviour in Riverbed Sediments of the Kavala–Philippi Area (Northern Greece). Geosciences. 2018; 8(5):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050187
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiouri, Katerina, Vasilios Melfos, Lamprini Papadopoulou, Michael Vavelidis, and Dimitrios Alifragkis. 2018. "Selected Metal Content and Binding Behaviour in Riverbed Sediments of the Kavala–Philippi Area (Northern Greece)" Geosciences 8, no. 5: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050187
APA StyleGiouri, K., Melfos, V., Papadopoulou, L., Vavelidis, M., & Alifragkis, D. (2018). Selected Metal Content and Binding Behaviour in Riverbed Sediments of the Kavala–Philippi Area (Northern Greece). Geosciences, 8(5), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8050187






