Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater Sources of Penghu Islands, Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
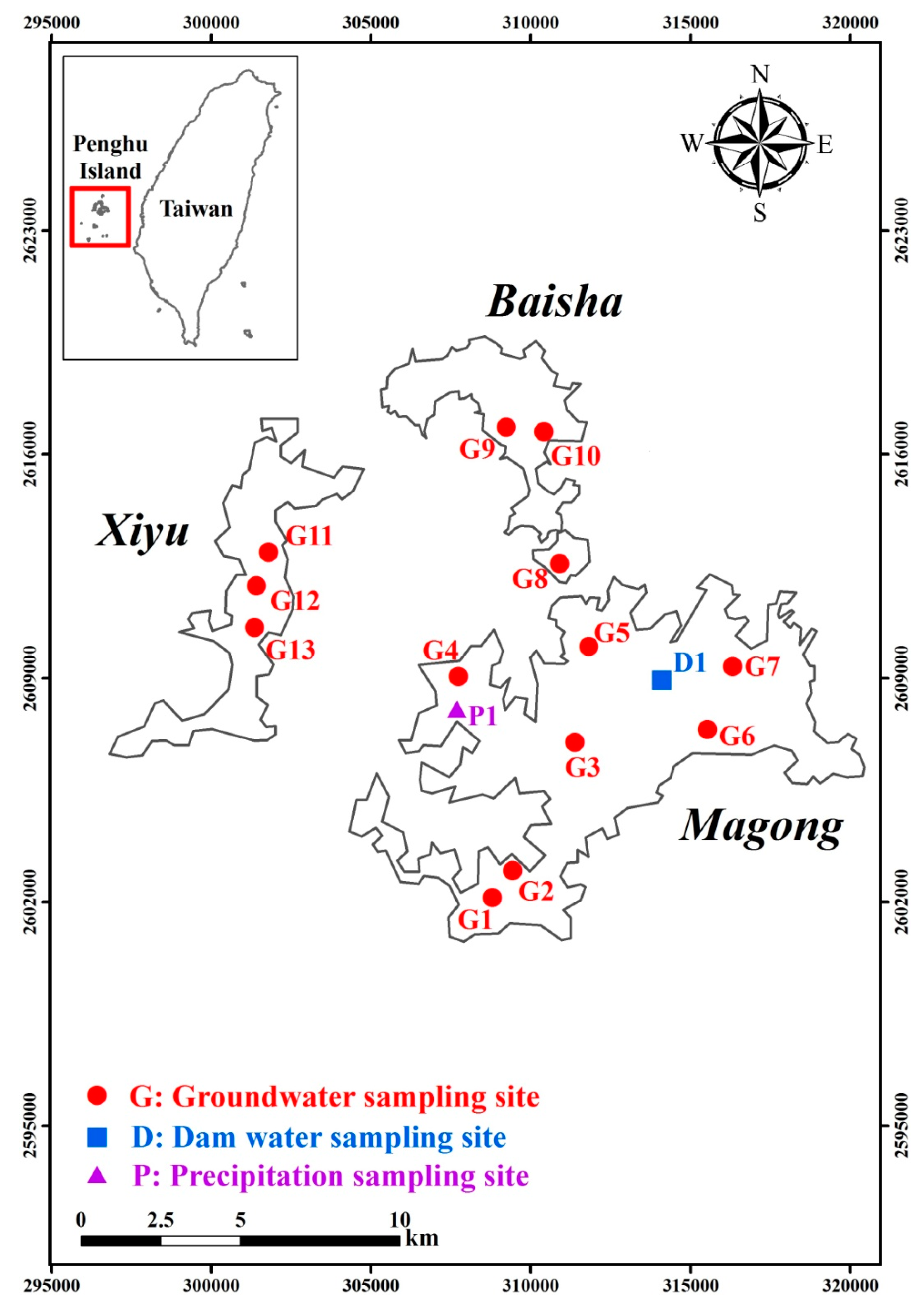
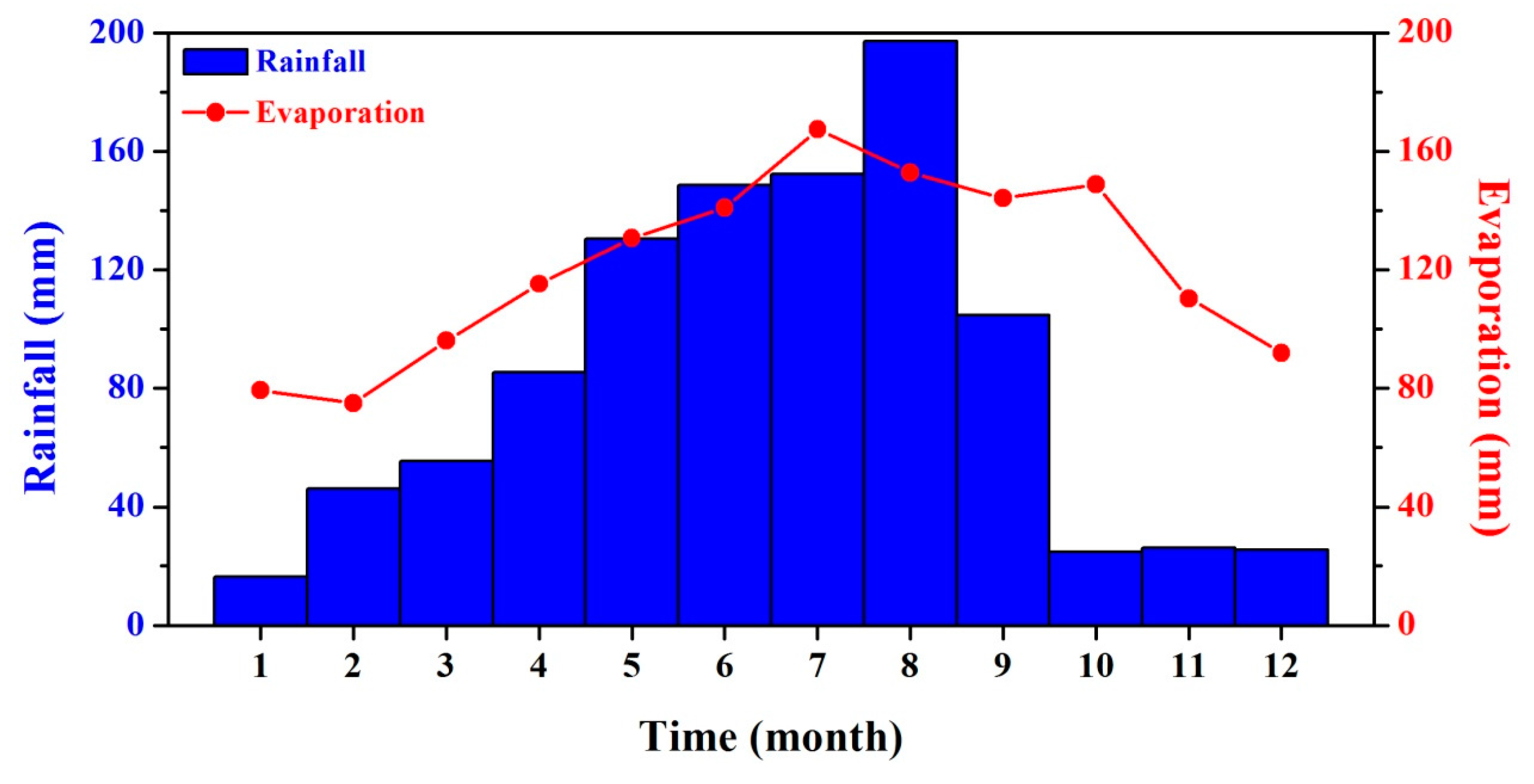
2. Study Area
3. Sampling and Analytical Techniques
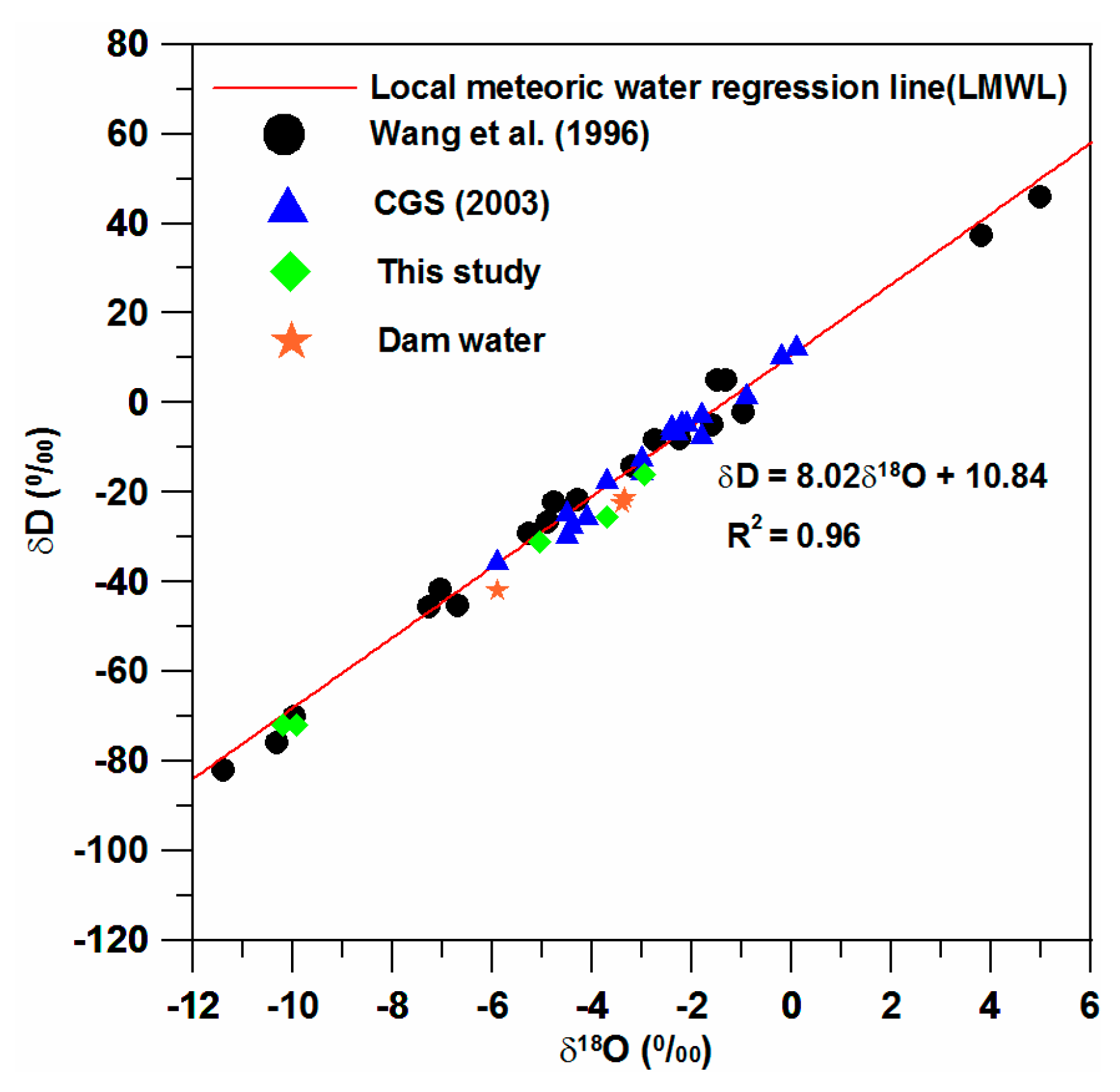
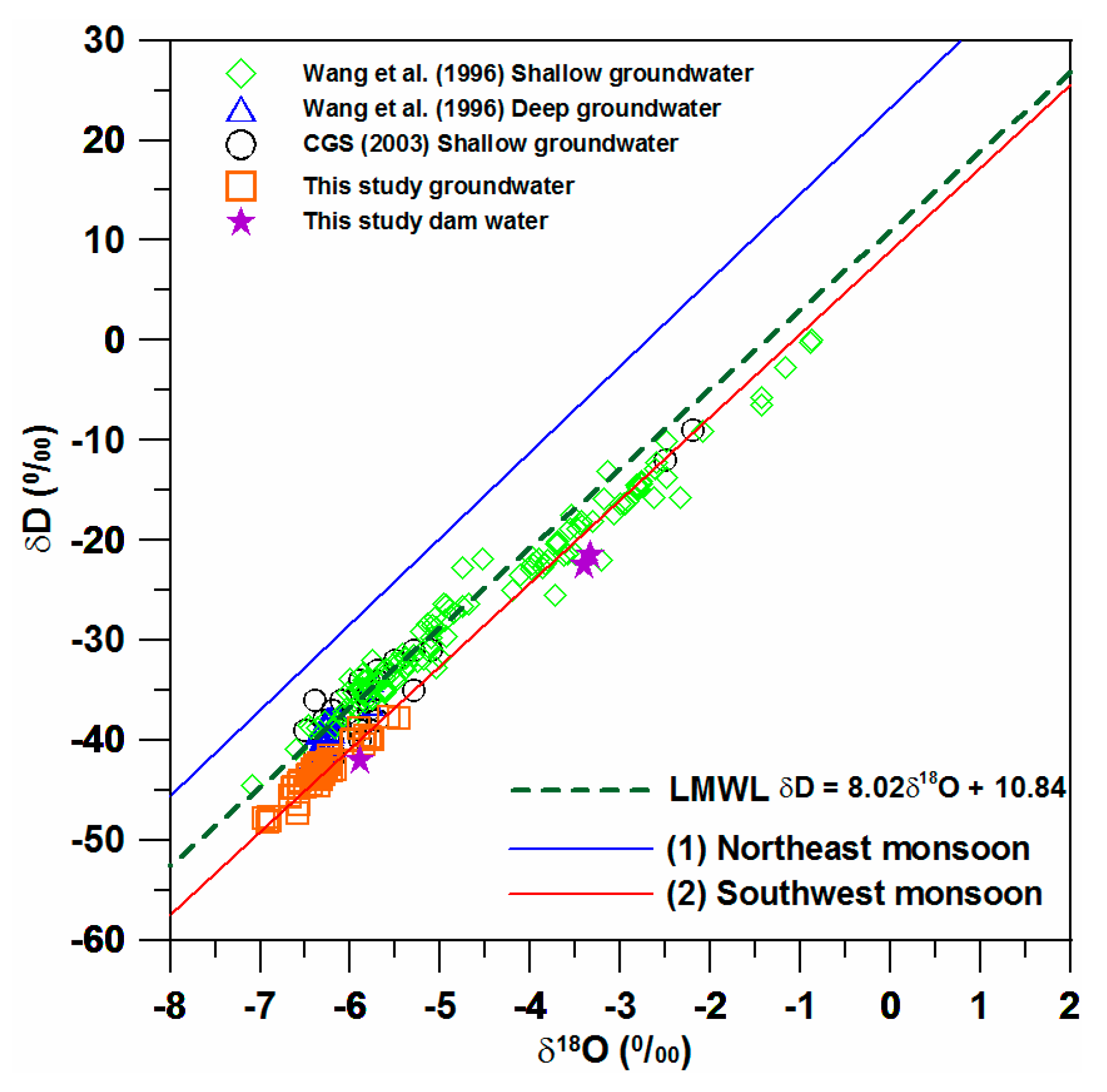
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrology; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gorski, G.; Strong, C.; Good, S.P.; Bares, R.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Bowen, G.J. Vapor hydrogen and oxygen isotopes reflect water of combustion in the urban atmosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 3247–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Huang, D.; Wang, T. Isotopic signatures of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater interactions, Poyang Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F. Stable isotope evidences on sources and mechanisms of groundwater recharge in Hohhot basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, P.M.; Marques, J.M.; Nunes, D. Source of groundwater salinity in coastline aquifers based on environmental isotopes (Portugal): Natural vs. human interference. A review and reinterpretation. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 41, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Ding, R.; Tong, L. Quantification of maize water uptake from different layers and root zones under alternate furrow irrigation using stable oxygen isotope. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothfuss, Y.; Merz, S.; Hermes, N.; Weuthen, A.; Pohlmeier, A.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Long-term and high-frequency non-destructive monitoring of water stable isotope profiles in an evaporating soil column. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4067–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Liang, X.; Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Nimmo, J.R.; Li, J. Evaluation of diffuse and preferential flow pathways of infiltrated precipitation and irrigation using oxygen and hydrogen isotopes. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes for the characteristics of groundwater recharge: A case study from the Chih-Ben Creek basin, Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yamanaka, T. Tracing groundwater recharge sources in a mountain–plain transitional area using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Love, A. Profiles of geochemical and isotopic signatures from the Helan Mountains to the eastern Tengger Desert, northwestern China. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 90, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.R.; Huang, C.C.; Zhan, W.J.; Wang, C.H. Assessing groundwater sources and their association with reservoir water using stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes: A case study of the Taipei Basin, northern Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lin, H.I.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Wu, C.S. Identifying seasonal groundwater recharge using environmental stable isotopes. Water 2014, 6, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.S.; Liu, C.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, W.S. Using a mass balance model to evaluate groundwater budget of seawater-intruded island aquifers. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Resources Agency. Integrated Groundwater Conservation Strategy Planning for Penghu Region; Ministry of Economic Affairs of the Republic of China: Taipei, Taiwan, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Water Resources Agency. Hydrological Year Book of Taiwan; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 2015. (In Chinese)
- Water Resources Agency. A Quantitative Investigation on Sea Water Intrusions in the Penghu Area and Its Related Remediation Strategy; Ministry of Economic Affairs of the Republic of China: Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Epstein, S.; Mayeda, T. Variation of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninkmeijer, C.A.M.; Kraft, P.; Mook, W.G. Oxygen isotope fractionation between CO2 and H2O. Isotope Geosci. 1983, 1, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.L.; Shepherd, T.J.; Durham, J.J.; Rouse, J.E.; Moore, G.R. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal. Chem. 1982, 54, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Yeh, H.W.; Tsai, P.S.; Wu, S.F. Hydrogen Stable Isotope Determination of Water Samples by Zinc Shot Reduction; Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica: Taipei, Taiwan, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Chen, P.F.; Peng, T.R.; Yeh, C.C. A Preliminary Report on Stable Isotope Geochemistry in Groundwater of the Penghu Islands; Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica: Taipei, Taiwan, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Peng, T.R.; Tsai, P.S.; Wu, S.F.; Shieh, Y.T.; Cherng, F.P. Stable isotopes compositions of groundwater from Penghu Islands and its implications. In Proceedings of the First Symposium on Groundwater Resources and Water Protection, Taipei, Taiwan, 29 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Chang, T.C.; Lee, L.A.; Lee, H.H.; Chuang, T.M.; Lin, K.; Lu, C.S. The Salinization of Groundwater in the Chih-Kan Subsurface Reservoir of Penghu Islands; Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica: Taipei, Taiwan, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Central Geological Survey (CGS). Study of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater in Penghu, Hsinchu-Miaoli and Chianan Areas; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 2003. (In Chinese)
- Peng, T.R.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Fei, L.Y.; Chen, C.T.A.; Hwong, J.L. Stable isotopic characteristic of Taiwan’s precipitation: A case study of western Pacific monsoon region. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, H.-F.; Lee, J.-W. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater Sources of Penghu Islands, Taiwan. Geosciences 2018, 8, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030084
Yeh H-F, Lee J-W. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater Sources of Penghu Islands, Taiwan. Geosciences. 2018; 8(3):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030084
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Hsin-Fu, and Jhe-Wei Lee. 2018. "Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater Sources of Penghu Islands, Taiwan" Geosciences 8, no. 3: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030084
APA StyleYeh, H.-F., & Lee, J.-W. (2018). Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Groundwater Sources of Penghu Islands, Taiwan. Geosciences, 8(3), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030084





