Melt Reintegration Modelling: Testing against a Subsolidus Reference Assemblage
Abstract
1. Introduction
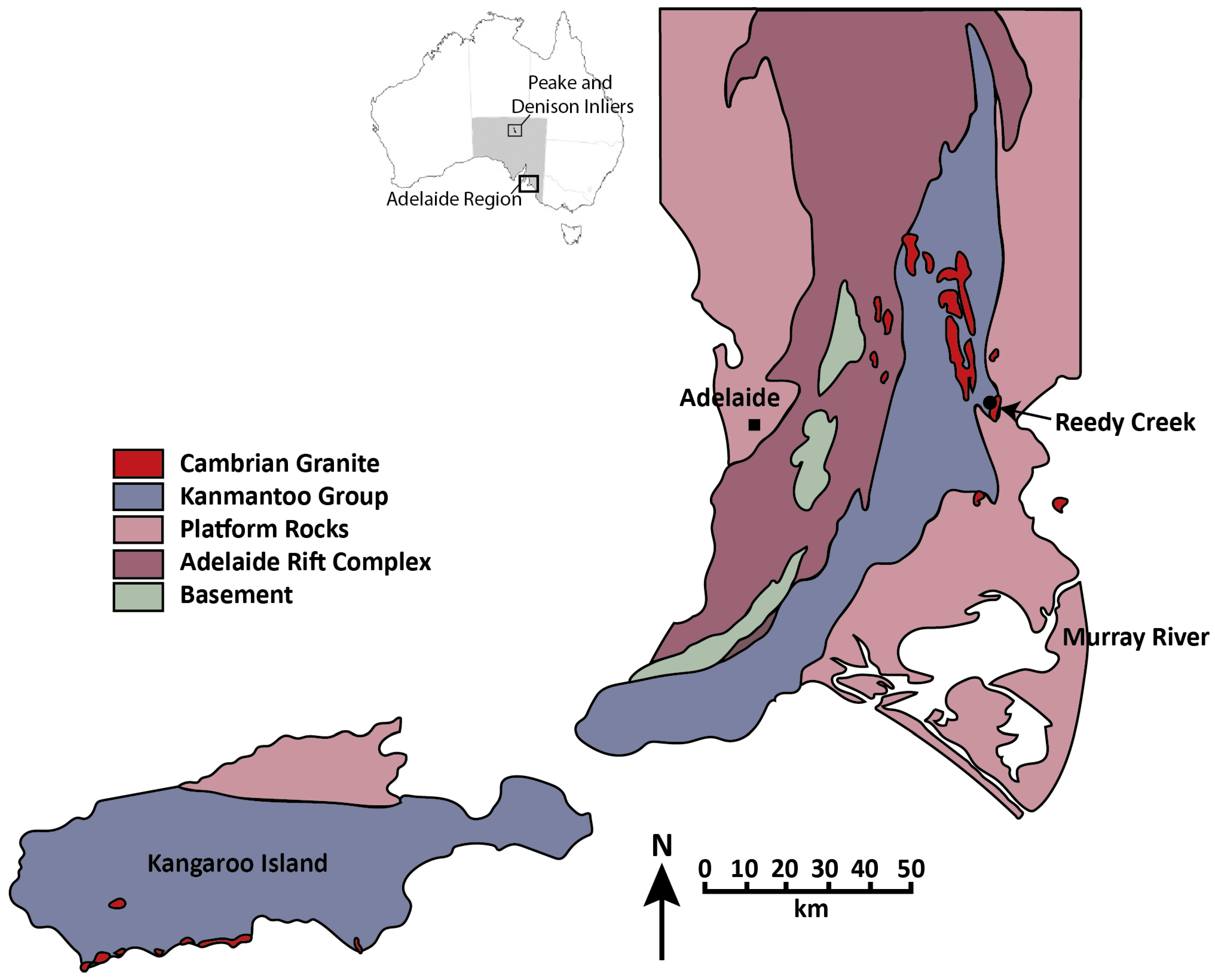
2. Geological Setting
Samples and Petrography
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Peak P–T Conditions
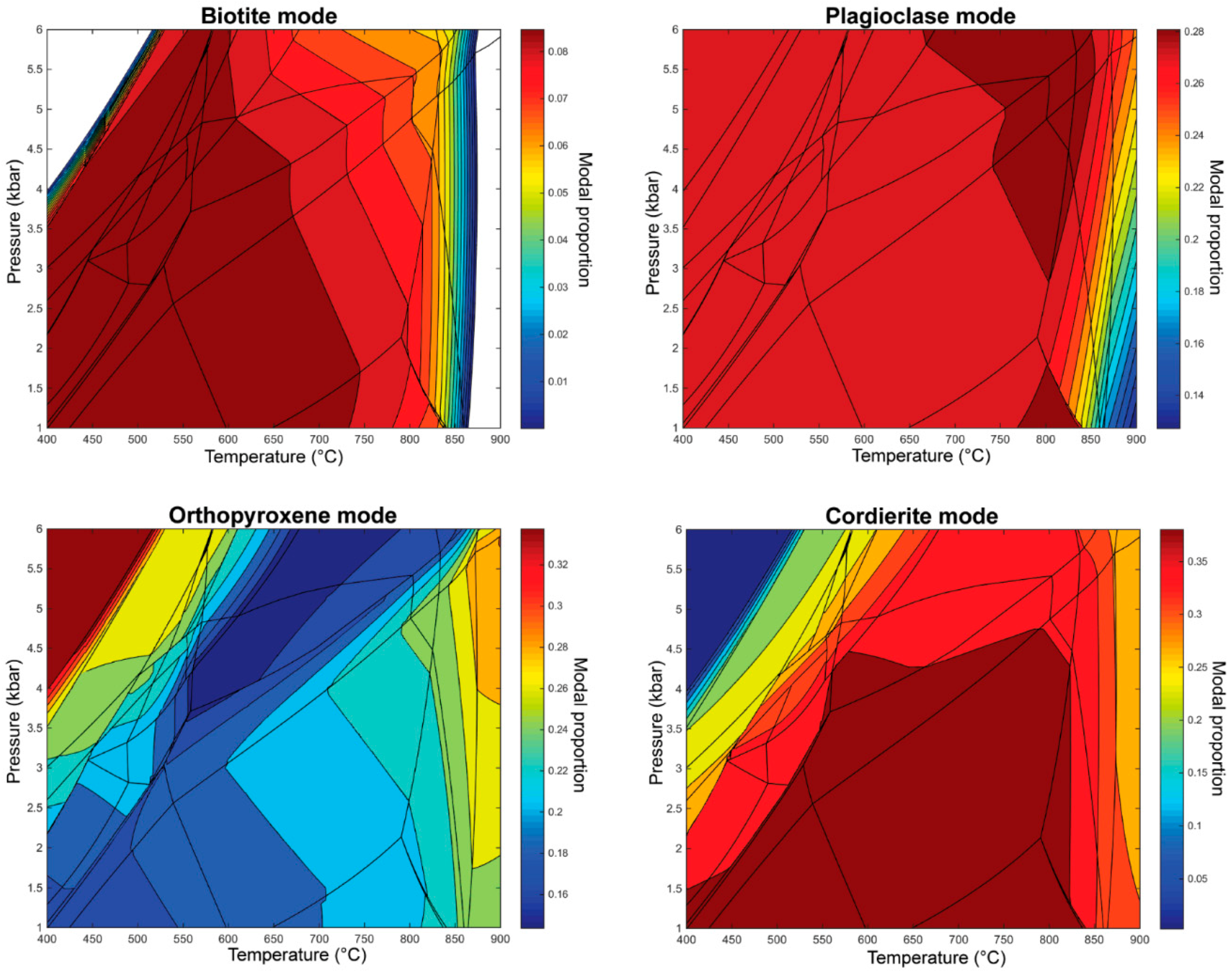
4.2. Melt Reintegration
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations of the Modelling
5.2. Implications of the Melt Reintegration Modelling
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
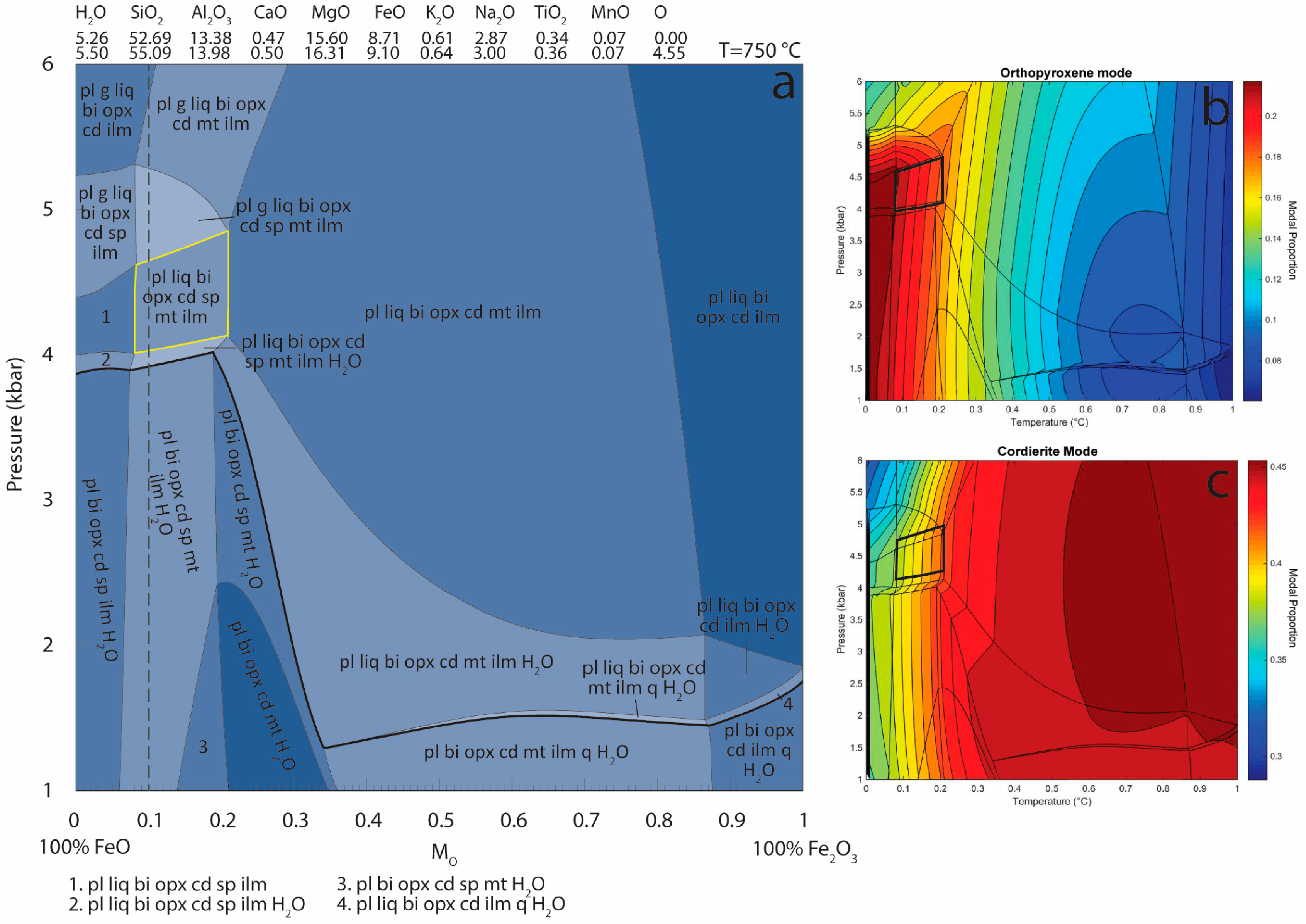
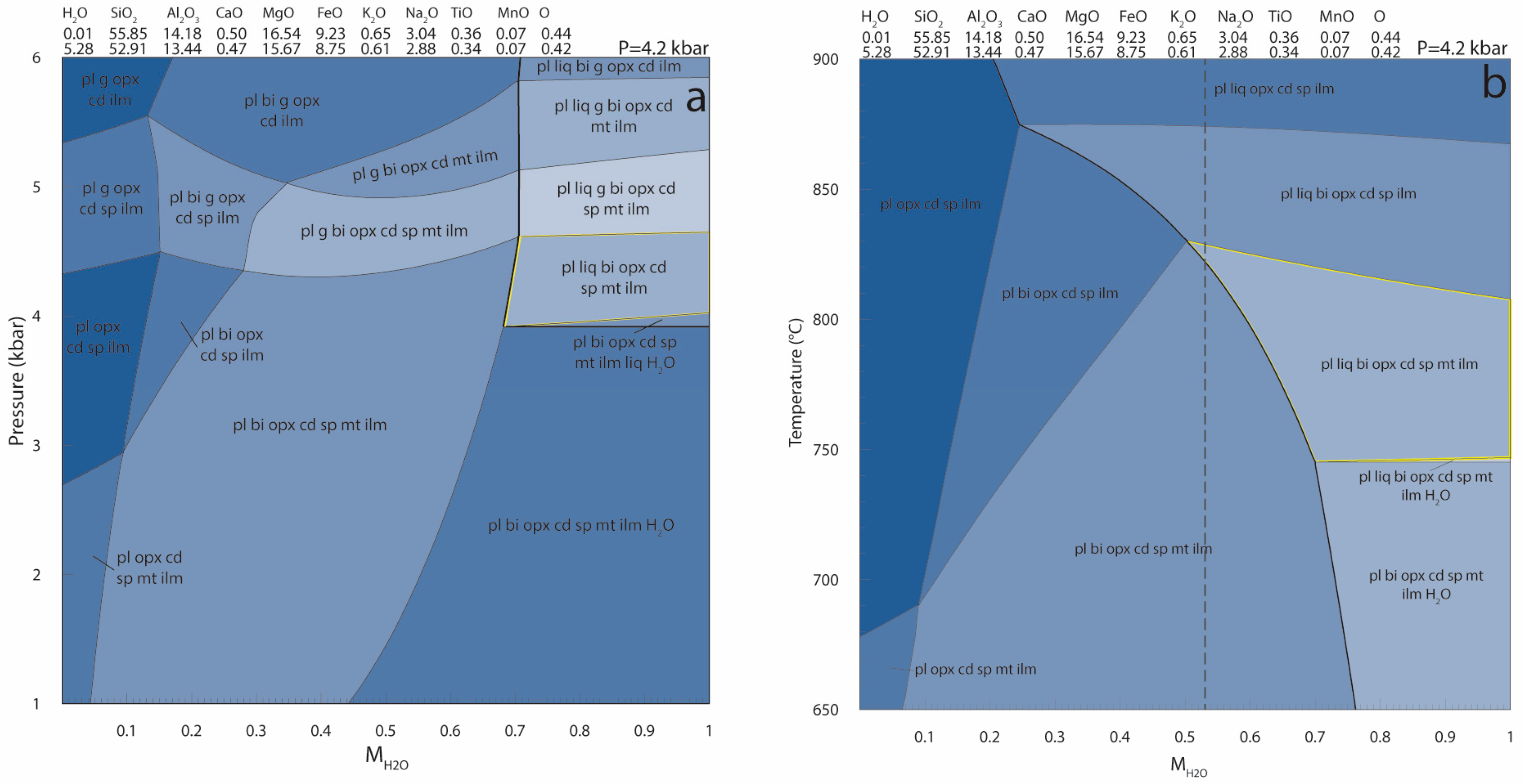
Appendix B
References
- Brown, M. Crustal melting and melt extraction, ascent and emplacement in orogens: Mechanisms and consequences. J. Geol. Soc. 2007, 164, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, K.S. Metamorphism and the chemical differentiation of the crust. GFF 1965, 87, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sighinolfi, G.P.; Gorgoni, C. Chemical evolution of high-grade metamorphic rocks—Anatexis and remotion of material from granulite terrains. Chem. Geol. 1978, 22, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Powell, R. Calculation of phase relations involving haplogranitic melts using an internally consistent thermodynamic dataset. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Holland, T. Progress relating to calculation of partial melting equilibria for metapelites. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2007, 25, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Holland, T.; Worley, B. The effect of TiO2 and Fe2O3 on metapelitic assemblages at greenschist and amphibolite facies conditions: Mineral equilibria calculations in the system K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–TiO2–Fe2O3. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2000, 18, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; White, R.; Powell, R. Partial melting of metagreywacke: A calculated mineral equilibria study. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2008, 26, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; White, R.; Green, E.; Holland, T.; Diener, J. On parameterizing thermodynamic descriptions of minerals for petrological calculations. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2014, 32, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Holland, T.; Johnson, T.; Green, E. New mineral activity–composition relations for thermodynamic calculations in metapelitic systems. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2014, 32, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Johnson, T. The effect of Mn on mineral stability in metapelites revisited: New a–x relations for manganese-bearing minerals. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2014, 32, 809–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, L.J.; Hand, M.; Lane, K.; Kelsey, D.E.; Dutch, R.A. Upgrading iron-ore deposits by melt loss during granulite facies metamorphism. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 74, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, J.; White, R.; Powell, R. Granulite facies metamorphism and subsolidus fluid-absent reworking, Strangways Range, Arunta Block, central Australia. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2008, 26, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakymchuk, C.; Brown, M. Consequences of open-system melting in tectonics. J. Geol. Soc. 2014, 171, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakymchuk, C.; Brown, M. Behaviour of zircon and monazite during crustal melting. J. Geol. Soc. 2014, 171, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, J.F.; Fagereng, Å. The influence of melting and melt drainage on crustal rheology during orogenesis. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 6193–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblinger, B.M.; Pattison, D.R. Crystallization of Heterogeneous Pelitic Migmatites: Insights from Thermodynamic Modelling. J. Petrol. 2017, 58, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, O. Phase equilibria modelling of residual migmatites and granulites: An evaluation of the melt-reintegration approach. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, F.; Brown, M.; Clark, C.; Bhattacharya, S. Osumilite–melt interactions in ultrahigh temperature granulites: Phase equilibria modelling and implications for the P–T–t evolution of the Eastern Ghats Province, India. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2013, 31, 881–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Halpin, J. Spatially-focussed melt formation in aluminous metapelites from Broken Hill, Australia. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2004, 22, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redler, C.; White, R.W.; Johnson, T.E. Migmatites in the Ivrea Zone (NW Italy): Constraints on partial melting and melt loss in metasedimentary rocks from Val Strona di Omegna. Lithos 2013, 175, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakymchuk, C.; Brown, M.; Clark, C.; Korhonen, F.; Piccoli, P.; Siddoway, C.; Taylor, R.; Vervoort, J. Decoding polyphase migmatites using geochronology and phase equilibria modelling. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2015, 33, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodge, J.W. Latest Neoproterozoic basin inversion of the Beardmore Group, central Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica. Tectonics 1997, 16, 682–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, E. The Ross Orogen of the Transantarctic Mountains; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Milnes, A.; Compston, W.; Daily, B. Pre-to syn-tectonic emplacement of early Palaeozoic granites in southeastern South Australia. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1977, 24, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, W.V. The Adelaide Geosyncline: Late Proterozoic Stratigraphy, Sedimentation, Palaeontology and Tectonics; Department of Mines and Energy: Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, 1987.
- Haines, P.W.; Flöttmann, T. Delamerian Orogeny and potential foreland sedimentation: A review of age and stratigraphic constraints. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1998, 45, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foden, J.; Elburg, M.A.; Dougherty-Page, J.; Burtt, A. The timing and duration of the Delamerian Orogeny: Correlation with the Ross Orogen and implications for Gondwana assembly. J. Geol. 2006, 114, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flöttmann, T.; James, P.; Rogers, J.; Johnson, T. Early Palaeozoic foreland thrusting and basin reactivation at the Palaeo-Pacific margin of the southeastern Australian Precambrian Craton: A reappraisal of the structural evolution of the Southern Adelaide Fold-Thrust Belt. Tectonophysics 1994, 234, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancktelow, N.S. The structure of the southern Adelaide fold belt, South Australia. In The evolution of a Late Precambrian–Early Palaeozoic Rift Complex: The Adelaide Geosyncline; Geological Society of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1990; Volume 16, pp. 369–395. [Google Scholar]
- Offler, R.; Fleming, P. A synthesis of folding and metamorphism in the Mt Lofty Ranges, South Australia. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1968, 15, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foden, J.; Sandiford, M.; Dougherty-Page, J.; Williams, I. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Rathjen Gneiss: Implications for the early tectonic evolution of the Delamerian Orogen. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1999, 46, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foden, J.; Elburg, M.; Turner, S.; Sandiford, M.; O’Callaghan, J.; Mitchell, S. Granite production in the Delamerian orogen, South Australia. J. Geol. Soc. 2002, 159, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Foden, J. Magma mingling in late-Delamerian A-type granites at Mannum, South Australia. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 56, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Kelley, S.; VandenBerg, A.; Foden, J.; Sandiford, M.; Flöttmann, T. Source of the Lachlan fold belt flysch linked to convective removal of the lithospheric mantle and rapid exhumation of the Delamerian-Ross fold belt. Geology 1996, 24, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandiford, M.; Eraser, G.; Arnold, J.; Foden, J.; Farrow, T. Some causes and consequences of high-temperature, low-pressure metamorphism in the eastern Mt Lofty Ranges, South Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1995, 42, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, T. The Petrology and Geochemistry of the Reedy Creek Granitoids and Migmatites. Honours Thesis, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sando, M. The Granitic and Metamorphic Rocks of the Reedy Creek Area, Mannum, South Australia. Master’s Thesis, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.; Powell, R. Melt loss and the preservation of granulite facies mineral assemblages. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- Dymoke, P.; Sandiford, M. Phase relationships in Buchan facies series pelitic assemblages: Calculations with application to andalusite-staurolite parageneses in the Mount Lofty Ranges, South Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 110, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, C.; Powell, R.; Clarke, G. Calculated mineral equilibria for eclogites in CaO–Na2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O: Application to the Pouébo Terrane, Pam Peninsula, New Caledonia. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1999, 17, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indares, A.; White, R.; Powell, R. Phase equilibria modelling of kyanite-bearing anatectic paragneisses from the central Grenville Province. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2008, 26, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palin, R.M.; Weller, O.M.; Waters, D.J.; Dyck, B. Quantifying geological uncertainty in metamorphic phase equilibria modelling; a Monte Carlo assessment and implications for tectonic interpretations. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Powell, R. An improved and extended internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for phases of petrological interest, involving a new equation of state for solids. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2011, 29, 333–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Holland, T. An internally consistent thermodynamic dataset with uncertainties and correlations: 3. Applications to geobarometry, worked examples and a computer program. J. Metamorphic Geol. 1988, 6, 173–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.A.; White, A.J.R.; Gazley, M.F. TCInvestigator: Automated calculation of mineral mode and composition contours for thermocalc pseudosections. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2015, 33, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.J.F.; Sandiford, M. Observations on the tectonic evolution of the southern Adelaide Fold Belt. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.L.; Handy, M.R. Experimental deformation of partially melted granite revisited: Implications for the continental crust. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2005, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, G.; Sandiford, M.; Hand, M.; Worley, B. The P–T record of synchronous magmatism, metamorphism and deformation at Petrel Cove, southern Adelaide Fold Belt. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R. Retrograde melt–residue interaction and the formation of near-anhydrous leucosomes in migmatites. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2010, 28, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkoltip, P.; Ashworth, J. Quantitative estimation of an open-system symplectite-forming reaction: Restricted diffusion of Al and Si in coronas around olivine. J. Petrol. 1983, 24, 635–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, D.E.; Hand, M. On ultrahigh temperature crustal metamorphism: Phase equilibria, trace element thermometry, bulk composition, heat sources, timescales and tectonic settings. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 311–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ague, J.J. Evidence for major mass transfer and volume strain during regional metamorphism of pelites. Geology 1991, 19, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.D.; Droop, G.T.; Stevens, G. High-grade metamorphism, dehydration and crustal melting: A reinvestigation based on new experiments in the silica-saturated portion of the system KAlO2–MgO–SiO2–H2O–CO2 at P ≤ 1.5 GPa. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1997, 129, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wyllie, P. Muscovite dehydration and melting in deep crust and subducted oceanic sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1973, 18, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashiro, A. Evolution of metamorphic belts. J. Petrol. 1961, 2, 277–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, G.; Powell, R.; McLaren, S. Phase equilibria constraints on the melt fertility of crustal rocks: The effect of subsolidus water loss. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2015, 33, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.; DeBuhr, C. Petrology of metapelites in the Bugaboo aureole, British Columbia, Canada. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2015, 33, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.; Chacko, T.; Kuehner, S. The effects of fluorine on the vapor-absent melting of phlogopite+ quartz; implications for deep-crustal processes. Am. Miner. 1991, 76, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, G.T.; Berry, R.F.; Green, D.H. Internally consistent gahnitic spinel-cordierite-garnet equilibria in the FMASHZn system: Geothermobarometry and applications. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 111, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.; Flöttmann, T.; Sandiford, M. Structural geometry and controls on basement-involved deformation in the northern Flinders Ranges, Adelaide Fold Belt, South Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1999, 46, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, C.E. Contact-metamorphism in the Comrie area of the Perthshire Highlands. Q. J. Geol. Soc. 1924, 80, 22–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.R.; Tracy, R.J. Phase equilibria and thermobarometry of metapelites. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1991, 26, 105–206. [Google Scholar]
- Droop, G.R.; Bucher-Nurminen, K. Reaction textures and metamorphic evolution of sapphirine-bearing granulites from the Gruf Complex, Italian Central Alps. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 766–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlov, D.E.; Johansson, L.; Van Den Kerkhof, A.; Förster, H.-J. The role of advective fluid flow and diffusion during localized, solid-state dehydration: Söndrum Stenhuggeriet, Halmstad, SW Sweden. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballèvre, M.; Hensen, B.J.; Reynard, B. Orthopyroxene-andalusite symplectites replacing cordierite in granulites from the Strangways Range (Arunta block, central Australia): A new twist to the pressure-temperature history. Geology 1997, 25, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, T.-L.; Lidwin, A. Magmatic CO2, brine and nitrogen inclusions in Sveconorwegian enderbitic dehydration veins and a gabbro from the Bamble sector, Southern Norway. Eur. J. Mineral. 1996, 1041–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlov, D.E.; Förster, H.-J. High-grade fluid metasomatism on both a local and a regional scale: The Seward peninsula, Alaska, and the Val Strona di Omegna, Ivrea–Verbano Zone, Northern Italy. Part I: Petrography and silicate mineral chemistry. J. Petrol. 2002, 43, 769–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, U.; Santosh, M. Shear-zone hosted graphite in southern Kerala, India: Implications for CO2 infiltration. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1996, 14, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, J.; Powell, R.; White, R. Quantitative phase petrology of cordierite–orthoamphibole gneisses and related rocks. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2008, 26, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Sandiford, M. Petrogenesis of cordierite-orthoamphibole assemblages from the Springton region, South Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1990, 106, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.; Spear, F.; Debuhr, C.; Cheney, J.; Guidotti, C. Thermodynamic modelling of the reaction muscovite + cordierite → Al2SiO5 + biotite + quartz + H2O: Constraints from natural assemblages and implications for the metapelitic petrogenetic grid. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Powell, R. An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1998, 16, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, J.; Powell, R.; White, R.; Holland, T. A new thermodynamic model for clino-and orthoamphiboles in the system Na2O–CaO–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–O. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2007, 25, 631–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, E.M.; Baker, J.; Powell, R.; Holland, T.; Howell, N. The effect of Mn on mineral stability in metapelites. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1997, 15, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Baker, J.; Powell, R. Mixing properties and activity-composition relationships of chlorites in the system MgO–FeO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O. Eur. J. Mineral. 1998, 10, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.; Powell, R. Activity–composition relations for phases in petrological calculations: An asymmetric multicomponent formulation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 145, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Powell, R.; Clarke, G. The interpretation of reaction textures in Fe-rich metapelitic granulites of the Musgrave Block, central Australia: Constraints from mineral equilibria calculations in the system K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–TiO2–Fe2O3. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilmette, C.; Indares, A.; Hébert, R. High-pressure anatectic paragneisses from the Namche Barwa, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis: Textural evidence for partial melting, phase equilibria modeling and tectonic implications. Lithos 2011, 124, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palin, R.; Searle, M.; Waters, D.; Parrish, R.; Roberts, N.; Horstwood, M.; Yeh, M.W.; Chung, S.L.; Anh, T. A geochronological and petrological study of anatectic paragneiss and associated granite dykes from the Day Nui Con Voi metamorphic core complex, North Vietnam: Constraints on the timing of metamorphism within the Red River shear zone. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2013, 31, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.; Harte, B. Evolution of structurally contrasting anatectic migmatites in the 3-kbar Ballachulish aureole, Scotland. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1988, 6, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.W.; Powell, R.; Holland, T.J.B. Calculation of partial melting equilibria in the system Na2O-CaO-K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O (NCKFMASH). J. Metamorph. Geol. 2001, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M. The spatial and temporal patterning of the deep crust and implications for the process of melt extraction. Philos. Trans. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 11–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.; White, R.; Brown, M. A year in the life of an aluminous metapelite xenolith—The role of heating rates, reaction overstep, H2O retention and melt loss. Lithos 2011, 124, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, D.; Lovegrove, D. Assessing the extent of disequilibrium and overstepping of prograde metamorphic reactions in metapelites from the Bushveld Complex aureole, South Africa. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeh, A.; Holness, M. The effect of reaction overstep on garnet microtextures in metapelitic rocks of the Ilesha Schist Belt, SW Nigeria. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 967–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, F.S.; Pattison, D.R. The implications of overstepping for metamorphic assemblage diagrams (MADs). Chem. Geol. 2017, 457, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; O’Brien, P.; Zhai, M. High-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China craton: Metamorphic evolution, P–T paths and geotectonic significance. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jian, P.; Kröner, A.; Xu, S. Dating of prograde metamorphic events deciphered from episodic zircon growth in rocks of the Dabie–Sulu UHP complex, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 250, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.D. Coesite inclusions and prograde compositional zonation of garnet in whiteschist of the HP-UHPM Kokchetav massif, Kazakhstan: A record of progressive UHP metamorphism. Lithos 2000, 52, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, M.; Toriumi, M. Prograde pressure–temperature paths in the pelitic schists of the Sambagawa metamorphic belt, SW Japan. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schertl, H.-P.; Schreyer, W.; Chopin, C. The pyrope-coesite rocks and their country rocks at Parigi, Dora Maira Massif, Western Alps: Detailed petrography, mineral chemistry and PT-path. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 108, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, F.S.; Selverstone, J.; Hickmott, D.; Crowley, P.; Hodges, K. PT paths from garnet zoning: A new technique for deciphering tectonic processes in crystalline terranes. Geology 1984, 12, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
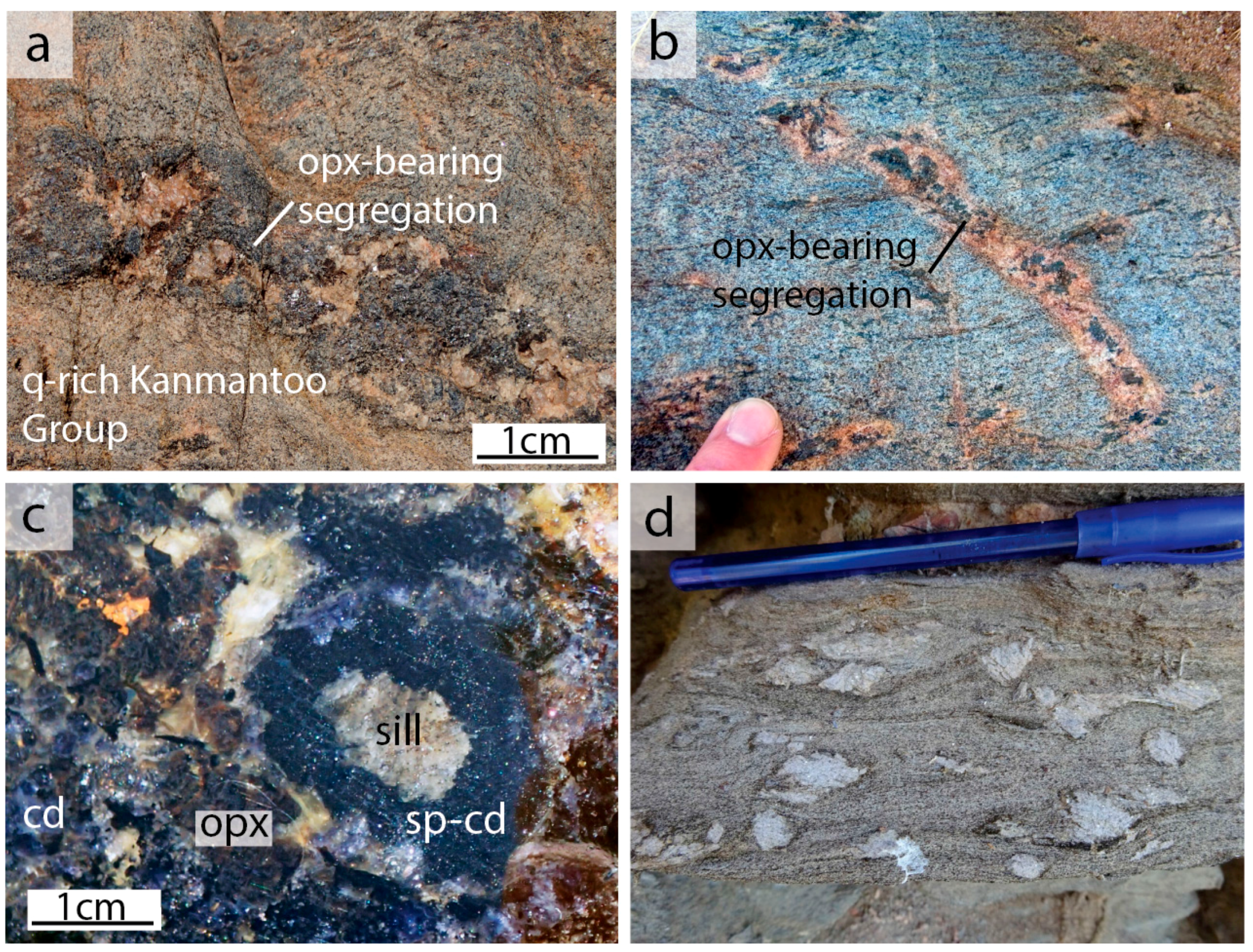

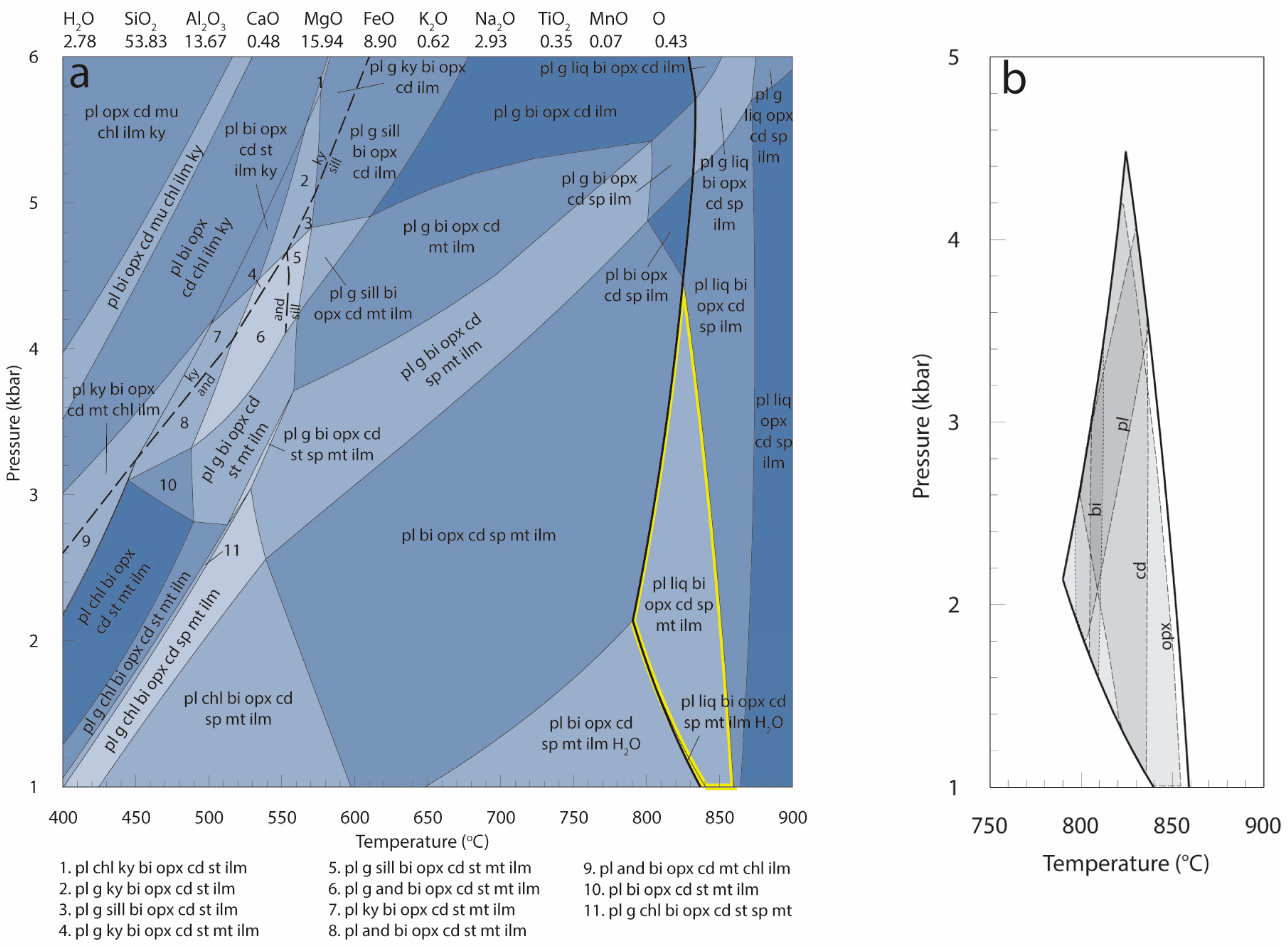
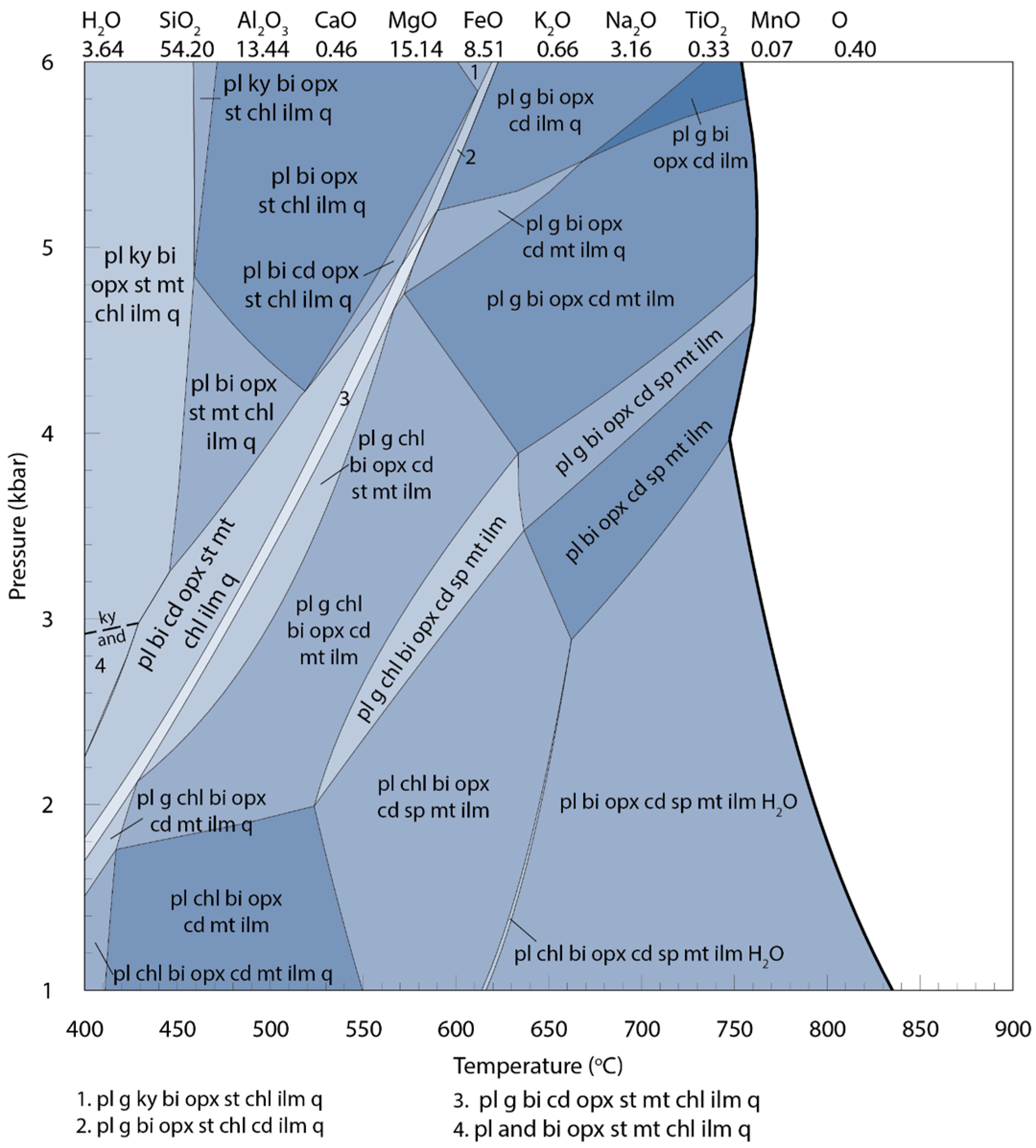
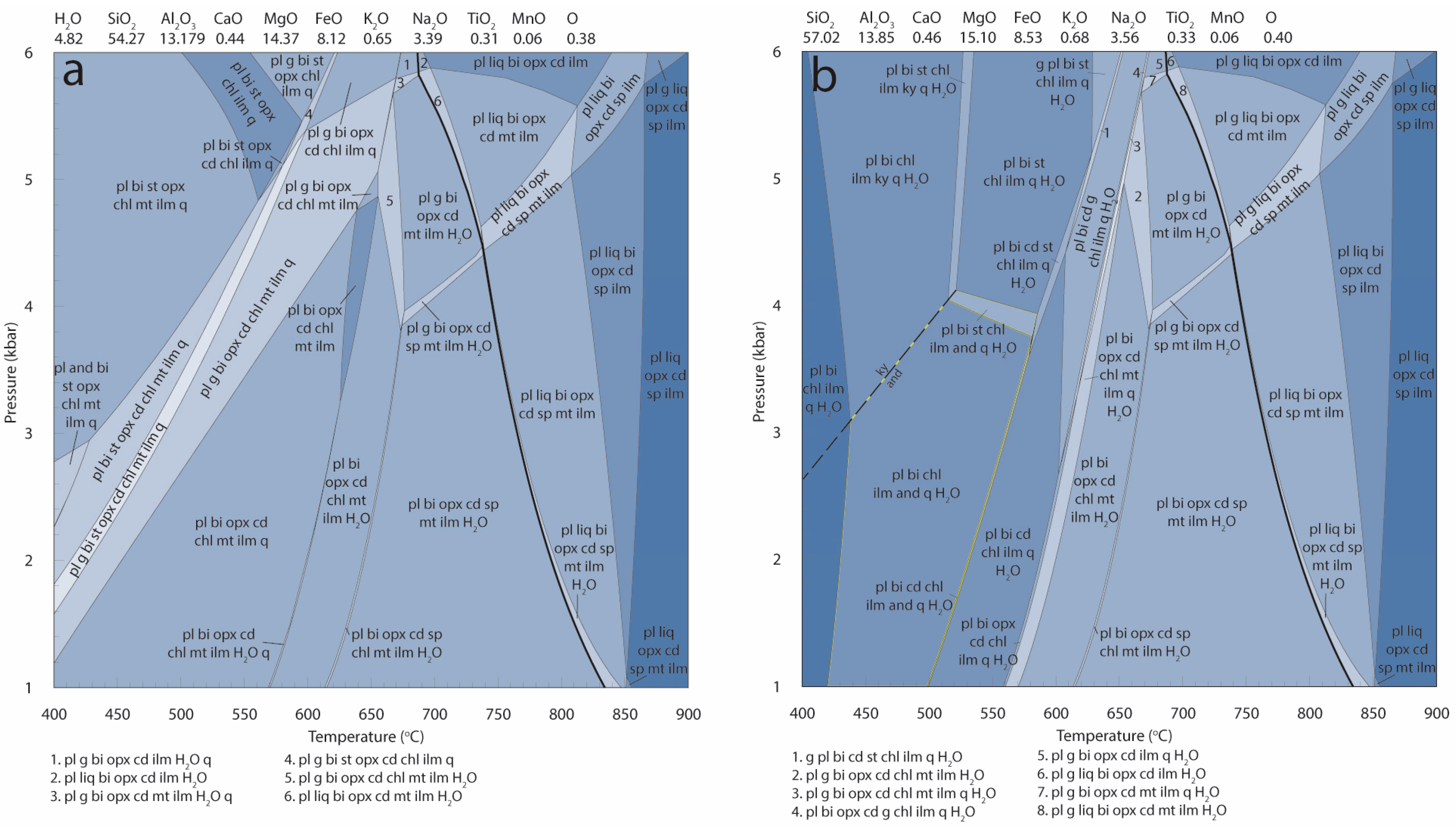
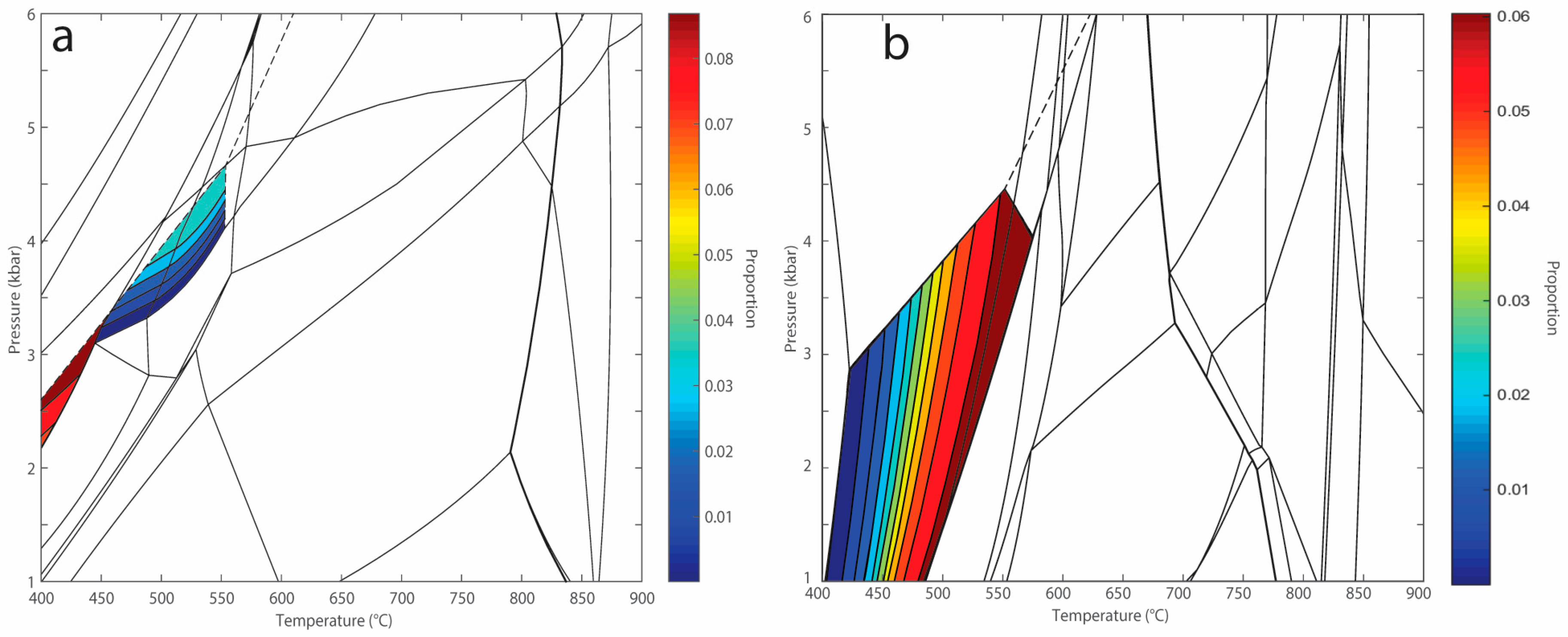
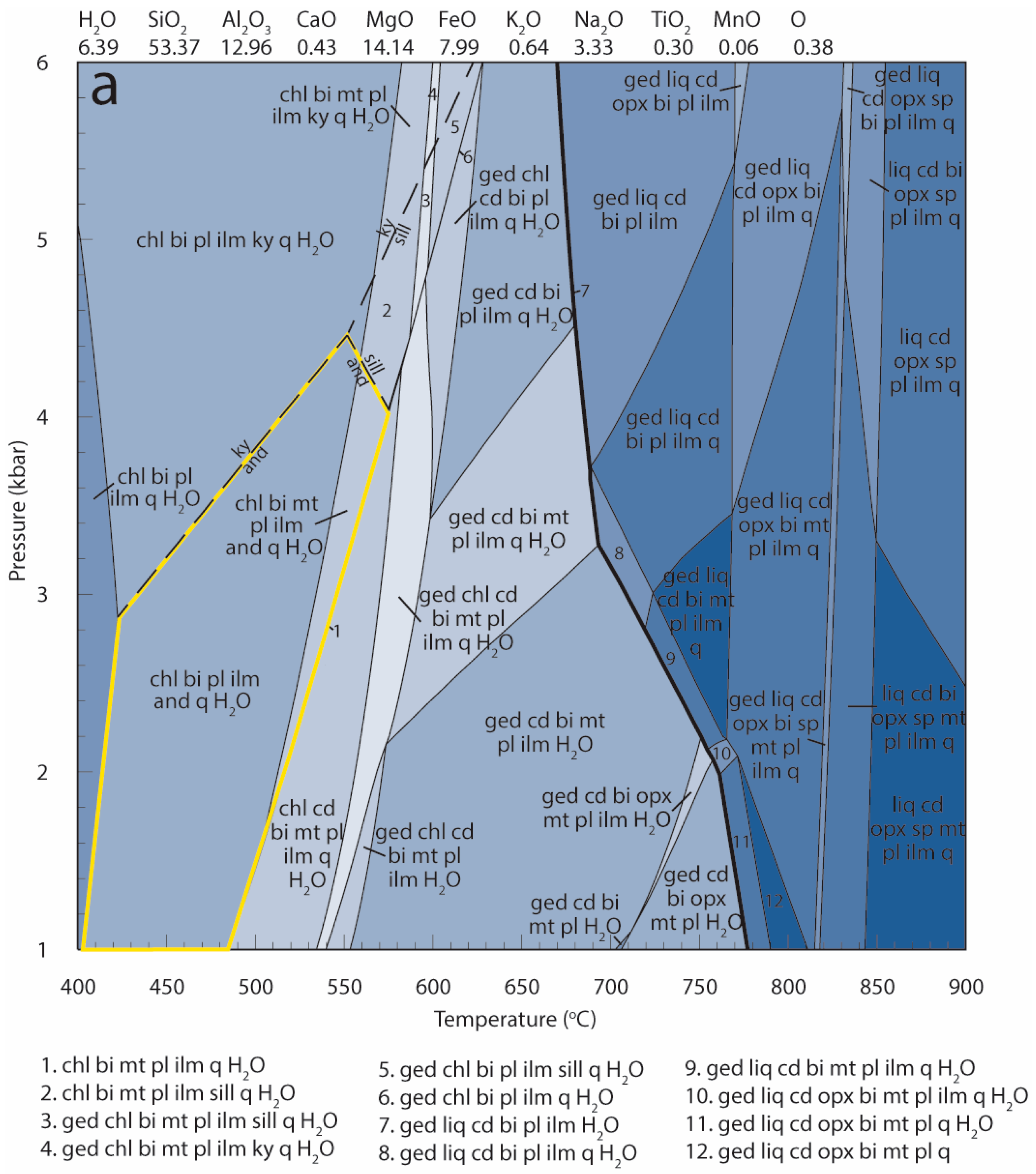
| Mineral | Bi | Cd | Opx | Sp | Pl | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode (wt %) | 9.93 | 34.59 | 21.41 | 6.41 | 27.67 | 100 | – |
| Mineral Density (kg/m3) | 2.9 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 2.6 | – | – |
| wt % | Bi | Cd | Opx | Sp | Pl | Average Bulk Composition | Final Bulk Composition |
| SiO2 | 37.99 | 49.39 | 52.65 | 0.09 | 68.77 | 51.16 | 50.61 |
| TiO2 | 3.48 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| Al2O3 | 15.17 | 33.06 | 2.22 | 58.04 | 19.68 | 22.58 | 22.34 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| FeO | 14.36 | 5.06 | 24.2 | 33.72 | 0 | 10.52 | 10.41 |
| MnO | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| MgO | 15.89 | 11.14 | 21.71 | 7.89 | 0 | 10.58 | 10.47 |
| ZnO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| CaO | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 1.5 | 0.42 | 0.42 |
| Na2O | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.04 | 2.79 | 2.76 |
| K2O | 8.68 | 0 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.86 | 0.85 |
| Cl | 0.49 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| F | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Total | 96.29 | 98.87 | 101.22 | 100.05 | 99.99 | 101.08 | 100 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alessio, K.L.; Hand, M.; Morrissey, L.J.; Kelsey, D.E.; Payne, J.L. Melt Reintegration Modelling: Testing against a Subsolidus Reference Assemblage. Geosciences 2017, 7, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030075
Alessio KL, Hand M, Morrissey LJ, Kelsey DE, Payne JL. Melt Reintegration Modelling: Testing against a Subsolidus Reference Assemblage. Geosciences. 2017; 7(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlessio, Kiara L., Martin Hand, Laura J. Morrissey, David E. Kelsey, and Justin L. Payne. 2017. "Melt Reintegration Modelling: Testing against a Subsolidus Reference Assemblage" Geosciences 7, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030075
APA StyleAlessio, K. L., Hand, M., Morrissey, L. J., Kelsey, D. E., & Payne, J. L. (2017). Melt Reintegration Modelling: Testing against a Subsolidus Reference Assemblage. Geosciences, 7(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030075