Architecture of Glaciotectonic Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classification of the Main Architectural Elements in Glaciotectonics
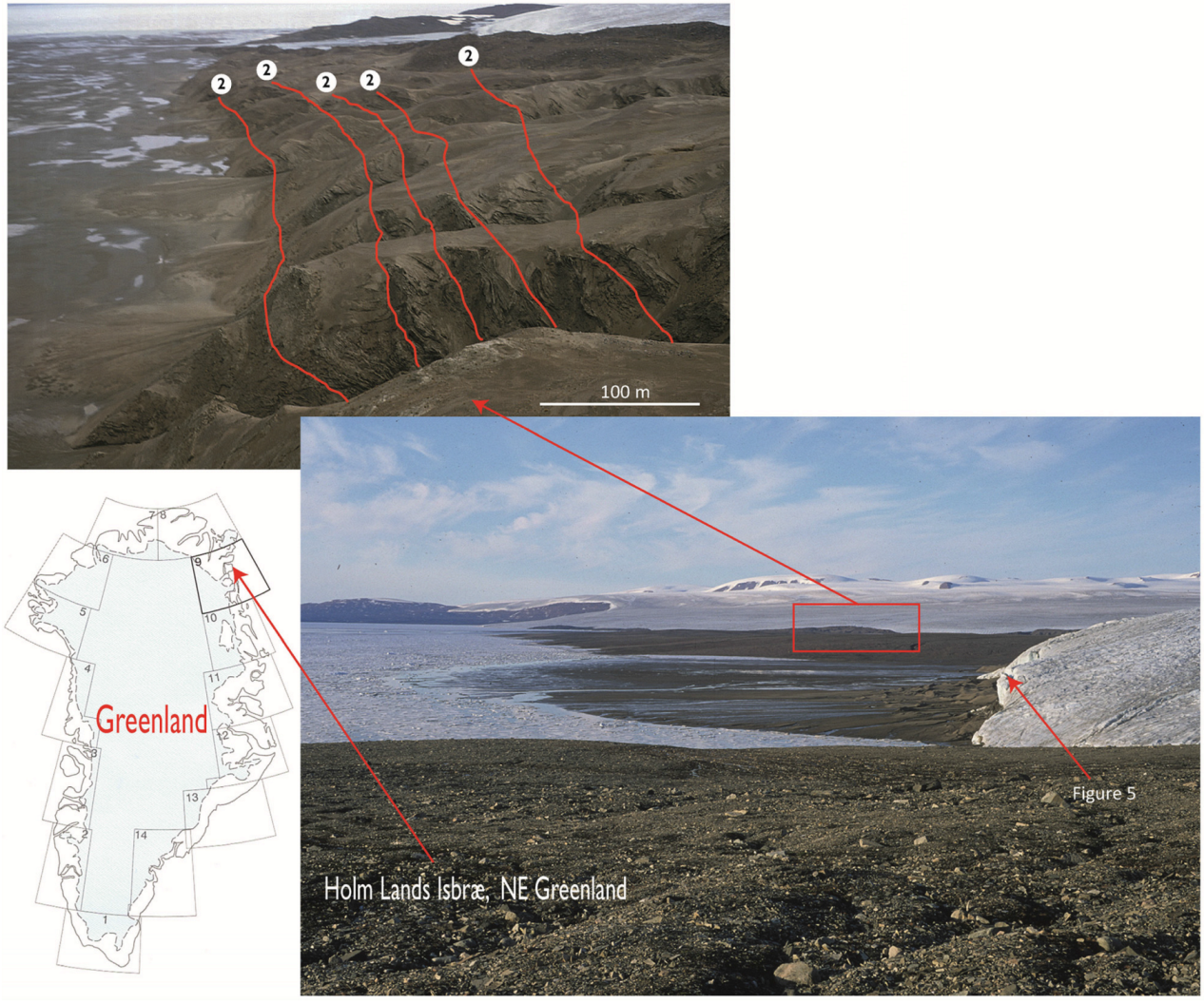
- First-Order surfaces are décollement surfaces and glaciotectonic unconformities.
- Second-Order surfaces are ramps and flats—the thrust faults.
- Third-Order surfaces are folded beds—anticlines and synclines
- Fourth-Order surfaces are small scale folds and faults—kink bands, conjugate faults, box folds, etc.
3. The First-Order Architectural Surfaces
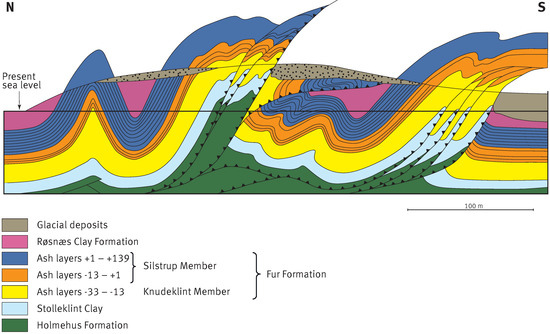
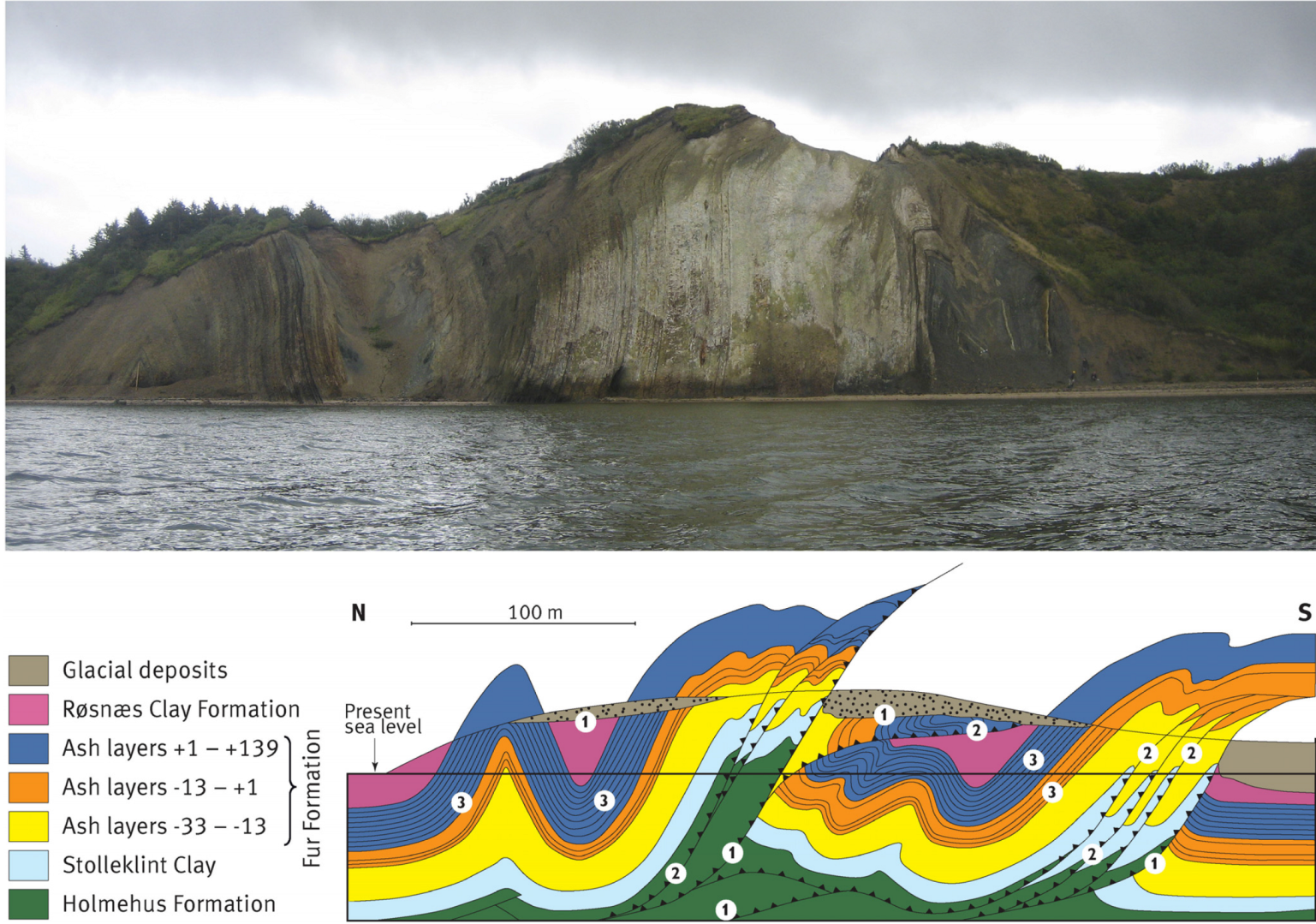
3.1. The Décollement Surface
3.2. The Glaciotectonic Unconformity
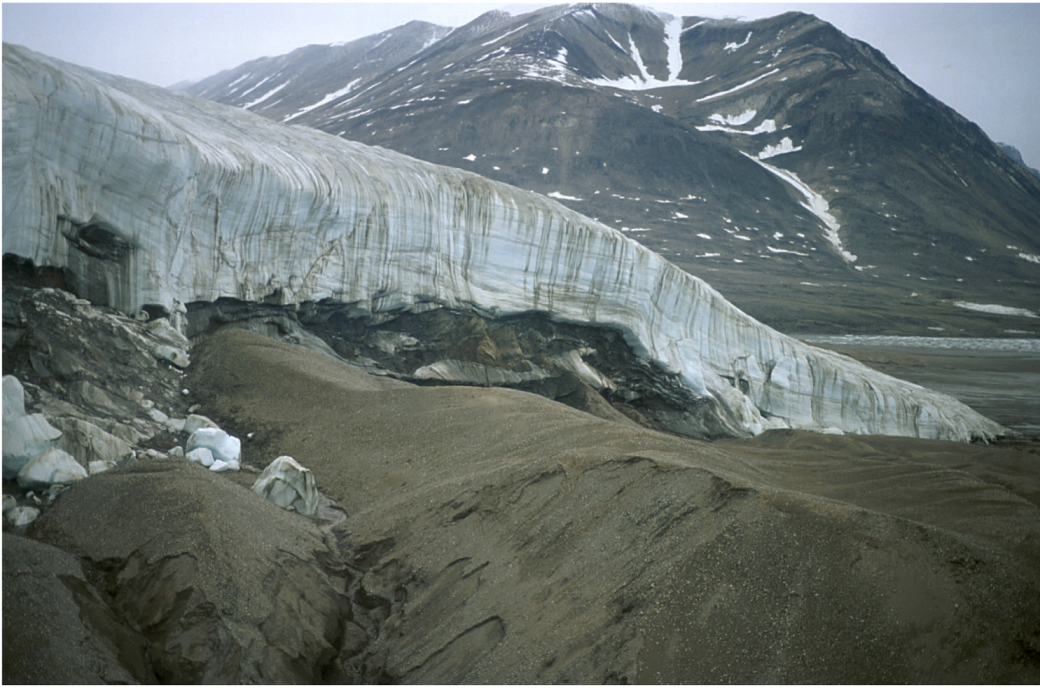
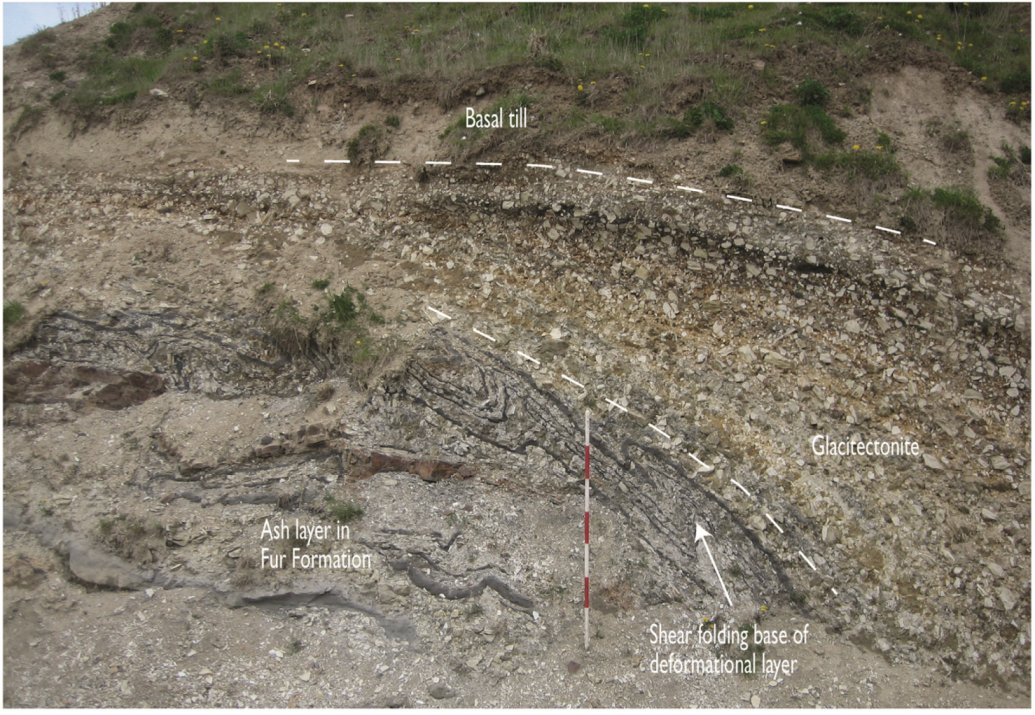
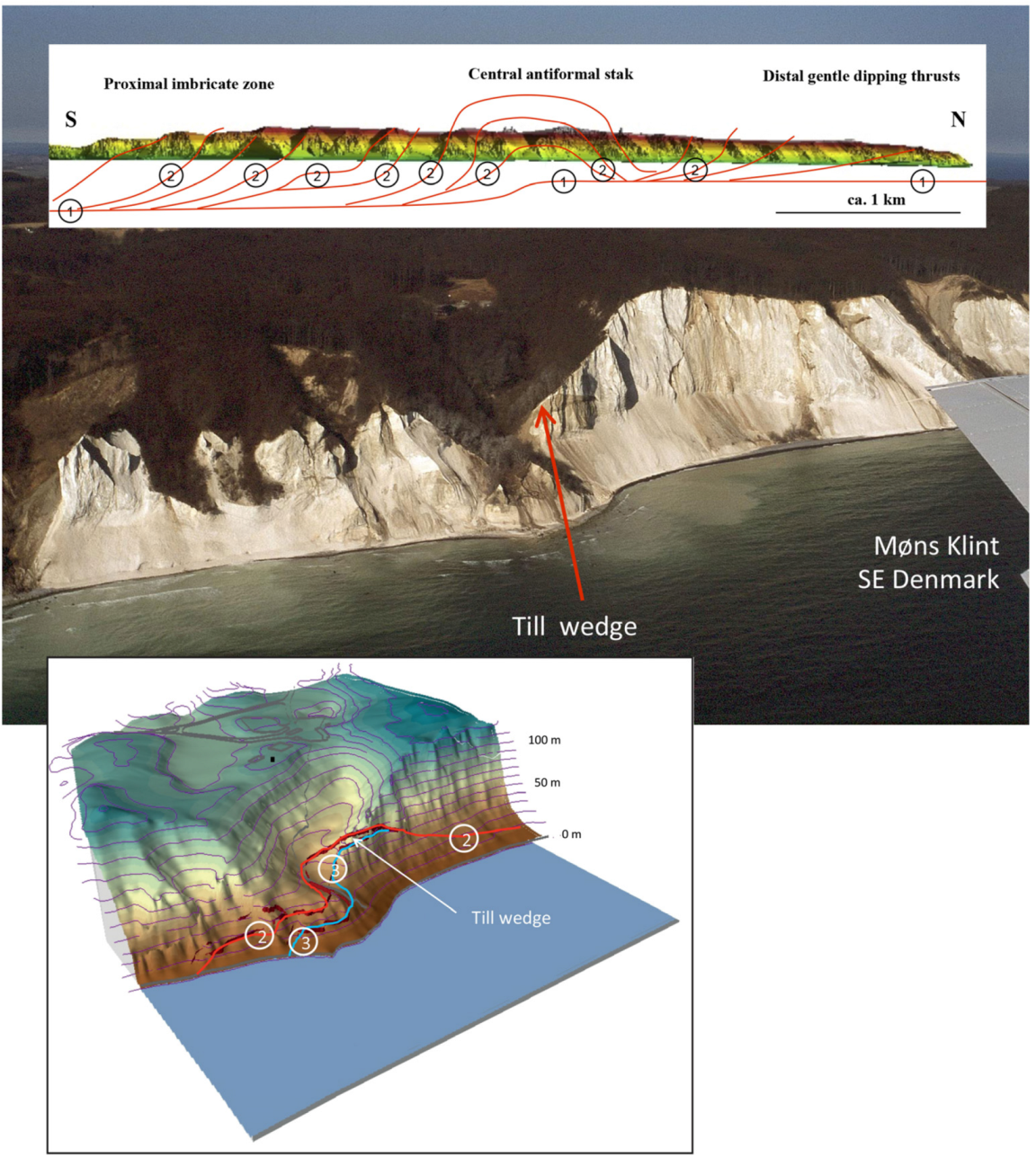


4. The Second-Order Architectural Surfaces
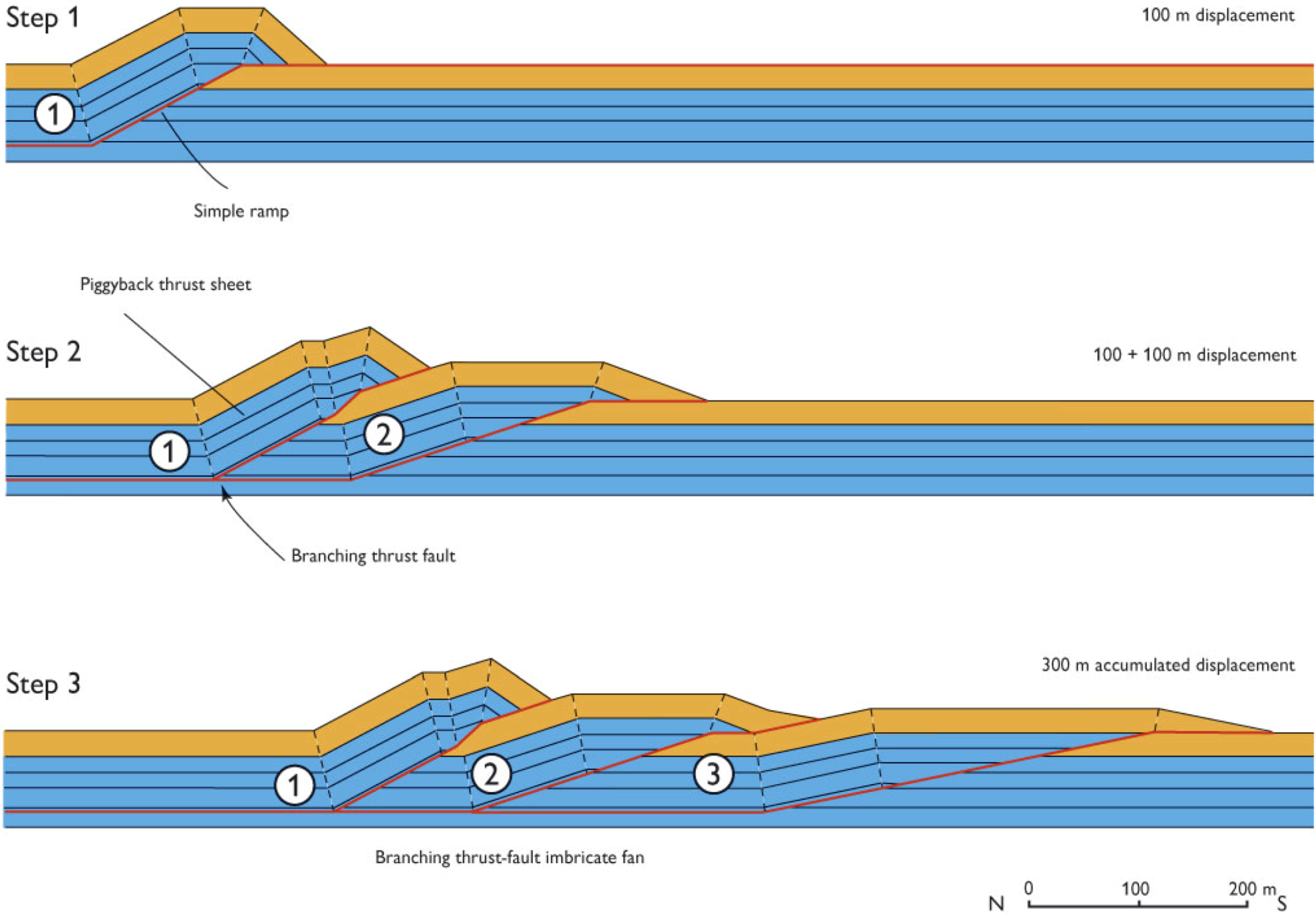
4.1. The Translated Thrust Sheets
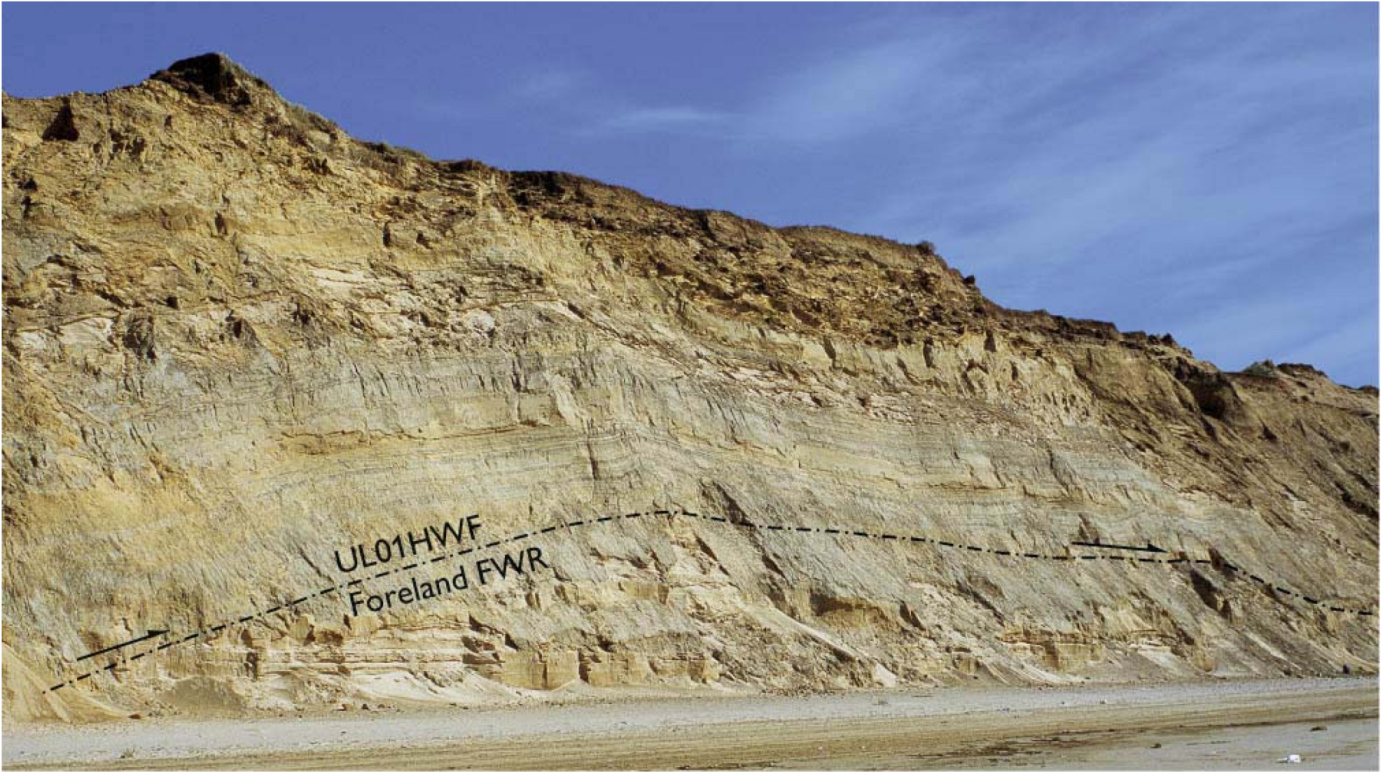

4.2. The Duplex Formation at Ramp Collapse
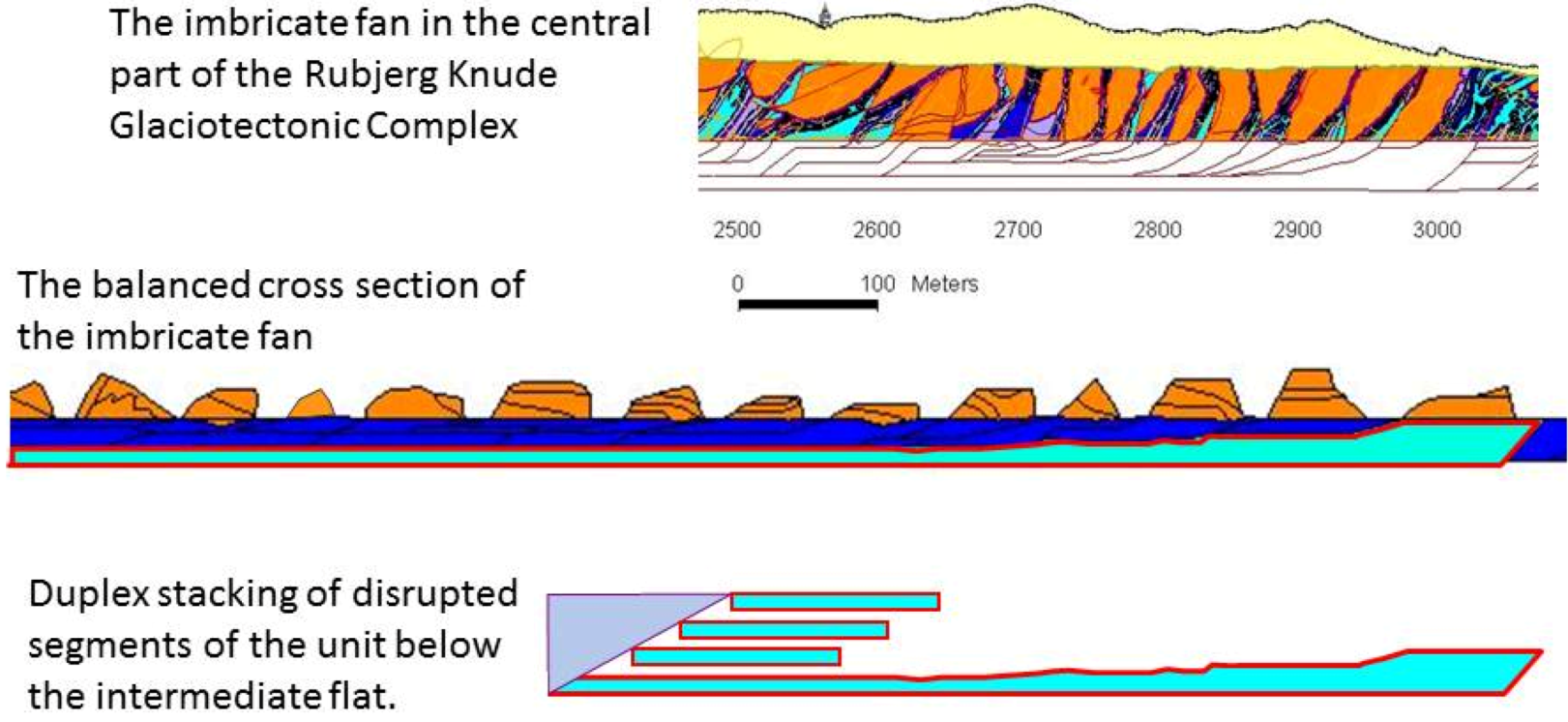
4.3. The Imbricate Fan
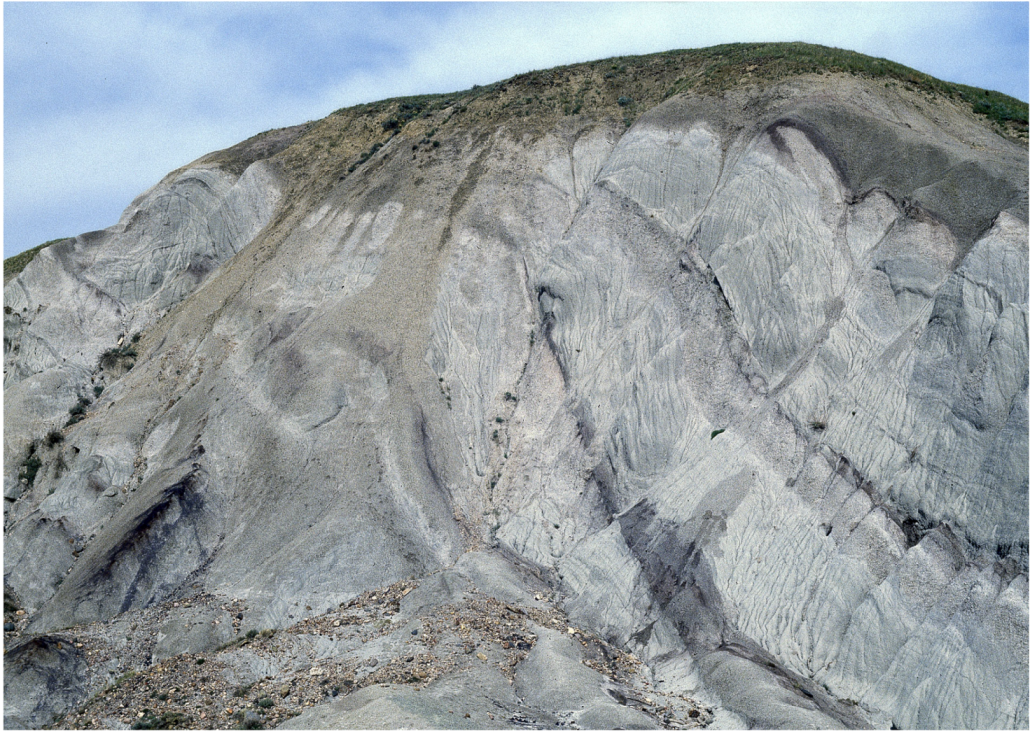

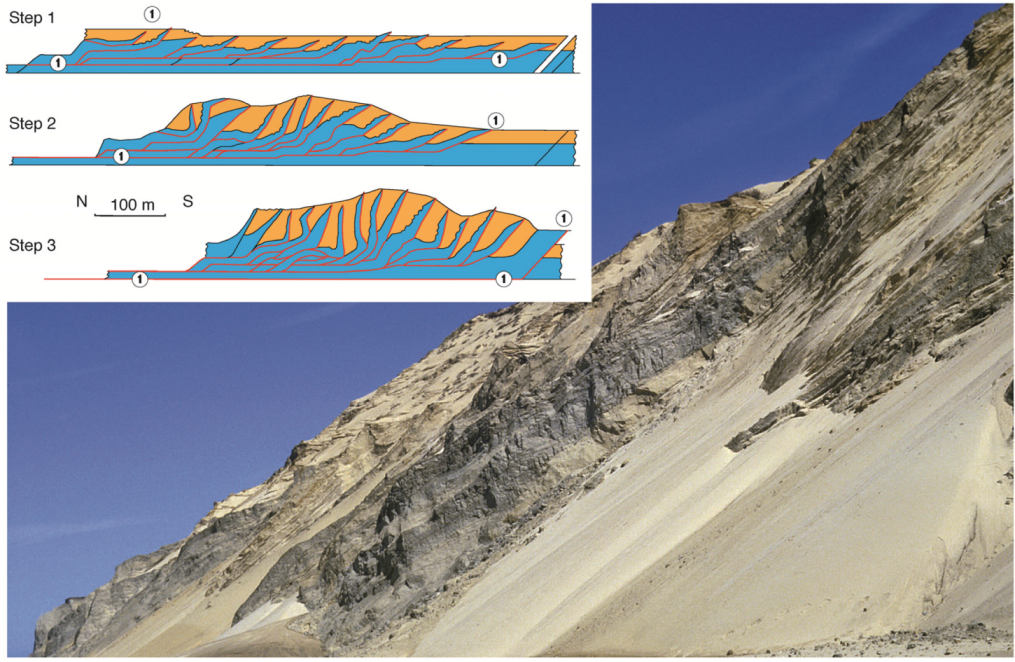
4.4. The Stacked Duplexes of Thrust Sheet Segments

5. The Third-Order Architectural Surfaces

The Hanging-Wall Anticlines
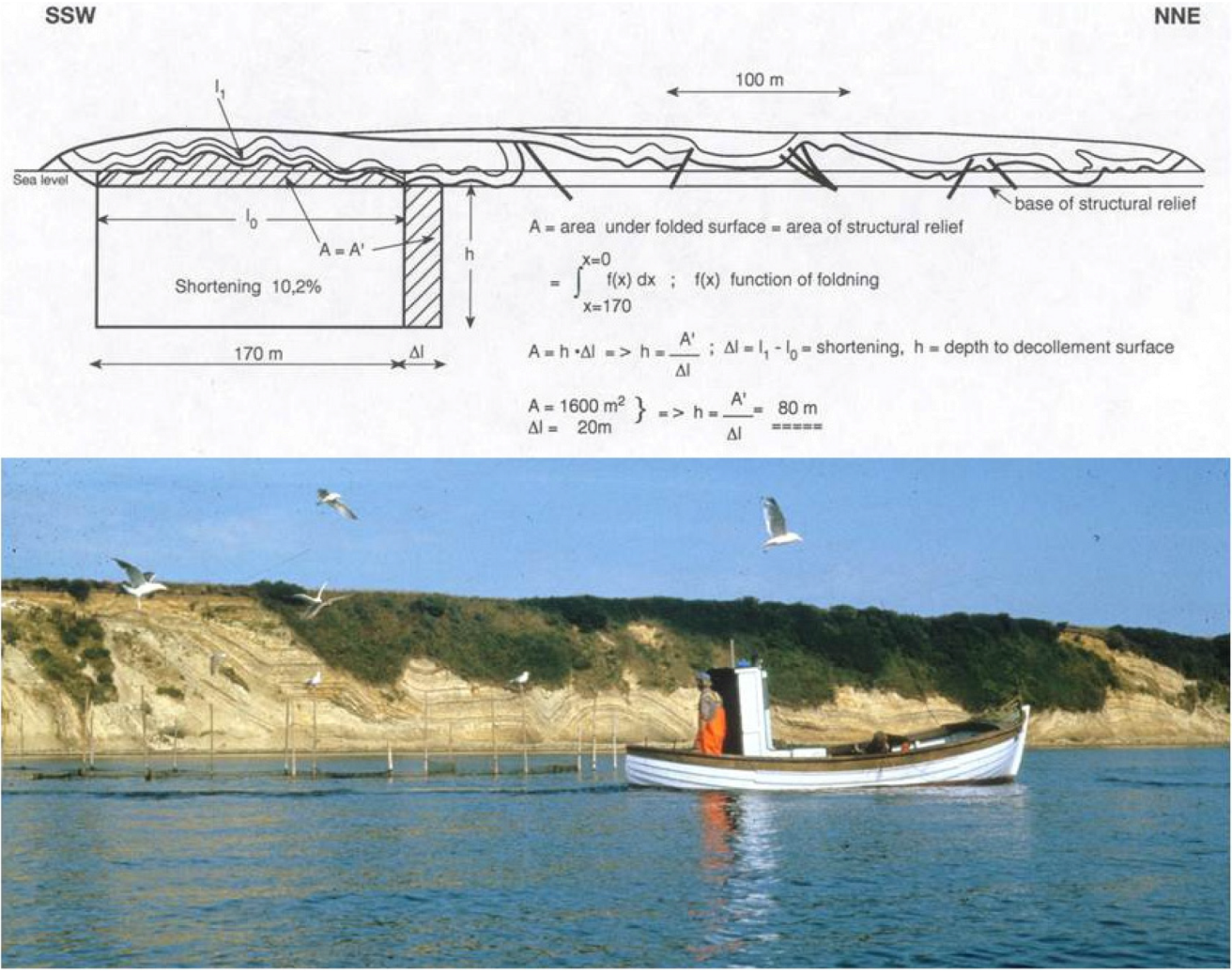
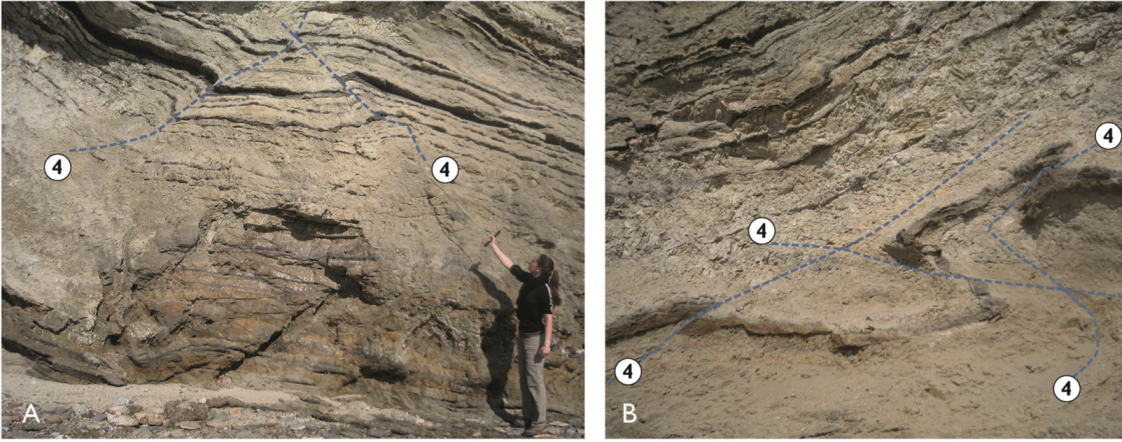
6. The Fourth-Order Architectural Surfaces
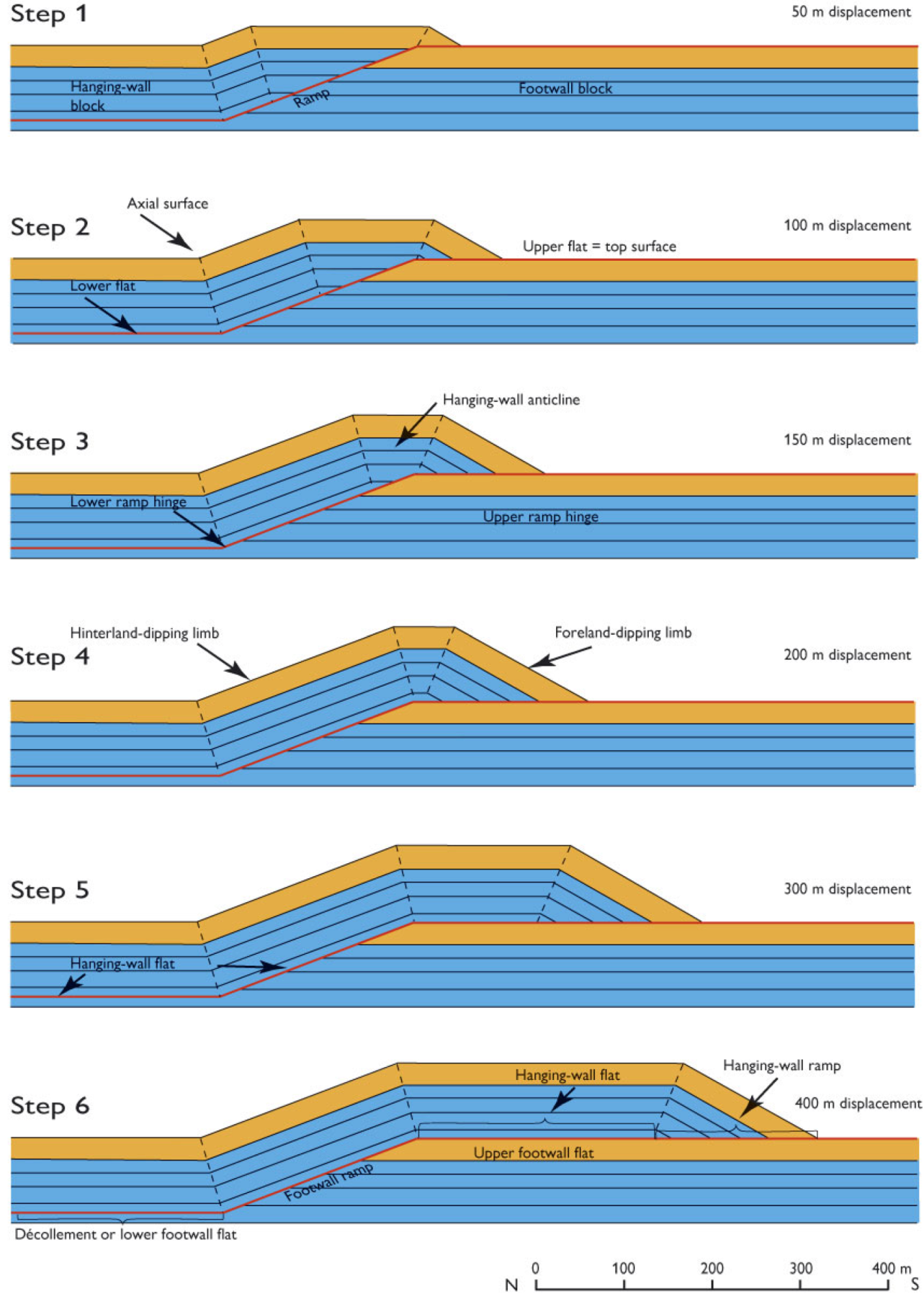


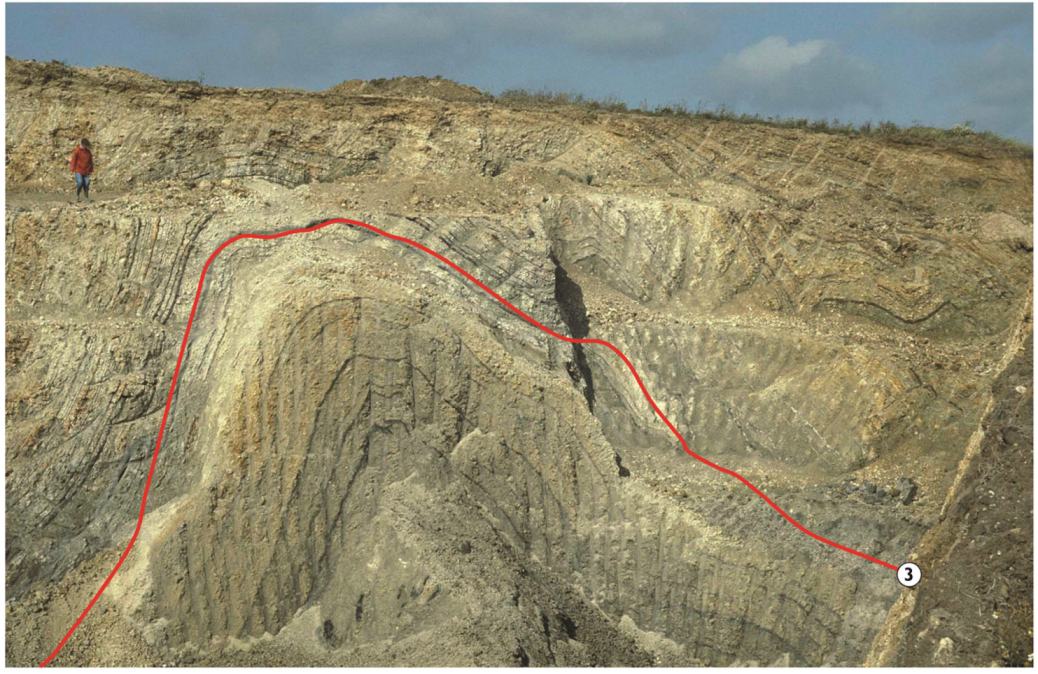
7. Discussions
7.1. Mapping Glaciotectonic Complexes
7.2. Application of Glaciotectonic Architecture
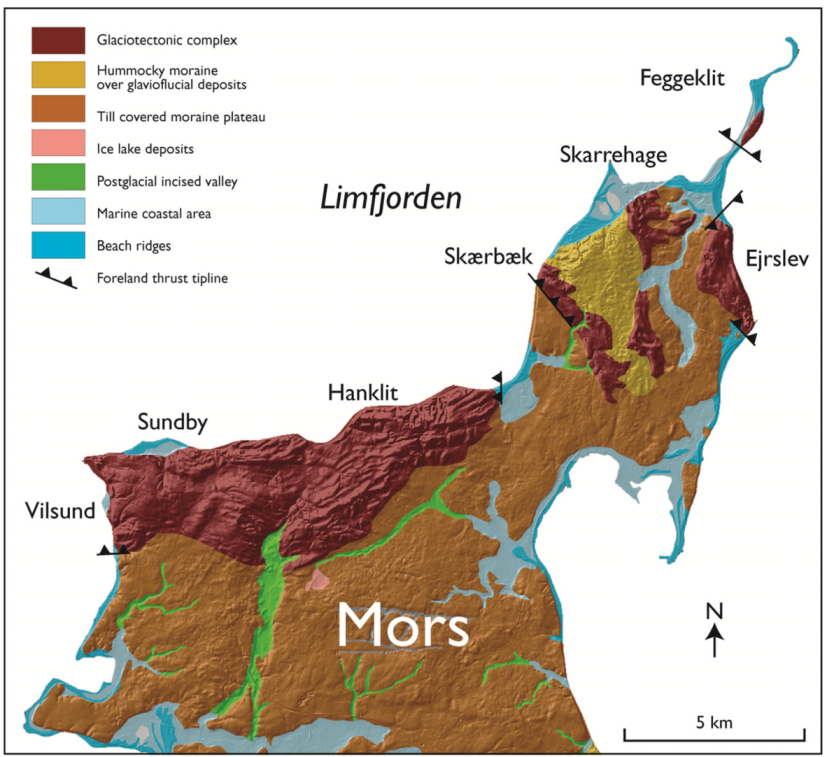
7.3. Limits of the Application of the Glaciotectonic Architecture Concept
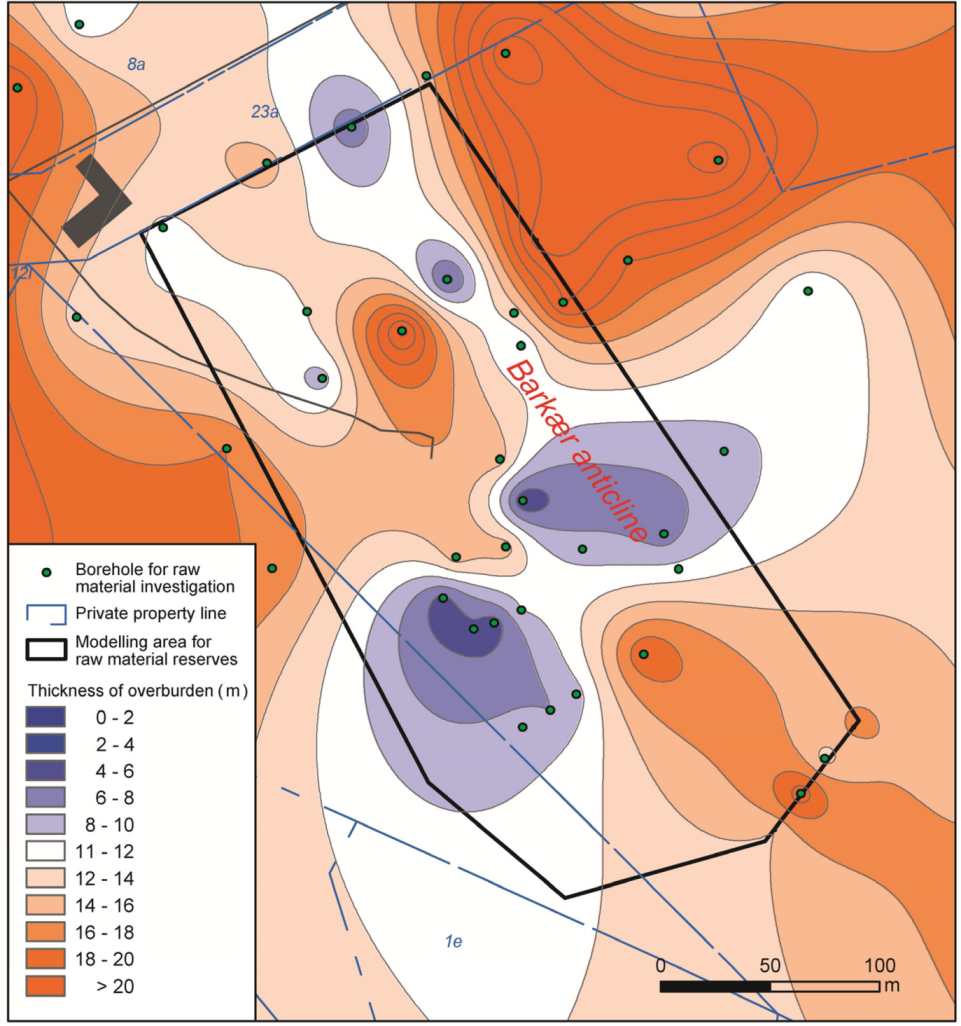

7.4. Proglacial versus Replicative Push during Retreat
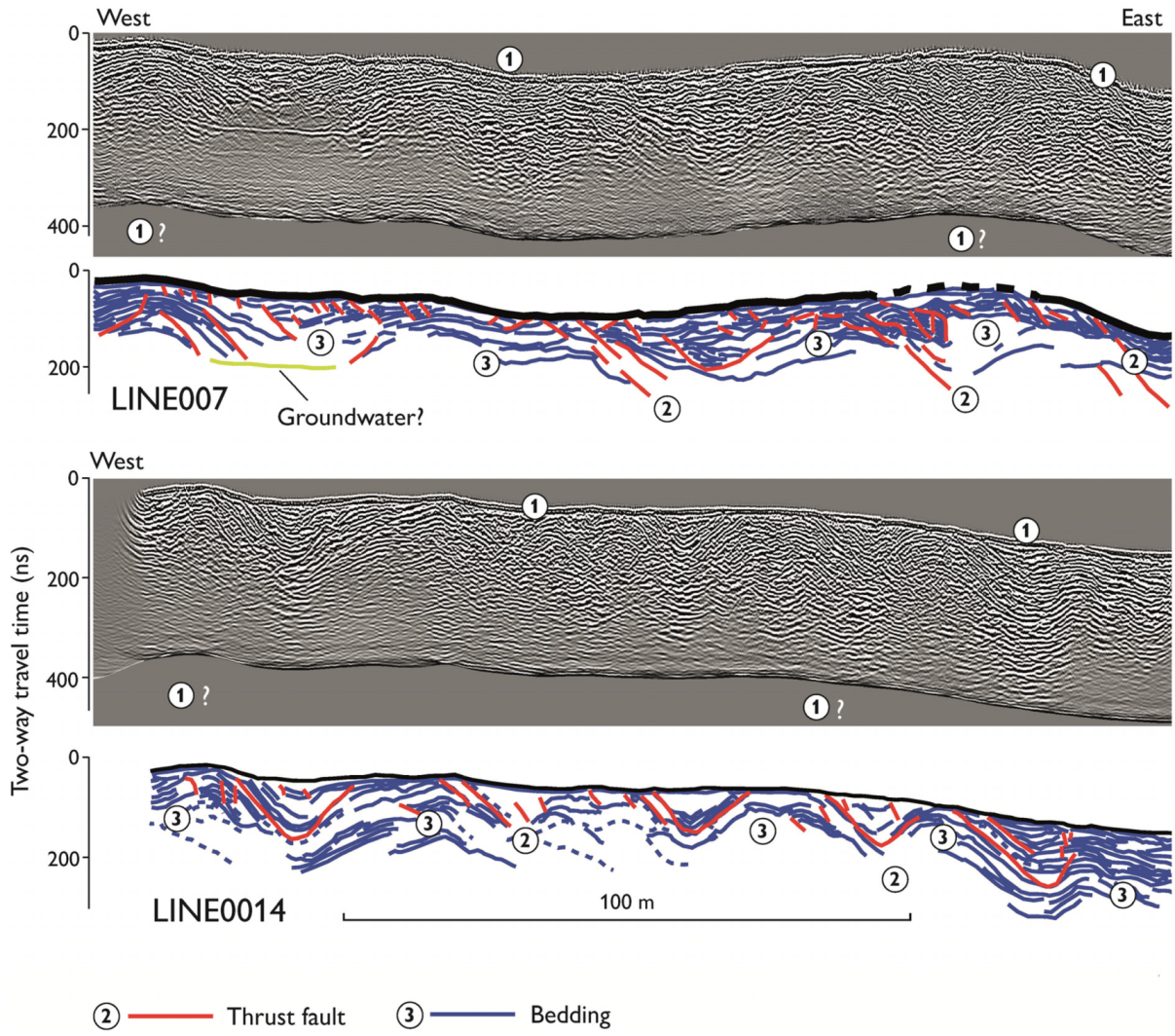
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Glaciodynamic sequence stratigraphy. In Glaciogenic Reservoirs and Hydrocarbon Systems; Special Publications Volume 368; Huuse, M., Redfern, J., Le Heron, D.P., Dixon, R.J., Moscariello, A., Craig, J., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2012; pp. 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, L.T. The Fanø Bugt Glaciotectonic Thrust Fault Complex, Southeastern Danish North Sea: A Study of Large-Scale Glaciotectonics Using High-Resolution Seismic Data and Numerical Modelling. PhD Thesis, Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Huuse, M.; Lykke-Andersen, H. Large-scale glaciotectonic thrust structures in the eastern Danish North Sea. In Deformation of Glacial Materials; Special Publications; Malbman, A., Hambrey, M., Hubbard, B., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2000; Volume 176, pp. 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Structural analysis of the Rubjerg Knude Glaciotectonic Complex, Vendsyssel, northern Denmark. Geol. Surv. Den. Greenl. Bull. 2005, 8, 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Aber, J.S.; Croot, D.; Fenton, M.M. Glaciotectonic Landforms and Structures; Glaciology and Quaternary Geology Series Volume 5; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Aber, J.S.; Ber, A. Glaciotectonism; Development in Quaternary Sciences Volume 5; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brookfield, M.E. The origin of bounding surfaces in aeolian sandstones. Sedimentology 1977, 24, 303–332. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.R.L. Studies in fluviatile sedimentation: Bars, bar-complexes and sandstone sheets (low-sinuosity braided streams) in the Brownstones (L. Devonian), Welsh Borders. Sediment. Geol. 1983, 33, 237–293. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits. Earth Sci. Rev. 1985, 22, 261–308. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. Architectural elements and bounding surfaces in fluvial deposits: Anatomy of the Kayenta Formation (Lower Jurassic), southwest Colorado. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 233–262. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.L.; Ashworth, P.J.; Bristow, C.S.; Roden, J. Three-dimensional sedimentary architecture of a large, mid-channel sand braid bar, Jamuna River, Bangladesh. J. Sediment. Res. 2003, 73, 516–530. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, G. Sedimentology of magmatically and structurally controlled outburst valleys along rifted volcanic margins: Examples from the Nuussuaq Basin, West Greenland. Sedimentology 2002, 49, 505–532. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, T.R.; Huuse, M.; Jørgensen, F.; Christensen, S. Seismic investigations of buried tunnel valleys on- and offshore Denmark. In Glaciogenic Reservoirs and Hydrocarbon Systems; Huuse, M., Redfern, J., Le Heron, D.P., Dixon, R.J., Moscariello, A., Craig, J., Eds.; Special Publications; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2012; Volume 368, pp. 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kolla, V.; Posamentier, H.W.; Wood, L.J. Deep-water and fluvial sinuous channels—Characteristics, similarities and dissimilarities, and modes of formation. Marin. Pet. Geol. 2007, 24, 388–405. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, T.B.; Huuse, M. Multistage erosion and infill of buried Pleistocene tunnel valleys and associated seismic velocity effects. In Glaciogenic Reservoirs and Hydrocarbon Systems; Special Publications Volume 368; Huuse, M., Redfern, J., Le Heron, D.P., Dixon, R.J., Moscariello, A., Craig, J., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2012; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, F.; Sandersen, P.B.E.; Auken, E. Imaging buried Quaternary valleys using the transient electromagnetic method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, F.; Sandersen, P.B.E.; Auken, E.; Lykke-Andersen, H.; Sørensen, K. Contributions to the geological mapping of Mors, Denmark—A study based on a large-scale TEM survey. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 2005, 52, 53–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sandersen, P.B.E.; Jørgensen, F. Buried Quaternary Valleys in western Denmark—Occurrence and inferred implications for groundwater resources and vulnerability. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 229–248. [Google Scholar]
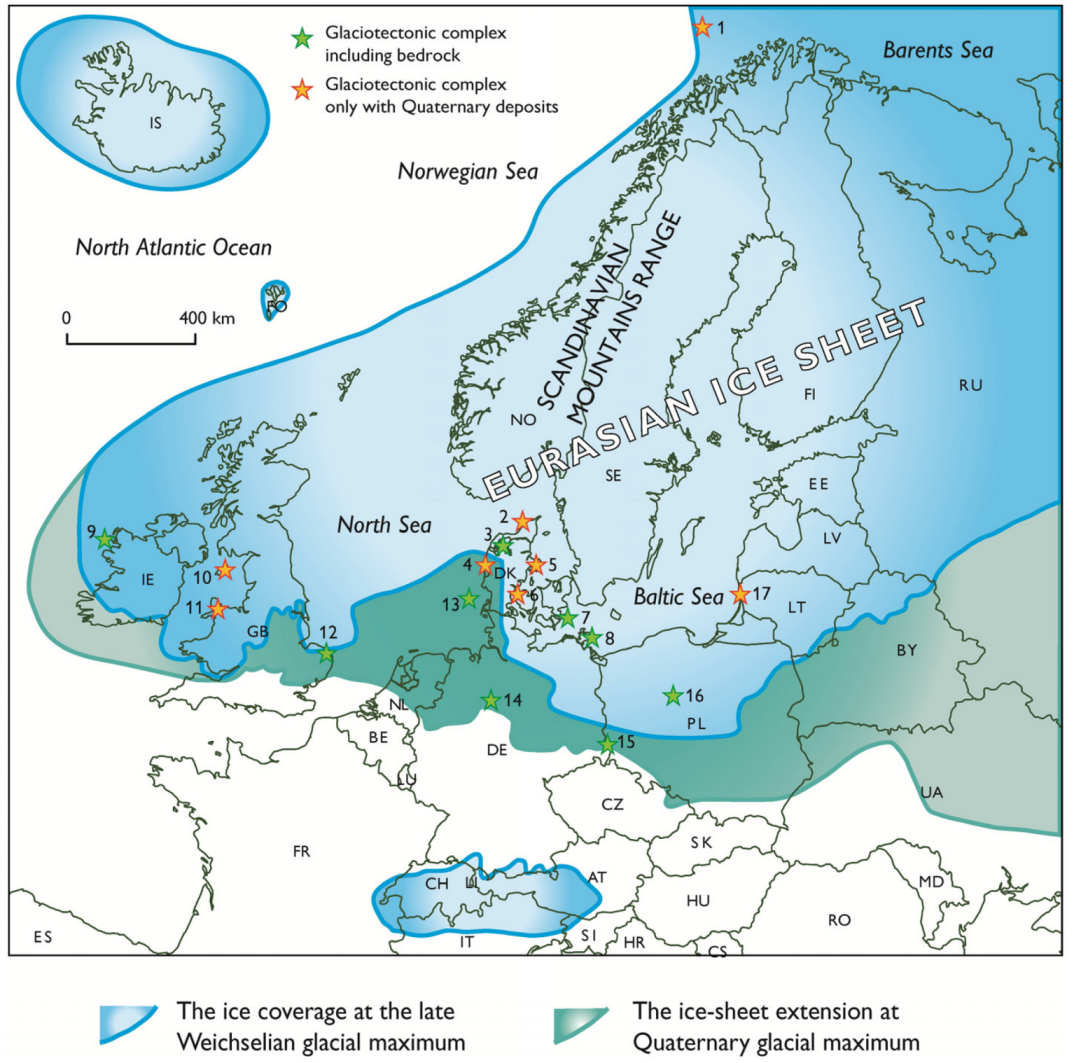
- Svendsen, J.I.; Alexanderson, H.; Stakhov, V.I.; Demidov, I.; Dowdeswell, J.A.; Funder, S.; Gaataullin, V.; Henriksen, M.; Hjort, C.; Houmark-Nielsen, M.; et al. Late Quaternary ice sheet history of northern Eurasia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 1229–1271. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rafaelsen, B.; Andreassen, K.; Hogstad, K.; Kuilman, L.W. Large-scale glaciotectonic imbricated thrust sheets on three-dimensional seismic data: Facts or artefacts? Basin Res. 2007, 19, 87–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gry, H. De istektoniske Forhold i Moleret. Med bemærkninger om vore dislocerede klinters dannelse og om den negative askeserie. Meddelelser fra Dansk Geologisk Forening 1940, 9, 586–627. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Klint, K.E.S.; Pedersen, S.A.S. The Hanklit glaciotectonic thrust fault complex, Mors, Denmark; DGU Serie A Volume 35; Geological Survey of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Progressive glaciotectonic deformation in Weichselian and Palaeogene deposits at Feggeklit, northern Denmark. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 1996, 42, 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Superimposed deformation in glaciotectonics. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 2000, 46, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S.; Petersen, K.S.; Rasmussen, L.A. Observations on glaciodynamic structures at the Main Stationary Line in western Jutland, Denmark. In Glaciotectonic Forms and Processes; Croot, D.G., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S.; Petersen, K.S. Djurslands Geologi; Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1997. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, T.M.; Piotrowski, J.A. Genesis of the glaciotectonic thrust-fault complex at Halk Hoved, southern Denmark. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 2012, 60, 61–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S.; Gravesen, P. Structural development of Maglevandsfald: A key to understanding the glaciotectonic architecture of Møns Klint, SE Denmark. Geol. Surv. Den. Greenl. Bull. 2009, 17, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gribb, K. Jasmund und Moen eine glacialmorphologische Untersuchung. Zeithschrift für Erdkunde 1947, 1, 75–182. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, A.O. Zwei markante Stauchmoränen: Peski/Belorussland und Jasmund, Ostseeinsel Rügen/Nordostdeutschland—Gemeinsame Merkmale und Unterschiede. Eisezeitalter und Gegenwart Quaternary Science Journal 2011, 60, 464–487. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Steinich, G. Endogene tektonik in den Unter-Maastricht-Vorkommen auf Jasmund (Rügen). Geologie 1972, 71–72, 1–207. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Warren, W. Field Guide for Excursion; For INQUA Commission on Formation and Properties of Glacial Deposits. Dublin, Ireland, May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, C.; Le Heron, D.P. The glaciotectonic deformation of Quaternary sediments by fault-propagation folding. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2010, 121, 270–280. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.P. The origin of the glacio-dynamic structures of the Bride Moraine, Isle of Man. Boreas 1984, 13, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, H.; Phillips, E.; Lee, J.R.; Wilkinson, I.P. Imbricate thrust stack model for the formation of glaciotectonic rafts: An example from the Middle Pleistocene of north Norfolk, UK. Boreas 2009, 13, 620–637. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.K. Proglacial glaciotectonic deformation and the origin of the Cromer Ridge push moraine complex, North Norfolk, England. Boreas 1990, 19, 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.K.; Boulton, G.S. The glacial drifts of northeastern Norfolk. In Glacial Deposits in Great Britain and Ireland; Ehlers, J., Gibbard, P.L., Rose, J., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kupetz, M. Geologischer Bau und Genese der Stauchmoräne Muskauer Faltenbogen. Brandenburgische Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe 1997, 2, 1–20. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Kupetz, A.; Kupetz, M.; Rascher, J. Der muskauer Faltenbogen—Ein geologisches Phänomen, Grundlage einer 130 jährigen standortgebundenen Wirtschaftsentwwicklung und Geopark in Brandenburg, Sachsen under Wojewodschaft Lubuser Land; Gesellschaft für Geowissenschaften e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2004. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Włodarski, W. Geometry and kinematics of glaciotectonic deformation superimposed on the Cenozoic fault-tectonic framework in the central Polish Lowlands. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 94, 44–61. [Google Scholar]
- Molodkov, A.; Bitinas, A.; Damusyte, A. IR-OSL studies of till and inter-till deposits from the Lithuanian Maritime Region. Quat. Geochronol. 2010, 5, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Croot, D.G. Morphological, structural and mechanical analysis of neoglacial ice-pushed ridges in Iceland. In Glaciotectonics Forms and Processes; Croot, D.G., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, G.S.; van der Meer, J.J.M.; Beets, K.J.; Hart, J.K.; Ruegg, G.H.J. The sedimentary and structural evolution of a recent push moraine complex: Holmströmbreen, Spitsbergen. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1999, 18, 339–371. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Isfoldede lag i de danske kystklinter. In Geologiske Naturperler—Danske Brikker til Jorden Puslespil; Lindow, B., Krüger, J., Eds.; Gyldendal: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011; pp. 113–127. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, G.S.; Caban, P. Groundwater flow beneath ice sheets: Part II—Its impact on glacier tectonic structures and moraine formation. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1995, 14, 563–587. [Google Scholar]
- Banham, P.H. Glacitectonites in till stratigraphy. Boreas 1977, 6, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Glacitectonite: Brecciated sediments and cataclastic sedimentary rocks formed subglacially. In Genetic Classification of Glacigenic Deposits; Goldthwait, R.P., Matsch, C.L., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, G.S.; Hindmarsh, R.C.A. Sediment deformation beneath glaciers: Rheology and geological consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 9059–9082. [Google Scholar]
- Fenton, M.; Langenberg, W.; Pawlowicz, J. Glacial Deformation Phenomena of East-Central Alberta in the Stettler-Coronation Region; Field Trip Guidebook; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoline, M.; Pedersen, G.K.; Pedersen, S.A.S. Lacustrine sedimentation and tectonics: An example from the Weichselian at Lønstrup Klint, Denmark. Boreas 1997, 26, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fossen, H. Structural Geology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Suppe, J. Principles of Structural Geology; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S.; Jakobsen, P.R. Geological Map of Denmark: Mors; Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; Map Sheet, 1:50000. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.A.S. Palaeogene diatomite deposits in Denmark: Geological investigations and applied aspects. Geol. Surv. Den. Greenl. Bull. 2008, 15, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen, P.R.; Nielsen, A.M.; Pedersen, S.A.S. Geological Map of Denmark: Mariager; Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; Map Sheet, 1:50000. [Google Scholar]
- Lerche, H.; Jakobsen, P.R.; Pedersen, S.A.S. Ribbed moraines formed during the retreat of the Scandinavian ice sheet from eastern Himmerland, NE Jylland, Denmark. Geol. Surv. Den. Greenl. Bull. 2014, 31, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sandersen, P.B.E.; Jørgensen, F.; Larsen, N.K.; Westergaard, J.H.; Auken, E. Rapid tunnel-valley formation beneath the receding Late Weichselian ice sheet in Vendsyssel, Denmark. Boreas 2009, 28, 834–851. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedersen, S.A.S. Architecture of Glaciotectonic Complexes. Geosciences 2014, 4, 269-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences4040269
Pedersen SAS. Architecture of Glaciotectonic Complexes. Geosciences. 2014; 4(4):269-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences4040269
Chicago/Turabian StylePedersen, Stig A. Schack. 2014. "Architecture of Glaciotectonic Complexes" Geosciences 4, no. 4: 269-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences4040269
APA StylePedersen, S. A. S. (2014). Architecture of Glaciotectonic Complexes. Geosciences, 4(4), 269-296. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences4040269