Geodynamic Reconstructions of the Australides—1: Palaeozoic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
3. Geodynamic Reconstructions
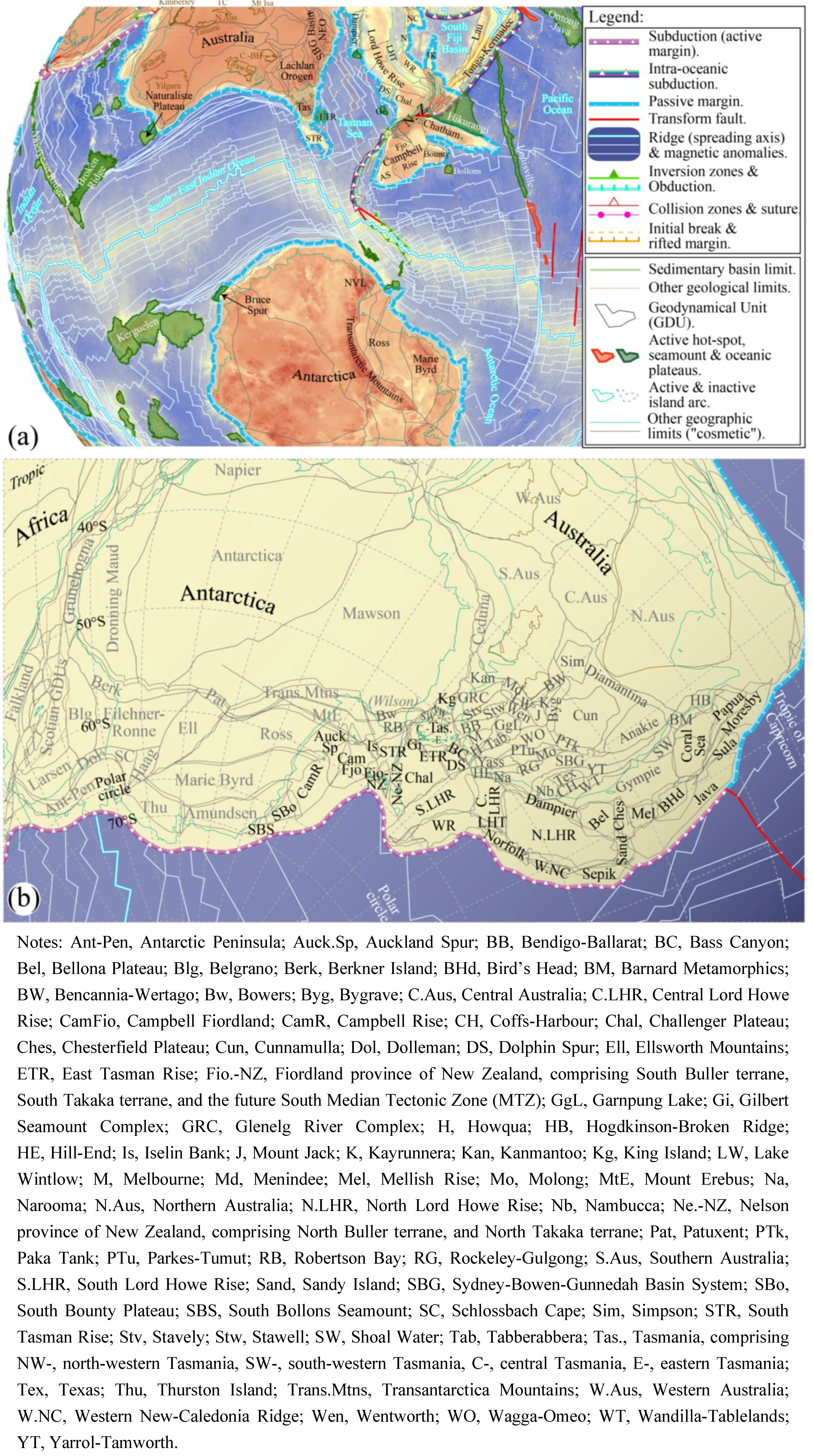
3.1. The Delamerian Cycle (Figure 2a–h)
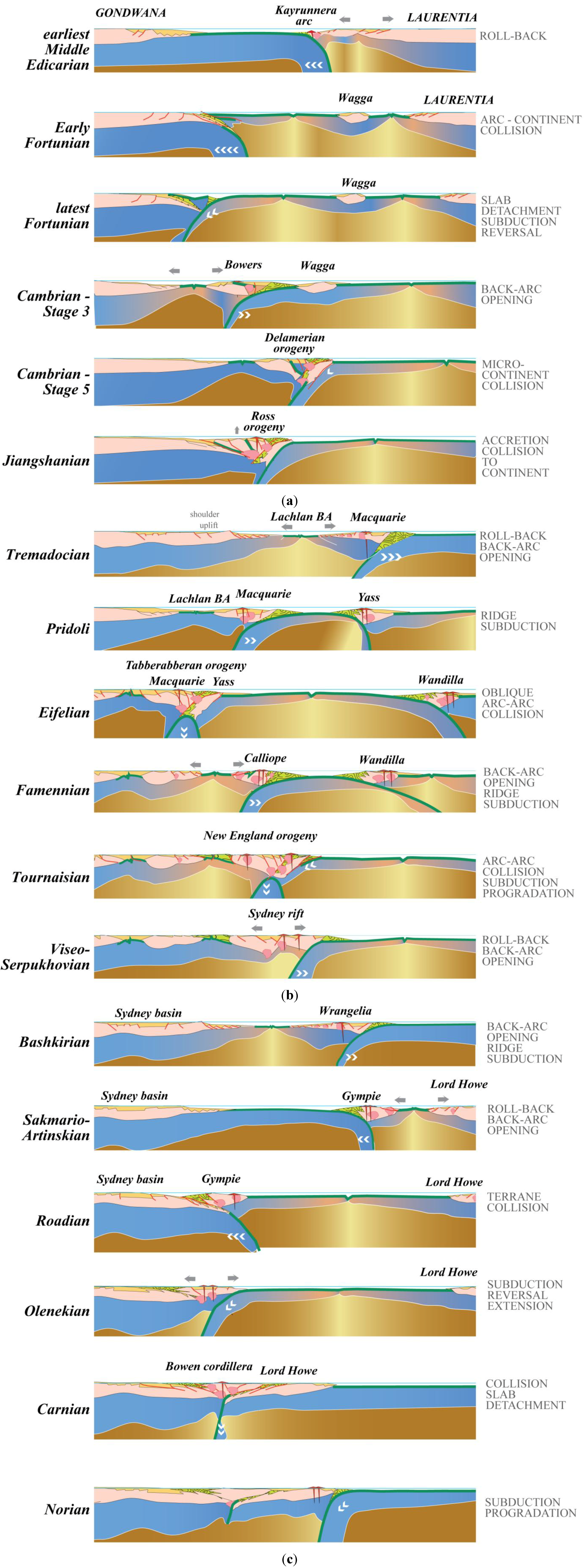
3.2. The Lachlan Cycle (Figure 2h–o)
3.3. The New England Cycle (Figure 2p–y)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Declare
References
- Vaughan, A.; Leat, P.; Pankurst, R. Terrane processes at the margin of Gondwana: Introduction. Geological Society London Special Publications 2005, 246, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vérard, C. Palaeozoic Palaeomagnetism of Southeastern Australia: Implications for the APW Path of Gondwana. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Glen, R. The Tasmanides of eastern Australia. Geological Society London Special Publications 2005, 246, 23–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vérard, C.; Stampfli, G.M. Geodynamic reconstructions of the Australides—2: Mesozoic–Cainozoic. Geosciences 2013, 3. in press. [Google Scholar]
- Stump, E.; White, A.; Borg, S. Reconstruction of Australia and Antarctica: Evidence from granites and recent mapping. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1986, 79, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, S.; de Paolo, D. A tectonic model of the Antarctic Gondwana margin with implications for southeastern Australia: Isotopic and geochemical evidence. Tectonophysics 1991, 196, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.; Tulloch, A. Early Palaeozoic terranes in New Zealand and their relationship to the Lachlan Fold Belt. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G. Medium-high-pressure metamorphic rocks of the Tuhua Orogen, western New Zealand, as lower crustal analogues of the Lachlan Fold Belt, SE Australia. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glen, R.; Dallmeyer, R.; Black, L. Isotopic dating of basin inversion—The Palaeozoic Cobar Basin, Lachlan Orogen, Australia. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glen, R.; Scheibner, E.; van den Berg, A. Paleozoic intraplate escape tectonics in Gondwanaland and major strike-slip duplication in the Lachlan Orogen of southeastern Australia. Geology 1992, 20, 795–798. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R. Basement geology and tectonic development of the greater New Zealand region: An interpretation from regional magnetic data. Tectonophysics 1999, 308, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veevers, J. Phanerozoic Earth History of Australia; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Veevers, J. Billion-Year Earth History of Australia and Neighbours in Gondwanaland; GEMOC Press: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Veevers, J. Atlas of Billion-Year Earth History of Australia and Neighbours in Gondwanaland; GEMOC Press: Sydney, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Veevers, J. Gondwanaland from 650–500 Ma assembly through 320 Ma merger in Pangea to 185–100 Ma breakup: Supercontinental tectonics via stratigraphy and radiometric dating. Earth Sci. Rev. 2004, 68, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veevers, J. Pan-African is Pan-Gondwanaland: Oblique convergence drives rotation during 650–500 Ma assembly. Geology 2010, 31, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, D.; Foster, D. Orogenic concepts—Application and definition: Lachlan Fold Belt, eastern Australia. Am. J. Sci. 1997, 297, 859–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.; Foster, D.; Bierlein, F. Geodynamics and metallogeny of the Lachlan Orogen. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 2002, 49, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, C.; Coney, P. Convergence and intraplate deformation in the Lachlan Fold Belt of southeastern Australia. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.; Vernon, R. Palaeozoic arc growth, deformation and migration across the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.; Gray, D.; Spaggiari, C.; Kamenov, G.; Bierlein, F. Palaeozoic Lachlan Orogen, Australia; Accretion and construction of continental crust in a marginal ocean setting: Isotopic evidence from cambrian metavolcanic rocks. Geological Society London Special Publications 2009, 318, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfli, G.; Borel, G. A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrons. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 196, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfli, G.; Borel, G. The TRANSMED transects in space and time: Constraints on the Paleotectonic evolution of the Mediterranean domain. In The TRANSMED Atlas: The Mediterranean Region from Crust to Mantle; Cavazza, W., Roure, F., Spakman, W., Stampfli, G., Ziegler, P., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 53–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hochard, C. GIS and Geodatabases Application to Global Scale Plate Tectonic Modelling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 18 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stampfli, G.; Hochard, C.; Vérard, C.; Wilhem, C.; von Raumer, J. The formation of Pangæa. Tectonophysics 2013, 593, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Roest, W.; Royer, J.-Y.; Gahagan, L.; Sclater, J. Digital isochrones of the world’s ocean floor. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 3211–3214. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, D.; Sdrolias, M.; Gaina, C.; Roest, R. Age, spreading rates and spreading symmetry of the world’s ocean crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008, 9, Q04006:1–Q04006:19. [Google Scholar]
- De Mets, C.; Gordon, R.; Argus, D.; Stein, S. Effect of recent revisions to the geomagnetic reversal time scale on estimates of current plate motions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Baes, M.; Govers, R.; Wortel, R. Switching between alternative responses of the lithosphere to continental collision. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 187, 1151–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Hafkenscheid, E.; Wortel, R.; Spakman, W. Subduction history of the Tethyan region derived from seismic tomography and tectonic reconstructions. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B08401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P. Mantle Circulation Models: Constraining Mantle Dynamics, Testing Plate Motion History and Calculating Dynamic Topography. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cardiff, Cardiff, UK, 1 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik, T.; van der Voo, R. Refining Gondwana and Pangea palaeogeography: Estimates of Phanerozoic non-dipole (octupole) fields. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 151, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amante, C.; Eakins, B. Etopo1—1 Arc-minute Global Relief Model: Procedures, Data Sources and Analysis; NOAA Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24; National Geophysical Data Center, Marine Geology and Geophysics Division: Boulder, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Stratigraphy. International Chronostratigraphic Chart, Version 2013/01. Available online: http://www.stratigraphy.org/ICSchart/ChronostratChart2013-01.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2013).
- Crawford, A.; Stevens, B.; Fanning, M. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of some Neoproterozoic and Early Cambrian volcanics in western New South Wales. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 1997, 44, 831–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; McMechan, M.; Potter, D. Structure and Architecture of the Western Canada Basin—Chapter 3. Online Version of the Geological Atlas of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin (WCSB). 2008. Available online: http://www.ags.gov.ab.ca/publications/wcsb_atlas/atlas.html (accessed on 23 May 2013).
- Burchfiel, B.; Lipman, P.; Zoback, M. The Cordilleran Orogen: Conterminous U.S. The Geology of North America: Volume G-3; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons, I. Proterozoic basement provinces of southern and southwestern Australia, and their Correlation with Antarctica. Geological Society London Special Publications 2003, 206, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.J. Geological Survey of New South Wales, Broken Hill, Australia. Personal communication, 2 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stump, E. The Ross Orogen of the Transantarctic Mountains; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tessensohn, F.; Henjes-Kunst, F. Northern Victoria land terranes, Antarctica: Far-travelled or local products? Geological Society London Special Publications 2005, 246, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapalini, A. The Accretionary history of the southern South America from the latest Proterozoic to the late Palaeozoic: Some palaeomagnetic constraints. Geological Society London Special Publications 2005, 246, 305–328. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg, A.; Stewart, I. Ordovician terranes of the southeastern Lachlan Fold Belt: Statigraphy, structure and palaeogeographic reconstruction. Tectonophysics 1992, 214, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, C.; Tye, S. Provenance of early Palaeozoic sandstones, southeastern Australia, Part 1: Vertical changes through the Bengal fan-type deposit. Sediment. Geol. 1999, 125, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquoun, G.; Fergusson, C.; Tye, S. Provenance of early Palaeozoic sandstones, southeastern Australia, Part 2: Cratonic to arc switching. Sediment. Geol. 1999, 125, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.; Willman, C.; Maher, S. The Tasman Fold Belt System in Victoria: Geology and Mineralisation of Proterozoic to Carboniferous Rocks; Geological Survey of Victoria Special Publication; Geological Survey: Victoria, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tingey, R. The Geology of Antarctica; Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics 17; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.; Williams, I.; Chappell, B. Berridale 1:100’000 Geological Sheet 8625; Geological Survey of New South Wales: Sydney, Austraila, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Scheibner, E.; Basden, H. Geology of New South Wales—Synthesis. Volume 1 Structural Framework; Geological Survey of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Spaggiari, C.; Gray, D.; Foster, D. Ophiolite accretion in the Lachlan Orogen, Southeastern Australia. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk, C. Carboniferous palaeomagnetism of the Rocky Creek Block, northern Tamworth Belt, and the New England pole path. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 2002, 49, 375–405. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, P.; McElhinny, M.; Klootwijk, C. Discussion and reply: Carboniferous palaeomagnetism of the Rocky Creek Block, northern Tamworth Belt, and the New England pole path. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 2003, 50, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Geeve, R.; Schmidt, P.; Roberts, J. Paleomagnetic results indicate pre-Permian counter-clockwise rotation of the southern Tamworth Belt, southern New England Orogen, Australia. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, EPM.4.1–EPM.4.16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Rosenbaum, G.; Donchak, P. Structural evolution of the Texas Orocline, eastern Australia. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, O.; Hochard, C.; Stampfli, G. An alternative plate tectonic model for the Palaeozoic–Early Mesozoic Palaeotethyan evolution of Southeast Asia (Northern Thailand–Burma. Tectonophysics 2008, 451, 346–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhem, C. Plate Tectonics of the Altaids. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 11 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Glen, R.; Wyborn, D. Inferred thrust imbrication, deformation gradients and the Lachlan transverse zone in the eastern belt of the Lachlan Orogen. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 1997, 44, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Glen, R.; Walsche, J. Cross-structures in the Lachlan Orogen: The Lachlan Transverse Zone example. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 1999, 46, 641–658. [Google Scholar]
- Vérard, C.; Glen, R. Magnetic fabrics of Palaeozoic rocks across the Lachlan Transverse Zone from eastern New South Wales. Austr. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 55, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, S.; Borel, G. The odyssey of the Cache Creek terrane, Canadian Cordillera: Implications for accretionary orogens, tectonic setting of Panthalassa, the Pacific superwell, and break-up of Pangea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 253, 415–428. [Google Scholar]
- Chablais, J.; Martini, R.; Kobayashi, F.; Stampfli, G. Upper Triassic foraminifers from Japanese Panthalassan mid-oceanic carbonate buildups (Sambosan Accretionary Complex): palaeobiogeographic implications. Micropaleontology 2011, 57, 93–124. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Reyes, K. Mesozoic Oceanic Terranes of Southern Central America—Geology, Geochemistry and Geodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 18 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Korsch, R.; Wake-Dyster, K.; Johnstone, D. Seismic imaging of Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic extensional and contractional structures in the Bowen and Surat basins, eastern Australia. Tectonophysics 1992, 215, 273–294. [Google Scholar]
- Korsch, R.; Wake-Dyster, K.; Johnstone, D. The Gunnedah Basin–New England Orogen deep seismic reflection profile: Implications for New England tectonics. In Abstract Volume, Conference on the New England Orogen, Eastern Australia; Flood, P., Aitchison, J., Eds.; University of New England: Armidale, Australia, 1993; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vérard, C.; Stampfli, G.M. Geodynamic Reconstructions of the Australides—1: Palaeozoic. Geosciences 2013, 3, 311-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences3020311
Vérard C, Stampfli GM. Geodynamic Reconstructions of the Australides—1: Palaeozoic. Geosciences. 2013; 3(2):311-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences3020311
Chicago/Turabian StyleVérard, Christian, and Gérard M. Stampfli. 2013. "Geodynamic Reconstructions of the Australides—1: Palaeozoic" Geosciences 3, no. 2: 311-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences3020311
APA StyleVérard, C., & Stampfli, G. M. (2013). Geodynamic Reconstructions of the Australides—1: Palaeozoic. Geosciences, 3(2), 311-330. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences3020311



