Review and Inventory of Pedological and Stratigraphical Knowledge for Investigating Shallow Landslides: A Case Study of the Cervinara Area (Central Campanian Apennines, Southern Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
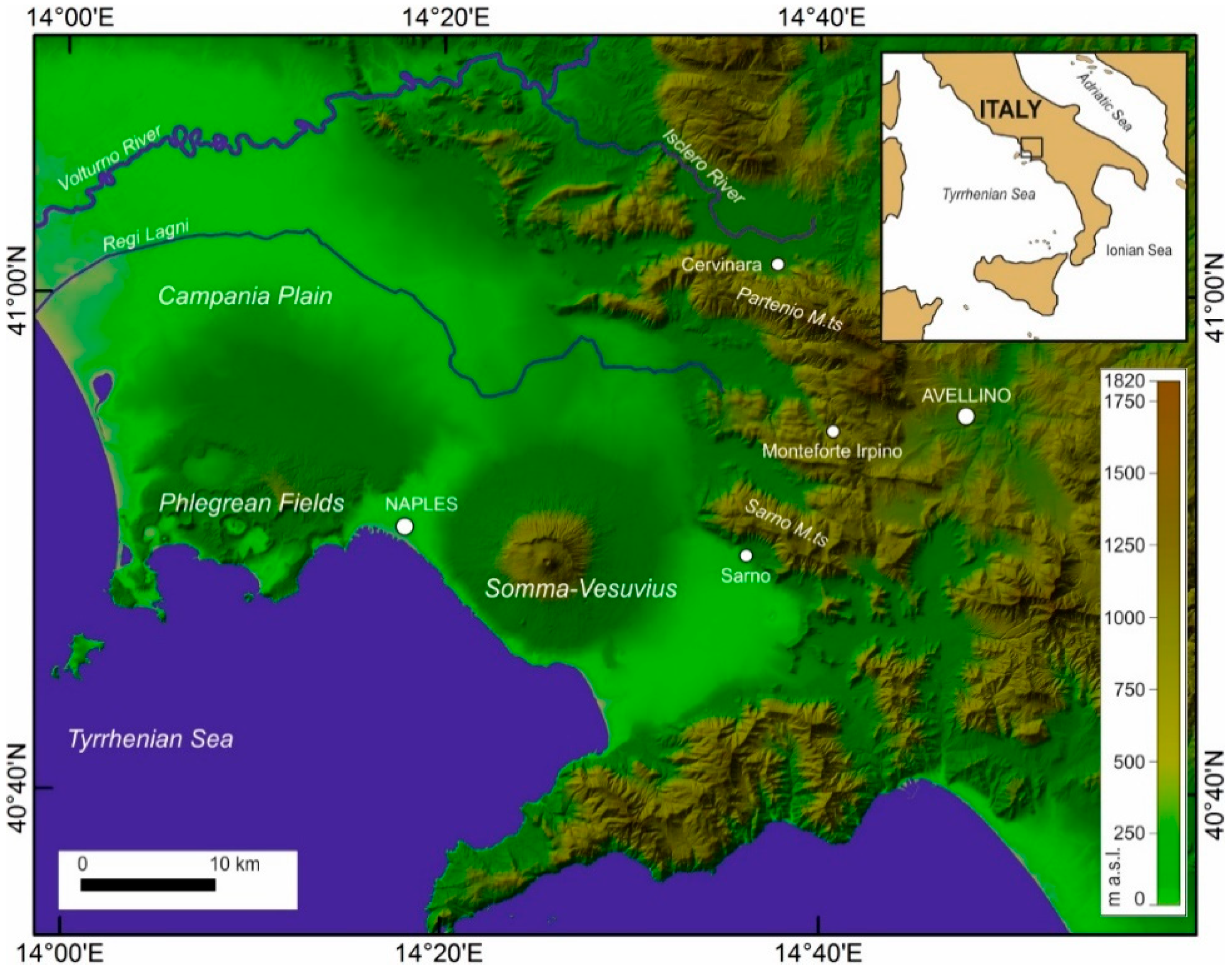
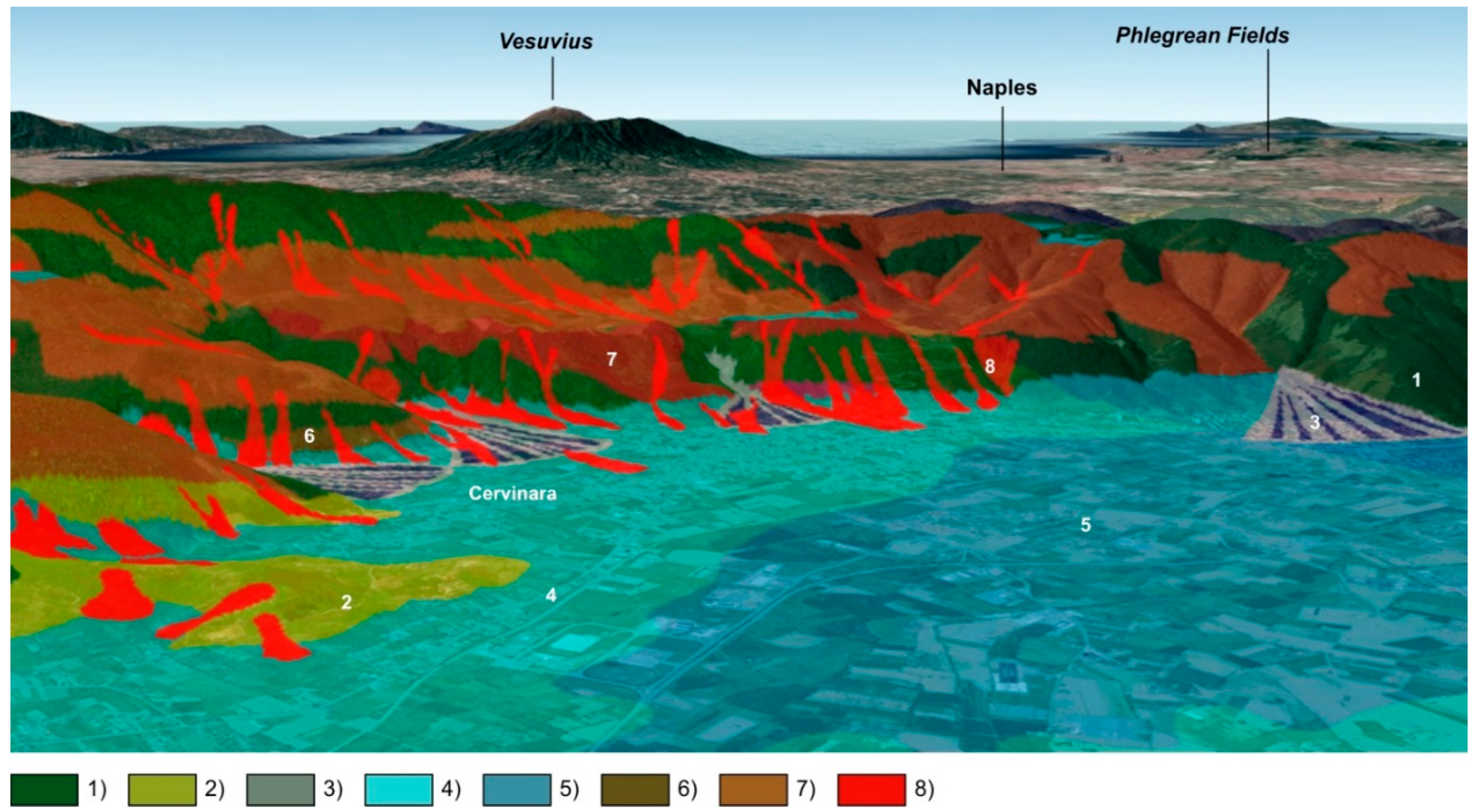
2. Geological Framework of the Cervinara Area
3. Study Criteria
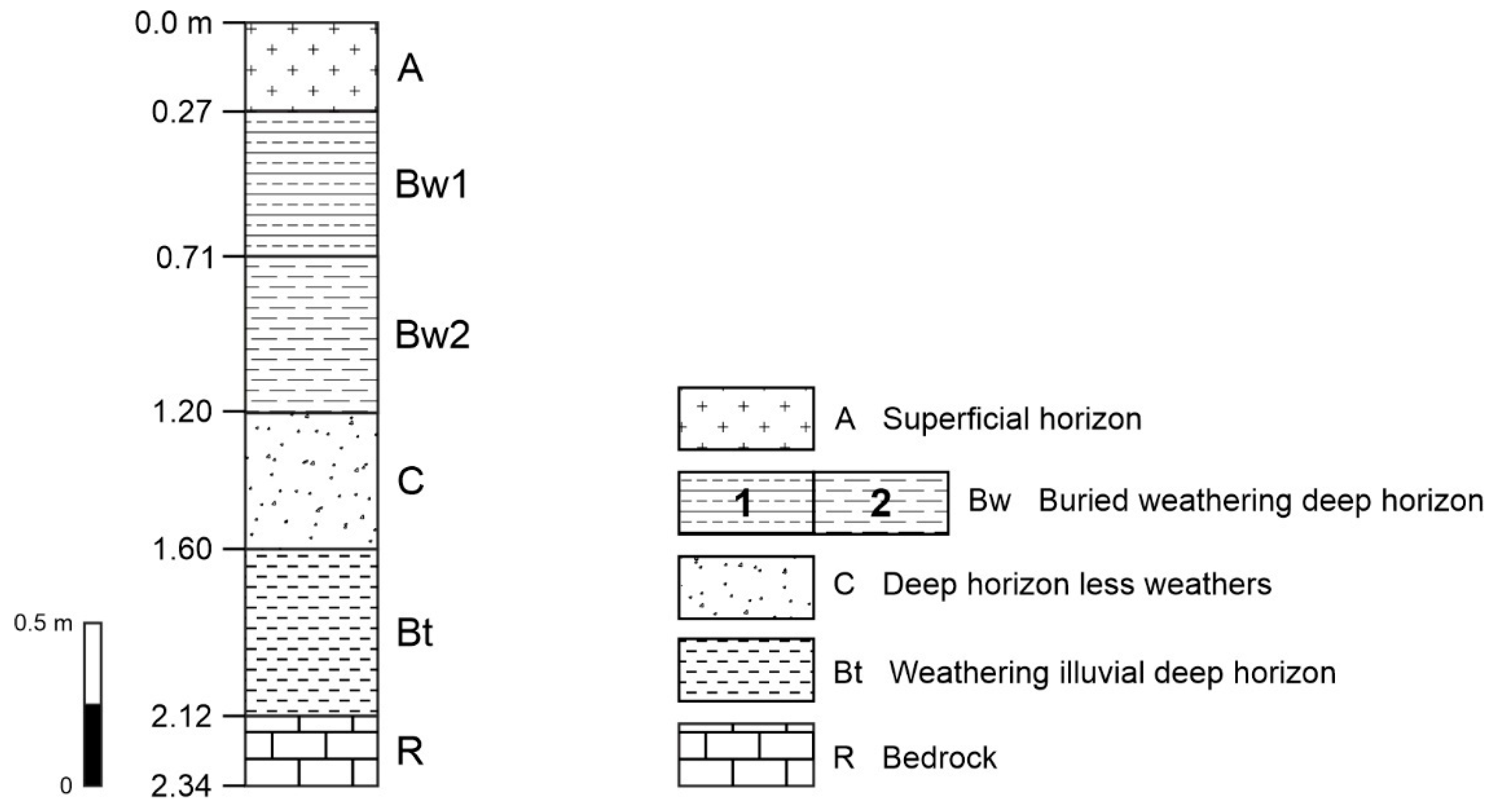
4. Pedological Approach
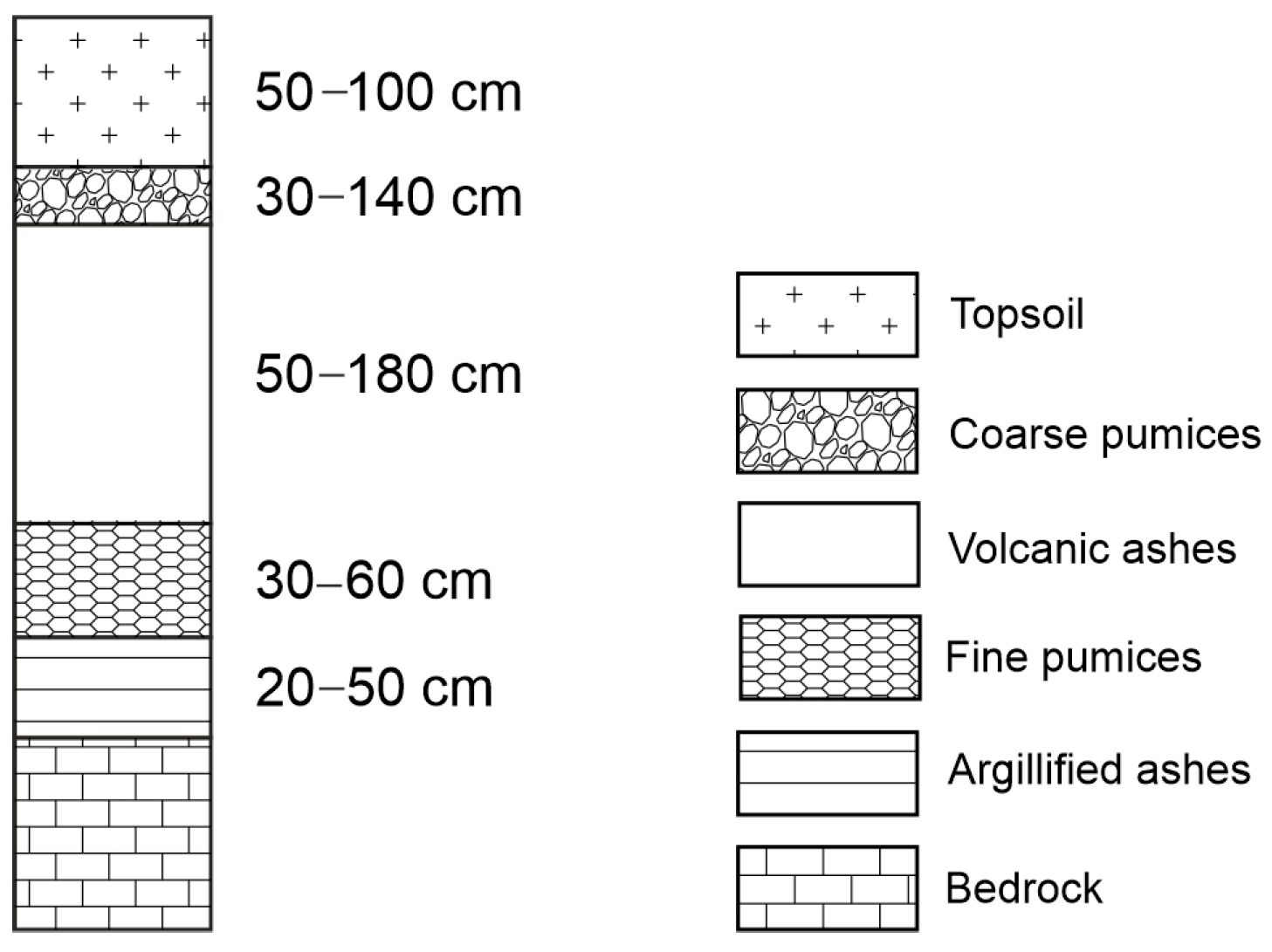
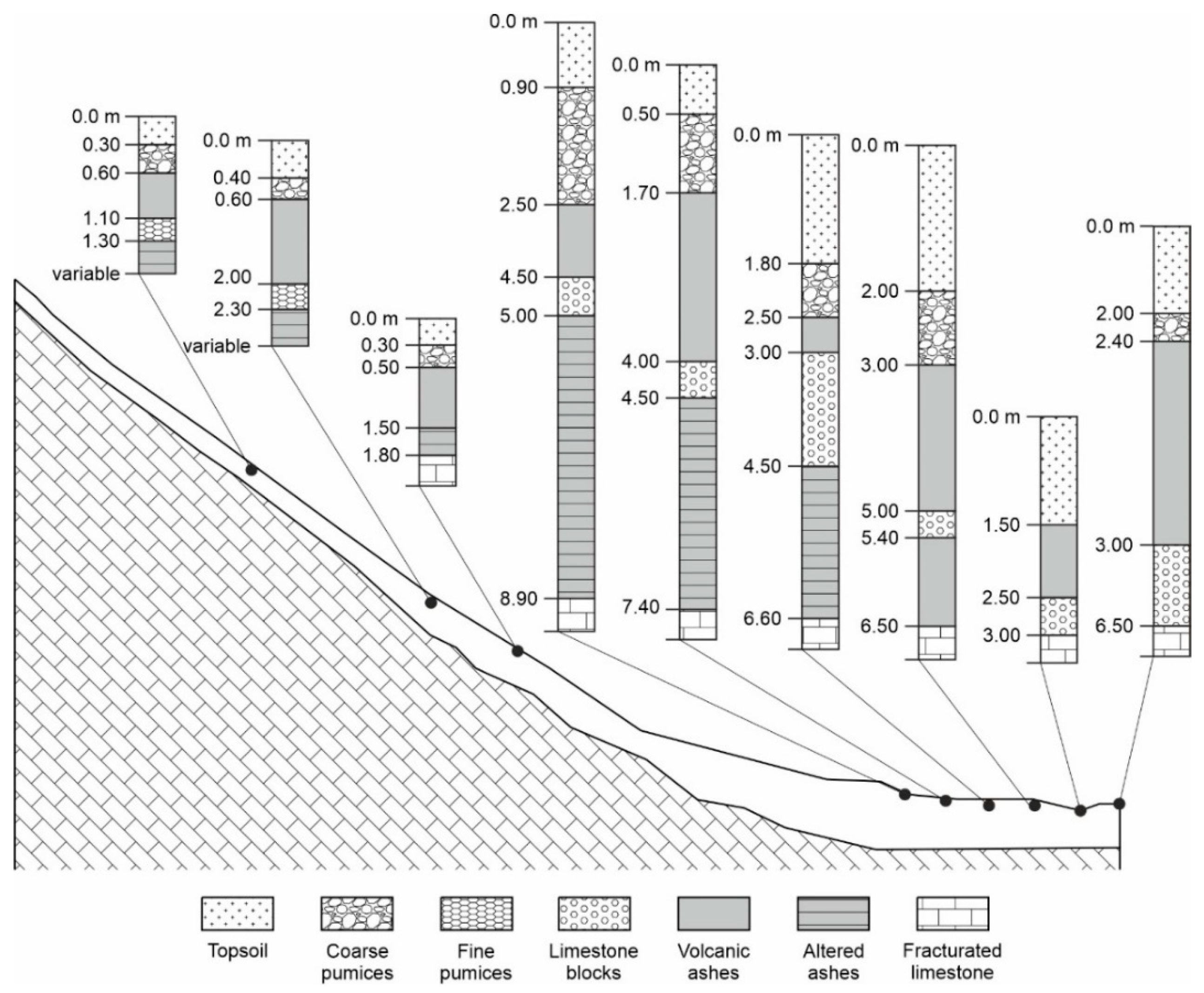
5. Lithostratigraphic Approach
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herath, S.; Wang, Y. Case Studies and National Experiences. In Landslides—Disaster Risk Reduction; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 475–497. [Google Scholar]
- Petley, D. Global Patterns of Loss of Life from Landslides. Geology 2012, 40, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Zêzere, J.L.; Quaresma, I.; Santos, P.P.; Santos, M. Mortality Patterns of Hydro-Geomorphologic Disasters. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 1188–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froude, M.J.; Petley, D.N. Global Fatal Landslide Occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 2161–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Arnáez, J.; Sanjuán, Y.; Lana-Renault, N.; Gómez-Villar, A.; Álvarez-Martínez, J.; Coba-Pérez, P. Deforestation Induces Shallow Landsliding in the Montane and Subalpine Belts of the Urbión Mountains, Iberian Range, Northern Spain. Geomorphology 2017, 296, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, J.; Dietrich, W.E. Valley Incision by Debris Flows: Evidence of a Topographic Signature. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Dunne, T. A Stochastic Sediment Delivery Model for a Steep Mediterranean Landscape. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaphy, M.J.; Lowe, D.J.; Palmer, D.J.; Jones, H.S.; Gielen, G.J.; Oliver, G.R.; Pearce, S.H. Assessing Drivers of Plantation Forest Productivity on Eroded and Non-Eroded Soils in Hilly Land, Eastern North Island, New Zealand. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2014, 44, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleotti, P.; Chowdhury, R. Landslide Hazard Assessment: Summary Review and New Perspectives. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 1999, 58, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Westen, C.J.; Rengers, N.; Soeters, R. Use of Geomorphological Information in Indirect Landslide Susceptibility Assessment. Nat. Hazards 2003, 30, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L. Applicability of Landslide Susceptibility and Hazard Zoning at Different Scales. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, J.; van Westen, C.; Frattini, P.; Cascini, L.; Malet, J.P.; Fotopoulou, S.; Catani, F.; Van Den Eeckhaut, M.; Mavrouli, O.; Agliardi, F.; et al. Recommendations for the Quantitative Analysis of Landslide Risk. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 209–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara-Ayala, I.; Sassa, K. Landslide Risk Management: From Hazard to Disaster Risk Reduction. Landslides 2023, 20, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, U.; da Silva, P.F.; Devoli, G.; Pilz, J.; Zhao, B.; Khaloua, A.; Wilopo, W.; Andersen, P.; Lu, P.; Lee, J.; et al. The Human Cost of Global Warming: Deadly Landslides and Their Triggers (1995–2014). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezak, N.; Mikoš, M. Changes in the Rainfall Event Characteristics above the Empirical Global Rainfall Thresholds for Landslide Initiation at the Pan-European Level. Landslides 2021, 18, 1859–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Schwarz, M. Tree-Root Control of Shallow Landslides. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2017, 5, 451–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, I.; Giadrossich, F.; Mao, Z.; Cohen, D.; Capra, G.F.; Schwarz, M. Modeling Shallow Landslides and Root Reinforcement: A Review. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 181, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, H.; Tang, B.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Y. Accelerating Effect of Vegetation on the Instability of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H.; Minagawa, T. Impact of Vegetation Differences on Shallow Landslides: A Case Study in Aso, Japan. Water 2023, 15, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, W. Decoding Vegetation’s Role in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: An Integrated Review of Techniques and Future Directions. Biogeotechnics 2024, 2, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Di Martino, P.; Di Pasquale, G.; Mazzoleni, S.; Migliozzi, A.; Strumia, S. Il Ruolo Della Vegetazione Nelle Frane Di Quindici. Quad. Geol. Appl. 2000, 7, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, Z. Hydraulic Properties in Different Soil Architectures of a Small Agricultural Watershed: Implications for Runoffgeneration. Water 2019, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Mele, G.; Terribile, F. Soil Hydraulic Behaviour of a Selected Benchmark Soil Involved in the Landslide of Sarno 1998. Geoderma 2003, 117, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirus, B.B. Evaluating the Importance of Characterizing Soil Structure and Horizons in Parameterizing a Hydrologic Process Model. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4611–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, F.; Allocca, V.; De Vita, P. Hydro-Geomorphological Modelling of Ash-Fall Pyroclastic Soils for Debris Flow Initiation and Groundwater Recharge in Campania (Southern Italy). Catena 2017, 158, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, F.; Mirus, B.; Baum, R.; Calcaterra, D.; De Vita, P. Incorporating the Effects of Complex Soil Layering and Thickness Local Variability into Distributed Landslide Susceptibility Assessments. Water 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, E. Effects of Layering on Triggering Mechanisms of Rainfall-Induced Landslides in Unsaturated Pyroclastic Granular Soils. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, R.; Günther, T.; Heller, K.; Noell, U.; Kleber, A. Impacts of a Capillary Barrier on Infiltration and Subsurface Stormflow in Layered Slope Deposits Monitored with 3-D ERT and Hydrometric Measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5181–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terribile, F.; Basile, A.; Bonfante, A.; Carbone, A.; Colombo, C.; Langella, G.; Iamarino, M.; Manna, P.; Minieri, L.; Vingiani, S. Future Soil Issues. In The soils of Italy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 303–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hartemink, A.E. Into the Pedocene—Pedology of a Changing World. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandi, G.; De Natale, G.; Kilburn, C.R.J.; Troise, C.; Somma, R.; Di Lascio, M.; Fedele, A.; Rolandi, R. The 39 Ka Campanian Ignimbrite Eruption: New Data on Source Area in the Campanian Plain. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H.E., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 175–205. ISBN 9780128164549. [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti, D.; Vigliotti, M.; Rolandi, R.; Di Lascio, M. Effect of Paleomorphology on Facies Distribution of the Campania Ignimbrite in the Northern Campania Plain, Southern Italy. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 207–229. ISBN 9780128164549. [Google Scholar]
- Celico, P.; Guadagno, F. Le Instabilità Delle Coltri Piroclastiche Delle Dorsali Carbonatiche in Campania: Attuali Conoscenze. Quad. Geol. Appl. 1998, 5, 73–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ermice, A. A Pedological Case Study of Volcanoclastically Impacted Landscapes: The Vesuvian Avellino Air-Fall Deposits, Southern Italy. CATENA 2017, 149, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermice, A.; Pugliano, M.; Murolo, M.; Buondonno, A.; Flaminio, G.; Buondonno, C. Volcanic Ejecta as Soil Forming Factor on Carbonate Relieves of the Partenio Mountain (Campanian Apennines). Boll. DELLA Soc. Geol. Ital. 1999, 118, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Ermice, A.; Marzaioli, R.; Vigliotti, M.; Lamberti, P.; Ruberti, D. Soils in Understanding Land Surface Construction: An Example from Campania Plain, Southern Italy. Quaternary 2024, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiera, V.V.; Takahashi, T. Characteristics of Soils Derived from Tephra and Pyroclastic Flow Deposits from Taal Volcano, the Philippines. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1997, 43, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.J.; Palmer, D.J. Andisols of New Zealand and Australia. J. Integr. F. Sci. 2005, 2, 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, M.; Devnita, R.; Anda, M.; Goenadi, D.H.; Nugraha, A. Characteristics of Andisols Developed from Andesitic and Basaltic Volcanic Ash in Different Agro-Climatic Zones. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharikhina, L.V. Soil Formation on Acid and Basic Volcanic Ashes of Different Ages in Kamchatka. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2006, 39, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, I.A.; Tsutsuki, K.; Kondo, R.; Asio, V.B. Genesis of Soils across a Late Quaternary Volcanic Landscape in the Humid Tropical Island of Leyte, Philippines. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2008, 46, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonneijck, F.H.; Hageman, J.A.; Sevink, J.; Verstraten, J.M. Tephra Stratification of Volcanic Ash Soils in Northern Ecuador. Geoderma 2008, 144, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.J.; Lanigan, K.M.; Palmer, D.J. Where Geology Meets Pedology: Late Quaternary Tephras, Loess, and Paleosols in the Mamaku Plateau and Lake Rerewhakaaitu Areas. In Field Trip Guides, Geosciences 2012 Conference, Hamilton, New Zealand; Pittari, A. (Compiler) Geoscience Society of New Zealand Miscellaneous Publication: Newtown, WLG, New Zeland, 2021; pp. 2.1–2.45. ISBN 978-1-877480-26-3. ISSN (online): 2230-4487. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, O.; Ono, M. Relationship of Tephra Stratigraphy and Hydraulic Conductivity with Slide Depth in Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides in Aso Volcano, Japan. Landslides 2016, 13, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.J. Using Soil Stratigraphy and Tephrochronology to Understand the Origin, Age, and Classification of a Unique Late Quaternary Tephra-Derived Ultisol in Aotearoa New Zealand. Quaternary 2019, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurcholis, M.; Herlambang, S.; Suwartikaningsih, S.A.; Fiantis, D.; Yudiantoro, D.F. Soil Layers Properties of a Profile Developed on the Past Depositional Series on Merbabu Volcano Central Java Indonesia. J. Trop. Soils 2019, 24, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, Y.; Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C. Topographic Features and Stratified Soil Characteristics of a Hillslope with Fissures Formed by the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, S.; Dahlgren, R.; Nanzyo, M. Classification of Volcanic Ash Soils. Volcan. Ash Soils 1993, 21, 73–100. [Google Scholar]
- Temme, A.J.A.M. Relations Between Soil Development and Landslides. In Hydrogeology, Chemical Weathering, and Soil Formation; Hunt, H., Egli, M., Faybishenko, B., Eds.; Book Series: Geophysical Monograph Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 177–185. ISBN 9781119563952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvoie, M.; Delmelle, P.; Rattez, H.; Pereira, J.-M.; Tang, A.M. Hydraulic and Mechanical Behaviour of Volcanic Soils and Implications for Evaluating Slope Stability. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Picarelli, L.; Evangelista, A.; Rolandi, G. Mechanical Properties of Pyroclastic Soils in Campania Region. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Characterisation and Engineering Properties of Natural Soils, Singapore, 5–7 December 2006; Volume 4, pp. 2331–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli, F.; Regalado, C.M.; Basile, A.; Buurman, P.; Coppola, A. Physical Properties in European Volcanic Soils: A Synthesis and Recent Developments. In Soils of Volcanic Regions in Europe; Arnalds, Ó., Óskarsson, H., Bartoli, F., Buurman, P., Stoops, G., García-Rodeja, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 515–537. ISBN 3540487107. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 13th ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; ISBN 0926487221.
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, F.; Tufano, R.; De Vita, P.; Di Martire, D.; Di Napoli, M.; Guerriero, L.; Mileti, F.A.; Terribile, F.; Calcaterra, D. A Revised Landslide Inventory of the Campania Region (Italy). Sci. Data 2023, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFFI—Inventario dei Fenomeni Franosi in Italia. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/progetti/cartella-progetti-in-corso/suolo-e-territorio-1/iffi-inventario-dei-fenomeni-franosi-in-italia (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- IdroGEO. Available online: https://idrogeo.isprambiente.it/app/ (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Rolandi, G.; Di Lascio, M.; Rolandi, R. The Neapolitan Yellow Tuff Eruption as the Source of the Campi Flegrei Caldera. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 273–296. ISBN 9780128164549. [Google Scholar]
- Rolandi, G.; Bertollini, F.; Cozzolino, G.; Esposito, N.; Sannino, D. Sull’origine Delle Coltri Piroclastiche Presenti Sul Versante Occidentale Del Pizzo d’Alvano (Sarno-Campania). Quad. Geol. Appl. 2000, 7, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rolandi, G.; Maraffi, S.; Petrosino, P.; Lirer, L. The Ottaviano Eruption of Somma-Vesuvio (8000 y B.P.): A Magmatic Alternating Fall and Flow-Forming Eruption. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1993, 58, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandi, G.; Mastrolorenzo, G.; Barrella, A.M.; Borrelli, A. The Avellino Plinian Eruption of Somma-Vesuvius (3760 y.B.P.): The Progressive Evolution from Magmatic to Hydromagmatic Style. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1993, 58, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirer, L.; Pescatore, T.; Booth, B.; Walker, G.P.L. Two Plinian Pumice-Fall Deposits from Somma-Vesuvius, Italy. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1973, 84, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandi, G.; Petrosino, P.; Mc Geehin, J. The Interplinian Activity at Somma-Vesuvius in the Last 3500 Years. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 82, 19–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Principe, C.; Vecci, R. The 1631 Vesuvius Eruption. A Reconstruction Based on Historical and Stratigraphical Data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1993, 58, 151–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, P.D.; Scarpati, C. The 1944 Eruption of Vesuvius, Italy: Combining Contemporary Accounts and Field Studies for a New Volcanological Reconstruction. Geol. Mag. 2010, 147, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, P.; Agrello, D.; Ambrosino, F. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in Ash-Fall Pyroclastic Deposits Surrounding Mount Somma-Vesuvius: Application of Geophysical Surveys for Soil Thickness Mapping. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 59, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, P.; Nappi, M. Regional Distribution of Ash-Fall Pyroclastic Soils for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment. Landslide Sci. Pract. Spat. Anal. Model. 2013, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crescenzo, G.; Santo, A. Debris Slides-Rapid Earth Flows in the Carbonate Massifs of the Campania Region (Southern Italy): Morphological and Morphometric Data for Evaluating Triggering Susceptibility. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Pazzi, V.; Segoni, S.; De Vita, P.; Tofani, V.; Moretti, S. Spatial Modeling of Pyroclastic Cover Deposit Thickness (Depth to Bedrock) in Peri-Volcanic Areas of Campania (Southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carannante, G.; Cesarano, M.; Pappone, G.; Putignano, M.L. Note Illustrative Della Carta Geologica d’Italia in Scala 1:50.000, Foglio n. 431; Caserta Est. Servizio Geologico d’Italia (ISPRA): Rome, Italy, 2012. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/Media/carg/note_illustrative/431_Caserta_est.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Trigila, A. (Ed.) Rapporto Sulle Frane in Italia. Il Progetto IFFI: Metodologia, Risultati e Rapporti Regionali; Rapporti 78/2007; APAT—Agenzia per la Protezione dell’Ambiente e per i Servizi Tecnici: Rome, Italy, 2007; ISBN 978-88-448-0310-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein, H.R.; Hopewell, S. Grey Literature. In The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis; Cooper, H., Hedges, L.V., Valentine, J.C., Eds.; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 103–125. ISBN 9781610448864. [Google Scholar]
- Terribile, F.; Di Gennaro, A.; Aronne, G.; Basile, A.; Buonanno, M.; Mele, G.; Vingiani, S. I Suoli Delle Aree Di Crisi Di Quindici e Sarno: Proprietà e Comportamenti in Relazione Ai Fenomeni Franosi Del 1998. Quad. Geol. Appl. 2000, 7, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Terribile, F.; Basile, A.; De Mascellis, R.; Iamarino, M.; Magliulo, P.; Pepe, S.; Vingiani, S. Landslide processes and Andosols: The case study of the Campania region, Italy. In Soils of Volcanic Regions in Europe; Arnalds, O., Bartoli, F., Buurman, P., Oskarsson, H., Stoops, G., García-Rodeja, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Guadagno, F.; Aquino, S.; De Blasio, A. The December 1999 Cervinara Landslides: Further Debris Flows in the Pyroclastic Deposits of Campania (Southern Italy). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2001, 60, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, F.M.; Martino, S.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. Influence of Man-Made Cuts on the Stability of Pyroclastic Covers (Campania, Southern Italy): A Numerical Modelling Approach. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Wilson, R.C. Rainfall Induced Debris Flows in Pyroclastic Deposits, Campania (Southern Italy). Eng. Geol. 2004, 75, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellino, P.; Hungr, O.; Guadagno, F.M.; Evans, S.G. Velocity and Runout Simulation of Destructive Debris Flows and Debris Avalanches in Pyroclastic Deposits, Campania Region, Italy. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, F.M.; Forte, R.; Revellino, P.; Fiorillo, F.; Focareta, M. Some Aspects of the Initiation of Debris Avalanches in the Campania Region: The Role of Morphological Slope Discontinuities and the Development of Failure. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, C.; Merola, M.C.; Álvarez-Romero, M.; Coppola, E.; Minale, M. Rheology of Natural Slurries Involved in a Rapid Mudflow with Different Soil Organic Carbon Content. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, C.; Minale, M. Effect of the Soil Organic Content on Slurries Involved in Mudflows. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 16, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crescenzo, G.; Rotella, M.; Santo, A. Il Contributo della Geologia per lo Studio dei Meccanismi di Innesco di Colate Rapide di Fango al Campo Sperimentale di Monteforte Irpino (AV). In Piattaforme Evolute di Telecomunicazioni e di Information Technology per l’Offerta di Servizi al Settore Ambiente, Progetto PETIT-OSA; Aracne Edizioni: Rome, Italy, 2007; pp. 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- de Riso, R.; Santo, A. I contesti geologici e le caratteristiche delle colate di fango. In Un Laboratorio Integrato Finalizzato Allo Studio Delle Colate di Fango in Terreni Piroclastici; Picarelli, L., Vinale, F., Eds.; AMRA: Naples, Italy, 2009; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L.; Andreozzi, L.; Avorio, B.; Damiano, E.; Lampitiello, S. Scenari di pericolosità di frana in terreni sciolti di natura piroclastica. In Proceedings of the XXI Convegno Nazionale di Geotecnica L’Aquila: Opere Geotecniche in Ambiente Urbano, L’Aquila, Italy, 11–13 September 2002; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, E. Meccanismi D’Innesco Di Colate Di Fango in Terreni Piroclastici. Ph.D. Thesis, Seconda Università degli Studi di Napoli, Naples, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Picarelli, L.; Vinale, F. AMRA: Messa a Punto di Modelli Geotecnici per la Simuliazione Degli Effetti al Suolo delle Precipitazioni; Report; Fondazione CMCC—Centro Euro-Mediterraneo sui Cambiamenti Climatici: Lecce, Italy, 2007; ISBN 978-88-97666-15-8. [Google Scholar]
- Picarelli, L. Conoscere per Prevedere (Dall’ Equilibrio Limite Alla Meccanica Dei Pendii). Riv. Ital. Geotec. 2009, 4, 12–69. [Google Scholar]
- Picarelli, L.; Versace, P.; Olivares, L.; Damiano, E. Prediction of Rainfall-Induced Landslides in Unsaturated Granular Soils for Setting up of Early Warning Systems. In Proceedings of the International Forum on Landslide Disaster Management, Hong Kong, 10–12 December 2007; Volume 1, pp. 643–665. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, E.; Olivares, L. The Role of Infiltration Processes in Steep Slope Stability of Pyroclastic Granular Soils: Laboratory and Numerical Investigation. Nat. Hazards 2010, 52, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Guida, A.; Damiano, E.; Olivares, L. Soil Water Content and Suction Monitoring in Model Slopes for Shallow Flowslides Early Warning Applications. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, E.; Mercogliano, P.; Netti, N.; Olivares, L. A “Simulation Chain” to Define a Multidisciplinary Decision Support System for Landslide Risk Management in Pyroclastic Soils. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 989–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, E.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Steep-Slope Monitoring in Unsaturated Pyroclastic Soils. Eng. Geol. 2012, 137–138, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirone, M.; Damiano, E.; Picarelli, L.; Olivares, L.; Urciuoli, G. Groundwater-Atmosphere Interaction in Unsaturated Pyroclastic Slopes at Two Sites in Italy. Ital. Geotech. J. 2012, 66, 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Guida, A.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Effects of the Vegetation on the Hydrological Behavior of a Loose Pyroclastic Deposit. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Guida, A.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Hydrological Modelling of a Slope Covered with Shallow Pyroclastic Deposits from Field Monitoring Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4001–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Guida, A.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Conceptual Hydrological Modeling of the Soil-Bedrock Interface at the Bottom of the Pyroclastic Cover of Cervinara (Italy). Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 9, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Guida, A.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Field Hydrological Monitoring of a Sloping Shallow Pyroclastic Deposit. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urcioli, G.; Pirone, M.; Comegna, L.; Picarelli, L. Long-Term Investigations on the Pore Pressure Regime in Saturated and Unsaturated Sloping Soils. Eng. Geol. 2016, 212, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Guida, A.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Investigation on Rainwater Infiltration into Layered Shallow Covers in Pyroclastic Soils and Its Effect on Slope Stability. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Marino, P.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Damiano, E. Interaction between Perched Epikarst Aquifer and Unsaturated Soil Cover in the Initiation of Shallow Landslides in Pyroclastic Soils. Water 2018, 10, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, L.; Damiano, E.; Netti, N.; de Cristofaro, M. Geotechnical Properties of Two Pyroclastic Deposits Involved in Catastrophic Flowslides for Implementation in Early Warning Systems. Geosciences 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, P.; Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Olivares, L.; Greco, R. Monitoring the Hydrological Balance of a Landslide-Prone Slope Covered by Pyroclastic Deposits over Limestone Fractured Bedrock. Water 2020, 12, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, P.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Fan, X.; Greco, R. Prediction of Shallow Landslides in Pyroclastic-Covered Slopes by Coupled Modeling of Unsaturated and Saturated Groundwater Flow. Landslides 2021, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comegna, L.; Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. The Hysteretic Response of a Shallow Pyroclastic Deposit. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, E.; Foresta, V. Alcuni Effetti Del Rimaneggiamento Sulle Rigidezze Immediate e Differite Di Una Cenere Vulcanica. In Proceedings of the Incontro Annuale dei Ricercatori di Geotecnica 2006—IARG 2006, Pisa, Italy, 26–28 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, M.C.; Lizcano, A.; Santamarina, J.C. Colombian Volcanic Ash Soils; Tan, T.S., Phoon, K.K., Hight, D.W., Leroueil, S., Eds.; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 2007; Volume 3–4, ISBN 9780415402675. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, D.; Parise, M.; Palma, B.; Pelella, L. The influence of meteoric events in triggering shallow landslides in pyroclastic deposits of Campania, Italy. In Landslides in Research, Theory and Practice, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Landslides, Cardiff, UK, 26–30 June 2000; Bromhead, E., Dixon, N., Ibsen, M.L., Eds.; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Budetta, P.; de Riso, R. The mobility of some debris flows in pyroclastic deposits of the northwestern Campanian region (southern Italy). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2004, 63, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; Sorbino, G. Flow-like Mass Movements in Pyroclastic Soils: Remarks on the Modelling of Triggering Mechanisms. Riv. Ital. Di Geotec. 2005, 4, 11–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; Guida, D. Typical source areas of May 1998 flow-like mass movements in the Campania region, Southern Italy. Eng. Geol. 2008, 96, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; Pastor, M.; Sorbino, G. Modeling of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides of the Flow-Type. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2010, 136, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, F.M.; Revellino, P.; Grelle, G. The 1998 Sarno Landslides: Conflicting Interpretations of a Natural Event. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 17, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbino, G.; Nicotera, M.V. Unsaturated soil mechanics in rainfall-induced flow landslides. Eng. Geol. 2013, 165, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.A.; Calcaterra, D.; Petrosino, P.; Zanchetta, G.; de Vita, S.; Marotta, E.; Cesarano, M.; De Simone, A.; Sansivero, F.; Rucco, I. Landslides, volcanism and volcano-tectonics: The fragility of the Neapolitan territory. Cities on Volcanoes 10 Meeting—Napoli. Geol. F. Trips Maps 2019, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Fusi, N.; Dal Negro, P. Shallow Landslides in Pyroclastic Soils: A Distributed Modelling Approach for Hazard Assessment. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, E.; Cascini, L.; Foresta, V.; Sorbino, G. Geotechnical Characterisation of Pyroclastic Soils Involved in Huge Flowslides. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2005, 23, 365–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, E.; Fusco, F.; De Vita, P. Control of Hydrological Seasonal Variability of Ash-Fall Pyroclastic Deposits on Rainfall Triggering Debris Flows in Campania (Southern Italy). Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, P.; Fusco, F.; Tufano, R.; Cusano, D. Seasonal and event-based hydrological response of ash-fall pyroclastic cover in Campania (Southern Italy) for debris flow hazard assessment. Water 2018, 10, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, S.; Basile, A.; Calcaterra, D.; Iamarino, M.; Langella, G.; Moretti, P.; Vingiani, S.; Terribile, F. Andic soils and flow-like landslides: Cause–effect evidence from Italy. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 30, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDRR. Hazard Definition and Classification Review; Technical Report; UNDRR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkki, M.; Reeve, N. European Missions Overview. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on European Missions, Brussels, 29.9.2021 COM(2021) 609 Final 2021. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/7e2fad00-2716-11ec-bd8e-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Al Sayah, M.J.; Abdallah, C.; Der Sarkissian, R.; Abboud, M. A framework for investigating the land degradation neutrality—Disaster risk reduction nexus at the sub-national scales. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 195, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.C.; Green, C.; Newnham, G.J.; England, J.R.; Held, A.; Wulder, M.A.; Herold, M.; Cox, S.J.D.; Huete, A.R.; Kumar, L.; et al. Good Practice Guidance. SDG Indicator 15.3.1. Proportion of Land That Is Degraded Over Total Land Area; UNCCD-SPI: Bonn, Germany, 2017; Available online: https://www.unccd.int/sites/default/files/relevant-links/2017-10/Good%20Practice%20Guidance_SDG%20Indicator%2015.3.1_Version%201.0.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Feng, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhan, T.; Yan, Y.; Pereira, P. Land degradation neutrality: A review of progress and perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | Author(s) Name | Year of Publication | Reference Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pedostratigraphic approach | |||
| Group A | Terribile et al. | 2000 | [73] |
| Terribile et al. | 2007 | [74] | |
| Group B | Fiorillo et al. | 2001 | [75] |
| Guadagno et al. | 2003 | [76] | |
| Fiorillo et Wilson | 2004 | [77] | |
| Revellino et al. | 2004 | [78] | |
| Guadagno et al. | 2005 | [79] | |
| Group C | Carotenuto et al. | 2015 | [80] |
| Carotenuto and Minale | 2016 | [81] | |
| Litostratigraphic approach | |||
| Group D | Di Crescenzo and Santo | 2006 | [68] |
| Di Crescenzo et al. | 2007 | [82] | |
| De Riso and Santo | 2009 | [83] | |
| Group E | Olivares et al. | 2002 | [84] |
| Damiano | 2004 | [85] | |
| Picarelli et al. | 2006 | [51] | |
| Picareli and Vinale | 2007 | [86] | |
| Picarelli | 2009 | [87] | |
| Picarelli et al. | 2009 | [88] | |
| Damiano et Olivares | 2010 | [89] | |
| Greco et al. | 2010 | [90] | |
| Damiano et al. | 2012 | [91] | |
| Damiano et al. | 2012 | [92] | |
| Pirone et al. | 2012 | [93] | |
| Comegna et al. | 2013 | [94] | |
| Greco et al. | 2013 | [95] | |
| Greco et al. | 2014 | [96] | |
| Comegna et al. | 2016 | [97] | |
| Urciuoli et al. | 2016 | [98] | |
| Damiano et al. | 2017 | [99] | |
| Damiano | 2019 | [27] | |
| Greco et al. | 2019 | [100] | |
| Olivares et al. | 2019 | [101] | |
| Marino et al. | 2020 | [102] | |
| Marino et al. | 2021 | [103] | |
| Comegna et al. | 2021 | [104] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ermice, A.; Buffardi, C.; Marzaioli, R.; Vigliotti, M.; Ruberti, D. Review and Inventory of Pedological and Stratigraphical Knowledge for Investigating Shallow Landslides: A Case Study of the Cervinara Area (Central Campanian Apennines, Southern Italy). Geosciences 2025, 15, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040151
Ermice A, Buffardi C, Marzaioli R, Vigliotti M, Ruberti D. Review and Inventory of Pedological and Stratigraphical Knowledge for Investigating Shallow Landslides: A Case Study of the Cervinara Area (Central Campanian Apennines, Southern Italy). Geosciences. 2025; 15(4):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040151
Chicago/Turabian StyleErmice, Antonella, Carla Buffardi, Rossana Marzaioli, Marco Vigliotti, and Daniela Ruberti. 2025. "Review and Inventory of Pedological and Stratigraphical Knowledge for Investigating Shallow Landslides: A Case Study of the Cervinara Area (Central Campanian Apennines, Southern Italy)" Geosciences 15, no. 4: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040151
APA StyleErmice, A., Buffardi, C., Marzaioli, R., Vigliotti, M., & Ruberti, D. (2025). Review and Inventory of Pedological and Stratigraphical Knowledge for Investigating Shallow Landslides: A Case Study of the Cervinara Area (Central Campanian Apennines, Southern Italy). Geosciences, 15(4), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15040151









