Sedimentary Architecture Prediction Using Facies Interpretation and Forward Seismic Modeling: Application to a Mediterranean Land–Sea Pliocene Infill (Roussillon Basin, France)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
2.1. Geodynamics
2.2. Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC) Event
2.3. Post-MSC
2.4. Onshore Pliocene Geological Records
2.5. Offshore Pliocene Seismic Records
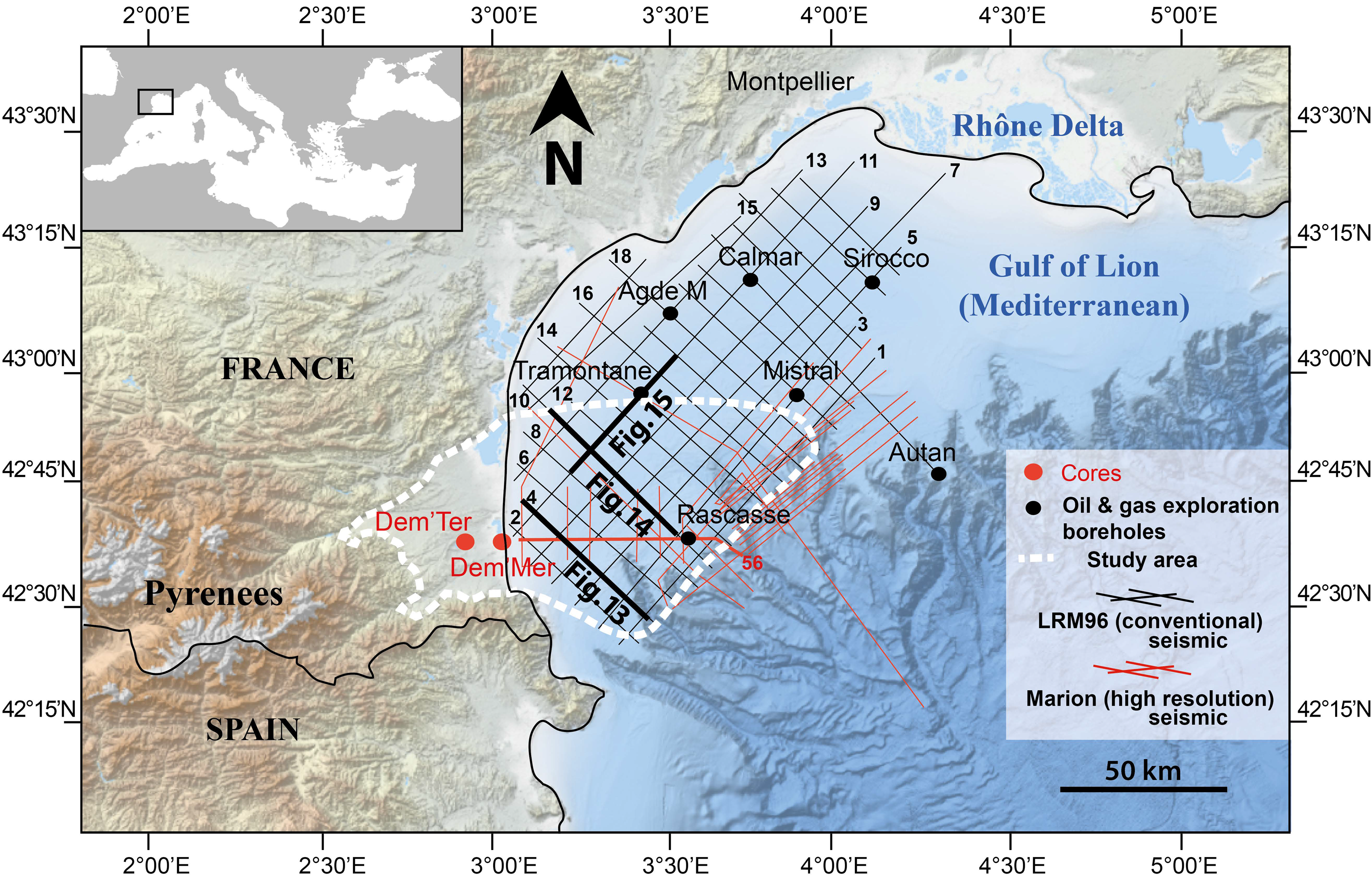
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Onshore
3.2. Offshore
3.3. Synthetic Seismic Modeling
3.4. Analysis of the Interpreted Facies Distribution
4. Results
4.1. Borehole and Outcrop Sedimentary Records
4.1.1. Sedimentary Facies Associations

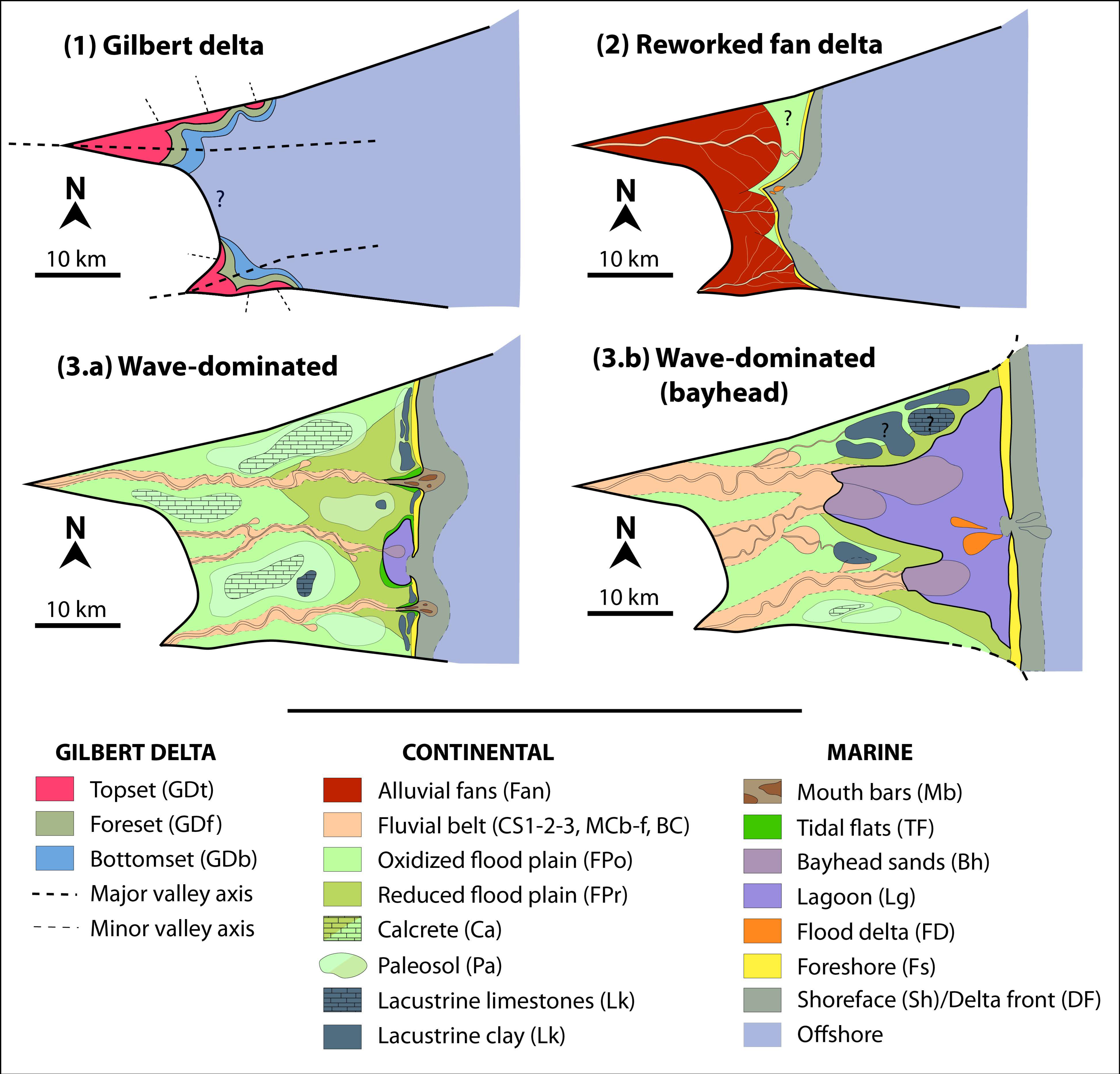
- AF1_Gilbert Deltas
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF2_Confined Alluvial Plain
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF3_Unconfined Alluvial Plain
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF4_Delta/Coastal Plain
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF5_Embayment
- Description:
- Depositional system:
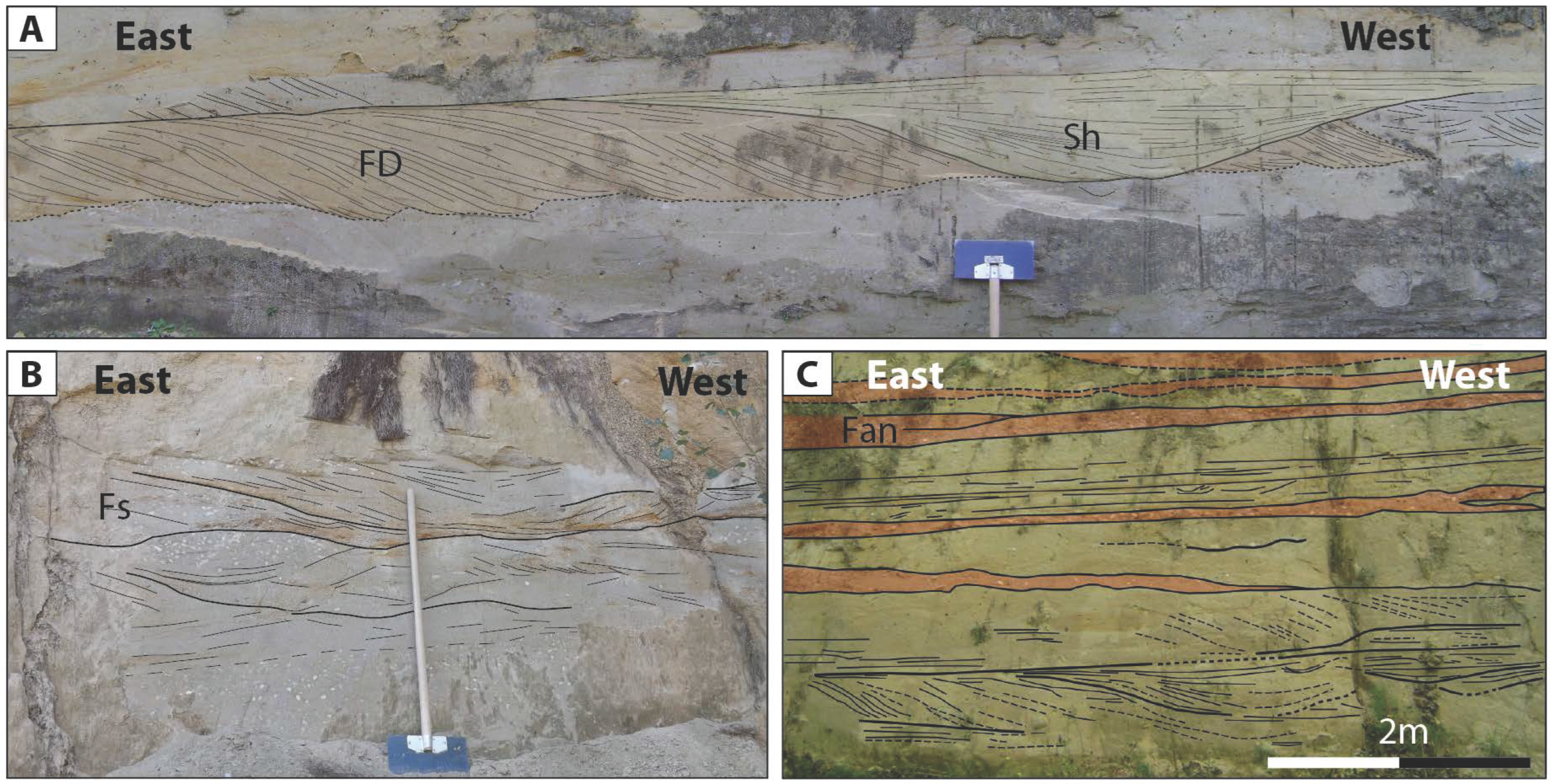
- AF6_ Shallow Marine Sands 1
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF7_Shallow Marine Sands 2
- Description:
- Depositional system:
- AF8_Upper Offshore
- Description:
- Depositional system:
4.1.2. Synthesis of Sedimentary Facies and Environments
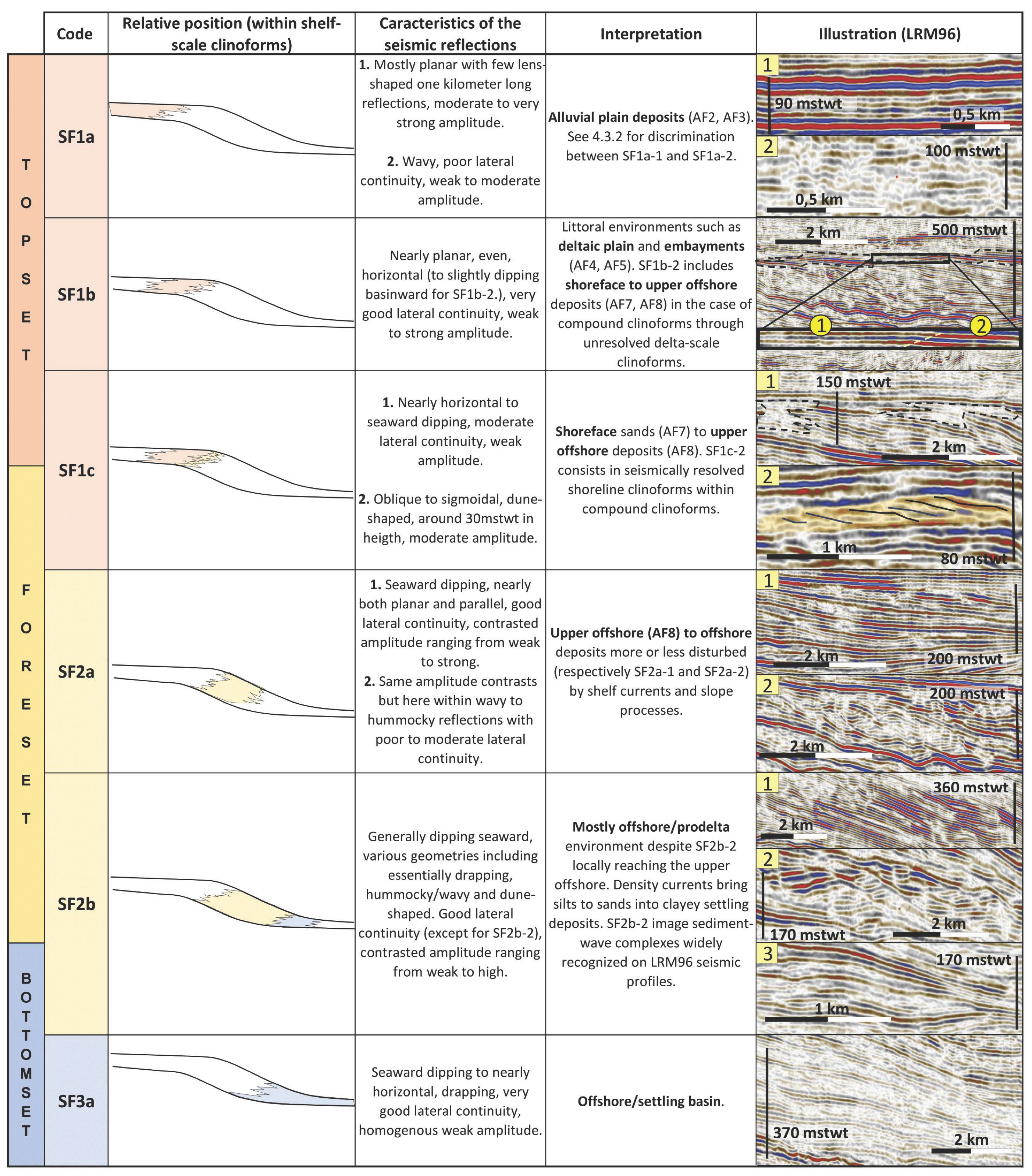
4.2. Seismic Facies
4.2.1. Topset
SF1a
SF1b
SF1c
4.2.2. Foreset
SF2a
SF2b
4.2.3. Bottomset
SF3a
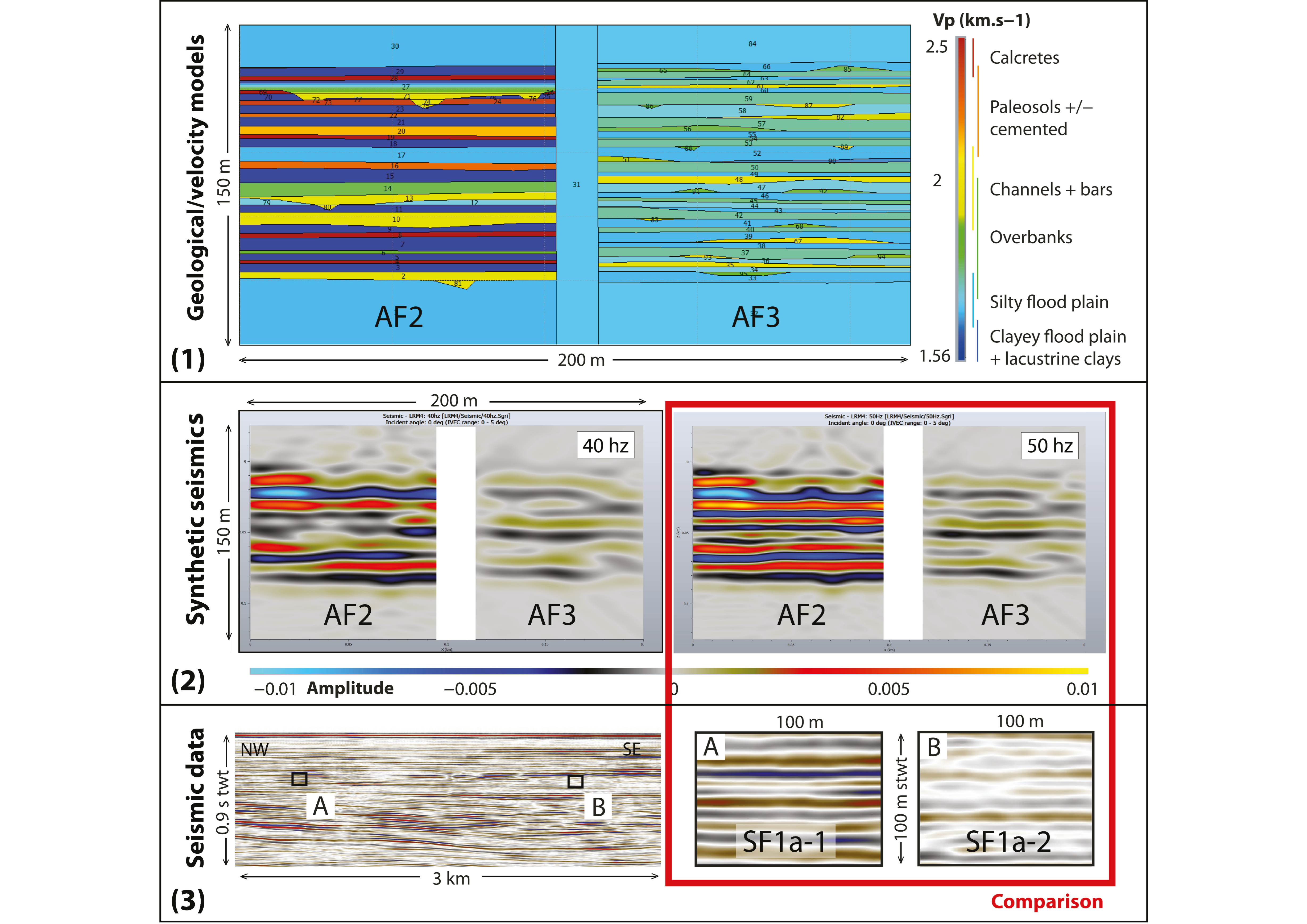
4.3. Forward Seismic Modeling
4.3.1. Sensitivity Test
4.3.2. Modeling of Topset Facies (SF1a and SF1b)
Discriminating Between Alluvial and Littoral Deposits
Discriminating Confined vs. Unconfined Alluvial Plain
4.3.3. Modeling of Delta-Scale Clinoforms
4.4. Revisited Interpretation of Offshore Seismic Profiles
4.4.1. LRM4
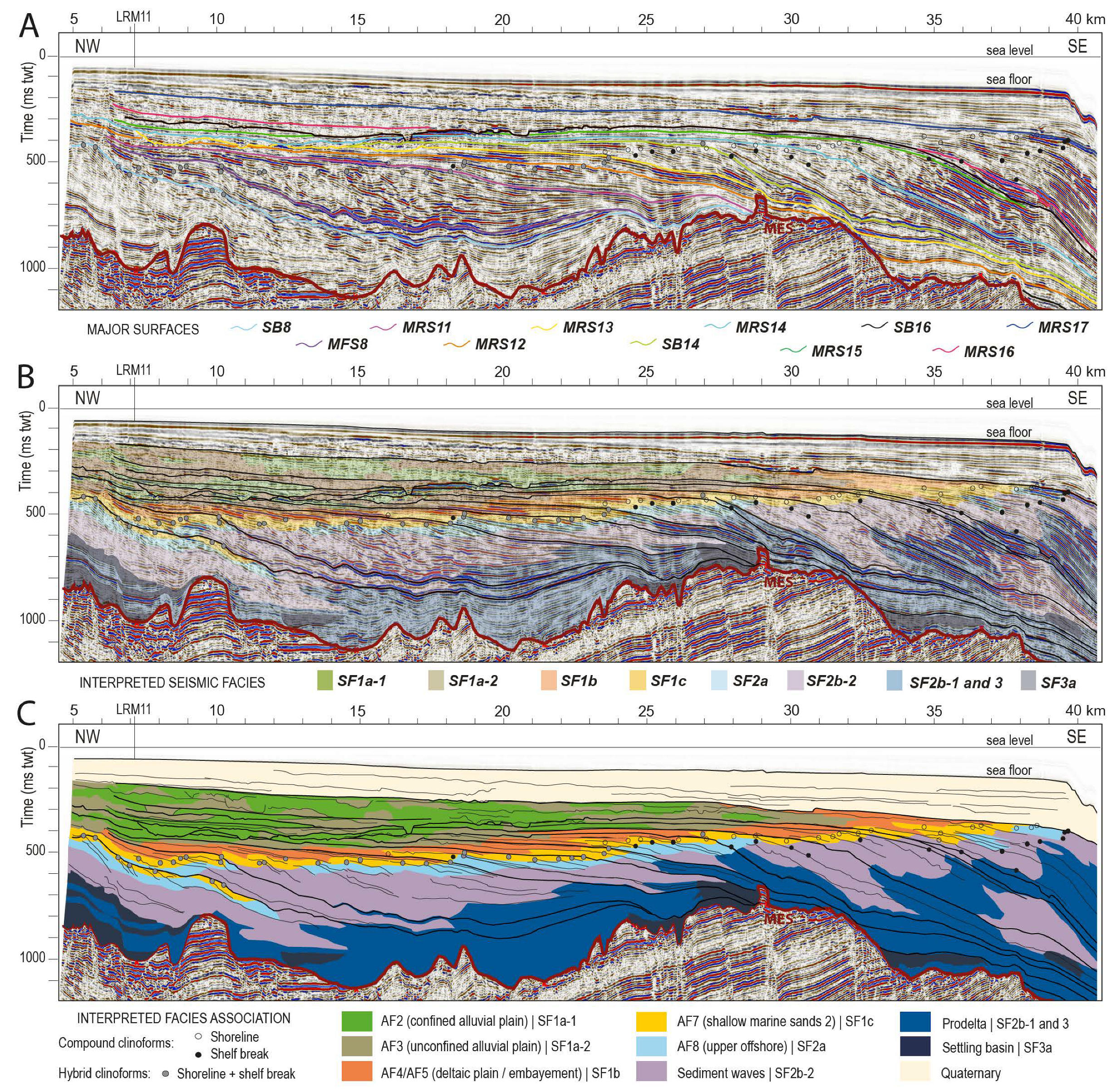
4.4.2. LRM10
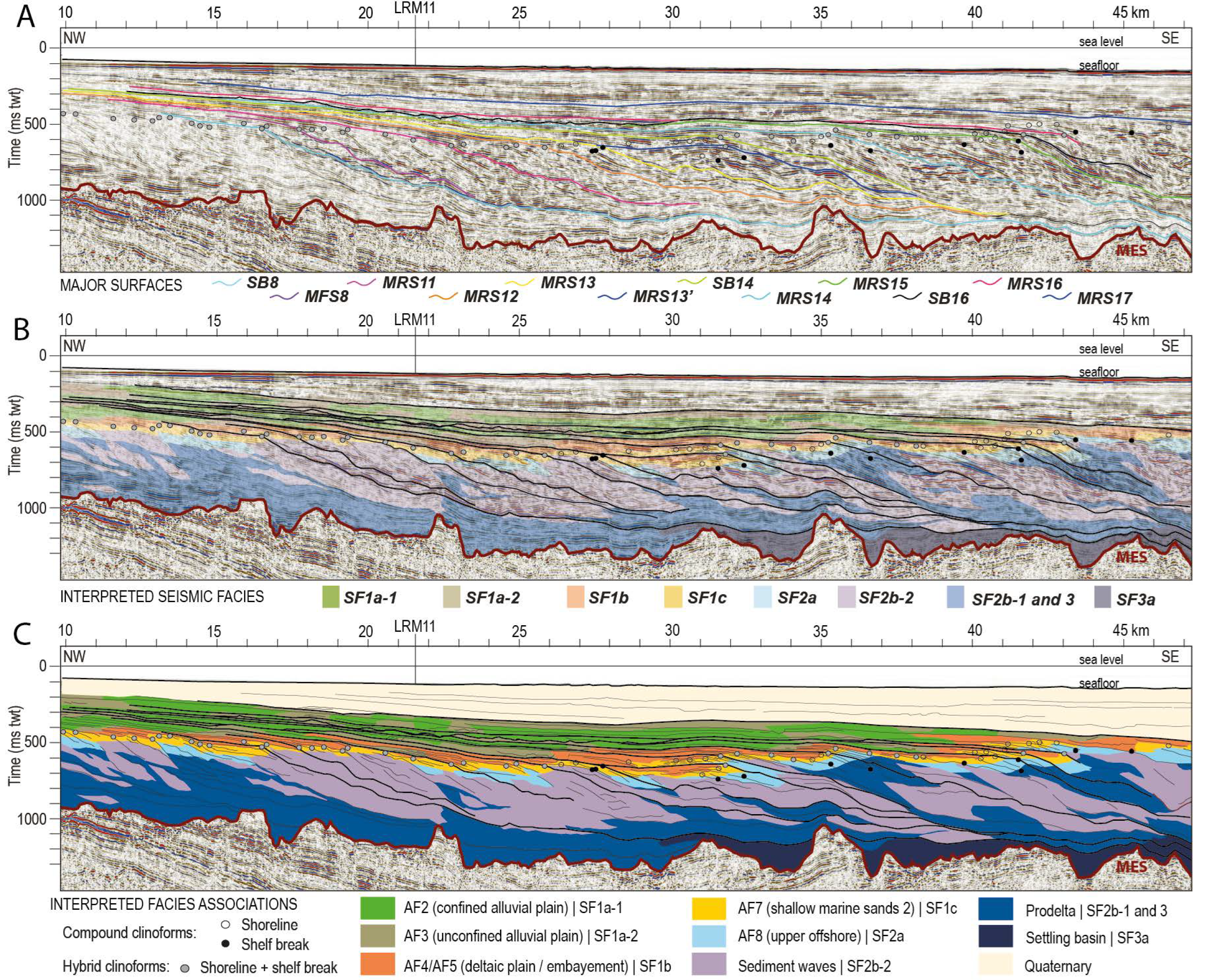
4.4.3. LRM11

5. Discussion
5.1. Coherence of the Model
5.2. Shoreline Trajectory Offshore, Evolution in Clinoform Configuration, and Forcing Factors
5.3. Implication for Coastal Aquifers
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Mitchum, R.M.; Vail, P.R. Seismic Stratigraphy and Global Changes of Sea-Level: Part 7. Seismic Stratigraphic Interpretation Procedure: Section 2. Application of Seismic Reflection Configuration to Stratigraphic Interpretation; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Vail, P.R.; Mitchum, R.M.; Thompson, S. Seismic Stratigraphy and Global Changes of Sea Level, Part 4: Global Cycles of Relative Changes of Sea Level; American Association Of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, D.; Castagna, J.; Meza, R.; Chen, S.; Jiang, R. Case study: Seismic resolution and reservoir characterization of thin sands using multiattribute analysis and bandwidth extension in the Daqing field, China. Interpretation 2020, 8, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangree, J.B.; Widmier, J.M. Seismic Stratigraphy and Global Changes of Sea Level: Part 9. Seismic Interpretation of Clastic Depositional Facies: Section 2. Application of Seismic Reflection Configuration to Stratigraphic Interpretation; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Sangree, J.B.; Widmier, J.M. Interpretation of depositional facies from seismic data. Geophysics 1979, 44, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Haq, B.U. Seismic facies analysis: Past, present and future. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 224, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, J.C.; Mitchum, R.M.; Campion, K.M.; Rahmanian, V.D. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy in Well Logs, Cores, and Outcrops: Concepts for High-Resolution Correlation of Time and Facies; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1990; Volume 7, 55p. [Google Scholar]
- Homewood, P.; Mauraud, P.; Lafont, F. Best practice in Sequence Stratigraphy for Explorationists and Reservoir Engineers—Elf EP Editions; Elf EP-Editions: Pau, France, 2000; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, O.R. Seismic detection and evaluation of delta and turbidite sequences: Their application to exploration for the subtle trap. AAPG Bull. 1982, 66, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, S.; Helland-Hansen, W. Clinoforms and clinoform systems: Review and dynamic classification scheme for shorelines, subaqueous deltas, shelf edges and continental margins. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 202–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, J.L. Three critical environments of deposition, and criteria for recognition of rocks deposited in each of them. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1951, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, S.; Hampson, G.J.; Jackson, C.A.-L. Quantitative characterisation of deltaic and subaqueous clinoforms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 142, 79–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Patruno, S.; Helland-Hansen, W.; Steel, R.-J.; Trincardi, F. Clinoforms and clinothems: Fundamental elements of basin infill. Basin Res. 2020, 32, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.J.; Olariu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. What is the topset of a shelf-margin prism? Basin Res. 2020, 32, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez, D.; Simó, J.A.; Lobo, F.J.; Barnolas, A.; Carrera, J.; Vázquez-Suñé, E. Onshore–offshore correlation of the Llobregat deltaic system, Spain: Development of deltaic geometries under different relative sea-level and growth fault influences. Sediment. Geol. 2009, 217, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Steel, R.J.; Olariu, C.; Li, S. Rapid subsidence and preservation of fluvial signals in an otherwise wave-reworked delta front succession: Early-mid Pliocene Orinoco continental-margin growth, SE Trinidad. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 395, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteverde, D.H.; Miller, K.G.; Mountain, G.S. Correlation of offshore seismic profiles with onshore New Jersey Miocene sediments. Sediment. Geol. 2000, 134, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, E. Coastal aquifers of Europe: An overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvail, C.; Le Strat, P. Architecture et géométrie haute résolution des prismes sédimentaires plio-quaternaires au droit du Roussillon suivant un profil terre-mer. Report BRGM/RP-51972-FR 2002, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Duvail, C.; Gorini, C.; Lofi, J.; Le Strat, P.; Clauzon, G.; Dos Reis, A.T. Correlation between onshore and offshore Pliocene–Quaternary systems tracts below the Roussillon Basin (eastern Pyrenees, France). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, E.; Aslanian, D.; Rabineau, M.; Moulin, M.; Granjeon, D.; Gorini, C.; Droz, L. Sedimentary markers in the Provençal Basin (western Mediterranean): A window into deep geodynamic processes. Terra Nova 2015, 27, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauzon, G.; Suc, J.-P.; Aguilar, J.-P.; Ambert, P.; Cappetta, H.; Cravatte, J.; Drivaliari, A.; Domenech, R.; Dubar, M.; Leroy, S.; et al. Pliocene geodynamic and climatic evolutions in the French Mediterranean region. Paleontol. Evol. 1990, 2, 132–186. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, Y.; Balouin, Y.; Baudouy, L.; Berne, S.; Bouchette, F.; Bourgine, B.; Bourrin, F.; Brun, L.; Champollion, C.; Duvail, C.; et al. Caractérisation transdisciplinaire d’un aquifère côtier complexe, pour une exploitation maitrisée et durable de sa ressource en eau en contexte méditerranéen: Le Projet Dem’Eaux Roussillon. Rapport final. In Proceedings of the Colloque “La Gestion des eaux Souterraines au 21e Siècle”, BRGM/RP-71814-FR, Pessac, France, 15–17 February 2023; 73p. Available online: http://infoterre.brgm.fr/rapports//RP-71814-FR.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Rabineau, M. Un Modèle Géométrique et Stratigraphique des Séquences de Dépôts Quaternaires sur la Marge du Golfe du Lion: Enregistrement des Cycles Climatiques de 100 000 Ans. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Rennes 1, Rennes, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rabineau, M.; Leroux, E.; Aslanian, D.; Bache, F.; Gorini, C.; Moulin, M.; Molliex, S.; Droz, L.; Dos Reis, A.T.; Rubino, J.L.; et al. Quantifying subsidence and isostatic readjustment using sedimentary paleomarkers, example from the Gulf of Lion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 388, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunay, B.; Duvail, C.; Le Strat, P.; Dörfliger, N.; Lachassagne, P.; Pistre, S. Importance of a high resolution lithological and geometrical knowledge for Mediterranean coastal sedimentary aquifers management: Application to the Roussillon Basin, South of France. In Proceedings of the Groundwater and Saline Intrusion, 18th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting–IAH, IHP-UNESCO, IGME, Cartagena, Spain, 31 May–3 June 2004; Volume 15, pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Guerrot, C.; Aunay, B.; Dörfliger, N. Origins and processes of salinization of a Plio-Quaternary coastal Mediterranean multilayer aquifer: The Roussillon Basin case study. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, Y.; Ladouche, B. Impact of climate change on groundwater in a confined Mediterranean aquifer. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 10109–10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorpp, L.; Dall’Alba, V.; Renard, P.; Lanini, S.; Caballero, Y. Hydrogeological modeling of the Roussillon coastal aquifer (France): Stochastic inversion and analysis of future stresses. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Person, M.; Berndt, C.; Bertoni, C.; Cohen, D.; Evans, R.; Haroon, A.; Hensen, C.; Jegen, M.; Key, K.; et al. Offshore freshened groundwater in continental margins. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2020RG000706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, B.; Pellegrini, C.; Sammartino, I.; Trincardi, F.; Amorosi, A. New perspectives on offshore groundwater exploration through integrated sequence-stratigraphy and source-to-sink analysis: Insights from the late Quaternary succession of the western Central Adriatic system, Italy. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 256, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, K.; Petersen, S.; Martinsen, O.; Johansen, T.A.; Len, T.; Thurmond, J. Seismic modeling of outcrop analogues: Techniques and applications. GeoScienceWorld 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mauffret, A.; de Grossouvre, B.D.; Dos Reis, A.T.; Gorini, C.; Nercessian, A. Structural geometry in the eastern Pyrenees and western Gulf of Lion (Western Mediterranean). J. Struct. Geol. 2001, 23, 1701–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séranne, M.; Couëffé, R.; Husson, E.; Baral, C.; Villard, J. The transition from Pyrenean shortening to Gulf of Lion rifting in Languedoc (South France)—A tectonic-sedimentation analysis. Bull. Société Géologique Fr. 2021, 192, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternois, S.; Odlum, M.; Ford, M.; Pik, R.; Stockli, D.; Tibari, B.; Bernard, V. Thermochronological evidence of early orogenesis, eastern Pyrenees, France. Tectonics 2019, 38, 1308–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Romagny, A.; Gorini, C.; Maillard, A.; Thinon, I.; Couëffé, R.; Ducoux, M.; Séranne, M. Fast dismantling of a mountain belt by mantle flow: Late-orogenic evolution of Pyrenees and Liguro-Provençal rifting. Tectonophysics 2020, 776, 228–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séranne, M. The Gulf of Lion continental margin (NW Mediterranean) revisited by IBS: An overview. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1999, 156, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Baudin, T.; Calassou, S.; Chevrot, S.; Ford, M.; Issautier, B.; Lasseur, E.; Masini, E.; Manatschal, G.; Mouthereau, F.; et al. Geodynamic evolution of a wide plate boundary in the Western Mediterranean, near-field versus far-field interactions. BSGF-Earth Sci. Bull. 2021, 192, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, M. Morphogenèse d’Une Montagne Méditerranéenne, les Pyrénées Orientales. Doctoral Dissertation, Document du BRGM, University of Paris, Paris, France, 1996; 255p. [Google Scholar]
- Milesi, G.; Monié, P.; Soliva, R.; Münch, P.; Valla, P.G.; Brichau, S.; Bonno, M.; Martin, C.; Bellanger, M. Deciphering the Cenozoic Exhumation History of the Eastern Pyrenees Along a Crustal-Scale Normal Fault Using Low-Temperature Thermochronology. Tectonics 2022, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsü, K.J.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Cita, M.B. Late Miocene desiccation of the Mediterranean. Nature 1973, 242, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveri, M.; Flecker, R.; Krijgsman, W.; Lofi, J.; Lugli, S.; Manzi, V.; Sierro, F.J.; Bertini, A.; Camerlenghi, A.; de Lange, G.; et al. The Messinian Salinity Crisis: Past and future of a great challenge for marine sciences. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 25–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heida, H.; Raad, F.; Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Jiménez-Munt, I.; Maillard, A.; Lofi, J. Flexural-isostatic reconstruction of the Western Mediterranean during the Messinian Salinity Crisis: Implications for water level and basin connectivity. Basin Res. 2022, 34, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Gorini, C.; Berne, S.; Clauzon, G.; Dos Reis, A.T.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Steckler, M.S. Erosional processes and paleo-environmental changes in the Western Gulf of Lion (SW France) during the Messinian Salinity Crisis. Mar. Geol. 2005, 217, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Deverchere, J.; Gaullier, V.; Gillet, H.; Gorini, C.; Guennoc, P.; Loncke, L.; Maillard, A.; Sage, F.; Thinon, I. Atlas of the “Messinian Salinity Crisis” seismic markers in the Mediterranean and Black seas. Comm. Geol. Map World Mémoires Société Géologique Fr. Nouv. Série 2011, 179, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Clauzon, G. The eustatic hypothesis and the pre-Pliocene cutting of the Rhône Valley. Initial. Rep. Deep. Sea Drill. Proj. XIII 1973, 13, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Guennoc, P.; Gorini, C.; Mauffret, A. Histoire géologique du golfe du Lion et cartographie du rift oligo-aquitanien et de la surface messinienne. Géologie Fr. 2000, 3, 67–97. [Google Scholar]
- Clauzon, G. Le canyon messinien de la Durance (Provence, France): Une preuve paléogéographique du bassin profond de dessiccation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1979, 29, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Estrada, F.; Jiménez-Munt, I.; Gorini, C.; Fernandez, M.; Verges, J.; De Vicente, R. Catastrophic flood of the Mediterranean after the Messinian salinity crisis. Nature 2009, 462, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Browning, J.V.; Schmelz, W.J.; Kopp, R.E.; Mountain, G.S.; Wright, J.D. Cenozoic sea-level and cryospheric evolution from deep-sea geochemical and continental margin records. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Rabineau, M.; Gorini, C.; Berne, S.; Clauzon, G.; De Clarens, P.; Tadeu Dos Reis, A.; Mountain, G.S.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Steckler, M.S.; et al. Plio–Quaternary prograding clinoform wedges of the western Gulf of Lion continental margin (NW Mediterranean) after the Messinian Salinity Crisis. Mar. Geol. 2003, 198, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvail, C. Expression des Facteurs Régionaux et Locaux dans l’Enregistrement Sédimentaire d’Une Marge Passive. Exemple de la Marge du Golfe du Lion, Étudiée Selon un Continuum Terre-Mer. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, E. Quantification des Flux Sédimentaires et de la Subsidence du Bassin Provençal. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Brest, Brest, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, E.; Rabineau, M.; Aslanian, D.; Granjeon, D.; Droz, L.; Gorini, C. Stratigraphic simulations of the shelf of the Gulf of Lions: Testing subsidence rates and sea-level curves during the Pliocene and Pleistocene. Terra Nova 2014, 26, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, C.; Le Marrec, A.; Mauffret, A. Structural and sedimentary history of the Gulf of Lions (Western Mediterranean), from the ECORS profiles, seismic industrial lines and well data. Bull. Société Géologique Fr. 1993, 164, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Cravatte, J.; Dufaure, P.; Prim, M.; Rouaix, S. Les sondages du Golfe du Lion, stratigraphie, sédimentologie. Notes et mémoires. Cie. Française Pétroles 1974, 11, 209–274. [Google Scholar]
- Huyghe, D.; Mouthereau, F.; Segalen, L.; Furió, M. Long-term dynamic topographic support during post-orogenic crustal thinning revealed by stable isotope (δ18O) paleo-altimetry in eastern Pyrenees. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, G.; Valla, P.G.; Münch, P.; Huyghe, D. Tectono-geomorphological evolution of the Eastern Pyrenees: Insights from thermo-kinematic modeling. Tectonophysics 2023, 866, 230057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauzon, G.; Le Strat, P.; Duvail, C.; Do Couto, D.; Suc, J.-P.; Molliex, S.; Bache, F.; Besson, D.; Lindsay, E.H.; Opdyke, N.D.; et al. The Roussillon Basin (S. France): A case-study to distinguish local and regional events between 6 and 3 Ma. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 18–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, G.K. The Topographic Features of Lake Shores; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1885; Volume 5, pp. 75–123. [Google Scholar]
- Clauzon, G.; Aguilar, J.-P.; Michaux, J. Le bassin pliocène du Roussillon (Pyrénées orientales, France): Exemple d’évolution géodynamique d’une ria méditerranéenne consécutive à la crise de salinité messinienne. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Sci. 1987, 304, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Clauzon, G.; Rubino, J.-L. Les Gilbert-deltas pliocènes du Golfe du Lion et de Ligurie: Des constructions sédimentaires originales consécutives à la crise de salinité messinienne. Livret Guide l’Excursion ANDRA 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Breda, A.; Mellere, D.; Massari, F. Facies and processes in a Gilbert-delta-filled incised valley (Pliocene of Ventimiglia, NW Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2007, 200, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauzon, G. Le détritisme néogène du bassin du Roussillon (Pyrénées-Orientales, France). Géologie Alp. 1987, 13, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Depéret, C. Description Géologique du Bassin Tertiaire du Roussillon; Masson: Paris, France, 1885; 274p. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, G.M.; Fonteilles, M.; Leblanc, D.; Clauzon, G.; Marchal, J.P.; Vautrelle, C. Rivesaltes. Carte géologique de la France à 1/50000 (No. 1090). BRGM 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Aunay, B. Apport de la Stratigraphie Séquentielle à la Gestion et à la Modélisation des Ressources en eau des Aquifères Côtiers. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Duvail, C.; Le Strat, P.; Bourgine, B. Atlas géologique des formations plio-quaternaires de la plaine du Roussillon (Pyrénées Orientales). Rapp. No RP-51197-FR BRGM 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Alba, V.; Renard, P.; Straubhaar, J.; Issautier, B.; Duvail, C.; Caballero, Y. 3D multiple-point statistics simulations of the Roussillon Continental Pliocene aquifer using DeeSse. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 4997–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju-Duval, B.; Letouzey, J.; Montadert, L.; Courrier, P.; Mugniot, J.F.; Sancho, J. Geology of the Mediterranean Sea basins. In The Geology of Continental Margins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1974; pp. 695–721. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, E.; Rabineau, M.; Aslanian, D.; Gorini, C.; Molliex, S.; Bache, F.; Robin, C.; Droz, L.; Moulin, M.; Poort, J.; et al. High-resolution evolution of terrigenous sediment yields in the Provence Basin during the last 6 Ma: Relation with climate and tectonics. Basin Res. 2017, 29, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, M.; Calvet, M.; Gunnell, Y.; Voinchet, P.; Manel, C.; Braucher, R.; Tissoux, H.; Bahain, J.-J.; Perrenoud, C.; Saos, T. Terrestrial 10Be and electron spin resonance dating of fluvial terraces quantifies Quaternary tectonic uplift gradients in the eastern Pyrenees. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 193, 188–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezard, P.A.; Lofi, J.; Le Ber, E.; Henry, G.; Brun, L.; Geeraert, M.; Hamel, C.; Gee, R.; Brillouet, N.; Neyens, D.; et al. Petrophysical characterisation of a clastic coastal aquifer with implications for saltwater intrusion and the evolution of groundwater resources. The GRAIN D’SEL and DEM’EAUX ROUSSILLON projects, Occitanie, France. In Proceedings of the IAHS-AISH XIth Scientific Assembly, Montpellier, France, 29 May–3 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, E.; Aslanian, D.; Rabineau, M.; Gorini, C.; Rubino, J.-L.; Poort, J.; Suc, J.P.; Bache, F.; Blanpied, C. Atlas of the Stratigraphic Markers in the Western Mediterranean with Focus on the Messinian, Pliocene and Pleistocene of the Gulf of Lion; CCGM-CGMW: Paris, France, 2019; ISBN 9782917310380. [Google Scholar]
- Helland-Hansen, W.; Hampson, G.J. Trajectory analysis: Concepts and applications. Basin Res. 2009, 21, 454–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proust, J.N.; Pouderoux, H.; Ando, H.; Hesselbo, S.P.; Hodgson, D.M.; Lofi, J.; Rabineau, M.; Sugarman, P.J. Facies architecture of Miocene subaqueous clinothems of the New Jersey passive margin: Results from IODP-ICDP Expedition 313. Geosphere 2018, 14, 1564–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, I. Resolution and illumination analyses in PSDM: A ray-based approach. Lead. Edge 2008, 27, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, I.; Lavadera, P.L.; Botter, C.; Anell, I.; Buckley, S.J.; Eide, C.; Grippa, A.; Mascolo, V.; Kjoberg, S. 2(3)D convolution modelling of complex geological targets beyond–1D convolution. First Break 2016, 34, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J. La Crise de Salinité Messinienne: Incidences Directes et Différées sur l’Evolution Sédimentaire de la Marge du Golfe du Lion. PhD Thesis, University of Lille 1, Lille, France, 2002; 285p. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.G.; Browning, J.V.; Mountain, G.S.; Bassetti, M.A.; Monteverde, D.; Katz, M.; Inwood, J.; Lofi, J.; Proust, J.N. Sequence boundaries are impedance contrasts: Core-seismic-log integration of Oligocene–Miocene sequences, New Jersey shallow shelf. Geosphere 2013, 9, 1257–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, R.; Kenny, G.S.; McClure, C.D. A method for determining and displaying the shear-velocity reflectivities of a geologic formation. Eur. Pat. Appl. 1983, 113944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ber, L.; et al. Université de Montpellier: Montpellier, France; CNRS: Perpignan, France; manuscript in preparation.
- Reineck, H.E.; Singh, I.B. Depositional environments. In Depositional Sedimentary Environments: With Reference to TerrigenFous Clastics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Postma, G.; Roep, T.B. Resedimented conglomerates in the bottomsets of Gilbert-type gravel deltas. J. Sediment. Res. 1985, 55, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauzon, G. Restitution de l’évolution géodynamique néogène du bassin du Roussillon et de l’unité adjacente des Corbières d’après les données écostratigraphiques et paléogéographiques. Paléobiologie Cont. 1990, 17, 125–155. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, T.; Steel, R.; Hogseth, K.; Skar, T.; Roe, S. Sequential architecture in a fluvial succession: Sequence stratigraphy in the Upper Cretaceous Mesaverde Group, Price Canyon, Utah. J. Sediment. Res. 1995, 65, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauzon, G.; Cravatte, J. Révision chronostratigraphique de la série marine pliocène traversée par le sondage Canet 1 (Pyrénées-Orientales, France): Apports à la connaissance du Néogène du Roussillon. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Sci. 1985, 301, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.; Dalrymple, R.; Zaitlin, B.A. Classification of clastic coastal depositional environments. Sediment. Geol. 1992, 80, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anell, I. The quintessential s-shape in sedimentology: A review on the formation and controls of clinoform shape. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 254, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berné, S.; Loubrieu, B.; l’équipe de Calmar embarquée. Canyons et processus sédimentaires récents sur la marge occidentale du Golfe du Lion. Premiers résultats de la campagne Calamar. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Sci. Paris 1999, 328, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Baztan, J.; Berne, S.; Olivet, J.L.; Rabineau, M.; Aslanian, D.; Gaudin, M.; Réhault, J.-P.; Canals, M. Axial incision: The key to understand submarine canyon evolution (in the western Gulf of Lion). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, H.A.; Baars, T.; Wang, Y.; Alharbi, A.; Storms, J.; Martinius, A. Implementing orbital climate control on alluvial stratigraphy in subsurface predictive models. First Break 2020, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Hilgen, F.J.; Luijk, G.M.; Sluijs, A.; Kraus, M.J.; Parés, J.M.; Gingerich, P.D. Astronomical climate control on paleosol stacking patterns in the upper Paleocene–lower Eocene Willwood Formation, Bighorn Basin, Wyoming. Geology 2008, 36, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabineau, M.; Berné, S.; Aslanian, D.; Olivet, J.-L.; Joseph, P.; Guillocheau, F.; Bourillet, J.-F.; Ledrezen, E.; Granjeon, D. Sedimentary sequences in the Gulf of Lions: A record of 100,000 years climatic cycles. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 775–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabineau, M.; Berné, S.; Olivet, J.L.; Aslanian, D.; Guillocheau, F.; Joseph, P. Paleo sea levels reconsidered from direct observation of paleoshoreline position during glacial maxima (for the last 500,000 yr). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 252, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesson, M.; Posamentier, H.W.; Gensous, B. Stratigraphic organization of Late Pleistocene deposits of the western part of the Golfe du Lion Shelf (Languedoc Shelf), Western Mediterranean Sea, using high-resolution seismic and core data. AAPG Bull. 2000, 84, 119–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, C.; Steel, R.; Petter, A. Sediment supply: The main driver of shelf-margin growth. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, T.; Steel, R. Role of autoretreat and A/S changes in the understanding of deltaic shoreline trajectory: A semi-quantitative approach. Basin Res. 2002, 14, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, P.; Steel, R.; Granjeon, D. Stratigraphic forward modeling of basin-margin clinoform systems: Implications for controls on topset and shelf width and timing of formation of shelf-edge deltas. In Recent Advances in Models of Siliciclastic Shallow-Marine Stratigraphy; SEPM Special Publication: Claremore, OK, USA, 2008; Volume 90, pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, Y.; Ladouche, B.; Dewandel, B. Modèle conceptuel du comportement des eaux souterraines de l’aquifère Plio-Quaternaire de la plaine du Roussillon, de 1960 à nos jours. In Production #23 du Projet Dem’Eaux Roussillon; BRGM/RP-71763-FR: Orléans, France, 2022; 111p; Available online: http://infoterre.brgm.fr/rapports//RP-71763-FR.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Aunay, B.; Ladouche, B.; Bailly-Comte, V.; Guerrot, C.; Flehoc, C.; Pezard, P.; Lofi, J.; Dörfliger, N. Coastal groundwater salinization: Focus on the vertical variability in a multi-layered aquifer through a multi-isotope fingerprinting (Roussillon Basin, France). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewandel, B.; Ladouche, B.; Caballero, Y. Synthèse et valorisation des données d’essais par pompage réalisés sur les sites Dem’Mer et Dem’Ter dans le cadre du projet Dem’Eaux Roussillon. In Production #22b du Projet Dem’Eaux Roussillon; BRGM/RP-71514-FR: Orléans, France, 2022; 99p. [Google Scholar]
- Lofi, J.; Inwood, J.; Proust, J.N.; Monteverde, D.H.; Loggia, D.; Basile, C.; Otsuka, H.; Hayashi, T.; Stadler, S.; Mottl, M.; et al. Fresh-water and salt-water distribution in passive margin sediments: Insights from Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Expedition 313 on the New Jersey Margin. Geosphere 2013, 9, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sedimentary Facies Associations (AF) | Sedimentary Facies |
|---|---|
| AF1 | GDt, GDf, GDb. |
| AF2 | FPo, MC, BC, Df, CS1, CS2, CS3, Lk, Lkl, Ca, Pa. |
| AF3 | FPo, MC, Df, CS1, CS2, CS3, Lk, Lkl, Ca, Pa. |
| AF4 | FPr, MC, Df, CS1, CS2, CS3, Lk, Lkl, Ca, Pa. |
| AF5 | Lg, Bh, Pa. |
| AF6 | Fan, FD, Fs, Sh. |
| AF7 | TF, Mb, DF, (Fs, Sh). |
| AF8 | PD. |
| Modeled Sedimentary Facies | Vp (km·s−1) | Vs (km·s−1) | Mv (g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel (MC, BC) | 2 | 1 | 1.96 |
| Overbank deposits (Df, CS1, CS2, CS3) | 1.8–1.85 | 0.9–0.93 | 2.04 |
| Paleosols (Pa, Ca) | 2.2–2.5 | 1.1–1.25 | 2.25–2.35 |
| Silty flood plain (FPo, FPr) | 1.7–1.72 | 0.85–0.86 | 2.11 |
| Clays (FPo, FPr, Lg, Lk) | 1.56 | 0.78 | 2.11 |
| Marine sands (FD, Mb, Fs, Sh, DF) | 2.31 | 1.155 | 1.95 |
| Offshore clays (PD) | 2.12 | 1.06 | 2.12 |
| Position | Seismic Facies | AF | Sedimentary Content/Environment | Seismic Modeling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | AF1 | Gilbert deltas | No |
| Topsets | SF1a-1 | AF2 | Confined alluvial plain with Ca/Pa development | Yes |
| SF1a-2 | AF3; AF2 * | Overbank dominated alluvial plain | Yes | |
| SF1b | AF4; AF5 | Deltaic plain and embayments | Yes | |
| Topsets/Foresets | SF1c | AF7 | Shallow marine sands including TF and Mb | Yes |
| Foresets | SF2a | AF8 | Upper offshore classic clay/silt/sand alternations | Yes |
| Foresets/Bottomsets | SF2b | - | Mixed-processes prodelta | No |
| Bottomsets | SF3a | - | Settling basin | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widemann, T.; Lasseur, E.; Lofi, J.; Berné, S.; Grélaud, C.; Issautier, B.; Pezard, P.-A.; Caballero, Y. Sedimentary Architecture Prediction Using Facies Interpretation and Forward Seismic Modeling: Application to a Mediterranean Land–Sea Pliocene Infill (Roussillon Basin, France). Geosciences 2025, 15, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100383
Widemann T, Lasseur E, Lofi J, Berné S, Grélaud C, Issautier B, Pezard P-A, Caballero Y. Sedimentary Architecture Prediction Using Facies Interpretation and Forward Seismic Modeling: Application to a Mediterranean Land–Sea Pliocene Infill (Roussillon Basin, France). Geosciences. 2025; 15(10):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100383
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidemann, Teddy, Eric Lasseur, Johanna Lofi, Serge Berné, Carine Grélaud, Benoît Issautier, Philippe-A. Pezard, and Yvan Caballero. 2025. "Sedimentary Architecture Prediction Using Facies Interpretation and Forward Seismic Modeling: Application to a Mediterranean Land–Sea Pliocene Infill (Roussillon Basin, France)" Geosciences 15, no. 10: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100383
APA StyleWidemann, T., Lasseur, E., Lofi, J., Berné, S., Grélaud, C., Issautier, B., Pezard, P.-A., & Caballero, Y. (2025). Sedimentary Architecture Prediction Using Facies Interpretation and Forward Seismic Modeling: Application to a Mediterranean Land–Sea Pliocene Infill (Roussillon Basin, France). Geosciences, 15(10), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100383






