Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Trenggalek Karst Springs and Underground Rivers as a Drinking Water Source
Abstract
1. Summary
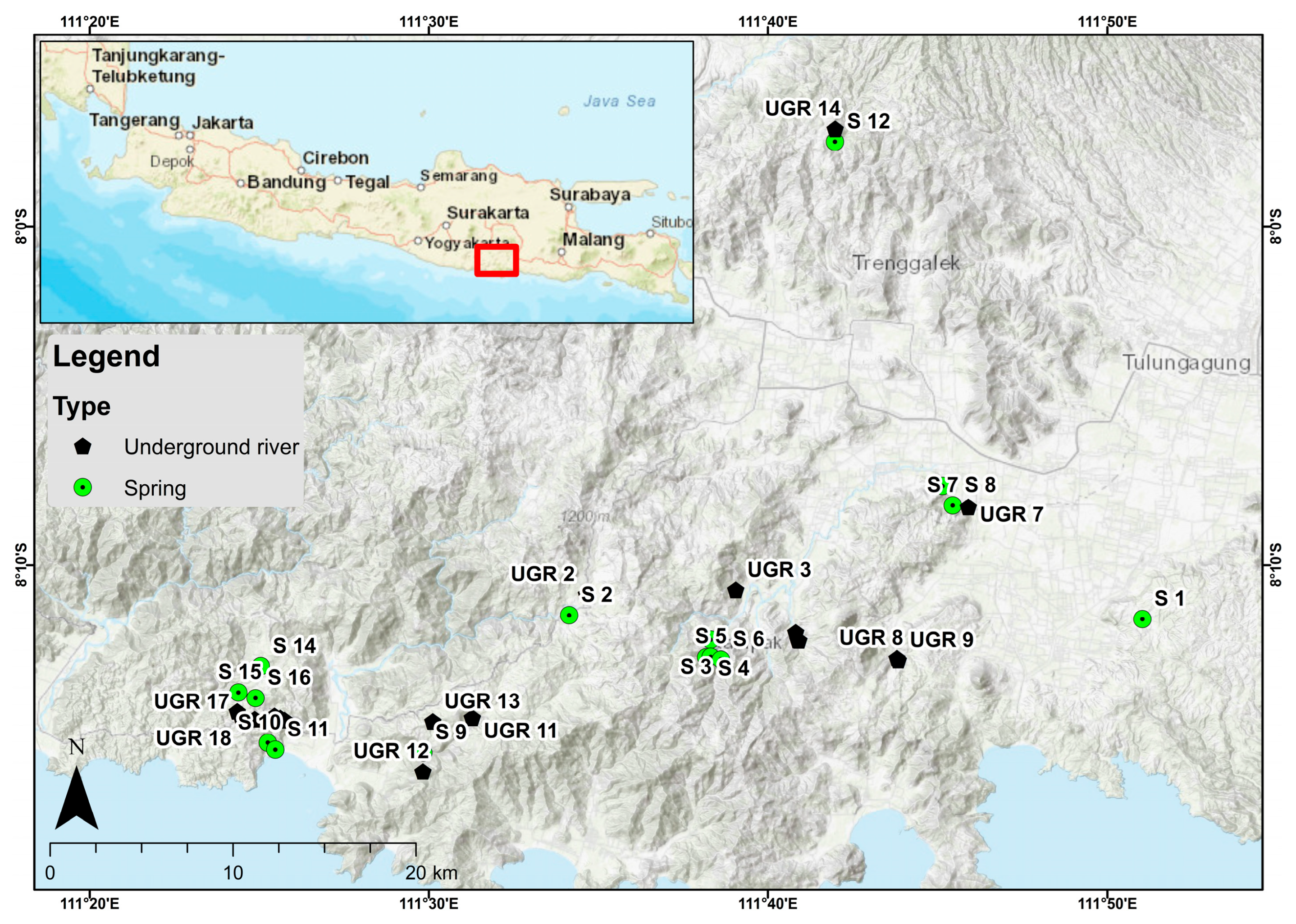
2. Introduction
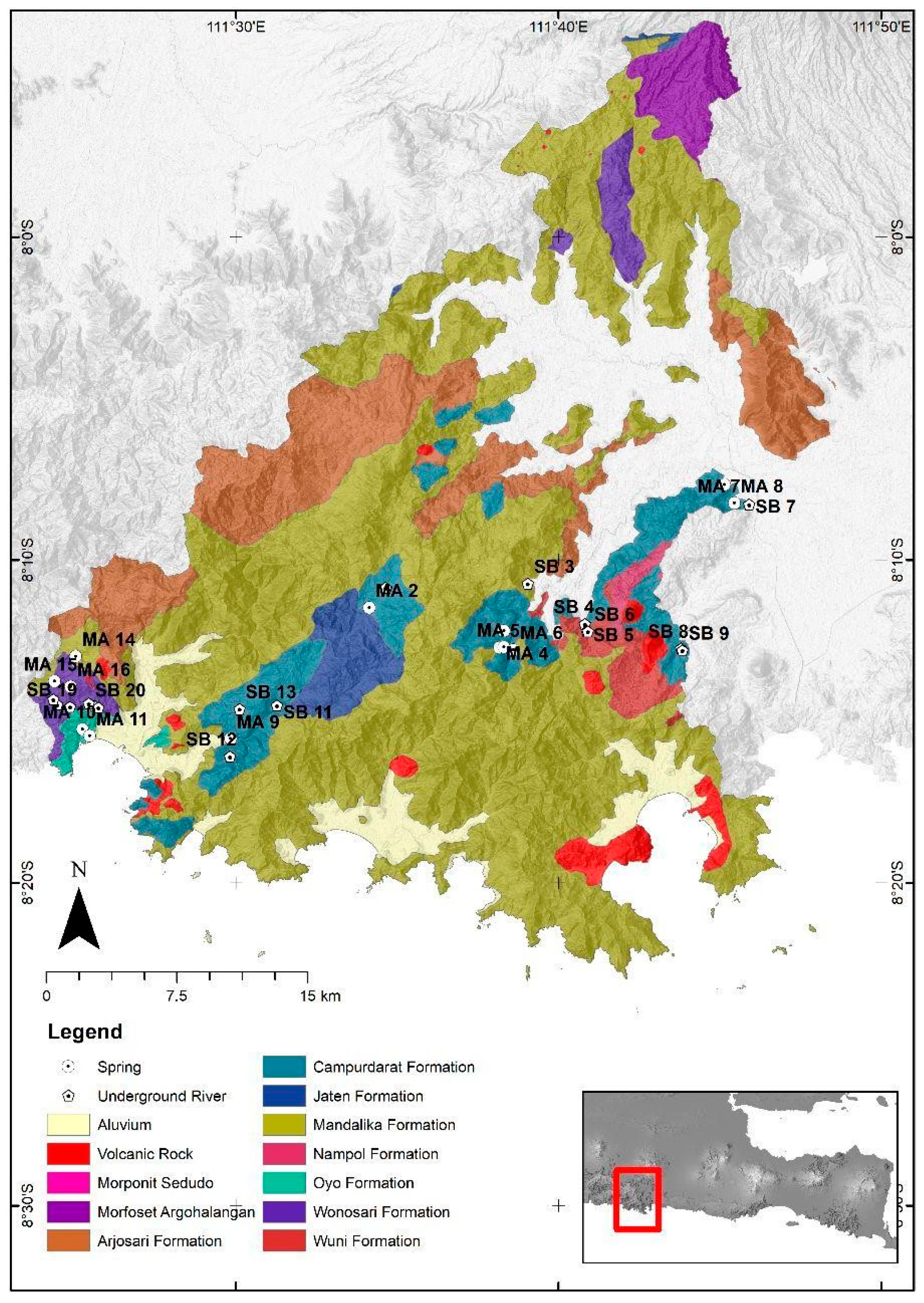
Geology and Hydrogeological Setting of the Study Area
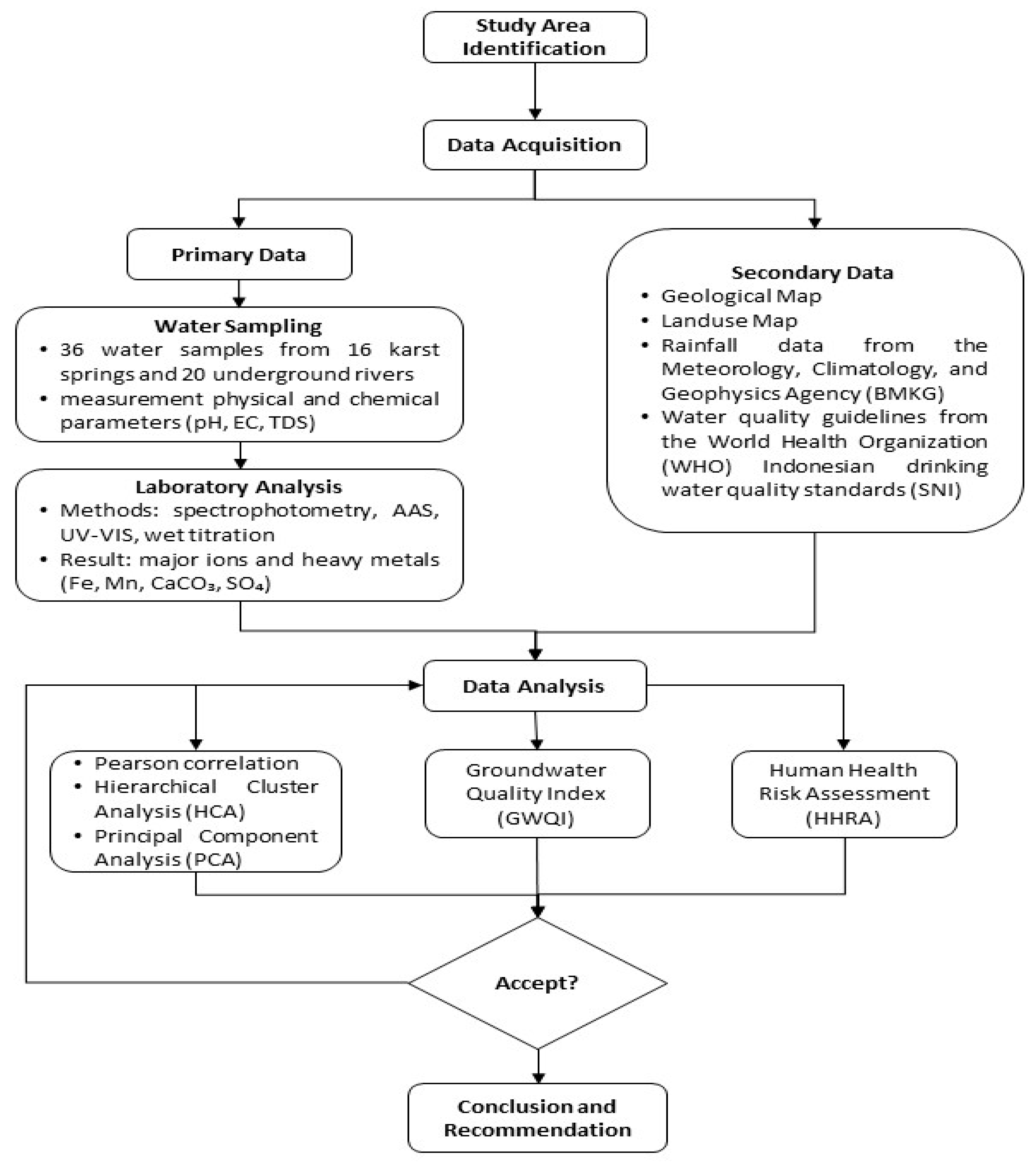
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Groundwater Quality Index
- Wi: weight of each indicator;
- Wi: relative weight;
- Qi: ranking for each parameter;
- Wi: weight for each indicator was determined according to the value of water quality;
- Ci: measured concentration;
- Si: guideline value according to the drinking water quality guidelines [21].
3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
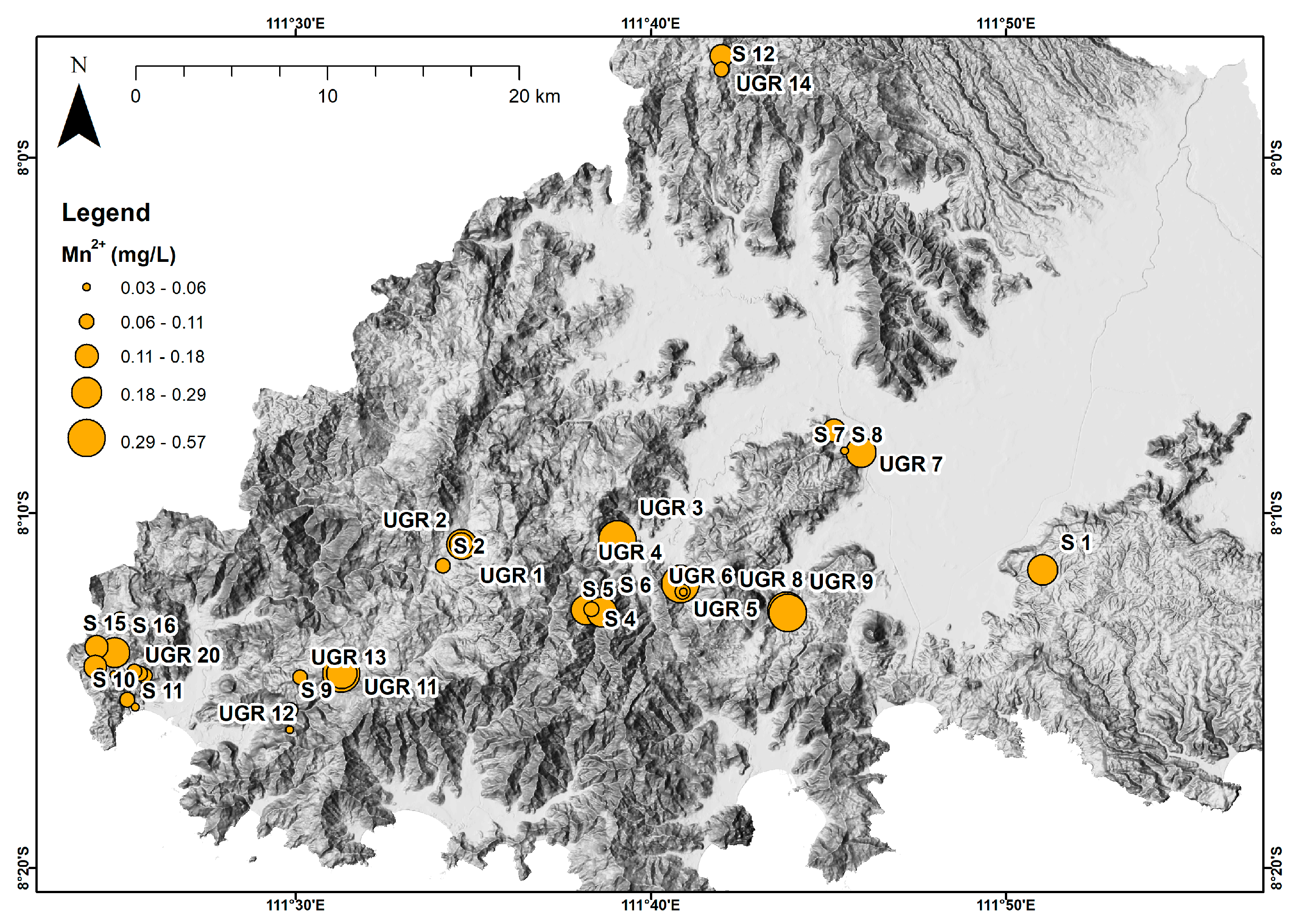
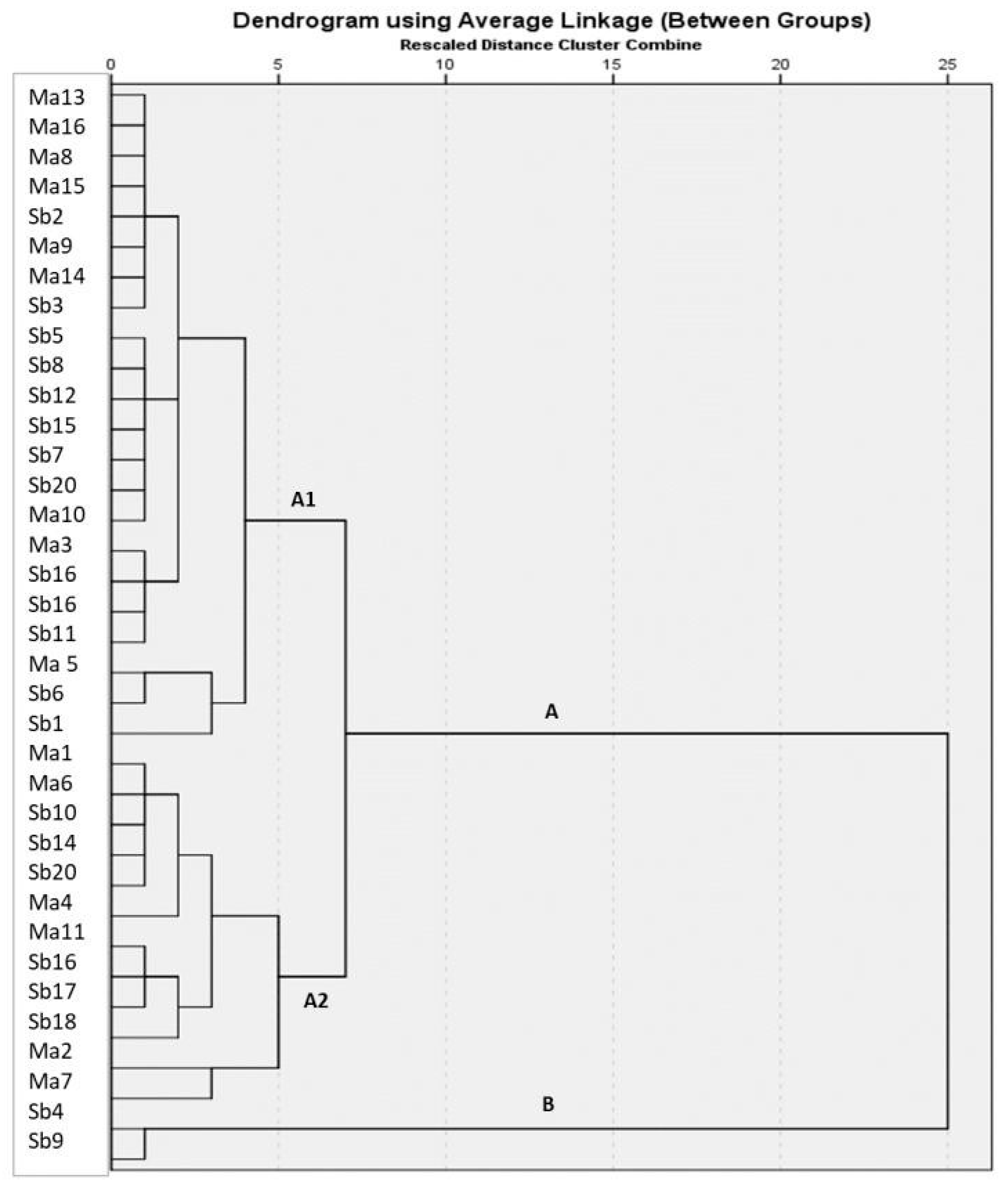
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Groundwater Quality Index
5.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| NO3− | Nitrate |
| Ca2+ | Calcium Ion |
| Mg2+ | Magnesium Ion |
| HRA | Health Risk Assessment |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| IR | Intake Rate |
| HQ | Hazard Quotient |
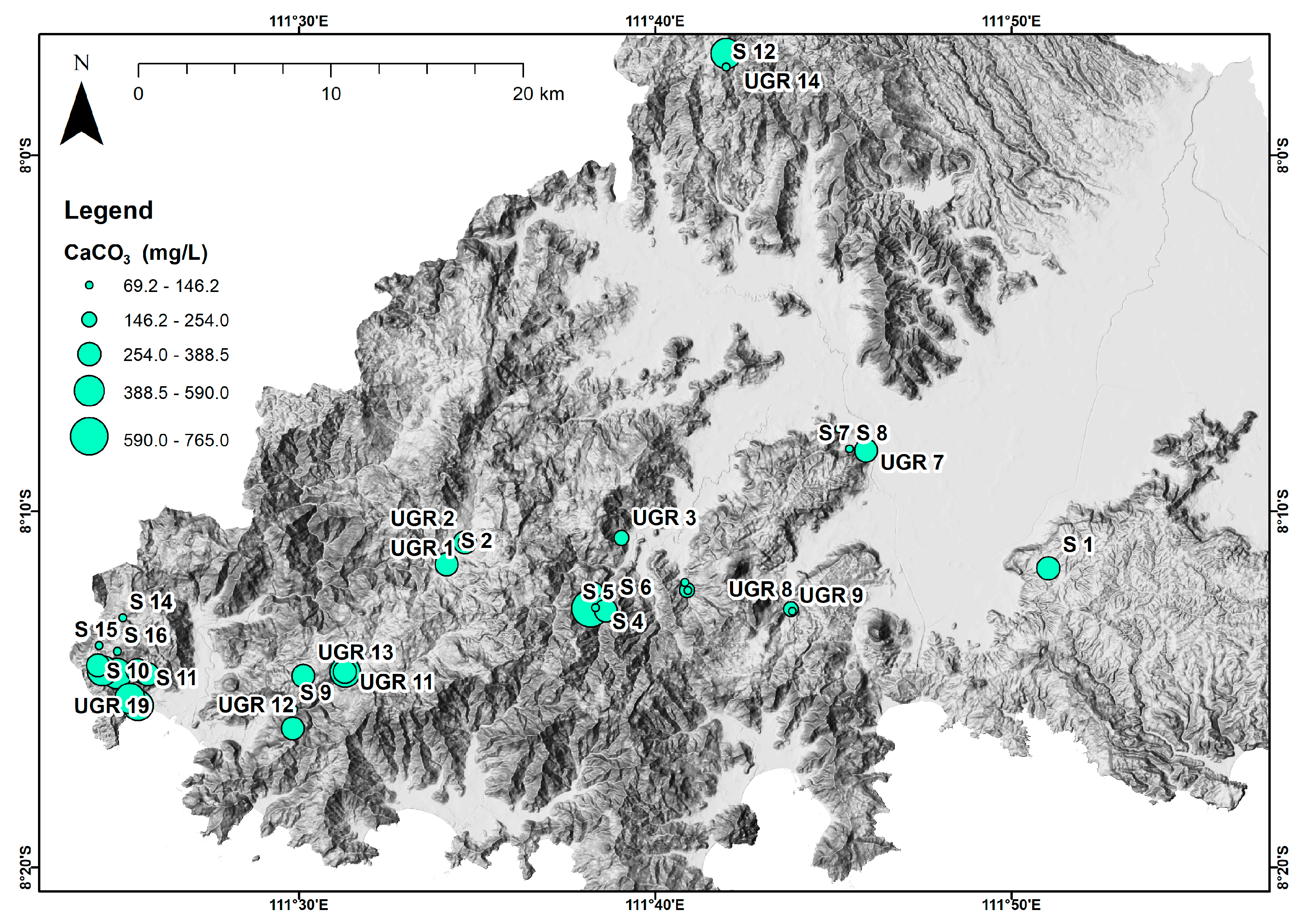
Appendix A. Detailed Physicochemical Parameters of Groundwater Samples
| No | Code | Type | EC (µS/cm) | TDS (mg/L) | pH | Fe2+ (mg/L) | Mn2+ (mg/L) | CaCO3 (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S 1 | Spring | 915.5 | 443.5 | 6.88 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 322 | 234.5 |
| 2 | S 2 | Spring | 732 | 356.5 | 7.43 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 344.5 | 652 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 36 | UGR 20 | Ug-River | 1284 | 887.5 | 6.55 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 332 | 237.5 |
Appendix B. Groundwater Quality Index (GWQI) Values
| No | Code | Type | GWQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1 | Spring | 97.43 | Good |
| 2 | S2 | Spring | 72.94 | Good |
| … | ||||
| 36 | UGR 20 | Underground river | 81.54 | Good |
References
- Paternoster, M.; Buccione, R.; Canora, F.; Buttitta, D.; Panebianco, S.; Rizzo, G.; Sinisi, R.; Summa, V.; Mongelli, G. Hydrogeochemistry and Groundwater Quality Assessment in the High Agri Valley (Southern Italy). Geofluids 2021, 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Kumar, S.; Al-Reza, S.M. Drinking water quality, exposure and health risk assessment for the school-going children at school time in the southwest coastal of Bangladesh. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2021, 11, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, R.; Iskandarsyah, T.Y.W.M.; Suganda, B.R.; Rusydi, A.F.; Hendarmawan, H. Impact of natural conditions and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in Puntang volcanic area, West Java, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1047, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönwall, J.; Danert, K. Regarding Groundwater and Drinking Water Access through A Human Rights Lens: Self-Supply as A Norm. Water 2020, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geldern, R.; Schulte, P.; Mader, M.; Baier, A.; Barth, J.A.C.; Juhlke, T.R.; Lee, K. Insights into agricultural influences and weathering processes from major ion patterns. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoaghia, M.-A.; Moldovan, A.; Kovacs, E.; Mirea, I.; Kenesz, M.; Brad, T.; Cadar, O.; Micle, V.; Levei, E.; Moldovan, O. Water Quality and Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Some Karst Water Sources in Apuseni Mountains, Romania. Water 2021, 13, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Török, A.I.; Mirea, I.C.; Micle, V.; Moldovan, O.T.; Levei, E.A. Health Risk Assessment in Southern Carpathians Small Rural Communities Using Karst Springs as a Drinking Water Source. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiawan, T.; Syah Alam, B.Y.C.S.S.; Haryono, E.; Hendarmawan, H. Spatio-temporal variation of karst spring parameters for characterizing of the aquifer system of Watuputih Area, Indonesia. J. Water Land. Dev. 2020, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwiputra, D.S.; Adji, T.N.; Pratama, A.D.; Haryono, E. Estimation of atmospheric carbon sequestration rate through carbonate rock dissolution in Karst Jonggrangan, Java Island, Indonesia (case study: The underground river of Anjani Cave). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 451, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samodra, H.; Gafoer, S. Geological Map of the Tulungagung Quadrangle; Geological Research and Development Centre: Bandung, Indonesia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Baharuddin; Brata, K.; Hartono, U. Peta Geologi Lembar Madiun, Jawa. Geological Map of the Madiun Quadrangle, Jawa; Geological Research and Development Centre: Bandung, Indonesia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Adeola Fashae, O.; Abiola Ayorinde, H.; Oludapo Olusola, A.; Oluseyi Obateru, R. Landuse and surface water quality in an emerging urban city. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, R.; Purwoarminta, A.; Lubis, R.F. Hidrokimia Mata Air Karst untuk Irigasi Studi Kasus Desa Ligarmukti, Kabupaten Bogor. J. Irig. 2019, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pal, S.C. Assessment of groundwater recharge and its potential zone identification in groundwater-stressed Goghat-I block of Hugli District, West Bengal, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 5905–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; O’Connor, M.F. A Water Quality Index—Crashing the Psychological Barrier. In Indicators of Environmental Quality; Thomas, W.A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1972; pp. 173–182. ISBN 978-1-4684-2858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, M.; Goswami, D.C. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index (WQI): Case study of the Kolong River, Assam, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.G.; Huynh, N.T.H. Characterization of Groundwater Quality and Human Health Risk Assessment. Civ. Eng. J. 2023, 9, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; McClelland, N.; Deininger, R.; O’Connor, M. A water quality index—Crashing the physiological barrier. Indic. Environ. Qual. 1972, 1, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): History, Models, Attempts and Perspectives; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 22, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, No. Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschy, R.W. Water Quality for Drinking: WHO Guidelines. In Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs; Bengtsson, L., Herschy, R.W., Fairbridge, R.W., Eds.; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 876–883. ISBN 978-1-4020-5616-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, S.; Sener, S.; Davraz, A. ‘Evaluation of water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kate, S.; Kumbhar, S.; Jamale, P. Water quality analysis of Urun-Islampur City, Maharashtra, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, M.H.; Ahmed, F.; Ishiga, H. Assessment of metal concentrations in lake sediments of southwest Japan based on sediment quality guidelines. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawo, N.S.; Karuppannan, S. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index and GIS technique in Modjo River Basin, central Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kom, K.P.; Gurugnanam, B.; Bairavi, S. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride contamination in the groundwater of Noyyal basin, India. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.C.; Khan, M.J.H.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Zaman, S.; Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Tanaka, H. Human health risk assessment of elevated and variable iron and manganese intake with arsenic-safe groundwater in Jashore, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Li, H.; Tudi, M.; Yuan, X.; Yang, L. Comparison of characteristics, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water and groundwater in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandindi, W.Z.; Nyaba, L.; Mketo, N.; Nomngongo, P.N. Seasonal Variation of Drinking Water Quality and Human Health Risk Assessment: A Case Study in Rural Village of the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Water 2022, 14, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idoko, O.M. Seasonal Variation in Iron in Rural Groundwater of Benue State, Middle Belt, Nigeria. Pak. J. Nutr. 2010, 9, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirana, K.H.; Novala, G.C.; Fitriani, D.; Agustine, E.; Rahmaputri, M.D.; Fathurrohman, F.; Rizkita, N.R.; Andrianto, N.; Juniarti, N.; Zaenudinna, R.A.; et al. Identifikasi Kualitas Air Sungai Citarum Hulu Melalui Analisa Parameter Hidrologi Dan Kandungan Logam Berat (Studi Kasus: Sungai Citarum Sektor 7). Wahana Fis. 2019, 4, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhou, P.; Chen, C. Spatial and temporal distribution and affecting factors of iron and manganese in the groundwater in the middle area of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61204–61221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskita, R.S.A.; Wijayanti, H.D. Studi Provenance dan Analisis Granulometri Endapan Pasir di Daerah Tambakrom, Ponjong, Gunung Kidul, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta. Geoda 2020, 1, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Wu, J.; Guo, W. Karst Spring Protection for the Sustainable and Healthy Living: The Examples of Niangziguan Spring and Shuishentang Spring in Shanxi, China. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Unit | Weight (wi) | Relative Weights (Wi) | Si * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5 | 0.23 | 8.5 | |
| EC | μS/cm | 4 | 0.18 | 500 |
| TDS | mg/L | 4 | 0.18 | 500 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | 3 | 0.14 | 0.3 |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | 3 | 0.14 | 0.1 |
| CaCO3 | mg/L | 2 | 0.09 | 300 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 1 | 0.05 | 250 |
| No | Code | Type | EC (µS/cm) | TDS (mg L−1) | pH | Fe2+ (mg L−1) | Mn2+ (mg L−1) | CaCO3 (mg L−1) | SO42− (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S 1 | Spring | 915.5 | 443.5 | 6.88 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 322 | 234.5 |
| 2 | S 2 | Spring | 732 | 356.5 | 7.43 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 344.5 | 652 |
| 3 | S 3 | Spring | 1137.5 | 739.375 | 6.44 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 223 | 445 |
| 4 | S 4 | Spring | 886.5 | 576.225 | 6.74 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 765 | 356.5 |
| 5 | S 5 | Spring | 1451 | 912.5 | 7.22 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 112.3 | 145 |
| 6 | S 6 | Spring | 883 | 573.95 | 7.11 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 321 | 243 |
| 7 | S 7 | Spring | 326.5 | 234 | 6.35 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 89.4 | 164 |
| 8 | S 8 | Spring | 1154 | 50.1 | 7.23 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 87.3 | 157 |
| 9 | S 9 | Spring | 987 | 661.5 | 7.51 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 69.2 | 321 |
| 10 | S 10 | Spring | 1276 | 779 | 6.44 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 443 | 228 |
| 11 | S 11 | Spring | 665 | 432.25 | 7.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 590 | 398.5 |
| 12 | S 12 | Spring | 734 | 421 | 7.11 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 78.4 | 149 |
| 13 | S 13 | Spring | 1115.5 | 725.075 | 6.63 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 146.2 | 187.5 |
| 14 | S 14 | Spring | 998 | 634 | 6.44 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 115 | 342 |
| 15 | S 15 | Spring | 1187 | 771.55 | 7.23 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 89.2 | 221 |
| 16 | S 16 | Spring | 1099.5 | 714.67 | 6.14 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 117.3 | 167.5 |
| 17 | UGR 1 | Underground river | 1766.5 | 1148.2 | 6.23 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 187 | 226.5 |
| 18 | UGR 2 | Underground river | 987 | 769.5 | 6.67 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 298.5 | 199 |
| 19 | UGR 3 | Underground river | 945 | 614.25 | 7.18 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 177.5 | 334 |
| 20 | UGR 4 | Underground river | 2117 | 1366 | 7.23 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 87.43 | 187 |
| 21 | UGR 5 | Underground river | 1284 | 784.5 | 7.18 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 254 | 186 |
| 22 | UGR 6 | Underground river | 1469.5 | 835.5 | 6.21 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 74.22 | 211 |
| 23 | UGR 7 | Underground river | 1287 | 836.55 | 7.06 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 338 | 332 |
| 24 | UGR 8 | Underground river | 1349 | 876.85 | 7.25 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 218 | 167 |
| 25 | UGR 9 | Underground river | 2216 | 1548 | 6.44 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 123 | 204 |
| 26 | UGR 10 | Underground river | 966 | 627.9 | 6.5 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 498.5 | 312 |
| 27 | UGR 11 | Underground river | 1087 | 886.5 | 6.88 | 0.42 | 0.37 | 338 | 446.5 |
| 28 | UGR 12 | Underground river | 1289 | 899 | 6.66 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 366 | 347.5 |
| 29 | UGR 13 | Underground river | 1187 | 774 | 6.82 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 388.5 | 555 |
| 30 | UGR 14 | Underground river | 1011 | 657.15 | 6.22 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 442.5 | 346.5 |
| 31 | UGR 15 | Underground river | 1341 | 871.65 | 7.11 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 366 | 334.5 |
| 32 | UGR 16 | Underground river | 1094 | 711.1 | 7.05 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 288.5 | 333 |
| 33 | UGR 17 | Underground river | 663.5 | 431.28 | 6.22 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 522 | 240 |
| 34 | UGR 18 | Underground river | 554 | 360.1 | 6.75 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 345.5 | 332 |
| 35 | UGR 19 | Underground river | 889 | 547.5 | 6.88 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 544 | 239 |
| 36 | UGR 20 | Underground river | 1284 | 887.5 | 6.55 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 332 | 237.5 |
| EC | TDS | pH | Fe | Mn | CaCO3 | SO4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1 | ||||||
| TDS | 0.974 ** | 1 | |||||
| pH | −0.022 | −0.050 | 1 | ||||
| Fe | 0.510 ** | 0.551 ** | −0.063 | 1 | |||
| Mn | 0.441 ** | 0.486 ** | 0.103 | 0.808 ** | 1 | ||
| CaCO3 | −0.335 * | −0.307 | −0.125 | −0.161 | −0.095 | 1 | |
| SO4 | −0.244 | −0.225 | 0.134 | −0.211 | −0.115 | 0.428 ** | 1 |
| Parameter | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 0.88 | −0.04 | −0.02 |
| TDS | 0.89 | 0.01 | −0.06 |
| pH | −0.02 | 0.12 | 0.96 |
| Fe2+ | 0.80 | 0.34 | −0.09 |
| Mn2+ | 0.74 | 0.46 | 0.09 |
| CaCO3 | −0.44 | 0.68 | −0.33 |
| SO42− | −0.41 | 0.68 | 0.15 |
| % of Variance | 44.45 | 18.29 | 15.46 |
| Cumulative % | 44.45 | 62.73 | 78.19 |
| No | Code | Type | GWQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S 1 | Spring | 97.43 | Good |
| 2 | S 2 | Spring | 72.94 | Good |
| 3 | S 3 | Spring | 88.39 | Good |
| 4 | S 4 | Spring | 109.33 | Poor |
| 5 | S 5 | Spring | 81.93 | Good |
| 6 | S 6 | Spring | 92.97 | Good |
| 7 | S 7 | Spring | 48.03 | Good |
| 8 | S 8 | Spring | 69.75 | Good |
| 9 | S 9 | Spring | 71.66 | Good |
| 10 | S 10 | Spring | 87.95 | Good |
| 11 | S 11 | Spring | 68.15 | Good |
| 12 | S 12 | Spring | 57.49 | Good |
| 13 | S 13 | Spring | 88.72 | Good |
| 14 | S 14 | Spring | 76.71 | Good |
| 15 | S 15 | Spring | 95.84 | Good |
| 16 | S 16 | Spring | 94.40 | Good |
| 17 | UGR 1 | Underground river | 132.75 | Poor |
| 18 | UGR 2 | Underground river | 96.35 | Good |
| 19 | UGR 3 | Underground river | 123.64 | Poor |
| 20 | UGR 4 | Underground river | 159.90 | Poor |
| 21 | UGR 5 | Underground river | 95.75 | Good |
| 22 | UGR 6 | Underground river | 74.58 | Good |
| 23 | UGR 7 | Underground river | 126.05 | Poor |
| 24 | UGR 8 | Underground river | 169.15 | Poor |
| 25 | UGR 9 | Underground river | 177.34 | Poor |
| 26 | UGR 10 | Underground river | 107.69 | Poor |
| 27 | UGR 11 | Underground river | 140.55 | Poor |
| 28 | UGR 12 | Underground river | 83.08 | Good |
| 29 | UGR 13 | Underground river | 85.85 | Good |
| 30 | UGR 14 | Underground river | 96.29 | Poor |
| 31 | UGR 15 | Underground river | 91.94 | Poor |
| 32 | UGR 16 | Underground river | 86.75 | Good |
| 33 | UGR 17 | Underground river | 61.47 | Good |
| 34 | UGR 18 | Underground river | 76.04 | Good |
| 35 | UGR 19 | Underground river | 69.78 | Good |
| 36 | UGR 20 | Underground river | 81.54 | Good |
| No. | Fe2+ = 0.3 | Mn2+ = 0.4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Average Concentration (mg/L) | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| 2 | Old | Children | Adults | Children | Adults |
| 3 | R (liter) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | Fe2+ (day/year) | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 |
| 5 | Dt (year) | 6 | 30 | 6 | 30 |
| 6 | Wb (kg) | 15 | 55 | 15 | 55 |
| 7 | t avg (day) | 10,950 | 10,950 | 10,950 | 10,950 |
| 8 | RFd (mg/kg.day) | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| appe9 | CDI (mg/kg.day) | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 10 | Risk Characterization | 0.47 | 1.27 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 11 | Status | Unsafe | Unsafe | Safe | Safe |
| 12 | Safe Concentration (mg/L) | 0.47 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aminuddin; Madiutomo, N.; Zulfahmi; Cahyadi, T.A.; Firmansyah, I.; Maria, R.; Nurohman, H.; Siswanto, N.D. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Trenggalek Karst Springs and Underground Rivers as a Drinking Water Source. Geosciences 2025, 15, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100381
Aminuddin, Madiutomo N, Zulfahmi, Cahyadi TA, Firmansyah I, Maria R, Nurohman H, Siswanto ND. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Trenggalek Karst Springs and Underground Rivers as a Drinking Water Source. Geosciences. 2025; 15(10):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100381
Chicago/Turabian StyleAminuddin, Nendaryono Madiutomo, Zulfahmi, Tedy Agung Cahyadi, Ilham Firmansyah, Rizka Maria, Heri Nurohman, and Nopri Dwi Siswanto. 2025. "Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Trenggalek Karst Springs and Underground Rivers as a Drinking Water Source" Geosciences 15, no. 10: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100381
APA StyleAminuddin, Madiutomo, N., Zulfahmi, Cahyadi, T. A., Firmansyah, I., Maria, R., Nurohman, H., & Siswanto, N. D. (2025). Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Trenggalek Karst Springs and Underground Rivers as a Drinking Water Source. Geosciences, 15(10), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100381







