Multidecadal Land-Use Changes and Implications on Soil Protection in the Calore River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
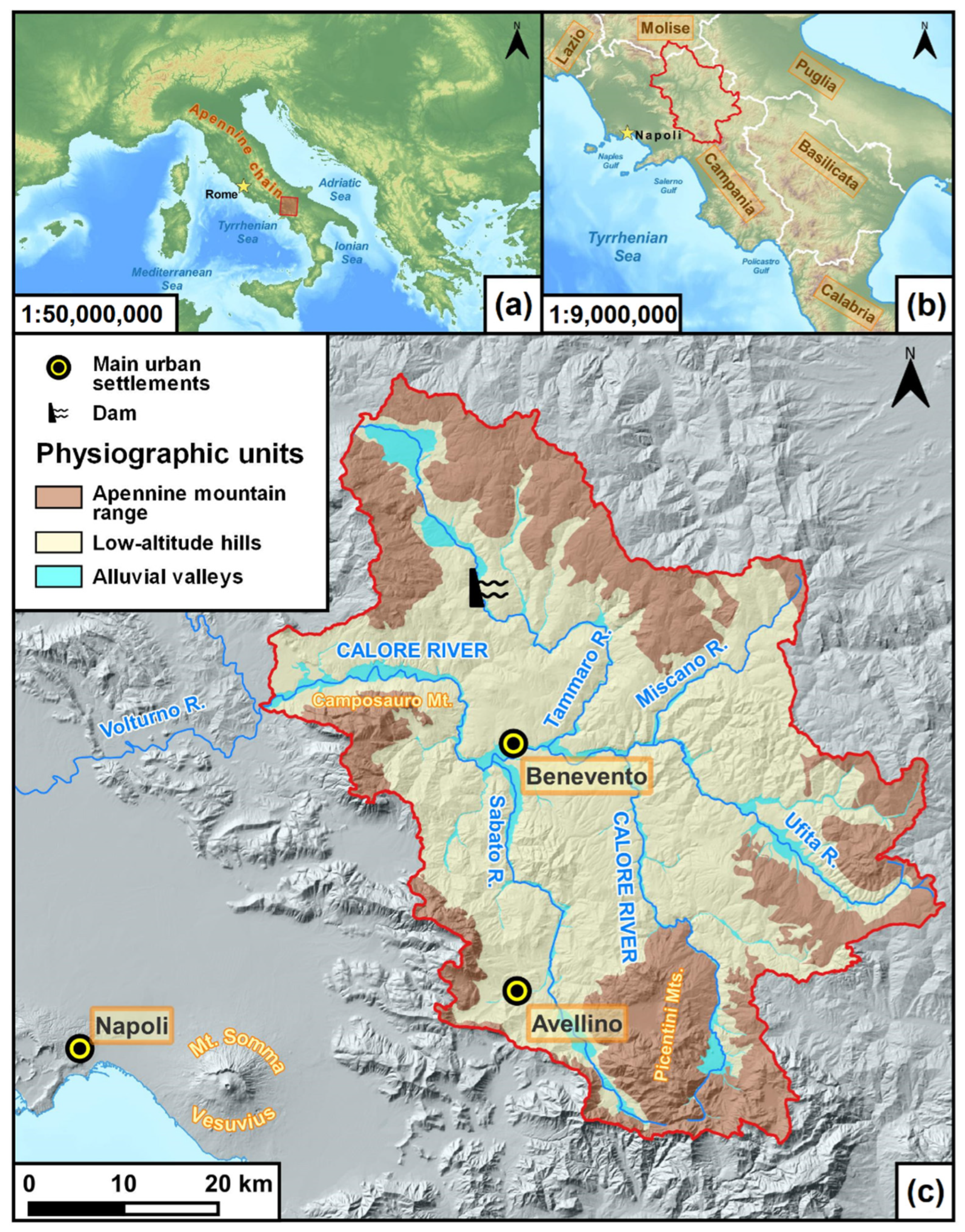
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Methodology
3. Results
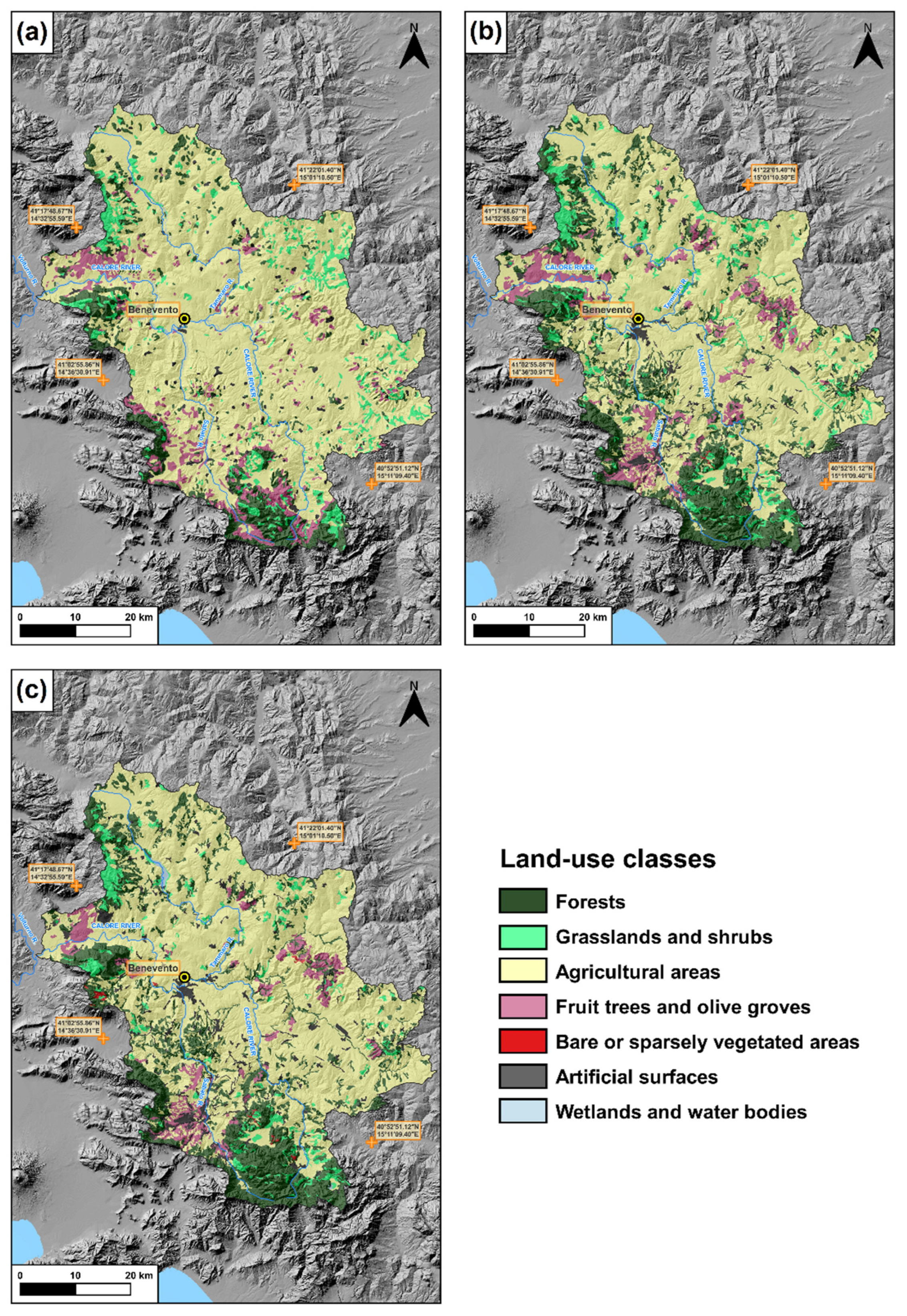
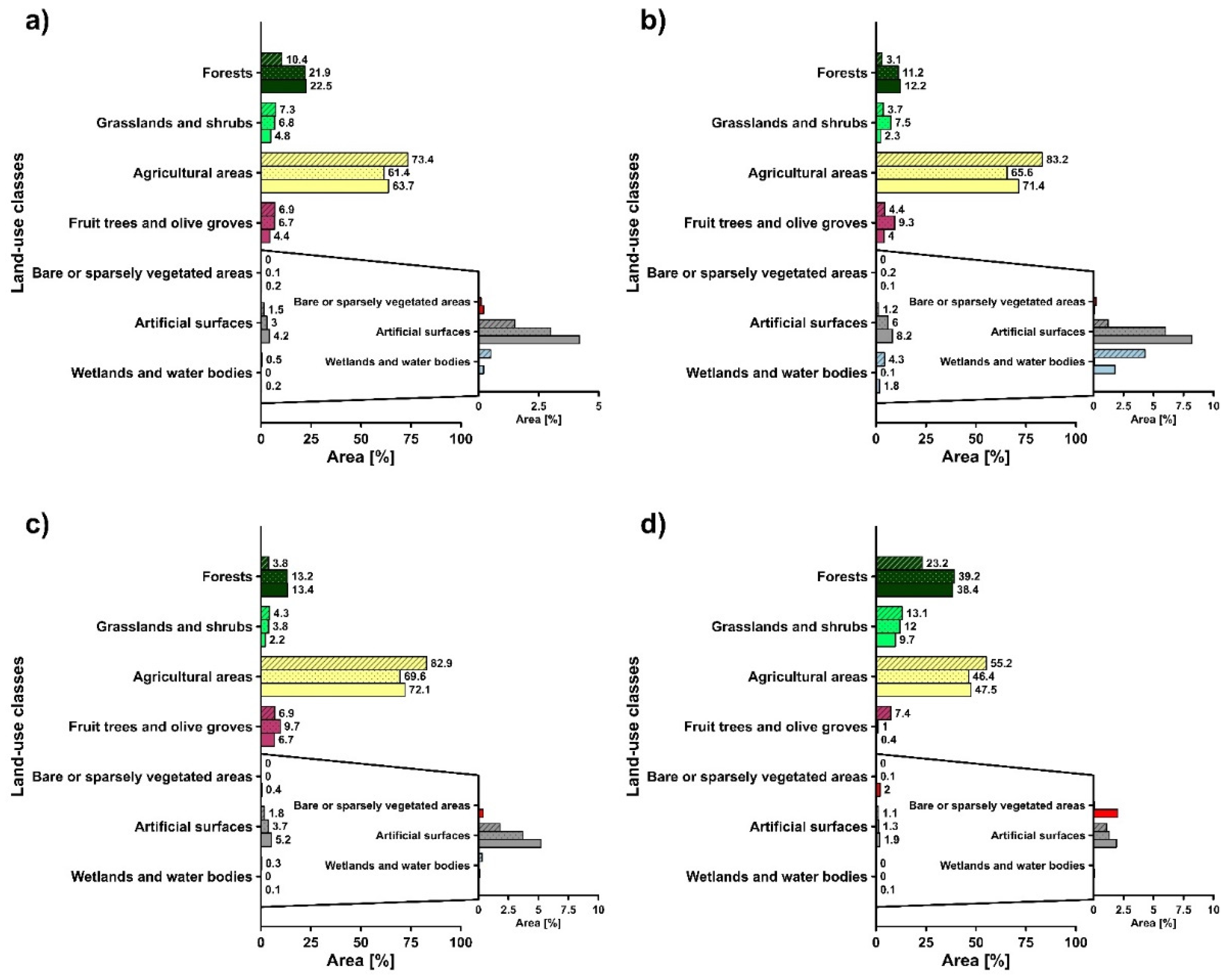
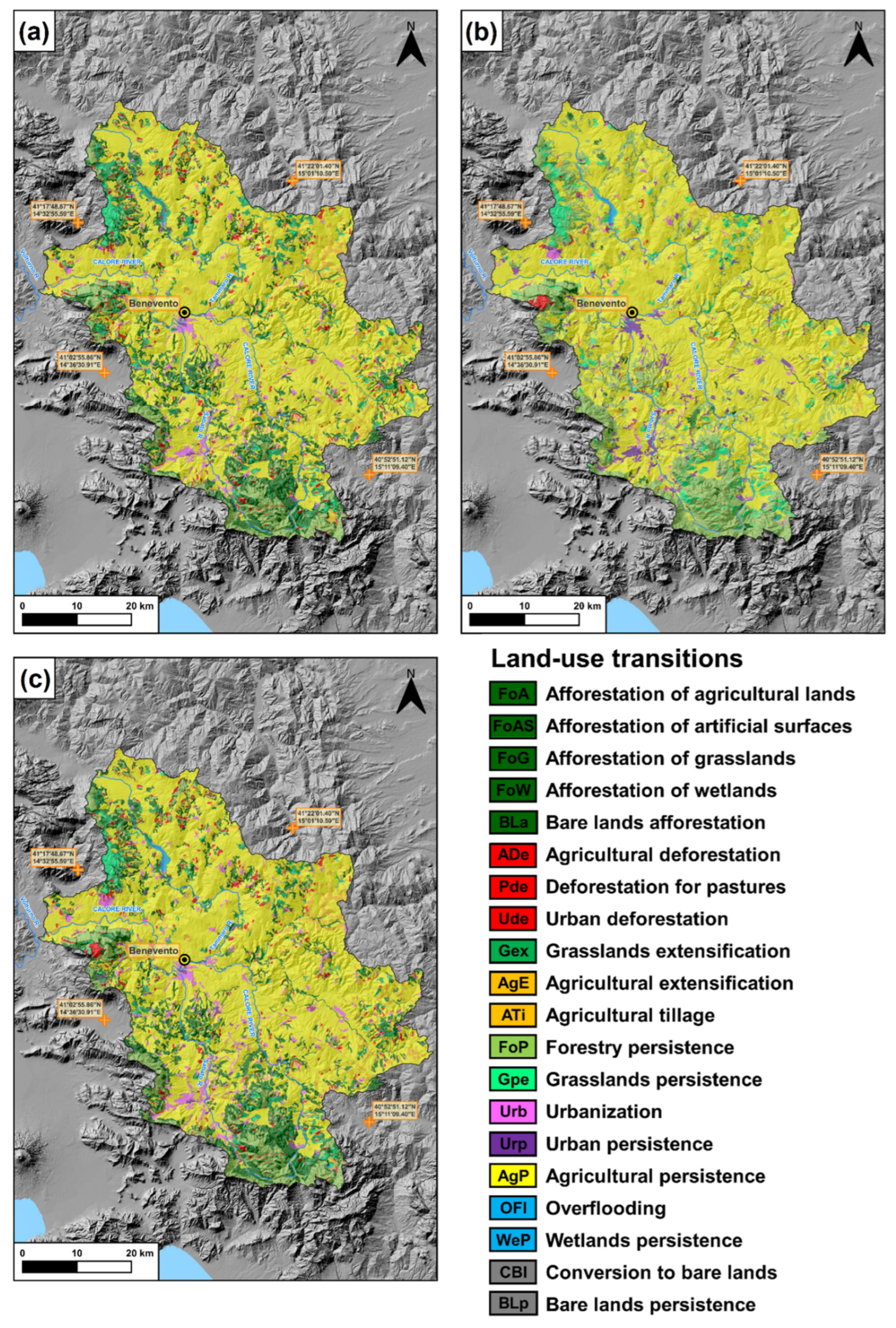
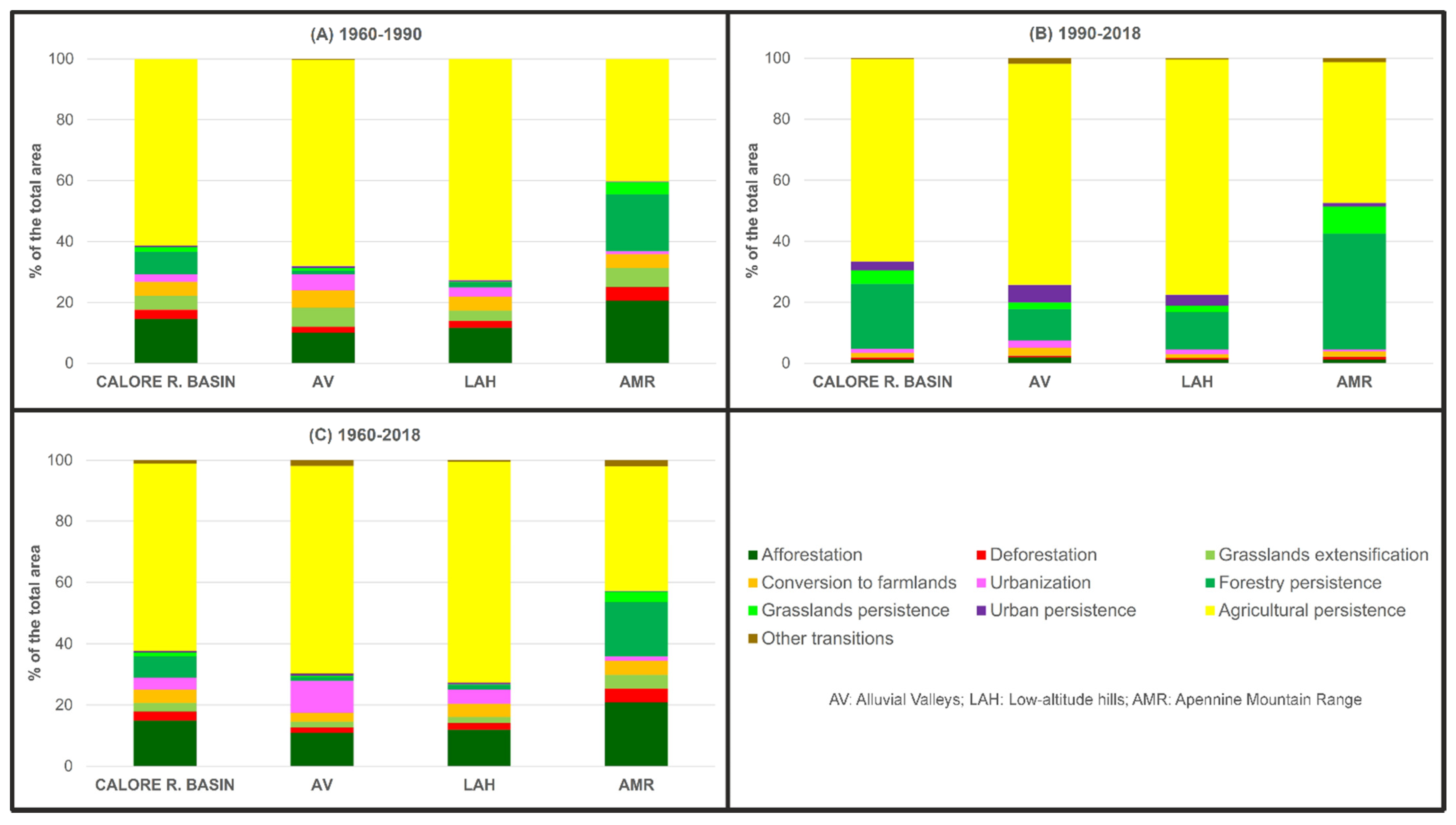
3.1. Land-Use Changes in the Period 1960–1990
3.2. Land-Use Changes in the Period 1990–2018
3.3. Land-Use Changes in the Period 1960–2018
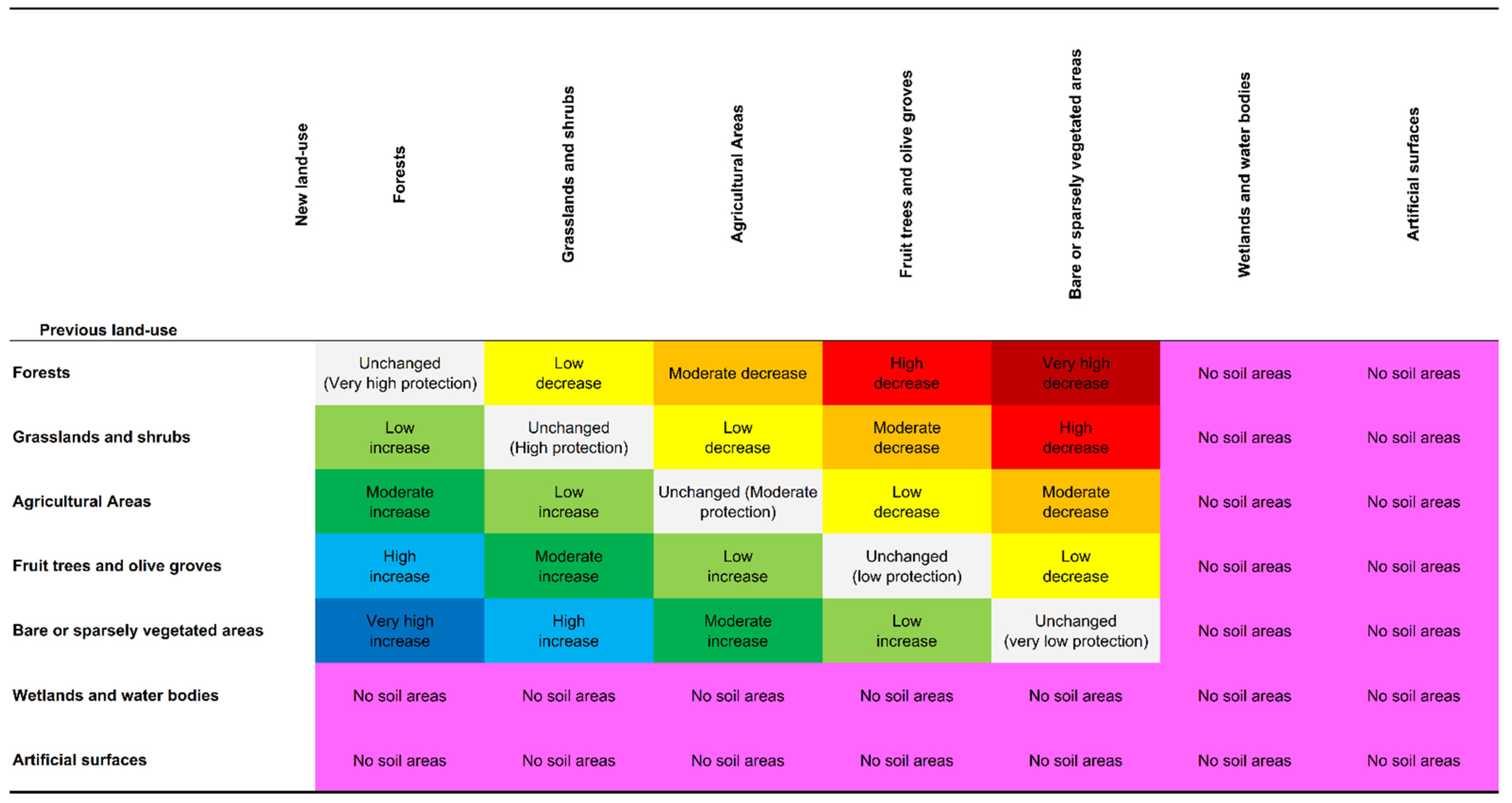
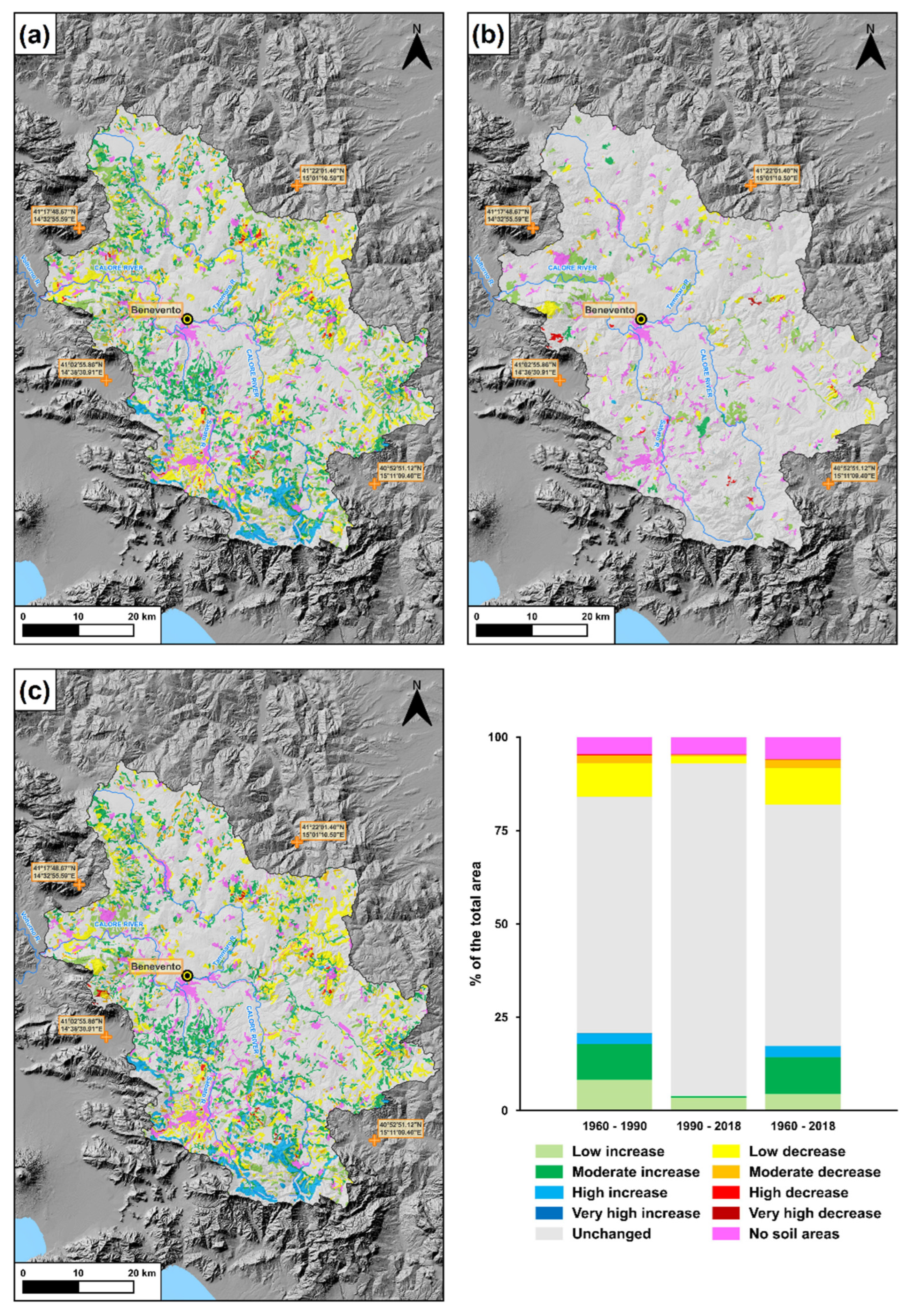
3.4. Variations in Soil Protection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falcucci, A.; Maiorano, L.; Boitani, L. Changes in land-use/land-cover patterns in Italy and their implications for biodiversity conservation. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ruiz, J.M. The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: A review. Catena 2010, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñate, J.J.; Peco, B. Policy impact on desertification: Stakeholders’ perceptions in southeast Spain. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forino, G.; Ciccarelli, S.; Bonamici, S.; Perini, L.; Salvati, L. Developmental policies, long-term land-use changes and the way towards soil degradation: Evidence from Southern Italy. Scott. Geogr. J. 2015, 131, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, A.; Loddo, S.; Ollesch, G.; Puddu, R.; Serra, G.; Tomasi, D.; Aru, A. Measurement of runoff and soil erosion in three areas under different land use in Sardinia (Italy). Catena 2000, 40, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornes, J.B. The interaction of erosional and vegetational dynamics in land degradation: Spatial outcomes. In Vegetation and Erosion: Processes and Environments; Thornes, J.B., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1990; pp. 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmas, C.; Danalatos, N.G.; López Bermúdez, F.; Romero Díaz, M.A. The effect of land use on soil erosion and land degradation under Mediterranean conditions. In Mediterranean Desertification: A Mosaic of Processes and Responses; Geeson, N.A., Brandt, C.J., Thornes, J.B., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2002; pp. 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, J.; Thornes, J.B. Environmental Issues in the Mediterranean: Processes and Perspectives from the Past and Present; Routledge: London, UK, 2004; p. 479. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldi, F.; Chiocchini, U. Effects of land use changes on badland erosion in clayey drainage basins, Radicofani, Central Italy. Geomorphology 2012, 169, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosino, A.; Omran, A.; Maerker, M. Identification, characterisation and analysis of the Oltrepo’ Pavese calanchi in the Northern Apennines (Italy). Geomorphology 2019, 340, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coratza, P.; Parenti, C. Controlling factors of badland morphological changes in the Emilia Apennines (Northern Italy). Water 2021, 13, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, C.; Canu, A.; Della Peruta, R. Effects of land use and landscape on spatial distribution and morphological features of gullies in an agropastoral area in Sardinia (Italy). Catena 2006, 68, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, C.; Canu, A.; Previtali, F. Soil degradation by land use change in an agropastoral area in Sardinia (Italy). Catena 2010, 83, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P.; Russo, F.; Lo Curzio, S. Detection of permanently eroded landsurfaces through multitemporal analysis of Landsat data: A case study from an agricultural area in southern Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortugno, D.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Quiñonero-Rubio, J.M.; Tamburino, V.; Zema, D.A. Adjustments in channel morphology due to land-use changes and check dam installation in mountain torrents of Calabria (southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2469–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.D.; Lake, P.S.; Sabater, S.; Melack, J.M.; Sabo, J.L. The effects of land use changes on streams and rivers in Mediterranean climates. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 383–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P.; Bozzi, F.; Leone, G.; Fiorillo, F.; Leone, N.; Russo, F.; Valente, A. Channel adjustments over 140 years in response to extreme floods and land-use change, Tammaro River, southern Italy. Geomorphology 2021, 383, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, V.; Piégay, H. Is afforestation a driver of change in Italian rivers within the Anthropocene era? Catena 2021, 198, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brath, A.; Montanari, A.; Moretti, G. Assessing the effect on flood frequency of land use change via hydrological simulation (with uncertainty). J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, D. The analysis of the impact of land-use changes on flood exposure of Wuhan in Yangtze River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2507–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, C.; Balacco, G.; Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Piccinni, A.F. Land use change impact on flooding areas: The case study of Cervaro Basin (Italy). Sustainability 2016, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U. Impact of land use changes on mountain vegetation. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2002, 5, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K.; Balla, D. Impact of agricultural land use in Central Asia: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, A.; Baldi, G.; Hirota, M.; Syktus, J.; McAlpine, C. Land use and land cover change impacts on the regional climate of non-Amazonian South America: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 128, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, I.; Sanz-Sánchez, M.J. Effects of historical land-use change in the Mediterranean environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmas, C.; Danalatos, N.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Chabart, M.; Diamantopoulos, J.; Farand, R.; Gutierrez, L.; Jacob, A.; Marques, H.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; et al. The effect of land use on runoff and soil erosion rates under Mediterranean conditions. Catena 1997, 29, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Reay, D.S. Land use and climate change in the UK. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, S160–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Z.; Li, Z.H. A review on historical trajectories and spatially explicit scenarios of land-use and land-cover changes in China. J. Land Use Sci. 2016, 11, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Bajocco, S. Land sensitivity to desertification across Italy: Past, present, and future. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.; Valentini, R. Predicting hot-spots of land use changes in Italy by ensemble forecasting. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccarreta, M.; Capolongo, D.; Boenzi, F.; Bentivenga, M. Implications of decadal changes in precipitation and land use policy to soil erosion in Basilicata, Italy. Catena 2006, 65, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łowicki, D. Land use changes in Poland during transformation: Case study of Wielkopolska region. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 87, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, M.; Martínez-Vega, J. Three decades of land-use changes in the region of Madrid and how they relate to territorial planning. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2016, 24, 1016–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, E.C.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Lightman, D.; Ramankutty, N. Anthropogenic transformation of the biomes, 1700 to 2000. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.E.; López Granados, E.; Geneletti, D.; Pérez-Salicrup, D.R.; Salinas, V. Analysing land cover and land use change processes at watershed level: A multitemporal study in the Lake Cuitzeo Watershed, Mexico (1975–2003). Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.K.; Das Chatterjee, N.; Das, K. Land use and land cover change and its resultant erosion susceptible level: An appraisal using RUSLE and Logistic Regression in a tropical plateau basin of West Bengal, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 1411–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.E.; Bartley, R.; Wilkinson, S.N.; Bainbridge, Z.T.; Henderson, A.E.; James, C.S.; Irvine, S.A.; Brodie, J.E. Land use change in the river basins of the Great Barrier Reef, 1860 to 2019: A foundation for understanding environmental history across the catchment to reef continuum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadese, M.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R.; Kogo, B.K. Mapping of land-use/land-cover changes and its dynamics in Awash River Basin using remote sensing and GIS. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 19, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, M.; Enne, G.; Madrau, S.; Percich, L.; Previtali, F.; Pulina, G.; Zucca, C. Mitigating land degradation in Mediterranean agro-silvo-pastoral systems: A GIS-based approach. Catena 2000, 40, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, S.; Cavalli, R.M.; Cuomo, V.; Fusilli, L.; Pascucci, S.; Poscolieri, M.; Santini, F. Evaluating Hyperion capability for land cover mapping in a fragmented ecosystem: Pollino National Park, Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, A.; Kumar, L. Investigating the use of Remote Sensing and GIS techniques to detect land use and land cover change: A review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amol, D.V.; Bharti, W.G. Analysis and modeling of agricultural land use using Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System: A Review. IJERA 2013, 3, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Attri, P.; Chaudhry, S.; Sharma, S. Remote Sensing & GIS based Approaches for LULC Change Detection—A Review. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 5, 3126–3137. [Google Scholar]
- MohanRajan, S.N.; Loganathan, A.; Manoharan, P. Survey on Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) change analysis in remote sensing and GIS environment: Techniques and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29900–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, A.; Innamorato, F.; Capone, S. La grande trasformazione: Land cover e land use in Campania. In Estimo e Territorio–Valutare e Gestire L’ambiente; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 2005; Volume 3 (LXVII), pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Magliulo, P.; Cusano, A.; Russo, F. Land-Use Changes in the Sele River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy) between 1960 and 2012: Comparisons and Implications for Soil Erosion Assessment. Geographies 2021, 1, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, A.; Ferrari, E.; Iovino, F.; Nicolaci, A.; Veltri, A. Reforestation and land use change in a drainage basin of southern Italy. iForest 2013, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricca, N.; Guagliardi, I. Multi-temporal dynamics of land use patterns in a site of community importance in Southern Italy. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 13, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Gentile, F. Modeling land use changes and their impact on sediment load in a Mediterranean watershed. Catena 2018, 163, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P.; Cusano, A.; Giannini, A.; Sessa, S.; Russo, F. Channel width variation phases of the major rivers of the Campania Region (Southern Italy) over 150 years: Preliminary results. Earth 2021, 2, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N. Modelling net erosion responses to enviroclimatic changes recorded upon multisecular timescales. Geomorphology 2006, 80, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. Guidebook for the Evaluation of Stream Morphological Conditions by the Morphological Quality Index (MQI); Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Mostardini, F.; Merlini, S. Appennino centro meridionale. Sezioni geologiche e proposta di modello strutturale. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1986, 35, 177–202. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, S.; Ciarcia, S. Tectono-stratigraphic setting of the Campania region (southern Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P. Quaternary deposits and geomorphological evolution of the Telesina Valley (Southern Apennines). Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2005, 28, 125–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cartojan, E.; Magliulo, P.; Massa, B.; Valente, A. Morphotectonic features of the Tammaro River basin, Southern Apennines, Italy. Rend. Lincei 2014, 25 (Suppl. 2), 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarcia, S.; Magliulo, P.; Russo, F.; Valente, A. Osservazioni geologiche e geomorfologiche preliminari sul bacino pleistocenico intermontano di Benevento (Appennino Campano). In Evoluzione Geomorfologica di Lungo Termine del Paesaggio nell’Italia Meridionale: Il Contributo Delle Università Locali; Rosskopf, C.M., Aucelli, P.P.C., Eds.; Università degli Studi del Molise, Associazione Italiana di Geografia Fisica e Geomorfologia (AIGeo) edition; Arti Grafiche la Regione: Ripalimosani, Italy, 2014; pp. 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Brancaccio, L.; Cinque, A. L’evoluzione geomorfologica dell’Appennino campano-lucano. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1988, 41, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Magliulo, P.; Russo, F.; Valente, A. Tectonic significance of geomorphological features in the Telesina Valley (Campanian Apennines). Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2007, 126, 397–409. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, A.P.; Tedeschi, P.; Wright, G.G.; Fragnito, F. Landsat satellite data for soil investigations in an Apennines region of southern Italy. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 1996, 19, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. Twelfth Edition, 2014. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/PA_NRCSConsumption (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Magliulo, P.; Valente, A.; Cartojan, E. Recent morphological changes of the middle and lower Calore River (Campania, Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2785–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandino, V. L’agricoltura sannita tra arretratezza e ammodernamento. Credito agrario e innovazione nel Novecento. In Mezzogiorno-Agricoltura. Processi Storici e Prospettive di Sviluppo Nello Spazio EuroMediterraneo; Bencardino, F., Ferrandino, V., Marotta, G., Eds.; Franco Angeli: Milano, Italy, 2011; 696p. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (CNR)—Direzione Generale del Catasto. Carta Dell’utilizzazione del Suolo in Italia Alla Scala 1:200,000; Touring Club: Milano, Italy, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus—Land Monitoring Service. 1990. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc-1990 (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Copernicus—Land Monitoring Service. 2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Chen, J.; Zhongwu, L.; Haibing, X.; Ke, N.; Chongjun, T. Effects of land use and land cover on soil erosion control in southern China: Implications from a systematic quantitative review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA, Science and Education Administration: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Parish, R. Mountains Environment; Routledge: London, UK, 2002; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, P.; Allocca, V.; Manna, F.; Fabbrocino, S. Coupled decadal variability of the North Atlantic Oscillation, regional rainfall and karst spring discharges in the Campania region (Southern Italy). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diodato, N. Climatic fluctuations in Southern Italy since the 17th century: Reconstruction with precipitation records at Benevento. Clim. Chang. 2007, 80, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, A.; Villani, P. Trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall time series in the Mediterranean area. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M. Recent channel adjustments in alluvial rivers of Tuscany, Central Italy. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CNR-TC (1960) | CLC (1990, 2018) | This Study | C-Factor (Panagos et al., 2015) | Class C-Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed forests | Mixed forest | Forests | 0.0011 | 0.0012 |
| Tall trees forests | Coniferous forest | 0.0011 | ||
| Broad-leaved forest | 0.0013 | |||
| Coppice woodlands | - | - | ||
| Pastures and natural grasslands | Pastures | Grasslands and shrubs | 0.0903 | 0.0520 |
| Natural grasslands | 0.0435 | |||
| Wooded grasslands (dry) | Transitional woodland and shrub | 0.0219 | ||
| - | Sclerophyllous vegetation | 0.0623 | ||
| Moors and heathland | 0.0420 | |||
| Dry arable lands | Annual crops associated with permanent crops | Agricultural areas | 0.2323 | 0.1869 |
| Irrigated arable lands | Complex cultivation patterns | 0.1384 | ||
| Wooded arable lands (dry) | Land principally used for agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation | 0.1232 | ||
| Wooded arable lands (irrigated) | Agro-forestry areas | 0.0881 | ||
| Vineyards | Vineyards | 0.3527 | ||
| Hazelnut groves | Fruit trees and berry plantations | Fruit trees and olive groves | 0.2188 | 0.2231 |
| Chestnuts | ||||
| Fruit trees plantations | ||||
| Olive groves | Olive groves | 0.2273 | ||
| Olive trees and vines associations | ||||
| Barren areas | Sparsely vegetated areas | Bare or sparsely vegetated areas | 0.2652 | 0.2652 |
| Beaches, dunes, sands | - | |||
| Water bodies | Water bodies | Wetlands and water bodies | - | N.D. |
| Water courses | - | |||
| Settlements and other utilization forms | Continuous urban fabric | Artificial surfaces | - | N.D. |
| Discontinuous urban fabric | - | |||
| Industrial or commercial units | - | |||
| Road and rail networks and associated land | - | |||
| Mineral extraction sites | - | |||
| Dump sites | - | |||
| Construction sites | - | |||
| Green urban areas | - |
| LULC Class | Calore River Basin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Variation (%) | |||||
| 1960 | 1990 | 2018 | 1960–1990 | 1990–2018 | 1960–2018 | |
| Artificial surfaces | 4682.3 | 9210.9 | 12,910.6 | 96.7 | 40.2 | 175.7 |
| Wetlands and water bodies | 1379.2 | 25.9 | 546.9 | −98.1 | 2009.2 | −60.3 |
| Forests | 31,739.2 | 66,915.6 | 68,756.3 | 110.8 | 2.8 | 116.6 |
| Fruit trees and olive groves | 21,045.8 | 20,483.5 | 13,414.4 | −2.7 | −34.5 | −36.3 |
| Bare or sparsely vegetated areas | - | 219.5 | 638.1 | - | 190.7 | - |
| Grasslands and shrubs | 22,167.6 | 20,829.4 | 14,538.6 | −6.0 | −30.2 | −34.4 |
| Agricultural areas | 224,065.9 | 187,397.8 | 194,277.5 | −16.4 | 3.7 | −13.3 |
| Alluvial Valleys (AV) | ||||||
| Artificial surfaces | 232.3 | 1158.3 | 1573.1 | 398.5 | 35.8 | 577.0 |
| Wetlands and water bodies | 829.2 | 25.8 | 345.1 | −96.9 | 1235.3 | −58.4 |
| Forests | 602.7 | 2137.1 | 2335.4 | 254.6 | 9.1 | 287.0 |
| Fruit trees and olive groves | 843.8 | 1787.8 | 770.7 | 111.9 | −56.9 | −8.7 |
| Bare or sparsely vegetated areas | - | 31.2 | 12.7 | - | −49.9 | - |
| Grasslands and shrubs | 714.7 | 1439.3 | 446.4 | 101.4 | −69.0 | −37.5 |
| Agricultural areas | 15,927.4 | 12,570.9 | 13,667.0 | −21.1 | 8.7 | −14.2 |
| Low-Altitude Hills (LAH) | ||||||
| Artificial surfaces | 3296.2 | 6710.3 | 9373.2 | 103.6 | 39.7 | 184.4 |
| Wetlands and water bodies | 540.7 | 0.0 | 149.6 | −100.0 | - | −72.3 |
| Forests | 6986.7 | 23,969.0 | 24,866.6 | 243.1 | 3.7 | 255.9 |
| Fruit trees and olive groves | 12,541.0 | 17,697.9 | 12,221.7 | 41.1 | −30.9 | −2.5 |
| Bare or sparsely vegetated areas | - | 89.3 | 137.3 | - | 53.8 | - |
| Grasslands and shrubs | 7810.4 | 6886.6 | 3986.9 | −11.8 | −42.1 | −49.0 |
| Agricultural areas | 150,778.7 | 126,602.1 | 131,220.0 | −16.0 | 3.6 | −13.0 |
| Apennine Mountain Range (AMR) | ||||||
| Artificial surfaces | 1153.8 | 1342.3 | 1964.3 | 16.3 | 46.3 | 70.3 |
| Wetlands and water bodies | 9.2 | - | 52.3 | - | - | 466.8 |
| Forests | 24,149.7 | 40,809.4 | 41,554.3 | 69.0 | 1.8 | 72.1 |
| Fruit trees and olive groves | 7661.0 | 997.7 | 422.0 | −87.0 | −57.7 | −94.5 |
| Bare or sparsely vegetated areas | - | 99.1 | 488.1 | - | 392.7 | - |
| Grasslands and shrubs | 13,642.5 | 12,503.6 | 10,105.3 | −8.3 | −19.2 | −25.9 |
| Agricultural areas | 57,359.3 | 48,224.8 | 49,390.5 | −15.9 | 2.4 | −13.9 |
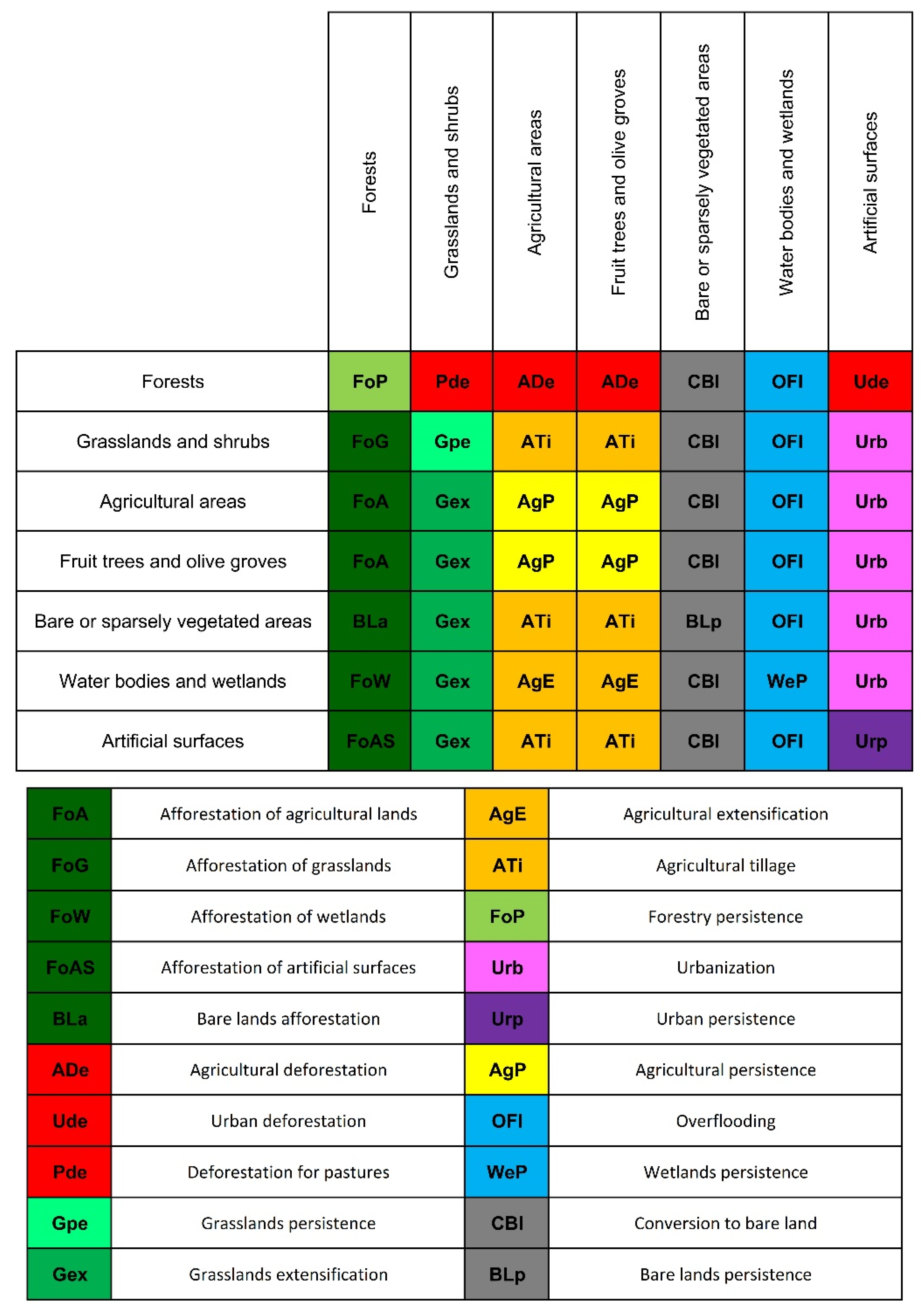
| LULC Change | 1960–1990 (%) | 1990–2018 (%) | 1960–2018 (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calore R. Basin | AV | LAH | AMR | Calore R. Basin | AV | LAH | AMR | Calore R. Basin | AV | LAH | AMR | |
| Afforestation of agricultural lands | 12.1 | 8.6 | 10.7 | 15.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 12.6 | 9.5 | 11.0 | 15.9 |
| Afforestation of artificial surfaces | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Afforestation of grasslands | 2.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 5.2 |
| Afforestation of wetlands | - | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Afforestation of bare lands | - | - | - | - | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | 0.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Agricultural deforestation | 2.2 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.6 |
| Deforestation for pastures | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.8 |
| Urban deforestation | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Grasslands extensification | 4.6 | 6.3 | 3.4 | 6.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 4.5 |
| Agricultural extensification | 0.3 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | 0.3 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Agricultural tillage | 4.3 | 2.5 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 4.3 | 2.7 | 4.3 | 4.6 |
| Urbanization | 2.5 | 5.3 | 3.1 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 7.4 | 4.4 | 1.5 |
| Forestry persistence | 7.4 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 18.7 | 21.2 | 10.3 | 12.5 | 38.3 | 7.4 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 18.6 |
| Grasslands persistence | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 4.0 | 4.4 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 8.8 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 3.4 |
| Urban persistence | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 3.6 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Agricultural persistence | 61.3 | 67.8 | 72.7 | 40.2 | 66.3 | 72.4 | 77.1 | 46.1 | 61.2 | 67.9 | 72.3 | 40.7 |
| Bare lands persistence | - | - | - | - | 0.0 | - | - | 0.1 | - | - | - | - |
| Overflooding | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | - | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Wetlands persistence | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | - | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Conversion to bare land | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magliulo, P.; Cusano, A.; Sessa, S.; Beatrice, M.; Russo, F. Multidecadal Land-Use Changes and Implications on Soil Protection in the Calore River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy). Geosciences 2022, 12, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12040156
Magliulo P, Cusano A, Sessa S, Beatrice M, Russo F. Multidecadal Land-Use Changes and Implications on Soil Protection in the Calore River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy). Geosciences. 2022; 12(4):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12040156
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagliulo, Paolo, Angelo Cusano, Sofia Sessa, Marika Beatrice, and Filippo Russo. 2022. "Multidecadal Land-Use Changes and Implications on Soil Protection in the Calore River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy)" Geosciences 12, no. 4: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12040156
APA StyleMagliulo, P., Cusano, A., Sessa, S., Beatrice, M., & Russo, F. (2022). Multidecadal Land-Use Changes and Implications on Soil Protection in the Calore River Basin Landscape (Southern Italy). Geosciences, 12(4), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12040156







