Seismic Reflection Methods in Offshore Groundwater Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Distribution of Offshore Groundwater
1.2. Methods and Approaches to the Study of Offshore Groundwater
- Active source, multi-channel reflection seismic (hereby referred to simply as ‘seismic data’);
- Electromagnetics (EM, CSEM);
- Seabed mapping tools (multibeam, water column backscatter, side-scan sonar and LIDAR);
- Thermal remote sensing;
- Sediment core and pore water geochemical analyses;
- Borehole geophysics, imaging and hydrogeology (e.g., spontaneous potential, nuclear magnetic resonance, resistivity, flow-meters, etc.).
2. Seismic Reflection Data
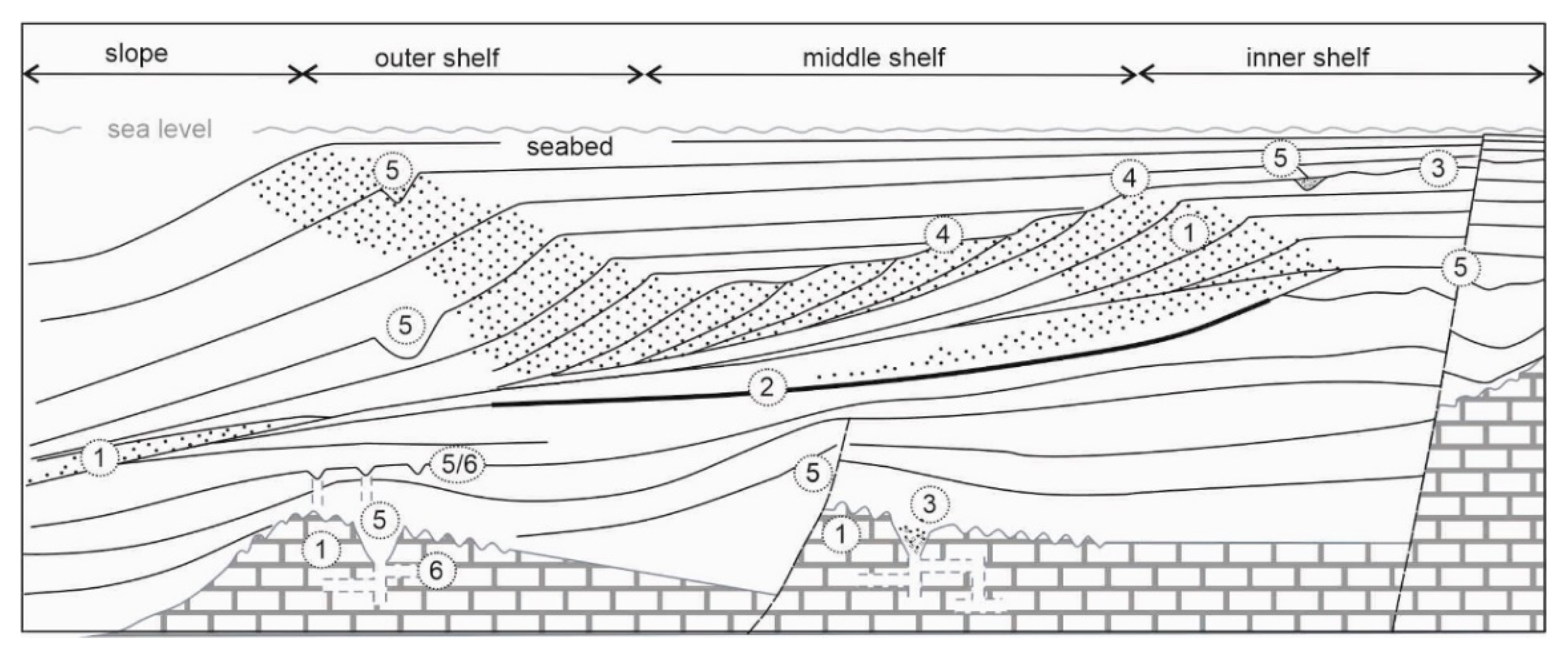
2.1. Seismic Stratigraphy, Sequence Stratigraphy and Attribute Analysis
2.2. Seismic Morpho-Structural Interpretation
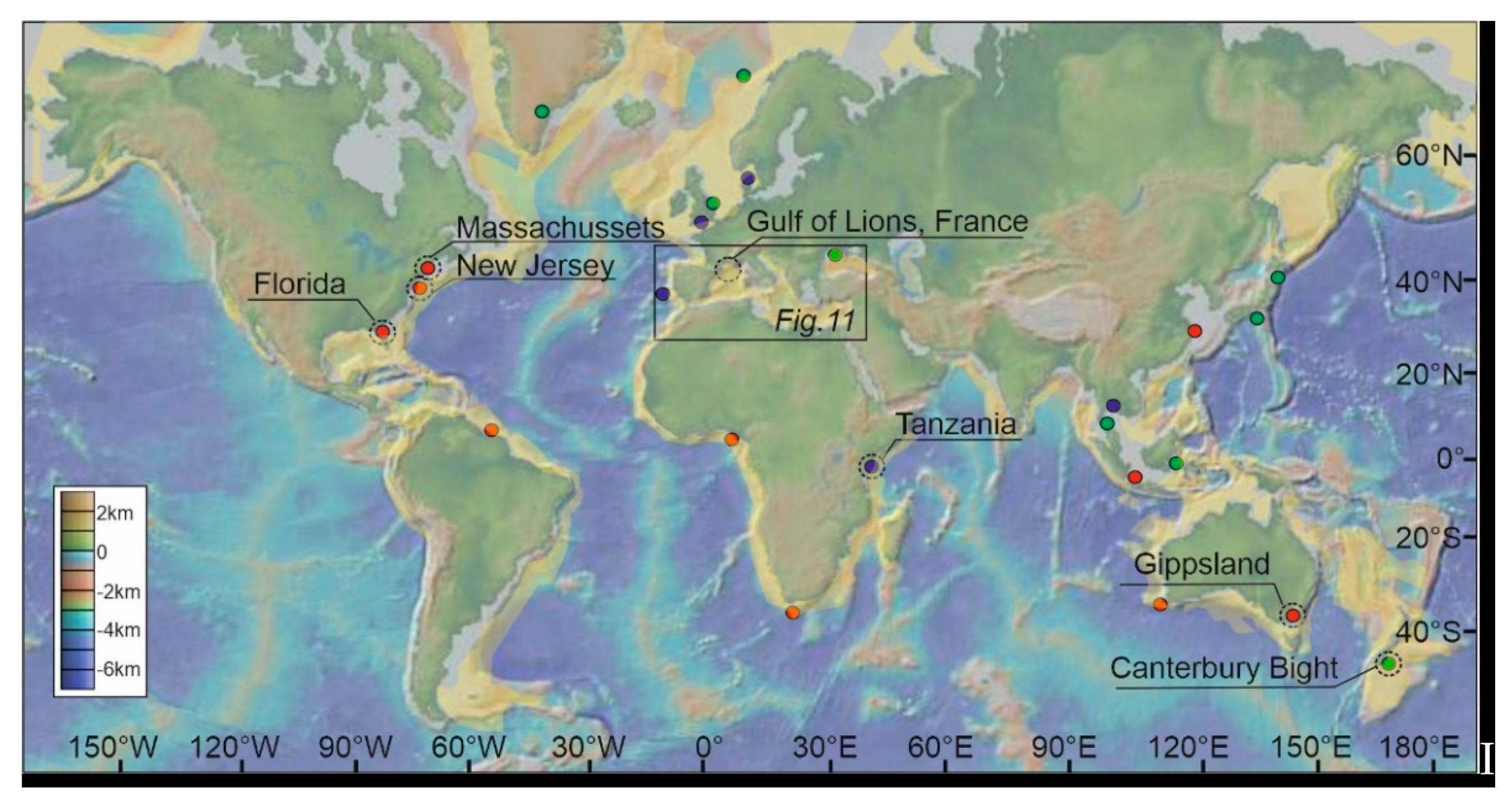
3. Case Studies
3.1. North Atlantic Margin
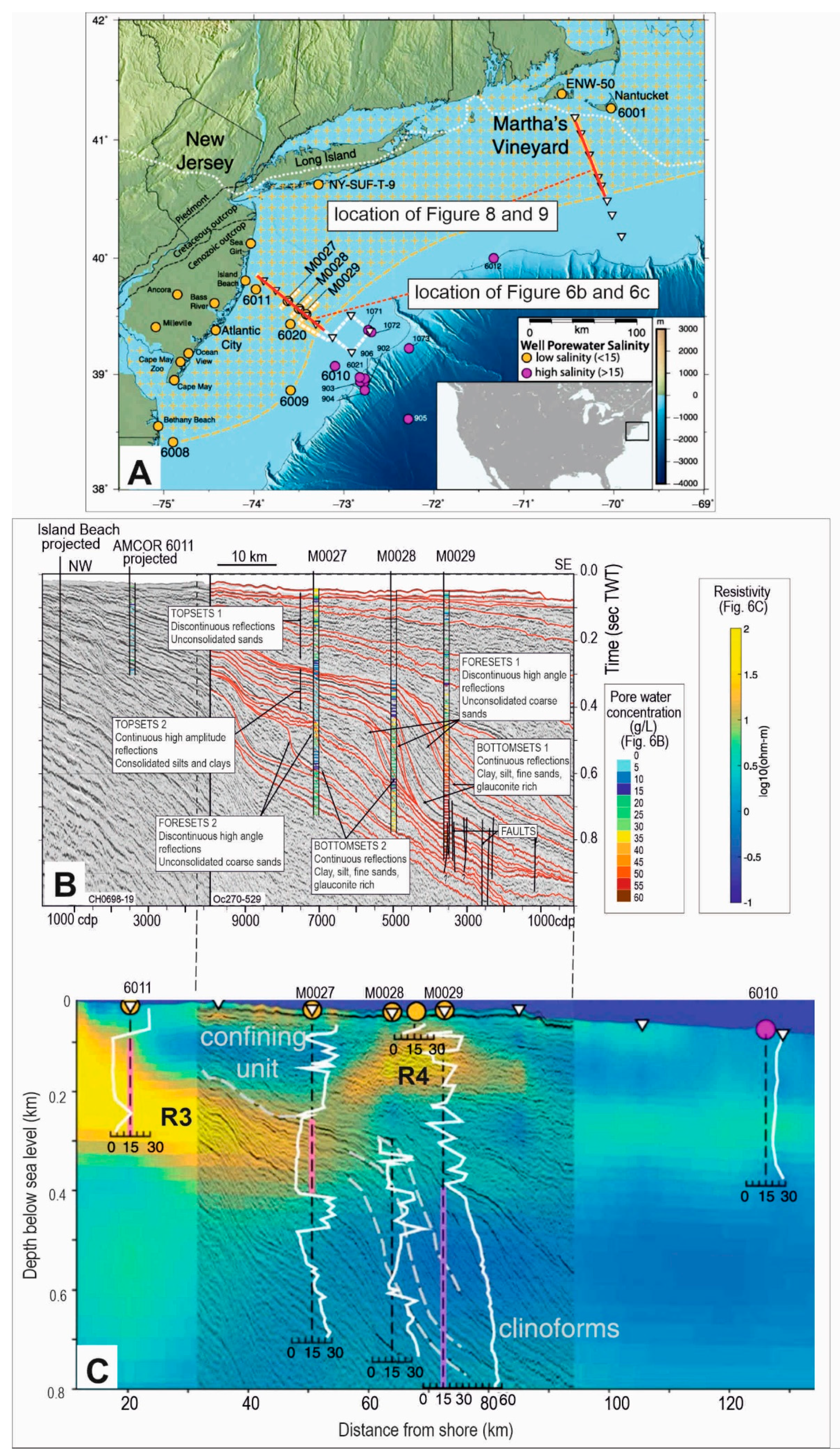
3.1.1. New Jersey
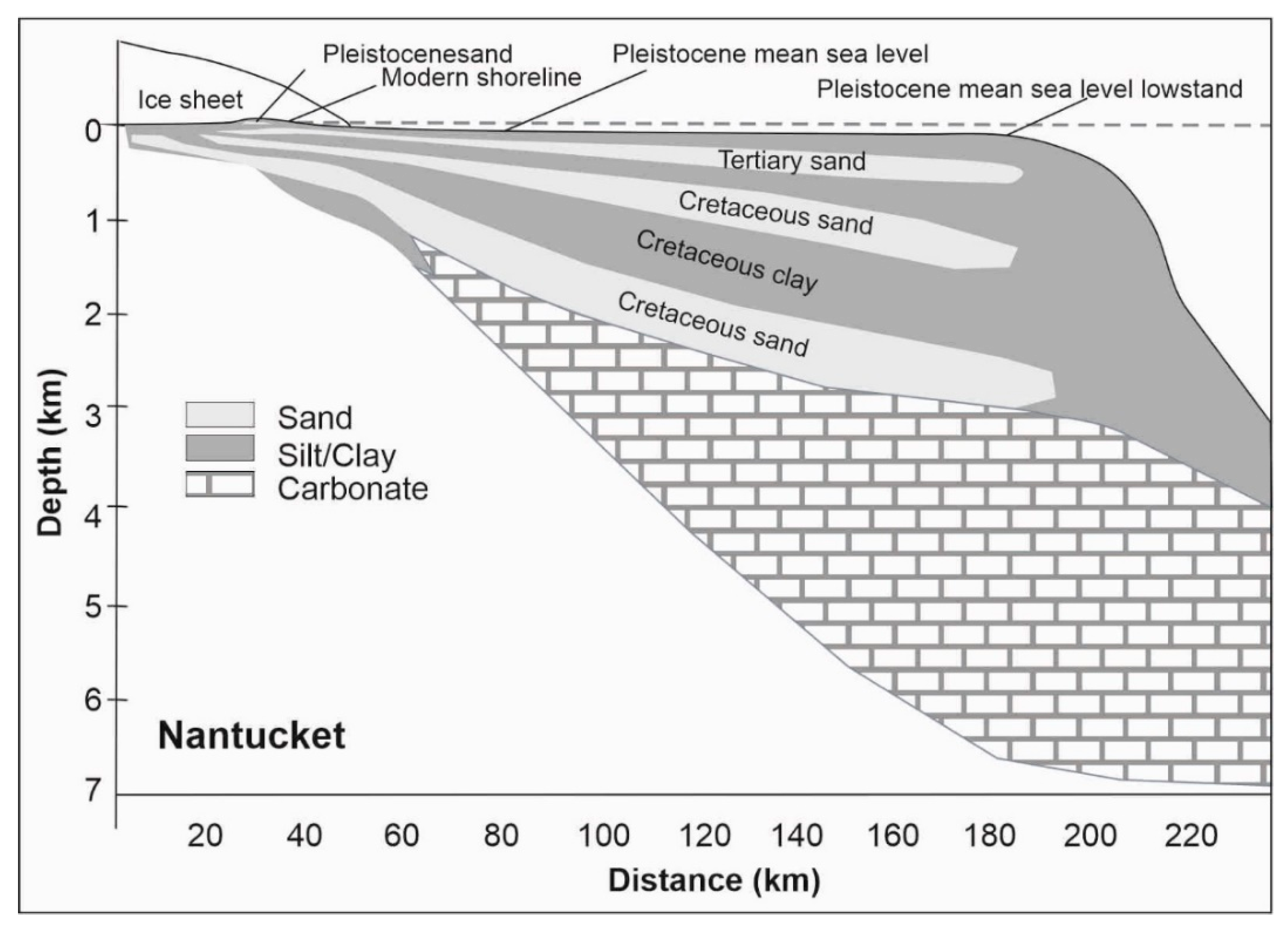
3.1.2. Martha’s Vineyard (Massachusetts)
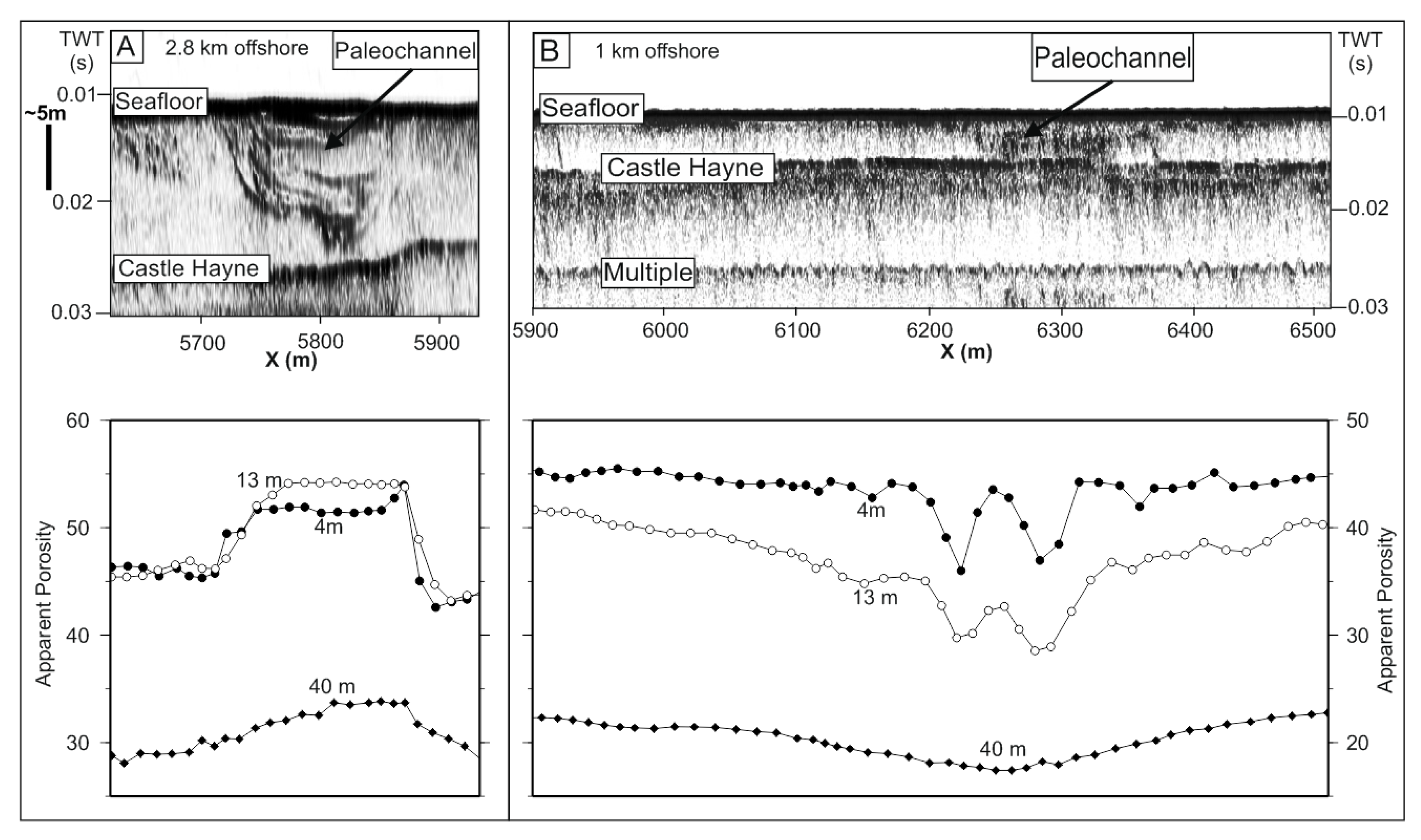
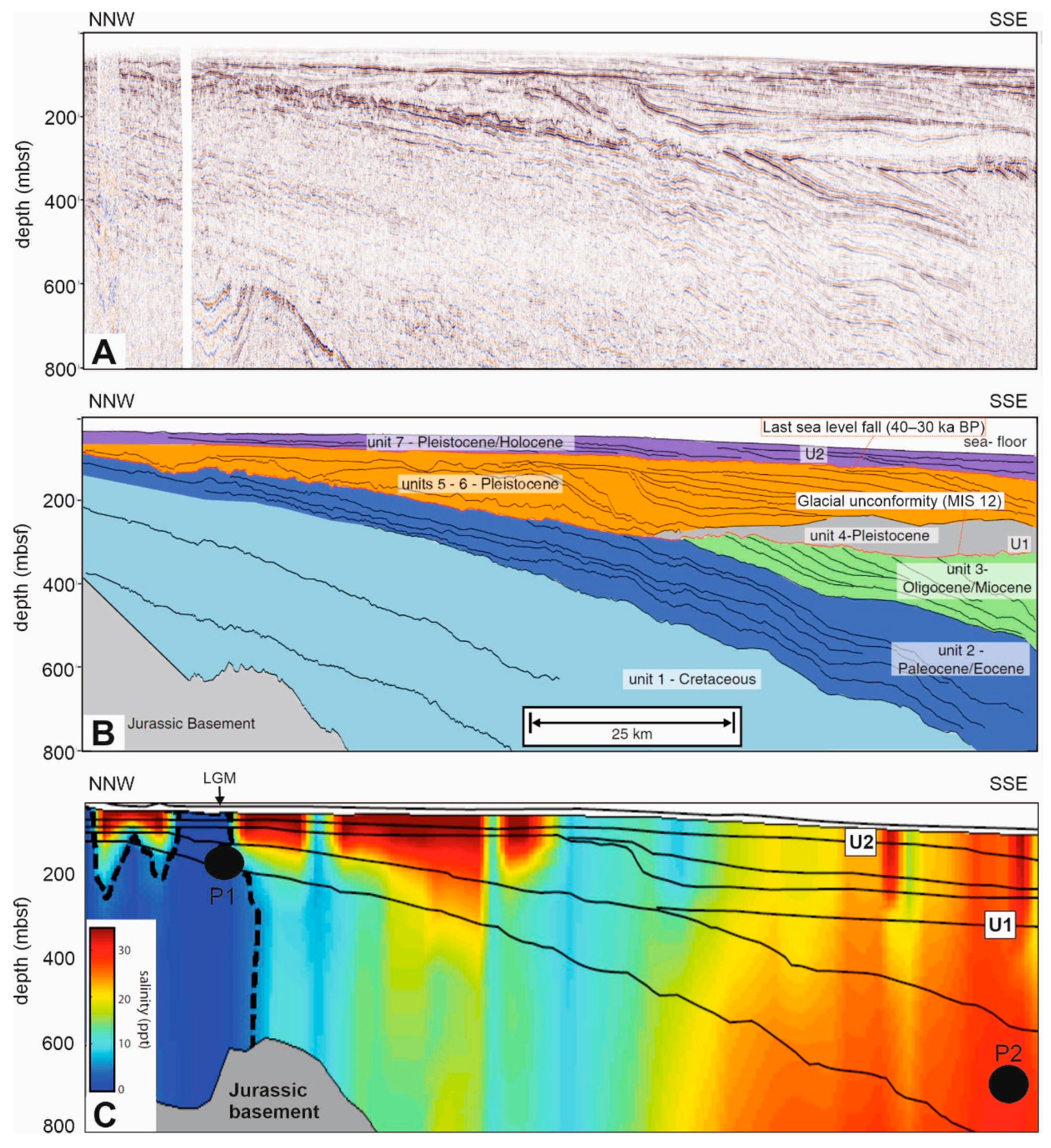
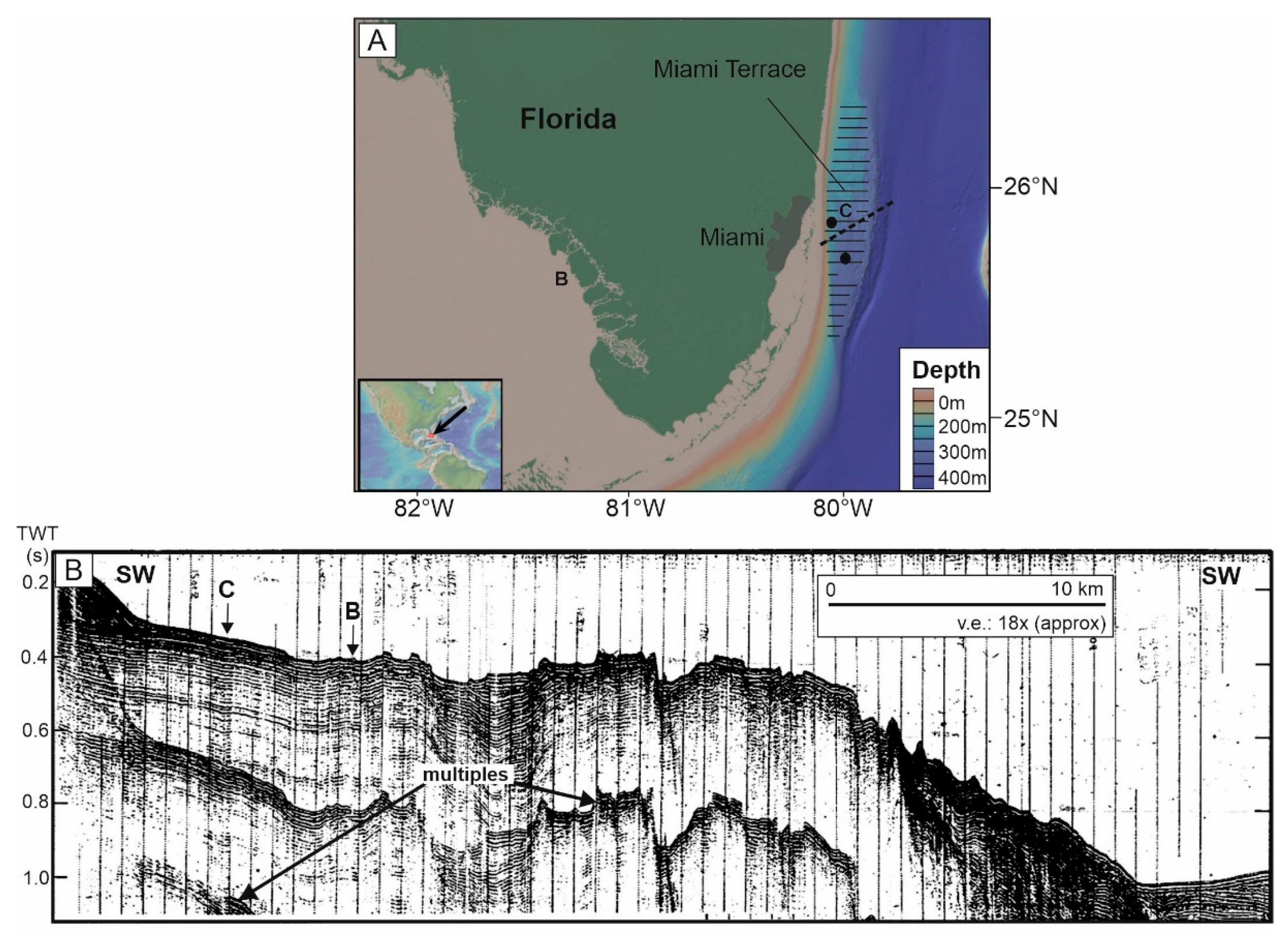
3.1.3. Florida
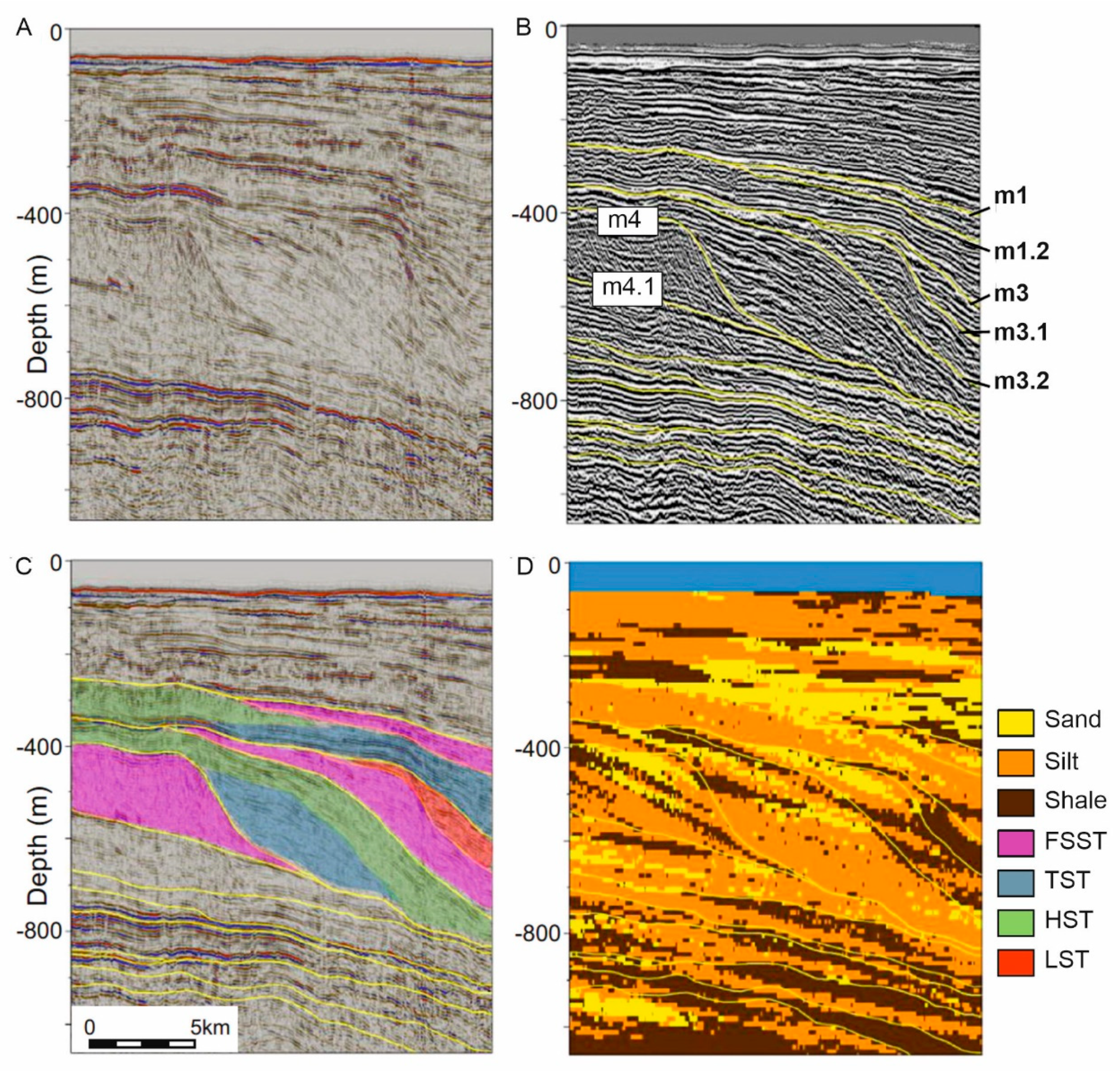
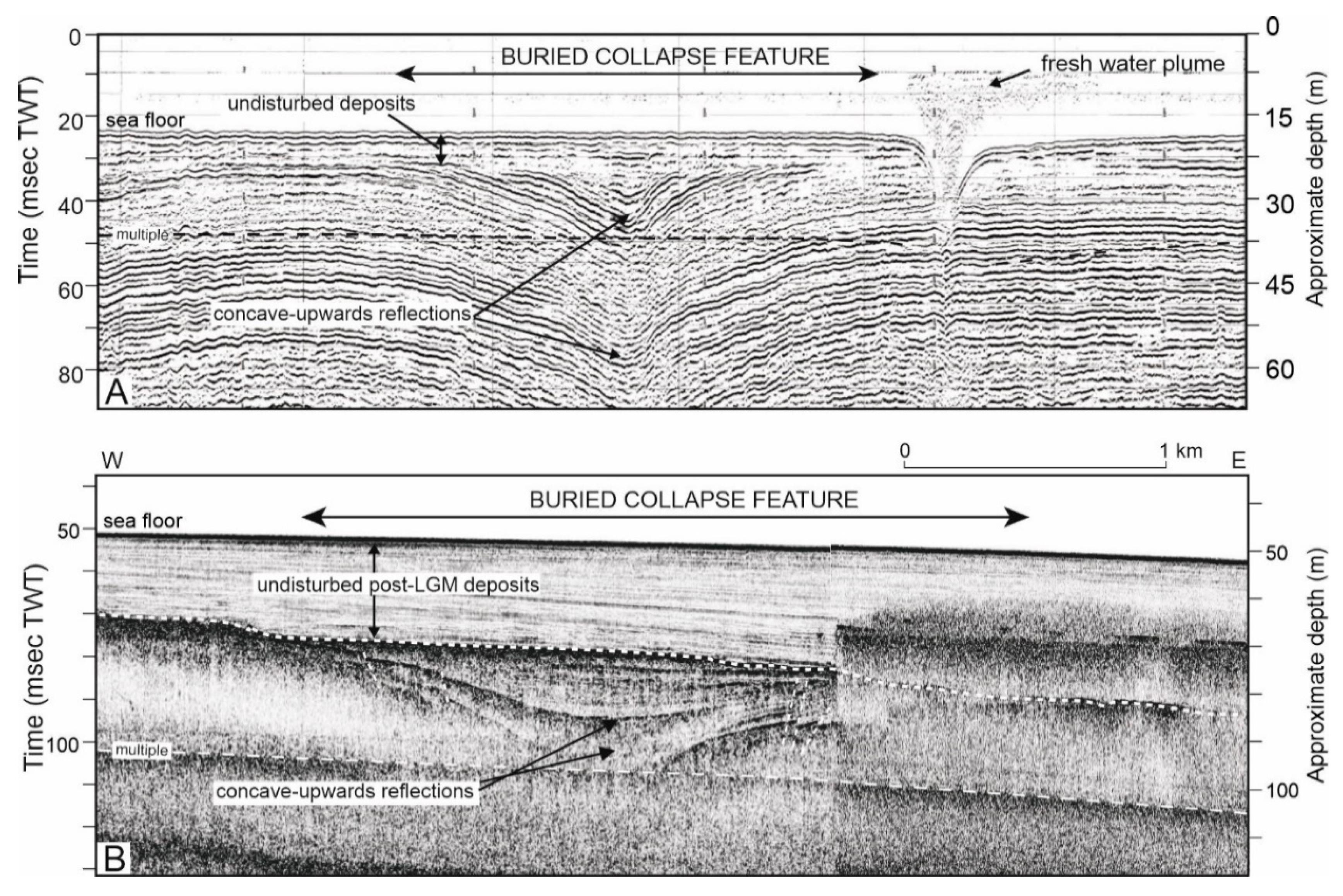
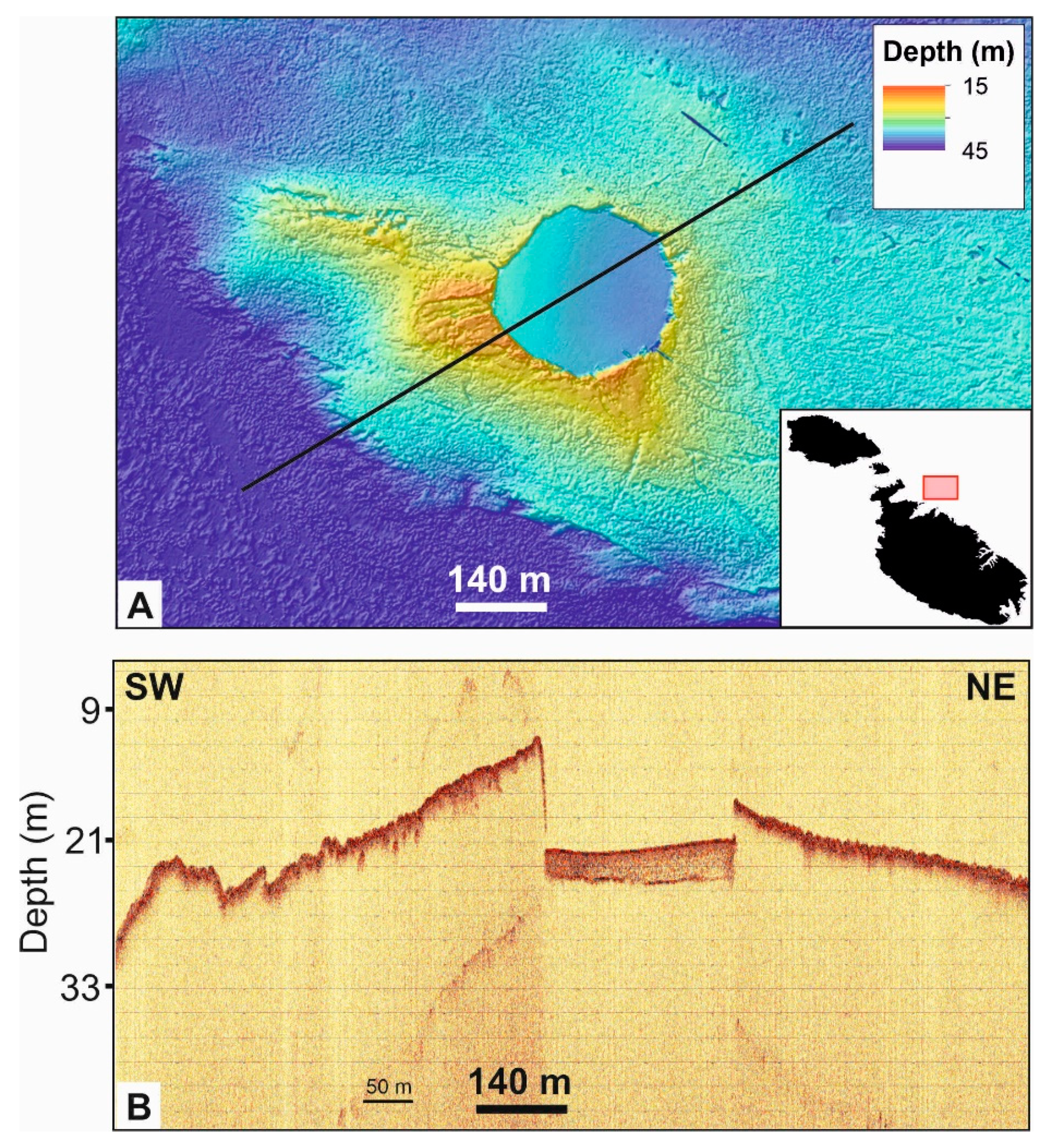
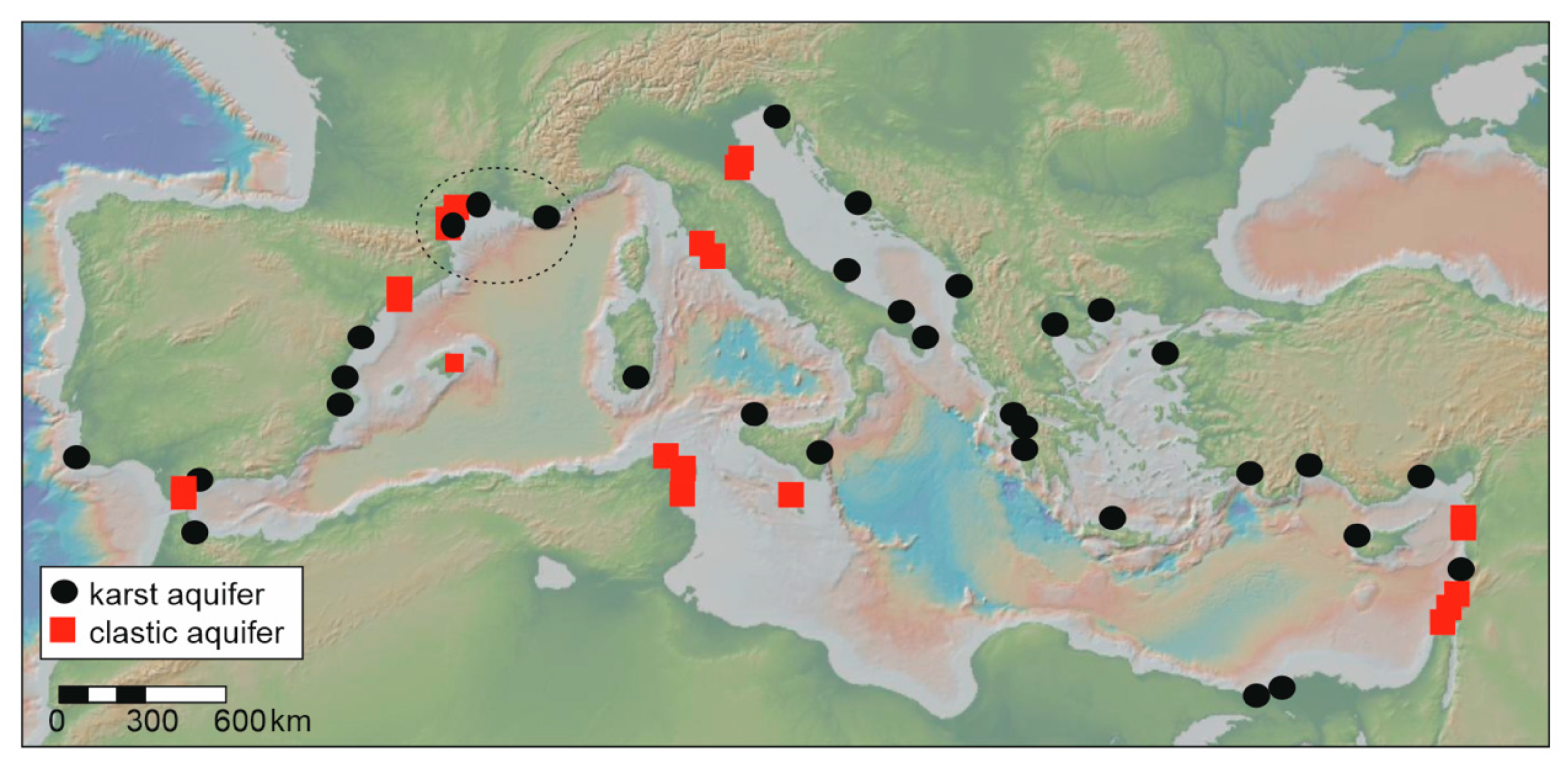
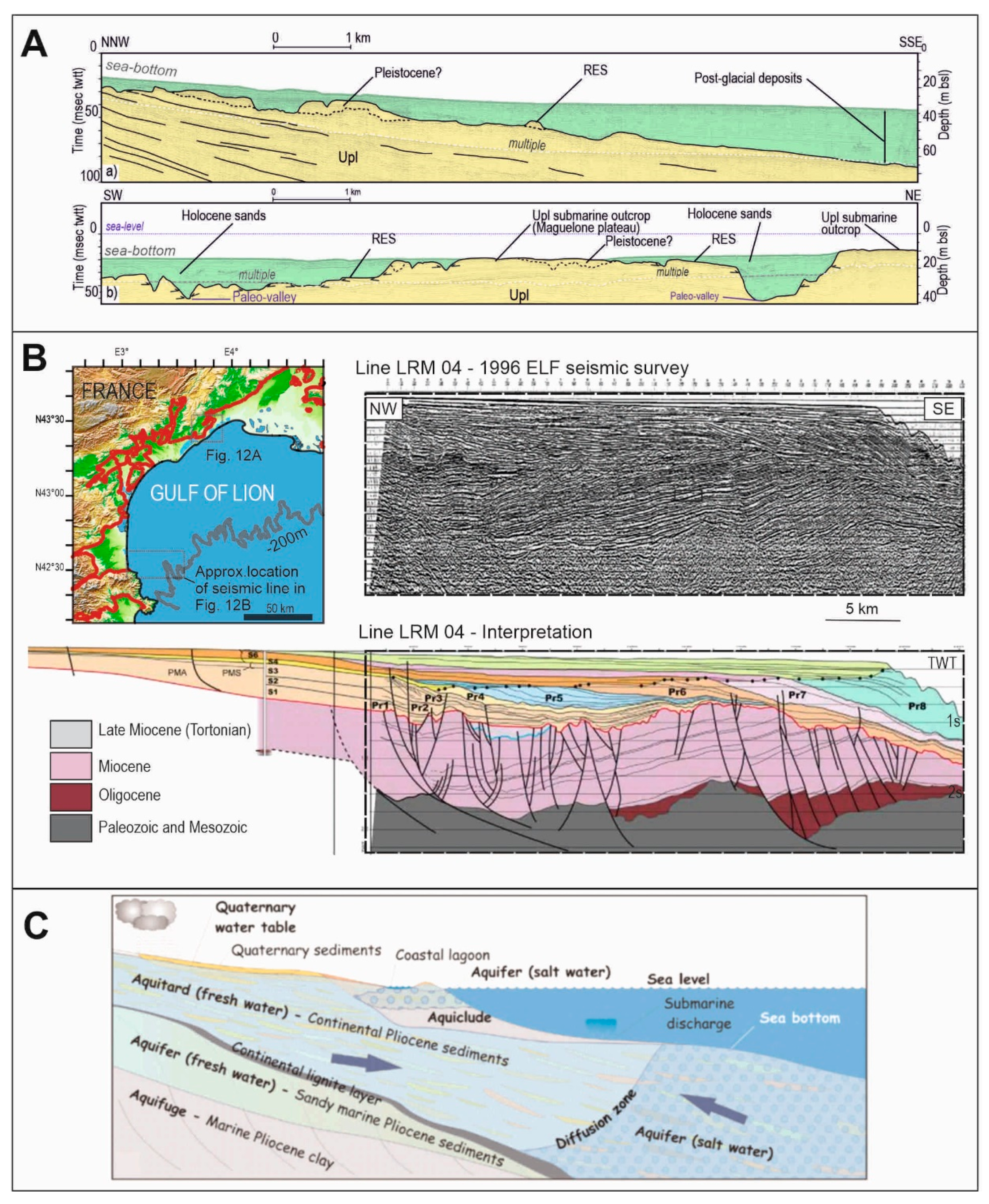
3.2. Mediterranean Region
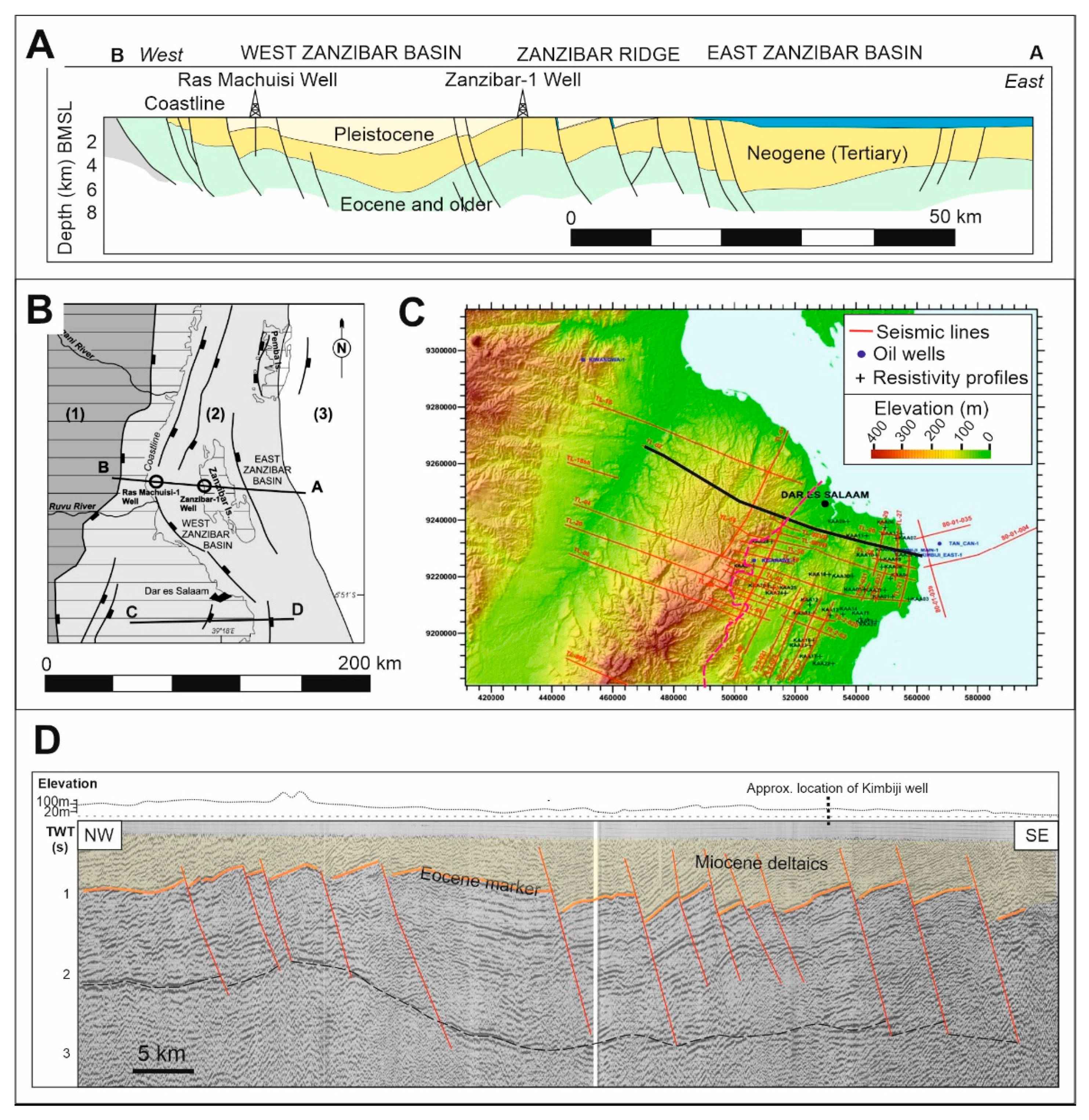
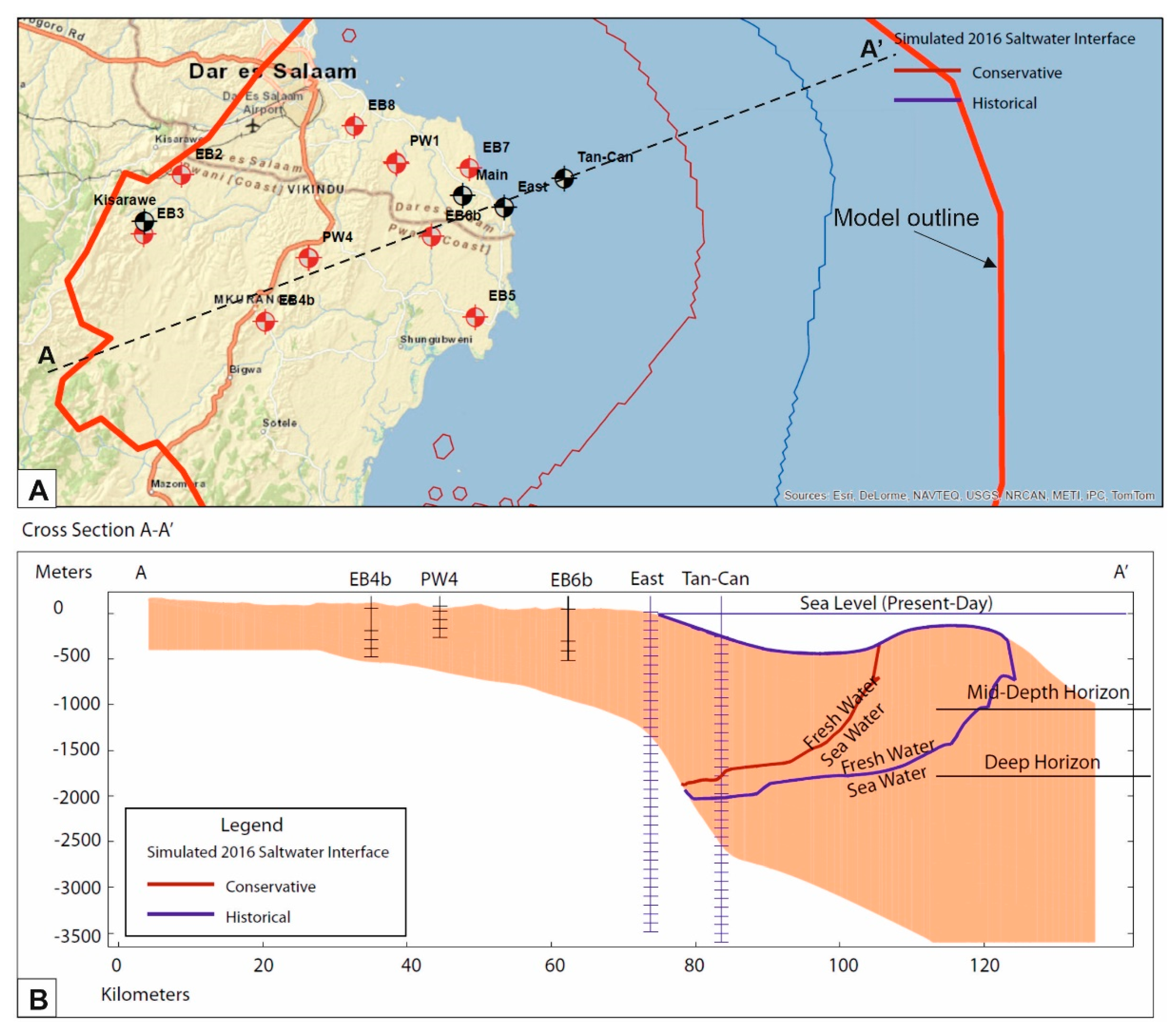
3.3. East Africa
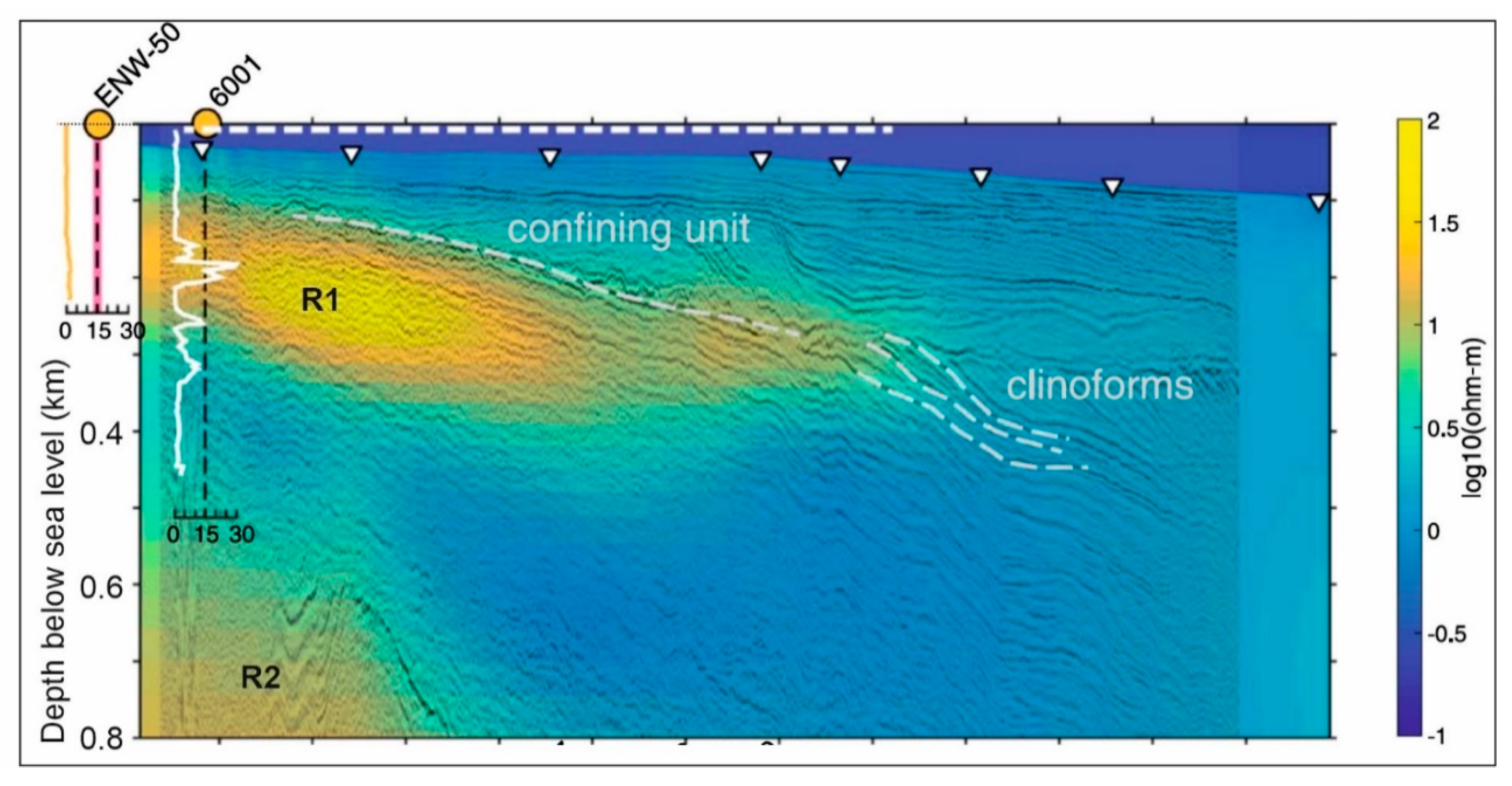
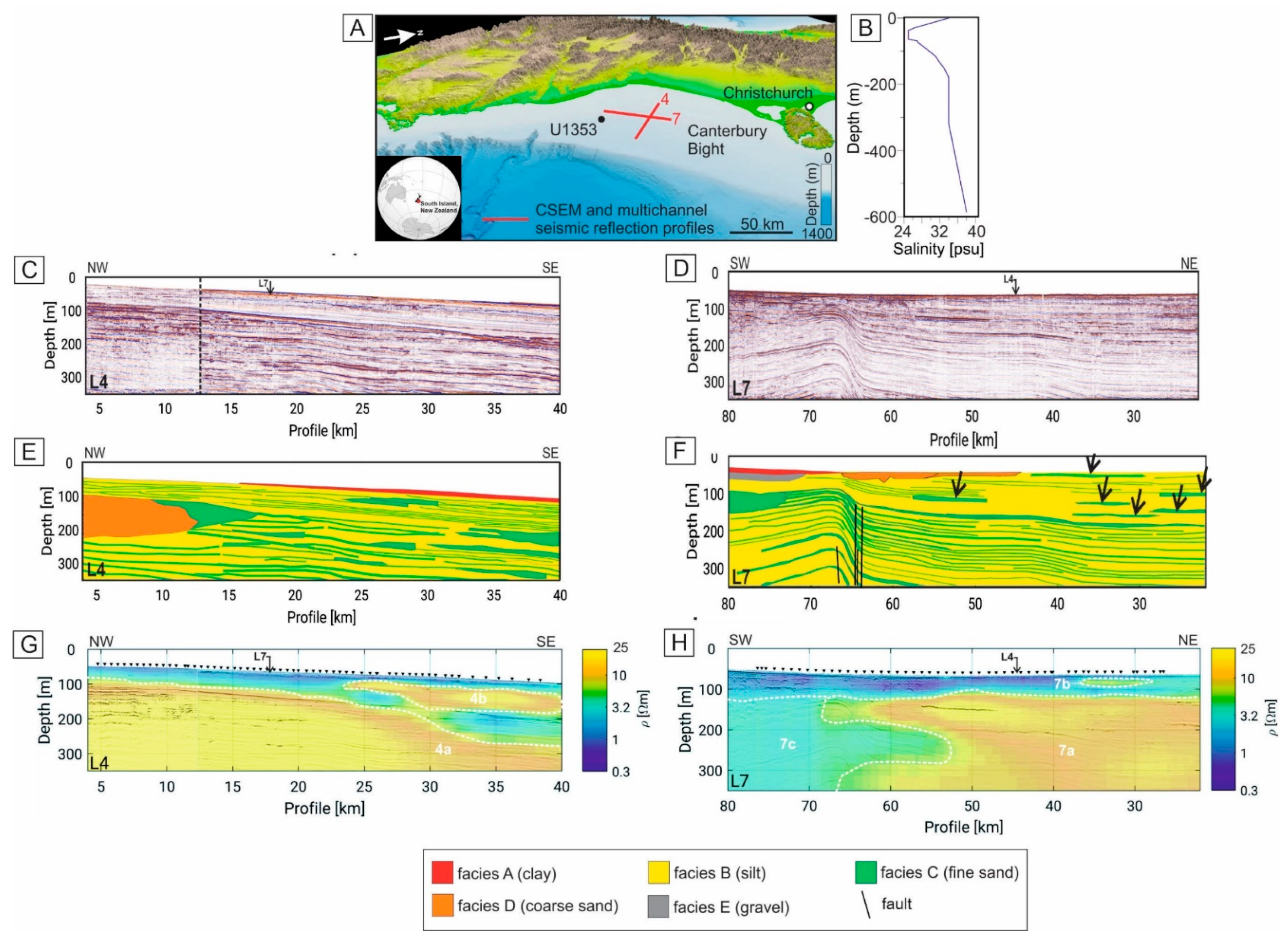
3.4. Canterbury Bight, New Zealand
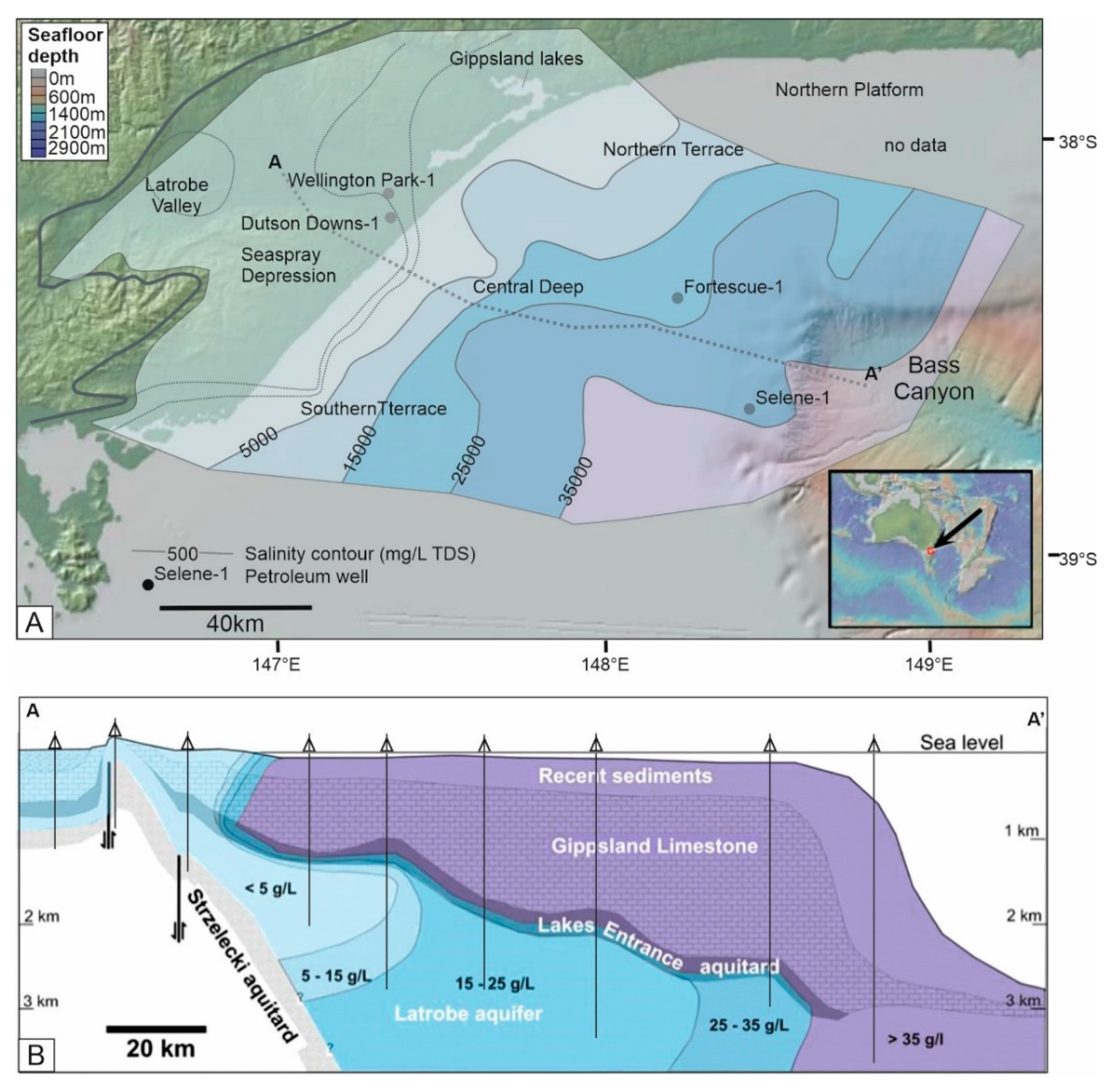
3.5. Gippsland Basin, Australia
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Summary of Use and Limitations of Seismic Reflection Data in Offshore Freshened Water Research
- Reservoir (aquifer) properties and architecture, for example, through spatial mapping of the permeability/porosity of sedimentary bodies, analysis of onshore-offshore aquifer connectivity, identification of the open or confined nature of offshore aquifers and their active or ‘fossil’ setting. In carbonate rocks, seismic data can also indicate areas of porosity and permeability enhancement due to karstification processes (Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4 and Section 3.5)
- Seal (aquitard/aquiclude), through the identification of permeability barriers, such as laterally extensive fine-grained sediments or tightly cemented layers (Section 3.1.1)
- Paleo-continental environments, through the detection of potential freshwater-bearing environments, such as fluvio-lacustrine systems or subaerially exposed karstic terranes (Section 3.1.3),
- Paleo-coastline and change to active aquifers: absolute and relative sea-level changes and shift of coastal facies through time and therefore potentially associated coastal aquifers (e.g., References [44,67]); The onlap shifts related to sea-level change are used to document shifting of the mixing zone and saltwater intrusion into coastal plain groundwater systems in the past (Section 3.1.2)
- Conduits, (paleo)channels and canyons, faults as conduits or indication of fractured reservoirs, sinkholes, pockmarks/pipes. Faults can alternatively act as barriers when juxtaposing the reservoir to sealing units. (Section 3.1.1, Section 3.1.3, Section 3.3 and Section 3.4)
- Aquifer indicators, subaerial sinkholes and other dissolution-related karstic features, pockmarks/pipes (Section 3.1.3)
4.2. Integration with Petroleum Geology Studies
4.3. Applicability and Future Avenues of Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Polemio, M. Monitoring and management of karstic coastal groundwater in a changing environment (Southern Italy): A review of a regional experience. Water 2016, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.T. Marine hydrogeology: Recent accomplishments and future opportunities. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 69–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.; Groen, J.; Kooi, H.; Person, M.; Ge, S.; Edmunds, W.M. Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon. Nature 2013, 504, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.-D.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods and Practices; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1999; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, P.M. Ground Water in Fresh Water-Salt Water Environments of the Atlantic; Geological Survey (USGS): Reston, VA, USA, 2003; Volume 1262.
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkelmann, R.; Sheta, H.; Class, H.; Helmig, R. A Comparison of Different Model Concepts for Saltwater Intrusion Processes; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kouzana, L.; Benassi, R. Geophysical and hydrochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi arid zones. Case of the Korba coastal aquifer (Cap-bon, Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowroozi, A.A.; Horrocks, S.B.; Henderson, P. Saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer in the eastern shore of Virginia: A reconnaissance electrical resistivity survey. J. Appl. Geophys. 1999, 42, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Spivack, A.J.; Artzi, Y.; Ayalon, A. Geochemical and boron, strontium and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1877–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinthal, E.; Vengosh, A.; Marei, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Kloppmann, W. The water crisis in the Gaza strip: Prospects for resolution. Groundwater 2005, 43, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, B.; Flemings, P.B. Overpressure and fluid flow in the New Jersey continental slope: Implications for slope failure and cold seeps. Science 2000, 289, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountain, G.; Proust, J.; McInroy, D.; Cotterill, C. The Expedition 313 Scientists: Proceedings of Integrated Ocean Drilling Program, 313; Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Management International, Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.; Person, M.; Wang, P.; Gable, C.W.; Hutchinson, D.; Marksamer, A.; Dugan, B.; Kooi, H.; Groen, K.; Lizarralde, D. Origin and extent of fresh paleowaters on the Atlantic continental shelf, USA. Groundwater 2010, 48, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofi, J.; Inwood, J.; Proust, J.-N.; Monteverde, D.H.; Loggia, D.; Basile, C.; Otsuka, H.; Hayashi, T.; Stadler, S.; Mottl, M.J. Fresh-water and salt-water distribution in passive margin sediments: Insights from integrated ocean drilling program expedition 313 on the New Jersey margin. Geosphere 2013, 9, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet, R. Karst et hydrocarbures. Rospo mare: Un paleokarst pétrolier exploité en mer Adriatique (Italie). Geochronique 2000, 76, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geldern, R.; Hayashi, T.; Böttcher, M.E.; Mottl, M.J.; Barth, J.A.; Stadler, S. Stable isotope geochemistry of pore waters and marine sediments from the New Jersey shelf: Methane formation and fluid origin. Geosphere 2013, 9, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, T.H.; Ruden, F.; Mangset, L.E. Submarine groundwater: A new concept for the supply of drinking water. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Micallef, A. Could offshore groundwater rescue coastal cities? Nature 2019, 574, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J. Gravitational Systems of Groundwater Flow: Theory, Evaluation, Utilization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, W.J.; Summa, L.L. Paleohydrology of the Gulf of Mexico basin. Am. J. Sci. 1991, 291, 109–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, E.C.; Cathles III, L.M.; Davis, B.W. Predicting depths of gypsum dehydration in evaporitic sedimentary basins. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1993, 77, 402–413. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørlykke, K. Fluid flow in sedimentary basins. Sediment. Geol. 1993, 86, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colten-Bradley, V.A. Role of pressure in smectite dehydration—Effects on geopressure and smectite-to-illite transformation. AAPG Bull. 1987, 71, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, M.; Gieskes, J. Opal-a to opal-ct transformation: A kinetic study. In Developments in Sedimentology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 36, pp. 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, R.J.; Cartwright, J. A fossilized opal a to opal c/t transformation on the northeast atlantic margin: Support for a significantly elevated palaeogeothermal gradient during the Neogene? Basin Res. 2002, 14, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Mountjoy, J.; Schwalenberg, K.; Jegen, M.; Weymer, B.; Woelz, S.; Gerring, P.; Luebben, N.; Spatola, D.; Cunarro Otero, D. How Offshore Groundwater Shapes the Seafloor. Eos Earth Space Sci. News 2018, 99, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micallef, A.; Person, M.; Haroon, A.; Weymer, B.; Jegen, M.; Schwalenberg, K.; Faghih, K.; Duan, S.; Cohen, D.; Mountjoy, J.; et al. 3d characterisation and quantification of an offshore freshened groundwater system in the Canterbury Bight. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrar, W.; Williams, A.; Barker, J.; Van Camp, M. Modelling scenarios for the emplacement of palaeowaters in aquifer systems. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2001, 189, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebritsen, S.; Sanford, W.; Neuzil, C. Groundwater in Geological Processes; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; p. 562. [Google Scholar]
- Bratton, J.F. The three scales of submarine groundwater flow and discharge across passive continental margins. J. Geol. 2010, 118, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destouni, G.; Prieto, C. On the possibility for generic modeling of submarine groundwater discharge. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Shaw, T.J. Chemical signals from submarine fluid advection onto the continental shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 21543–21552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosdorf, N.; Oehler, T. Societal use of fresh submarine groundwater discharge: An overlooked water resource. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Cable, J.E.; Turner, J.V. Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, P.L.; Moore, W.S.; Church, T.M. Submarine groundwater discharge. Nature 1996, 382, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W. Palaeowaters in european coastal aquifers—The goals and main conclusions of the Palaeaux project. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2001, 189, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffer, D. Hydrostratigraphy as a control on subduction zone mechanics through its effects on drainage: An example from the Nankai margin, sw Japan. Geofluids 2010, 10, 114–131. [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Milne, C. Palaeowaters in Coastal Europe: Evolution of Groundwater Since the Late Pleistocene; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.R. Interpretation of Three-Dimensional Seismic Data, 6th ed.; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, D.; Myers, K. Sequence Stratigraphy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, P.M. Part 7. Geophysical Methods. In Development Geology Reference Manual; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1992; Volume ME 10, p. 357. [Google Scholar]
- Micallef, A. Marine geomorphology: Geomorphological mapping and the study of submarine landslides. In Developments in Earth Surface Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 15, pp. 377–395. [Google Scholar]
- Posamentier, H.W.; Davies, R.J.; Cartwright, J.A.; Wood, L.J. Seismic Geomorphology—An Overview; Geological Society London Special Publications: London, UK, 2007; Volume 277, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Catuneanu, O. Sequence Stratigraphy: Guidelines for a Standard Methodology. In Stratigraphy Timescales; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Catuneanu, O.; Abreu, V.; Bhattacharya, J.; Blum, M.; Dalrymple, R.; Eriksson, P.; Fielding, C.R.; Fisher, W.; Galloway, W.; Gibling, M. Towards the Standardization of Sequence Stratigraphy. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 92, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland-Hansen, W.; Martinsen, O.J. Shoreline trajectories and sequences: Description of variable depositional-dip scenarios. J. Sediment. Res. 1996, 66, 670–688. [Google Scholar]
- Embry, A.; Johannessen, E. T–r sequence stratigraphy, facies analysis and reservoir distribution in the uppermost Triassic–lower Jurassic succession, western Sverdrup basin, arctic Canada. In Norwegian Petroleum Society Special Publications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 121–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, R.J.; Pape, J.; Roberts, D.G. Depositional Sequence Mapping as a Technique to Establish Tectonic and Stratigraphic Framework and Evaluate Hydrocarbon Potential on a Passive Continental Margin: Chapter 5; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, J.; Abreu, V. Sequence stratigraphy hierarchy and the accommodation succession method. Geology 2009, 37, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A. A Guide to Stratigraphic Classification, Terminology and Procedure; IUGS: Boulder, CO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Sarg, J.F. Carbonate Sequence Stratigraphy: Recent Developments and Applications, AAPG Memoir 57; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Pomar, L. High-resolution sequence stratigraphy in prograding Miocene carbonates: Application to seismic interpretation. Carbonate Seq. Stratigr. Recent Dev. Appl. AAPG Mem. 1993, 57, 389–407. [Google Scholar]
- Sarg, J. Carbonate Sequence Stratigraphy; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S. River response to baselevel change: Implications for sequence stratigraphy. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuneanu, O.; Sweet, A.R.; Miall, A.D. Concept and styles of reciprocal stratigraphies: Western Canada foreland system. Terra Nova Oxford 1999, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madof, A.S.; Christie-Blick, N.; Anders, M.H. Tectonically controlled nearshore deposition: Cozzette sandstone, Book Cliffs, Colorado, USA. J. Sediment. Res. 2015, 85, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Minervini, M.; Ghielmi, M. Drowning unconformities on hinged clastic shelves. Geology 2018, 46, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madof, A.S.; Harris, A.D.; Connell, S.D. Nearshore along-strike variability: Is the concept of the systems tract unhinged? Geology 2016, 44, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Catuneanu, O. Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schlager, W. Type 3 sequence boundaries. Spec. Publ. Soc. Econ. Paleontol. Mineral. 1999, 63, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vail, P. The stratigraphic signatures of tectonics, eustacy and sedimentology—An overview. In Cycles and Events in Stratigraphy; Einsele, G., Ricken, W., Seilacher, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germay; London, UK, 1991; pp. 617–659. [Google Scholar]
- Ridente, D.; Trincardi, F. Eustatic and tectonic control on deposition and lateral variability of Quaternary regressive sequences in the Adriatic basin (Italy). Mar. Geol. 2002, 184, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, B.U.; Hardenbol, J.; Vail, P.R. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic. Science 1987, 235, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavko, G.; Mukerji, T.; Dvorkin, J. The Rock Physics Handbook: Tools for Seismic Analysis in Porous Media; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Avseth, P.; Mukerji, T.; Mavko, G. Quantitative Seismic Interpretation: Applying Rock Physics Tools to Reduce Interpretation Risk; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Reiche, S.; Riedel, M.; Clauser, C. The fate of submarine fresh groundwater reservoirs at the New Jersey shelf, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2673–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Browning, J.V.; Mountain, G.S.; Bassetti, M.A.; Monteverde, D.; Katz, M.E.; Inwood, J.; Lofi, J.; Proust, J.-N. Sequence boundaries are impedance contrasts: Core-seismic-log integration of Oligocene–Miocene sequences, New Jersey shallow shelf. Geosphere 2013, 9, 1257–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.L.; Lizarralde, D. Geophysical evidence for karst formation associated with offshore groundwater transport: An example from North Carolina. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Pezard, P.; Bouchette, F.; Raynal, O.; Sabatier, P.; Denchik, N.; Levannier, A.; Dezileau, L.; Certain, R. Integrated onshore-offshore investigation of a Mediterranean layered coastal aquifer. Groundwater 2013, 51, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, A.E.; Evans, R.L.; Lizarralde, D. The role of paleochannels in groundwater/seawater exchange. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, L.; Paull, C. Submarine karst belt rimming the continental slope in the Straits of Florida. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2000, 20, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofi, J.; Berné, S.; Tesson, M.; Seranne, M.; Pezard, P. Giant solution-subsidence structure in the western Mediterranean related to deep substratum dissolution. Terra Nova 2012, 24, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, P.; Reich, C.; Spechler, R.; Kindinger, J.; Moore, W. Using multiple geochemical tracers to characterize the hydrogeology of the submarine spring off Crescent Beach, Florida. Chem. Geol. 2001, 179, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Judd, A.G. Seabed Pockmarks and Seepages: Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment; Graham & Trotman: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, A.G.; Hovland, M. Seabed Fluid Flow: The Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Micallef, A.; Foglini, F.; Le Bas, T.; Angeletti, L.; Maselli, V.; Pasuto, A.; Taviani, M. The submerged paleolandscape of the maltese islands: Morphology, evolution and relation to Quaternary environmental change. Mar. Geol. 2013, 335, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, L.A.; Paull, C.K.; Hobson, B. Genesis of a submarine sinkhole without subaerial exposure: Straits of Florida. Geology 1995, 23, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, L. Mixing of sea water with calcium carbonate ground water. Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 1975, 142, 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- Runnells, D.D. Diagenesis, chemical sediments and the mixing of natural waters. J. Sediment. Res. 1969, 39, 1188–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Micallef, A.; Georgiopoulou, A.; Bas, T.P.L.; Mountjoy, J.J.; Huvenne, V.A.; Iacono, C.L. Processes on the Precipice: Seafloor Dynamics Across the Upper Malta-Sicily Escarpment. In Proceedings of the CIESM 2013, Marseille, France, 28 October–1 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Audra, P.; Mocochain, L.; Camus, H.; Gilli, É.; Clauzon, G.; Bigot, J.-Y. The effect of the Messinian deep stage on karst development around the Mediterranean sea. Examples from southern France. Geodin. Acta 2004, 17, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalera, T.; Gilli, E.; Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Marmier, N. Mechanism of salt contamination of karstic springs related to the messinian deep stage. The speleological model of Port Miou (France). Geodin. Acta 2010, 23, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, É.; Audra, P. Les lithophages Pliocènes de la Fontaine de Vaucluse (Vaucluse, France). Un argument pour une phase Messinienne dans la genèse du plus grand karst noyé de France. C. R. Geosci. 2004, 336, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocochain, L.; Audra, P.; Bigot, J.-Y. Base level rise and per ascensum model of speleogenesis (pams). Interpretation of deep phreatic karsts, vauclusian springs and chimney-shafts. Bull. Société Géologique Fr. 2011, 182, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hovland, M. Geomorphological, geophysical and geochemical evidence of fluid flow through the seabed. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 78, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, D. Hydrocarbon-Induced Alteration of Soils and Sediments; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, A.; Loher, M.; Bouffard, D.; Moernaut, J.; Hellmich, F.; Anselmetti, F.S.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Hilbe, M.; Kopf, A.; Lilley, M.D. Giant lacustrine pockmarks with subaqueous groundwater discharge and subsurface sediment mobilization. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, J.C.; Poag, C.W.; Valent, P.C.; Miller, R.E.; Schultz, D.M.; Manhe, F.T.; Kohout, F.A.; Bothner, M.H.; Sangi, D.A. US Geological Survey core drilling on the Atlantic shelf. Science 1979, 206, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, F.; Hathaway, J.; Folger, D.; Bothner, M.; Walker, E.; Delaney, D.; Frimpter, M.; Weed, E.; Rhodehamel, E. Fresh ground water stored in aquifers under the continental shelf: Implications from a deep test, Nantucket island, Massachusetts. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1977, 13, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, N.M.; Geraghty, J.J. Geology and Ground-Water Conditions in Southern Nassau and Southeastern Queens Counties, Long Island, New York; USGPO: Washington, DC, USA, 1963.
- Person, M.; Dugan, B.; Swenson, J.B.; Urbano, L.; Stott, C.; Taylor, J.; Willett, M. Pleistocene hydrogeology of the Atlantic continental shelf, New England. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2003, 115, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, M.; Taylor, J.Z.; Dingman, S.L. Sharp interface models of salt water intrusion and wellhead delineation on Nantucket Island, Massachusetts. Groundwater 1998, 36, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolensky, D.A.; Buxton, H.T.; Shernoff, P.K. Hydrologic Framework of Long Island, New York; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Kominz, M.A.; Browning, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Mountain, G.S.; Katz, M.E.; Sugarman, P.J.; Cramer, B.S.; Christie-Blick, N.; Pekar, S.F. The Phanerozoic Record of Global Sea-Level Change. Science 2005, 310, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Mountain, G.S.; Wright, J.D.; Browning, J.V. A 180-million-year record of sea level and ice volume variations from continental margin and Deep-Sea isotopic records. Oceanography 2011, 24, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manheim, F.; Hall, R. Deep Evaporitic Strata off New York and New Jersey—Evidence from Interstitial Water Chemistry of Drill Cores. J. Res. 1976, 4, 697–702. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, G.J.; Storck, D.A.; Paulachok, G.N. Records of Wells, Exploratory Boreholes and Ground-Water Quality, Atlantic County and Vicinity, New Jersey; 2331-1258; US Geological Survey; Books and Open-File Reports Section [distributor]: Reston, VA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, Z.; Keller, E.A.; Defawe, R.M. Pore-Water Quality in the Clay-Silt Confining Units of the Lower Miocene Kirkwood Formation and Hypothetical Effects on Water Quality in the Atlantic City 800-Foot Sand, Northeastern Cape May County, New Jersey; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Sugarman, P.J.; Miller, K.G.; Browning, J.V.; Kulpecz, A.A.; McLaughlin, P.P.; Monteverde, D.H. Hydrostratigraphy of the New Jersey coastal plain: Sequences and facies predict continuity of aquifers and confining units. Stratigraphy 2005, 2, 259–275. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, C.; Key, K.; Evans, R.L. Aquifer systems extending far offshore on the US Atlantic Margin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, H.; Groen, J. Offshore continuation of coastal groundwater systems; predictions using sharp-interface approximations and variable-density flow modelling. J. Hydrol. 2001, 246, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M.; Reiche, S.; Aßhoff, K.; Buske, S. Seismic depth imaging of sequence boundaries beneath the New Jersey shelf. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2019, 40, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, C.; Blanc-Valleron, M.-M.; Boudouma, O.; Lofi, J. Carbonate and silicate cementation of siliciclastic sediments of the New Jersey shelf (IODP expedition 313): Relation with organic matter diagenesis and submarine groundwater discharge. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2017, 37, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guswa, J.H.; LeBlanc, D.R. Digital Models of Ground-Water Flow in the Cape Cod Aquifer System, Massachusetts; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1985.
- Hall, R.E.; Poppe, L.J.; Ferrebee, W.M. A Stratigraphic Test Well, Martha’s Vineyard, Massachusetts: Description of Pleistocene to Upper Cretaceous Sediments Recovered from 262 Meters of Test Coring; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1979.
- Mulligan, A.; Uchupi, E. New interpretation of glacial history of Cape Cod may have important implications for groundwater contaminant transport. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2003, 84, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, M.; Marksamer, A.; Dugan, B.; Sauer, P.E.; Brown, K.; Bish, D.; Licht, K.J.; Willett, M. Use of a vertical δ 18 o profile to constrain hydraulic properties and recharge rates across a glacio-lacustrine unit, Nantucket Island, Massachusetts, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, M.; McIntosh, J.; Bense, V.; Remenda, V. Pleistocene hydrology of North America: The role of ice sheets in reorganizing groundwater flow systems. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folger, D.W.; Hathaway, J.; Christopher, R.; Valentine, P.; Poag, C. Stratigraphic Test Well, Nantucket Island, Massachusetts; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1978; pp. 2330–5703.
- Denton, G.H.; Hughes, T.J. The Last Great Ice Sheets; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Christie-Blick, N.; Austin, J.A., Jr.; Party, S.S. Introduction: Oligocene to Pleistocene Eustatic Change at the New Jersey Continental Margin—A Test of Sequence Stratigraphy; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schlee, J.; Fritsch, J. Seismic Stratigraphy of the Georges Bank Basin Complex, Offshore New England: Rifted Margins: Field Investigations of Margin Structure and Stratigraphy; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, J.; Person, M.; Dugan, B.; Cohen, D.; Lizarralde, D.; Gable, C. Influence of late Pleistocene glaciations on the hydrogeology of the continental shelf offshore Massachusetts, USA. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2014, 15, 4651–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.; Dugan, B.; Lizarralde, D.; Person, M.; DeFoor, W.; Miller, N. Geophysical evidence of a late Pleistocene glaciation and paleo-ice stream on the Atlantic continental shelf offshore Massachusetts, USA. Mar. Geol. 2012, 303, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, J.; Flemings, P.B.; Christie-Blick, N.; Mountain, G.S.; Austin, J., Jr.; Hesselbo, S. Late Miocene to pleistocene sequences at the New Jersey outer continental shelf (ODP leg 174a, sites 1071 and 1072). Sediment. Geol. 2000, 134, 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marksamer, A. Integrating Geophysical, Hydrochemical and Hydrologic Data to Understand the Freshwater Resources on Nantucket Island, Massachusetts; Indiana University: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cable, J.E.; Burnett, W.C.; Chanton, J.P.; Weatherly, G.L. Estimating groundwater discharge into the northeastern Gulf of Mexico using radon-222. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 144, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.H. The saltwater-freshwater interface in the tertiary limestone aquifer, southeast Atlantic outer-continental shelf of the USA. J. Hydrol. 1983, 61, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leve, G.W. Relation of concealed faults to water quality and the formation of solution features in the Floridan aquifer, northeastern Florida, USA. J. Hydrol. 1983, 61, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringfield, V.T. Artesian Water in Tertiary Limestone in the Southeastern States; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1966.
- Meisburger, E.P.; Field, M.E. Neogene sediments of atlantic inner continental shelf off northern Florida. AAPG Bull. 1976, 60, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Manheim, F.T.; Krantz, D.E.; Bratton, J.F. Studying ground water under Delmarva Coastal Bays using electrical resistivity. Groundwater 2004, 42, 1052–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenau, J.C.; Faulkner, G.L.; Hendry, C.W., Jr.; Hull, R.W. Springs of Florida; Florida Department of Natural Resources: Bureau of Geology: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1977; Volume xxvii, p. 461. [Google Scholar]
- Meisler, H.; Leahy, P.P.; Knobel, L.L. Effect of Eustatic Sea-Level Changes on Saltwater-Freshwater Relations in the Northern Atlantic Coastal Plain; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; Volume 2255.
- Land, L. Processes and Manifestations of Fluid Exchange within Passive Continental Margins; University of North Carolina: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalowicz, M. Karst at depth below the sea level around the Mediterranean due to the Messinian crisis of salinity. Hydrogeological consequences and issues. Geol. Belg. 2014, 17, 1374–8505. [Google Scholar]
- Garing, C.; Luquot, L.; Pezard, P.; Gouze, P. Geochemical investigations of saltwater intrusion into the coastal carbonate aquifer of Mallorca, Spain. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunay, B.; Dörfliger, N.; Duvail, C.; Grelot, F.; Le Strat, P.; Montginoul, M.; Rinaudo, J.-D. A multidisciplinary approach for assessing the risk of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: The case of the Roussillon basin (France). Aquifer Syst. Manag. Darcy’s Leg. World Impending Water Short. Sel. Papers Hydrogeol. 2007, 10, 459. [Google Scholar]
- Duvail, C.; Gorini, C.; Lofi, J.; Le Strat, P.; Clauzon, G.; dos Reis, A.T. Correlation between onshore and offshore Pliocene–Quaternary systems tracts below the Roussillon basin (eastern Pyrenees, France). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yaouti, F.; El Mandour, A.; Khattach, D.; Benavente, J.; Kaufmann, O. Salinization processes in the unconfined aquifer of Bou-areg (ne Morocco): A geostatistical, geochemical and tomographic study. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Aunay, B.; Ladouche, B.; Bailly-Comte, V.; Guerrot, C.; Flehoc, C.; Pezard, P.; Lofi, J.; Dörfliger, N. Coastal groundwater salinization: Focus on the vertical variability in a multi-layered aquifer through a multi-isotope fingerprinting (roussillon basin, France). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodio, E. Coastal aquifers of europe: An overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, R.; Flecker, R.; Valdes, P.; Lunt, D.; Markwick, P. The Mediterranean hydrologic budget from a late miocene global climate simulation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 251, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montety, V.; Radakovitch, O.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Blavoux, B.; Hermitte, D.; Valles, V. Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in a confined coastal aquifer: Case of the Rhône delta (southern France). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruden, F. The discovery of a Neogene coastal aquifer in coastal Tanzania. Inst. Geol. Min. Esp. Coast. Aquifers Chall. Solut. 2007, 1, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, H.; Ruden, F.; Gamache, M. Exploration and hydrogeological assessment of a deep coastal aquifer system in Tanzania. In Proceedings of the Congress of the International Association of Hydrogeologists, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruden, F. Freshwater entrapment in offshore Zanzibar basins. In International Symposium on Efficient Groundwater Resources Management; IGS-TH: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe, S.A.; Horton, B.P. Holocene sea-level changes in the Indo-Pacific. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2005, 25, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voris, H.K. Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in southeast Asia: Shorelines, river systems and time durations. J. Biogeogr. 2000, 27, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, H.; Ruden, F. Use of exploration data for the assessment of deep groundwater resources in coastal Tanzania. In Irish Groundwater Newsletter; Geological Survey Ireland: Dublin, Ireland, 2009; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, G.H.; Naish, T.R. Facies development and sequence architecture of a late Quaternary fluvial-marine transition, Canterbury plains and shelf, New Zealand: Implications for forced regressive deposits. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 158, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Fulthorpe, C.S. Controls on sequence stratigraphy of a middle Miocene–Holocene, current-swept, passive margin: Offshore Canterbury basin, New Zealand. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2004, 116, 1345–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.M.; Fulthorpe, C.S.; Hoyanagi, K.; Blum, P.; Mountain, G.S.; Miller, K.G. The sedimentary imprint of Pleistocene glacio-eustasy: Implications for global correlations of seismic sequences. Geosphere 2018, 14, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor, T.; Jaeger, J.M.; Marsaglia, K.M.; Browne, G.H. Evaluation of the relative roles of global versus local sedimentary controls on middle to late Pleistocene formation of continental margin strata, Canterbury basin, New Zealand. Sedimentology 2015, 62, 1118–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A. Seismic Attributes in Your Facies: Canadian Society of Exploration Geophysicists Recorder 26. 2001. Available online: https://csegrecorder.com/articles/view/seismic-attributes-in-your-facies (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Fulthorpe, C.; Hoyanagi, K.; Blum, P. Expedition IO. IODP expedition 317: Exploring the record of sea-level change off New Zealand. Sci. Drill. 2011, 12, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.; Michael, K. Impact of multi-purpose aquifer utilisation on a variable-density groundwater flow system in the Gippsland basin, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, G.Y. The Hydrogeology of the Gippsland Basin and Its Role in the Genesis and Accumulation of Petroleum. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Earth Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 2002. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11343/39277 (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Gibson-Poole, C.; Svendsen, L.; Underschultz, J.; Watson, M.; Ennis-King, J.; Van Ruth, P.; Nelson, E.; Daniel, R.; Cinar, Y. Site characterisation of a basin-scale CO2 geological storage system: Gippsland basin, southeast Australia. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divko, L.G.; O’Brien, G.; Harrison, M.; Hamilton, J. Evaluation of the regional top seal in the Gippsland basin: Implications for geological carbon storage and hydrocarbon prospectivity. APPEA J. 2010, 50, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchin, M.; Catuneanu, O. High-resolution sequence stratigraphy of clastic shelves i: Units and bounding surfaces. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 39, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.J.; Shi, L.; Kuang, X.; Lee, C.M.; Yim, W.W.-S.; Yang, S. Reconstructed chloride concentration profiles below the seabed in Hong Kong (China) and their implications for offshore groundwater resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, H.T.; Jiao, J.J.; Chan, L.S. A preliminary study on the offshore stratigraphy in Hong Kong and its hydrogeological implications. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, H.T.; Jiao, J.J. Hydrochemical reactions and origin of offshore relatively fresh pore water from core samples in Hong Kong. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.K. Evaporites: Sediments, Resources and Hydrocarbons: Sediments, Resources and Hydrocarbons; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.K. Salt usually seals but sometimes leaks: Implications for mine and cavern stability in the short and long term. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 165, 302–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørlykke, K.; Gran, K. Salinity variations in North Sea formation waters: Implications for large-scale fluid movements. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1994, 11, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.; Velstra, J.; Meesters, A. Salinization processes in paleowaters in coastal sediments of Suriname: Evidence from δ37cl analysis and diffusion modelling. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, C.M. Inverse hydrologic analysis of the distribution and origin of Gulf Coast-type geopressured zones. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 6535–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, E.C. Applied Hydrodynamics in Petroleum Exploration; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D. The Millennium Atlas: Petroleum Geology of the Central and Northern North Sea; A Project of the Geological Society of London, the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland and the Norwegian Petroleum Society; Geological Society: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, P.; Sorriaux, P.; Soudet, H.-J. Rospo mare (Adriatique): Un paléokarst pétrolier du domaine méditerranéen. Karstologia 1993, 21, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournillon, A.; Bellentani, G.; Moccia, A.; Jumeaucourt, C.; Terdich, P.; Siliprandi, F.; Peruzzo, F. Characterization of a paleokarstic oil field (Rospo Mare, Italy): Sedimentologic and diagenetic outcomes and their integration in reservoir simulation. In Eurokarst 2016, Neuchâtel; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertoni, C.; Lofi, J.; Micallef, A.; Moe, H. Seismic Reflection Methods in Offshore Groundwater Research. Geosciences 2020, 10, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10080299
Bertoni C, Lofi J, Micallef A, Moe H. Seismic Reflection Methods in Offshore Groundwater Research. Geosciences. 2020; 10(8):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10080299
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertoni, Claudia, Johanna Lofi, Aaron Micallef, and Henning Moe. 2020. "Seismic Reflection Methods in Offshore Groundwater Research" Geosciences 10, no. 8: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10080299
APA StyleBertoni, C., Lofi, J., Micallef, A., & Moe, H. (2020). Seismic Reflection Methods in Offshore Groundwater Research. Geosciences, 10(8), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10080299




