Revisiting the Paleo Elbe Valley: Reconstruction of the Holocene, Sedimentary Development on Basis of High-Resolution Grain Size Data and Shallow Seismics
Abstract
1. Introduction
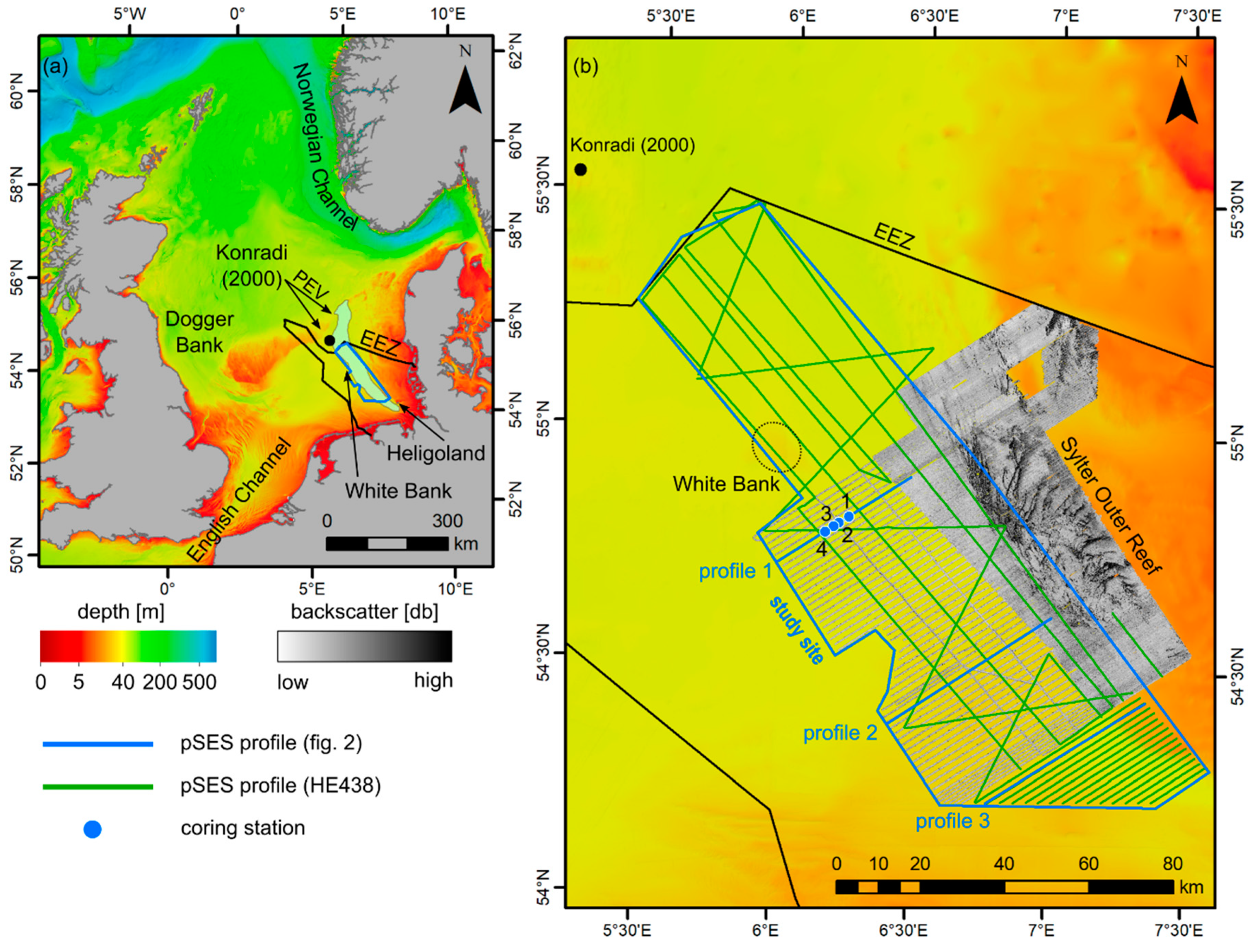
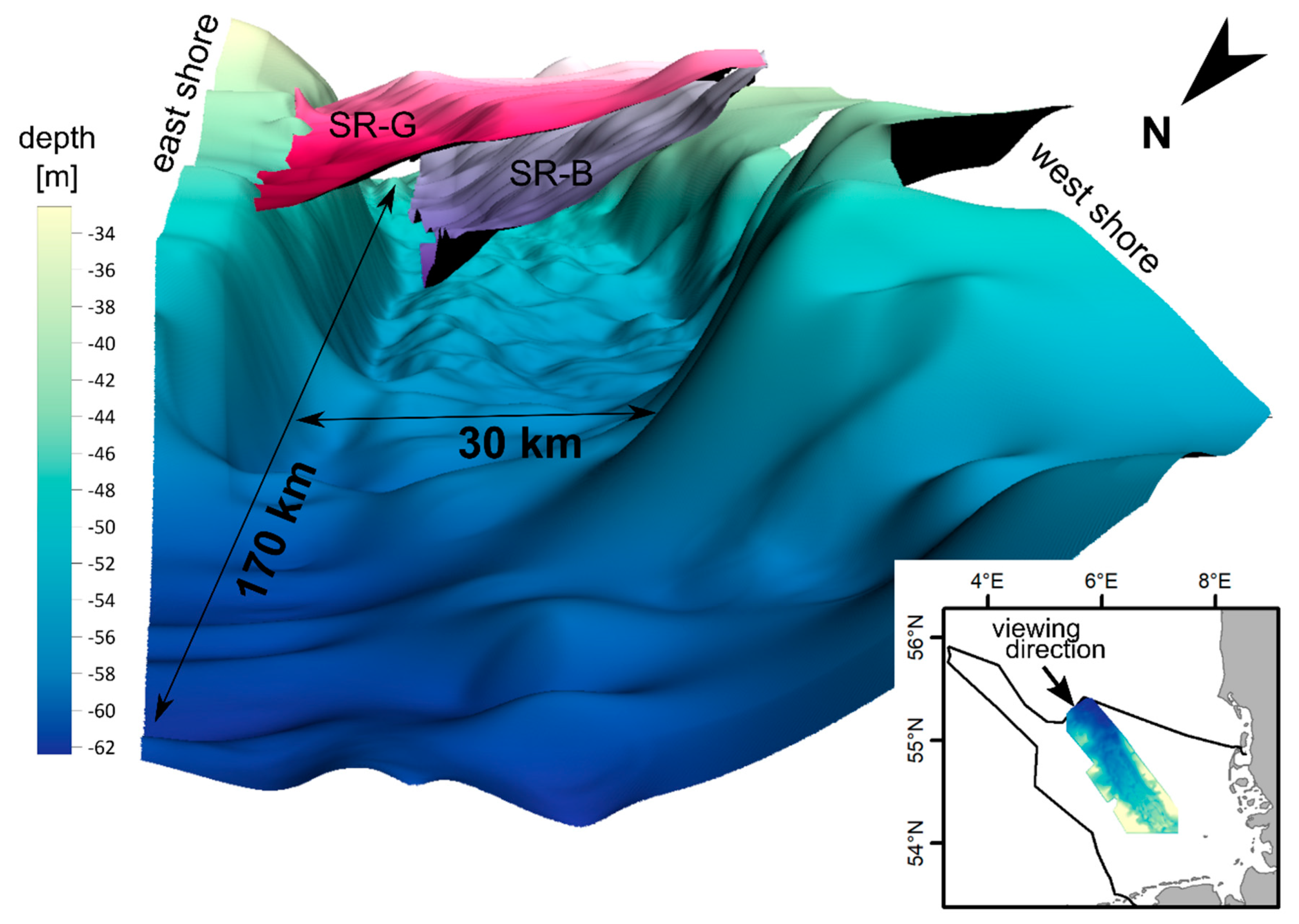
2. Study Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Shallow Seismic Data
3.2. Coring and Grain-Size Analysis
3.3. Age Determinations
4. Results
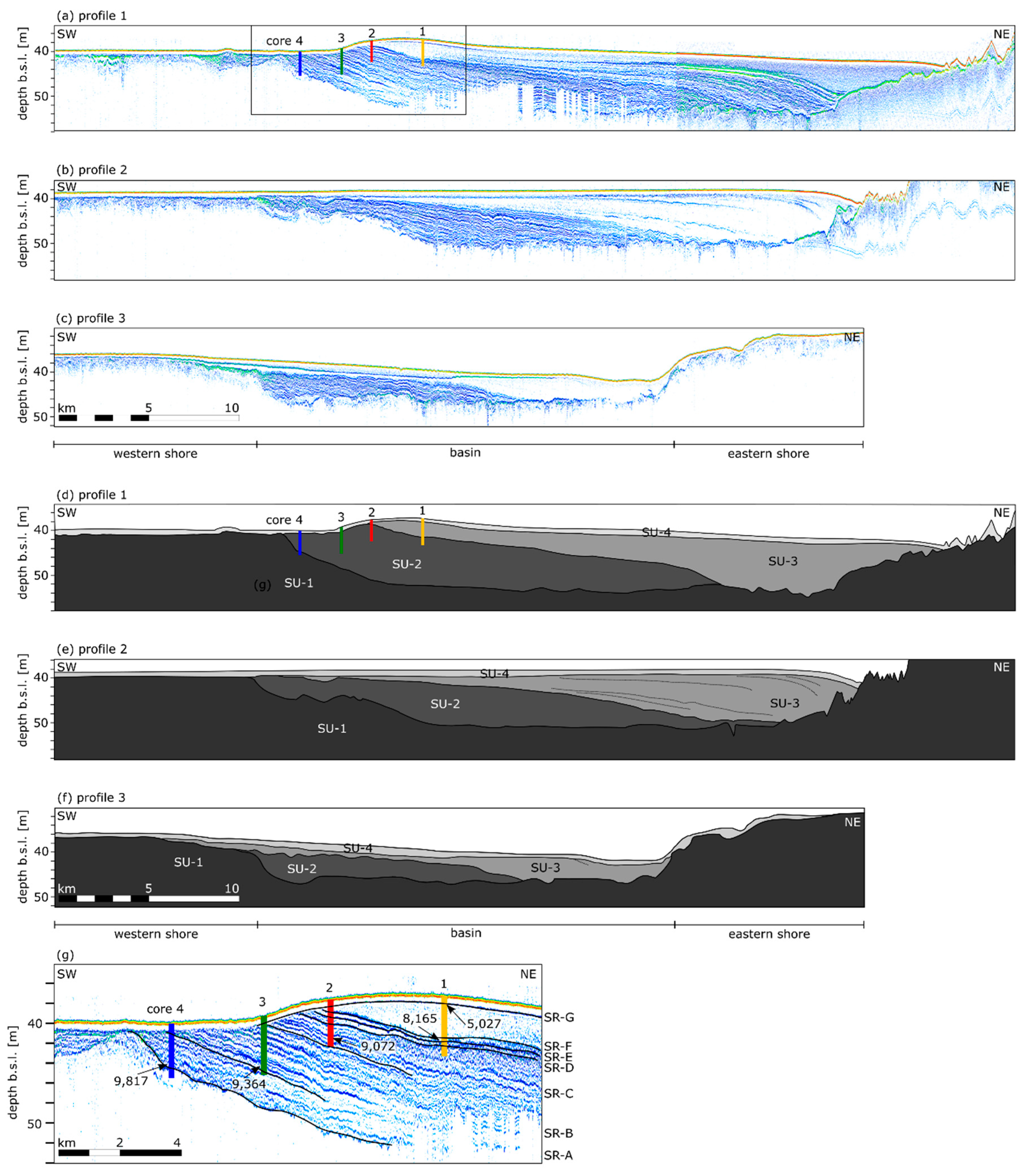
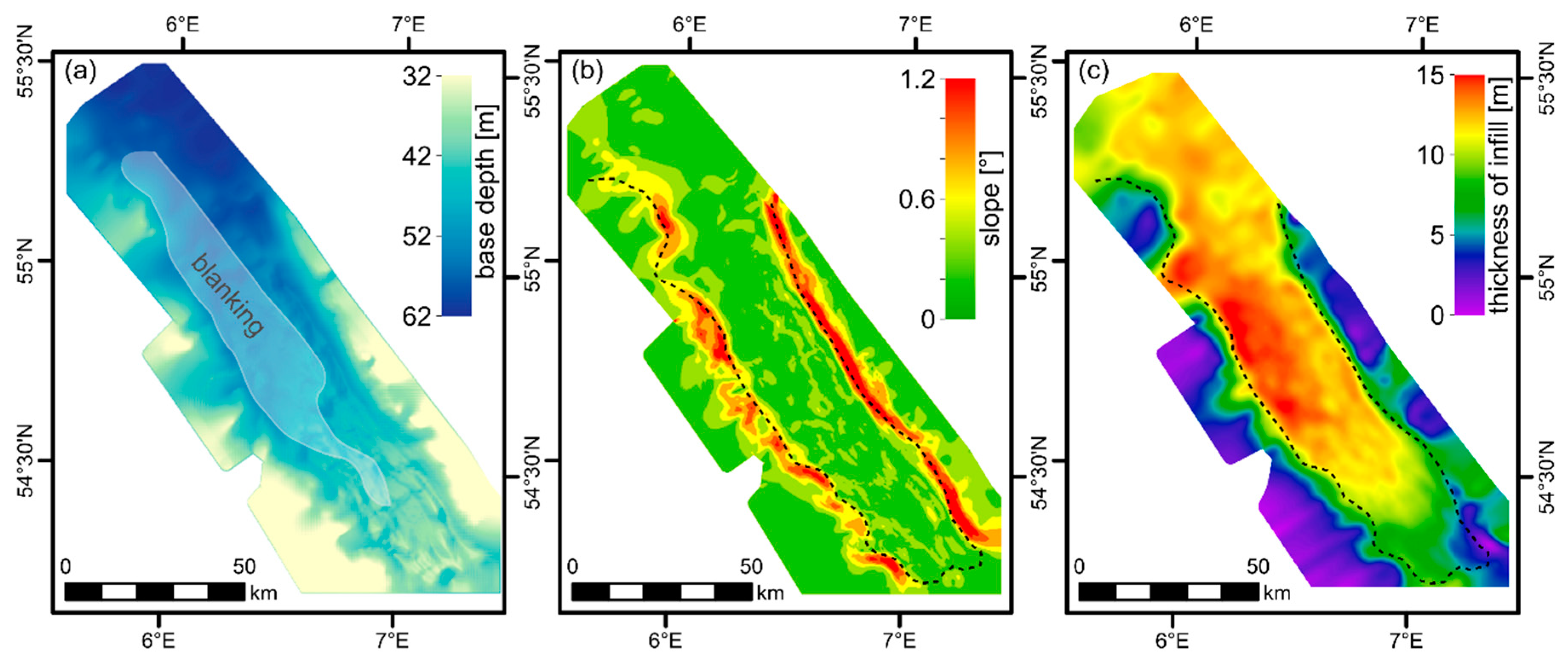
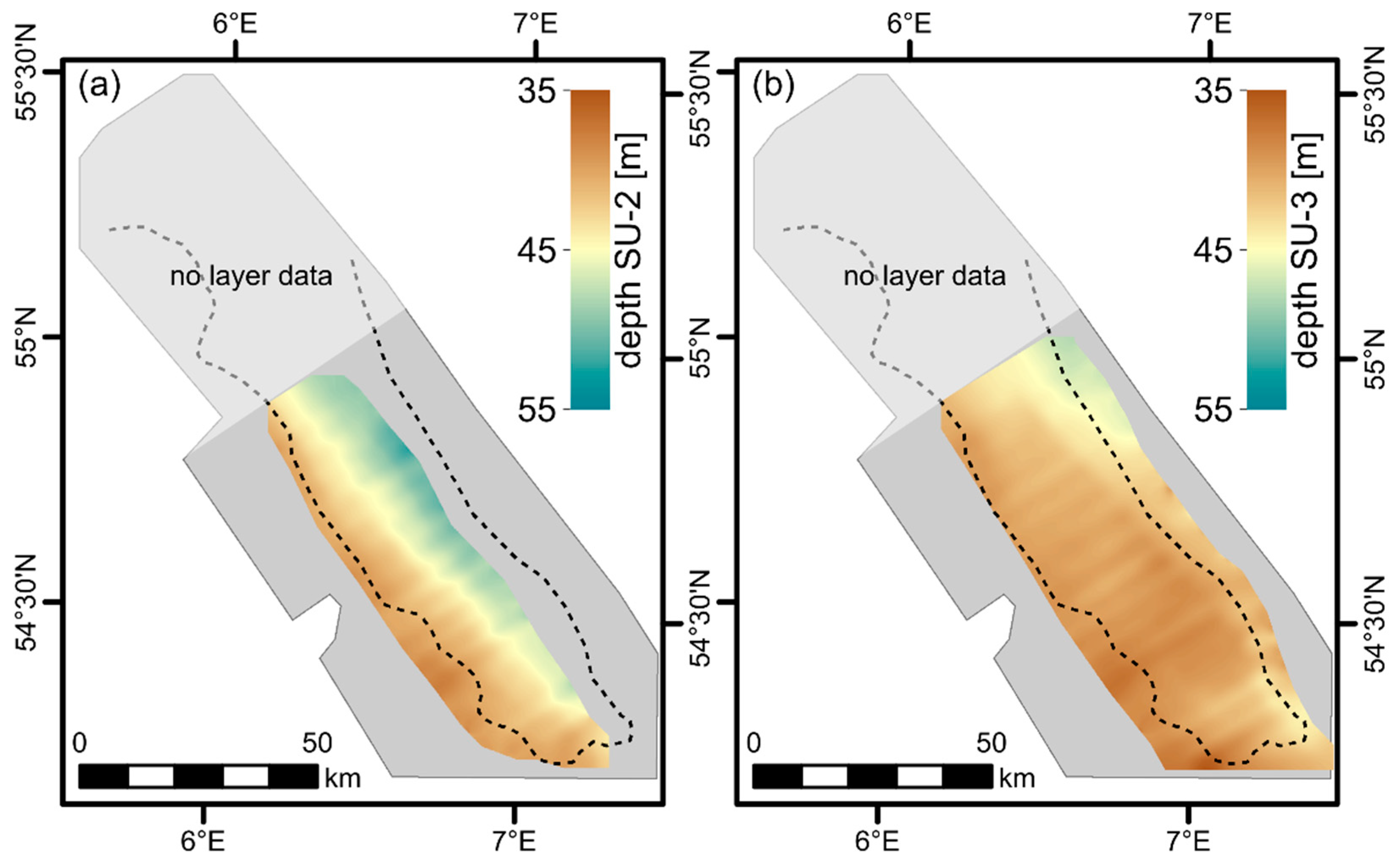
4.1. Seismic Facies Analysis
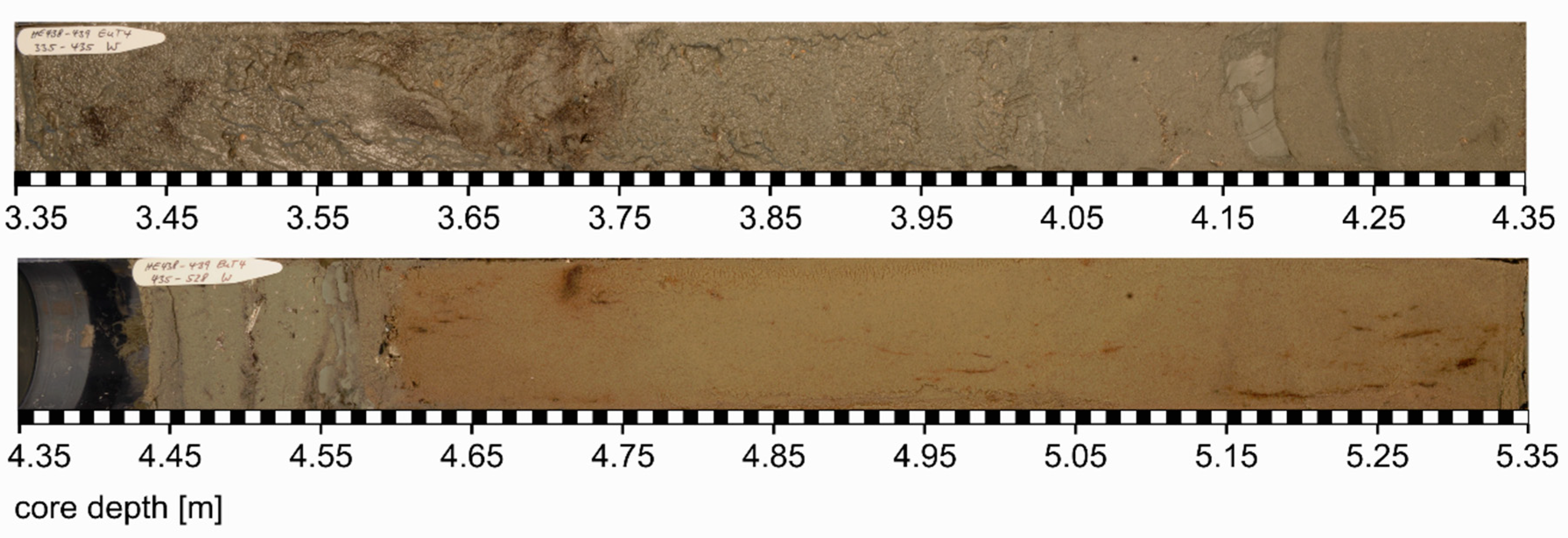
4.2. Macroscopic Core Description
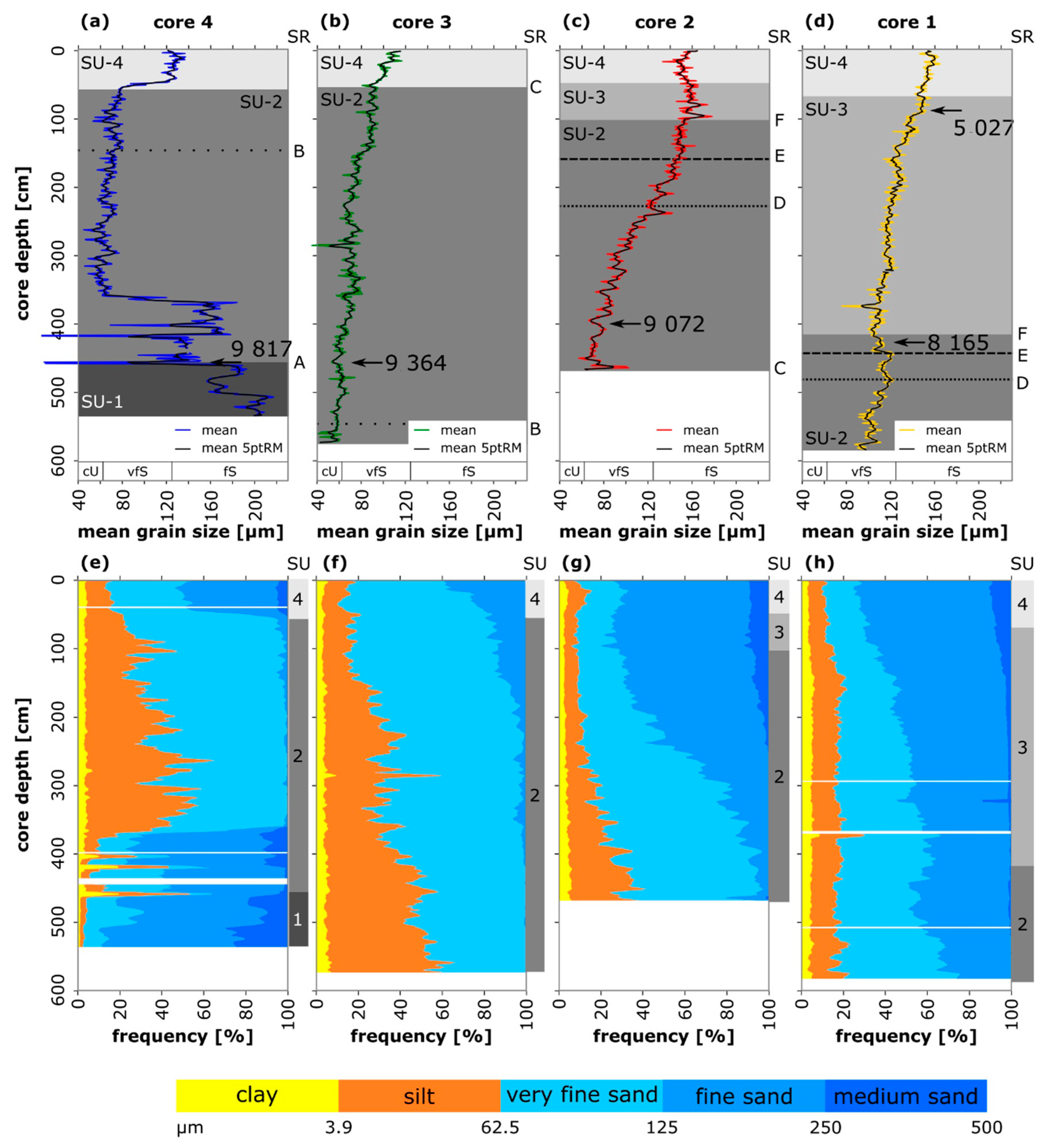
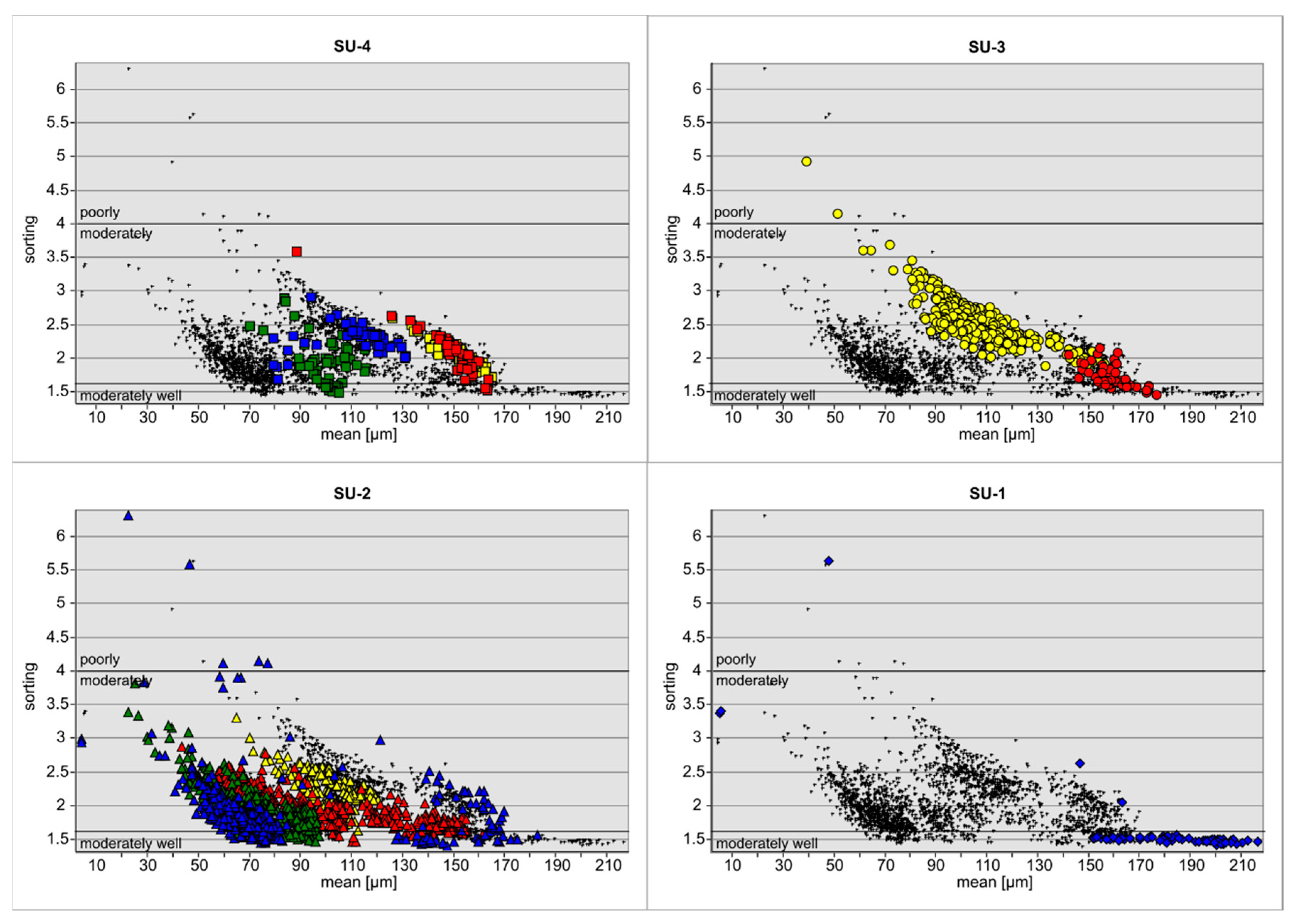
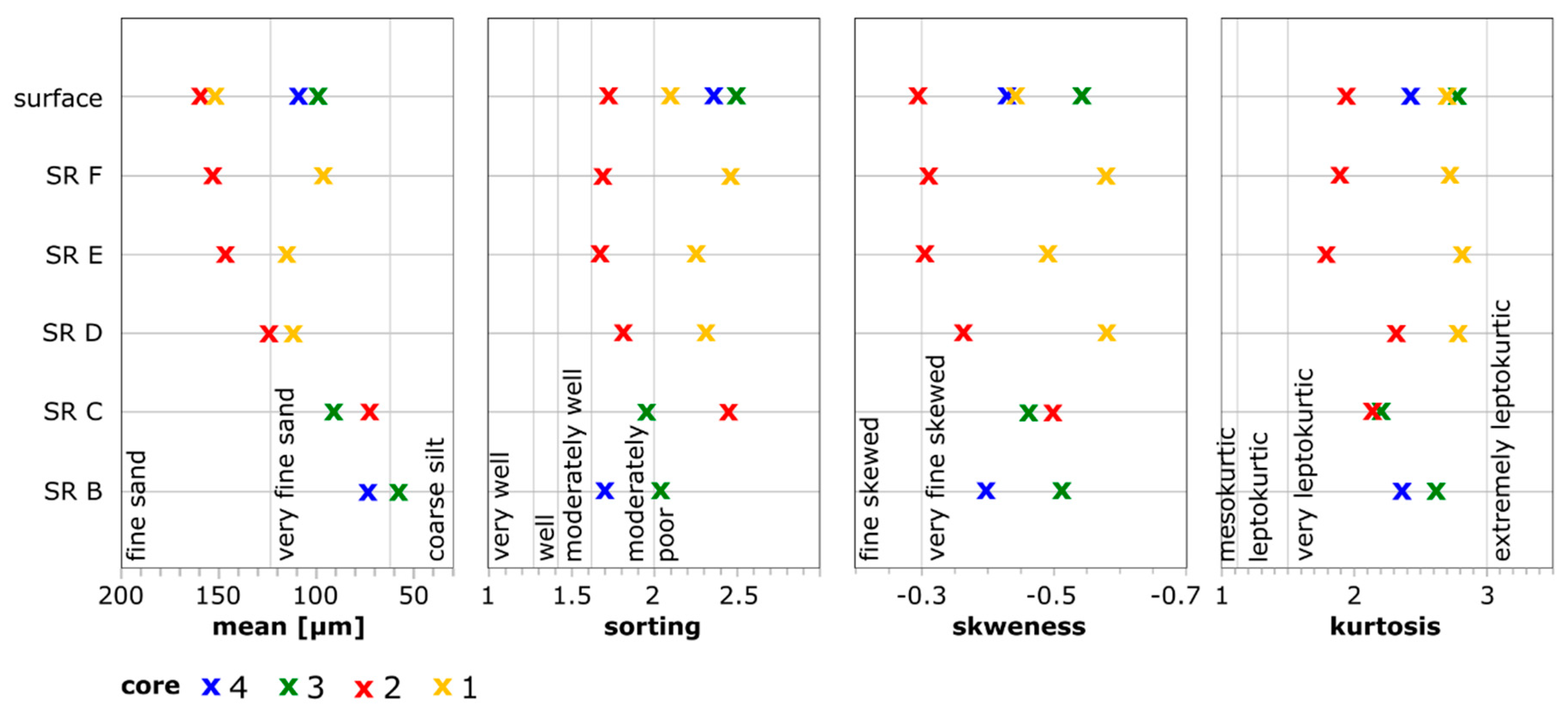
4.3. Grain-Size Analysis
4.4. Age-Depth Model and Sedimentation Rates
5. Discussion
5.1. Valley Geomorphology
5.2. Shallow Marine Conditions
5.3. Wind-/Wave-Driven Sedimentation
5.4. Tide-Driven Sedimentation
5.5. Present Mobile Sediment Layer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pratje, O. Dfie Deutung der Steingründe in der Nordsee als Endmoräne. Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 1951, 4, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, D.A.; Hebbeln, D.; Kreiter, S.; Keil, H.; Bathmann, C.; Ehlers, J.; Mörz, T. An east-west-trending Quaternary tunnel valley in the south-eastern North Sea and its seismic-sedimentological interpretation. J. Quat. Sci. 2012, 27, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrberg, A.; Schwarzer, K.; Unverricht, D.; Omlin, A.; Krastel, S. Architecture of tunnel valleys in the southeastern North Sea: New insights from high-resolution seismic imaging. J. Quat. Sci 2020, 35, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, J.; Grube, A.; Stephan, H.-J.; Wansa, S. Pleistocene Glaciations of North Germany—New Results. In Developments in Quaternary Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 15, pp. 149–162. ISBN 978-0-444-53447-7. [Google Scholar]
- Figge, K. Das Elbe-Urstromtal im Bereich der Deutschen Bucht (Nordsee). Eiszeitalter und Gegenwart 1980, 30, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradi, P.B. Biostratigraphy and environment of the Holocene marine transgression in the Heligoland Channel, North Sea. Bull. Geol. Soc. Denmark 2000, 47, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Özmaral, A. Climatically Controlled Sedimentary Processes on Continental Shelves. Master’s Thesis, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany, April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. The paleo Elbe River: 10.000 yrs after flooding. In Proceedings of the GEOHAB–Marine Geological and Biological Habitat Mapping, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 13–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. High-resolution area-wide sea-floor mapping: The paleo Elbe valley (S North Sea) revisited. In Proceedings of the Geophysical Research Abstracts; EGU—European General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 27 April–2 May 2014; EUG2014-11717-1. Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Diesing, M.; Schwarzer, K. Identifications of submarine hard-bottom substrates in the German North Sea and Baltic EEZ with high-resolution acoustic seafloor imaging. In Progress in Marine Conservation in Europe: Natura 2000 Sites in German Offshore Waters; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2006; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H. Detection of Stones in Marine Habitats Combining Simultaneous Hydroacoustic Surveys. Geosciences 2018, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, D.A.; Romero, O.E.; Mörz, T.; De Pol-Holz, R.; Hebbeln, D. How a river submerges into the sea: A geological record of changing a fluvial to a marine paleoenvironment during early Holocene sea level rise. J. Quat. Sci. 2019, 34, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMODnet Digital Terrain Model for European Sea Regions. 2020. Available online: https://portal.emodnet-bathymetry.eu (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Sturt, F.; Garrow, D.; Bradley, S. New models of North West European Holocene palaeogeography and inundation. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 3963–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.M.; Westley, K.; Erkens, G.; Hijma, M.P.; Weerts, H.J.T. The North Sea. In Submerged Landscapes of the European Continental Shelf; Flemming, N.C., Harff, J., Moura, D., Burgess, A., Bailey, G.N., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 147–186. ISBN 978-1-118-92782-3. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, M.P.; Long, A.J. Holocene coastal evolution and sea-level change on the southern coast of England: A review. J. Quat. Sci. 2003, 18, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, V.; Fitch, S.; Bates, M.; Ware, R.L.; Kinnaird, T.; Gearey, B.; Hill, T.; Telford, R.; Batt, C.; Stern, B.; et al. Multi-Proxy Characterisation of the Storegga Tsunami and Its Impact on the Early Holocene Landscapes of the Southern North Sea. Geosciences 2020, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, S.; Thomson, K.; Gaffney, V. Late Pleistocene and Holocene depositional systems and the palaeogeography of the Dogger Bank, North Sea. Quat. Res. 2005, 64, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behre, K.-E. A new Holocene sea-level curve for the southern North Sea. BOREAS 2007, 36, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, A.; Steffen, H.; Reinhardt, L.; Kaufmann, G. Holocene relative sea-level change, isostatic subsidence and the radial viscosity structure of the mantle of northwest Europe (Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, southern North Sea). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 3249–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeteman, C.; Waller, M.; Kiden, P. Reconstructing middle to late Holocene sea-level change: A methodological review with particular reference to ‘A new Holocene sea-level curve for the southern North Sea’ presented by K.-E. Behre: Reconstructing middle to late Holocene sea-level change. Boreas 2011, 40, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, S.P.; Scourse, J.D.; Uehara, K. Evolution of bed shear stress distribution over the northwest European shelf seas during the last 12,000 years. Ocean. Dyn. 2010, 60, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennan, I.; Lambeck, K.; Flather, R.; Horton, B.; McArthur, J.; Innes, J.; Lloyd, J.; Rutherford, M.; Wingfield, R. Modelling western North Sea palaeogeographies and tidal changes during the Holocene. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000, 166, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, K.; Scourse, J.D.; Horsburgh, K.J.; Lambeck, K.; Purcell, A.P. Tidal evolution of the northwest European shelf seas from the Last Glacial Maximum to the present. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C09025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Molen, J.; de Swart, H.E. Holocene tidal conditions and tide-induced sand transport in the southern North Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 9339–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Molen, J.; de Swart, H.E. Holocene wave conditions and wave-induced sand transport in the southern North Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 1723–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.L.; Neill, S.P.; Scourse, J.D.; Bradley, S.L.; Uehara, K. Sensitivity of palaeotidal models of the northwest European shelf seas to glacial isostatic adjustment since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 151, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.; Schulz-Ohlberg, J.; Figge, K. Mobile sand deposits and shoreface sediment dynamics in the inner German Bight (North Sea). Mar. Geol. 2000, 170, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, S.; Zeiler, M.; Bungenstock, F. Early Holocene environmental history of sunken landscapes: Pollen, plant macrofossil and geochemical analyses from the Borkum Riffgrund, southern North Sea. Int. J. Earth Sci. (Geol Rundsch) 2010, 99, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Galvez, D.; Günther, C.-P.; Pesch, R.; Propp, C.; Hass, H.C.; Schuchardt, B.; Zeiler, M. Winnowed gravel lag deposits between sandbanks in the German North Sea. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 451–460. ISBN 978-0-12-814960-7. [Google Scholar]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C.; Valerius, J.; Thiesen, M.; Mulckau, A. Map of sediment distribution in the German EEZ (1:10.000). 2019. Available online: www.geoseaportal.de/mapapps/rescources/apps/sedimentverteilung_auf_dem_meeresboden/index.html?lang=de (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Callies, U.; Gaslikova, L.; Kapitza, H.; Scharfe, M. German Bight residual current variability on a daily basis: Principal components of multi-decadal barotropic simulations. Geo-Mar. Lett 2017, 37, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sündermann, J.; Pohlmann, T. A brief analysis of North Sea physics. Oceanologia 2011, 53, 663–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.; Milbrandt, P.; Plüß, A.; Valerius, J. Modelling large scale sediment transport in the German Bight (North Sea). Die Küste 2014, 81, 369–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hass, H.C.; Papenmeier, S. Parametric Sediment Echo Sounder Survey during R/V Heincke Cruise HE400 in the German Bight with Link to Raw Data Files; Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Parametric Sediment Echo Sounder Survey during R/V Heincke Cruise HE415 and HE416 in the German Bight with Link to Raw Data Files; Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Parametric Sediment Echo Sounder Survey during R/V Heincke Cruise HE436 in the German Bight with Link to Raw Data Files; Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Parametric Sediment Echo Sounder Survey during R/V Heincke Cruise HE438 in the German Bight with Link to Raw Data Files; Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, J.; Wendt, G.; Müller, S. High-resolution Echo-sounding and Detection of Embedded Archaeological Objects with Nonlinear Sub-bottom Profilers. Mar. Geophys Res. 2005, 26, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, J.; Müller, S.; Hümbs, P.; Buch, T.; Endler, R. High-Resolution Acoustical Site Exploration in Very Shallow Water—A Case Study. In Proceedings of the EAGE Near Surface 2005—11th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Palermo, Italy, 4–7 September 2005; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hass, H.C.; Kuhn, G.; Monien, P.; Brumsack, H.-J.; Forwick, M. Climate fluctuations during the past two millennia as recorded in sediments from Maxwell Bay, South Shetland Islands, West Antarctica. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Pub. 2010, 344, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0–50,000 Years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, H.C.; Papenmeier, S. Documentation of Sediment Core HE439/06-1 (HE438-439_EUT1); Alfred Wegener Institute—Polarstern Core Repository, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, H.C.; Papenmeier, S. Documentation of Sediment Core HE439/07-1 (HE438-439_EUT2); Alfred Wegener Institute—Polarstern Core Repository, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, H.C.; Papenmeier, S. Documentation of sediment core HE439/08-1 (HE438-439_EUT3); Alfred Wegener Institute—Polarstern Core Repository, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, H.C.; Papenmeier, S. Documentation of Sediment Core HE439/09-1 (HE438-439_EUT4); Alfred Wegener Institute—Polarstern Core Repository, PANGAEA: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, D.S.; Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C.; Bartholomae, A.; Fofonova, V.; Wiltshire, K.H. Detecting shifts of submarine sediment boundaries using side-scan mosaics and GIS analyses. Mar. Geol. 2020, 430, 106343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, R.; Hass, H.C.; Mielck, F.; Papenmeier, S.; Sander, L.; Gutow, L.; Wiltshire, K.H. Epibenthic assemblages of hard-substrate habitats in the German Bight (south-eastern North Sea) described using drift videos. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, R.; Hass, H.C.; Mielck, F.; Papenmeier, S.; Sander, L.; Ebbe, B.; Gutow, L.; Wiltshire, K.H. Hard-substrate habitats in the German Bight (South-Eastern North Sea) observed using drift videos. J. Sea Res. 2019, 144, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Sidescan Sonar Survey (300 / 600 kHz) during R/V Heincke Cruise HE436 in the German Bight with Link to Raw Data Files; 111.3 GBytes; PANGAEA Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, K.; Holler, P.; Herbst, G.; Bratek, A.; Ahmerkamp, S.; Neumann, A.; Bartholomä, A.; van Beusekom, J.E.E.; Holtappels, M.; Winter, C. Abrupt emergence of a large pockmark field in the German Bight, southeastern North Sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindowski, K.-H. Das Quartär im Untergrund der Deutschen Bucht (Nordsee). Eiszeitalter und Gegenwart 1970, 21, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.P.; Posamentier, H.W. Sequence Stratigraphy and Facies Model of an Incised Valley Fill: The Gironde Estuary, France. SEPM J. Sediment Res. 1993, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wu, C. Holocene delta evolution and sequence stratigraphy of the Pearl River Delta in South China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, R.; Bimie, J. Holocene environmental change in the inner Severn estuary, UK: An example of the response of estuarine sedimentation to relative sea-level change. The Holocene 1996, 6, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinther, B.M.; Clausen, H.B.; Johnsen, S.J.; Rasmussen, S.O.; Andersen, K.K.; Buchardt, S.L.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Seierstad, I.K.; Siggaard-Andersen, M.-L.; Steffensen, J.P.; et al. A synchronized dating of three Greenland ice cores throughout the Holocene. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.L.; Rendell, H.M. The impact of North Atlantic storminess on western European coasts: A review. Quat. Int. 2009, 195, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsgaard, K.; Vad Odgaard, B. Dating sequences of buried horizons of podzols developed in wind-blown sand at Ulfborg, Western Jutland. Quat. Int. 2001, 78, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffenorde, H. Zur Gliederung des klastischen Holozäns im mittleren und nordwestlichen Teil der Deutschen Bucht (Nordsee) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Foraminiferen. E&G—Quat. Sci. J. 1982, 32, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Grain-Size Properties of Grab-Sampled Sediments from the German Bight during R/V Heincke Cruise HE436; PANGAEA Alfred Wegener Institute—Wadden Sea Station Sylt: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cruise | Date | pSES Low Frequency | pSES Pulse Length [µs] | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE400 | 05/2013 | 6 kHz | 2 | doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.899708, [36] |
| HE415 | 02/2014 | 10 kHz | 2 | doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.905842, [37] |
| HE436 | 11/2014 | 8 kHz | 2 | doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.899707, [38] |
| HE438 | 02/2015 | 8, 15 kHz | 1, 2 | doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.899497, [39] |
| Core Number | Short Number | Latitude | Longitude | Recovery | Water Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE439/006-1 | 1 | 54°49.21′ N | 06°14.77′ E | 5.98 m | 39.2 m |
| HE439/007-1 | 2 | 54°48.32′ N | 06°12.62′ E | 4.79 m | 39.4 m |
| HE439/008-1 | 3 | 54°47.85′ N | 06°11.38′ E | 5.86 m | 41.0 m |
| HE439/009-1 | 4 | 54°47.12′ N | 06°09.60′ E | 5.42 m | 41.5 m |
| Lab Code | Core | Sample Depth [cm] | Conventional Age [yr BP] | Calibrated Age [cal. yr BP] 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-416333 | 1 | 89–90 | 4730 ± 30 | 5027 ± 177 |
| Beta-416334 | 1 | 425–426 | 7680 ± 30 | 8165 ± 125 |
| Beta-416335 | 2 | 400–402 | 8420 ± 30 | 9072 ± 112 |
| Beta-416336 | 3 | 454–456 | 8670 ± 30 | 9364 ± 104 |
| Beta-416337 | 4 | 454–455 | 9100 ± 30 | 9817 ± 277 |
| Core Number | Short Number | Link to Core Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| HE439/006-1 | 1 | https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.847257, [46] |
| HE439/007-1 | 2 | https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.847258, [47] |
| HE439/008-1 | 3 | https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.847259, [48] |
| HE439/009-1 | 4 | https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.847260, [49] |
| Period [cal. yr BP] | Core 3 | Core 2 | Core 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8165–5027 | - | - | 0.1 |
| 9072–8165 | - | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| 9364–9072 | - | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| 9817–9364 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Revisiting the Paleo Elbe Valley: Reconstruction of the Holocene, Sedimentary Development on Basis of High-Resolution Grain Size Data and Shallow Seismics. Geosciences 2020, 10, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120505
Papenmeier S, Hass HC. Revisiting the Paleo Elbe Valley: Reconstruction of the Holocene, Sedimentary Development on Basis of High-Resolution Grain Size Data and Shallow Seismics. Geosciences. 2020; 10(12):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120505
Chicago/Turabian StylePapenmeier, Svenja, and H. Christian Hass. 2020. "Revisiting the Paleo Elbe Valley: Reconstruction of the Holocene, Sedimentary Development on Basis of High-Resolution Grain Size Data and Shallow Seismics" Geosciences 10, no. 12: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120505
APA StylePapenmeier, S., & Hass, H. C. (2020). Revisiting the Paleo Elbe Valley: Reconstruction of the Holocene, Sedimentary Development on Basis of High-Resolution Grain Size Data and Shallow Seismics. Geosciences, 10(12), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10120505






