Evaluation of the Geo-Mechanical Properties Property Recovery in Time of Conditioned Soil for EPB-TBM Tunneling
Abstract
1. Introduction
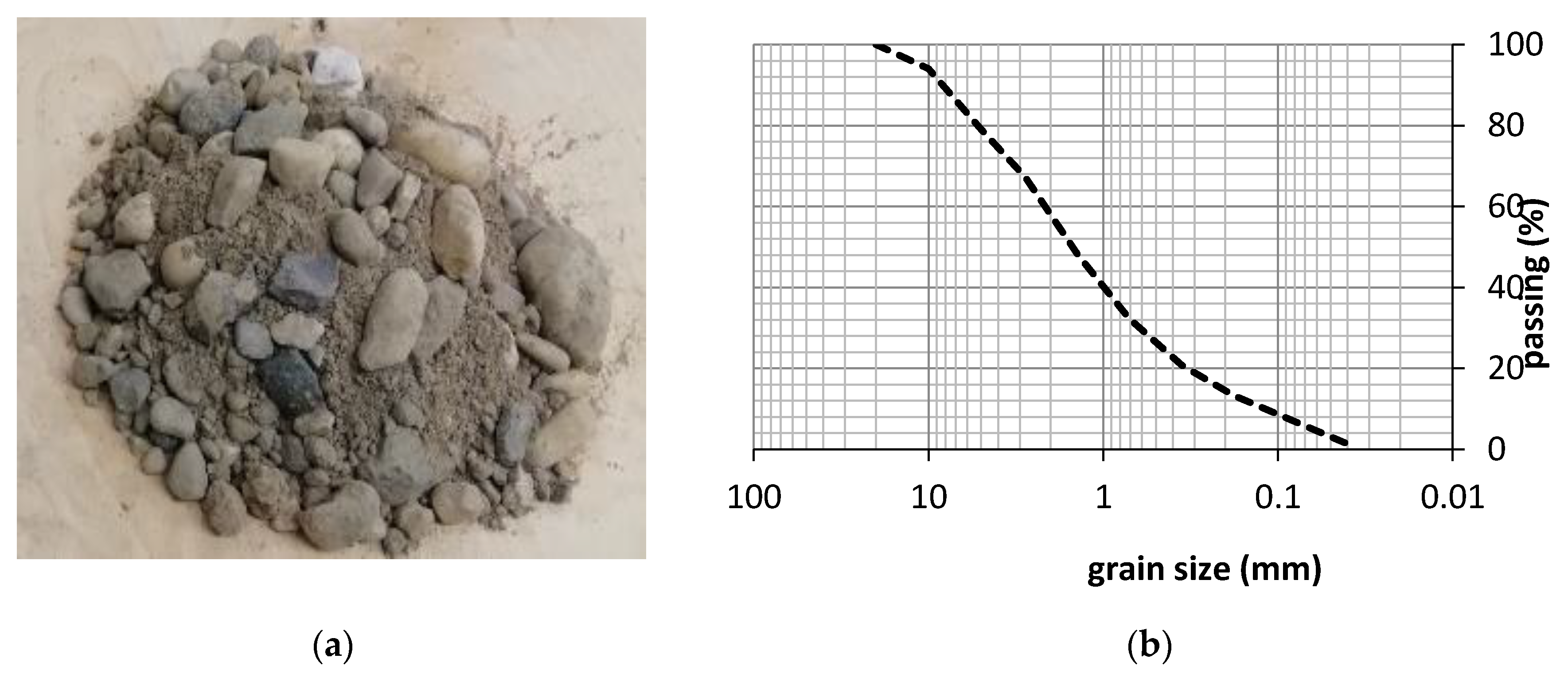
2. Materials and Methods
- total water content: (%), where the water is the sum of the natural water, the free water added to the sample, and the water added in the foam;
- concentration of foaming agent in the fluid: (%);
- Foam expansion ratio: ; that, globally, describes the quality of the foam;
- Foam injection ratio: (%); that, globally, describes the quality of the conditioning.
3. Results and Discussion
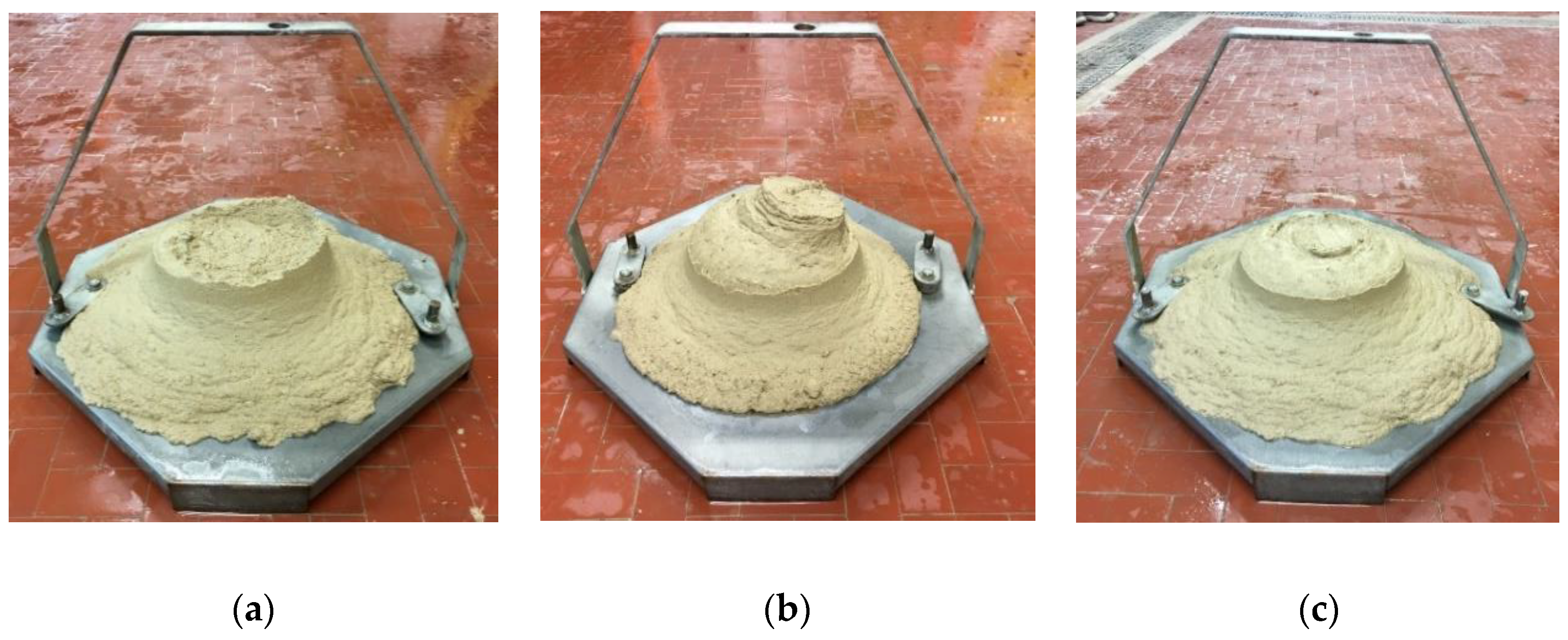
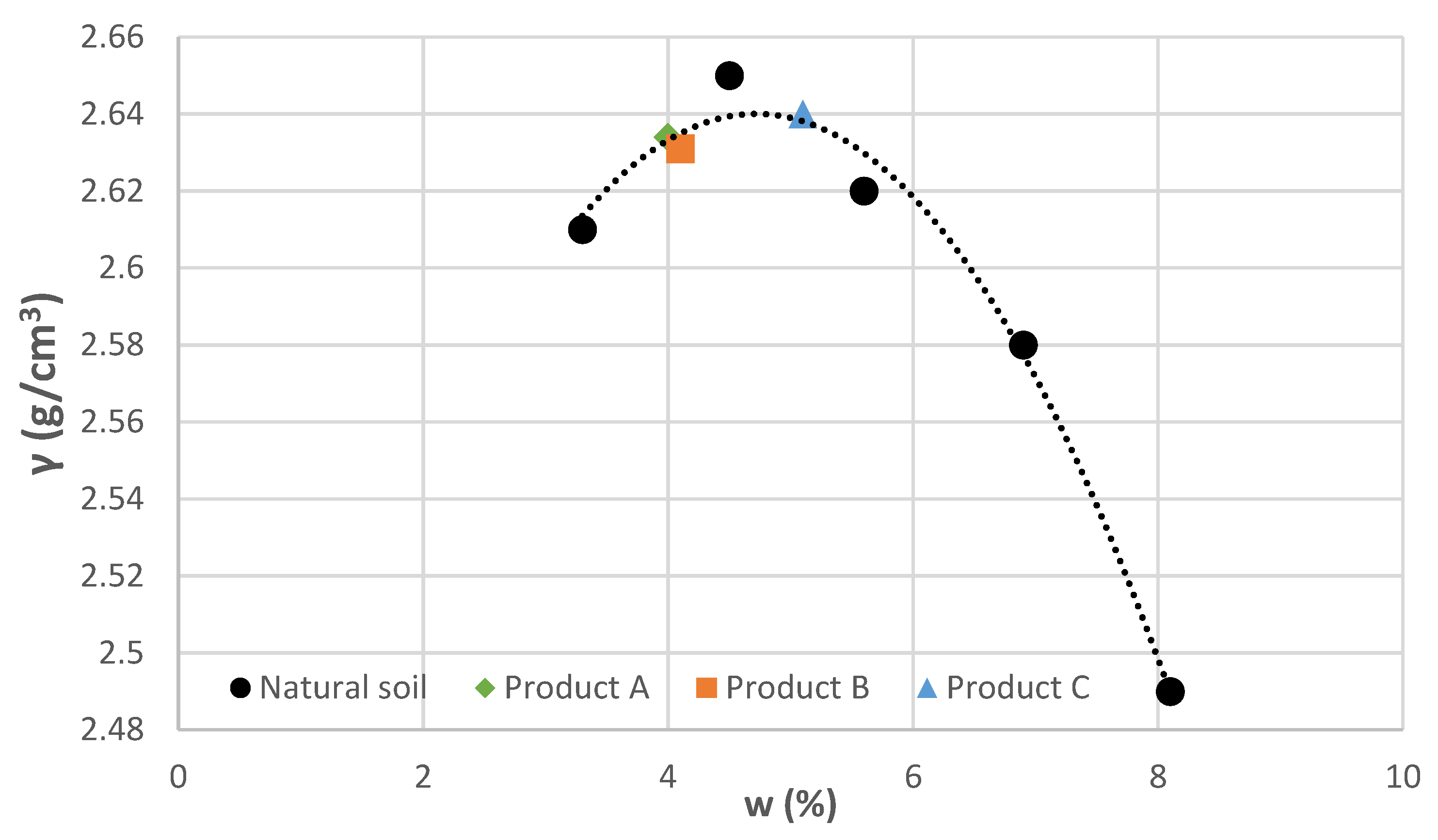
3.1. Modified Proctor Test
3.2. Vane Test
3.3. Direct Shear Test
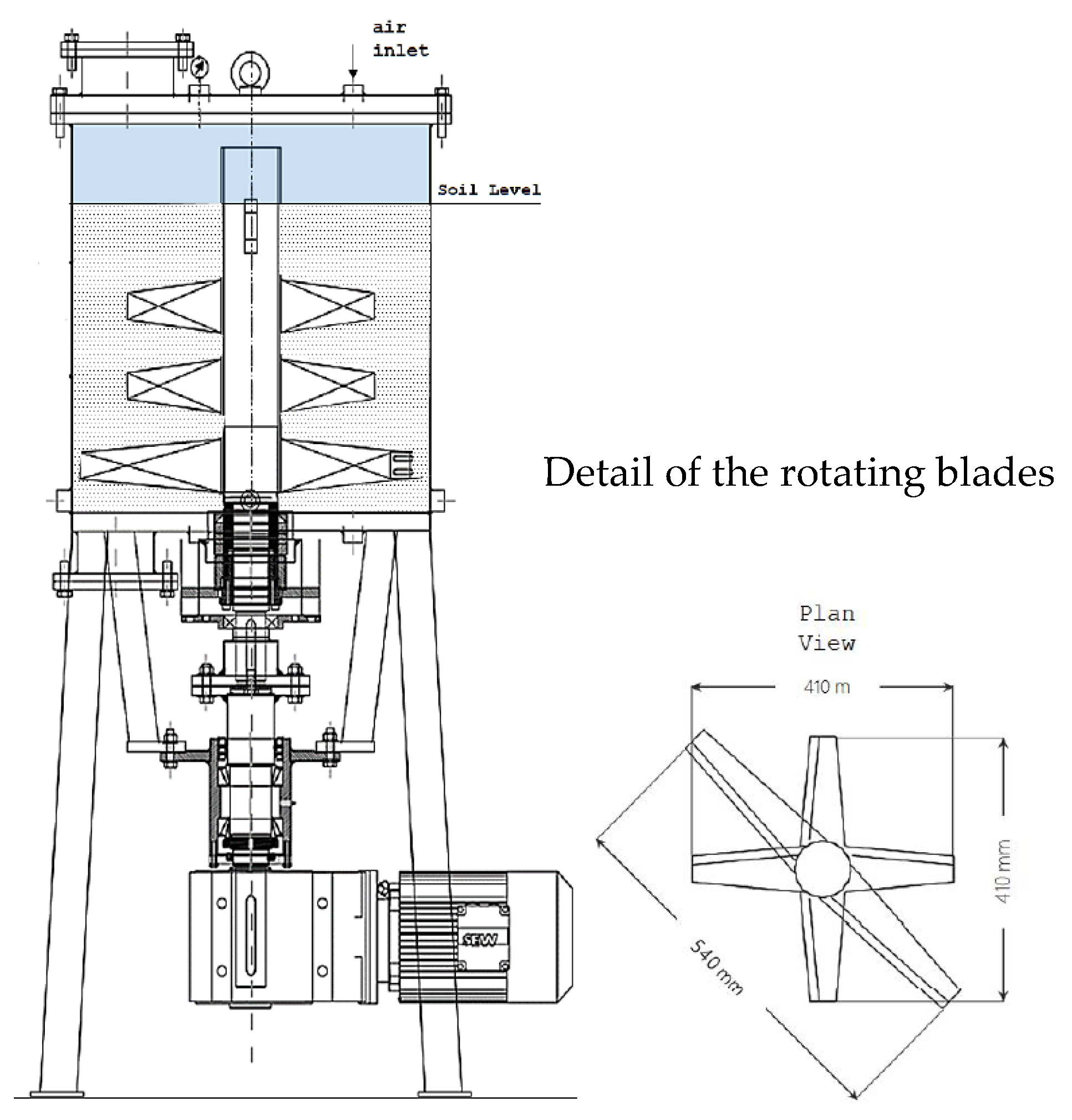
3.4. Rotational Mixer Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinai, R.; Oggeri, C.; Peila, D. Soil conditioning of sand for EPB applications: A laboratory research. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewes, M.; Budach, C.; Bezuijen, A. Foam conditioning in EPB tunnelling. In Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Viggiani, G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, D.; Todaro, C.; Luciani, A.; Peila, D. Use of a large triaxial cell for testing conditioned soil for EPBS tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 94, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, D.; Picchio, A.; Martinelli, D.; Dal Negro, E. Laboratory tests on soil conditioning of clayey soil. Acta Geotech. 2016, 11, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carigi, A.; Luciani, A.; Todaro, C.; Martinelli, D.; Peila, D. Influence of conditioning on the behaviour of alluvial soils with cobbles. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 96, 103–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, C. Analysis on the penetration of foams in excavation with EPB. Geoing. Ambient. Min. 2016, 147, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, C.G.O.; Todaro, C.; Luciani, A.; Boscaro, A.; Peila, D. Preliminary study of wear induced by granular soil on metallic parts of EPB tunnelling machines. Geoing. Ambient. Min. 2016, 148, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, C.G.O.; Todaro, C.; Bosio, F.; Bassini, E.; Ugues, D.; Peila, D. A new test device for the study of metal wear in conditioned granular soil used in EPB shield tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 73, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAUB. Recommendations for selection and evaluating tunnel boring machines. Tunnel 1997, 5, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Grenni, P.; Barra Caracciolo, A.; Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Rauseo, J.; Saccà, M.L.; Mingazzini, M.; Palumbo, M.T.; Galli, E.; Muzzini, V.G.; et al. A bioassay battery for the ecotoxicity assessment of soils conditioned with two different commercial foaming products. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firousei, Y.; Grenni, P.; Caracciolo, A.B.; Patrolecco, L.; Todaro, C.; Martinelli, D.; Carigi, A.; Hassanpour, J.; Peila, D. The most common laboratory procedures for the evaluation of the EPB TBMs excxavated material ecotoxicity in Italy: A review. Geoing. Ambient. Min. 2020, 162, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gertsch, L.; Fjeld, A.; Nielsen, B.; Gertsch, R. Use of TBM much as construction material. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2001, 15, 374–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Yin, J.; Xie, Y. Recycling of discharged soil from EPB shield tunnels as a sustainable raw material for synchronous grouting. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scröfelbauer, T.; Schreitl, B.; Kitzler, C. S1 Danube-Lobau tunnel—Recycling of tunnel spoil material. Geomech. Tunn. 2009, 5, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oggeri, C.; Fenoglio, T.M.; Vinai, R. Tunnel spoil classification and applicability of lime addition in weak formations for muck reuse. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 44, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, V. Low energy nobilitation of clay waste from tunnelling. In Proceedings of the ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress 2019, Naples, Italy, 3–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tommasi, P.; Lollino, P.; Di Giulio, A.; Belardi, G. Investigation on the geotechnical properties of a chemically conditioned spoil from EPB excavation, a case study. In Proceedings of the ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress 2019, Naples, Italy, 3–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, D. Mechanical Behaviour of Conditioned Material for EPBS Tunnelling. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peila, D.; Martinelli, D.; Todaro, C.; Luciani, A. Soil conditioning in EPB shield tunnelling—An overview of laboratory tests. Geomech. Tunn. 2019, 12, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewes, M.; Budach, C. Soil conditioning with foam during EPB tunnelling. Geomech. Tunn. 2010, 3, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, D.; Oggeri, C.; Borio, L. Using the slump test to assess the behavior of conditioned soil for EPB tunnelling. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2009, 15, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO. Guide for Design of Pavement Structures; AASHTO T193; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Field Vane Shear Test in Cohesive Soil; ASTM D2573-01; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Direct Shear Tests of Soils under Consolidated Drained Conditions; ASTM D3080; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
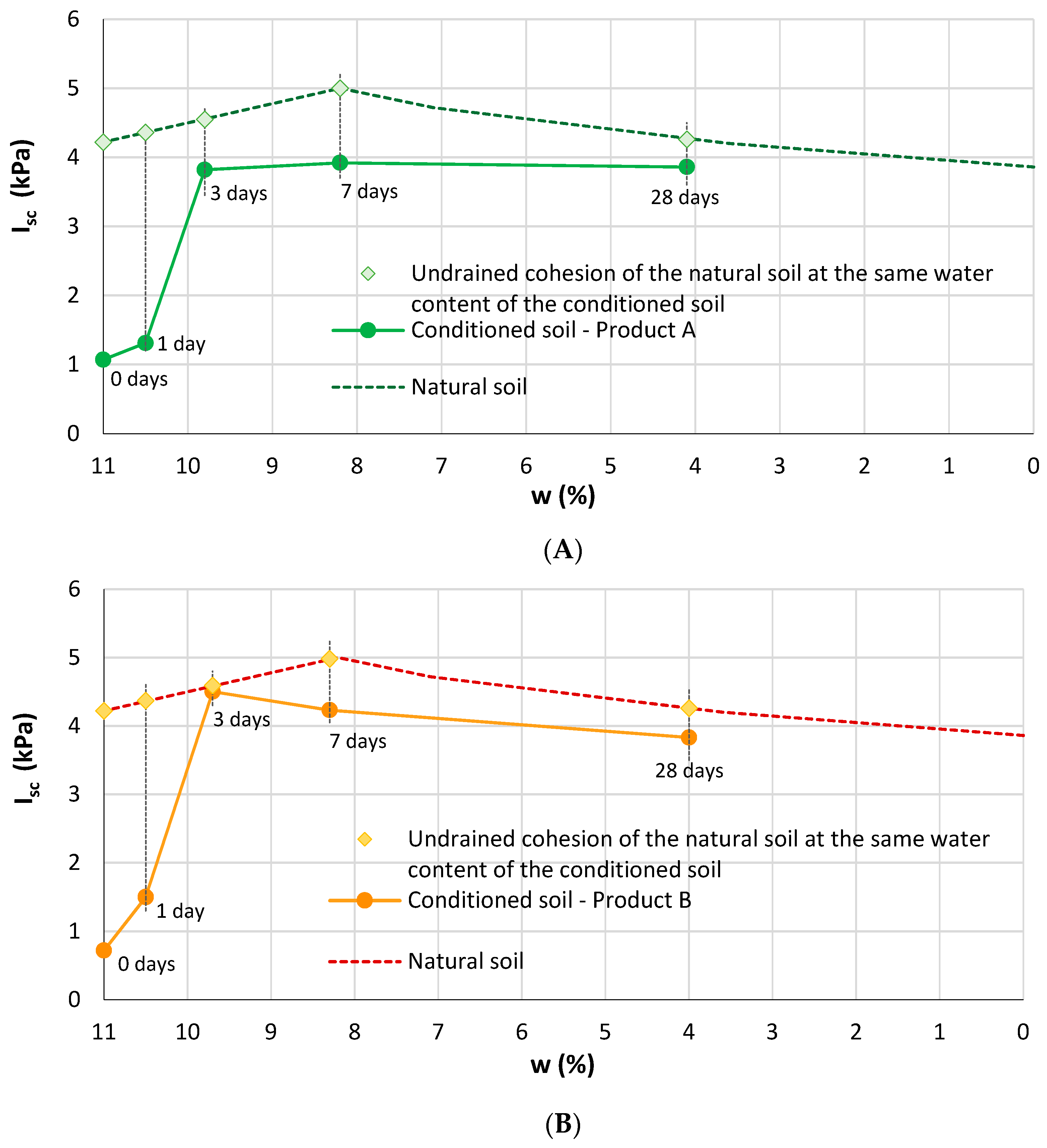
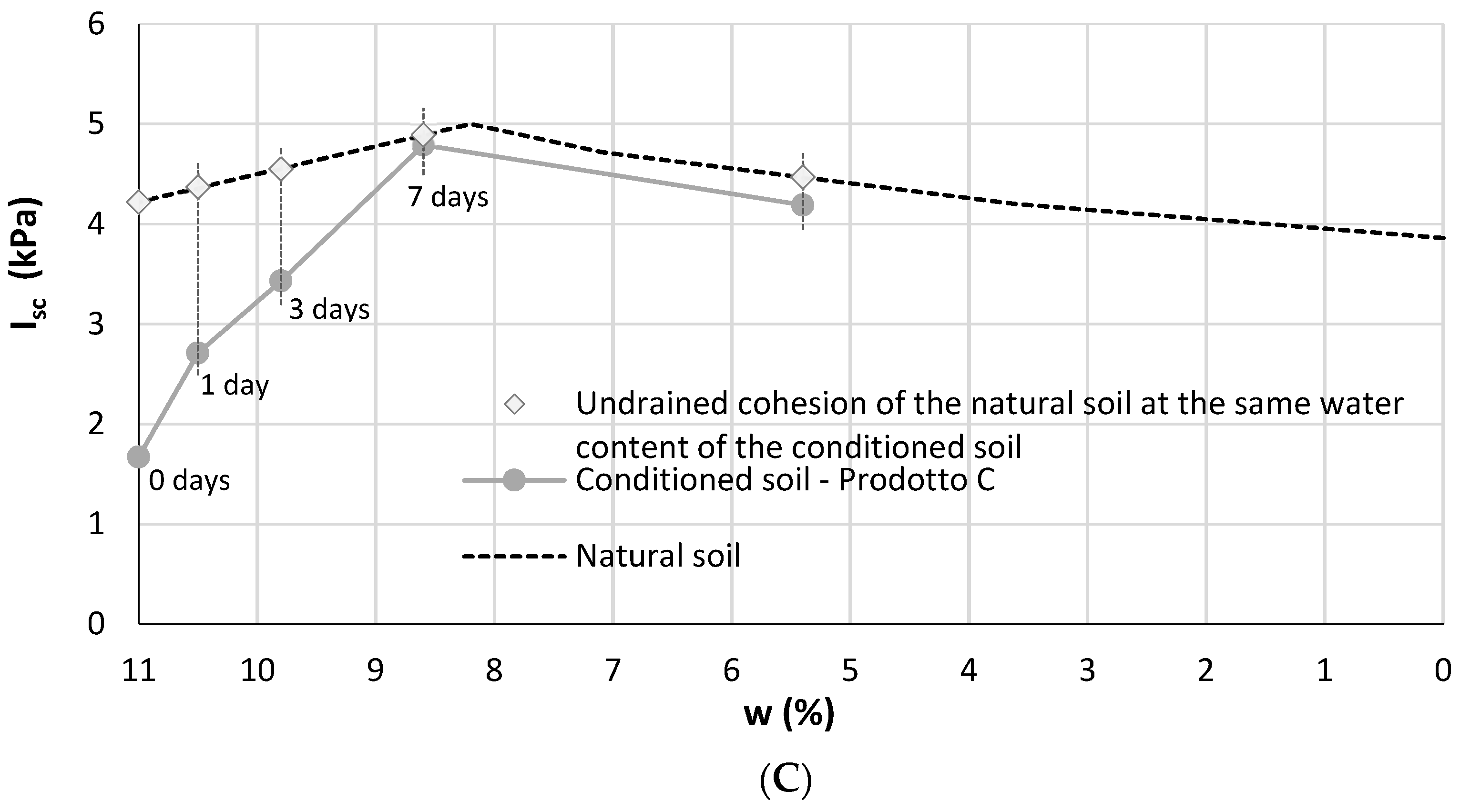
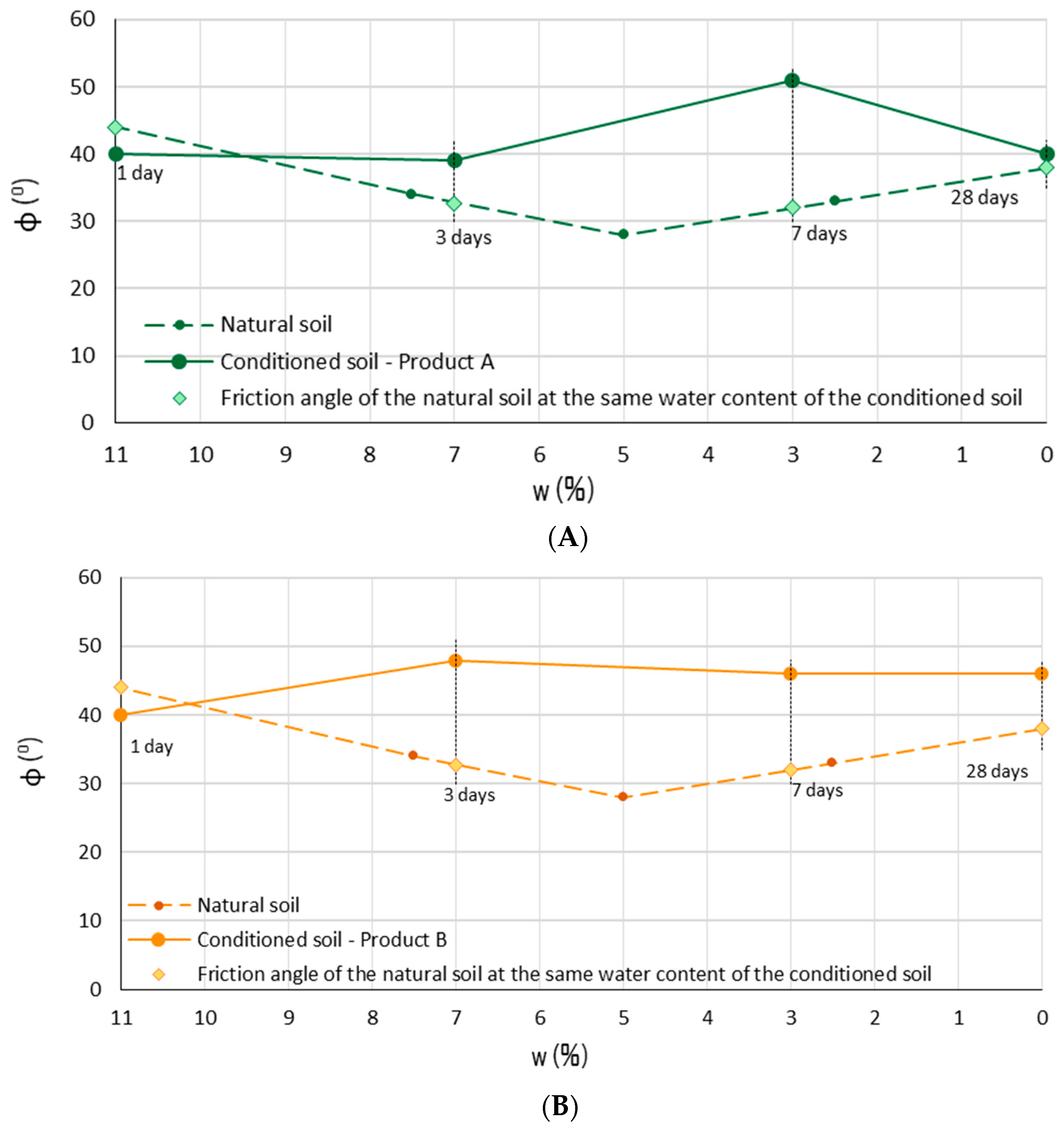
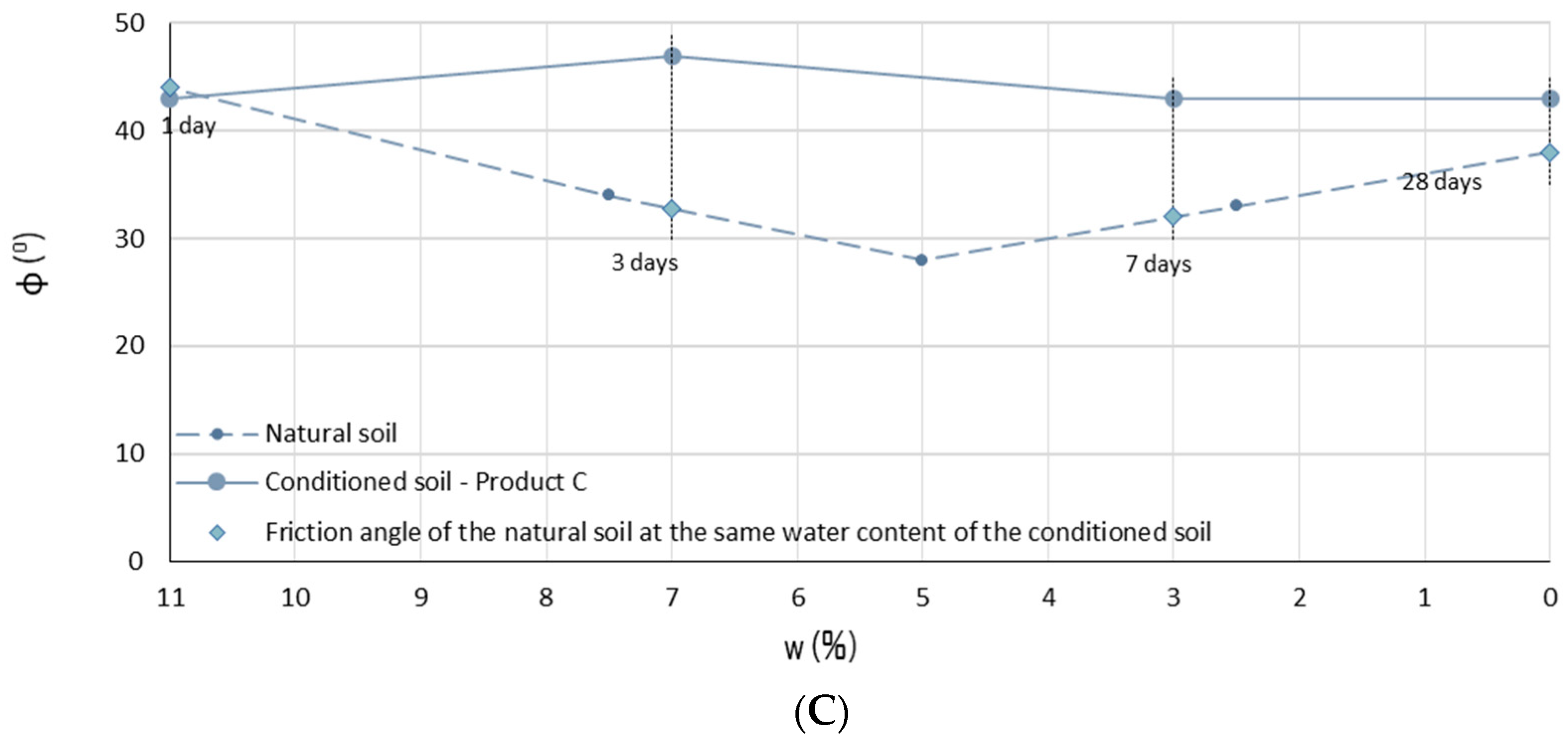
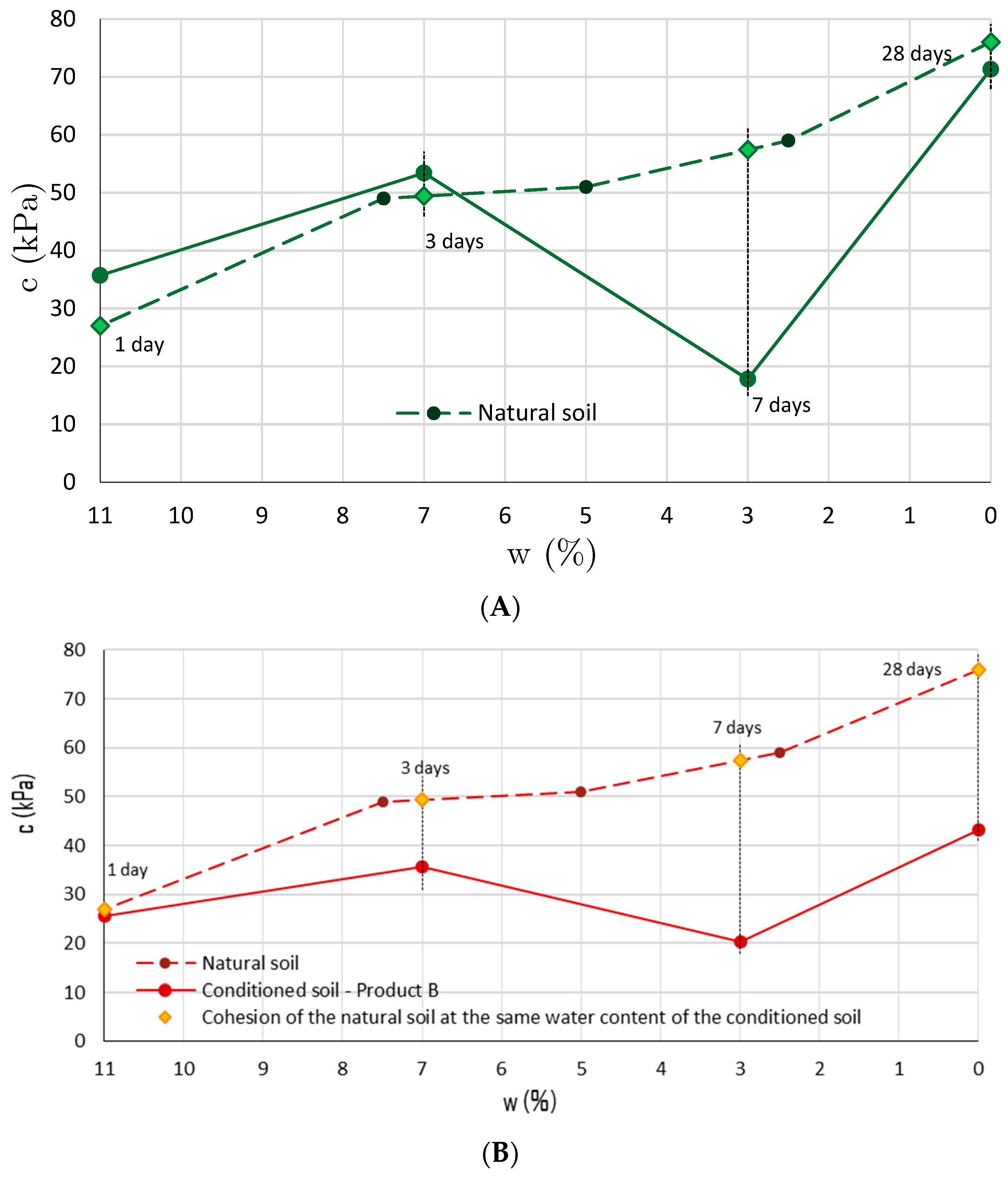
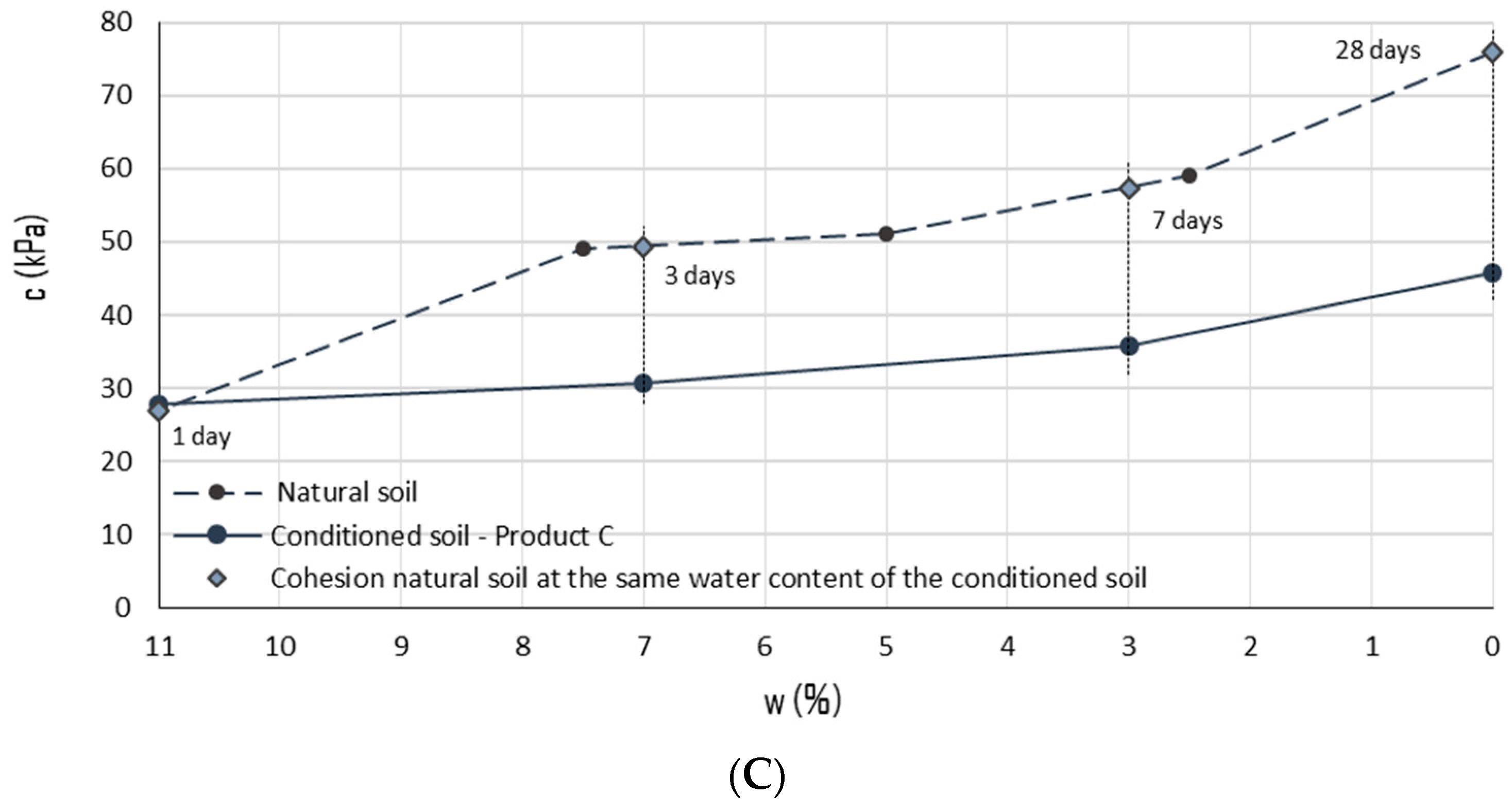
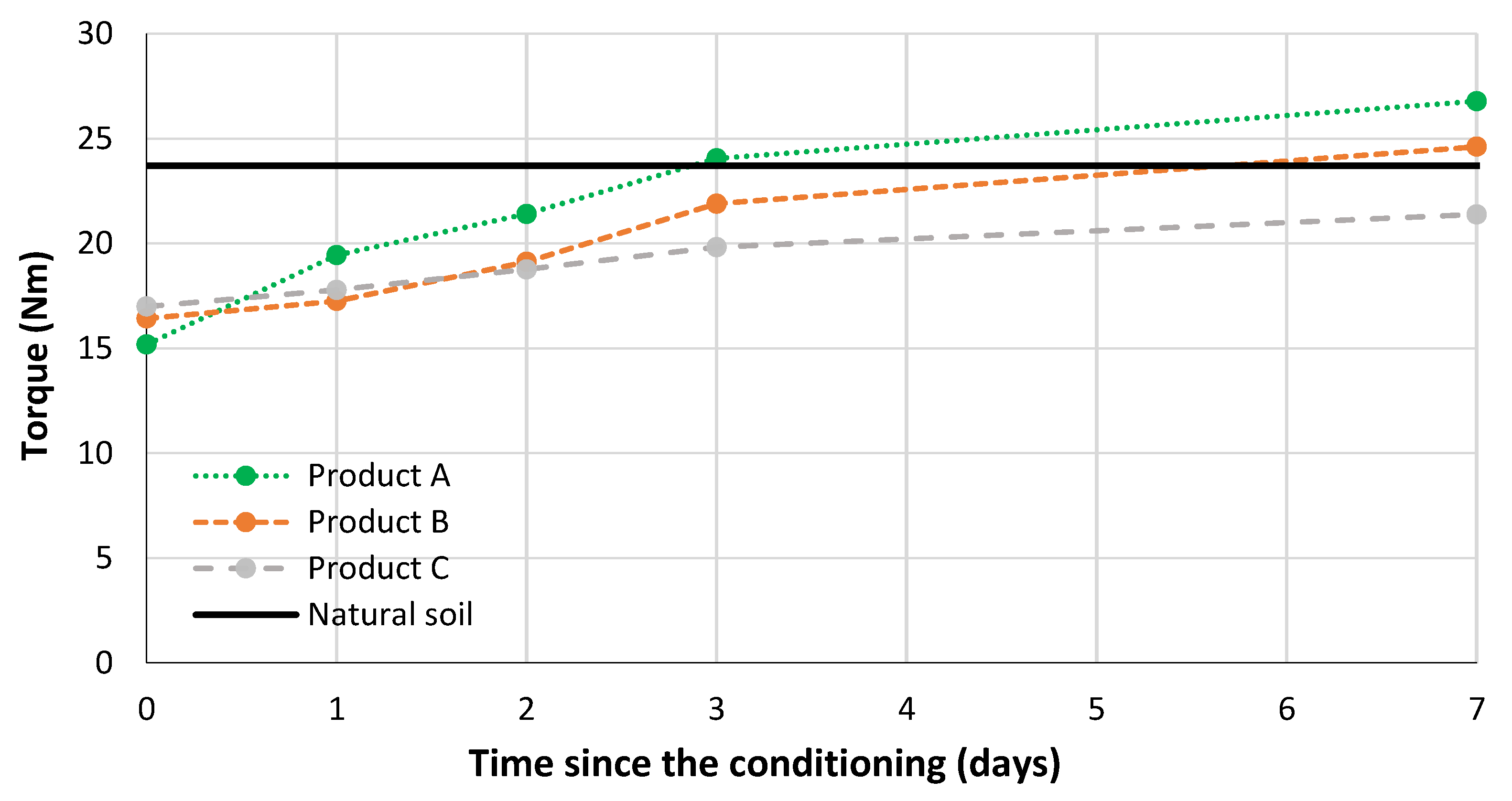
| Conditioning Product | wtot (%) | c (%) | FER (-) | FIR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 11.0 | 1.1 | 20 | 30 |
| B | 11.0 | 1.0 | 20 | 30 |
| C | 11.0 | 2.0 | 14 | 20 |
| Curing Time (Days) | Φ’ (°) | c’ (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 28 | 43 | 45.8 |
| 45 | 43 | 45.8 |
| 60 | 43 | 45.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carigi, A.; Todaro, C.; Martinelli, D.; Amoroso, C.; Peila, D. Evaluation of the Geo-Mechanical Properties Property Recovery in Time of Conditioned Soil for EPB-TBM Tunneling. Geosciences 2020, 10, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110438
Carigi A, Todaro C, Martinelli D, Amoroso C, Peila D. Evaluation of the Geo-Mechanical Properties Property Recovery in Time of Conditioned Soil for EPB-TBM Tunneling. Geosciences. 2020; 10(11):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110438
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarigi, Andrea, Carmine Todaro, Daniele Martinelli, Cristina Amoroso, and Daniele Peila. 2020. "Evaluation of the Geo-Mechanical Properties Property Recovery in Time of Conditioned Soil for EPB-TBM Tunneling" Geosciences 10, no. 11: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110438
APA StyleCarigi, A., Todaro, C., Martinelli, D., Amoroso, C., & Peila, D. (2020). Evaluation of the Geo-Mechanical Properties Property Recovery in Time of Conditioned Soil for EPB-TBM Tunneling. Geosciences, 10(11), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110438







