Simple Summary
With the increase in parasite resistance to anthelmintics in horses, it is becoming essential to look for new approaches to helminth control. Helminths not only cause health problems in horses but also generate economic losses. One promising solution is the use of helminthophagous fungi, which act on the larvae and eggs of parasites. These fungi can be incorporated into horse feed, helping to reduce infestations on pasture. This review explores the potential of these fungi as an effective and sustainable tool for controlling worms in horses, promoting animal health and environmental protection.
Abstract
Equine farming faces growing challenges with helminthoses, aggravated by the indiscriminate use of anthelmintics without technical criteria. This practice favors resistance to these drugs, generates residues in animal products, compromises food safety and human health, and, when excreted in large quantities, negatively impacts environmental health by affecting invertebrates and fecal microorganisms. This highlights the importance of the One Health approach. A promising alternative is biological control with nematophagous or helminthophagous fungi such as Duddingtonia flagrans, Pochonia chlamydosporia, Arthrobotrys oligospora, Monacrosporium thaumasium, Mucor circinelloides and Purpureocillium lilacinum. Due to their different mechanisms of action, ovicidal and predatory fungi, when used together, can act in a complementary and synergistic way in the biological control of helminths, increasing their effectiveness in reducing parasitic infections. The use of these fungi through biosynthesized nanoparticles from fungal filtrates is also emerging as a new approach to nematode control. It can be administered through feed supplementation in commercial formulations. The aim of this review is to explore the use of helminthophagous fungi in the control of helminthiases in horses, highlighting their potential as a biological alternative. It also aims to understand how these fungi can contribute effectively and sustainably to parasite management in horses.
1. Introduction
Businesses involving the breeding and utilization of horses play a crucial role in both developed and developing countries. The relevance of horses extends across several areas, being important for the economy, culture and science, in different social and productive contexts [1].
Horses are generally reared in extensive systems, where they are kept on pasture, almost all of which is contaminated with infective larvae and helminth eggs, which constantly contribute to helminthoses [2]. Parasitic diseases, especially those caused by endoparasites, which have a high prevalence and wide geographical distribution, are highly relevant due to their impact on animal production development [3].
Helminthiases cause direct economic losses, both in terms of treatment cost for clinical manifestations in animals and reduced production. However, due to the wide distribution of these parasites, some animals do not show any signs, and the impact of subclinical infections is more common [4]. Depending on the degree of parasite burden, helminths can cause anything from minor abdominal discomfort, weakness, and a rough coat to growth retardation, anemia and severe colic episodes, which can lead to the animal’s death [5].
Parasite control in horses on most farms is carried out exclusively using commercial antiparasitic compounds, due to their practicality, high efficiency, excellent cost–benefit ratio and ease of acquisition. However, these products are used in a suppressive and indiscriminate manner and without adequate control strategies, leading to the selection of increasingly resistant parasite populations [6].
Nematophagous or helminthophagous fungi, widely studied as natural predators of helminths, are globally distributed and naturally present in the soil, where they act as saprophytic or parasitic agents [7]. Due to their mechanism of action, fungi are classified as endoparasites, opportunists, toxin producers and predators [8,9]. The use of these fungi as biological parasite control agents is widely documented in the literature, with evidence reinforcing their potential as a crucial tool in the fight against helminthiases, helping to reduce dependence on conventional chemical control [10,11].
This review aims to explore the use of helminthophagous fungi in the control of helminthoses in horses, highlighting their potential as a biological alternative. Thus, understanding how these fungi can contribute effectively and sustainably to equine parasite management.
2. Methodology
This review was carried out with the aim of gathering and critically analyzing the available scientific evidence on the use of helminthophagous fungi in the control of helminthiases in horses. Given the growing concern about anthelmintic resistance and the need for sustainable alternatives in parasite management, the search for strategies based on biological control has intensified. Therefore, this study summarizes the advances in research, highlighting the mechanisms of action, efficacy and the advantages of applying these fungi in the environment and for horses, contributing to a better understanding of their potential in animal health.
A comprehensive literature review was conducted in the main databases, such as Web of Science, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect and PubMed. The search was carried out using combinations of pre-established keywords, with an emphasis on terms related to the use of helminthophagous fungi in the management of helminthiases in horses, such as ‘equine gastrointestinal nematodes’, parasite resistance to anthelmintics’ and ‘nematophagous fungi’. In addition, the keywords were adapted to align with the specific requirements of each section of the review. For the section on equine gastrointestinal nematodes, related terms were selected: ‘equine nematodes’, ‘gastrointestinal nematode control’, ‘cyathostomines’. In the ‘parasite resistance’ section, ‘macrocyclic lactones’ and ‘anthelmintic resistance’ were used. For the fungi section, keywords such as ‘biolophilic control’, ‘nematophagous fungi’, ‘duddingtonia flagrans’ and so on were used, sometimes in combination with the word ‘equine parasitosis’. In the initial stages of the writing process, 250 scientific papers were selected from the literature, covering a diverse range of formats, including literature reviews, books, research papers and articles aimed at a scientific audience. Subsequently, a bibliographic screening was carried out to eliminate articles with low relevance or published too early in the field. Research articles, reviews and clinical reports published after 2300 were selected for analysis, except for some basic theoretical studies. In addition, some articles using animals from other species were also retained for comparative reference. A total of 100 references were finally selected for this article.
3. Literature Review
3.1. Gastrointestinal Helminths in Horses
The parasite burden in horses comprises several families and genera, among which the strongylid nematodes stand out as the most prevalent. Of the 83 species described, the majority belong to the Strongylidae family and include the most common nematodes of economic importance to horses [12]. Gastrointestinal helminths in equidae have a cosmopolitan distribution across different geographic and climatic conditions [13].
Horses are among the most susceptible animal species to a wide variety of gastrointestinal parasites and can harbor several species simultaneously [14].
Strongylids are usually identified as endoparasites of the large intestine of horses, where they reach adulthood and sexual maturity. The free-living larvae develop in the pasture and the animals become infected during grazing, but they can also become infected in the stable by ingesting contaminated bedding and hay [15]. Small strongyles, also known as cyathostomes, are considered the most relevant helminths due to their prevalence, pathogenic potential and ability to develop resistance to anthelmintics [16]. These can parasitize horses of all ages, but are more pathogenic in young animals [17,18]. The most common genera of small strongyles are Cyathostomum spp. and Cylicostephanus spp. Other nematodes that affect horses are the large strongyles: Strongylus vulgaris, Strongylus equinus, Strongylus edentatus and Triodontophorus spp. In addition, there are nematodes such as Parascaris equorum, Oxyuris equi, Strongyloides westeri, Trichostrongylus axei, Dictyocaulus, all of which belong to the nematode phylum [19,20]. Fasciola hepatica is a parasite that belongs to the class Trematoda of the order Digenea and has a wide worldwide distribution [21]. From the Cestoda class, belonging to the Anoplocephalidae family, the species Anoplocephala magna, Anoplocephala perfoliata and Paranoplocephala mamillana are known to be relevant to horses [22].
The severity and clinical signs caused by helminth parasite infections will depend on the degree of parasite infection and the immunity of the affected animal [20]. These include anemia, fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, apathy, colic, dull hair, growth retardation, diarrhea and the possibility of death [23,24].
Climatic conditions have a significant impact on the helminth burden in horses, directly influencing the development of larvae in pastures. During spring and summer, high temperatures and rainfall favor greater proliferation of larvae, resulting in greater contamination of the environment and, consequently, in horses. In the dry season, the opposite happens. The water period is characterized by an increase in helminth infection rates, which makes strategic helminth control even more necessary [25,26].
3.2. Anthelmintic Resistance
The antiparasitic drugs used to control helminths in horses are predominantly grouped into four chemical classes: imidazothiazoles, benzimidazoles, pyrimidines and macrocyclic lactones. Rotation between these classes is widely adopted by breeders to minimize the impact of helminths on animal health and mitigate the risk of parasite resistance [27]. Among these, macrocyclic lactones are recognized as the most widely used class of anthelmintics [28].
The increasing indiscriminate use of these anthelmintics has contributed to the emergence of anthelmintic-resistant nematode populations, especially those belonging to the Cyathostominae subfamily, seriously threatening equine health, welfare and production in various locations around the world [29,30,31,32,33].
The current global situation is one of resistance to most of the classes of commercial anti-parasitic drugs available on the market. The worldwide occurrence of anthelmintic resistance to cyathostomes and Parascaris equorum is of great concern, as resistance has been reported to all currently available drug classes. Resistance in cyathostomes to benzimidazoles has been reported in 14 countries. Although less common, resistance to pyrantel in cyathostomes has been described in 12 countries [34].
The administration of anthelmintics, often carried out without the application of adequate technical criteria, occurs in an empirical and indiscriminate manner, which can compromise the effectiveness of these products, causing anthelmintic resistance to emerge and spread [35,36]. Drug resistance is hereditary, and repeated dosing will therefore select an increasing proportion of resistant parasites. The mechanisms involve differences in the metabolism of the anthelmintic within the parasite and/or mutations in the binding site of the drug molecule [37].
It is therefore extremely important to develop alternative strategies of parasite control, promoting a reduction in the number of infective larvae in pastures. This will reduce the reinfection of animals and, consequently, decrease the use of anthelmintics [2,38].
3.3. Helminthophagous Fungi
3.3.1. Virulence Mechanisms
More than 150 species of helminthophagous fungi have been catalogued. These fungi are also known as helminth destroyers [39]. Research using fungi to control nematodes has been gradually increasing [38,40,41,42,43]. The fungus Duddingtonia flagrans, presented in the Bioverm® product, has demonstrated efficacy in the biological control of gastrointestinal nematodes in horses kept on pasture over a period of six months [42]. According to [43], after oral administration of Bioverm, which contains the fungi Duddingtonia flagrans and Pochonia chlamydosporia, a significant reduction was observed in the number of infective larvae in the pasture and in the parasite load of treated horses, compared to untreated animals.
From an ecological point of view, the interaction between these fungi and nematodes can contribute to the maintenance and stability of the infective forms of helminths present in pastures [44,45].
According to [46], helminthophagous fungi can be divided into five groups: predators, opportunists or ovicides, endoparasites, toxin producers and producers of special attack devices. The fungi in the first group produce modified hyphae called traps, with which they bind and digest nematode larvae by a mechanical/enzymatic process. Fungi belonging to the ovicidal group produce hyphae, appressoria and enzymes that digest helminth eggs. Thus, they are the two groups that work best in preying on helminth parasites of animals [2,47]. On the other hand, the enzymatic activity of these organisms has sparked great interest in studies across different countries. For example, in China, a recombinant protein from Arthrobotrys oligospora, one of the widely studied nematode-capturing fungi, has been shown to have high chitinase activity, and it can degrade the eggshell of the following nematode species: Strongylus equinus, Caenorhabditis elegans and Haemonchus contortus, as well as the eggshell of the trematodes F. hepatica and Dicrocoelium chinensis [48].
Helminthophagic fungi act exogenously [49]. In other words, the presence of pre-parasitic stages (eggs and/or larvae) of helminths induces morphogenesis and the expression of virulence genes in these fungi, signaling the transition from the saprophytic stage to the phagocytic stage [2,8].
Predatory fungi develop specialized structures along their hyphae. The structures, with the function of capturing the nematodes, can be in the form of adhesive nets, adhesive buttons, constrictor and non-constrictor rings [50]. The formation of these traps occurs in response to the presence of the nematode or its excreta, biological compounds, or it can be induced by physiological stress conditions [47,51,52]. In addition to forming these specialized structures, predatory fungi produce chlamydospores interspersed with the hyphae [53]. Chlamydospores are resistant structures that guarantee the fungus’ great robustness [54] by stimulating its survival until the environmental factors are ideal for its development. It is the most widely researched group of fungi in the biological control of nematodes and has the greatest potential for industrialization [55].
The appearance of predatory structures occurs 30 min to 4 h after the fungus–nematode interaction. In the case of infective nematode larvae, the external cuticle can delay the infection process, but it does not provide protection against the predatory action of the fungi [56].
Opportunistic fungi are able to colonize nematode eggs and females through their appendages, entering the infective stage of the nematode [57]. The enzymes chitinases and proteases play an important role during the penetration of the eggshell, causing the destruction of its layers, and are therefore referred to as ovicides [55]. Among the most studied genera of this group of fungi are Purpureocillium, Mucor circinelloides and Pochonia chlamydosporia [8].
When present in the environment, they produce an extensive system of hyphae, thus forming traps that capture nematodes mechanically or by adhesion. They behave as natural antagonists, promoting seizure and the destruction of the nematode. According to their mechanism of action, they are classified as endoparasites, predators and opportunists, and the predator and opportunist groups have been studied for the biological control of helminthiases, with promising results [2,8,10,49,58].
The level of oxygen in the medium, as well as the substrate that makes up this culture medium, which influences a climatic environment that is favorable to the development of different stages of helminths, also makes it possible for fungi to survive, allowing them to prey on parasitic agents [39,55,59,60]. On the other hand, in the environment, these organisms can survive as saprophytic agents, feeding on environmental organic matter, or as parasites, feeding on a wide variety of helminths at all life stages, until they reach their infective stage [61,62].
As a characteristic shared by all types of helminthophagous fungi, recognition of the host and adherence to the cuticle of the infective larvae and/or eggs of the target organisms are the initial steps in infection [8].
3.3.2. Survival Mechanisms
The germination rate, sporulation and resistance of Duddingtonia flagrans chlamydospores are influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, ultraviolet radiation, osmotic pressure and the availability of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen in the soil. At temperatures around 25 °C and pH 7–9, the germination rate of chlamydospores reaches its maximum threshold, which favors mycelial production [63].
Another essential requirement for a fungal isolation to be possibly exploited in the biological control of parasites is to resist passage through the gastrointestinal system tract of equines after oral administration. In other words, it must tolerate stressful conditions and, once present in the feces, it must be able to germinate, colonize the fecal bolus and capture the larval stages hatched from the eggs before they migrate out of the fecal bolus [64]. In addition, it must have specificity of action, high reproductive capacity and withstand the environmental and climatic conditions of the geographical region where the control will be carried out [2].
Ref. [65] observed that Duddingtonia flagrans, Arthrobotrys cladodes and Pochonia chlamydosporia were not limited by temperature variations between 15 and 35 °C for nematode control under in vitro conditions, although they showed greater growth, chlamydospore production and nematicidal activity at intermediate temperatures (20, 25 and 30 °C).
3.3.3. Overview of Helminthophagous Fungi Species
Duddingtonia flagrans is a predator of L3 larvae of gastrointestinal parasitic nematodes and stands out as one of the most studied agents for use in biological control [2], acting by means of three-dimensional adhesive networks formed by its hyphae to capture the infective nematode larvae present in the environment, especially in animal feces. After capturing the larvae, the fungus penetrates it and uses enzymes to digest its internal contents, obtaining essential nutrients for its growth and reproduction. The formation of chlamydospores, resistant structures that protect the fungus in adverse conditions, allows it to survive as it passes through the gastrointestinal tract of horses. Once excreted in the feces, the chlamydospores germinate, forming capture nets that significantly reduce the number of infective larvae in the environment, reducing contamination and preventing reinfections [7,55].
It has significant potential for controlling Cyathostominae in laboratory conditions, and it is a promising biological agent for managing cyathostomin infections in horses [2,42,66,67]. Studies have shown that the fungus Duddingtonia flagrans, present in Bioverm®, contributed to the biological control of gastrointestinal nematodes in horses when tested under field conditions for a period of six months [42]. According to [43], after oral administration of Bioverm, which contains the fungi Duddingtonia flagrans and Pochonia chlamydosporia, reductions were observed in the number of infective larvae in the pasture and in the parasite load of horses compared to untreated animals.
This species has stood out due to its diversity of mechanisms of action and large production of chlamydospores [7]. However, Duddingtonia flagrans has shown other interesting aspects in its mechanism of action, since in addition to the traps, it has good enzyme production and nanoparticles, making it a species with a broad range of action, to be better explored for biological control [68,69].
The development of appressoria formed from undifferentiated hyphae, which colonize and penetrate the eggshell causing its destruction, is a characteristic of the Pochonia chlamydosporia species [55,58,69,70]. This fungus can produce enzymes with possible biotechnological applications [71]. The enzymes proteases, chitinases and lipases are necessary during the infection process, since the protective barriers of the nematode, cuticle and eggshell, are rich in macromolecules that are the substrates for these enzymes: proteins, chitin and lipids [71,72,73]. It was shown that Pochonia chlamydosporia maintained its viability and ability to attack Oxyuris equi eggs passing through the gastrointestinal tract of horses, demonstrating the viability of its application in biotechnology for parasite management [64].
The hyphae-forming structures of the fungi Pochonia chlamydosporia and Purpureocil-lium lilacinum embed themselves in the shells of trematode, ascarid and trichurid eggs, penetrating and destroying the embryo inside them [74,75].
The species Mucor circinelloides is also capable of adhering to the surface of helminth eggs, penetrating and feeding on their contents [76]. It has saprophytic capacity, acting against trematode eggs (Fasciola hepatica, Calicophoron daubneyi) [77], ascarids (Toxocara canis, Toxascaris leonina, Ascaris suum, Bayliscascaris procyonis) and trichurids (Trichuris spp.) [67,78]. Studies report that Mucor circinelloides can be associated with Duddingtonia flagrans, with a very practical ovicidal and larvicidal activity for the control of helminths, whose infective stages are eggs or larvae that develop in the environment [79].
3.3.4. Methods of Administering Helminthophagous Fungi
The most widely used form of helminthophagous fungi in field conditions is through feed supplementation [42,43] (Figure 1).
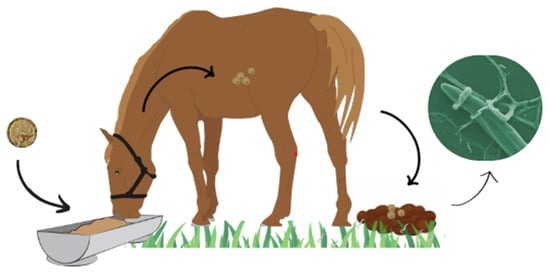
Figure 1.
Dynamics of helminth control in horses using helminthophagous fungi.
It is through the oral administration of these fungal isolates in animal feed that the so-called ‘classical biological control’ takes place, a term that can refer to the flooding of these biological agents into the soil [55]. In the fecal pat, the development of these fungi is stimulated by contact with an increasing number of free-living larvae. With colonization, the chlamydospores establish themselves in the pasture, followed by subsequent ingestion of the pasture by the animals [79]. The parasite load present in the pasture, i.e., when the helminths are not in their parasitic stage, represents around 95% of the total parasite population. As such, almost all of this load is found in the environment, and the fungi therefore act on the site of greatest relevance for control, reducing the number of third-stage larvae in the pastures and, consequently, reducing the infection rate [80,81].
3.3.5. Commercial Products—Biotechnological Innovation
Recently, commercial products with formulations containing Duddingtonia flagrans have started to become available. In Brazil (Bioverm-AC001, GhenVet Saúde Animal, Paulínia, Brazil), in Australia and in New Zealand (BioWorma-NCIMB 30336, BioWorma, Sydney, Australia), these products are already in use, with administration in animal feed [41,42,43,82,83,84] (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Commercial formulations containing Duddingtonia flagrans: BioVerm® (Brazil) and BioWorma® (Australia). Source: Ghenvet and IAHP.
Bioproducts formulated from helminthophagous fungi are found in different forms of administration. Some examples are found in the form of sodium alginate pellets, controlled administration cakes and homogenized cereal grains. The species that have already been successfully incorporated are Monacrosporium thaumasium, Arthrobotrys robusta and Duddingtonia flagrans. It is important to note that these formulations are preconditioned to withstand passing through the animals’ gastrointestinal tract without losing the viability of the fungi [7].
The administration interval of the formulations, as well as the dose to be given to the animals, seems to be crucial to guarantee the effectiveness of any biological control method [81]. After the administration of Duddingtonia flagrans is stopped, its effect on the population of nematode larvae decreases rapidly. Therefore, to achieve a significant and sustained reduction in infective larvae in pastures, it is essential to provide daily and continuous doses of the fungus for prolonged periods. This continuous strategy maintains the effectiveness of biological control, reducing the environmental parasite load and, consequently, the reinfection of animals [40].
Refs. [85,86] evaluated the ability of chlamydospores from the ovicidal fungus Mucor circinelloides and the larvicidal Duddingtonia flagrans to withstand the industrial pelleting process. The fungal spores were added in the process of mixing the feed components, which were then subjected to a temperature of 72 °C. The chlamydospores of both fungi were able to withstand the thermal challenge of the pelleting process, maintaining their ability to infect and destroy nematode eggs. When nutritional pellets containing chlamydospores of the fungi Mucor circinelloides and Duddingtonia flagrans (both incorporated into the same pellet) were fed to horses, a significant reduction in cyathostome egg counts was recorded, and no adverse effects were observed after administration, nor were any changes recorded in the values of cellular blood parameters [85,87].
The oral administration of grains containing nematophagous fungi previously cultivated and provided to animals to evaluate the reduction in infective forms of parasites in feces is also efficient [80,83], and it has been shown to be a commercially practical way [41].
Recently, a new possibility of using these fungi in nematode control was launched, by means of nanoparticles (NPs) biosynthesized from fungal filtrates [88]. The nanoparticles biosynthesized by D. flagrans were shown to be capable of destroying infective larvae of Ancyostoma caninum [89,90]. In the study by [91,92], it was observed that the extracellular enzymes produced by Duddingtonia flagrans show nematocidal activity against the infective larvae of cyathostomins. This indicates that enzymes such as chitinase play a fundamental role in the biological control of nematodes, acting directly on the third-stage larvae (L3), which is the infective form. Reference [69] investigated the effect of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from Duddingtonia flagrans on cyathostomin larvae. The study showed that AgNPs have nematicidal activity, specifically on infective Cyathostominae larvae. This discovery has opened up new ways for the use of this fungus and, therefore, new products, such as bio-antihelminthics may, in the future, serve as an alternative for more successful parasite control against the already established problem of parasite resistance [7].
Finally, an interesting way of administration involved the preparation of edible gelatins containing a mixture of chlamydospores of Mucor circinelloides and Duddingtonia flagrans. This formulation provided excellent results in reducing the risk of infection by trichostrongylids, roundworms, whipworms and hookworms affecting dogs and wild captive herbivores [9,93].
3.4. Biological and Sustainable Solution
Gastrointestinal nematode anthelmintic resistance has become a growing problem worldwide, especially due to the indiscriminate and empirical use of anthelmintics, without adequate technical criteria, exacerbating the resistance problem globally [32,33,94]. In addition, anthelmintics such as macrocyclic lactones (e.g., ivermectin and doramectin) are excreted in animal feces in large quantities without undergoing significant modifications, with more than 90% of the molecules being eliminated as the parent drug. This can negatively affect the community of invertebrates and microorganisms that depend on feces for their development and food, impacting the decomposition of feces and soil quality. The environmental effect of these residues is well documented in cattle [95]. In addition, the use of these drugs can leave residues in animal products such as meat, milk and eggs, which must be below the limits established to guarantee food safety, known as “maximum residue limits” [96].
The lack of adequate treatment of helminthoses in horses can result in serious gastrointestinal disorders, compromising the health and development of the animals, which can lead to significant losses, including death [97,98]. In this context, the use of nematophagous fungi, such as Duddingtonia flagrans and Pochonia chlamydosporia, has proven to be a viable and effective alternative. Unlike anthelmintics, these fungi do not negatively affect the microbial population of feces, which hinder the development of beneficial microorganisms [43]. Studies have shown that the oral administration of Duddingtonia flagrans does not cause any adverse effects on the health of horses, as there is no action on the animal during the passage of these fungi through the animal’s gastrointestinal tract, making nematophagous fungi a safe and sustainable option for nematode control compared to traditional chemical treatments [87,99]. In another study, ref. [100] showed that Duddingtonia flagrans did not cause damage or alterations to intestinal microvilli in Swiss mice infected with Strongyloides venezuelensis after oral ingestion of chlamydospores/conidia. In addition, it did not interfere with the levels of eosinophil peroxidase and myeloperoxidase, providing promising information for future research focused on the in vivo use of these enzymes. Thus, the use of nematophagous fungi represents an effective approach that is less harmful to the environment and safe for the health of animals and consumers.
4. Conclusions
The application of helminthophagous fungi in the biological control of gastrointestinal nematodes in horses is a promising and sustainable alternative to the challenges faced by equine farming, especially in relation to the presence of anthelmintic resistance caused by the indiscriminate use of chemical anthelmintics. Species such as Duddingtonia flagrans, Pochonia chlamydosporia, Arthrobotrys oligospora, Monacrosporium thaumasium, Mucor circinelloides and Purpureocillum liacinum have shown efficacy in reducing the parasite burden by acting on different stages of the nematode life cycle, from the larval stage to the egg stage.
The administration of these fungi is practical and can be carried out by means of feed supplementation or commercial formulations that guarantee the survival of the chlamydospores during their passage through the animals’ digestive tract. By being excreted in the feces, these fungi act directly on the environment, reducing the amount of infective larvae in pastures and reducing the reinfection of horses.
In view of this, the use of helminthophagous fungi can be considered a viable, efficient and ecologically correct strategy for the control of helminthiases in horses, offering a practical and long-lasting solution for anti-parasitic management.
Author Contributions
J.V.d.A. and T.A.d.C. developed with the concept for the article. All authors of the manuscript performed the literature search, wrote and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. The authors thank CNPq, CAPES, FAPEMIG, for all the financial support throughout the group’s research. This article does not contain any studies involving human or animal participants performed by the authors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lima, R.A.S. The importance and challenges of understanding the equine population in Brazil. Braz. J. Equine Med. 2023, 18, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Silva, A.R.; Araújo, J.M.; Carvalho, R.O.; Tavel, A.O.; Carvalho, G.R.; Campos, A.K. Biological control of horse cyathostomin (Nematoda: Cyathostominae) using the nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans in tropical southeastern Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barret, E.J.; Farlam, J.; Proudman, C.J. Field trial of the efficacy of a combination of ivermectin and praziquantel in horses infected with roundworms and tapeworms. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupello, F.; Vilarim, D.S.S.; Nogueira, G.R.; Campos, L.D.F.; Costa, M.P.B.; Marques, B.L.O.; Souza, G.O.; Monteiro, J.L.A.B.C.; Salema, M.H.M.; Pacheco, A. Challenge in the management and control of parasites in horses: Literature review. Ciências Agrárias 2024, 28, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaggio, V.R.A.; Jorge, L.L. Achados de formas parasitárias em camas de equinos Santa Maria-RS/Brasil. 2007. Available online: https://www.redevet.com.br/index.php/profissionais/na-rede/ibrajournal/113-geral/390-achados-de-formas-parasitarias-em-camas-de-equinos-1?showall=1 (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Molento, M.B. Resistência parasitária em helmintos de equídeos e propostas de manejo. Ciência Rural 2005, 35, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Mendoza-de-Gives, P.; Paz-Silva, A.; Vilela, V.L.R. Recent advances in the control of helminths of domestic animals by helminthophagous fungi. Parasitologia 2021, 1, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.Q.; Xu, J. Fungi-Nematode Interactions: Diversity, Ecology, and Biocontrol Prospects in Agriculture. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmo, R.; Viña, C.; Zubiria, I.; Malagón, J.Á.H.; Sanchís, J.M.; Cazapal, C.; Arias, M.S.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A. Formulating Parasiticidal Fungi in Dried Edible Gelatins to Reduce the Risk of Infection by Trichuris sp. among Continuous Grazing Bison. Pathogens 2024, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.O.; Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Araujo, J.M.; Silva, A.R.; Tavela, A.O. Predatory activity of nematophagous fungi on infective larvae of Ancylostoma sp.: Evaluation in vitro and after passing through the gastrointestinal tract of dogs. J. Helminthol. 2009, 83, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.R.; Machado, A.R.T.; Furtado, L.F.; Gomes, J.H.D.S.; de Almeida, R.M.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.; Maciel, V.N.; Barbosa, F.S.; Carvalho, L.M.; Bueno, L.L.; et al. Ketamine can be produced by Pochonia chlamydosporia: An old molecule and a new anthelmintic. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenfels, J.R.; Kharchenko, V.A.; Dvojnos, G.M. Illustrated identification keys to strongylid parasites (Strongylidae: Nematoda) of horses, zebras and asses (Equidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 4–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M. Sustainable equine parasite control: Perspectives and research needs. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbein, S.; Visser, M.; Winter, R. Koproskopische Untersuchun gen bei Pferden in Deutschland und Österreich. Pferdeheilkunde, 2002, 18:439–449. Pferdeheilkunde 2002, 18, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira de Carvalho, L.; Gomes, L.; Cernea, M.; Cernea, C.; Santos, C.A.; Bernardes, N.; Rosário, M.A.; Soares, M.J.; Fazendeiro, I. Parasitismo gastrointestinal e seu controlo em asininos e híbridos estabulados. Rev. Port. De Ciências Veterinárias 2007, 102, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, H.E.; Spanton, J.; Stratford, C.H.; Bartley, D.J.; Morgan, E.R.; Hodgkinson, J.E.; Coumbe, K.; Mair, T.; Swan, B.; Lemon, G.; et al. Anthelmintic efficacy against cyathostomins in horses in Southern England. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 197, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Nielsen, M.K. An evidence-based approach to equine parasite control: It ain’t the 60s anymore. Equine Vet. Educ. 2010, 22, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksovsky, J.; Craig, T.M.; Bingham, G.M.; Cir, T.; Forrets, D. Determining treatment to control two multidrug-resistant parasites on a Texas horse farm. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbein, S.; Martin, V.; Renate, W. Prevalence, intensity and seasonality of gastrointestinal parasites in abattoir horses in Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N. Equine lung worm: A systematic review. Glob. J. Med. Res. G Vet. Sci. Vet. Med. 2017, 17, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Esteban, J.G.; Bargues, M.D. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission and control. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2009, 2, 41–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide to the Treatment and Control of 8 Equine Gastrointestinal Parasite Infections. ESCCAP Guideline08 Second Edition—March. European Scientific Counsel Companion Animal Parasites. 2019. Available online: https://www.esccap.org/guidelines/gl8/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- El-Gameel, S.M.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Salaeh, N.M.K.; Attia, M.M. Morphomolecular characterization of Strongylus vulgaris isolated from donkeys with special reference to histopathological study on the affected organs. J. Parasit. Dis. 2022, 46, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, W.F.P.; Felippelli, G.; Cruz, B.C.; Maciel, W.G.; Fávero, F.C.; Gomes, L.V.C.; Buzzulini, C.; Prando, L.; Bichuette, M.A.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; et al. Endoparasites of horses from the Formiga city, located in center-west region of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2014, 23, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saes, I.L.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Do Carmo, T.A.; Mena, M.O.; De Almeida Cipriano, I.; De Favare, G.M.; Bello, H.J.S.; Guelpa, G.J.; de Soutello, R.V.G. Sazonalidade e dinâmica de helmintos gastrointestinais em equinos em pastejo. Acta Vet.-Beogr. 2022, 72, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutello RVG de Romão, D.S.; Carmo, T.A.; do Favare, G.M.; de Pagnozzi, F.C.; Cipriano, I.d.A. Seasonal dynamics of gastrointestinal helminths in naturally infected horses in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 324, 110358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canever, R.J.; Braga, P.R.; Boeckh, A.; Grycajuck, M.; Bier, D.; Molento, M.B. Lack of Cyathostomin sp. reduction after anthelmintic treatment in horses in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 194, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.; Taylor, N.M.; Wilsmore, A.J.; Garforth, C. Equine anthelmintics: Survey of the patterns of use, beliefs and attitudes among horse owners in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregrine, A.S.; Molento, M.B.; Kaplan, R.M.; Nielsen, M.K. Anthelmintic resistance in important parasites of horses: Does it really matter? Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 201, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saes, I.L.; Vera, J.H.S.; Fachiolli, D.F.; Yamada, P.H.; Dellaqua, J.V.T.; Saes, R.L.; Amaranto, A.F.; Soutello, R.V.G. Tempo necessário para diferentes anti-helmínticos atingirem os níveis de eficácia esperados em equinos infectados por estrongilídeos. Parasitol. Veterinária 2016, 229, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.H.S.; Fachioli, D.F.; Ramires, L.M.; Saes, I.L.; Yamada, P.H.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Oliveira, K.; Amarante, A.F.T.; Soutello, R.V.G. Eficacy of ivermectin, moxidectin and febendazole in equine in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 20, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, N.K.; Banahan, M.; Kaplan, R.M. Importation of macrocyclic lactone resistant cyathostomins on a US thoroughbred farm. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2020, 14, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Favare, G.M.; Cipriano, I.A.; do Carmo, T.A.; Mena, M.O.; Guelpa, G.J.; do Amarante, A.F.T.; de Soutello, R.V.G. Anthelmintic resistance of horse strongyle nematodes to ivermectin in São Paulo state, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2023, 41, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.K.; Reinemeyer, C.R.; Donecker, J.M.; Leathwick, D.M. Anthelmintic resistance in equine parasites—Current evidence and knowledge gaps. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 204, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.H.; Carvalho, N.; Rinaldi, L.; Oliveira, G.; Amarante, A.F.T. Diagnóstico da resistência anti-helmíntica em bovinos no Brasil: Uma comparação de diferentes metodologias. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 206, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.; Oliveira, C.B.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Oliveira, P.; Osmari, V.; Fernandes, F.; Sangioni, L.A.; Vogel, F.S.F. Avaliação molecular e de campo da resistência anti-helmíntica de populações de nematóides de bovinos e ovinos naturalmente infectados em pastagens mistas no Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 65, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Coop, R.L.; Wall, R.L. Veterinary Parasitology, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.V.; Guimarães, M.P.; Campos, A.K.; Sá, N.C.; Sarti, P.; Assis, R.C. Control of bovine gastrointestinal nematode parasites using pellets of the nematode-trapping fungus Monacrosporium thaumasium. Ciência Rural 2004, 34, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.A.; Campos, A.K.; Araújo, J.V. Biological control of animal parasitic helminths by nematophagous fungi. Braz. J. Parasitol. Vete 2003, 13, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-de-Gives, P.; López-Arellano, M.E.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Olazarán-Jenkins, S.; Reyes-Guerrero, D.; Oliveira, G.; Veja-Murillo, V.E. The nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans reduces the gastrointestinal parasitic nematode larvae population in faeces of orally treated calves maintained under tropical conditions—Dose/response assessment. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 263, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.R.; Oliveira, C.M.; Silva, E.M.; Araújo, J.V. Efficiency of the fungal formulation Bioverm (Duddingtonia flagrans) in the in vivo and in vitro control of Haemonchus contortus and Strongyloides papillosus in sheep. Biotecnologia 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausto, G.C.; Fausto, M.C.; Vieira, Í.S.; Freitas, S.G.; Carvalho, L.M.; Oliveira, I.C.; Silva, E.N.; Campos, A.K.; Araújo, J.V. Formulation of the nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans in the control of equine gastrointestinal parasitic nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 296, 109458–109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, T.A.; Mena, M.O.; Cipriano, I.A.; Favare, G.M.; Guelpa, G.J.; Pinto, S.C.; Amarante, A.F.T.; Araújo, J.V.; Soutello, R.V.G. Biological control of gastrointestinal nematodes in horses fed with grass in association with nematophagous fungi Duddingtonia flagrans and Pochonia chlamydosporia. Biol. Control 2023, 182, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza de Gives, P.; Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V. Nematophagous fungi, an extraordinary tool for controlling ruminant parasitic nematodes and other biotechnological applications. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y. Individual and combined application of nematophagous fungi as biological control agents against gastrointestinal nematodes in domestic animals. Pathogens 2022, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, F.E.D.F.; de Queiroz, J.H.; de Araújo, J.V.; Queiroz, P.V.; Gouveia, A.D.S.; Hiura, E.; Braga, F.R. Ação nematicida de quitinases produzidas pelo fungo Monacrosporium thaumasium em condições laboratoriais. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiang, M.; Che, Y. A estratégia viva dos fungos nematófagos. Micociência 2009, 50, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Chen, Y.; Gong, S.; Qiao, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tian, L.; Niu, Y. Enzymological properties and nematode-degrading activity of recombinant chitinase AO-379 of Arthrobotrys oligospora. Kafkas Üni. Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2019, 25, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Hyde, K.Q. Nematode-Trapping Fungi; Fungal Diversity Series 23; Mushroom Research Foundation: Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.u.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Fan, B. Predatory strategies of nematophagous fungi as biocontrol agents. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbring-Hertz, B.; Jansson, H.B.; Tunlid, A. Nematophagous fungi. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Macmillan Publishers Ltd.: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbring-Hertz, B. Ecology and recognition in the nematode-nematophagous fungus system. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Marshall, K.C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 10, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronvold, J.; Henriksen, S.A.; Larsen, M.; Nansen, P.; Wolstrup, J. Aspects of biological control with special reference to arthropods, protozoans and helminths of domesticated animals. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 64, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, T.; Ulloa, M. El Reino de los Hongos: Micología Básica y Aplicada; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Fondo de Cultura Económica: Mexico City, Mexico, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V. Nematophagous fungi for biological control of gastrointestinal nematodes in domestic animals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.G.; Araújo, F.B.; Molento, M.B. Kinetics of capture and infection of infective larvae of trichostrongylides and free-living nematodes Panagrellus sp. by Duddingtonia flagrans. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallemole-Giaretta, R.; Freitas, L.G.; Cavallin, I.C.; Marmentini, G.A.; Faria, C.M.R.; Resende, J.T.V. Evaluation of a Pochonia chlamydosporia based product, for the control of Meloidogyne javanica in culture and in carrot fields. Nematropica 2013, 43, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, J.M.; Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Carvalho, R.O.; Silva, A.R.; Campos, A.K. Interaction and ovicidal activity of the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia on Taenia saginata eggs. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, V.L.R.; Feitosa, T.F.; Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Souto, D.V.O.; Santos, H.E.S.; Athayde, A.C.R. Biological control of goat gastrointestinal helminthiasis by Duddingtonia flagrans in a semi-arid region of the Northeastern Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, V.L.R.; Feitosa, T.F.; Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Lucena, S.C.; Dantas, E.S.; Athayde, A.C.R.; Silva, A.R. Effect of Monacrosprorium thaumasium in the control of the goat gastrointestinal helminthiasis in the semi-arid of Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, G.; Mittal, N. Trap formation by conidia of nematode-trapping Monacrosporium spp. Mycol. Res 1995, 7, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M. Biological control of helminths. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, N.; Gong, P.T.; Li, J. Effect of temperature, pH, physical and chemical factors on germination rate of the chlamydospores of the nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Ribeiro, V.L.; Soares, F.E.F.; Araújo, J.M.; Silva, G.R. Viability of the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia after passage through the gastrointestinal tract of horses. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, Í.S.; Oliveira, I.C.; Campos, A.K.; Araújo, J.V. In vitro biological control of bovine parasitic nematodes by Arthrobotrys cladodes, Duddingtonia flagrans, and Pochonia chlamydosporia under different temperature conditions. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.P.; Padilha, T.; Rodrigues, M.L.A. Predatory activity of Arthrobotrys oligospora and Duddingtonia flagrans on pre-parasitic larval stages of cyathostominae under different constant temperatures. Ciência Rural 2001, 31, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.Á.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Sanchís, J.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Arias, M.S. Potential Usefulness of Filamentous Fungi to Prevent Zoonotic Soil-Transmitted Helminths. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Soares, F.E.F.; Araújo, J.M.; Geniêr, H.L.A.; Silva, A.R.; Carvalho, R.O.; Queiroz, J.H.; Ferreira, S.R. Optimizing protease production from an isolate of the nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans using response surface methodology and its larvicidal activity on horse cyathostomin. J. Helminthol. 2011, 85, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, C.M.; Costa Silva, L.P.; de Freitas Soares, F.E.; Souza, R.L.O.; Tobias, F.L.; de Araújo, J.V.; Rodrigues Veloso, F.B.; Laviola, F.P.; Endringer, D.C.; de Gives, P.M.; et al. Effect of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from Duddingtonia flagrans on cyathostomins larvae (subfamily: Cyathostominae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 175, 107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Kerry, B.R.; Manzanilla-López, R.H.; Mutua, G.; Devonshire, J.; Kimenju, J.; Hirsch, P.R. The Pochonia chlamydosporia Serine Protease Gene vcp1 is subject to regulation by carbon, nitrogen and pH: Implications for nematode biocontrol. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e35657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhao, F.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, R. Antagonistic activity of Pochonia chlamydosporia against three helminth eggs and characterization of its serine protease. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 334, 110374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, I.; Peteira, B.; Atkins, S.D.; Magan, N.; Kerry, B. Production of extracellular enzymes by different isolates of Pochonia chlamydosporia. Mycol. Res. 2009, 8, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Q.; Yang, J.; Ye, F.; Gan, Z.; Wu, C.; Niu, X.; Zou, C.; Zhang, K.Q. Clonagem e superexpressão do gene pcchi44 da quitinase de Pochonia chlamydosporia, um potencial fator de virulência na infecção contra nematoides. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.E.F.; Sufiate, B.L.; Queiroz, J.H. Fungos nematófagos: Muito além dos grupos endoparasita, predador e ovicida. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.; Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Benjamim, L.A.; Souza, D.L.; Carvalho, R.O. Análise comparativa da destruição das formas infectantes de Trichuris trichiura e Haemonchus contortus por fungos nematófagos Pochonia chlamydosporia, Duddingtonia flagrans e Monacrosporium thaumasium por microscopia eletrônica de varredura. Microbiol. Veterinária 2011, 147, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Hernández, J.A.; Arroyo, F.L. Analysing the effect of soil saprophytic fungi on Baylisascaris procyonis eggs. Res. Parasitol. 2015, 114, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.S.; Oliveira, C.F.; Souza, J.; Miguélez, S.; Oliveira, I.; Oliveira, F.L.; Suárez, J.L.; Paz-Silva, A.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; De Gives, P.M. Mixed production of filamentous fungal spores for preventing soil-transmitted helminth zoonoses: A preliminary analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 567876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, F.; Oliveira, J.A.; Oliveira, C.F.; Pedreira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Romasanta, Á.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Arias, M.S. Effect of the Filamentous Fungus Mucor circinelloides On The Development of Eggs of the Rumen Fluke Calicophoron daubneyi (Paramphistomidae). J. Parasitol. 2017, 103, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortiñas, F.J.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Hernández, J.A.; Arroyo, F.L.; Miguélez, S.; Suárez, J.; López de Arellano, M.E.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Mendoza de Gives, P.; Paz-Silva, A.; et al. Potential use of Mucor circinelloides for the biological control of certain helminths affecting livestock reared in a care farm. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinot, M.; Bonilla, R.; Sousa, S.; Sanchís, J.; Canhão-Dias, M.; Romero Delgado, J.; Lozano, J.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Sol Arias, M.; Madeira de Carvalho, L. Control of Strongyles in First-Season Grazing Ewe Lambs by Integrating Deworming and Thrice-Weekly Administration of Parasiticidal Fungal Spores. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Silva, A.; Francisco, I.; Valero-Coss, R.O. Ability of the fungus Duddingtonia flagrans to adapt to the cyathostomin egg-output by spreading chlamydospores. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duddington, C.L. Fungi that attack microscopic animals. Bot. Rev. 1955, 21, 377–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatti, A.; Santos, C.P.; Fernandes, M.A.M.; Yoshitani, U.Y.; Sprenger, L.K.; Molento, M.B. Duddingtonia flagrans no controle de nematoides gastrintestinais de equinos em fases de vida livre. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária E Zootec. 2015, 69, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Kos Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; Marcon, F. Scientific opinion on the safety and efficacy of BioWorma (Duddingtonia flagrans NCIMB 30336) as a feed additive for all grazing animals. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.S.S.C.B.; Dias, F.G.S.; Melo, A.L.T.; Carvalho, L.M.; Silva, E.N.; Araújo, J.V. Bioverm in the control of nematodes in beef cattle raised in the Central-West region of Brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Roque, F.L.; Alvares, F.B.V.; Silva, A.L.P.; Lima, E.F.; Silva Filho, G.M.; Feitosa, T.F.; Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Vilela, V.L.R. Efficacy of a commercial fungal formulation containing Duddingtonia flagrans (Bioverm) for controlling bovine gastrointestinal nematodes. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2021, 30, e026620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.; Arroyo, F.L.; Suárez, J.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Romasanta, A.; López-Arellano, M.E.; Pedreira, J.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.M.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Arias, M.S.; et al. Feeding horses with industrially manufactured pellets with fungal spores to promote nematode integrated control. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 229, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, F.L.; Arias, M.S.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Hernández, J.Á.; Suárez, J.; Miguélez, S.; Romasanta, A.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A. The capability of the fungus Mucor circinelloides to maintain parasiticidal activity after the industrial feed pelleting enhances the possibilities of biological control of livestock parasites. Biol. Control 2016, 92, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.Á.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.F.; Arroyo, F.L.; Sanchís, J.M.; Paz-Silva, A.; Arias, M.S. A combined effort to avoid strongyle infection in horses in an oceanic climate region: Rotational grazing and parasiticidal fungi. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Silva, L.P.; Pinto-Oliveira, J.; Keijok, W.J.; Silva, A.R.; Aguiar, A.R.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Ferraz, C.M.; Araújo, J.V.; Tobias, F.L.; Braga, F.R. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the cell-free filtrate of nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6373–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.C.M.S.; Silva, L.P.C.; Ferraz, C.M.; Tobias, F.L.; Araújo, J.V.; Loureiro, B.; Braga, G.M.A.M.; Veloso, F.B.R.; Soares, F.E.F.; Fronza, M. Nematicidal activity of silver nanoparticles from the fungus Duddingtonia flagrans. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, F.R.; Soares, F.E.F.; Giuberti, T.Z.; Lopes, A.D.C.G.; Lacerda, T.; Ayupe, T.D.H.; Queiroz, P.V.; Gouveia, A.d.S.; Pinheiro, L.; Araújo, A.L.; et al. Nematocidal activity of extracellular enzymes produced by the nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans on cyathostomin infective larvae. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, C.; Salmo, R.; Pena, M.V.; Palomero, A.M.; Hernández, J.Á.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.; Arias, M.S.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A. A New Comestible Formulation of Parasiticide Fungi to Reduce the Risk of Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in a Canine Shelter. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinemeyer, R. Anthelmintic resistance in non-strongylid parasites of horses. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredero, A.M.C.; Segato, G.; Menotta, S.; Faggionato, E.; Vismarra, A.; Genchi, M.; Bertini, S.A. new method for ivermectin detection and quantification through HPLC in organic matter (feed, soil, and water). J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2023, 2023, 6924263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.P.; Souza, J.R.; Caldas, E. Residues of veterinary medicines in milk and eggs. New Quim. 2014, 37, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar, A.S.; Catto, J.B.; Bianchin, I. Controle alternativo de nematódeos gastrintestinais dos ruminantes: Atualidade e perspectivas. Ciência Rural 2008, 38, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.C.D.F.; Chagas, J.D.R.; Ávila, L.M.; Marques, T.L.P.; Moraes, R.F.F.; Gomes, L.P.M.; Roier, E.C.R.; Baêta, B.A. Diagnosis and chemical control of helminthiases in cattle: Literature review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, 4089119908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira de Carvalho, L.M.; Gillespie, A.T.; Serra, P.M. Eficácia do fungo nematófago Duddingtonia flagrans no controlo biológico da estrongilidose equina no Ribatejo. Rev. Port. Ciências Veterinárias 2007, 102, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, J.M.; Braga, F.R.; Longo Ribeiro Vilela, V.; Soares, F.E.D.F.; Ferraz, C.M.; Bindaco, A.L.S.; Aguiar, D.F.; Negrão-Corrêa, D.A.; Fernandes Rodrigues, V.; de Araújo, J.V. Evaluation of the acute oral toxicity of the fungus Duddingtonia flagrans at the gut level. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).