Influence of Astragalus extract on Gut Microbiome Regulation and Ammonia Emission Mitigation in Laying Hens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Fermentation Test Analysis
2.2. Animals and Feeding
2.3. Measurement of NH3 Emissions
2.4. Recovery Rate of the Respiration Chambers
Measurement of NH3 production
2.5. Performance
2.6. Sample Collection
2.7. Blood Biochemical Parameters
2.8. Measurement of Cecal Profiles
2.9. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
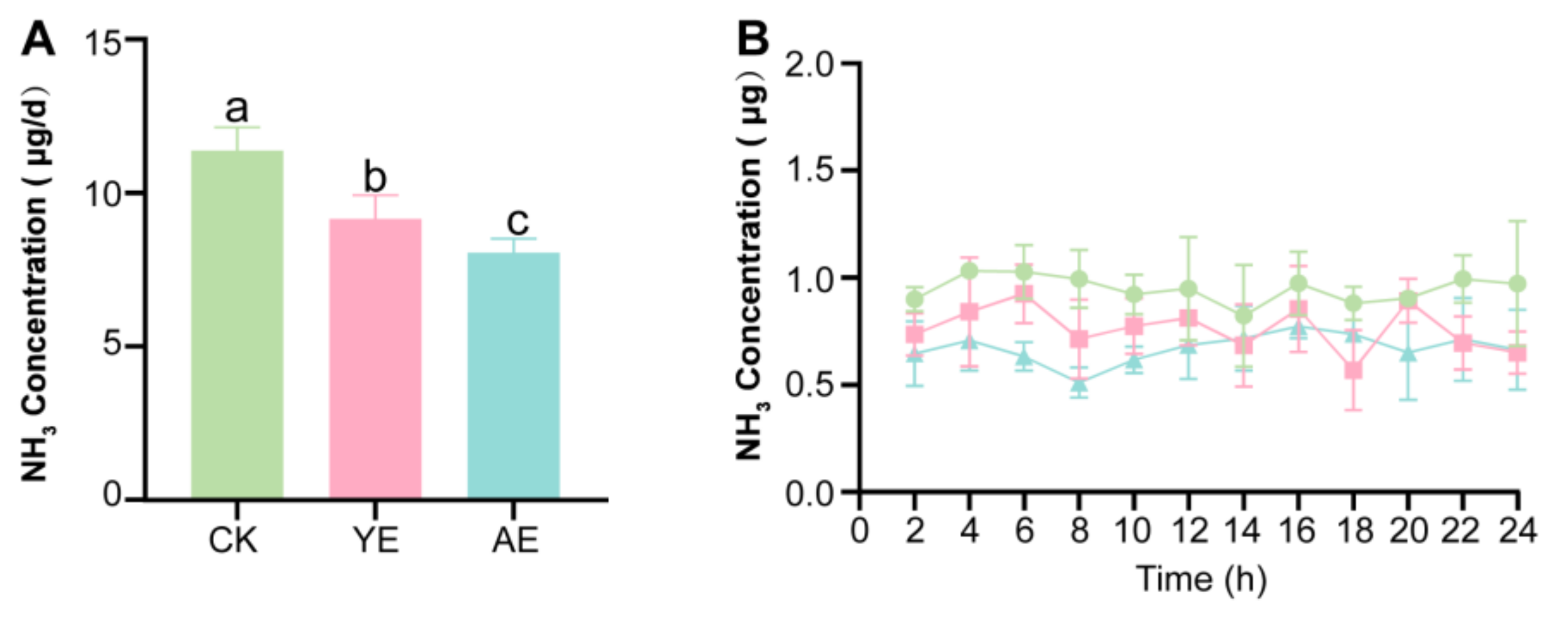
3.1. AE Supplementation Reduces NH3 Emission of Laying Hens
3.2. Effects on Production Performance and Serum Immune Parameters
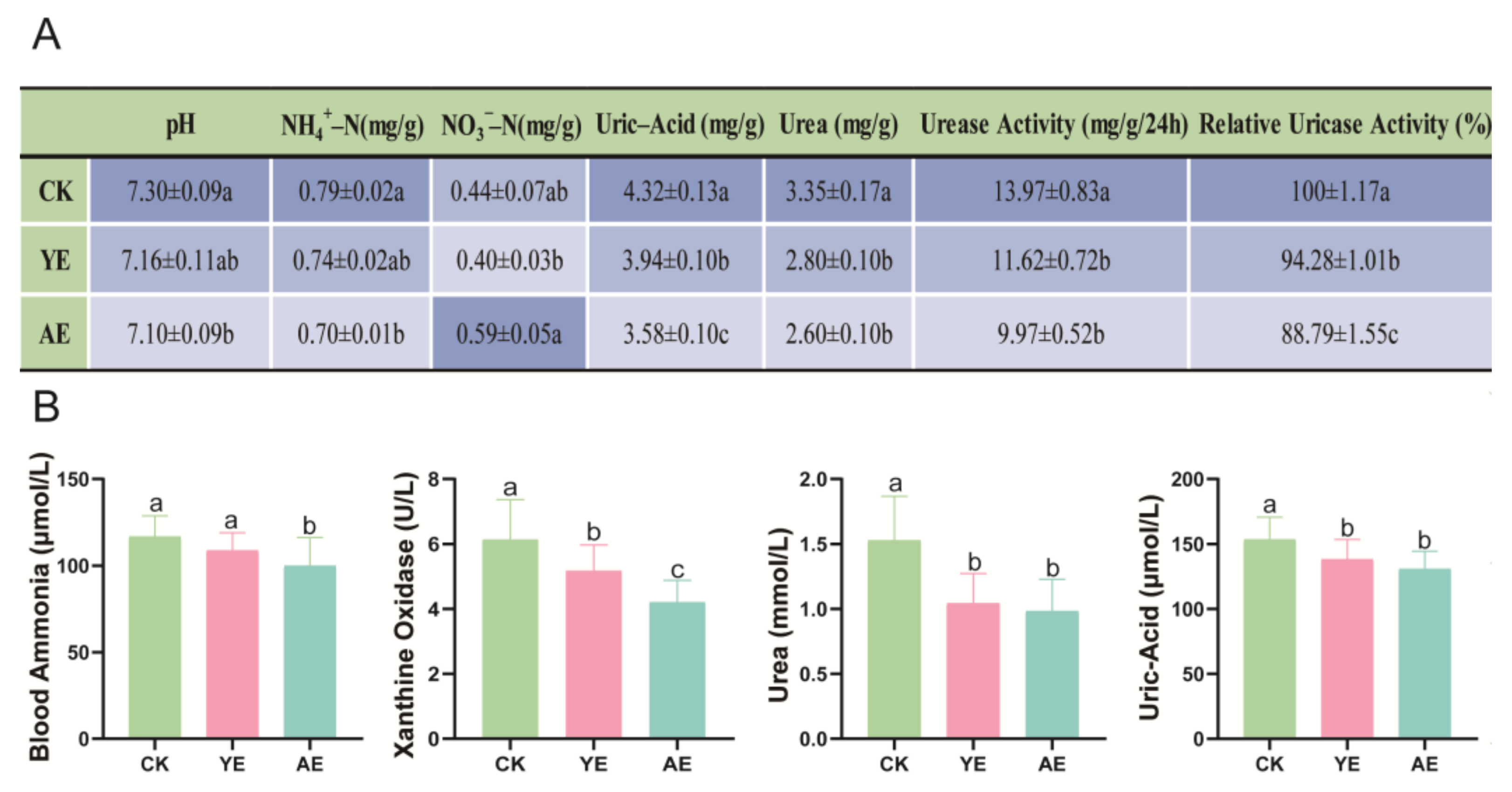
3.3. Effects on Gut and Serum Physicochemical Indicators
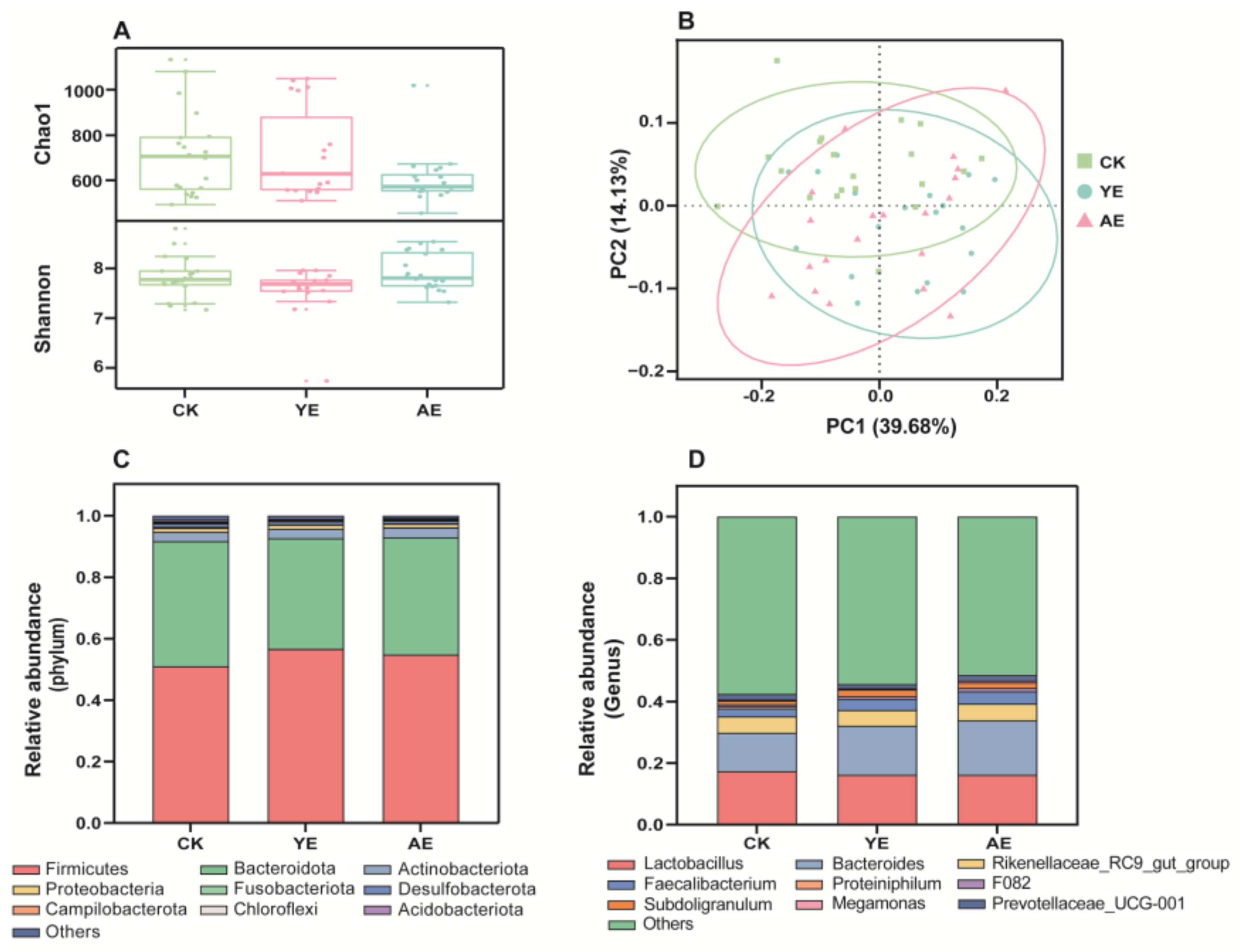
3.4. Effects on the Gut Microbiome Community
3.5. Correlation Analysis of NH3 Concentrations and Bacterial Genera
3.6. Microbial Function Prediction Analysis
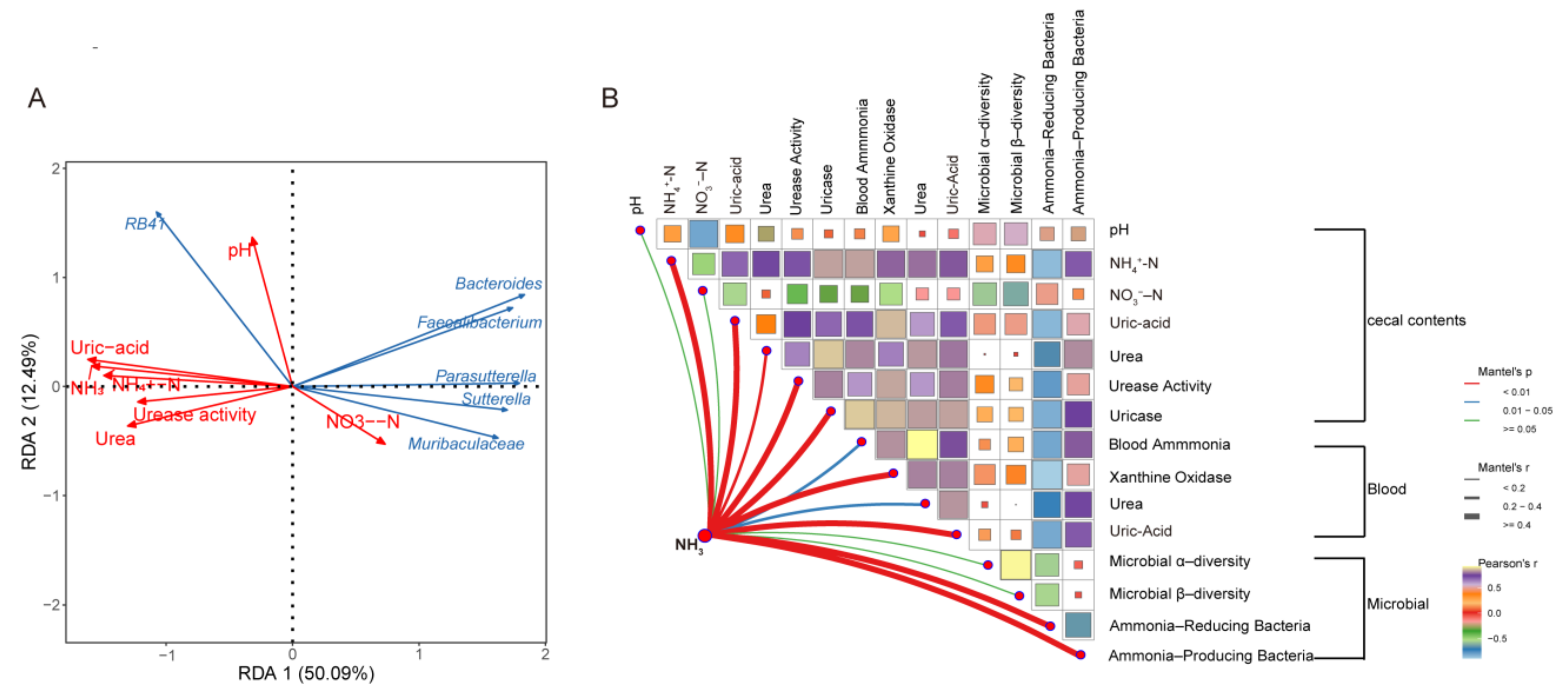
3.7. Factors Influencing NH3 Emissions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konkol, D.; Popiela, E.; Skrzypczak, D.; Izydorczyk, G.; Mikula, K.; Moustakas, K.; Opaliński, S.; Korczyński, M.; Anna, W.K.; Katarzyna, C. Recent innovations in various methods of harmful gases conversion and its mechanism in poultry farms. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bing, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Jiao, H. High ambient humidity aggravates ammonia-induced respiratory mucosal inflammation by eliciting Th1/Th2 imbalance and NF-κB pathway activation in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Tong, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Yan, G. Effects of cold stress and ammonia concentration on productive performance and egg quality traits of laying hens. Animals 2020, 10, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, C.; Yost, M.; Sampson, P.; Torres, E.; Arias, G.; Vasquez, V.B.; Hartin, K.; Armstrong, J.; Tchong, M.; Vedal, S.; et al. Ambient ammonia exposures in an agricultural community and pediatric asthma morbidity. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.; Andersson, K.; Feilberg, A.; Delin, S.; Hafner, S.; Nyord, T. Effect of exposed surface area on ammonia emissions from untreated, separated, and digested cattle manure. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 202, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyer, K.E.; Kelleghan, D.B.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Schauberger, G.; Curran, T.P. Ammonia emissions from agriculture and their contribution to fine particulate matter: A review of implications for human health. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Such, N.; Csitári, G.; Stankovics, P.; Wágner, L.; Koltay, I.A.; Farkas, V.; Pál, L.; Strifler, P.; Dublecz, K. Effects of probiotics and wheat bran supplementation of broiler diets on the ammonia emission from excreta. Animals 2021, 11, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro, D.; Hjorth, M.; Gioelli, F. Acidification of animal slurry—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 149, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, N.; Wang, T.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Yuan, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J. DNA shuffling of uricase gene leads to a more “human like” chimeric uricase with increased uricolytic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svane, S.; Sigurdarson, J.J.; Finkenwirth, F.; Eitinger, T.; Karring, H. nhibition of urease activity by different compounds provides insight into the modulation and association of bacterial nickel import and ureolysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.; Sipos, M.; Goldenfeld, N.D.; White, B.A. The microbiome of the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2012, 13, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.L.; Erickson, J.M.; Hess, J.M.; Gould, T.J.; Slavin, J.L. Prebiotic dietary fiber and gut health: Comparing the in vitro fermentations of beta-glucan, inulin and xylooligosaccharide. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, A.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, Z. Application of traditional Chinese herbal medicine by-products as dietary feed supplements and antibiotic replacements in animal production. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Jiang, J. Anti-fatigue effects of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1833–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M. New insights into purine metabolism in metabolic diseases: Role of xanthine oxidoreductase activity. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E827–E834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melekhovets, O.K.; Kovalenko, Y.L. Endothelial dysfunction correcting with normalizing of the hyperuricemia by the using of ILLLT in the systemic hypertension patients. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2018, 32, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Huang, T.; Yang, Q.; Peng, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X. Dietary supplementation Eucommia ulmoides extract at high content served as a feed additive in the hens industry. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegbeye, M.J.; Elghandour, M.M.; Monroy, J.C.; Abegunde, T.O.; Salem, A.Z.; Barbabosa-Pliego, A.; Faniyi, T.O. Potential influence of Yucca extract as feed additive on greenhouse gases emission for a cleaner livestock and aquaculture farming-A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Oh, I.; Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.E.; Jeon, B.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of compounds isolated from Astragalus sinicus L. in cytokine-induced keratinocytes and skin. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhao, G.D.; Xiong, W.; Linghu, K.G.; Ma, Q.S.; Cheang, W.S.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Immunomodulatory effects of a new whole ingredients extract from Astragalus: A combined evaluation on chemistry and pharmacology. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Wu, S.; Qi, G. Supplemental plant extracts from flos lonicerae in combination with baikal skullcap attenuate intestinal disruption and modulate gut microbiota in laying hens challenged by Salmonella pullorum. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.; Xie, G.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Qu, Q.; Long, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Effects of Astragalus, Epimedium, and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi extractive on antioxidant capacity, production performance, and immune mechanism of breeding pigeons under stress. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Feng, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y. Chinese Herbal Extracts Mitigate Ammonia Generation in the Cecum of Laying Hens: An In Vitro Study. Animals 2023, 13, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Xing, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Liang, J.B.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. The microbiota structure in the cecum of laying hens contributes to dissimilar H2S production. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese National Environmental Protection Standards (HJ 533-2009). Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/HJ533-2009 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- GB/T 11894–1989. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/GBT11894-1989 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- GB/T 7480–1987. Available online: https://transcustoms.com/GB_standards/GB_standards_english.asp?code=GB/T%207480-1987 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, J.A.; Vilgalys, R.; Jackson, R.B. Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon-specific quantitative pcr assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4117–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriseldi, R.; Tillman, P.B.; Jiang, Z.; Dozier, W.A. Effects of feeding reduced crude protein diets on growth performance, nitrogen excretion, and plasma uric acid concentration of broiler chicks during the starter period. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, R.; Liao, X.; Wu, Y.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y. Ammonia reduction by the gdhA and glnA genes from bacteria in laying hens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogut, M.H. Role of diet-microbiota interactions in precision nutrition of the chicken: Facts, gaps, and new concepts. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Classen, J.; Shah, S.B.; Sharma-Shivappa, R. Ammonia Fate and Transport Mechanisms in Broiler Litter. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.K.; Raval, K.; JagadeeshBabu, P.E. Enhancement of a Novel Extracellular Uricase Production by Media Optimization and Partial Purification by Aqueous Three-Phase System. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qu, L.; Dong, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. A Review of Recent Research Progress on the Astragalus Genus. Molecules 2014, 19, 18850–18880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, L.; Musiani, F.; Ciurli, S. The structure-based reaction mechanism of urease, a nickel dependent enzyme: Tale of a long debate. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 26, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Anwar, F.; Naz, F.; Mehmood, T.; Saari, N. Anti-Helicobacter pylori and Urease Inhibition Activities of Some Traditional Medicinal Plants. Molecules 2013, 18, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.K.; Aschenbach, J.R. Ureases in the gastrointestinal tracts of ruminant and monogastric animals and their implication in urea-N/ammonia metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Fan, Z. Astragalus polysaccharide supplementation improves production performance, egg quality, serum biochemical index and gut microbiota in Chongren hens. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuolo, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Gratteri, S.; Muscoli, C.; Mollace, V. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 213, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Deng, W.; Sun, C.; Wei, Q.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Shi, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, X. Anti-hyperuricemic and anti-gouty arthritis activities of polysaccharide purified from Lonicera japonica in model rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Leclerc, M.; Martin, R.; Chain, F.; Lenoir, M.; Raguideau, S.; Hudault, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Northen, T.; Bowen, B.; et al. Identification of Metabolic Signatures Linked to Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. mBio 2015, 6, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Lian, G.; Blachier, F.; Geng, M.; Yin, Y. Dietary supplementation with soybean oligosaccharides increases short-chain fatty acids but decreases protein-derived catabolites in the intestinal luminal content of weaned Huanjiang mini-piglets. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherly, T.; Ziemer, C.J. Bacteroides isolated from four mammalian hosts lack host-specific 16S rRNA gene phylogeny and carbon and nitrogen utilization patterns. Microbiologyopen 2014, 3, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, T.; Kong, J.Y.; Stothard, P.; Willing, B.P. Defining the role of Parasutterella, a previously uncharacterized member of the core gut microbiota. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Miller, R.A.; Ericsson, A.C.; Harrison, D.C.; Strong, R.; Schmidt, T.M. Changes in the gut microbiome and fermentation products concurrent with enhanced longevity in acarbose-treated mice. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, A. Plant phenolic compounds as immunomodulatory agents. In Phenolic Compounds-Biological Activity; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017; pp. 75–98. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Allen, A.; Stanley, C.A.; Smith, T.J. Glutamate Dehydrogenase: Structure, Allosteric Regulation, and Role in Insulin Homeostasis. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.M.; Horowitz, A.; Lynch, E.M.; Farrell, D.P.; Quispe, J.; DiMaio, F.; Kollman, J.M. Cryo-EM structures of CTP synthase filaments reveal mechanism of pH-sensitive assembly during budding yeast starvation. eLife 2021, 10, e73368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | NH3 Concentration (μg) |
|---|---|
| CK | 23.84 ± 1.66 a |
| 0.01% YE | 24.80 ± 0.57 a |
| 0.1% YE | 19.10 ± 0.60 b |
| 0.01% AE | 24.88 ± 1.65 a |
| 0.05% AE | 23.49 ± 1.27 a |
| 0.1% AE | 18.82 ± 0.39 b |
| 0.2% AE | 17.26 ± 0.63 b |
| 0.3% AE | 17.97 ± 0.37 b |
| CK | YE | AE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgA (mg/dL) | 38.12 ± 2.85 b | 44.81 ± 5.56 a (p = 0.012) | 39.83 ± 6.40 ab (p = 0.564) |
| IgM (mg/dL) | 106.91 ± 4.84 b | 120.27 ± 3.21 ab (p = 0.052) | 128.68 ± 6.22 a (p = 0.0002) |
| IgG (mg/dL) | 385.17 ± 6.89 b | 408.00 ± 8.99 b (p = 0.079) | 442.83 ± 6.50 a (p = 0.006) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, S.; Feng, K.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Yan, X.; Wu, Y.; Mi, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y. Influence of Astragalus extract on Gut Microbiome Regulation and Ammonia Emission Mitigation in Laying Hens. Animals 2025, 15, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050620
Xiao S, Feng K, Li S, Li M, Yan X, Wu Y, Mi J, Liao X, Wang Y. Influence of Astragalus extract on Gut Microbiome Regulation and Ammonia Emission Mitigation in Laying Hens. Animals. 2025; 15(5):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050620
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Shasha, Kunxian Feng, Shikai Li, Miao Li, Xiliang Yan, Yinbao Wu, Jiandui Mi, Xindi Liao, and Yan Wang. 2025. "Influence of Astragalus extract on Gut Microbiome Regulation and Ammonia Emission Mitigation in Laying Hens" Animals 15, no. 5: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050620
APA StyleXiao, S., Feng, K., Li, S., Li, M., Yan, X., Wu, Y., Mi, J., Liao, X., & Wang, Y. (2025). Influence of Astragalus extract on Gut Microbiome Regulation and Ammonia Emission Mitigation in Laying Hens. Animals, 15(5), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050620





