Impact of Threonine Supply in Early Ages on Gut Tissue Morphology, Liver Histology, and the Possible Changes in Leukocyte Numbers of Broilers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hatching Protocol and Treatment Groups
2.2. In Ovo Intervention
2.3. Identification, Feeding Management, and Housing
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
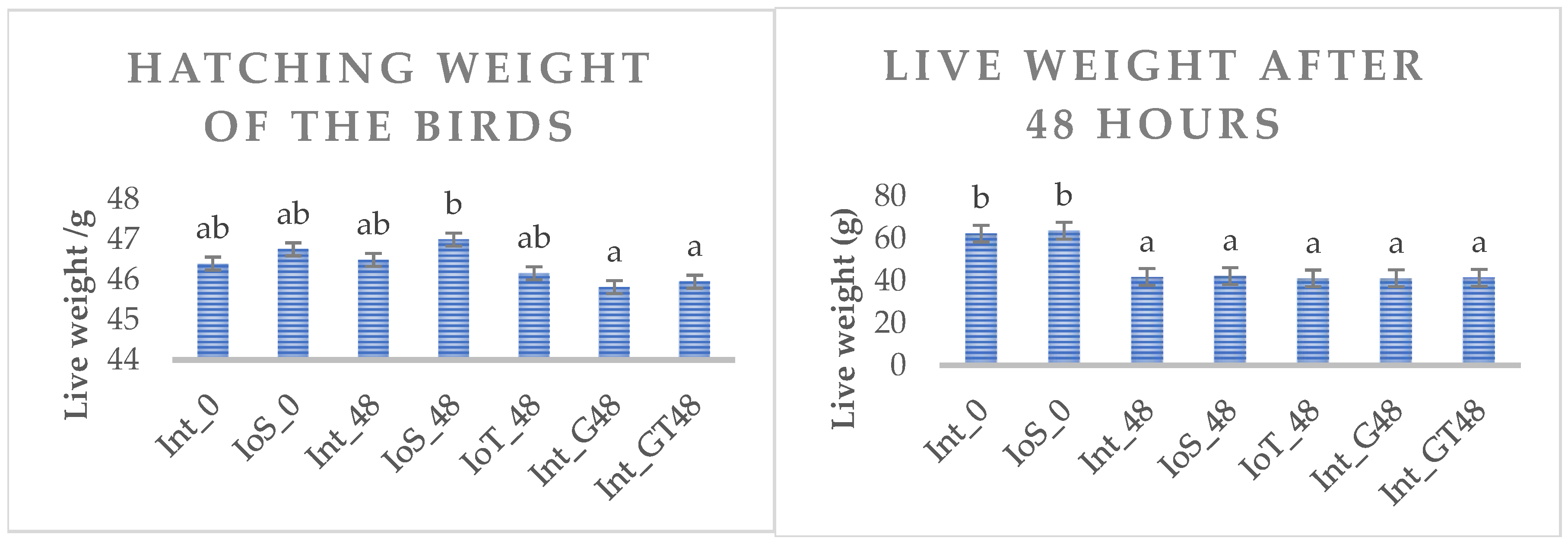
3.1. Growth Performance and Feed Efficiency
3.2. Intestinal Morphometry
3.3. Liver Histology and Blood Cell Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzschentke, B.; Plagemann, A. Imprinting and critical periods in early development. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2006, 62, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzschentke, B. Editorial—Early Development and Epigenetic Programming of Body Functions in Birds. Open Ornithol. J. 2010, 3, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Jong, I.C.; van Emous, R.A. Broiler breeding flocks: Management and animal welfare. In Achieving Sustainable Production of Poultry Meat; Applegate, T., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, P.; Tong, Y.; He, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z. Metabolomic analysis of the egg yolk during the embryonic development of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101014. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, F.M.; Santos, V.L.; Contreira, C.L.; Farina, G.; Kreuz, B.S.; Gentilini, F.P.; Anciuti, M.A.; Rutz, F. In-ovo nutrition: Strategy for precision nutrition in poultry industry. Arch Zootec. 2013, 62, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Riva, S.; Monjo, T.P. The importance of early nutrition in broiler chickens: Hydrated gels enriched with nutrients, an innovative feeding system. Anim. Husb. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, L.J.F.; van Wagenberg, A.V.; Debonne, M.; Decuypere, E.; Kemp, B.; van den Brand, H. Hatching system and time effects on broiler physiology and posthatch growth. Poult. Sci. 2011, 6, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, S.; Berrocoso, J.F.D.; Mishra, B. Early Nutrition Programming (in ovo and Post-hatch Feeding) as a Strategy to Modulate Gut Health of Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 21, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uni, Z.; Ferket, R.P. Methods for early nutrition and their potential. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2004, 60, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, Y.; Sklan, D. Yolk utilization in the newly hatched poult. Br. Poult Sci. 2001, 39, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyra, A.; Uni, Z.; Sklan, D. Enterocyte dynamics and mucosal development in the posthatch chick. Poult Sci. 2001, 80, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.L.; Moran, E.T. Effects of delayed placement and used litter on broiler yields. J. App. Poult. Res. 1999, 8, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Burmester, B. Resistance of Marek’s disease at hatching in chickens vaccinated as embryos with the turkey herpesvirus. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocoso, J.D.; Kida, R.; Singh, A.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Jha, R. Effect of in ovo injection of raffinose on growth performance and gut health parameters of broiler chicken. Poult Sci. 2017, 96, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, S.K.; Mandal, A.B. Effect of in ovo injection of critical amino acids on pre- and post-hatch growth, immunocompetence and development of digestive organs in broiler chickens. Asian Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Tsushima, N.; Kidd, M.T. The needle bore diameter for in ovo amino acid injection has no effect on hatching performance in broiler breeder eggs. J. Poult. Sci. 2002, 39, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, S.H.; Lewis, F.; van der Klis, J.D.; Mroz, Z.; Rebel, J.M.; ter Huurne, A.A. Parameters and techniques to determine intestinal health of poultry as constituted by immunity, integrity, and functionality. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2002, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gore, A.B.; Qureshi, M.A. Enhancement of humoral and cellular immunity by vitamin E after embryonic exposure. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M.T. Nutritional modulation of immune function in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M.T.; Peebles, E.D.; Whitmarsh, S.K.; Yeatman, J.B.; Wideman, R.F. Growth and immunity of broiler chicks as affected by dietary arginine. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H.; Klasing, K. An immunologist’s perspective on nutrition, immunity, and infectious diseases: Introduction and overview. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2009, 18, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsat, S.D.; Chaitrashree, A.R.; Ramteke, B.N. Early post-hatch feeding chicks and practical constrains—A review. Agric. Rev. 2018, 39, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehad, E.E.; Samar, H.A.; Hossam, A.A.; Fathy, F.M. Effect of in ovo injection of L-threonine on hatchability followed by post-hatch extra level of dietary threonine on the performance of broilers. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2022, 5, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Pesti-Asbóth, G.; Szilágyi, E.; Bíróné-Molnár, P.; Oláh, J.; Babinszky, L.; Czeglédi, L.; Cziáky, Z.; Paholcsek, M.; Stündl, L.; Remenyik, J. Monitoring physiological processes of fast growing broilers during the whole life cycle: Changes of redox-homeostasis effected to trassulfuration pathway predicting the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviagen Hatching Management Guide. 2009. Available online: https://en.aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Tech_Articles/RossTechInvestigatingHatcheryPractice.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Uni, Z.; Ferket, P.R. Enhancement of Development of Oviparous Species by in Ovo Feeding. US. Regular Patent EP1638608A1, 29 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aviagen. Ross Broiler Management Handbook. 2019. Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross-BroilerHandbook2018-EN.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 19th ed.; Official Method 2008.01; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH Protoc. 2008, 1, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, B.I.; Penny, E.; Purchase, I.F.H. Hepatocyte vacuolation and increased liver weight occurring in anoxic rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1976, 36, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonne, C.; Dietz, R.; Leifsson, P.; Born, E.; Letcher, R.; Kirkegaard, M.; Muir, D.; Riget, F.; Hyldstrup, L. Do Organohalogen Contaminants Contribute to Liver Histopathology in East Greenland Polar Bears. Environ. Health Persp. 2005, 113, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLachlan, N.J.; Cullen, J.M. Liver, biliary system and exocrine pancreas. In Thomsons Special Veterinary Pathology; Carlton, W.W., McGavin, M.D., Eds.; Mosby Year Book: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1995; pp. 81–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.R. The liver and biliary system. In Pathology of Domestic Animals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 319–406. [Google Scholar]
- Kogut, M.H. Avian Immunology, 3rd ed.; Kaspers, B., Schat, K.A., Göbel, T.W., Vervelde, L., Eds.; Subchapter 8.2—Avian granulocytes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Nain, S.; Renema, R.; Zuidhof, M.; Korver, D. Effect of metabolic efficiency and intestinal morphology on variability in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid enrichment of eggs. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.; Arsi, K.; Donoghue, A.M. Production and characterization of avian crypt-villus enteroids and the effect of chemicals. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, A.A.; Chaves, L.S.; Lopes KLLeandro, A.M.; Café, N.S.M.; Stringhini, J.H. Inoculação de nutrientes em ovos de matrizes pesadas. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2006, 35, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.L.; Wei, Z.H.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.Q.; Yu, F. Effect of in-ovo feeding maltose on the embryo growth and intestine development of broiler chicken. Ind. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 81, 503–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, W.; Gerard, P.D.; Pulikanti, R.; Peebles, E. Effects of in ovo injection of carbohydrates on embryonic metabolism, hatchability, and subsequent somatic characteristics of broiler hatchlings. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retes, P.L. In ovo feeding of carbohydrates for broilers-a systematic review. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, M.M.; Bhanja, S.K.; Mandal, A.B.; Thakur, R.; Vasan, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Tyagi, J.S. Effect of in ovo threonine supplementation on early growth, immunological responses and digestive enzyme activities in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2008, 49, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, M.; Barekatain, R.; Bhanja Kumar, S.; Iji, P. Prospects of in ovo feeding and nutrient supplementation for poultry: The science and commercial applications—A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3654–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, J.O.; Fafiolu, A.O.; Bhanja, S.K.; Oluwatosin, O.O.; Onagbesan, O.M.; Dada, I.D.; Goel, A.; Mehra, M.; Gopi, M.; Rokade, J.J.; et al. In ovo L-Threonine feeding modulates the blood profile and liver enzymes activity of CARIBRO Vishal broiler chickens. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 2022, 57, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.L.; Wang, J.S.; Liu, L.J.; Li, K.; Xu, Y.B.; Ding, X.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xie, L.Y.; Liang, S.; et al. Effects of early post-hatch feeding on the growth performance, hormone secretion, intestinal morphology, and intestinal microbiota structure in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, S.I.; Robinson, F.E.; Renema, R.A.; Fasenko, G.M. Administering Oasis Hatching Supplement Prior to Chick Placement Increases Initial Growth with No Effect on Body Weight Uniformity of Female Broiler Breeders After Three Weeks of Age. J. App. Poult. Res. 2003, 12, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Huwaizi, H.J.N.; Ammar, H.A. The effect of fasting and early feeding after hatching with the nutritional supplement gel 95 and the safmannan prebiotic gel and the mixture between them on the productive performance of broiler chicks. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 735, 012082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wagt, I.; de Jong, I.C.; Mitchell, M.A.; Molenaar, R.; van den Brand, H. A review on yolk sac utilization in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2162–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Foroudi, F.; Baghi, F.; Shivazad, M.; Ghahri, H. The effects of in ovo feeding of threonine and carbohydrates on growth performance of broiler chickens. Proc. Br. Soc. Anim. Sci. 2009, 2009, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Toghyani, M. Effect of arginine and threonine administered in ovo on digestive organ developments and subsequent growth performance of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 100, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanshahi, H.; Golian, A.; Khodambashi Emami, N.; Daneshmand, A.; Ghofrani Tabari, D.; Ibrahim, S.A. Effects of in ovo injection of threonine on hatchability, intestinal morphology, and somatic attributes in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). J. App. Anim. Res. 2016, 45, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filho, A.; Ferket, P.; Malheiros, R.; Bruno de Oliveira, C.J.; Aristimunha, P.; Wilsmann, D.; Patricia, G. Enrichment of the amnion with threonine in chicken embryos affects the small intestine development, ileal gene expression and performance of broilers between 1 and 21 days of age. Poult. Sci. 2018, 98, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Cheng, Y.F.; Li, X.H.; Yang, W.L.; Wen, C.; Zhuang, S.; Zhou, Y.M. Effects of threonine supplementation on the growth performance, immunity, oxidative status, intestinal integrity, and barrier function of broilers at the early age. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, G.K.; Bertolo, R.F.; Adjiri-Awere, A.; Pencharz, P.B.; Ball, R.O. Adequate oral threonine is critical for mucin production and gut function in neonatal piglets. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1293–G1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Mao, X.; Wu, G.; Qiao, S. Optimal dietary true ileal digestible threonine for supporting the mucosal barrier in small intestine of weanling pigs. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, K.A.; Sauer, W.C.; Mosenthin, R.; Souffrant, W.B.; Dugan, M.E. Evaluation of the 15N-isotope dilution technique for determining the recovery of endogenous protein in ileal digestion of pigs: Effect of dilution in the precursor pool for endogenous nitrogen secretion. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Lugo, M.; Su, C.-L.; Austic, R.E. Threonine Requirement and Threonine Imbalance in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Rojas, I.; Murakami, A.; Oliveira, C.; Guerra, A. Supplemental glycine and threonine effects on performance, intestinal mucosa development, and nutrient utilization of growing broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2724–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Poultry, 9th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Corzo, A.; Kidd, M.T.; Dozier, W.A.; Pharr, G.T.; Koutsos, D.A. Dietary threonine needs for growth and immunity of broilers raised under different litter conditions. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 574582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, M.M.M.; Dong, X.Y.; Xie, P.; Zou, X.T. Influence of L-threonine supplementation on goblet cell numbers, histological structure and antioxidant enzyme activities of laying hens reared in a hot and humid climate Br. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Star, L.; Rovers, M.; Corrent, E.; Van der Klis, J.D. Threonine requirement of broiler chickens during subclinical intestinal Clostridium infection. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyra, A.; Uni, Z.; Sklan, D. The effect of fasting at different ages on growth and tissue dynamics in the small intestine of the young chick. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, K.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Picard, M.; Tesseraud, S. Effects of delayed feed intake on body, intestine, and muscle development in neonate broilers. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamot, D.M.; Van De Linde, I.B.; Molenaar, R.; Van Der Pol, C.W.; Wijtten, P.J.A.; Kemp, B.; Van Den Brand, H. Effects of moment of hatch and feed access on chicken development. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M.; Schreier, L.L.; Kahl, S.; Miska, K.B.; Russell, B.; Elsasser, T.H. Effect of delayed feeding post-hatch on expression of tight junction- and gut barrier-related genes in the small intestine of broiler chickens during neonatal development. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4714–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Filho, A.L.D.B.; Oliveira, C.J.; Freitas Neto, O.C.; de Leon, C.M.; Saraiva, M.M.; Andrade, M.F.; White, B.; Givisiez, P.E. Intra-Amnionic Threonine Administered to Chicken Embryos Reduces Enteritidis Cecal Counts and Improves Posthatch Intestinal Development. J. Immun. Res. 2018, 9, 9795829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oort, J.; Scheper, R.J. Histopathology of acute and chronic inflammation. Agents Actions Suppl. 1977, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zaefarian, F.; Abdollahi, M.R.; Cowieson, A.; Ravindran, V. Avian Liver: The Forgotten Organ. Animal 2019, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonus, M.; Nisa, Q.; Munir, M.; Jamil, T.; Kaboudi, K.; Rehman, Z.; Shah, M. Viral hepatitis in chicken and turkeys. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 73, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, N.M.K.; Miyaji, C.I.; Lima, E.A.; Okabayashi, S.; Claure, R.A.; Graça, E.O. Entero-hepatic pathobiology: Histopathology and semi-quantitative bacteriology of the duodenum. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 6, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.G. Avian Heterophils in Inflammation and Disease Resistance. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Mishra, P.; Jha, R. In ovo Feeding as a Tool for Improving Performance and Gut Health of Poultry: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 754246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Hatching Day | °C | Humidity % | CO2 Concentration % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incubation | 37.9 | 70 | 0.60 |
| 2 | 37.9 | 70 | 0.60 | |
| 3 | 37.9 | 70 | 0.60 | |
| 4 | 37.9 | 62 | 0.60 | |
| 5 | 37.9 | 56 | 0.60 | |
| 6 | 37.9 | 56 | 0.60 | |
| 7 | 37.8 | 55 | 0.60 | |
| 8 | 37.8 | 56 | 0.60 | |
| 9 | 37.6 | 55 | 0.60 | |
| 10 | Candling | 37.6 | 56 | 0.60 |
| 11 | 37.5 | 56 | 0.35 | |
| 12 | 37.5 | 56 | 0.35 | |
| 13 | 37.4 | 55 | 0.35 | |
| 14 | 37.3 | 55 | 0.35 | |
| 15 | 37.3 | 55 | 0.35 | |
| 16 | 37.2 | 56 | 0.35 | |
| 17 | Candling, in ovo intervention, placing into the incubator | 37.1 | 56 | 0.35 |
| 18 | 37.0/36.7 | 56 | 0.35/0.60 | |
| 19 | 36.7 | 55 | 0.60 | |
| 20 | 36.5 | 56 | 0.60 | |
| 21 | 36.2 | 56 | 0.60 | |
| 22 | 36.2/35.8 | 62 | 0.35 |
| Treatment Code | Feed Access | Early Nutrition Method | Number of Eggs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Int_0 | Immediate | - | 160 |
| IoS_0 | in ovo, saline | 160 | |
| Int_48 | 48 h delayed solid feed access | - | 160 |
| IoS_48 | in ovo, saline | 160 | |
| IoT_48 | in ovo Thr | 160 | |
| Int_G48 | Hydrogel | 160 | |
| Int_GT48 | Hydrogel + Thr | 160 |
| Ingredients | Starter (1–10) | Grower (11–21) | Finisher (22–35) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn (grain) | 551 | 577 | 601 |
| Corn gluten (60%) | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| Sunflower meal | 53.5 | 53.5 | 75 |
| Soybean meal (CP 44.2%) | 262 | 230 | 175 |
| Fat, vegetable | 44.7 | 55 | 67.00 |
| Monocalcium phosphate | 18.7 | 17.5 | 15 |
| Limestone | 15 | 13.5 | 12.2 |
| NaCl | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| L-Lysin HCl | 5.2 | 4.6 | 4.3 |
| DL-Methionine | 4.5 | 3.9 | 3.2 |
| L-Threonine | 2.6 | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| Premix 1 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Total | 1000.00 | 1000.00 | 1000.00 |
| Nutrient content (g/kg) | |||
| AMEn (MJ/kg) | 12.5 | 12.9 | 13.4 |
| DM % | 90 | 91.3 | 91.1 |
| Crude protein | 204.2 | 190.7 | 174.9 |
| Crude fat | 71.87 | 82.3 | 94.4 |
| Crude fiber | 41.5 | 41.1 | 44.8 |
| Lysine * | 13.5 | 12.1 | 10.8 |
| Methionine + Cystine * | 10.8 | 9.9 | 9.0 |
| Threonine * | 9.7 | 8,8 | 7.8 |
| Tryptophane * | 2.4 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| Ca | 9.6 | 8.7 | 7.8 |
| Pavailable | 4.7 | 4.5 | 3.9 |
| Na | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | RMSE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | |||||||||
| d10 | 233 a | 245 b | 191 c | 193 c | 196 c | 194 c | 192 c | 25.8 | <0.0001 |
| d21 | 855 ab | 882 a | 766 d | 782 cd | 809 bc | 777 cd | 785 cd | 95.3 | <0.0001 |
| d35 | 2218 a | 2238 a | 2072 b | 2113 ab | 2086 b | 2096 ab | 2100 ab | 257.4 | <0.0001 |
| Feed intake (kg/day/pen) | |||||||||
| d1-10 | 23.2 a | 24.0 a | 17.9 b | 17.7 b | 17.8 b | 17.1 b | 17.9 b | 1.72 | <0.0001 |
| d11-21 | 72.8 ab | 75.6 a | 66.8 c | 66.7 c | 69.1 bc | 67.3 c | 66.8 c | 1.36 | <0.0001 |
| d22-35 | 145.6 a | 144.4 a | 136.9 b | 138.6 ab | 137.6 b | 138.6 ab | 140.1 ab | 6.22 | 0.04 |
| d1-35 | 85.35 a | 86.3 a | 78.3 b | 78.2 b | 79.3 b | 78.9 b | 79.1 b | 3.52 | <0.0001 |
| Feed conversion ratio (kg feed/kg gain) | |||||||||
| d1-10 | 1.24 a | 1.21 ab | 1.24 a | 1.21 ab | 1.18 b | 1.15 b | 1.23 ab | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| d11-21 | 1.28 ab | 1.30 a | 1.28 ab | 1.24 ab | 1.24 b | 1.26 ab | 1.23 b | 0.77 | 0.001 |
| d22-35 | 1.49 b | 1.48 b | 1.45 ab | 1.45 a | 1.50 b | 1.46 a | 1.48 b | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| d1-35 | 1.37 ab | 1.37 ab | 1.35 b | 1.32 bc | 1.36 ac | 1.34 c | 1.34 c | 0.13 | 0.043 |
| Average daily gain (g/d) | |||||||||
| d1-10 | 18.6 b | 19.8 a | 14.4 c | 14.6 c | 15.0 b | 14.8 b | 14.5 b | 2.57 | <0.0001 |
| d11-21 | 56.5 ab | 57.9 a | 52.1 c | 53.5 bc | 55.6 ab | 53.0 bc | 53.9 bc | 7.1 | <0.0001 |
| d22-35 | 97.5 | 97.1 | 93.8 | 95.0 | 91.2 | 94.5 | 94.2 | 14.28 | 0.13 |
| d1-35 | 62.0 a | 62.6 a | 57.8 b | 59 ab | 58.3 b | 58.5 ab | 58.7 ab | 7.19 | <0.0001 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus height (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 580.8 ab | 506.5 a | 673.2 b | 639.8 ab | 621.8 ab | 579.2 ab | 586.1 ab | 0.032 |
| I | 302.6 a | 295.4 a | 363.6 ab | 375.3 b | 358.7 ab | 400 b | 364.5 ab | 0.0011 |
| C | 318.3 ab | 377.8 a | 347.2 ab | 308.1 ab | 357.3 a | 310.5 ab | 258.2 b | 0.0055 |
| Crypt depth (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 111.3 a | 110.3 a | 109.5 a | 80.5 b | 115.4 a | 100.1 ab | 103.9 ab | 0.001 |
| I | 88.1 | 94.6 | 93.3 | 94.9 | 83.4 | 106.0 | 85.6 | 0.16 |
| C | 92.5 ab | 87.4 a | 104.5 b | 81.4 a | 110.5 b | 94.4 ab | 82.0 a | 0.0004 |
| Villus height/Crypt depth ratio | ||||||||
| D | 4.3 a | 4.6 a | 4.8 a | 8.2 b | 5.5 a | 5.1 a | 3.9 a | <0.001 |
| I | 3.4 ab | 3.0 a | 3.8 ab | 4.0 ab | 3.8 ab | 3.8 ab | 4.4 b | 0.0082 |
| C | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 0.28 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus height (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 340.6 c | 214.9 a | 288.5 b | 240.8 b | 283.4 b | 321.6 bc | 250.0 ab | <0.001 |
| I | 158.6 | 140.2 | 167.4 | 140.8 | 154.7 | 157.1 | 142.9 | 0.057 |
| C | 164.2 b | 126.4 a | 159.8 ab | 146.4 ab | 156.5 ab | 132.1 ab | 130.0 ab | 0.0085 |
| Crypt depth (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 36.3 | 29.2 | 35.6 | 34.0 | 36.5 | 31.8 | 35.6 | 0.43 |
| I | 32.5 | 30.3 | 33.7 | 29.6 | 32.6 | 33.6 | 32.8 | 0.14 |
| C | 29.9 | 25.3 | 30.3 | 29.1 | 28.3 | 26.5 | 26.7 | 0.059 |
| Villus height/Crypt depth ratio | ||||||||
| D | 7.7 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 7.6 | 7.8 | 9.2 | 7.2 | 0.28 |
| I | 4.8 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 0.96 |
| C | 5.7 b | 5.1 b | 3.7 a | 4.5 ab | 4.5 ab | 4.9 b | 4.9 b | 0.006 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus height (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 768.9 ab | 748.8 ab | 830.9 a | 790.8 ab | 755.6 ab | 690.1 b | 765.8 ab | 0.04 |
| I | 210.6 a | 221.3 ab | 216.1 a | 199.3 a | 282.8 b | 218.7 a | 180.4 a | 0.0004 |
| C | 214.9 | 235.3 | 220.8 | 237.9 | 205.2 | 211.1 | 217.2 | 0.45 |
| Crypt depth (µm) | ||||||||
| D | 86.1 | 103.5 | 106.8 | 89.5 | 97.4 | 104.5 | 113.2 | 0.09 |
| I | 61.8 | 59.2 | 55.3 | 58.4 | 72.0 | 66.8 | 60.7 | 0.08 |
| C | 61.9 | 64.3 | 54.3 | 56.1 | 58.8 | 56.1 | 55.2 | 0.26 |
| Villus height/Crypt depth ratio | ||||||||
| D | 9.6 a | 7.8 ab | 8.1 ab | 9.1 ab | 8.2 ab | 6.6 b | 7.4 ab | 0.01 |
| I | 3.5 ab | 3.8 ab | 4.0 ab | 3.5 ab | 4.2 a | 3.3 ab | 3.0 b | 0.01 |
| C | 3.6 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 0.29 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterophil granulocyte infiltration | ||||||||
| day 1 | 0.66 ab | 0.75 ab | 1.0 b | 0.58 a | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | 0.01 |
| day 3 | 0.41 ab | 1.00 b | 0.25 a | 0.57 ab | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | 0.75 ab | 0.0007 |
| day 21 | 1.10 ab | 0.30 a | 0.58 a | 1.41 b | 1.66 b | 1.19 ab | 1.60 b | <0.001 |
| Vacuolization | ||||||||
| day 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| day 3 | 0.16 ab | 0 a | 0 a | 0.42 b | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.017 |
| day 21 | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.28 b | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.007 |
| Mononuclear infiltration | ||||||||
| day 1 | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.25 b | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.01 |
| day 3 | 1.41 b | 0.33 a | 0 a | 0.71 ab | 0.50 a | 1.00 ab | 0 a | 0.008 |
| day 21 | 1.77 ab | 2.00 b | 1.60 ab | 1.30 ab | 2.33 b | 1.33 a | 1.33 a | <0.001 |
| Lipid accumulation in liver cells | ||||||||
| day 1 | 1.00 a | 1.20 b | 1.00 a | 1.00 a | 1.00 a | 1.00 a | 1.00 a | 0.014 |
| day 3 | 0.25 a | 1.66 c | 0.75 ab | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | 1.00 b | <0.001 |
| day 21 | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0.80 b | 0.40 ab | <0.001 |
| Int_0 | IoS_0 | Int_48 | IoS_48 | IoT_48 | Int_G48 | Int_GT48 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At hatch | ||||||||
| HE | -- | 0.715 | 0.6 | 0.728 | 0.586 | 0.676 | 0.715 | 0.09 |
| LYM | - | 0.216 | 0.316 | 0.198 | 0.305 | 0.241 | 0.216 | 0.13 |
| MON | - | 0.019 | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.025 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 0.10 |
| EOS | - | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.068 | 0.067 | 0.048 | 0.86 |
| 48 h post-hatch | ||||||||
| HE | 0.629 | 0.529 | 0.619 | 0.597 | 0.610 | 0.525 | 0.629 | 0.052 |
| LYM | 0.291 | 0.386 | 0.305 | 0.339 | 0.314 | 0.397 | 0.291 | 0.79 |
| MON | 0.035 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.025 | 0.034 | 0.028 | 0.035 | 0.90 |
| EOS | 0.045 | 0.038 | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.050 | 0.045 | 0.05 |
| 21 days of age | ||||||||
| HE | 0.314 | 0.323 | 0.296 | 0.346 | 0.317 | 0.357 | 0.314 | 0.33 |
| LYM | 0.578 | 0.579 | 0.613 | 0.570 | 0.571 | 0.563 | 0.578 | 0.82 |
| MON | 0.054 | 0.043 | 0.040 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.040 | 0.054 | 0.47 |
| EOS | 0.053 | 0.055 | 0.051 | 0.049 | 0.065 | 0.040 | 0.053 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halas, V.; Áprily, S.; Nagy, J.; Turbók, J.; Tischler, A.; Szeli, N.K.; Petneházy, Ö.; Csötönyi, O.; Enyezdi, J.; Ács, V. Impact of Threonine Supply in Early Ages on Gut Tissue Morphology, Liver Histology, and the Possible Changes in Leukocyte Numbers of Broilers. Animals 2025, 15, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030370
Halas V, Áprily S, Nagy J, Turbók J, Tischler A, Szeli NK, Petneházy Ö, Csötönyi O, Enyezdi J, Ács V. Impact of Threonine Supply in Early Ages on Gut Tissue Morphology, Liver Histology, and the Possible Changes in Leukocyte Numbers of Broilers. Animals. 2025; 15(3):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030370
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalas, Veronika, Szilvia Áprily, József Nagy, Janka Turbók, Annamária Tischler, Nóra Katalin Szeli, Örs Petneházy, Orsolya Csötönyi, Judit Enyezdi, and Virág Ács. 2025. "Impact of Threonine Supply in Early Ages on Gut Tissue Morphology, Liver Histology, and the Possible Changes in Leukocyte Numbers of Broilers" Animals 15, no. 3: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030370
APA StyleHalas, V., Áprily, S., Nagy, J., Turbók, J., Tischler, A., Szeli, N. K., Petneházy, Ö., Csötönyi, O., Enyezdi, J., & Ács, V. (2025). Impact of Threonine Supply in Early Ages on Gut Tissue Morphology, Liver Histology, and the Possible Changes in Leukocyte Numbers of Broilers. Animals, 15(3), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15030370






