Tissue Cytometry Assay with Nuclear Segmentation for Quantifying NETotic Cells in Neutrophils Stimulated by Spermatozoa in Veterinary Species
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Canine Sperm Sample Acquisition
2.2. Bovine Sperm Selection
2.3. Canine PMN Isolation
2.4. Bovine PMN Isolation
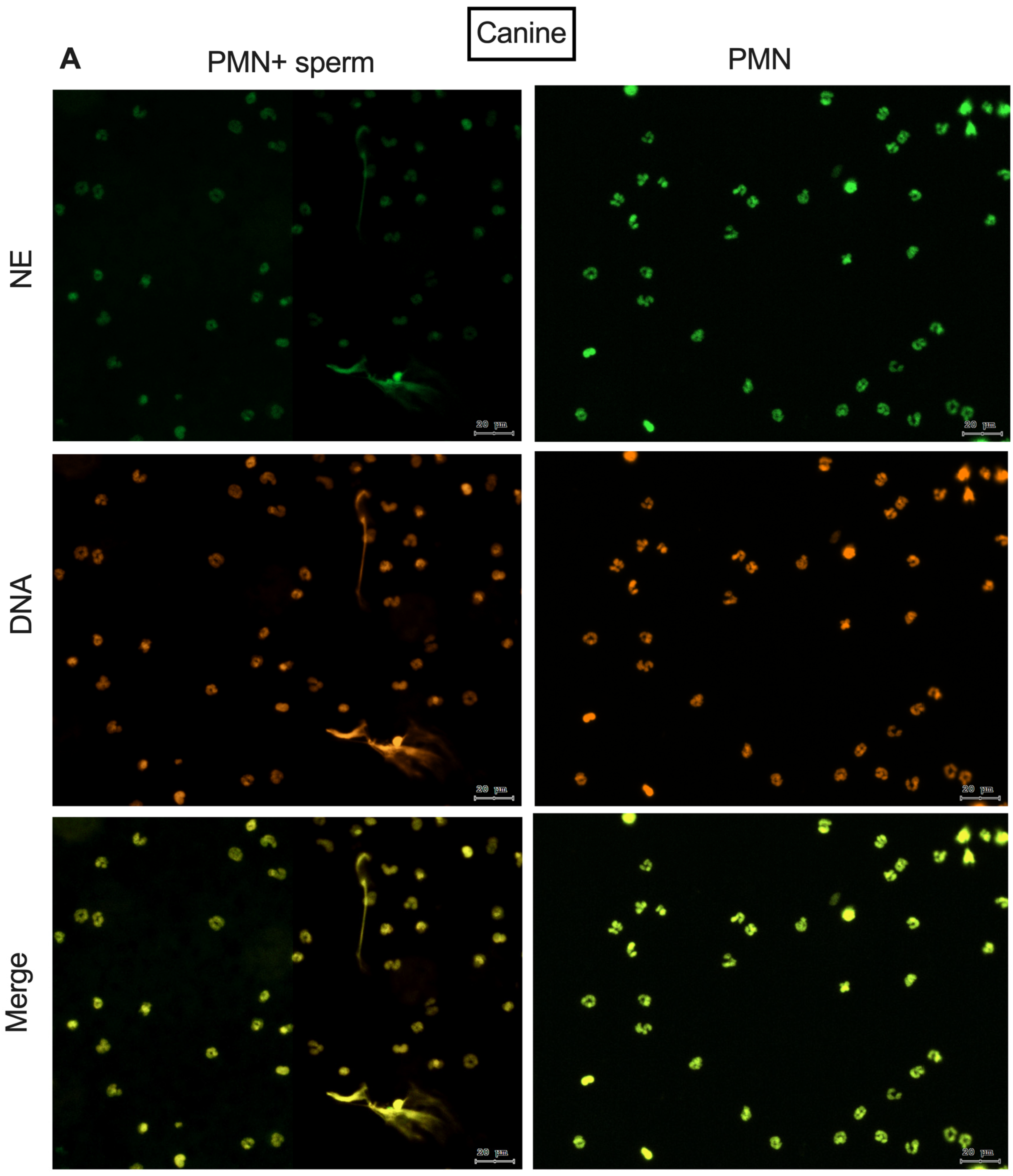
2.5. Immunofluorescence of NE
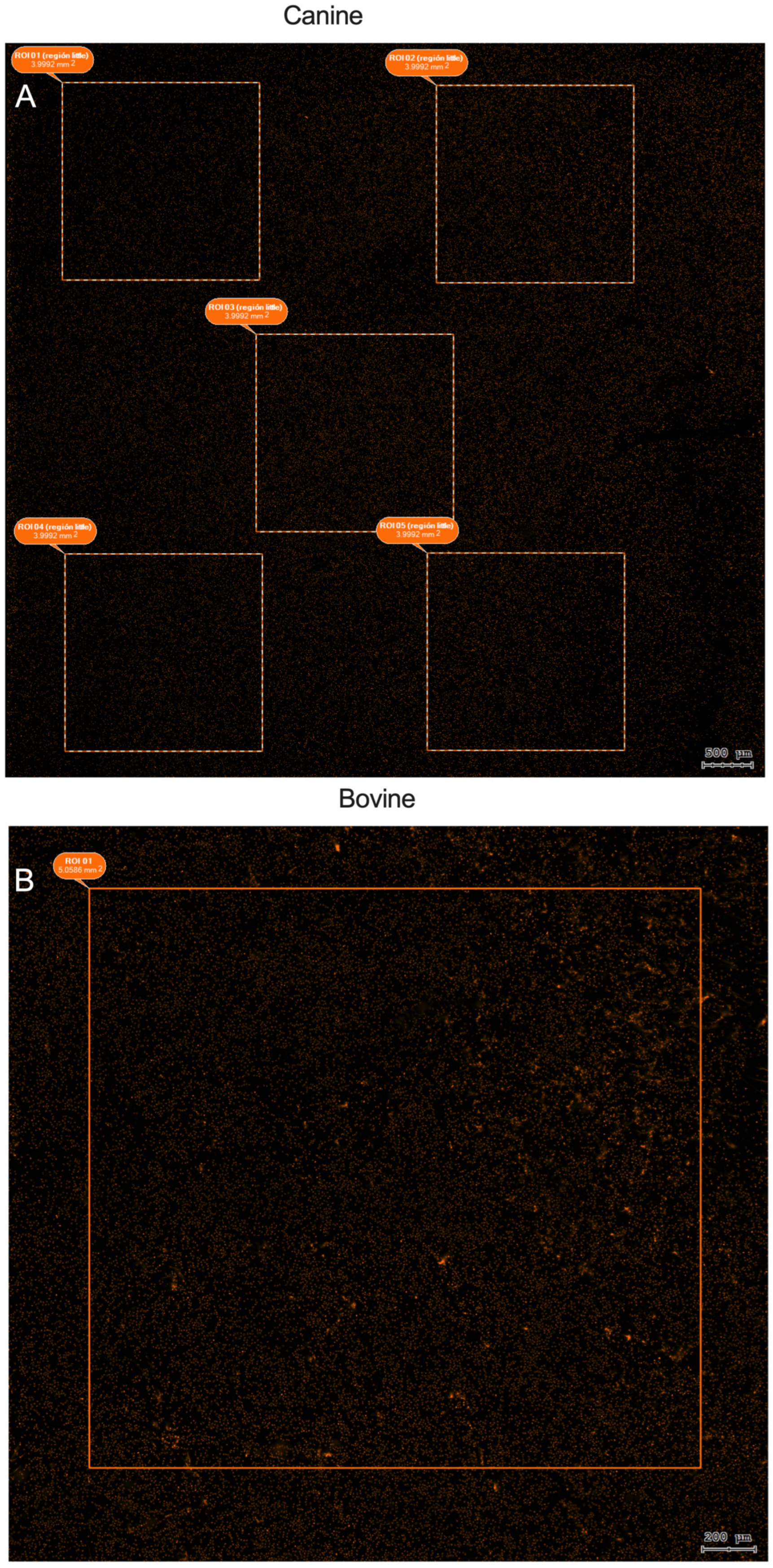
2.6. TissueFAXS i Plus Cytometry System
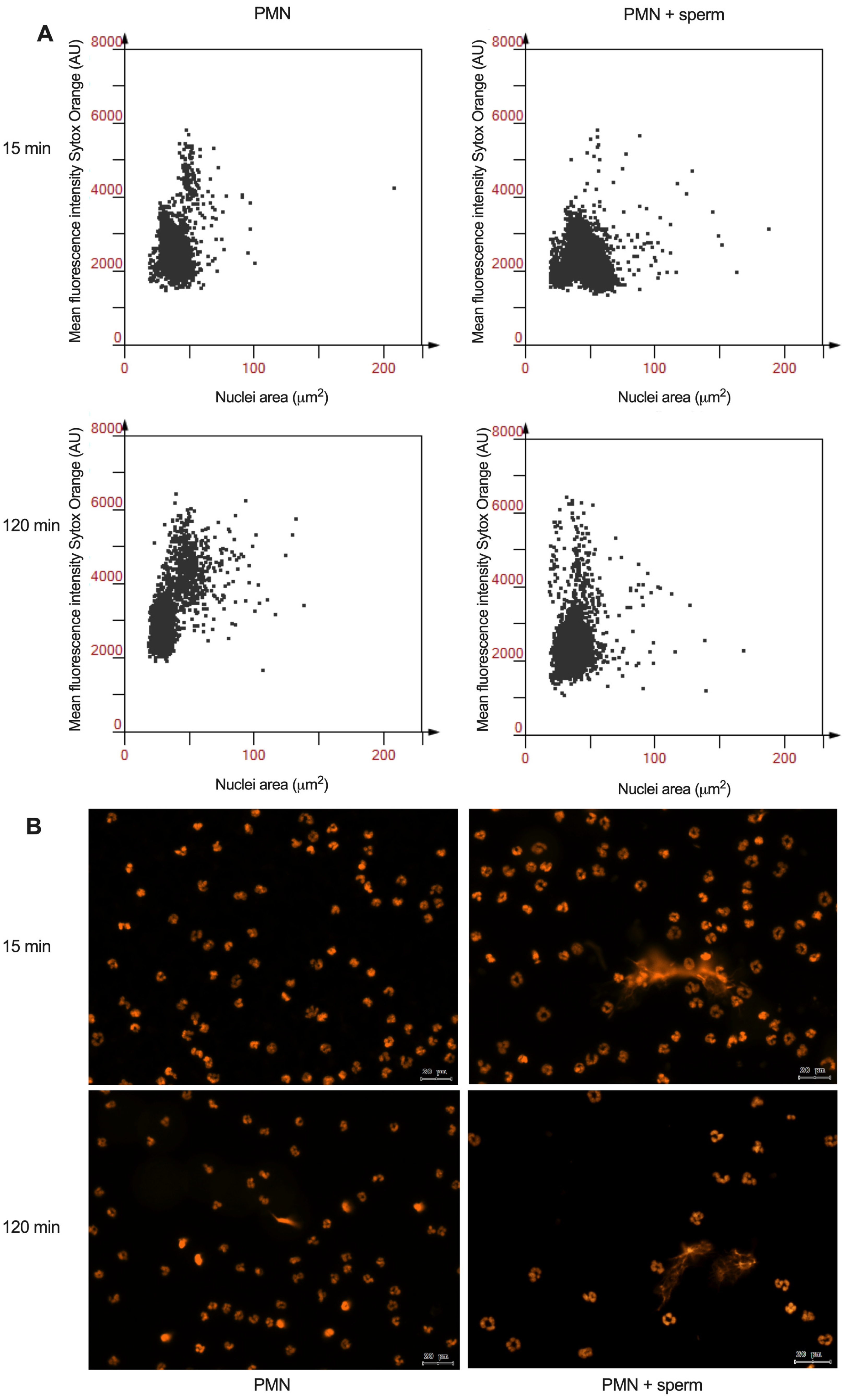
2.7. Analysis of NETotic Cells by Nuclear Area Expansion (NAE)
2.8. Ethics Statement
2.9. Statistical Analysis
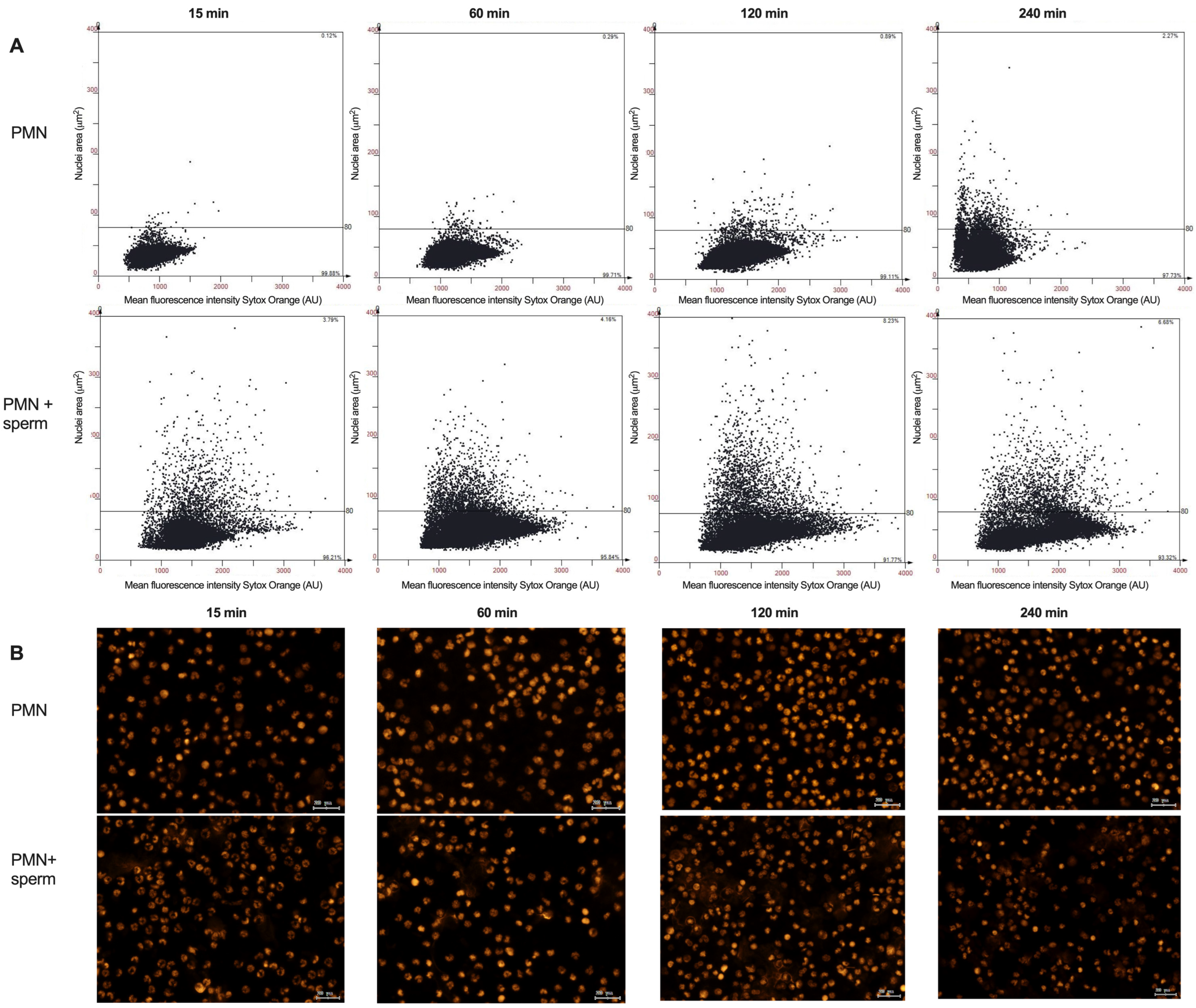
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARTs | Assisted reproductive techniques. |
| FI | Fluorescence intensity. |
| FRT | Female reproductive tract. |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution. |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase. |
| NAE | Nuclear area expansion. |
| NE | Neutrophil elastase. |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps. |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase. |
| PAD4 | Peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV. |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells. |
| PMN | Polymorphonuclear neutrophils. |
| ROI | Region of interest. |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species. |
| RT | Room temperature. |
References
- Punt, J.; Owen, J.A.; Stranford, S.A.; Jones, P.P.; Kuby, J. Kuby Immunology, 8th ed.; W.H. Freeman/Macmillan Learning: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 1319114709. [Google Scholar]
- Amulic, B.; Cazalet, C.; Hayes, G.L.; Metzler, K.D.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Function: From Mechanisms to Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, H.R.; Wong, S.L.; Wagner, D.D.; Waterman, C.M. Cellular Mechanisms of NETosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Elastase and Myeloperoxidase Regulate the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, K.D.; Fuchs, T.A.; Nauseef, W.M.; Reumaux, D.; Roesler, J.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Myeloperoxidase Is Required for Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation: Implications for Innate Immunity. Blood 2011, 117, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, C.F.; Ermert, D.; Schmid, M.; Abu-Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Nacken, W.; Brinkmann, V.; Jungblut, P.R.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contain Calprotectin, a Cytosolic Protein Complex Involved in Host Defense against Candida Albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bengoa, M.; Meurer, M.; Stehr, M.; Elamin, A.A.; Singh, M.; Oehlmann, W.; Mörgelin, M.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis PE/PPE Proteins Enhance the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species and Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1206529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, C.F.; Reichard, U.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Capture and Kill Candida Albicans Yeast and Hyphal Forms. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.K.; Lawson, K.; Ozment, T.R.; Scherer, A.; Hopke, A. Caging Giants: Characterizing the Molecular Mechanisms of Neutrophil Swarming against Candida Albicans Hyphae. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiaf082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.R.; Muñoz Caro, T.; Gerstberger, R.; Vila-Viçosa, M.J.M.; Cortes, H.C.E.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. The Apicomplexan Parasite Eimeria Arloingi Induces Caprine Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2797–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grob, D.; Conejeros, I.; Velásquez, Z.D.; Preußer, C.; Gärtner, U.; Alarcón, P.; Burgos, R.A.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Trypanosoma Brucei Brucei Induces Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil Activation and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Release. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 559561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, F.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Ho, C.-L.; Muratore, K.; Johnson, P.J. Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes (PMN) Use Different, Strain-Dependent Mechanisms to Kill the Parasite Trichomonas Vaginalis. mBio 2025, 16, e0368024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilsczek, F.H.; Salina, D.; Poon, K.K.H.; Fahey, C.; Yipp, B.G.; Sibley, C.D.; Robbins, S.M.; Green, F.H.Y.; Surette, M.G.; Sugai, M.; et al. A Novel Mechanism of Rapid Nuclear Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Response to Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7413–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Immunity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinaka, Y.; Arai, T.; Adachi, S.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Yamashita, K. Singlet Oxygen Is Essential for Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 413, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Stadler, S.; Correll, S.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Hayama, R.; Leonelli, L.; Han, H.; Grigoryev, S.A.; et al. Histone Hypercitrullination Mediates Chromatin Decondensation and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.J.; Radic, M. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Double-Edged Swords of Innate Immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, B.M.; Senger, P.L.; Widders, P.R. Neutrophil Migration into the Bovine Uterine Lumen Following Intrauterine Inoculation with Killed Haemophilus Somnus. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1991, 93, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.-C.; Yamaguchi, S.; Funahashi, H. Boar Seminal Plasma or Hen’s Egg Yolk Decrease the In-Vitro Chemotactic and Phagocytotic Activities of Neutrophils When Co-Incubated with Boar or Bull Sperm. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, D.; Conejeros, I.; López-Osorio, S.; Velásquez, Z.D.; Segeritz, L.; Gärtner, U.; Schaper, R.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Canine Angiostrongylus Vasorum-Induced Early Innate Immune Reactions Based on NETs Formation and Canine Vascular Endothelial Cell Activation In Vitro. Biology 2021, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, M.; Moya, C.; Rivera-Concha, R.; Pezo, F.; Uribe, P.; Schulz, M.; Sánchez, R.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Zambrano, F. Extrusion of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Negatively Impacts Canine Sperm Functions: Implications in Reproductive Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
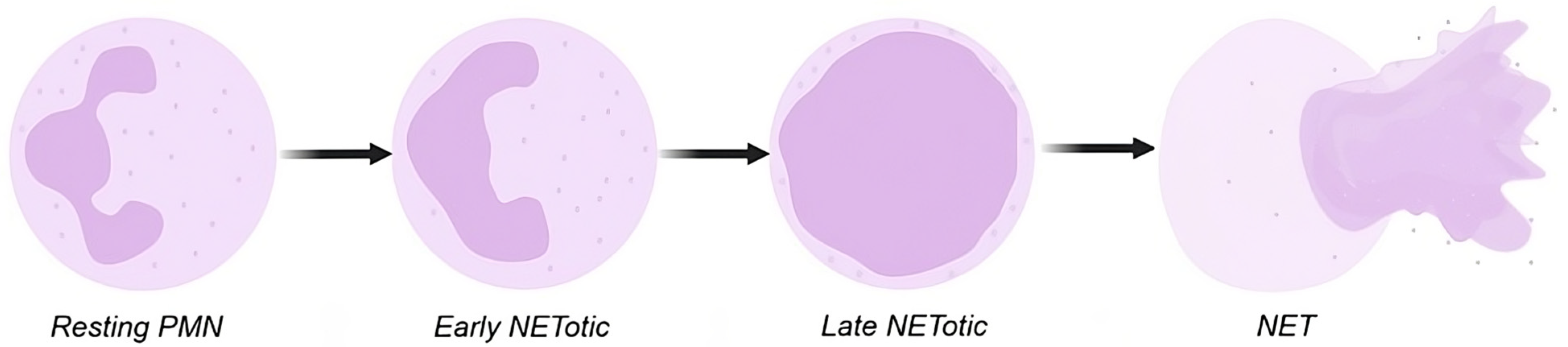
- Inozemtsev, V.; Sergunova, V.; Vorobjeva, N.; Kozlova, E.; Sherstyukova, E.; Lyapunova, S.; Chernysh, A. Stages of NETosis Development upon Stimulation of Neutrophils with Activators of Different Types. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.S.; Bardoel, B.W.; Harbort, C.J.; Zychlinsky, A. Induction and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. In Neutrophil Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1124, pp. 307–318. ISBN 9781627038454. [Google Scholar]
- Zambrano, F.; Melo, A.; Rivera-Concha, R.; Schulz, M.; Uribe, P.; Fonseca-Salamanca, F.; Ossa, X.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Sánchez, R. High Presence of NETotic Cells and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Vaginal Discharges of Women with Vaginitis: An Exploratory Study. Cells 2022, 11, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoberidze, N.; Cimini, B.A. Defining the Boundaries: Challenges and Advances in Identifying Cells in Microscopy Images. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 85, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Tong, B.; Liu, Y.; Pan, T.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S. Review of Research on the Instance Segmentation of Cell Images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 227, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, R.C.; Steiner, G.E. Microscopy-Based Multicolor Tissue Cytometry at the Single-Cell Level. Cytom. Part A 2004, 59A, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, R.C.; Rogojanu, R.; Streit, M.; Oesterreicher, K.; Steiner, G.E. An Improved Method for Discrimination of Cell Populations in Tissue Sections Using Microscopy-Based Multicolor Tissue Cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2006, 69A, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.; Seo, M.; Nam, J.-Y. Microscopic Cell Nuclei Segmentation Based on Adaptive Attention Window. J. Digit. Imaging 2009, 22, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Concha, R.; Moya, C.; León, M.; Uribe, P.; Schulz, M.; Prado, A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Sánchez, R.; Zambrano, F. Effect of Different Sperm Populations on Neutrophils Extracellular Traps (NETs) Formation in Cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 164, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavister, B.D.; Yanagimachi, R. The Effects of Sperm Extracts and Energy Sources on the Motility and Acrosome Reaction of Hamster Spermatozoa in Vitro. Biol. Reprod. 1977, 16, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, J.J.; Susko-Parrish, J.L.; First, N.L. Effect of Heparin and Chondroitin Sulfate on the Acrosome Reaction and Fertility of Bovine Sperm In Vitro. Theriogenology 1985, 24, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Kaeberle, M.L. Isolation of Neutrophils and Eosinophils from the Peripheral Blood of Cattle and Comparison of Their Functional Activities. J. Immunol. Methods 1981, 45, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conejeros, I.; Gibson, A.J.; Werling, D.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; Burgos, R.A. Effect of the Synthetic Toll-like Receptor Ligands LPS, Pam3CSK4, HKLM and FSL-1 in the Function of Bovine Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, L.P.; Shariff, A.; Murphy, R.F. Nuclear Segmentation in Microscope Cell Images: A Hand-Segmented Dataset and Comparison of Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Boston, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 518–521. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, L.C.; Cronin, J.G.; Sheldon, I.M. Mechanisms Linking Bacterial Infections of the Bovine Endometrium to Disease and Infertility. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, E.S.; Gomes, G.; Greco, L.F.; Cerri, R.L.A.; Vieira-Neto, A.; Monteiro, P.L.J.; Lima, F.S.; Bisinotto, R.S.; Thatcher, W.W.; Santos, J.E.P. Carryover Effect of Postpartum Inflammatory Diseases on Developmental Biology and Fertility in Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 2016, 99, 2201–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, T.; Kotarski, F.; Gärtner, U.; Conejeros, I.; Hermosilla, C.; Wrenzycki, C.; Taubert, A. Bovine Sperm Samples Induce Different NET Phenotypes in a NADPH Oxidase-, PAD4-, and Ca-Dependent Process. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 102, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, T.; Kotarski, F.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; Wrenzycki, C. Semen Extender and Seminal Plasma Alter the Extent of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NET) Formation in Cattle. Theriogenology 2021, 160, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.A.; Feldman, E.; Davidson, A. Evaluation of Infertility in the Bitch. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 17, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebernick, R.; Fahmy, L.; Glover, C.; Bawadekar, M.; Shim, D.; Holmes, C.L.; Rademacher, N.; Potluri, H.; Bartels, C.M.; Shelef, M.A. DNA Area and NETosis Analysis (DANA): A High-Throughput Method to Quantify Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Fluorescent Microscope Images. Biol. Proced. Online 2018, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Goosmann, C.; Kühn, L.I.; Zychlinsky, A. Automatic Quantification of in Vitro NET Formation. Front. Immunol. 2013, 3, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejeros, I.; Velásquez, Z.D.; Espinosa, G.; Rojas-Baron, L.; Grabbe, M.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. AMPK and CAMKK Activation Participate in Early Events of Toxoplasma Gondii-Triggered NET Formation in Bovine Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1557509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, B.A. Creating and Troubleshooting Microscopy Analysis Workflows: Common Challenges and Common Solutions. J. Microsc. 2024, 295, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| (A) Canine | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell types | Incubation time (min) | Mean area PMN (μm2) | Standard deviation | Confidence interval | p value |
| PMN | 15 | 37.33 | 1.923 | (33.55–42.10) | 0.00061 * |
| PMN + sperm | 47.40 | 2.670 | (40.77–54.04) | ||
| PMN | 120 | 35.18 | 5.214 | (22.23–48.14) | 0.0058 * |
| PMN + sperm | 38.99 | 9.216 | (16.10–61.88) | ||
| (B) Bovine | |||||
| Cell types | Incubation time (min) | % nuclei PMN > 80 μm2 | Standard deviation | Confidence interval | p value |
| PMN | 15 | 0.4250 | 0.1595 | (0.1712–0.6788) | 0.0200 * |
| PMN + sperm | 4.005 | 1.350 | (1.856–6.154) | ||
| PMN | 60 | 0.4725 | 0.1702 | (0.2017–0.7433) | 0.0251 * |
| PMN + sperm | 4.865 | 2.359 | (0.8242–8.906) | ||
| PMN | 120 | 0.7750 | 0.4691 | (0.0286–1.521) | 0.0039 * |
| PMN + sperm | 5.640 | 2.1706 | (2.177–9.103) | ||
| PMN | 240 | 0.6075 | 0.3705 | (0.0179–1.197) | 0.0680 |
| PMN + sperm | 4.5430 | 1.884 | (1.545–7.540) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera-Concha, R.; León, M.; Ponce-Rojas, N.; Prado-Sanhueza, A.; Uribe, P.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Sánchez, R.; Zambrano, F. Tissue Cytometry Assay with Nuclear Segmentation for Quantifying NETotic Cells in Neutrophils Stimulated by Spermatozoa in Veterinary Species. Animals 2025, 15, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182742
Rivera-Concha R, León M, Ponce-Rojas N, Prado-Sanhueza A, Uribe P, Taubert A, Hermosilla C, Sánchez R, Zambrano F. Tissue Cytometry Assay with Nuclear Segmentation for Quantifying NETotic Cells in Neutrophils Stimulated by Spermatozoa in Veterinary Species. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182742
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera-Concha, Rodrigo, Marion León, Nikol Ponce-Rojas, Aurora Prado-Sanhueza, Pamela Uribe, Anja Taubert, Carlos Hermosilla, Raúl Sánchez, and Fabiola Zambrano. 2025. "Tissue Cytometry Assay with Nuclear Segmentation for Quantifying NETotic Cells in Neutrophils Stimulated by Spermatozoa in Veterinary Species" Animals 15, no. 18: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182742
APA StyleRivera-Concha, R., León, M., Ponce-Rojas, N., Prado-Sanhueza, A., Uribe, P., Taubert, A., Hermosilla, C., Sánchez, R., & Zambrano, F. (2025). Tissue Cytometry Assay with Nuclear Segmentation for Quantifying NETotic Cells in Neutrophils Stimulated by Spermatozoa in Veterinary Species. Animals, 15(18), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182742






