Development of an In-House ELISA for Serological Detection of Equine Herpesvirus-1/4 Antibodies in Turkish Horses
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Samples
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Virus Neutralization Assay
2.4. Development of In-House ELISA
2.4.1. Purification of the Viruses
2.4.2. Inactivation of the Viruses
2.4.3. Detection of Antigen Integrity Post-Inactivation
2.4.4. Viral Protein Quantification
2.4.5. Optimization of the In-House ELISA
2.4.6. The Determination of the Blocking Solution and Concentration
2.4.7. Validation of the In-House ELISA
2.4.8. Testing Sera Samples with Commercial ELISA
3. Results
3.1. Virus Inoculation and Virus Titration Assay
3.2. VN and SN50 Assay
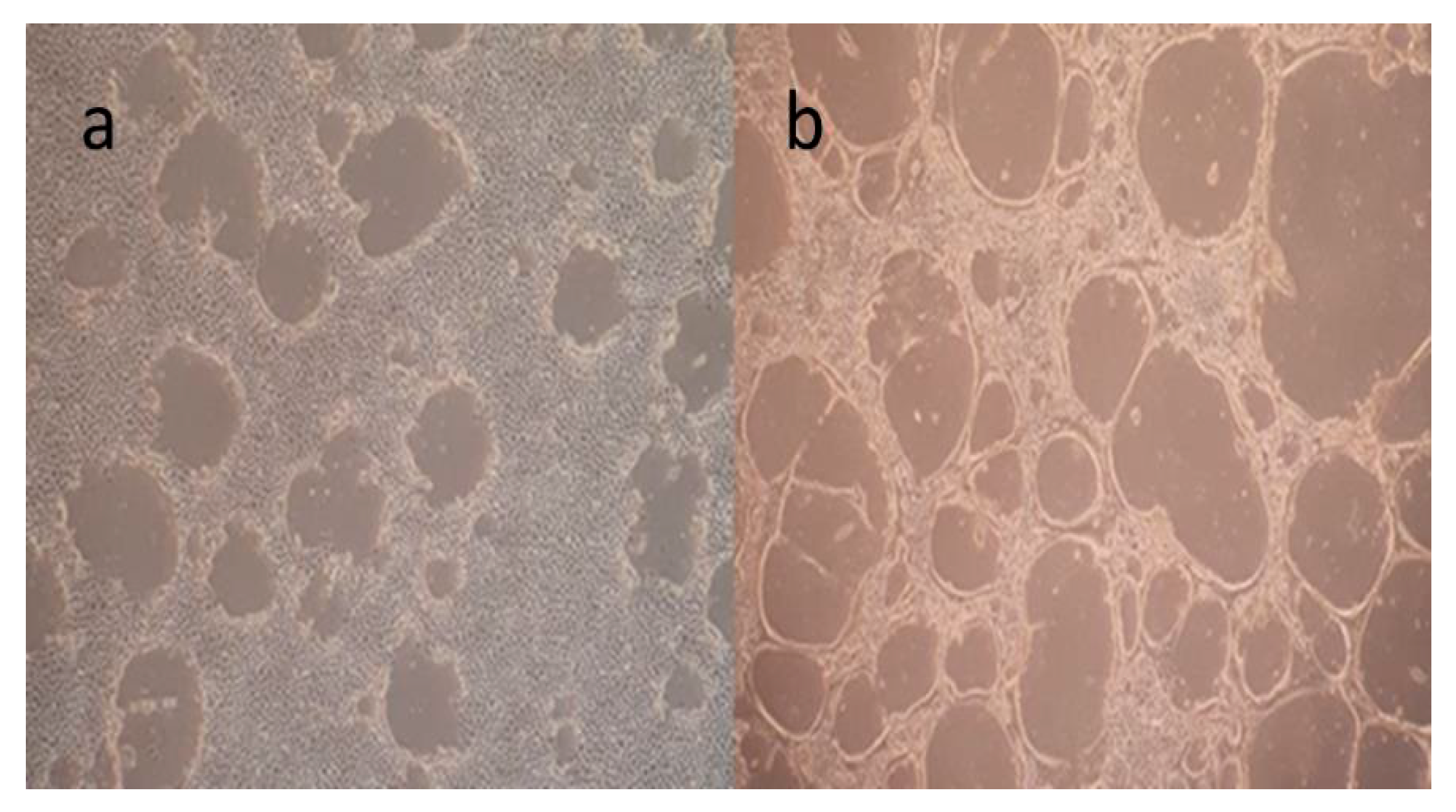
3.3. Assessment of Antigen Integrity Post-Inactivation
3.4. Evaluation of In-House ELISA
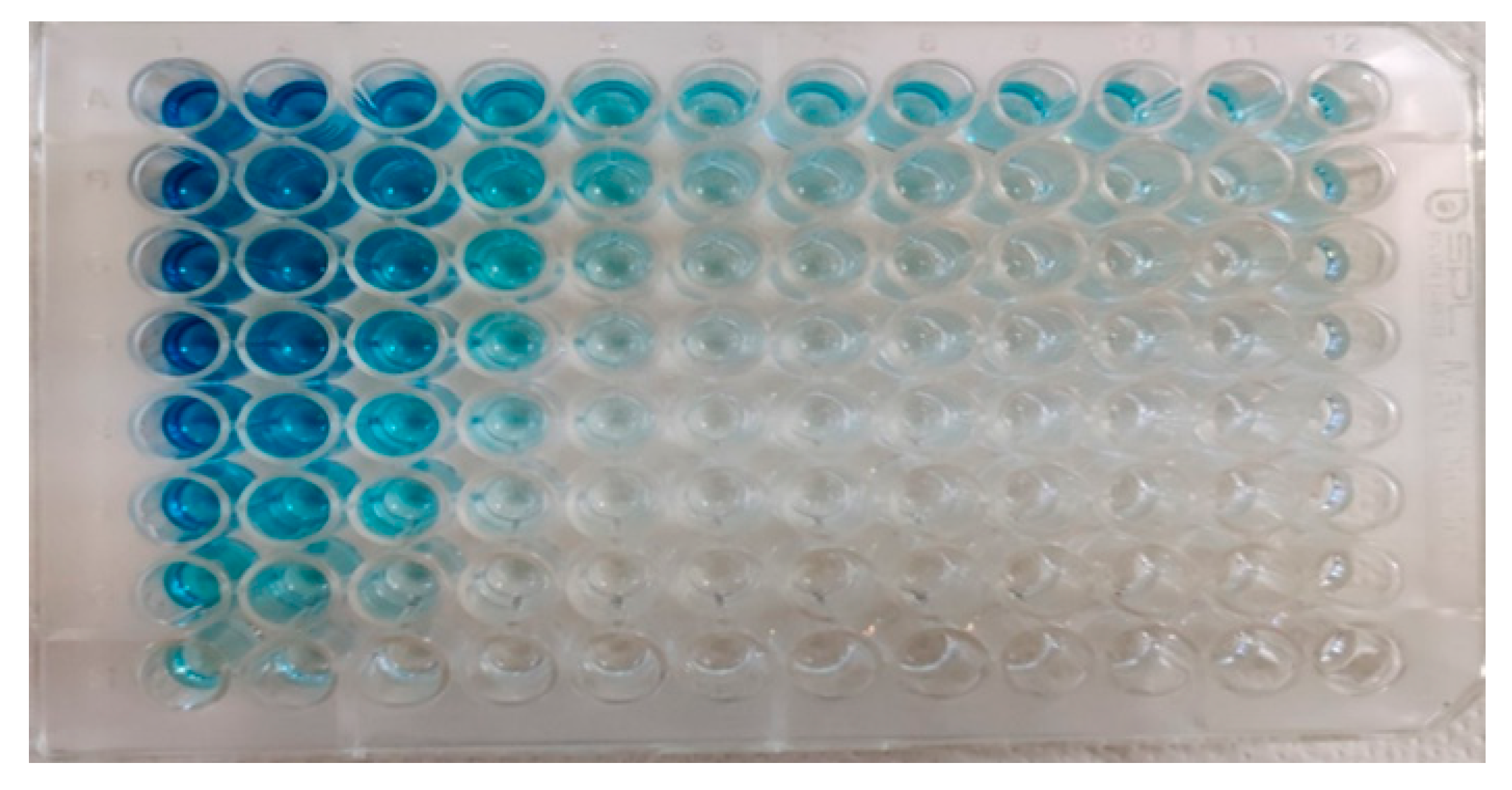
3.4.1. Optimization of In-House ELISA
3.4.2. Evaluation of Sera Samples with In-House ELISA, Comparison with VN Assay and Commercial ELISA
3.4.3. Validation of In-House ELISA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| °C | Degrees Celsius |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| C.V. | Coefficient of Variation |
| CF | Complement Fixation |
| CFT | Complement Fixation Test |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| ED | Equine Dermis (cell line) |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| EHM | Equine Herpesvirus Myeloencephalopathy |
| EHV-1 | Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 |
| EHV-4 | Equine Herpesvirus Type 4 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FCS | Fetal Calf Serum |
| gG | Glycoprotein G |
| ICTV | International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| kDa | Kilodalton |
| mL | Milliliter |
| NaCl | Sodium Chloride |
| OD | Optical Density |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| rpm | Revolutions Per Minute |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| SN50 | Serum Neutralization 50% Endpoint |
| TCID50 | Tissue Culture Infective Dose 50% |
| µg | Microgram |
| VN | Virus Neutralization |
| VNT | Virus Neutralization Test |
| WOAH | World Organisation for Animal Health (formerly OIE) |
References
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). Chapter 2.5.9.—Equine Rhinopneumonitis (Infection with Equid Herpesvirus-1 and -4). In OIE Terrestrial Manual; WOAH: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Davison, A.J.; Eberle, R.; Ehlers, B.; Hayward, G.S.; McGeoch, D.J.; Minson, A.C.; Pellett, P.E.; Roizman, B.; Studdert, M.J.; Thiry, E. The Order Herpesvirales. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, H.; Tomita, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Ochiai, Y.; Kirisawa, R.; Matsumura, T.; Yanai, T.; Masegi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hirai, K. Gazelle Herpesvirus 1: A New Neurotropic Herpesvirus Immunologically Related to Equine Herpesvirus 1. Virology 1997, 227, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.R.; Heldens, J. Equine Herpesviruses 1 (EHV-1) and 4 (EHV-4)–Epidemiology, Disease and Immunoprophylaxis: A Brief Review. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, K.; Poelaert, K.C.K.; Van Cleemput, J.; Zhao, J.; Vandekerckhove, A.P.; Gryspeerdt, A.C.; Garré, B.; van der Meulen, K.; Baghi, H.B.; Dubale, H.N. The Pathogenesis and Immune Evasive Mechanisms of Equine Herpesvirus Type 1. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, J. Equine Herpesviruses 14. In Equine Infectious Diseases E-Book; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 6, p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Edington, N.; Bridges, C.G.; Patel, J.R. Endothelial Cell Infection and Thrombosis in Paralysis Caused by Equid Herpesvirus-1: Equine Stroke. Arch. Virol. 1986, 90, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydd, J.H.; Smith, K.C.; Hannant, D.; Livesay, G.J.; Mumford, J.A. Distribution of Equid Herpesvirus-1 (EHV-1) in Respiratory Tract Associated Lymphoid Tissue: Implications for Cellular Immunity. Equine Vet. J. 1994, 26, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.R.; Edington, N.; Mumford, J.A. Variation in Cellular Tropism between Isolates of Equine Herpesvirus-1 in Foals. Arch. Virol. 1982, 74, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.M.; Studdert, M.J. Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 (EHV1). 1982. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/19832218924 (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Slater, J.D.; Borchers, K.; Thackray, A.M.; Field, H.J. The Trigeminal Ganglion Is a Location for Equine Herpesvirus 1 Latency and Reactivation in the Horse. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, H.M.; Bridges, C.G.; Lyon, A.M.; Griffiths, L.; Edington, N. Latent Equid Herpesviruses 1 and 4: Detection and Distinction Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Co-Cultivation from Lymphoid Tissues. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillot, R.; Case, R.; Ross, J.; Newton, R.; Nugent, J. Equine Herpes Virus-1: Virus, Immunity and Vaccines. Open Vet. Sci. J. 2008, 2, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, F.S.; Horohov, D.W.; Chambers, T.M. EHV-1: A Constant Threat to the Horse Industry. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, B.S.; Allen, G.P.; Studdert, M.J. Characterization of the Major Glycoproteins of Equine Herpesviruses 4 and 1 and Asinine Herpesvirus 3 Using Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavulraj, S.; Eschke, K.; Theisen, J.; Westhoff, S.; Reimers, G.; Andreotti, S.; Osterrieder, N.; Azab, W. Equine Herpesvirus Type 4 (EHV-4) Outbreak in Germany: Virological, Serological, and Molecular Investigations. Pathogens 2021, 10, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animal Health Diagnostic Center, C.U. Equine Herpesvirus-1 (EHV-1) Serum Neutralization. 2021. Available online: https://www.vet.cornell.edu/animal-health-diagnostic-center/testing-laboratories/virology/test-data/equine-herpesvirus-1-ehv-1-serum-neutralization (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Telford, E.A.R.; Watson, M.S.; McBride, K.; Davison, A.J. The DNA Sequence of Equine Herpesvirus-1. Virology 1992, 189, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, E.A.; Watson, M.S.; Perry, J.; Cullinane, A.A.; Davison, A.J. The DNA Sequence of Equine Herpesvirus-4. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, B.S.; MacPherson, C.M.; Reubel, G.H.; Browning, G.F.; Studdert, M.J.; Drummer, H.E. A Type-Specific Serological Test to Distinguish Antibodies to Equine Herpesviruses 4 and 1. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H.; Liess, B. Vermehrungskinetik Und Verwendbarkeit Eines Stark Zytopathogenen VD-MD-Virusstammes Für Diagnostische Untersuchungen Mit Der Mikrotiter-Methode. Zentralblatt Für Veterinärmedizin Reihe B 1971, 18, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.-K.; De Miroschedji, K.; Doeppner, T.R.; Börger, V.; Ruesing, J.; Rebmann, V.; Durst, S.; Jansen, S.; Bremer, M.; Behrmann, E. Precipitation with Polyethylene Glycol Followed by Washing and Pelleting by Ultracentrifugation Enriches Extracellular Vesicles from Tissue Culture Supernatants in Small and Large Scales. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1528109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, A.; Keen, A.; Sinclair-Smith, C.; Furminger, I.G.S. Polyethylene Glycol Purification of Influenza Virus with Respect to Aggregation and Antigenicity. Epidemiol. Infect. 1972, 70, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, L.; Schünadel, L.; Nitsche, A.; Schwebke, I.; Hanisch, M.; Laue, M. Evaluation of Virus Inactivation by Formaldehyde to Enhance Biosafety of Diagnostic Electron Microscopy. Viruses 2015, 7, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, J.R. The ELISA Guidebook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 149, ISBN 1-59259-049-7. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Isaacs, S.N. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and Blocking with Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)—Not All BSAs Are Alike. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 384, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). Chapter 1.1.6.—Principles and Methods of Validation of Diagnostic Assays for Infectious Diseases. In WOAH Terrestrial Manual 2023; WOAH: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.M.; Toribio, R.E. Equine Herpesvirus 1 and 4. In Veterinary Clinics: Equine Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 20, pp. 631–642. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, S. Isoelectric Focusing of Herpes Simplex Virus. Arch. Virol. 1975, 49, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, E.; Kitai, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Harada, S. Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Human Sera: Problems and Solutions with Casein-Based ELISA in the Detection of Natural Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infections. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 63, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Brini, Z.; Fassi Fihri, O.; Paillot, R.; Lotfi, C.; Amraoui, F.; El Ouadi, H.; Dehhaoui, M.; Colitti, B.; Alyakine, H.; Piro, M. Seroprevalence of Equine Herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) and Equine Herpesvirus 4 (EHV-4) in the Northern Moroccan Horse Populations. Animals 2021, 11, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Passos, L.M.F.; Gouvea, A.M.G.; Resende, M.; Martins, A.S.; Franco, G.C. Use of an ELISA System for Detection of Equine Herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) Antibodies in Non-Symptomatic Pregnant Mares and Neonatal Foals. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2000, 52, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.F.; Salem, S.A.H.; El-Sanousi, A.A.; Shalaby, M. Development of a Novel Homemade ELISA Kit for Antigen Detection of EHV Causing Abortion in Egypt. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344754905_Development_of_a_Novel_Homemade_ELISA_kit_for_Antigen_Detection_of_EHV_Causing_Abortion_in_Egypt (accessed on 26 May 2024).



| EHV-1 VNT | EHV-1 Commercial ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHV-1 in-house ELISA | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Suspected |
| Positive | 93 | 37 | 112 | 0 | 18 |
| Negative | 0 | 25 | 1 | 23 | 1 |
| Total | 93 (60%) | 62 (40%) | 113 (72.90%) | 23 (14.83%) | 19 (12.25%) |
| 155 | 155 | ||||
| EHV-4 VNT | EHV-4 Commercial ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHV-4 in-house ELISA | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Suspected |
| Positive | 117 | 11 | 127 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 3 | 24 | 6 | 22 | 0 |
| Total | 120 (77.41%) | 35 (22.59%) | 133 (85.80%) | 22 (14.20%) | 0 |
| 155 | 155 | ||||
| EHV-1/4 VNT | EHV-1/4 Commercial ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHV-1/4 in-house ELISA | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Suspected |
| Positive | 126 | 5 | 132 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 24 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| Total | 126 (81.29%) | 29 (18.71%) | 132 (85.16%) | 23 (14.84%) | 0 |
| 155 | 155 | ||||
| Sampled Animals | VNT EHV-1 | VNT EHV-4 | In-House ELISA EHV-1 | In-House ELISA EHV-4 | Commercial ELISA EHV-1 | Commercial ELISA EHV-4 | The Number of Tested Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naturally infected | 23 (65.71%) | 31 (88.57%) | 34 (97.14%) | 33 (94.28%) | 28 (80%) | 35 (100%) | 35 |
| Vaccinated | 70 (71.42%) | 89 (90.81%) | 97 (98.97%) | 97 (98.97%) | 87 (88.77%) | 98 (100%) | 98 |
| Precolostral | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 16 |
| Total | 93 | 120 | 131 | 130 | 115 | 133 | 149 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Şahinkesen, İ.; Bilge-Dağalp, S. Development of an In-House ELISA for Serological Detection of Equine Herpesvirus-1/4 Antibodies in Turkish Horses. Animals 2025, 15, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172523
Şahinkesen İ, Bilge-Dağalp S. Development of an In-House ELISA for Serological Detection of Equine Herpesvirus-1/4 Antibodies in Turkish Horses. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172523
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞahinkesen, İlker, and Seval Bilge-Dağalp. 2025. "Development of an In-House ELISA for Serological Detection of Equine Herpesvirus-1/4 Antibodies in Turkish Horses" Animals 15, no. 17: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172523
APA StyleŞahinkesen, İ., & Bilge-Dağalp, S. (2025). Development of an In-House ELISA for Serological Detection of Equine Herpesvirus-1/4 Antibodies in Turkish Horses. Animals, 15(17), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172523





