Fermentation Characteristics, Nutrient Content, and Microbial Population of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage Produced with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Additives
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Preparation
2.2. Fermentation Quality
2.3. Chemical Composition
2.4. In Vitro Digestibility
2.5. Aerobic Stability Analysis
2.6. SMRT Analysis of Microbial Composition
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fermentation Quality of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
3.2. Chemical Composition of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
3.3. In Vitro Digestibility and Aerobic Stability of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
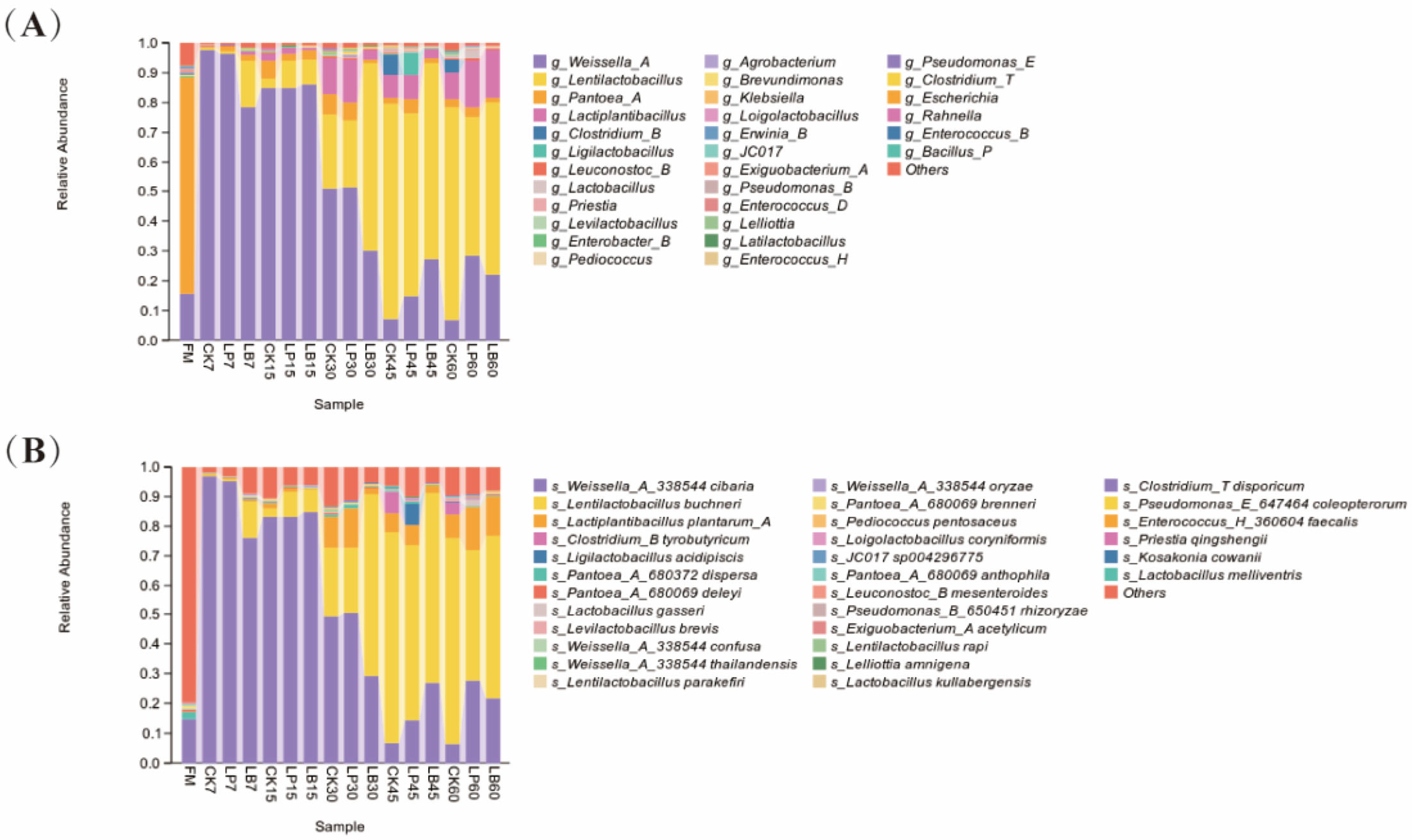
3.4. Bacterial Community Diversity of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
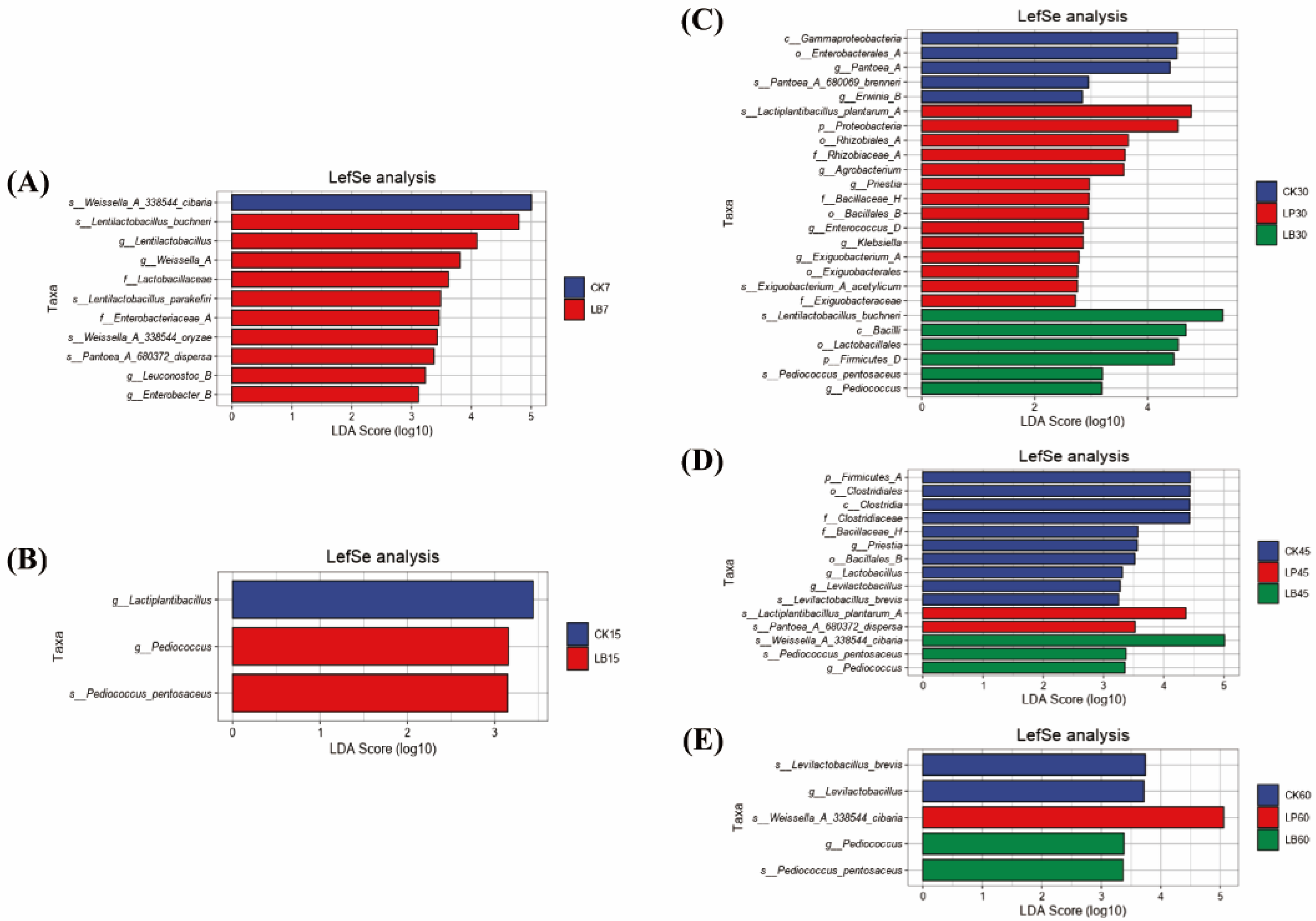
3.5. Bacterial Community Composition and Succession of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
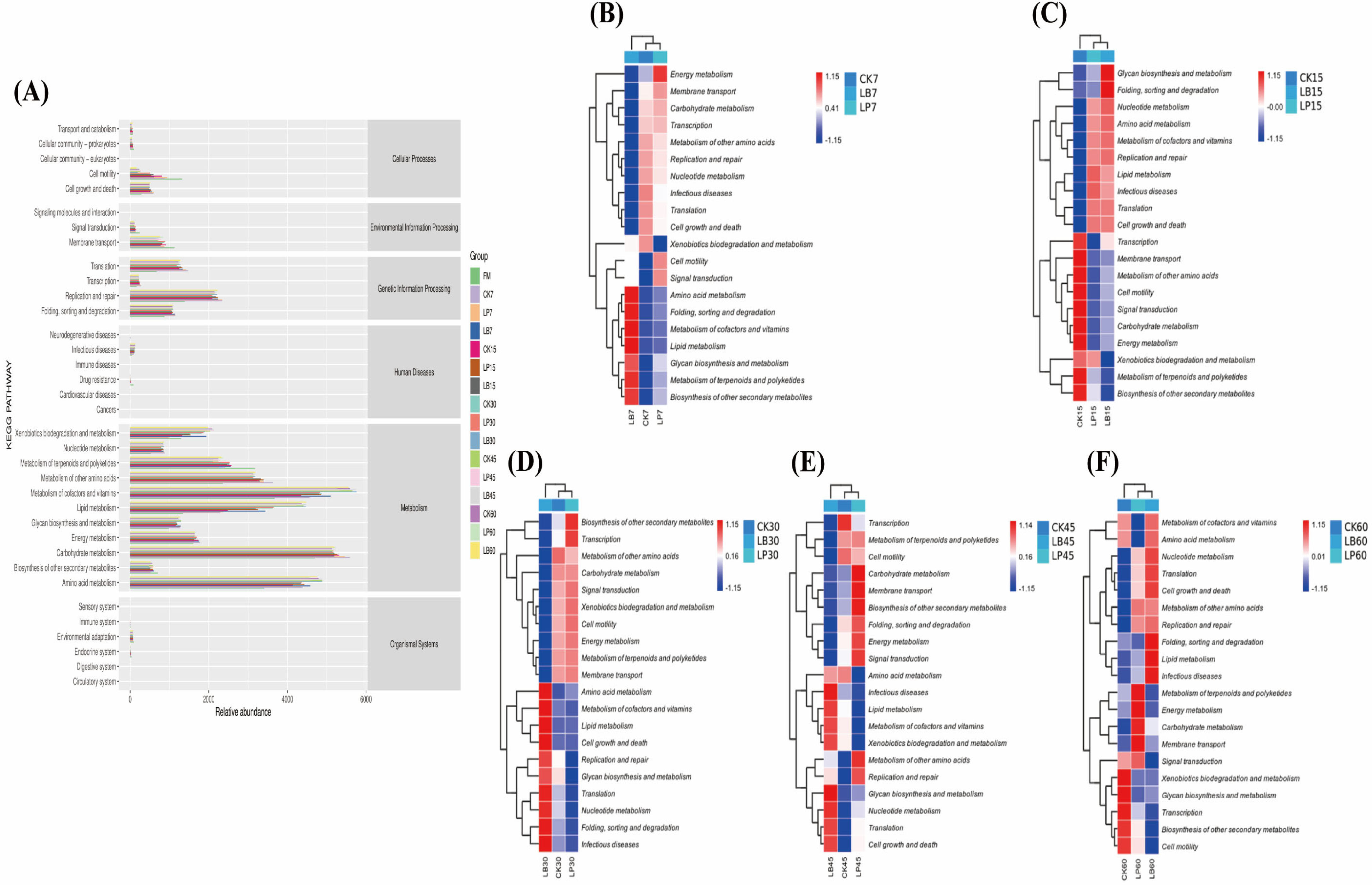
3.6. Functional Predictions of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
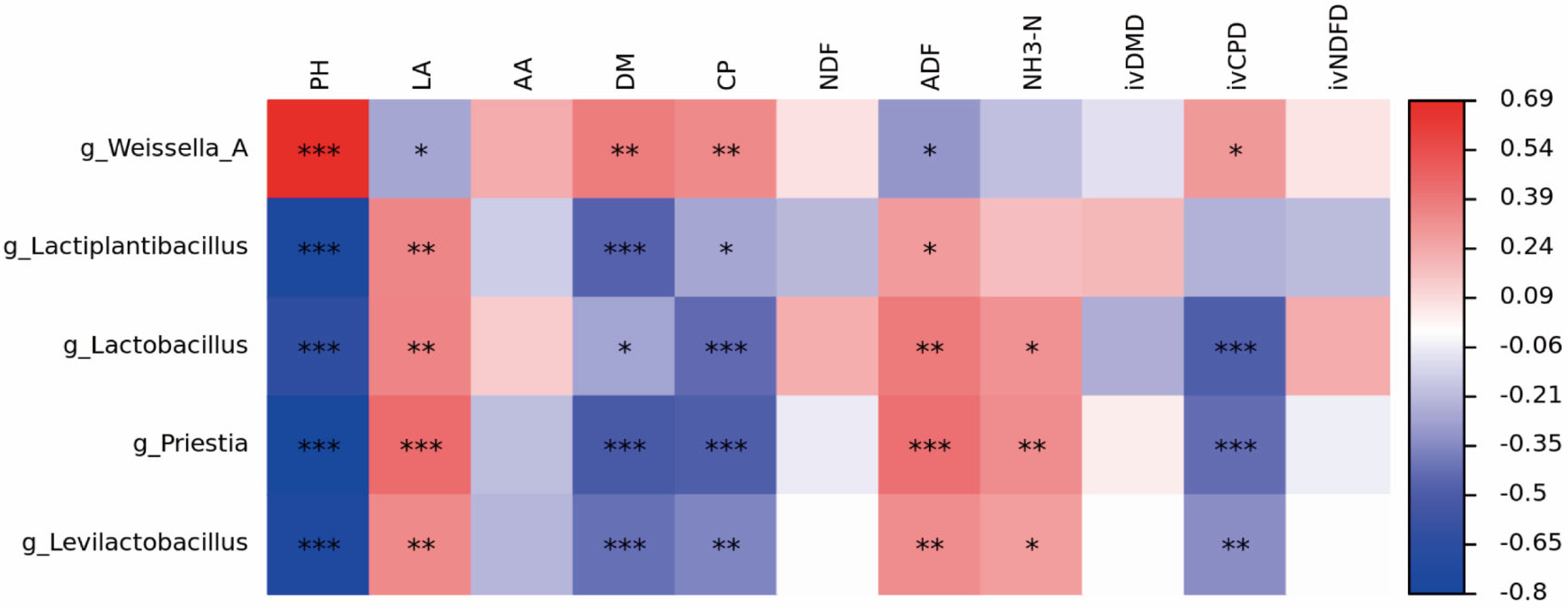
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Different Types of LAB on the Fermentation Quality of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
4.2. Effect of Different Types of LAB on the Chemical Composition of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
4.3. Effect of Different Types of LAB on the In Vitro Digestibility and Aerobic Stability of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
4.4. Effect of Different Types of LAB on the Bacterial Community Diversity, Composition and Succession of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
4.4.1. Dynamics of Bacterial Community Diversity
4.4.2. Changes in Dominant Bacterial Communities
4.4.3. Comparative Analysis with Past Studies
4.5. Effect of Different Types of LAB on the Functional Predictions of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgavi, D.P.; Kelly, W.J.; Janssen, P.H.; Attwood, G.T. Rumen microbial (meta)genomics and its application to ruminant production Rumen microbial (meta)genomics and its application to ruminant production. Animal 2013, 7, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Pu, Z.; Han, S.; Yu, H.; Guo, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Managing forage for grain: Strategies and mechanisms for enhancing forage production to ensure feed grain security Managing forage for grain: Strategies and mechanisms for enhancing forage production to ensure feed grain security. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 2025–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Li, X.; Qian, J.; Du, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, X. Impact of Enzymatic Hydrolyzed Protein Feeding on Rumen Microbial Population, Blood Metabolites and Performance Parameters of Lactating Dairy Cows. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Țîței, V. Biological peculiarities of cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) and utilization possibilities in the Republic of Moldova. 2014. Available online: http://www.uaiasi.ro/revagrois/PDF/2014-1/rez/2014-57(1)-rez-55.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Bernas, J.; Bernasová, T.; Gerstberger, P.; Moudrý, J.; Konvalina, P.; Moudrý, J. Cup plant, an alternative to conventional silage from a LCA perspective. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansberger, M.; Montgomery, L.F.R.; Liebhard, P. Botanical characteristics, crop management and potential of Silphium perfoliatum L. as a renewable resource for biogas production: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Enzyme-assisted extraction of a cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) Polysaccharide and its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. Comparison of different extraction methods of polysaccharides from cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.). Process Biochem. 2020, 90, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblentz, W.K.; Akins, M.S. Silage review: Recent advances and future technologies for baled silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4075–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, G.; Pankiewicz, U.; Kowalski, R. Evaluation of Chemical Composition of Some Silphium L. Species as Alternative Raw Materials. Agriculture 2020, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Sharif, M.; Naeem, M.F.; Munir, H.; Rafique, A.; Chishti, M.F.A.; Anwar, U.; Bilal, Q.; Riaz, M.; Hussain, M.; et al. Effect of lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus buchneri on composition, aerobic stability, total lactic acid bacteria and E. Coli count of ensiled corn stover with or without molasses supplementation. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; He, J.; Yang, X.; Xie, X. Fermentation characteristics and microbial community composition of wet brewer’s grains and corn stover mixed silage prepared with cellulase and lactic acid bacteria supplementation. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yan, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, X.; Liu, M.; Na, R.; Jia, Y.; Cha, S.; Ge, G. Characteristics of isolated lactic acid bacteria at low temperature and their effects on the silage quality. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0319424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Du, S. Influence of Cellulase or Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the Ensiling Performance and Bacterial Community in Mixed Silage of Alfalfa and Leymus chinensis. Microorganism 2023, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazian, Z.A.; Xu, D.; Su, R.; Guo, X. Effects of inoculation and dry matter content on microbiome dynamics and metabolome profiling of sorghum silage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Jiang, C.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, M.; Luo, J.; Du, S.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Effects of cellulase or Lactobacillus plantarum on ensiling performance and bacterial community of sorghum straw. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Xu, L.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, Y. Novel strategy to understand the bacteria-enzyme synergy action regulates the ensiling performance of wheat straw silage by multi-omics analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Te, R.; Wu, X.; Na, N.; Wu, N.; Qili, M.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y. Community Synergy of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Cleaner Fermentation of Oat Silage Prepared with a Multispecies Microbial Inoculant. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0070523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferink, S.J.W.H.O.; Krooneman, J.; Gottschal, J.C.; Spoelstra, S.F.; Faber, F.; Driehuis, F. Anaerobic Conversion of Lactic Acid to Acetic Acid and 1,2-Propanediol by Lactobacillus buchneri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Usman, S.; Huang, W.; Jia, M.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Ran, T.; Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Guo, X. Effects of inoculating feruloyl esterase-producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum A1 on ensiling characteristics, in vitro ruminal fermentation and microbiota of alfalfa silage. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Li, F.; Liang, Y.; Sheoran, N.; Bai, J.; Hao, L.; Ke, W.; Hu, C.; Jia, M.; Usman, S.; et al. Responses of microbial community dynamics, co-occurrences, functional shifts, and natural fermentation profiles of Elymus nutans silage to altitudinal gradients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0251623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Mudassar, S.; Muhammad, I.; Guo, X. Ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase pretreatments of corn stalk silage at two different temperatures: Ensiling characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D. Compensatory changes in the partitioning of dry matter in relation to nitrogen uptake and optimal variations in growth. Ann. Bot. 1986, 58, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playne, M.J.; McDonald, P. The buffering constituents of herbage and of silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1966, 17, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longland, A.C.; Theodorou, M.K.; Sanderson, R.; Lister, S.J.; Powell, C.J.; Morris, P. Non-starch polysaccharide composition and in vitro fermentability of tropical forage legumes varying in phenolic content. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1995, 55, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpila, C.; Khota, W.; Gunun, P.; Kesorn, P.; Cherdthong, A. Strategic addition of different additives to improve silage fermentation, aerobic stability and in vitro digestibility of napier grasses at late maturity stage. Agriculture 2020, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Bai, J.; Li, F.H.; Xu, D.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Bu, D.P.; Zhao, L.S. Effects of malate, citrate, succinate and fumarate on fermentation, chemical composition, aerobic stability and digestibility of alfalfa silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 268, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, E.C.; Basso, F.C.; de Assis, F.B.; Souza, F.A.; Berchielli, T.T.; Reis, R.A. Changes in the nutritive value and aerobic stability of corn silages inoculated with Bacillus subtilis alone or combined with Lactobacillus plantarum. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Su, R.; Wang, M.; Cheng, M.; Xie, D.; Guo, X. Storage Temperature Is More Effective Than Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculations in Manipulating Fermentation and Bacterial Community Diversity, Co-Occurrence and Functionality of the Whole-Plant Corn Silage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0010122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.; Spoelstra, S.F. Anaerobic lactic acid degradation during ensilage of whole crop maize inoculated with Lactobacillus buchneri inhibits yeast growth and improves aerobic stability. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lád, F.; Čermák, B.; Homolka, B.; Jančík, F. Determination of indigestible neutral detergent fibre contents of grasses and its prediction from chemical composition. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 53, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Bao, W.; Li, W.; Zhao, F.; Kwok, L.-y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Changes in physico-chemical characteristics and viable bacterial communities during fermentation of alfalfa silages inoculated with Lactobacillus plantarum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Bao, W.; Yao, C.; Zhao, F.; Jin, H.; Huang, W.; Li, B.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Liu, W. Changes in chemical composition, structural and functional microbiome during alfalfa (Medicago sativa) ensilage with Lactobacillus plantarum PS-8. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L., Jr. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stypinski, J.D.; Weiss, W.P.; Carroll, A.L.; Kononoff, P.J. Effect of acid detergent lignin concentration for diets formulated to be similar in neutral detergent fiber content on energy utilization in lactating Jersey cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cai, R.; Zuo, S.; Niu, D.; Yang, F.; Xu, C. Enhanced lignin degradation by Irpex lacteus through expanded sterilization further improved the fermentation quality and microbial community during the silage preservation process. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, D.R. Creating a System for Meeting the Fiber Requirements of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Masri, M.R. An in vitro nutritive evaluation and rumen fermentation kinetics of Sesbania aculeate as affected by harvest time and cutting regimen. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media1. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méchin, V.; Argillier, O.; Menanteau, V.; Barrière, Y.; Mila, I.; Pollet, B.; Lapierre, C. Relationship of cell wall composition to in vitro cell wall digestibility of maize inbred line stems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Yu, M.; Du, J.; Zhao, T.; Yi, Q.; Tang, H.; Yuan, B. The Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility, and Aerobic Stability of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage. Animal 2024, 14, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.; Huaxin, N.; Andrada, E.; Yang, H.-E.; Chevaux, E.; Drouin, P.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Effects of inoculation of corn silage with Lactobacillus hilgardii and Lactobacillus buchneri on silage quality, aerobic stability, nutrient digestibility, and growth performance of growing beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Guo, G.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, T. The effect of different additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of a total mixed ration silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ding, W.; Ke, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X. Modulation of Metabolome and Bacterial Community in Whole Crop Corn Silage by Inoculating Homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and Heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Bai, C.; Xu, H.; Na, N.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y. Succession of Bacterial Community During the Initial Aerobic, Intense Fermentation, and Stable Phases of Whole-Plant Corn Silages Treated With Lactic Acid Bacteria Suspensions Prepared From Other Silages. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Pian, R.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of citric acid on fermentation characteristics and bacterial diversity of Amomum villosum silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Effects of Cellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality, Chemical Composition, and Microbial Community of Mixed Silage of Whole-Plant Corn and Peanut Vines. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiong, H.; Wen, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of Different Concentrations of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus licheniformis on Silage Quality, In Vitro Fermentation and Microbial Community of Hybrid Pennisetum. Animal 2022, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, N.H.; Wojcińska, M.; Drost-Karbowska, K.; Matławska, I.; Williams, J.; Mabry, T.J. Kaempferol triosides from Silphium perfoliatum. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. The Potential of Pre-fermented Juice or Lactobacillus Inoculants to Improve the Fermentation Quality of Mixed Silage of Agro-Residue and Lucerne. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstrup, M.; Hammer, K.; Ruhdal Jensen, P.; Martinussen, J. Nucleotide metabolism and its control in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items ‡ | Chemical Composition |
|---|---|
| Dry matter (% FW) | 31.04 |
| Organic matter (% DM) | 85.07 |
| Crude protein (% DM) | 19.25 |
| Neutral detergent fibre (% DM) | 38.64 |
| Acid detergent fibre (% DM) | 29.72 |
| Acid detergent lignin (% DM) | 8.73 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrate (% DM) | 5.98 |
| Buffering capacity (mEq kg−1 DM) | 321.54 |
| Item | Day | Additives | Mean | SEM | Significance of Main Effects and Interactions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LP | LB | D | A | D × A | ||||
| pH value | 7 | 4.87 B | 4.79 C | 4.96 C | 4.87 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 4.82 B | 4.76 C | 4.88 C | 4.82 | |||||
| 30 | 4.51 Aa | 4.54 Ba | 4.71 Bb | 4.59 | |||||
| 45 | 4.47 Aa | 4.36 Aa | 4.80 BCb | 4.54 | |||||
| 60 | 4.51 Ab | 4.31 Aa | 4.55 Ab | 4.45 | |||||
| avg | 4.64 | 4.55 | 4.78 | ||||||
| NH3-N (%TN) | 7 | 3.72 A | 3.81 AB | 4.05 B | 3.86 | 0.052 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 4.49 Ab | 3.31 Aa | 2.78 Aa | 3.53 | |||||
| 30 | 3.15 Ab | 3.72 ABb | 2.15 Aa | 3.00 | |||||
| 45 | 4.26 Ab | 4.77 Bb | 2.21 Aa | 3.75 | |||||
| 60 | 7.86 Bb | 6.34 Cb | 2.58 Aa | 5.59 | |||||
| avg | 4.70 | 4.39 | 2.75 | ||||||
| LA (%DM) | 7 | 0.40 | 0.44 AB | 0.47 C | 0.44 | 0.010 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 0.36 b | 0.39 Bb | 0.26 Aa | 0.34 | |||||
| 30 | 0.45 b | 0.46 ABb | 0.30 Aa | 0.40 | |||||
| 45 | 0.52 b | 0.54 BCb | 0.34 ABa | 0.46 | |||||
| 60 | 0.42 a | 0.58 Cb | 0.40 BCa | 0.46 | |||||
| avg | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.35 | ||||||
| AA (%DM) | 7 | 0.13 B | 0.12 | 0.13 AB | 0.13 | ||||
| 15 | 0.09 A | 0.11 | 0.06 A | 0.09 | |||||
| 30 | 0.07 A | 0.07 | 0.08 AB | 0.07 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.392 | 0.005 | |
| 45 | 0.07 A | 0.08 | 0.08 AB | 0.08 | |||||
| 60 | 0.10 Aa | 0.11 a | 0.14 Bb | 0.12 | |||||
| avg | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | ||||||
| Item | Day | Additives | Mean | SEM | Significance of Main Effects and Interactions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LP | LB | D | A | D × A | ||||
| DM (%FW) | 7 | 27.30 | 27.70 C | 27.06 A | 27.35 | 0.205 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 25.66 a | 27.38 Ca | 31.83 Bb | 28.29 | |||||
| 30 | 27.18 a | 24.54 ABa | 32.25 Bb | 27.99 | |||||
| 45 | 25.45 | 23.47 A | 26.45 A | 25.12 | |||||
| 60 | 25.40 | 25.94 BC | 27.87 A | 26.41 | |||||
| avg | 26.20 | 25.81 | 29.09 | ||||||
| OM (%DM) | 7 | 84.60 B | 84.85 | 84.58 | 84.68 | 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.802 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 84.85 Cb | 84.96 b | 84.49 a | 84.76 | |||||
| 30 | 84.35 A | 84.62 | 84.59 | 84.52 | |||||
| 45 | 84.51 ABa | 84.57 ab | 84.72 b | 84.60 | |||||
| 60 | 85.02 Db | 84.77 a | 84.55 a | 84.78 | |||||
| avg | 84.67 | 84.75 | 84.59 | ||||||
| CP (%DM) | 7 | 17.36 B | 16.90 B | 17.12 A | 17.13 | 0.038 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 16.63 Ba | 18.00 Cb | 18.91 Bc | 17.85 | |||||
| 30 | 18.80 Cb | 16.89 Ba | 19.61 Cc | 18.43 | |||||
| 45 | 15.53 Aa | 15.87 Aa | 19.29 BCb | 16.90 | |||||
| 60 | 15.21 Aa | 16.18 ABb | 17.58 Ac | 16.32 | |||||
| avg | 16.71 | 16.77 | 18.50 | ||||||
| NDF (%DM) | 7 | 37.73 BC | 39.38 C | 37.28 C | 38.13 | 0.132 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 35.85 ABb | 36.43 Bb | 32.45 ABa | 34.91 | |||||
| 30 | 33.44 A | 32.74 A | 35.22 BC | 33.80 | |||||
| 45 | 36.50 Bc | 34.48 Ab | 31.03 Aa | 34.00 | |||||
| 60 | 39.68 Cb | 38.98 Cb | 34.69 BCa | 37.78 | |||||
| avg | 36.68 | 36.40 | 34.13 | ||||||
| ADF (%DM) | 7 | 26.16 A | 26.82 AB | 26.29 C | 26.42 | 0.115 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 28.10 Bb | 25.50 Aa | 25.28 BCa | 26.30 | |||||
| 30 | 24.93 Aa | 27.85 BCb | 24.26 ABa | 25.68 | |||||
| 45 | 29.66 Cb | 29.04 Cb | 23.03 Aa | 27.24 | |||||
| 60 | 29.27 BCb | 28.14 BCb | 25.90 BCa | 27.77 | |||||
| avg | 27.62 | 27.47 | 24.95 | ||||||
| ADL (%DM) | 7 | 8.39 C | 7.86 C | 8.59 D | 8.28 | 0.069 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 3.25 Aa | 3.86 ABa | 4.91 BCb | 4.01 | |||||
| 30 | 4.74 Bab | 3.36 Aa | 5.62 Cb | 4.57 | |||||
| 45 | 5.17 B | 4.92 B | 3.87 AB | 4.65 | |||||
| 60 | 4.12 AB | 4.29 AB | 3.45 A | 3.95 | |||||
| avg | 5.13 | 4.86 | 5.29 | ||||||
| Item | Day | Additives | Mean | SEM | Significance of Main Effects and Interactions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LP | LB | D | A | D × A | ||||
| ivDMD (%DM) | 7 | 66.15 AB | 65.19 A | 66.41 A | 65.91 | 0.076 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 67.24 BCa | 66.90 Ba | 69.21 BCb | 67.78 | |||||
| 30 | 68.64 C | 69.04 C | 67.61 AB | 68.43 | |||||
| 45 | 66.86 Ba | 68.03 Cb | 70.03 Cc | 68.31 | |||||
| 60 | 65.01 Aa | 65.42 Aa | 67.91 ABb | 66.12 | |||||
| avg | 66.78 | 66.92 | 67.79 | ||||||
| ivOMD (%DM) | 7 | 69.88 AB | 68.93 A | 70.13 A | 69.65 | 0.075 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 70.95 BCa | 70.62 Ba | 72.90 BCb | 71.49 | |||||
| 30 | 72.34 C | 72.74 C | 71.32 AB | 72.13 | |||||
| 45 | 70.58 Ba | 71.74 Cb | 73.71 Cc | 72.01 | |||||
| 60 | 68.76 Aa | 69.16 Aa | 71.62 ABb | 69.85 | |||||
| avg | 70.50 | 70.64 | 71.49 | ||||||
| ivCPD (%DM) | 7 | 57.71 Db | 56.33 Aa | 56.92 Aa | 56.99 | 0.043 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 56.75 Ca | 57.86 Bb | 59.40 Bc | 58.00 | |||||
| 30 | 59.12 Eb | 57.55 Ba | 59.51 B | 58.72 | |||||
| 45 | 55.65 Ba | 56.32 Aa | 60.89 Cb | 57.62 | |||||
| 60 | 54.77 Aa | 55.77 Ab | 57.80 Ac | 56.11 | |||||
| avg | 56.80 | 56.77 | 59.11 | ||||||
| ivNDFD (%DM) | 7 | 36.50 BC | 37.85 C | 36.12 C | 36.82 | 0.112 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 34.84 ABb | 35.32 Bb | 32.03 ABa | 34.06 | |||||
| 30 | 32.90 A | 32.25 A | 34.36 BC | 33.17 | |||||
| 45 | 35.47 Bc | 33.74 Ab | 30.77 Aa | 33.33 | |||||
| 60 | 38.07 Cb | 37.52 Cb | 33.92 BCa | 36.50 | |||||
| avg | 35.58 | 35.34 | 33.44 | ||||||
| ivGED (%DM) | 7 | 69.74 AB | 68.81 A | 69.99 A | 69.52 | 0.074 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 15 | 70.80 BCa | 70.47 Ba | 72.70 BCb | 71.32 | |||||
| 30 | 72.15 C | 72.54 C | 71.15 AB | 71.95 | |||||
| 45 | 70.43 Ba | 71.56 Cb | 73.50 Cc | 71.83 | |||||
| 60 | 68.65 Aa | 69.04 Aa | 71.45 ABb | 69.71 | |||||
| avg | 70.35 | 70.48 | 71.32 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Yuan, B.; Li, F.; Du, J.; Yu, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P. Fermentation Characteristics, Nutrient Content, and Microbial Population of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage Produced with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Additives. Animals 2025, 15, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131955
Jin Y, Yuan B, Li F, Du J, Yu M, Tang H, Zhang L, Wang P. Fermentation Characteristics, Nutrient Content, and Microbial Population of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage Produced with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Additives. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131955
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yitong, Bao Yuan, Fuhou Li, Jiarui Du, Meng Yu, Hongyu Tang, Lixia Zhang, and Peng Wang. 2025. "Fermentation Characteristics, Nutrient Content, and Microbial Population of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage Produced with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Additives" Animals 15, no. 13: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131955
APA StyleJin, Y., Yuan, B., Li, F., Du, J., Yu, M., Tang, H., Zhang, L., & Wang, P. (2025). Fermentation Characteristics, Nutrient Content, and Microbial Population of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage Produced with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Additives. Animals, 15(13), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131955







