Efficacy and Safety Assessment of a Dietary Supplement in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis and Dogs with Arthritic Signs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Supplement
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Complete Blood Count and Blood Chemistry
2.4. Analysis of Serum Markers
2.5. Histopathologic Evaluation
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis (QRT-PCR)
2.7. Clinical Evaluation with Dogs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
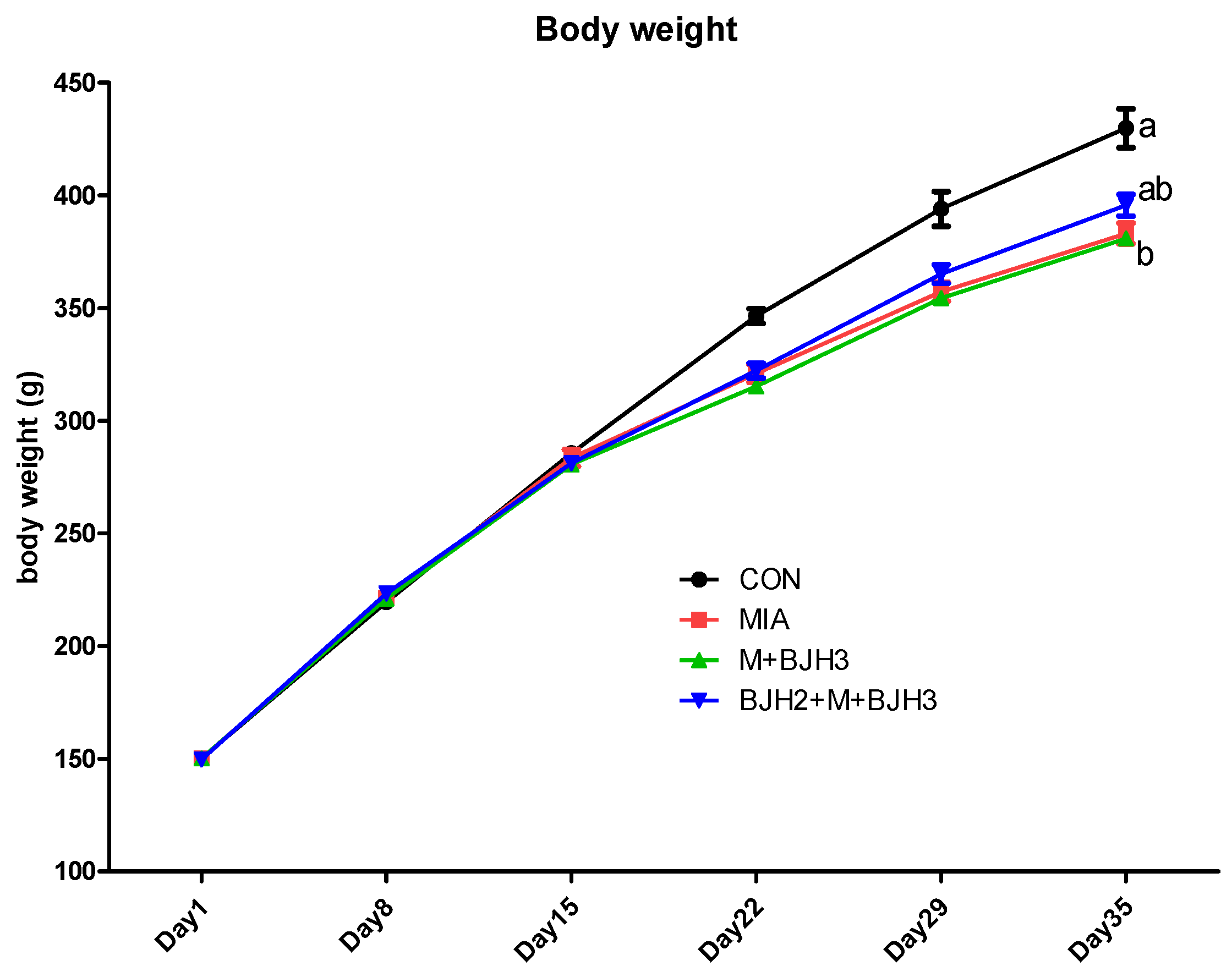
3.1. Body Weight Assessment
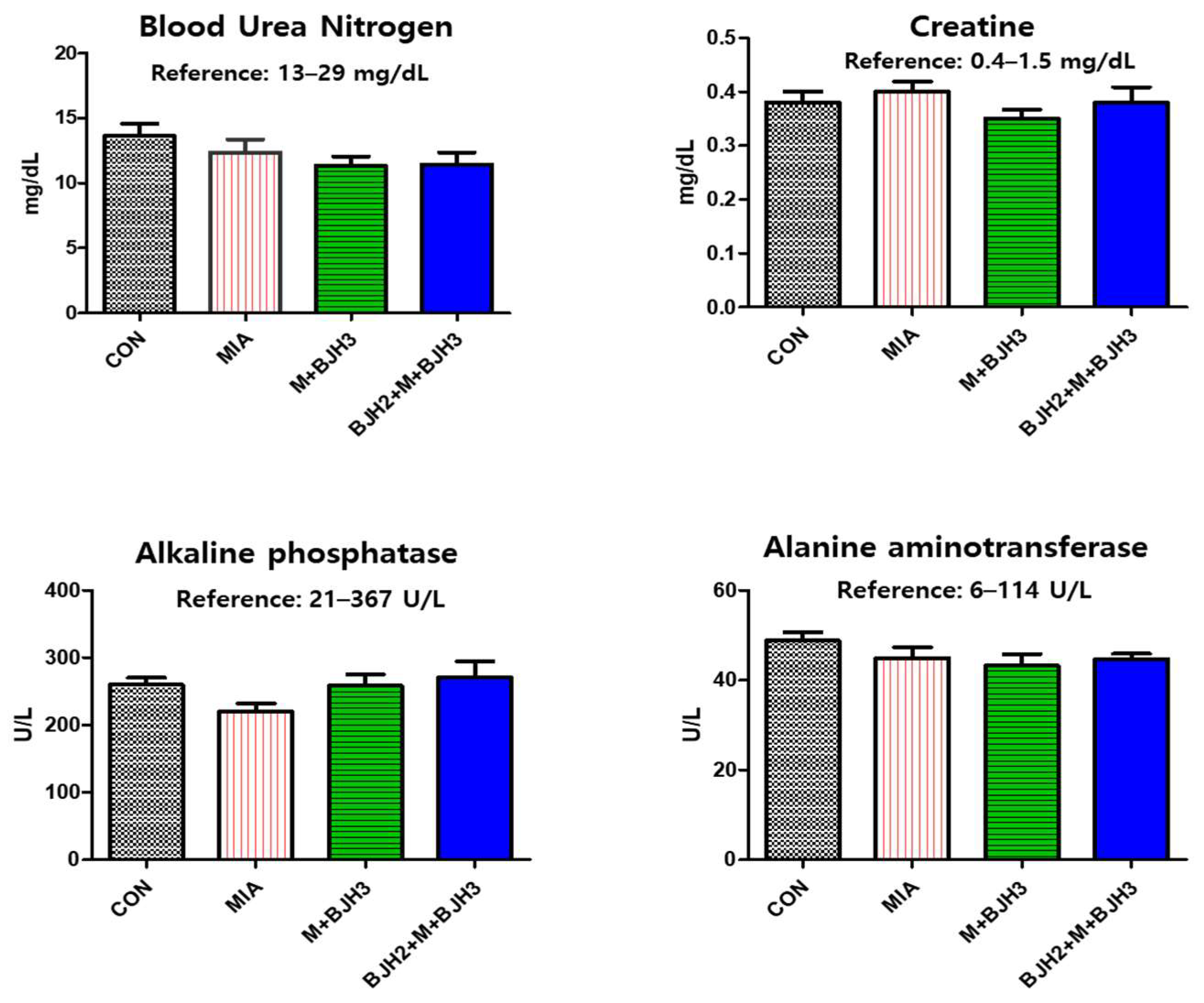
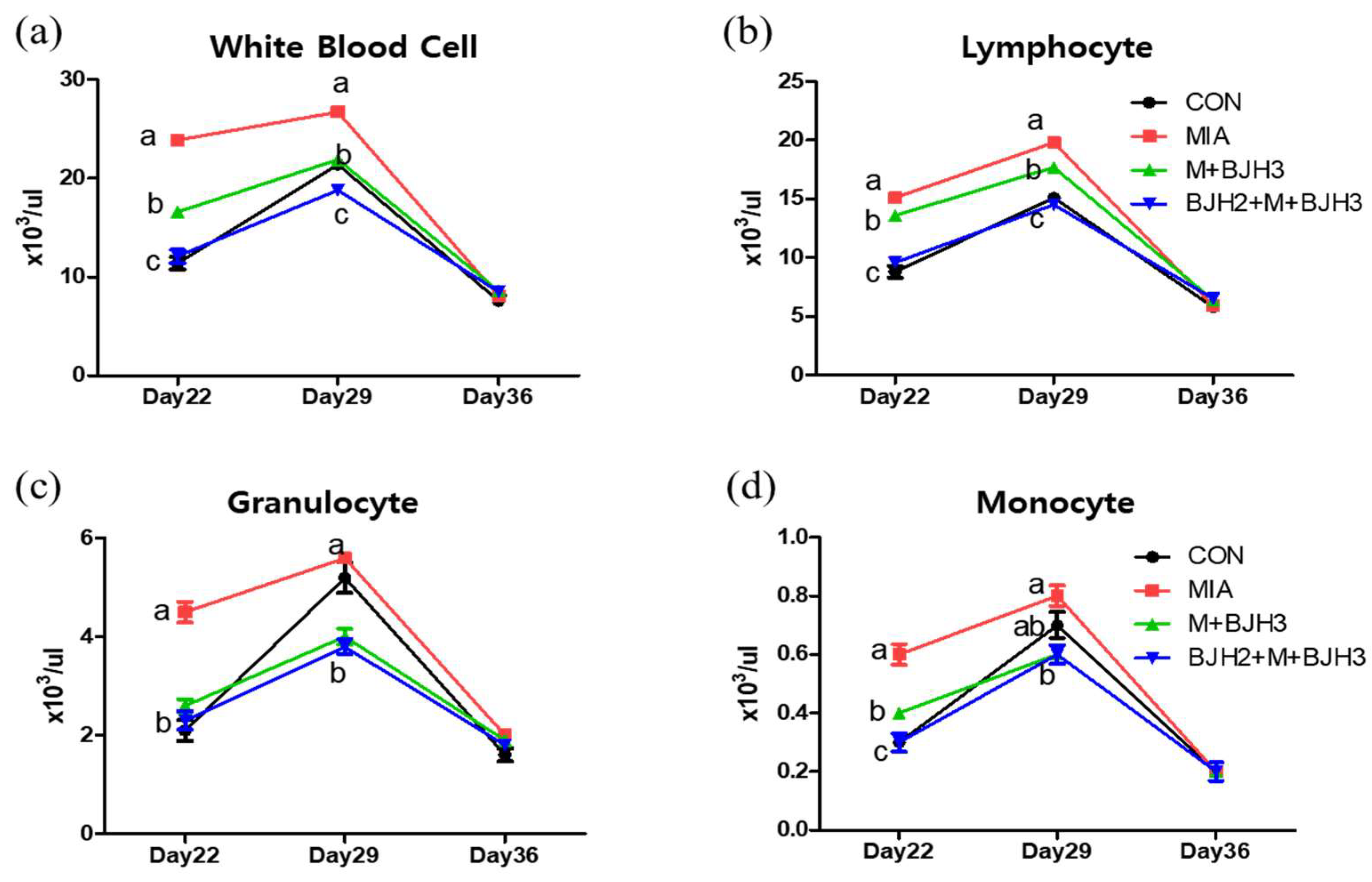
3.2. Hematology and Blood Chemistry
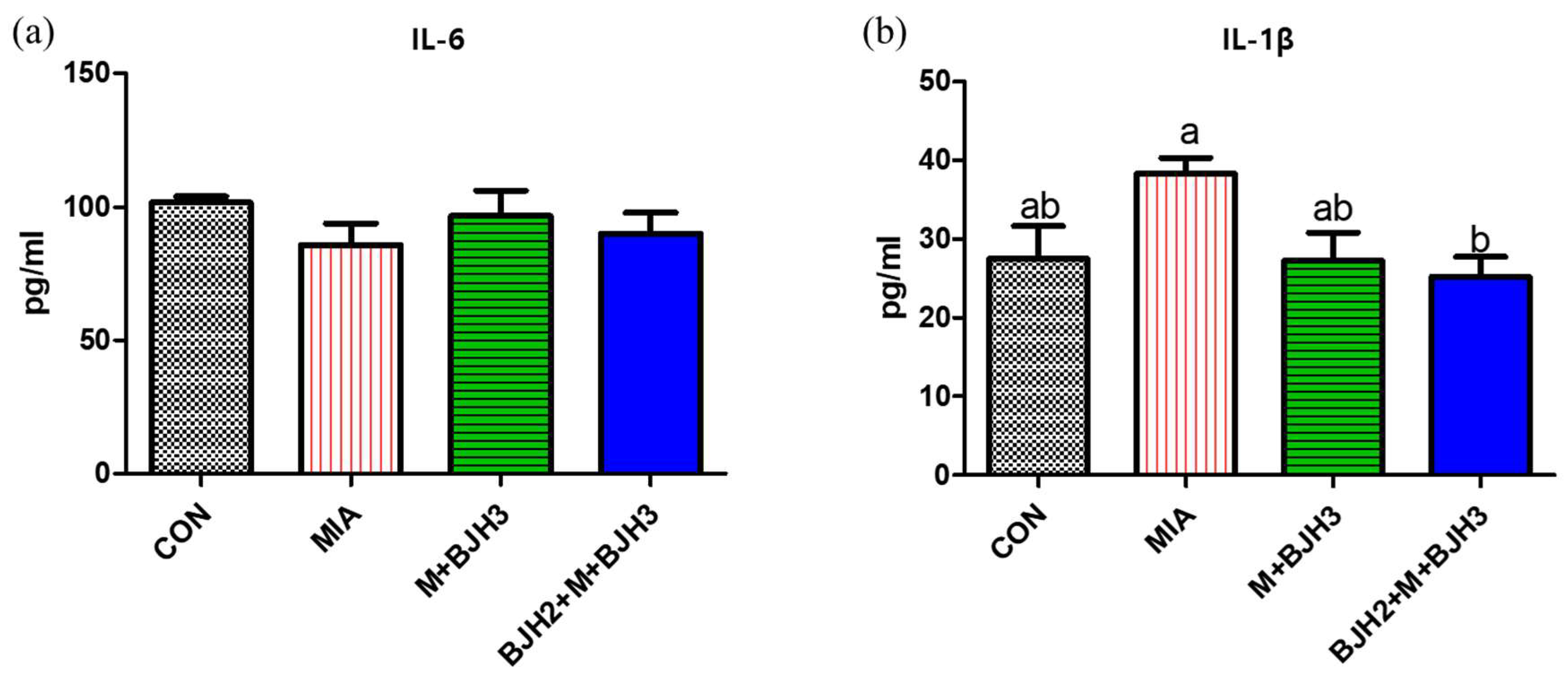
3.3. Serum IL-6 and IL-1β of Rats
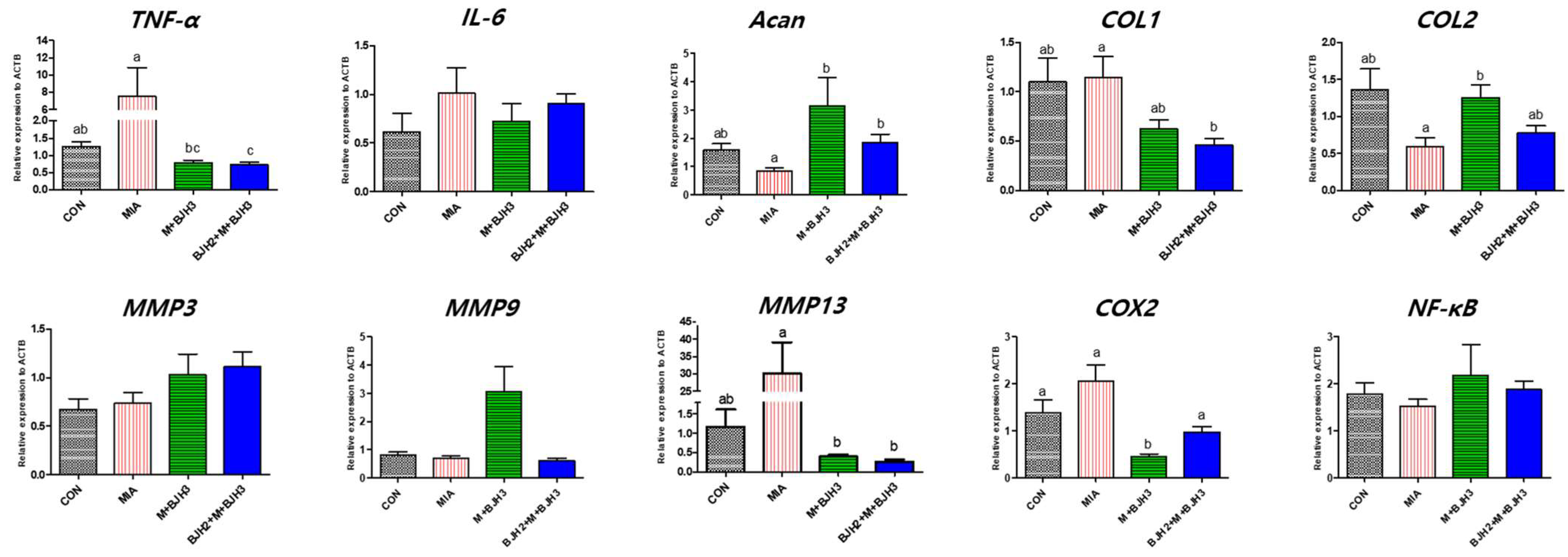
3.4. Relative Gene Expression of OA and Inflammation Factors
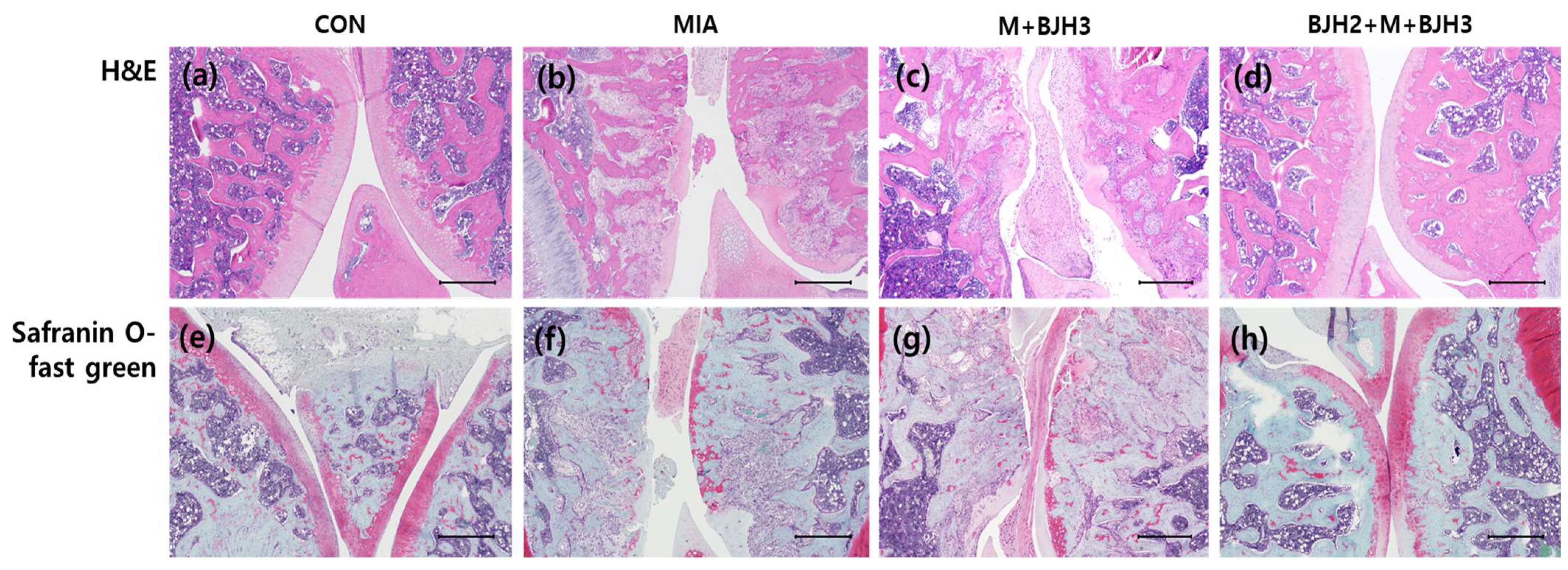
3.5. Effect of BJH Observed in the Histological Assessment
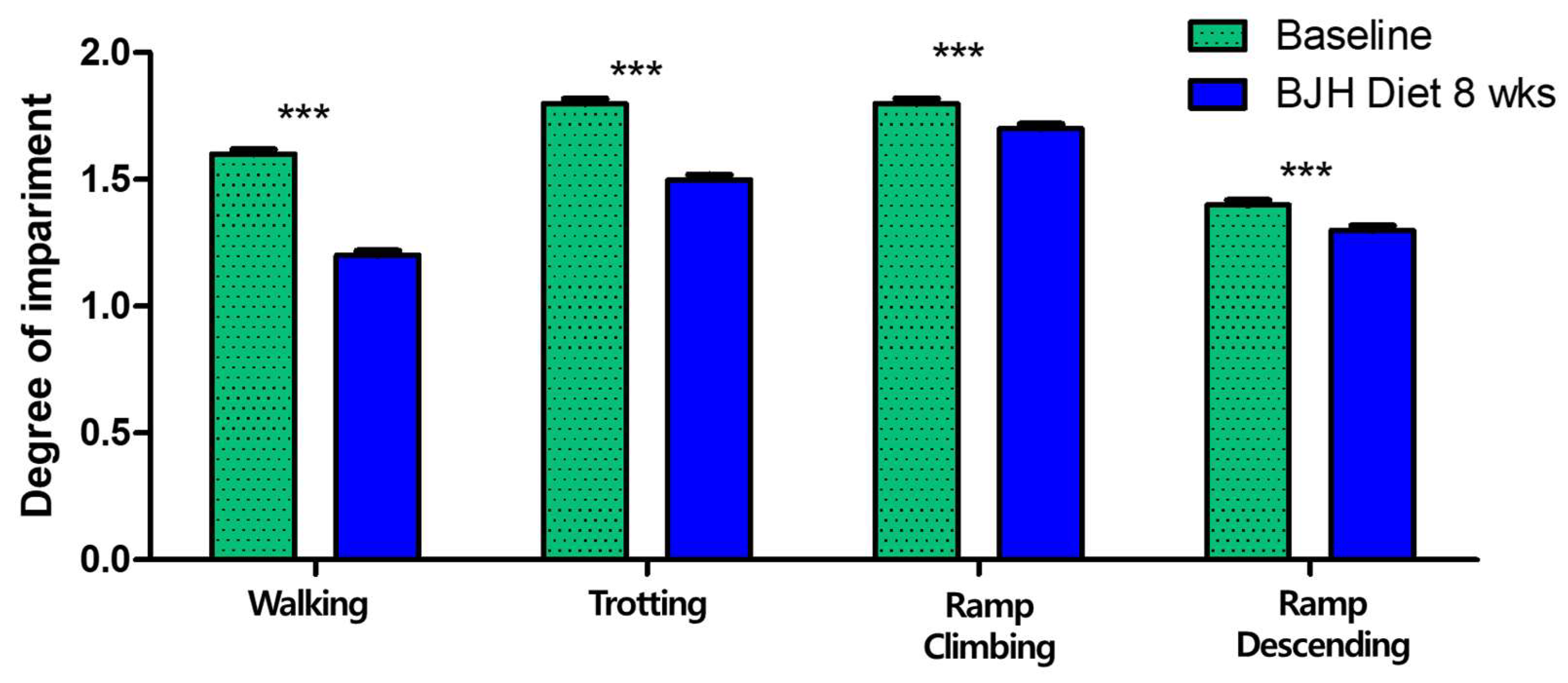
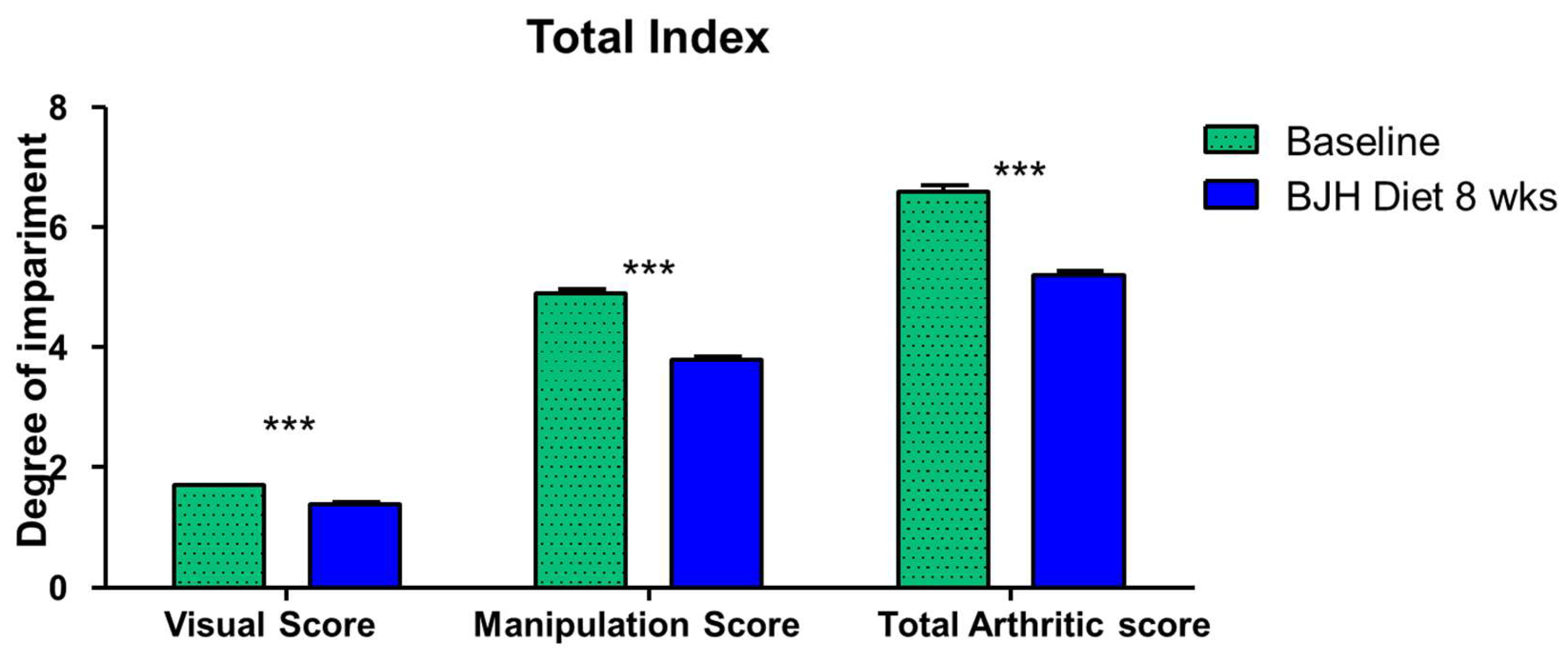
3.6. Effect of BJH Observed in Clinical Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in articular tissues. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 33, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.P.; Mellor, D.; Clements, D.N.; Gemmill, T.; Farrell, M.; Carmichael, S.; Bennett, D. Prevalence of radiographic signs of degenerative joint disease in a hospital population of cats. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, D.R. Osteoarthritis in cats: A retrospective radiological study. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 46, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, E.M.; Roe, S.C.; Martin, F.R. Radiographic evidence of degenerative joint disease in geriatric cats: 100 cases (1994–1997). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.; Robertson, I.; Bondell, H.D.; Brown, J.; Hash, J.; Pease, A.P.; Lascelles, B.D. Radiographic evaluation of feline appendicular degenerative joint disease vs. Macroscopic appearance of articular cartilage. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2011, 52, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingerland, L.I.; Hazewinkel, H.A.; Meij, B.P.; Picavet, P.; Voorhout, G. Cross-sectional study of the prevalence and clinical features of osteoarthritis in 100 cats. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascelles, B.D.; Henry, J.B., 3rd; Brown, J.; Robertson, I.; Sumrell, A.T.; Simpson, W.; Wheeler, S.; Hansen, B.D.; Zamprogno, H.; Freire, M.; et al. Cross-sectional study of the prevalence of radiographic degenerative joint disease in domesticated cats. Vet. Surg. 2010, 39, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.N.; Carter, S.D.; Innes, J.F.; Ollier, W.E. Genetic basis of secondary osteoarthritis in dogs with joint dysplasia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitznagel, M.B.; Jacobson, D.M.; Cox, M.D.; Carlson, M.D. Caregiver burden in owners of a sick companion animal: A cross-sectional observational study. Vet. Rec. 2017, 181, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch-Derra, L.; Huebner, M.; Wofford, J.; Rhodes, L. A Prospective, Randomized, Masked, Placebo-Controlled Multisite Clinical Study of Grapiprant, an EP4 Prostaglandin Receptor Antagonist (PRA), in Dogs with Osteoarthritis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmeyer, J. Pharmacological basis for the therapy of pain and inflammation with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arthritis Res. 2000, 2, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, M.S.; Budsberg, S.C. The coxib NSAIDs: Potential clinical and pharmacologic importance in veterinary medicine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KuKanich, B.; Bidgood, T.; Knesl, O. Clinical pharmacology of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2012, 39, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhathal, A.; Spryszak, M.; Louizos, C.; Frankel, G. Glucosamine and chondroitin use in canines for osteoarthritis: A review. Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Alves, A.; Ferreira, B.M.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reys, L.L.; Ferreira, R.J.F.; Sousa, R.A.; Silva, S.S.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Materials of marine origin: A review on polymers and ceramics of biomedical interest. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 276–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.M.; Fernández, N.; Matias, A.A.; Bronze, M.d.R. Hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate from marine and terrestrial sources: Extraction and purification methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, L.H.C.; Vasconcelos, B.M.F.; Silva, M.B.; Souza, A.A., Jr.; Chavante, S.F.; Andrade, G.P.V. Chondroitin sulfate from fish waste exhibits strong intracellular antioxidant potential. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.M.; Fosmire, G.J.; Leach, R.M., Jr. Chicken keel cartilage as a source of chondroitin sulfate. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, M.H.; Hall, B.; Hofmanm, K. Isolation and characterisation of major and minor collagens from hyaline cartilage of hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencoglu, H.; Orhan, C.; Sahin, E.; Sahin, K. Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) in Joint Health and Disease: A Review on the Current Knowledge of Companion Animals. Animals 2020, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, R.H.; Chang, J.L.; Konda, V.; Desai, A.; Montalto, M.B. Nutritional Approach for Relief of Joint Discomfort: A 12-week, Open-case Series and Illustrative Case Report. Integr. Med. 2015, 14, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Zhao, W.; Wu, Y.Q.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Q.T.; Zhang, L.L.; Wei, W. Chicken type II collagen induced immune balance of main subtype of helper T cells in mesenteric lymph node lymphocytes in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.H.; Ullah, H.M.A.; Goo, M.J.; Ghim, S.G.; Hong, I.H.; Kim, A.Y.; Jeon, S.M.; Choi, M.S.; Elfadl, A.K.; Chung, M.J.; et al. Effects of oral glucosamine hydrochloride and mucopolysaccharide protein in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppedisano, F.; Bulotta, R.M.; Maiuolo, J.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Ilari, S.; Serra, M.; Muscoli, C.; Gratteri, S.; et al. The Role of Nutraceuticals in Osteoarthritis Prevention and Treatment: Focus on n-3 PUFAs. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 4878562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abshirini, M.; Ilesanmi-Oyelere, B.L.; Kruger, M.C. Potential modulatory mechanisms of action by long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on bone cell and chondrocyte metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 83, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servet, E.; Biourge, V.; Marniquet, P. Dietary Intervention Can Improve Clinical Signs in Osteoarthritic Dogs. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1995S–1997S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, C.; Juturu, V.; Sahin, E.; Tuzcu, M.; Ozercan, I.H.; Durmus, A.S.; Sahin, N.; Sahin, K. Undenatured Type II Collagen Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses and Articular Cartilage Damage in the Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 617789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenei-Lanzl, Z.; Meurer, A.; Zaucke, F. Interleukin-1beta signaling in osteoarthritis-chondrocytes in focus. Cell. Signal. 2019, 53, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, V.; Matisic, V.; Kodvanj, I.; Bjelica, R.; Jelec, Z.; Hudetz, D.; Rod, E.; Cukelj, F.; Vrdoljak, T.; Vidovic, D.; et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawl, M.; Geetha, T.; Burnett, D.; Babu, J.R. Omega-3 Supplementation and Its Effects on Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Funovits, J.; Smolen, J.S. Physical disability in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with cartilage damage rather than bone destruction. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrina, A.I.; Lampa, J.; Ernestam, S.; af Klint, E.; Bratt, J.; Klareskog, L.; Ulfgren, A.K. Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha therapy (etanercept) down-regulates serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and MMP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, N.; Palmer, G.D.; Pilapil, C.; Liu, F.; Wells, J.W.; Muller, P.E.; Evans, C.H.; Porter, R.M. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit chondrogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells through NF-kappaB-dependent pathways. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Hong, T.; Ye, Q.; et al. The IL-1beta/AP-1/miR-30a/ADAMTS-5 axis regulates cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, L.; Danger, R.; Cabon, Q.; Rabillard, M.; Brouard, S.; Bouvy, B.; Gauthier, O. MMP-2 as an early synovial biomarker for cranial cruciate ligament disease in dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 27, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, B.L.; Ma, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Chlorogenic acid prevents inflammatory responses in IL-1beta-stimulated human SW-1353 chondrocytes, a model for osteoarthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Rong, X.F.; Li, R.H.; Wu, X.Y. Icariin inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL-1beta-stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, L.A.; Szukiewicz, D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 561459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, P. Profiling of inflammatory mediators in the synovial fluid related to pain in knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Blas, J.A.; Jimenez, S.A. NF-kappaB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glade, M.J. Polysulfated glycosaminoglycan accelerates net synthesis of collagen and glycosaminoglycans by arthritic equine cartilage tissues and chondrocytes. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 51, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfort, J.; Pelletier, J.P.; Garcia-Giralt, N.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Biochemical basis of the effect of chondroitin sulphate on osteoarthritis articular tissues. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, K.M.; Caron, J.P.; Orth, M.W. The role of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate in treatment for and prevention of osteoarthritis in animals. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 226, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierer, T.L.; Bui, L.B. Improvement of arthritic signs in dogs fed green-lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus). J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1634S–1636S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainsford, K.D.; Whitehouse, M.W. Gastroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of green-lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus) preparation. Arzneim. Forsch. 1980, 30, 2128–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, L.M.; Bierer, T.L. Influence of green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus) in alleviating signs of arthritis in dogs. Vet. Ther. 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Mongkon, N.; Soontornvipart, K. Preliminary study of the clinical outcome of using PCSO-524 polyunsaturated fatty acid compound in the treatment of canine osteoarthritis and degenerative spinal diseases. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2012, 42, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soontornvipart, K.; Mongkhon, N.; Nganvongpanit, K.; Kongtawelert, P. Effect of PCSO-524 on OA biomarkers and weight-bearing properties in canine shoulder and coxofemeral osteoarthritis. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2015, 45, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwananocha, I.; Vijarnsorn, M.; Kashemsant, N.; Lekcharoensuk, C. Effectiveness of disease modifying osteoarthritis agents and carprofen for treatment of canine osteoarthritis. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2016, 46, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijarnsorn, M.; Kwananocha, I.; Kashemsant, N.; Jarudecha, T.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Beale, B.; Peirone, B.; Lascelles, B.D.X. The effectiveness of marine based fatty acid compound (PCSO-524) and firocoxib in the treatment of canine osteoarthritis. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, M.; Samarelli, R.; Trerotoli, P.; Fracassi, L.; Lacitignola, L.; Crovace, A.; Staffieri, F. Evaluation of the Effects of Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) as Compared to Robenacoxib on the Mobility Impairment Induced by Osteoarthritis in Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.C.; Canerdy, T.D.; Lindley, J.; Konemann, M.; Minniear, J.; Carroll, B.A.; Hendrick, C.; Goad, J.T.; Rohde, K.; Doss, R.; et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy and safety of type-II collagen (UC-II), glucosamine and chondroitin in arthritic dogs: Pain evaluation by ground force plate. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martello, E.; Bigliati, M.; Adami, R.; Biasibetti, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Meineri, G.; Bruni, N. Efficacy of a dietary supplement in dogs with osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, T.; Jährling-Butkus, M.; Louton, H.; Burg-Roderfeld, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N.; Hesse, K.; Petridis, A.K.; Kožár, T.; Steinmeyer, J.; et al. Efficacy of Chondroprotective Food Supplements Based on Collagen Hydrolysate and Compounds Isolated from Marine Organisms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musco, N.; Vassalotti, G.; Mastellone, V.; Cortese, L.; della Rocca, G.; Molinari, M.L.; Calabrò, S.; Tudisco, R.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Lombardi, P. Effects of a nutritional supplement in dogs affected by osteoarthritis. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nutrients | Contents (mg/g) in Supplement (mg/g) |
|---|---|
| Mucopolysaccharide protein | 600 |
| Chondroitin sulfate | 120 |
| Type II collagen | 48 |
| Omega 3 fatty acid | 50 |
| Gene | Official Full Name | Primer Sequence | Gene Bank No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha | ACAAGGCTGCCCCGACTAT | X66539.1 |
| CTCCTGGTATGAAGTGGCAAATC | |||
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 | GCCCTTCAGGAACAGCTATGA | M26744.1 |
| TGTCAACAACATCAGTCCCAAGA | |||
| Acan | aggrecan | GAAGTGGCGTCCAAACCAA | NM_022190.1 |
| CGTTCCATTCACCCCTCTCA | |||
| COL1 | collagen type I | CTGGTGAACAGGGTGTTCCT | BC133728 |
| GGAAACCTCTCTCGCCTCTT | |||
| COL2 | collagen type II | CGAGGTGACAAAGGAGAAGC | L48440 |
| AGGGCCAGAAGTACCCTGAT | |||
| MMP3 | matrix metallo proteinases 3 | GAGTGTGGATTCTGCCATTGAG | NM_133523.2 |
| TTATGTCAGCCTCTCCTTCAG A | |||
| MMP9 | matrix metallo proteinases 9 | GCGCCAGCCGACTTATGT | NM_031055.1 |
| AATCCTCTGCCAGCTGTGTGT | |||
| MMP13 | matrix metallo proteinases 13 | ACGTTCAAGGAATCCAGTCTC | NM_133530.1 |
| GGATAGGGCTGGGTCACACTT | |||
| COX2 | cyclooxygenase isoform COX-2 | AGAGAAAGAAATGGCTGCAGAGT | S67722.1 |
| AGCAGGGCGGGATACAGT | |||
| NF-kB | nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 | GCACCAAGACCGAAGCAATT | NM_001276711.1 |
| GAAACCCCACATCCTCTTCCTT | |||
| ACTB | β-actin | AGGCCAACCGTGAAAAGATG | NM_031144.3 |
| ACCAGAGGCATACAGGGACAA |
| No. | Breed | Age (Years) | Gender | Body Weight (kg) | Joint Evaluation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Score | Manipulation Score | Total Arthritic Score | |||||||||
| Before | 8 Weeks | Before | 8 Weeks | Before | 8 Weeks | Before | 8 Weeks | ||||
| 1 | Maltese | 6 | CM | 2.98 | 3.07 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 |
| 2 | Cocker Spaniel | 10 | FS | 10.90 | 11.2 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 5.50 | 4.00 |
| 3 | Poodle | 10 | FS | 2.70 | 2.70 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 5.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 5.00 |
| 4 | Poodle | 10 | FS | 4.80 | 4.90 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
| 5 | Chihuahua | 7 | CM | 3.25 | 3.47 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 8.00 | 6.50 |
| 6 | Poodle | 7 | FS | 4.34 | 4.38 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 7 | Bichon Frise | 1 | FS | 4.87 | 4.90 | 1.75 | 1.75 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 6.75 | 5.75 |
| 8 | Bichon Frise | 4 | FS | 2.90 | 3.10 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 8.00 | 7.00 |
| 9 | Maltipoo | 4 | CM | 4.00 | 4.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| 10 | Poodle | 4 | CM | 2.70 | 2.70 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.50 |
| 11 | Japanese Spitz | 4 | CM | 6.80 | 6.88 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 6.50 | 6.00 |
| 12 | Maltese | 4 | CM | 5.98 | 5.91 | 2.25 | 2.00 | 8.00 | 6.00 | 10.25 | 8.00 |
| 13 | Japanese Spitz | 10 | CM | 4.90 | 5.10 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
| 14 | Maltese | 11 | CM | 5.20 | 5.26 | 2.25 | 2.00 | 7.00 | 5.00 | 9.25 | 7.00 |
| 15 | Pomeranian | 1 | CM | 2.34 | 2.47 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 7.00 | 6.00 |
| 16 | Poodle | 9 | CM | 4.80 | 4.68 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 3.00 | 7.25 | 4.00 |
| 17 | Japanese Spitz | 9 | CM | 10.20 | 10.50 | 1.75 | 1.50 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 6.75 | 5.50 |
| 18 | Pomeranian | 6 | CM | 3.90 | 3.80 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.75 | 2.75 |
| 19 | Pekingese | 4 | CM | 6.60 | 6.72 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 4.25 | 4.00 |
| 20 | Maltese | 7 | FS | 3.08 | 3.12 | 1.75 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 4.00 | 7.75 | 5.00 |
| 21 | Maltese | 7 | FS | 3.46 | 3.40 | 2.25 | 1.75 | 8.00 | 6.00 | 10.25 | 7.75 |
| 22 | Maltese | 9 | FS | 2.46 | 2.20 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 6.00 | 4.00 | 8.00 | 5.50 |
| 23 | Bichon Frise | 4 | FS | 6.86 | 6.90 | 1.50 | 1.25 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 5.5. | 4.25 |
| 24 | Mixed | 13 | FS | 3.90 | 4.00 | 1.75 | 1.50 | 9.00 | 7.00 | 10.75 | 8.50 |
| 25 | Poodle | 4 | CM | 3.48 | 3.52 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 26 | Poodle | 7 | CM | 6.30 | 6.20 | 1.50 | 1.25 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 6.50 | 5.25 |
| 27 | Maltipoo | 2 | CM | 2.00 | 1.90 | 1.75 | 1.50 | 7.00 | 6.00 | 8.75 | 7.50 |
| 28 | Shiba Inu | 6 | CM | 11.60 | 12.00 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 4.50 | 3.00 |
| 29 | Pomeranian | 1 | FS | 2.50 | 2.60 | 2.00 | 1.75 | 7.00 | 5.00 | 9.00 | 6.75 |
| 30 | Maltese | 7 | CM | 3.46 | 3.60 | 2.50 | 2.00 | 8.00 | 7.00 | 10.50 | 9.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.A.; Lee, M.-J.; Kim, E.P.; Heo, G.H.; Oh, S.G.; Park, S.C.; Lee, B.C.; Park, S.O. Efficacy and Safety Assessment of a Dietary Supplement in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis and Dogs with Arthritic Signs. Animals 2025, 15, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131825
Kim GA, Lee M-J, Kim EP, Heo GH, Oh SG, Park SC, Lee BC, Park SO. Efficacy and Safety Assessment of a Dietary Supplement in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis and Dogs with Arthritic Signs. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Geon A, Mi-Jin Lee, Eun Pyo Kim, Gun Ho Heo, Seung Gyu Oh, Se Chang Park, Byeong Chun Lee, and Sang O Park. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety Assessment of a Dietary Supplement in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis and Dogs with Arthritic Signs" Animals 15, no. 13: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131825
APA StyleKim, G. A., Lee, M.-J., Kim, E. P., Heo, G. H., Oh, S. G., Park, S. C., Lee, B. C., & Park, S. O. (2025). Efficacy and Safety Assessment of a Dietary Supplement in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis and Dogs with Arthritic Signs. Animals, 15(13), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131825








